At Haverah Park on a glorious day with Professor Alan Watson, FRS, an emeritus professor at the University of Leeds, and emeritus spokesperson for the Pierre Auger Observatory, who spent many years working here in the pursuit of high energy cosmic rays.
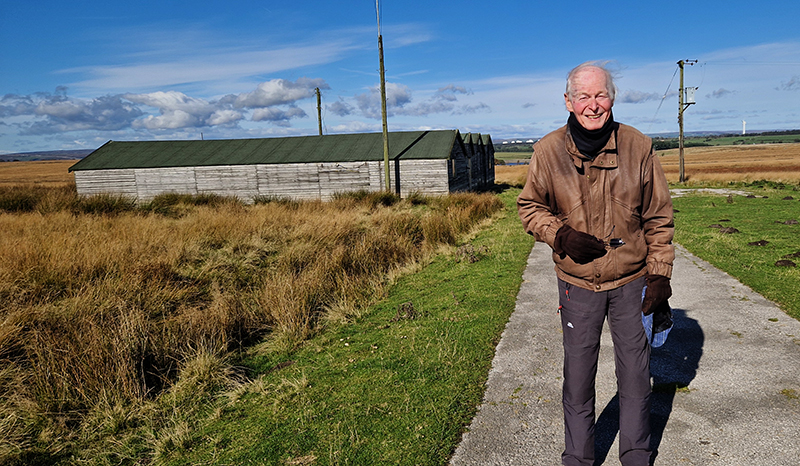


Alan gained his PhD in 1964 for his thesis involving cloud chambers and went on to work for J.G. Wilson, who in turn had worked for C.T.R. Wilson, the inventor of the original cloud chamber. Alan was a leading member of the UK Extensive Air Shower project at Haverah Park from 1964 until its closure in the early 1990s, directing the project from 1976. The work there led to the best estimates of the energy spectrum, mass composition and arrival direction distribution of cosmic rays available at that time and was regarded as the premier project in the field for about 15 years. He was the UK Principal Investigator for the South Pole Air Shower Experiment which ran from 1987 to 1994 and was instrumental, along with J W Cronin, in the creation of the Pierre Auger Observatory in Argentina, which covers 3000 square kilometres and has led to major discoveries in cosmic-ray astronomy.
Cosmic rays are fast-moving particles from space that constantly bombard the earth from all directions. Wherever they come from, the highest-energy particles hold secrets to the origin of their enormous energies, many millions of times greater than any earthbound particle accelerator can create.
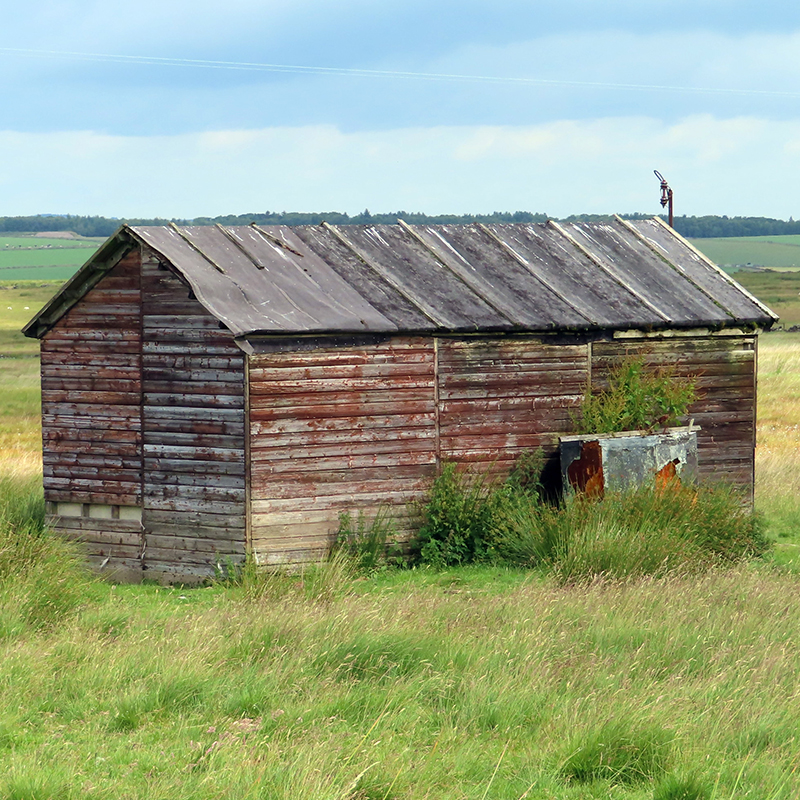
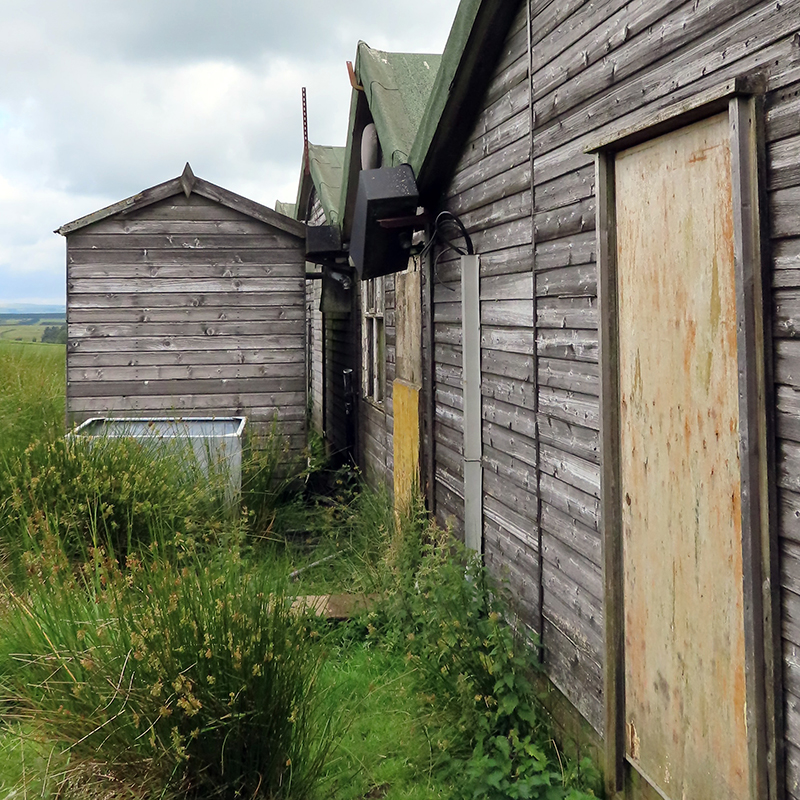
It is extraordinary that these infinitesimal particles powering across the universe at close to the speed of light can be observed and recorded as they interact with our atmosphere. Alan was very generous in giving his time to visit Haverah Park with me and patient in explaining some of the physics. Having been involved in so many pioneering projects that had many obstacles to overcome in their development, he has many stories to tell. We walked to the site of the main control huts, which are the best preserved of the project, most detector huts have been removed or are in a state of collapse. Peering through the windows, Alan pointed out where the dark room used to be and explained that when the project started in the 1960’s there were just two main huts here for data analysis, and a sort of caravan alongside with no heating where film was developed.
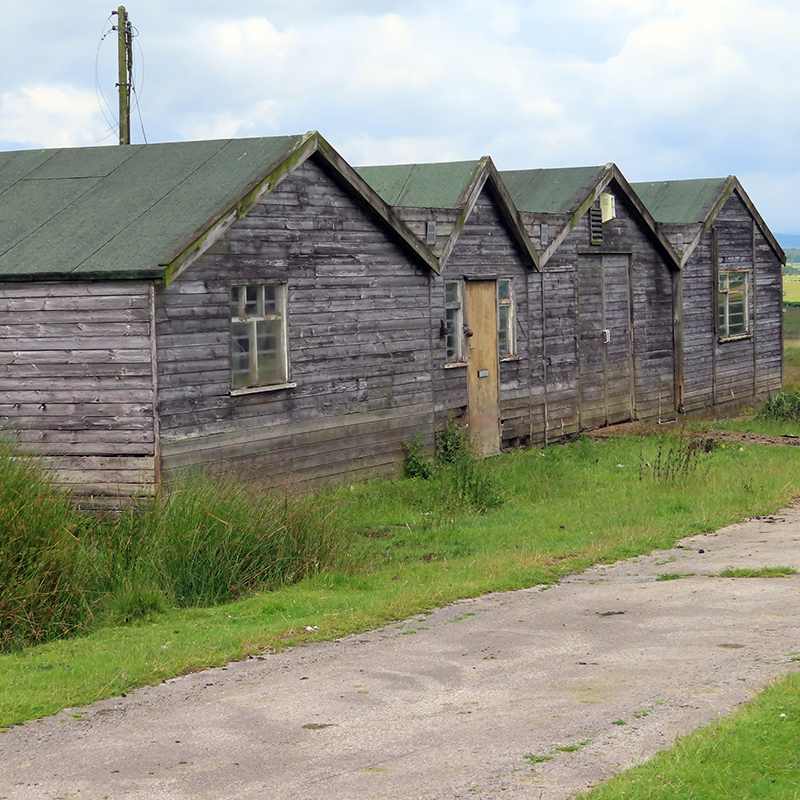


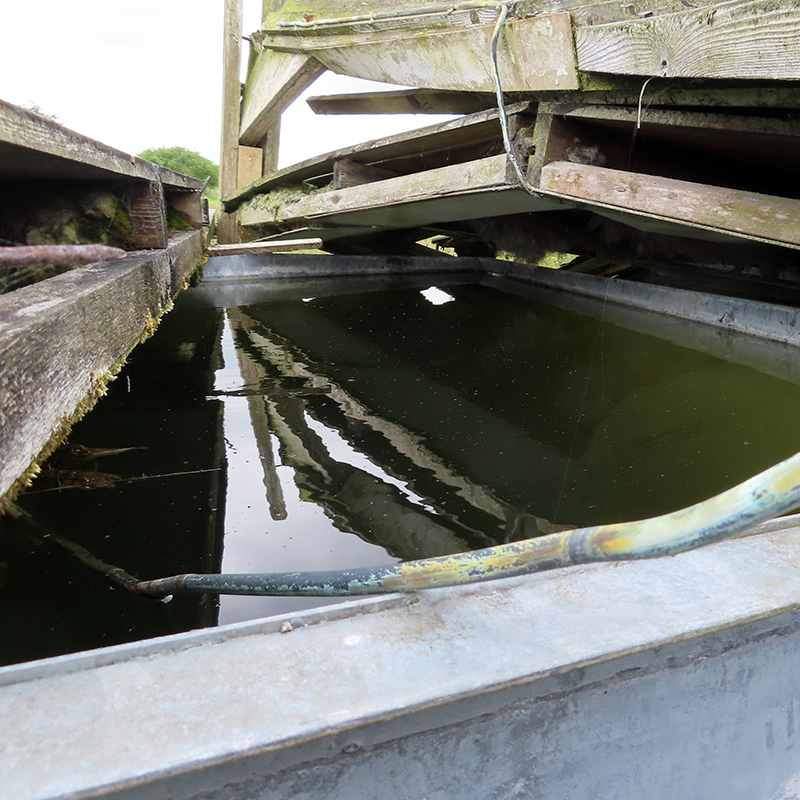
Wooden huts, arranged across 12 square kilometres of moorland, in groups of three, were built to house the water Cherenkov detectors which had to be protected from freezing temperatures. If the water had frozen it would have cracked the photomultipliers which dipped into the water to capture the flashes of Cherenkov light emitted as high energy particles passed through.
Moving equipment around the site was not always easy. When foot and mouth came along it was prohibited to take the Land Rover on to the site so all the equipment had to be carried by hand and this was often very heavy electronics with many thermodynamic valves. The large steel tanks are also very heavy, over 300kg, and it was found that even 6 strong men with bars couldn’t lift them across the rough ground, so before a trolley was found, they had to be rolled end over end into position.
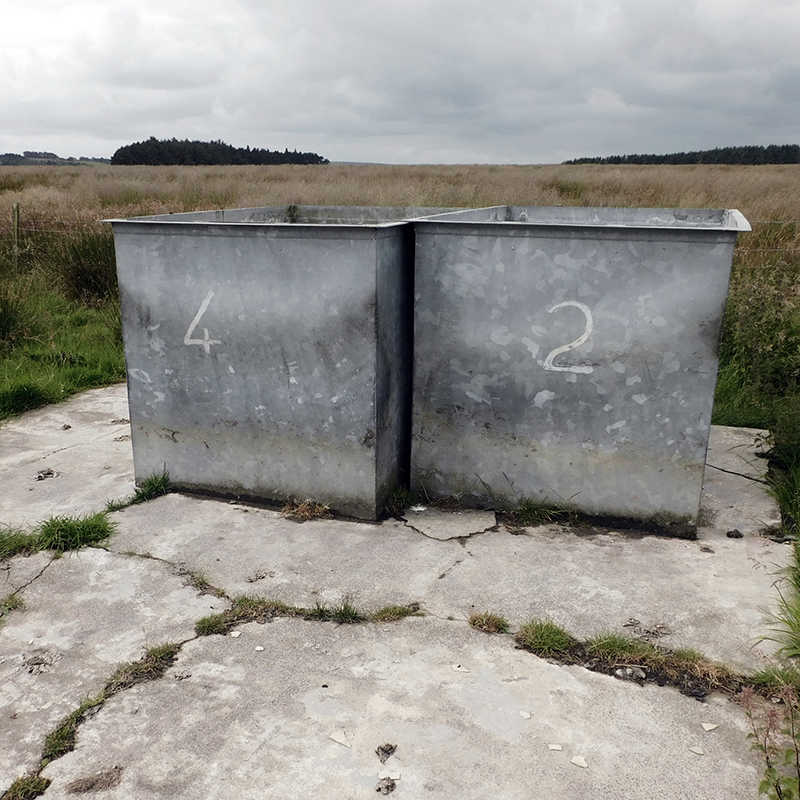


As technology progressed, by the 1970’s, new insulated tanks were developed by Durham University. About twenty of these octagon shaped tanks were set out at spacings of 150m in order to look at cosmic ray showers in more detail with some really interesting results. Six small huts were set around the main huts, but just one remains now, the others having been removed by the farmer who rents this land for his sheep.


At the height of the project three electronic technicians worked here full-time and a handy man who kept the place tidy, got the fish and chips on a Friday from Harrogate and was responsible for fetching water from the reservoir just down the road. No running water was ever installed as the initial plan was for the project to run for just five years so the cost didn’t seem practicable at the time. Researchers had to make do with a chemical toilet known as hut seven.

The pure water for the tanks came from a borehole on nearby Marston Moor, ingeniously it was transported via a milk tanker which could be sterilised and used when not needed for delivering milk. In order to fill the tanks, lengths of unwieldly hose pipe were borrowed from Leeds fire brigade, joined to stretch across 200 – 300 metres with pails placed underneath the junctions to catch any precious water leaking out. The pump used was purchased from a junk yard in London and towed back north by Land Rover. It had originally been in service to put out fires during the second world war and proved its worth again during the heatwave of 1976 when the smaller of the local reservoirs supplying Harrogate was in danger of drying up. The pump was used to move water from the larger reservoirs to the smaller one to maintain the Harrogate water supply.


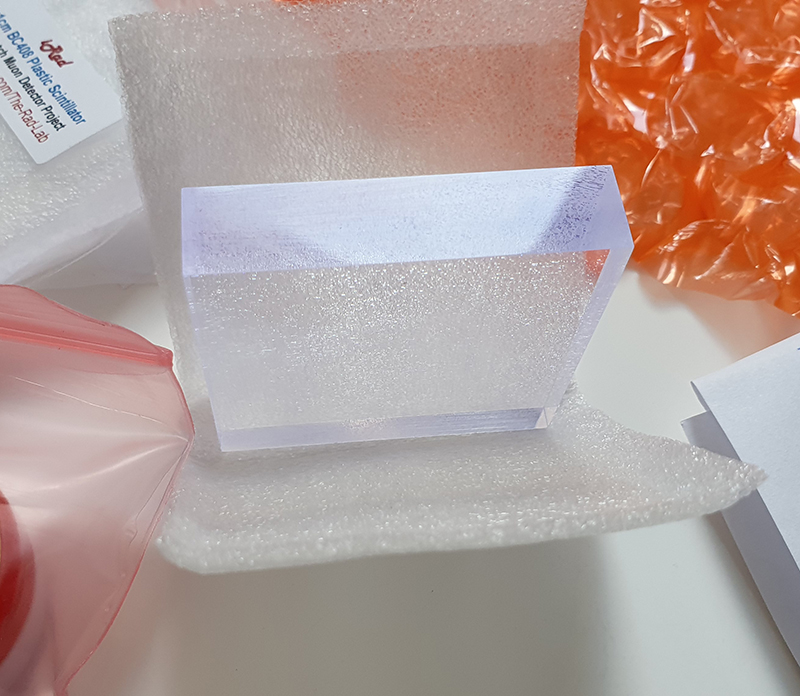
Plastic scintillator used in cosmic ray detectors is expensive. Just two 5x5x1cm blocks I bought for my own cosmic ray detectors cost about £60. There was a possibility of getting some for Haverah Park from a friend of Alan’s in the US but the import duties to the UK were prohibitive. An opportunity then arose when Imperial College, who had once set up a cosmic ray lab. in the depths of the London underground, were asked to remove a quantity of scintillator they had stored at Holborn. It was offered to Leeds University for free but meant sweet-talking the underground station managers over a whisky fuelled lunch to arrange to take possession of the line for a weekend or two, stationing a guard with a red flag and light at one end of the tunnel while the heavy scintillator blocks were loaded onto a trolley and pushed between the tracks a quarter of a mile up an incline to the (now defunct) Aldwych station where there was a lift to bring them up to ground level. When Haverah Park closed the scintillator was passed on to to schools in the Netherlands for their cosmic ray science projects. That from the states ended up being used at The South Pole Air Shower Experiment during its operation before being shipped back to Albuquerque to become a physicist’s unique dark skies garden feature.


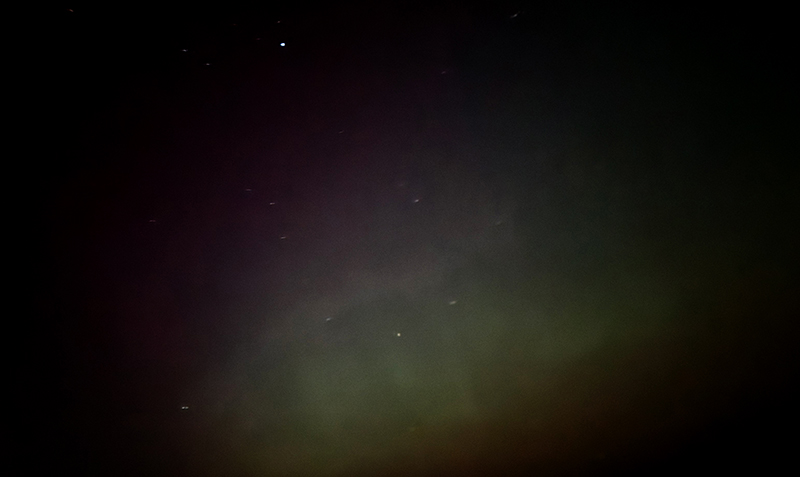
While in Yorkshire I was excited to get an alert for intense solar activity with the possibility of the Northern Lights being visible anywhere in the UK. There were even clear skies. I’ve missed all the aurora displays this year so far and it didn’t happen here either. I went and stood in a dark field around midnight and there was a faint glow but nothing like the images being posted online, some in the same town as I was staying and some annoyingly back south. First image back garden with bright street light interference. Second image with enhanced camera settings. Third image is what it looked like to my inadequate eye.



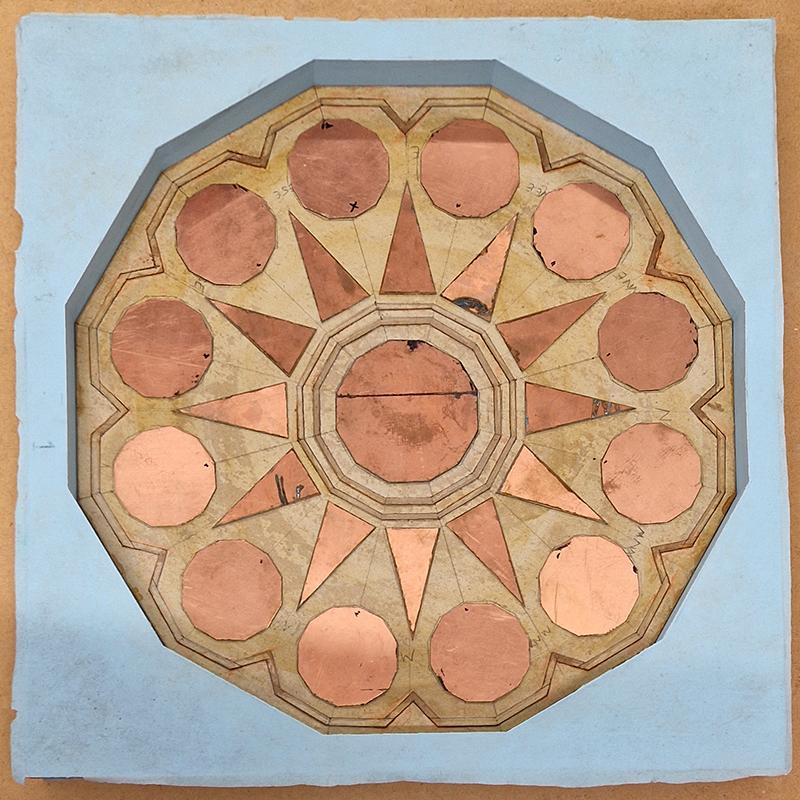
Work in progress on new tablet for Instruments of the Anemoi series of sculptures. The copper dodecagons have been inked and sealed and placed face down onto the collagraph in the silicon mould ready for casting in Snowcrete.


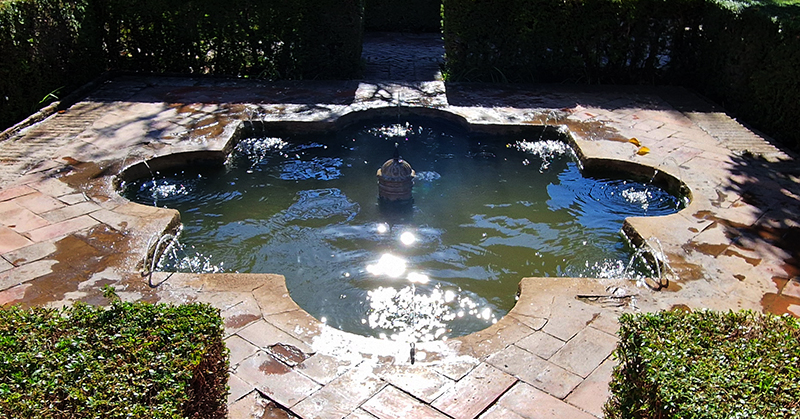
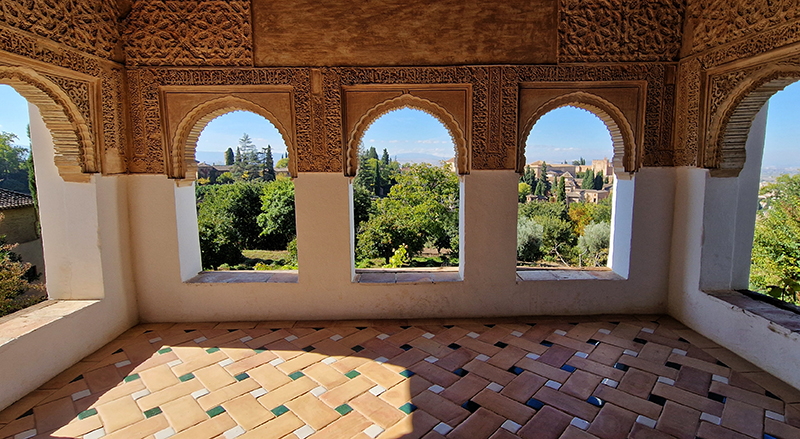
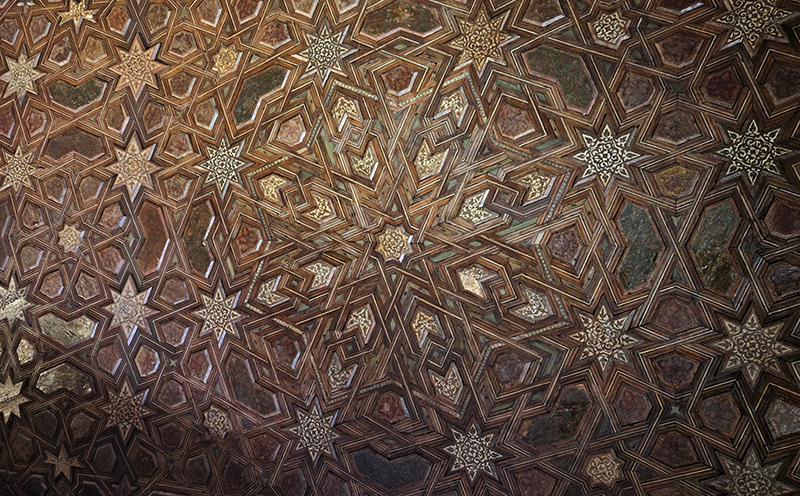
Finally got to visit The Alhambra and it didn’t disappoint.

Designed by poets, philosophers and mathematicians, it is said to bring the harmony of paradise to earth in its perfect symmetries and idyllic gardens. The complex was begun in 1238 by Muhammad I Ibn al-Ahmar, the first Nasrid emir and founder of the Emirate of Granada, the last Muslim state of Al-Andalus and has been expanded, modified and repurposed over the centuries. It is a vast network of garden pools, fountains, courtyards, palaces and fortress towers with jaw dropping vistas. Water runs down from the mountains in an ingenious systems of open channels intertwining through pathways to feed the many pools and fountains. Every ceiling is a vault of heaven, inlaid or sculpted to draw the eye upward. Every wall tiled or stuccoed. Pavements interlaced with patterns set in stones accept cooling water splashed onto their surfaces without it immediately evaporating as it would on a smooth path.
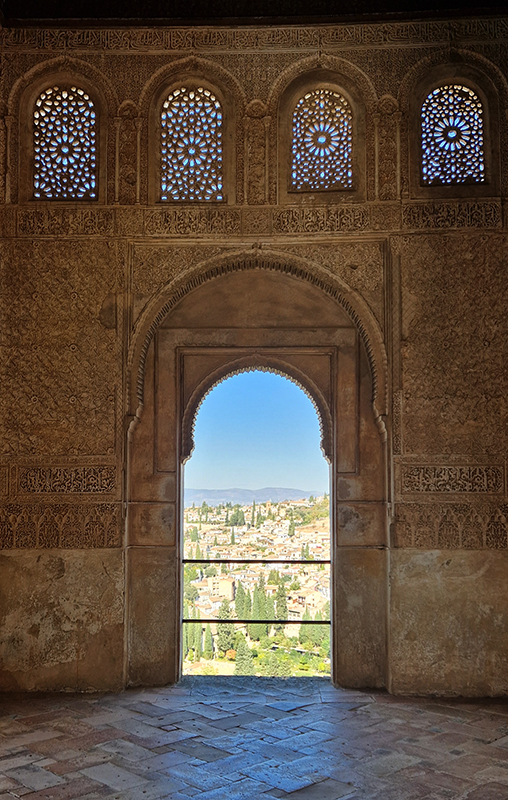
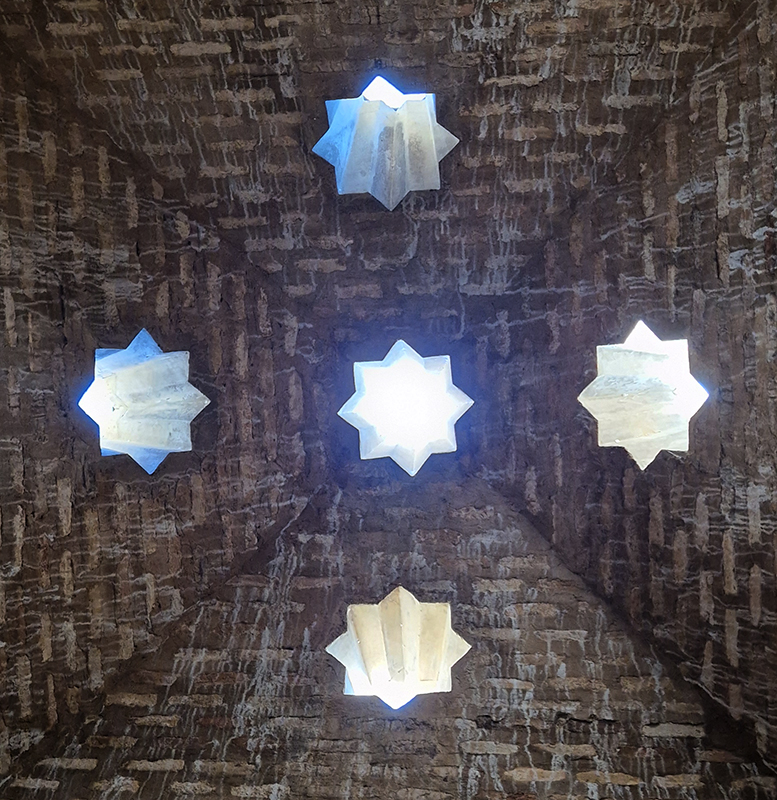
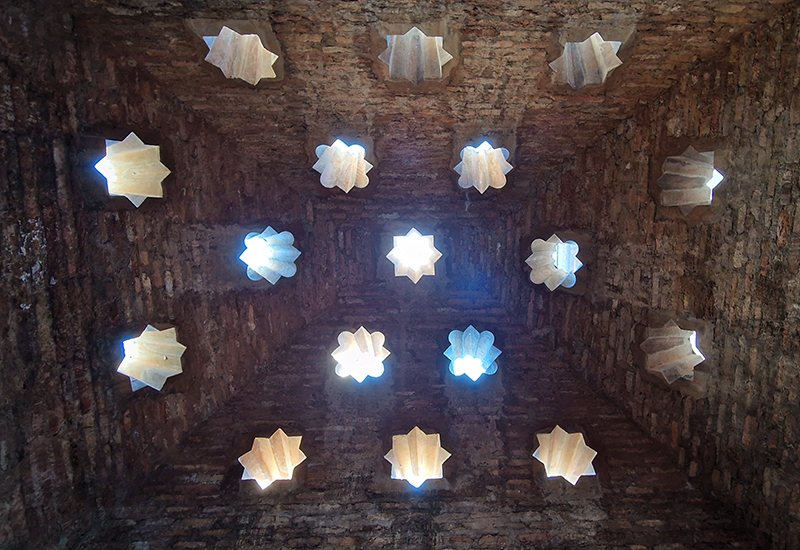
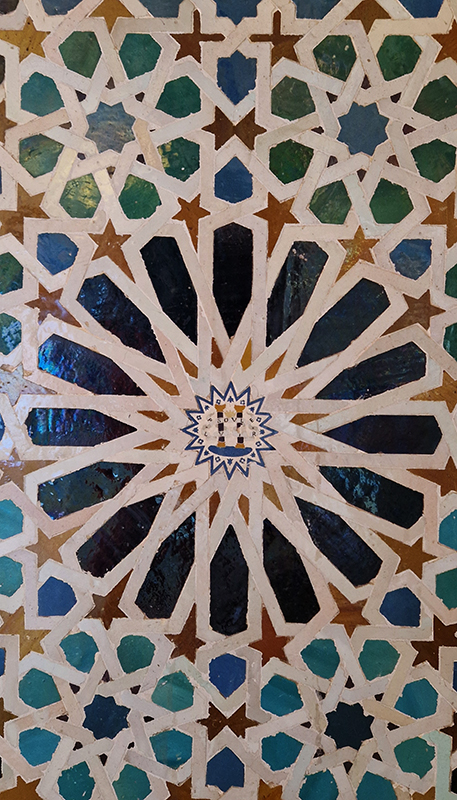
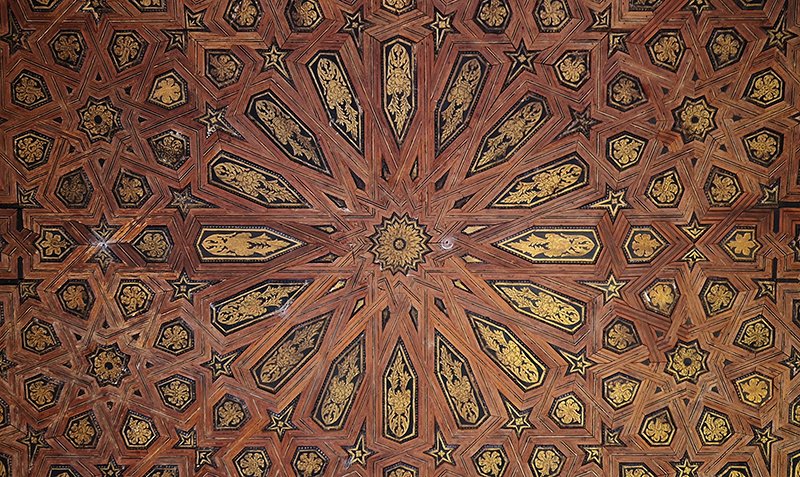
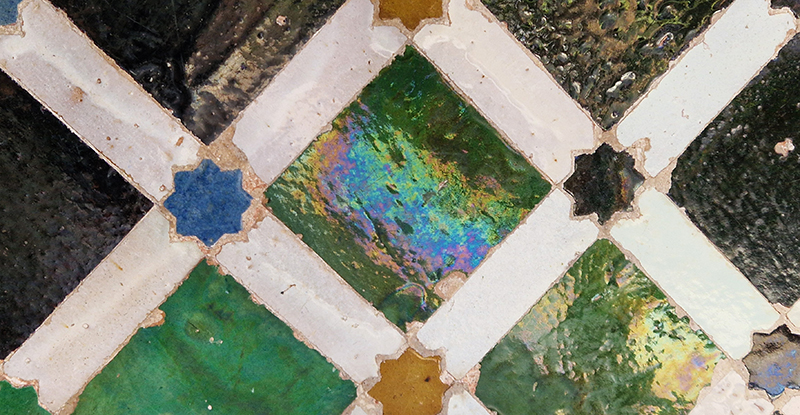
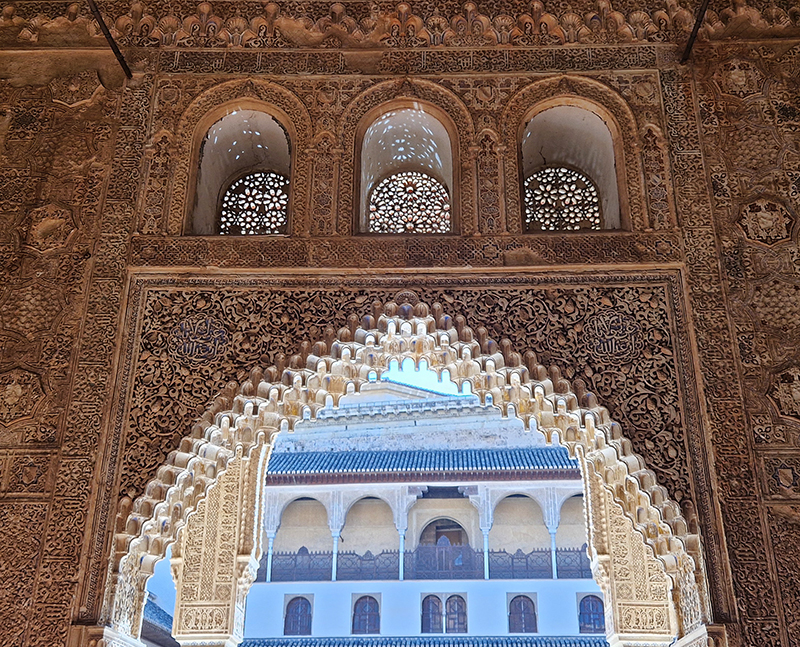
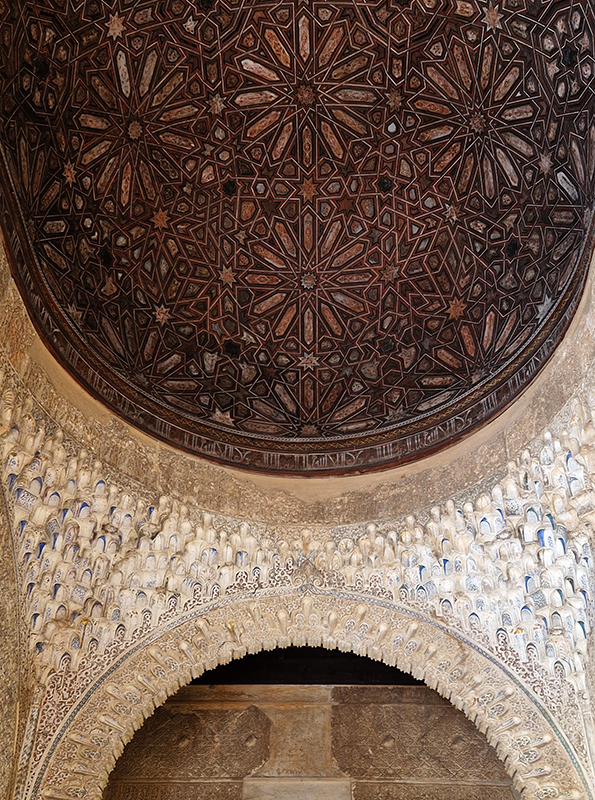
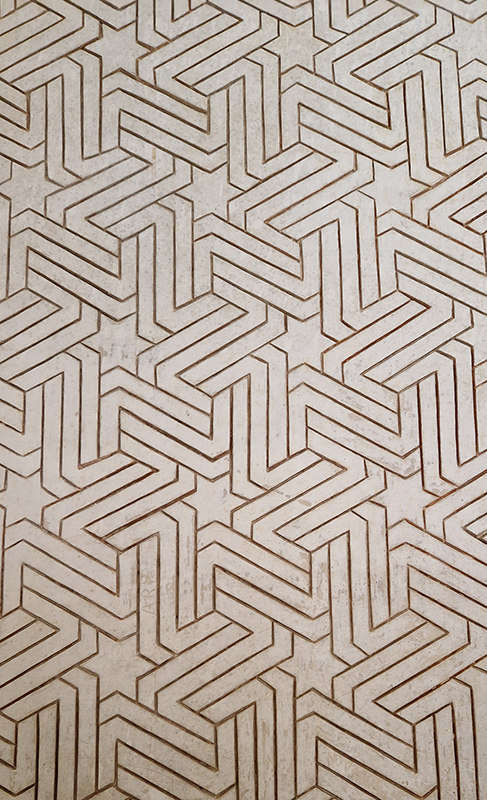
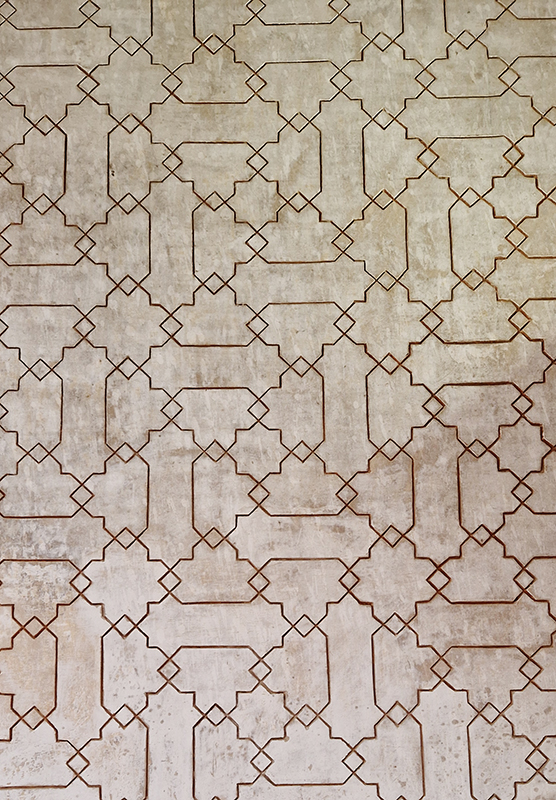
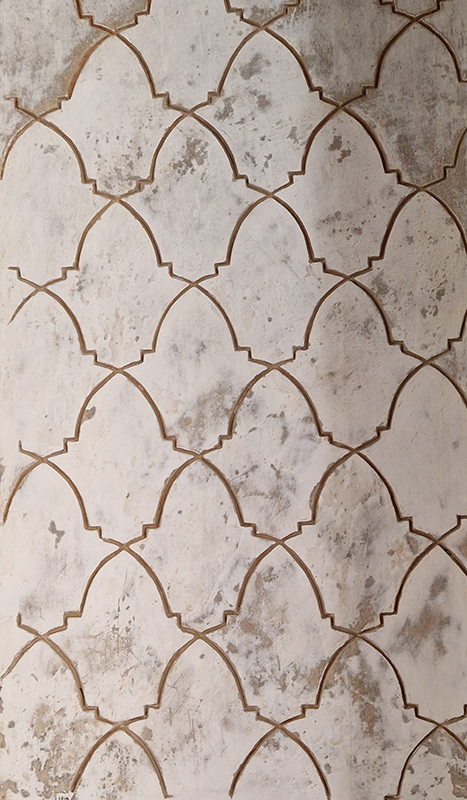
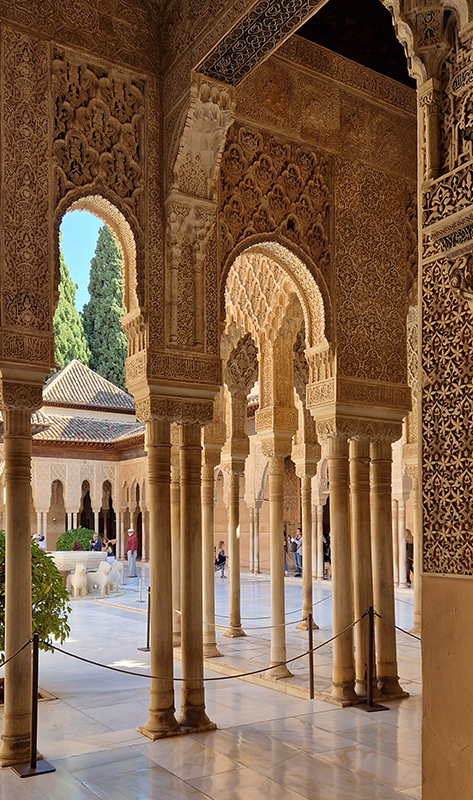
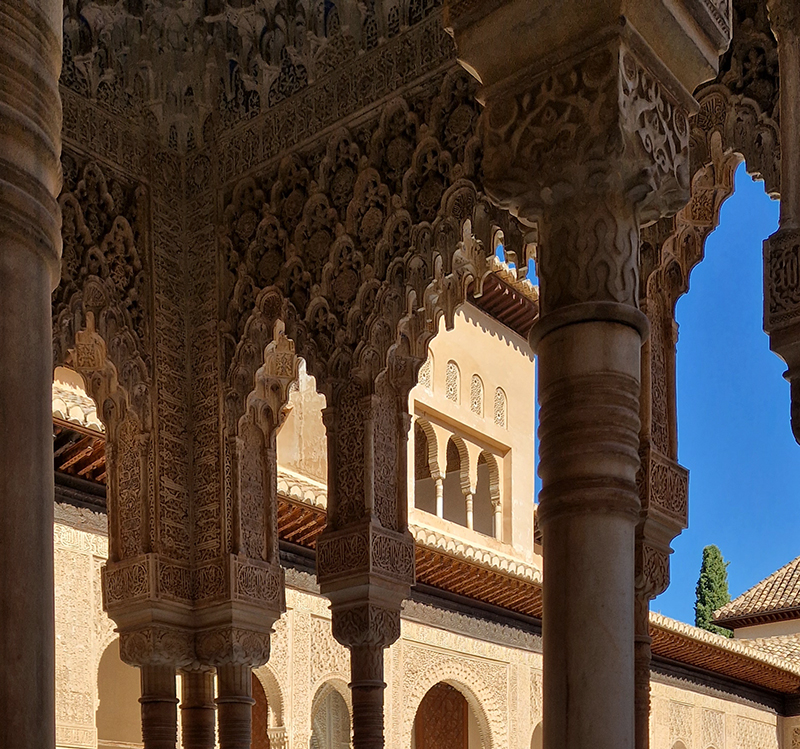
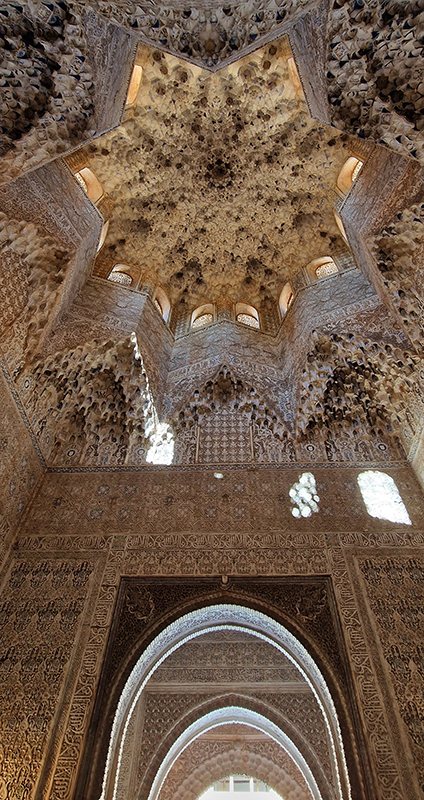
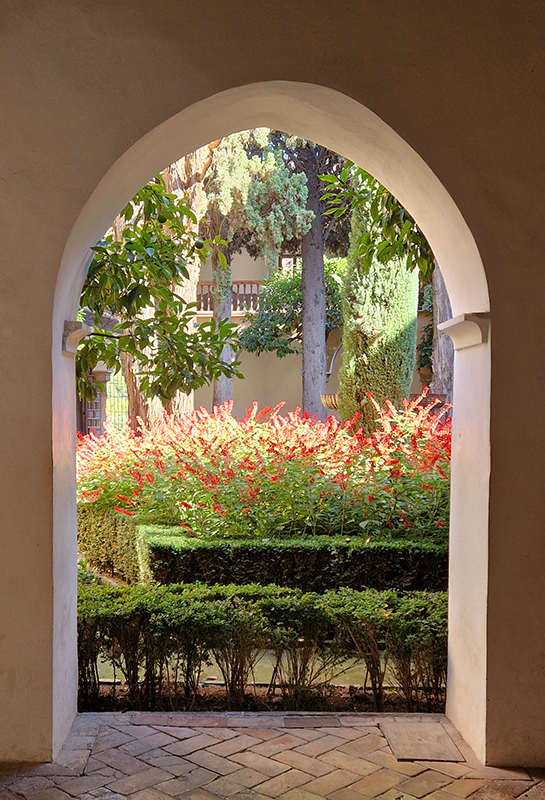
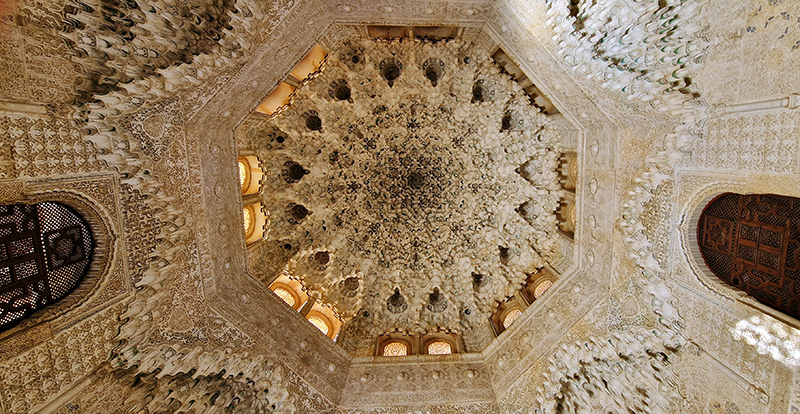












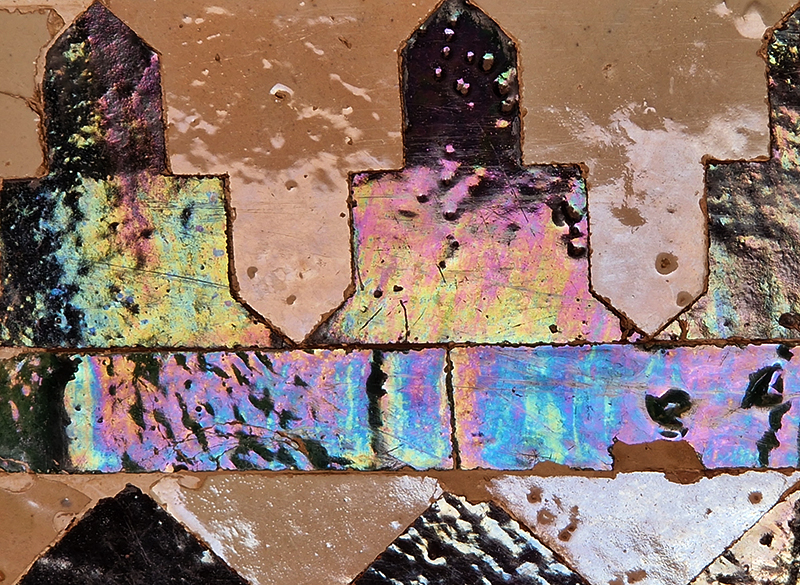
























After the stunning intricacies of sacred geometry and calligraphy, the cast plaster and carved stucco in sunblushed pinks and ochres coloured with mineral pigments of the Alhambra came the Roman Catholics with an alternative interpretation of spirituality. The Cathedrals, Abbeys and Monasteries they built are also astonishing in their scale, architecture and decoration. But this new regime conveyed its power with overwhelming opulence and extravagance, gleaming with gold and spilling over with iconography.
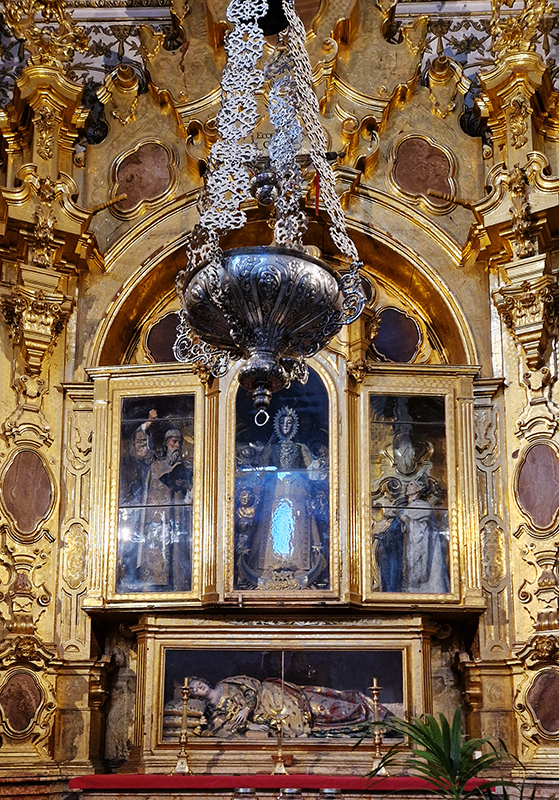
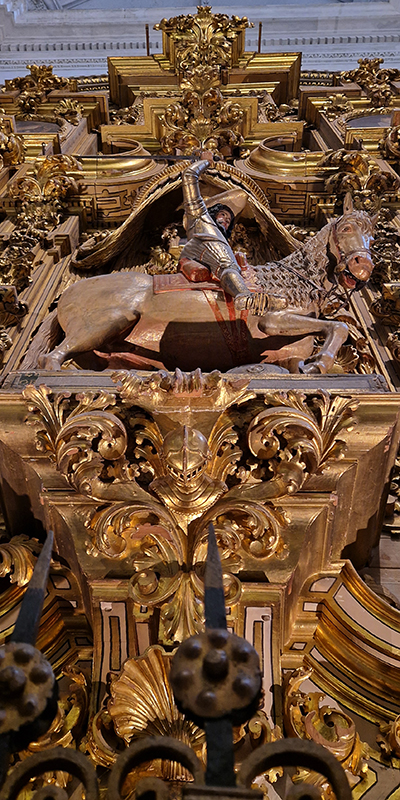
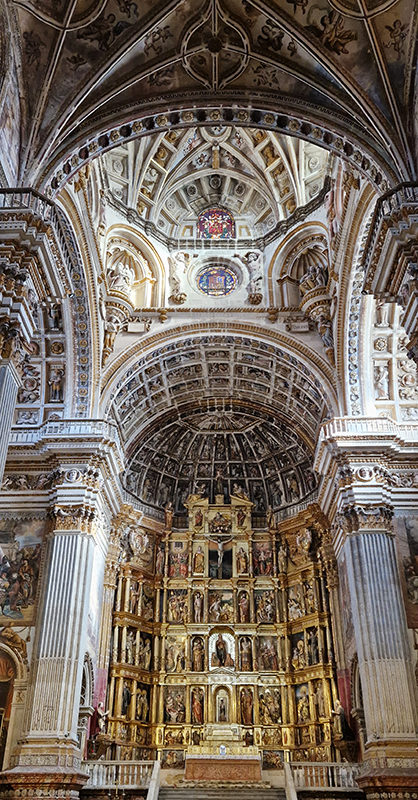
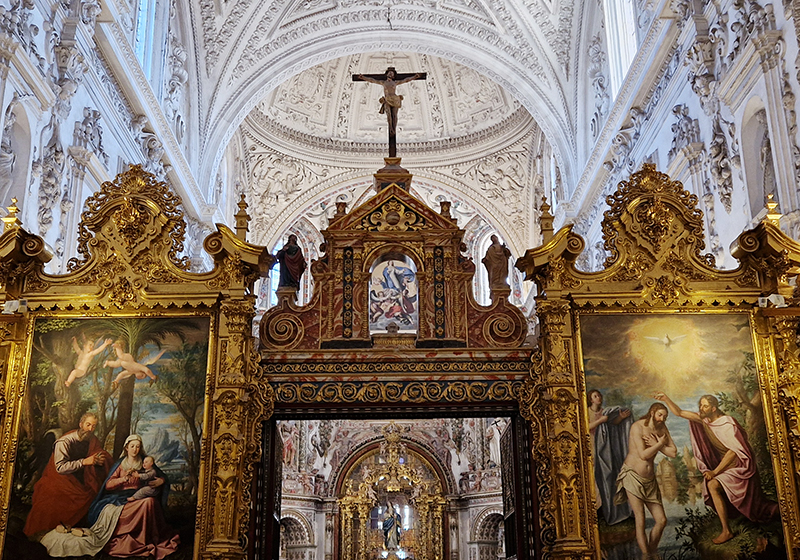
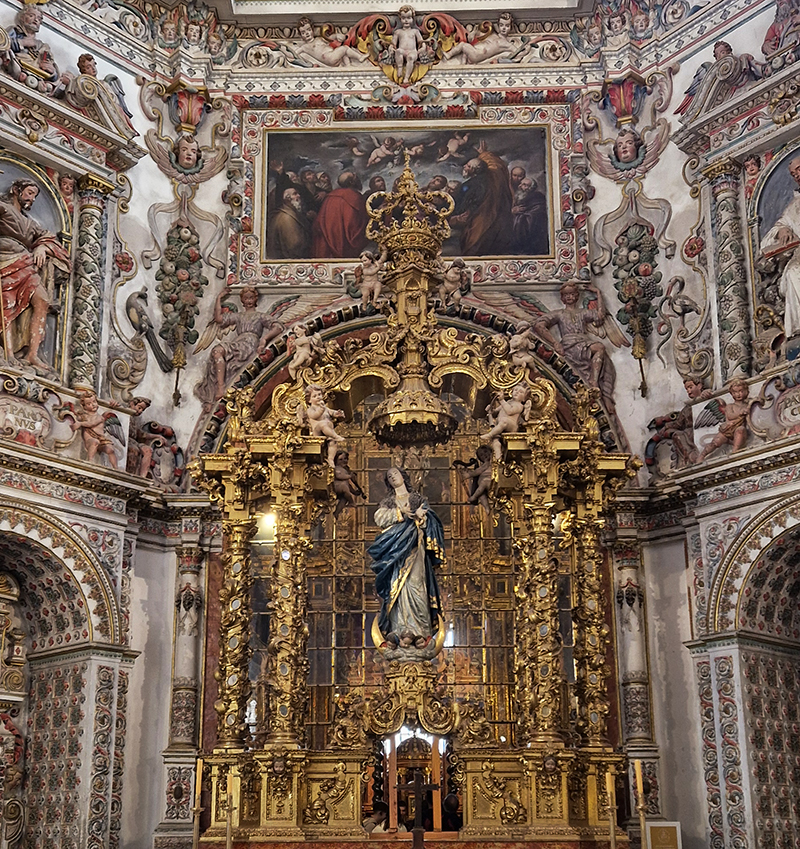


















Of course all our cities are built in stone but here the stone shouts of its materiality and origins.
What could a monument be? Is it the thing we build or the thing we have taken away from? A place of emptiness is the monument to remind us there is no possibility of getting back to what has been – Otobong Nkanga
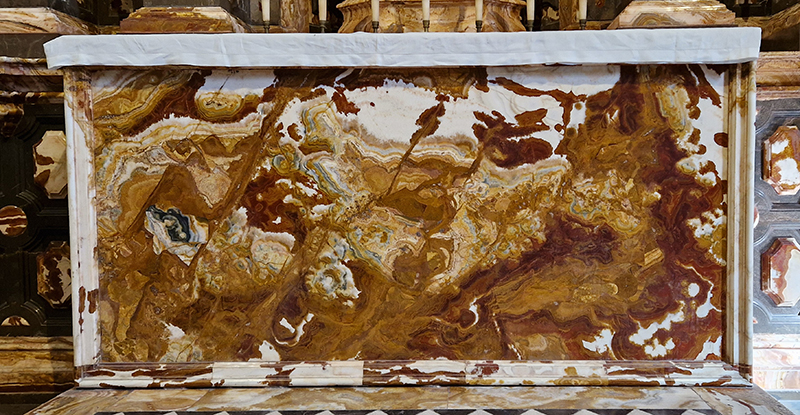
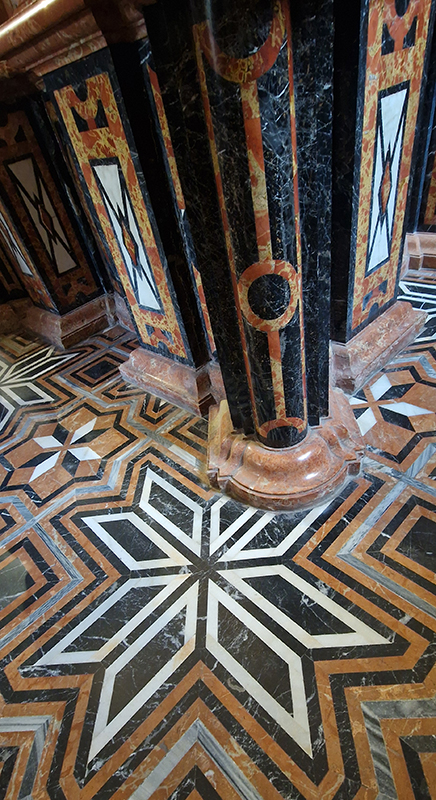
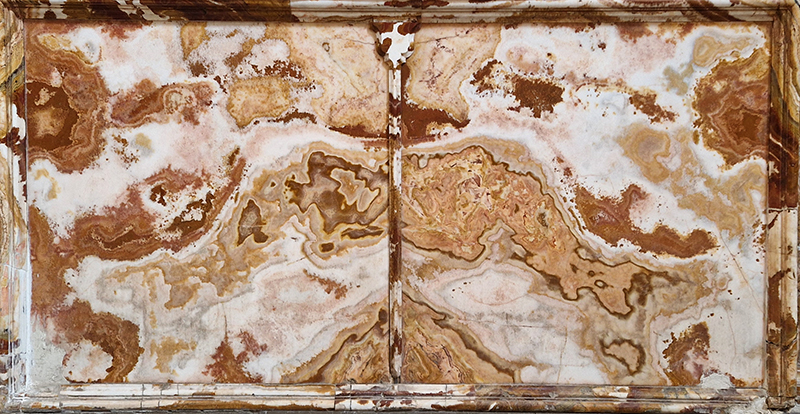







The circular Palace of Charles V was built inside the Alhambra beginning in 1527 to symbolize the royal imperial status and the imposition of Christianity over Islam achieved by the Roman Catholic monarchs. I was intrigued by the Doric colonnade of conglomerate stone and wonder how these were polished so smooth.


The Museums of Granada hold some fascinating ancient instruments. The Astrolabe of Ibn Zawal: molten, cast and etched bronze, 1481, used to determine position and time based on observation of the heavenly bodies. This one served to mark the times of prayer, beginning of Ramadan and qibla (direction of prayer). This is the only example known built specifically for the latitude of Granada. A marble Sun Dial with missing gnomon, this solar quadrant marks the hours of the day in relation to the seasons. Winter and summer solstices are marked by two semicircles. It has some signs of the zodiac and inscriptions in Kufic characters which mark the times of daily prayers. A bronze celestial globe.
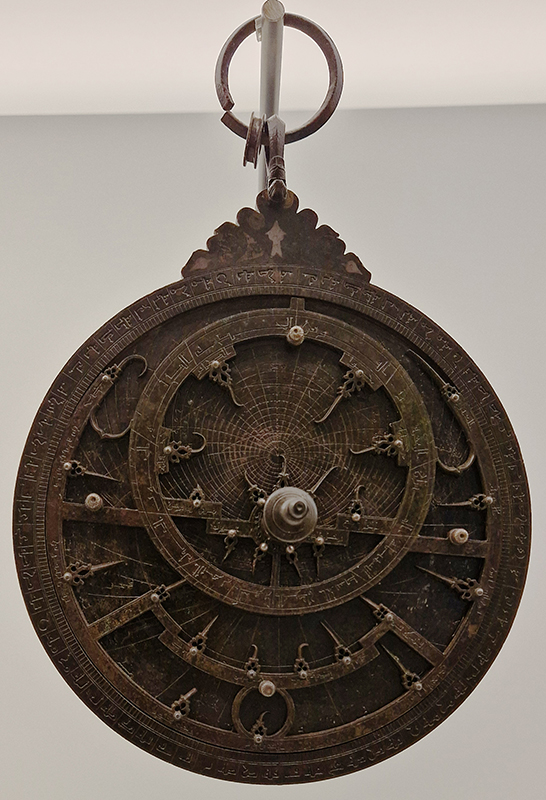
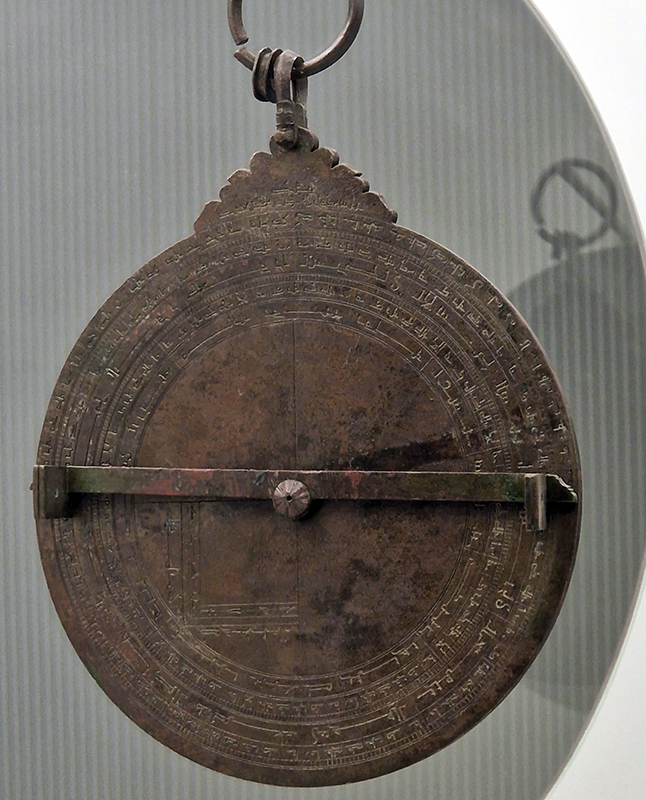




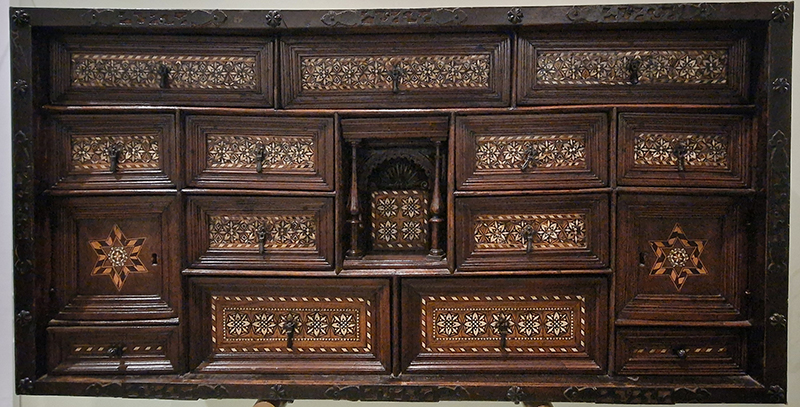
Seeing these instruments along with the intricate patterns of the 13th–15thC larder doors from the Palacio de los Infantes of cypress decorated with intarsia of inlaid wood, bone and ivory and other pieces seen at Granada Cartuja Monastery and Granada Casa de Los Trios, while smelling spices sold loose on the streets brings to mind the ‘Matter of Objects’ project instigated by Queen Mary University that I took part in. Humanities researchers and artists were paired in interdisciplinary conversation to open the way for reinvigorated readings of objects from the past. I was paired with Bruno Martinho from the European University Institute in Florence researching exotic objects found on the Iberian Peninsula during the 16thC.




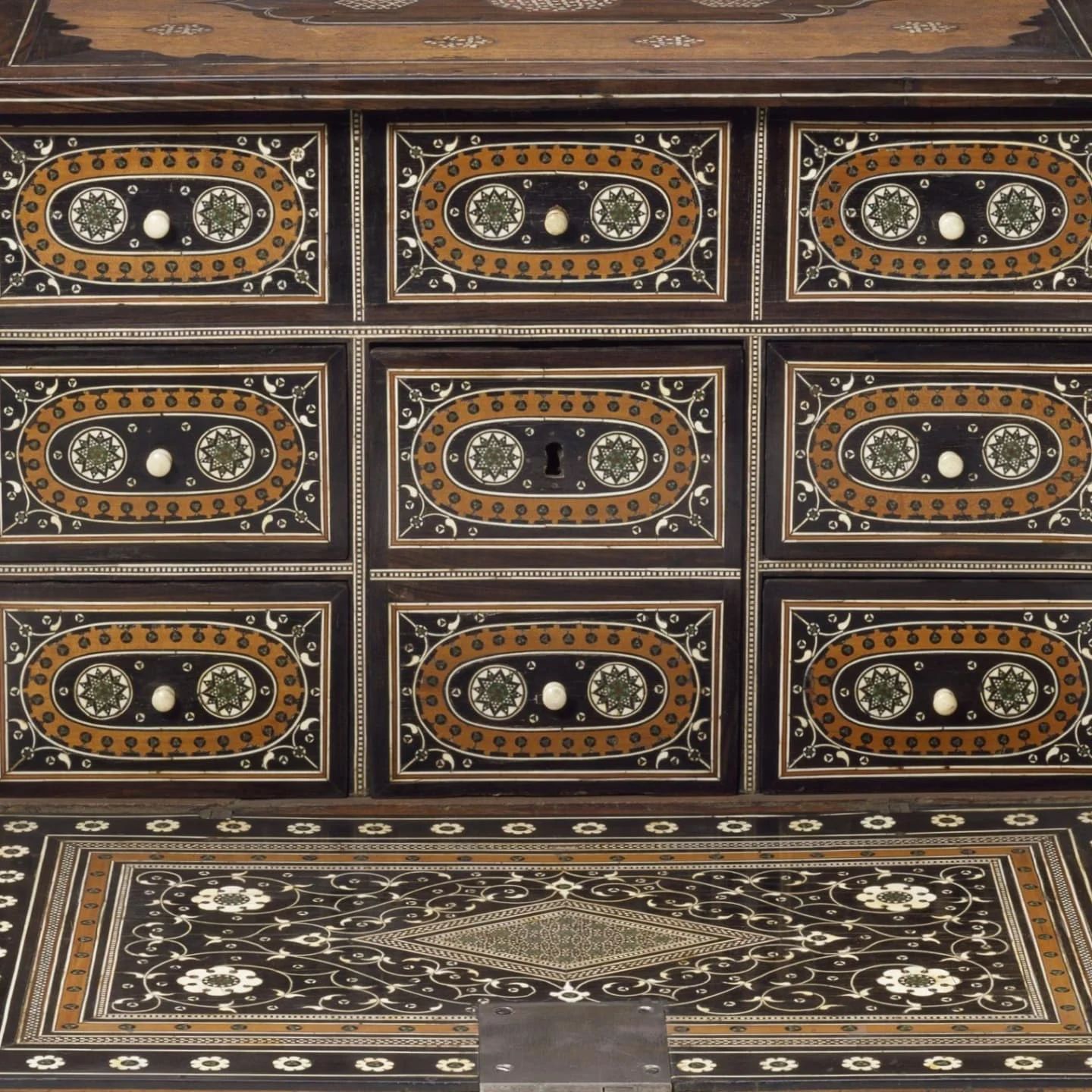
The work containment was made in response to objects traded by merchants that journeyed across the globe five hundred years ago when navigation was reliant on reading the stars. The deep etched lines of the metal plates were filled with inks made from different spices, inviting the viewer to lean in and inhale the aromas. These markers plot the spice route from India around Africa to Europe along the latitude and longitude lines taken from 16th maps of Mercator and Ortelius. A fall-fronted cabinet from 16thC held at the V&A was chosen by Bruno as an object to respond to



Gallery Visits
Liz Elton in Emerging Landscape Painting Today at Messums Cork Street. Assessing the conversation on how landscape and our collective wellbeing mirror each other. Liz’s delicate work Habitat creating a focal point here was first shown in Lifeboat at APT gallery.


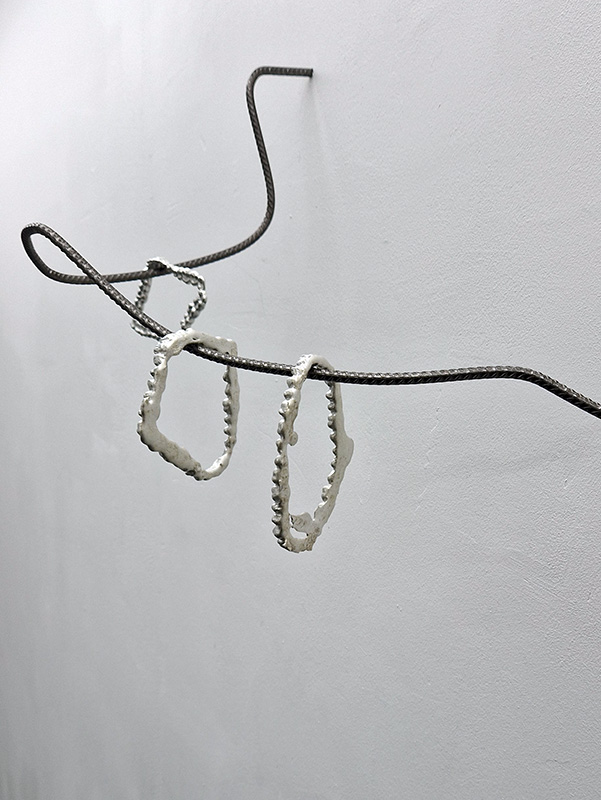
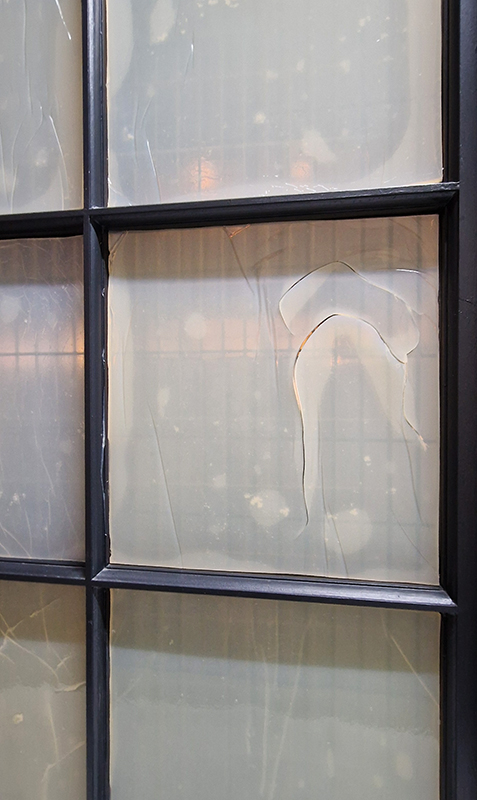
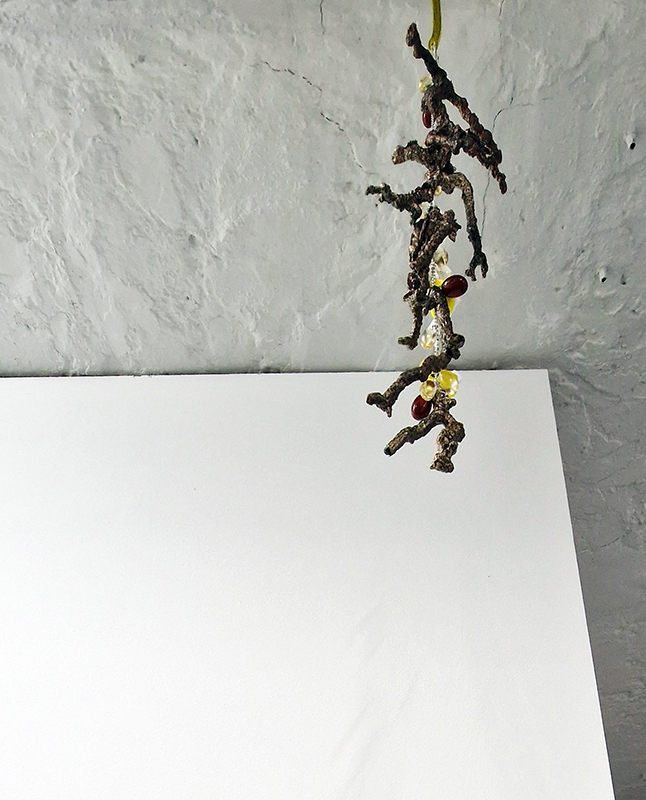
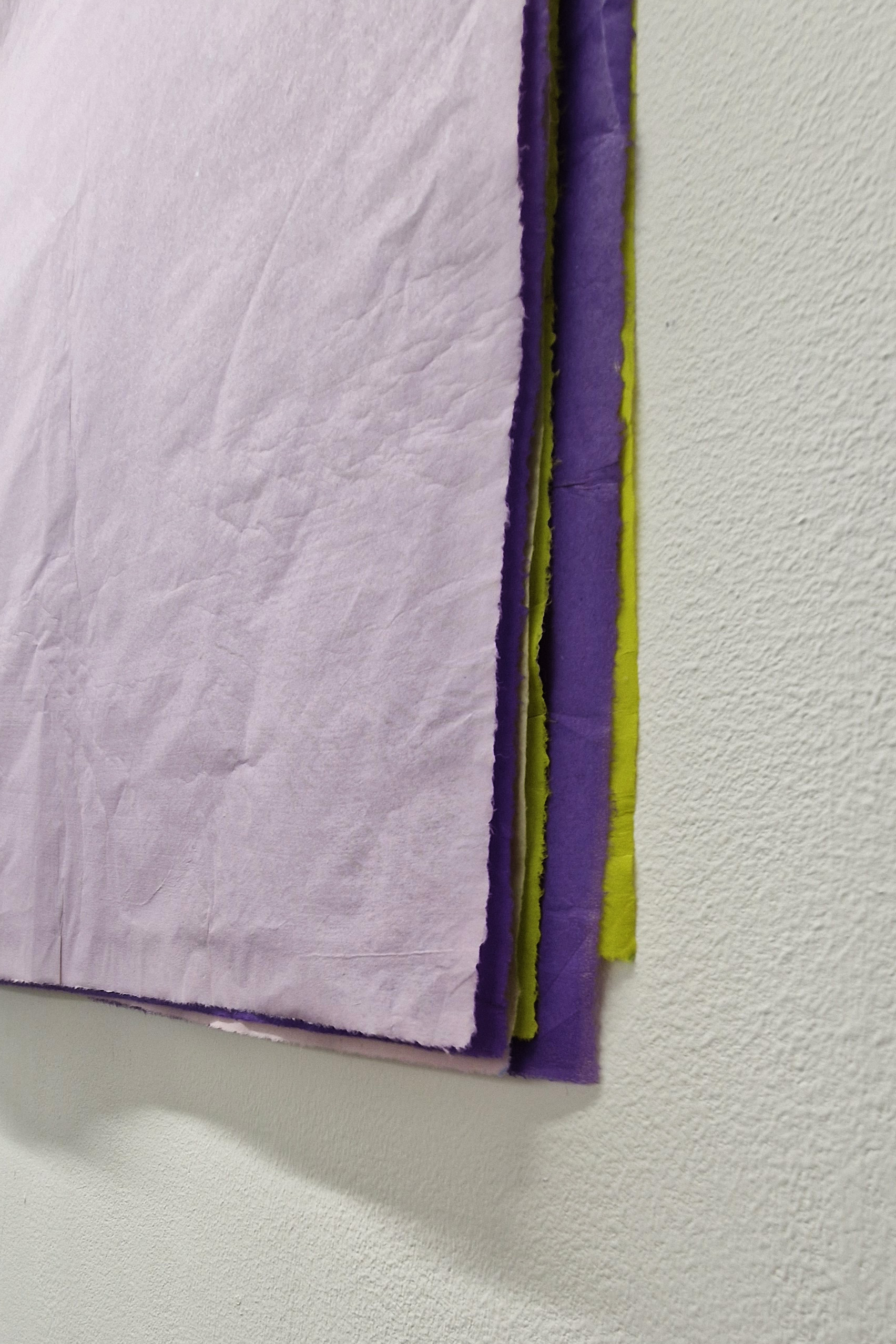
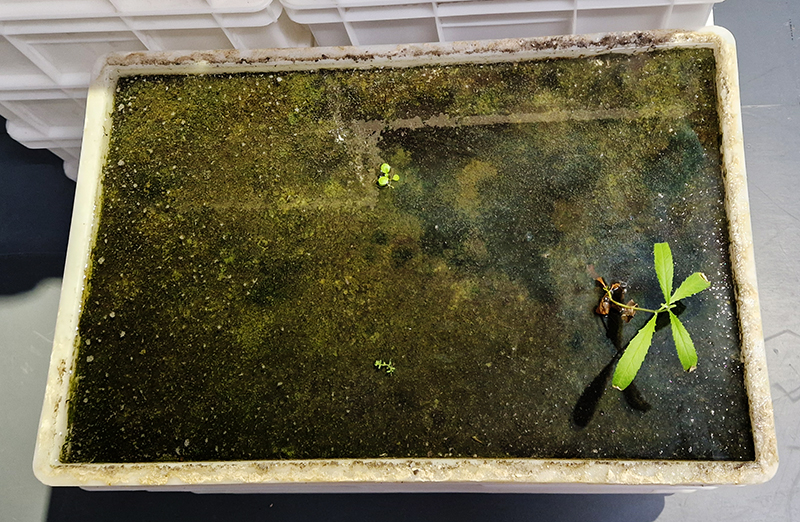
Kate Fahey, Lizzie Munn and Timo Kube in As it is – with works at Commonage Projects and No Show Space. The exhibition talks about subjective experience of time, the past echoing into the future. I find the title ‘As it is’ echoes from my past of Sunday School mantras ‘…on earth as it is in heaven’. That unknown questionable idyll. Aluminium teeth frozen in open cry, strung like trophies; wood sculpted in foetal shapes echoing a folding unfolding, bronze twigs strung with vitamins dangle chirping and chiming over head – hoisted in place with salt blocks, window panes obscured with sheets of semi translucent jelly poised to fall. These works from Kate Fahey encourage an assessment of what is natural, what can be transformed and what can be preserved. Lizzie Munn hangs blocks of hand printed paper in layers of rich colours, the installation draws attention to the vibrant edges and the weight of the paper as object rather than substrate. The manmade bogs in Timo Kube’s plastic tanks also took me back to childhood and the delight of finding strange lifeforms in the rusted water butts of neighbours gardens when taken on trips to renew flowers in the graveyard. Like these bogs his other pieces exploit their surfaces as uncertain, both reflecting and revealing.
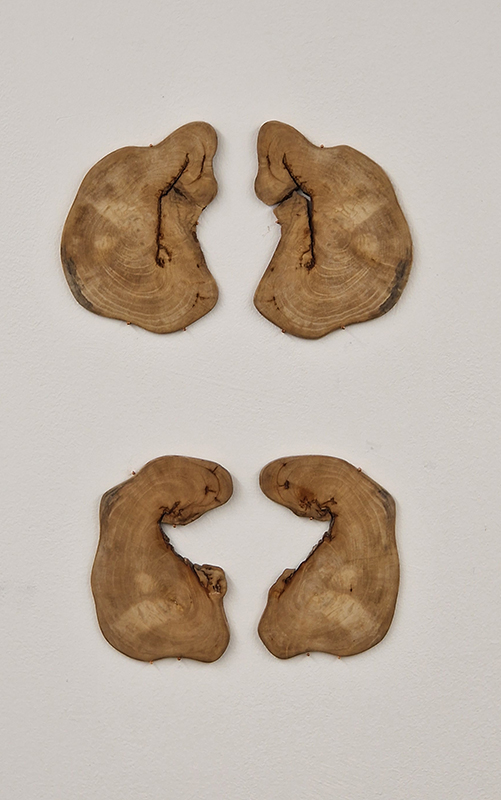
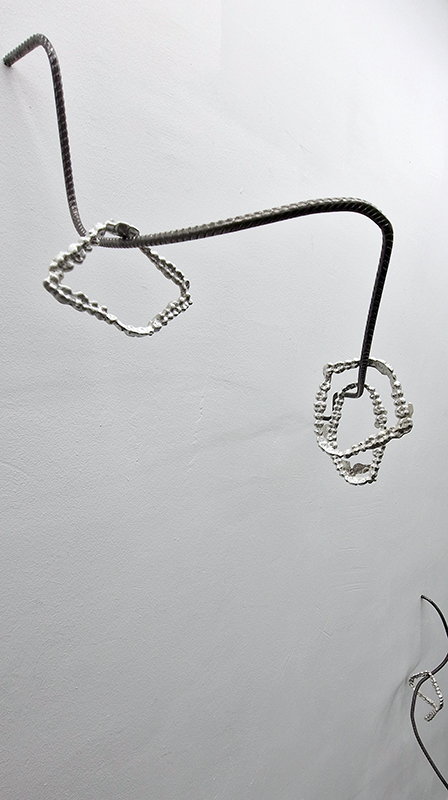
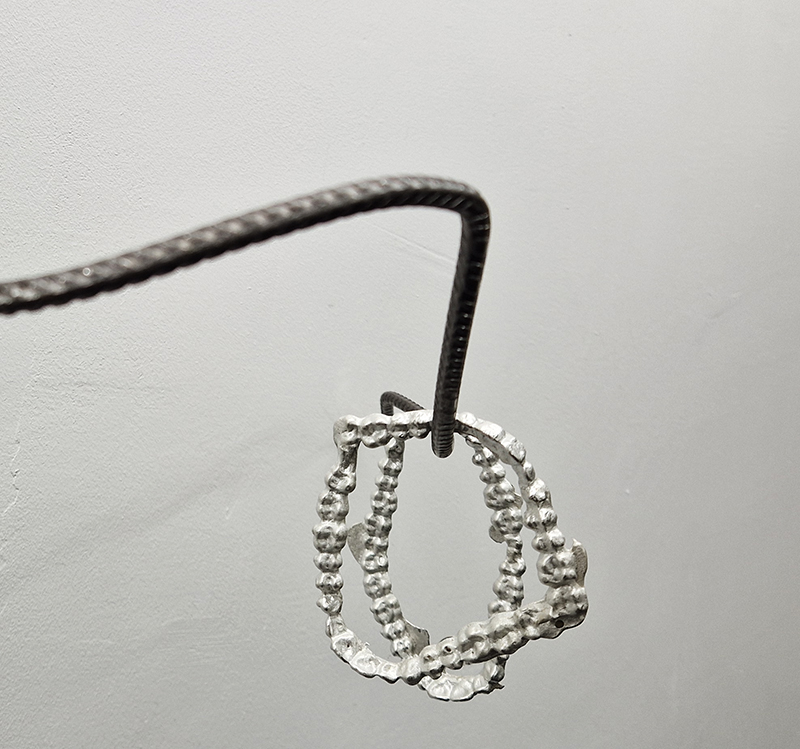
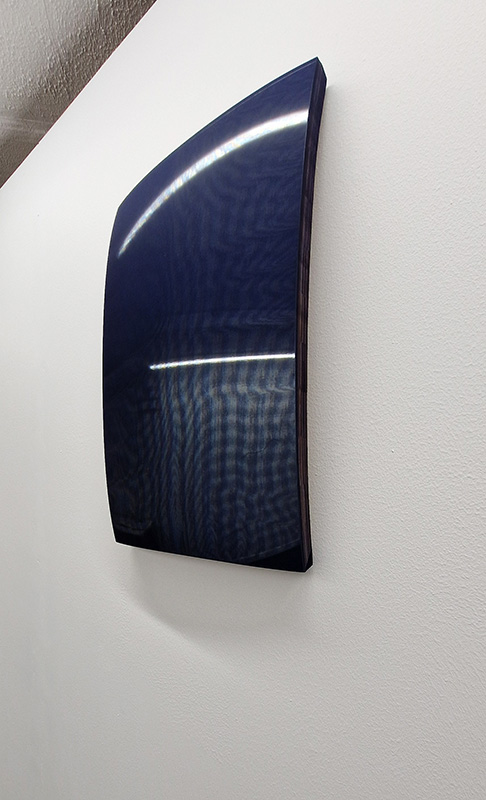















Venetia Nevill We Belong to the Earth at The Bhavan. Venetia has an extraordinary talent of opening pathways into the soul of the natural world allowing us to enter a calm and meditative space. Through her own passion for nature and her deep knowledge of ancient rituals and passing seasons in tune with cosmological cycles she gives us access to the unseen but felt experience of connecting with nature. I walked the cedar mandala and stirred the iron rich water of the scared spring. I pressed damp clay against my skin and the contours of the cedar cone to create an addition to the Mandala of Hope, a growing collection of tiny ceramic vessels, like casts of little hugs.
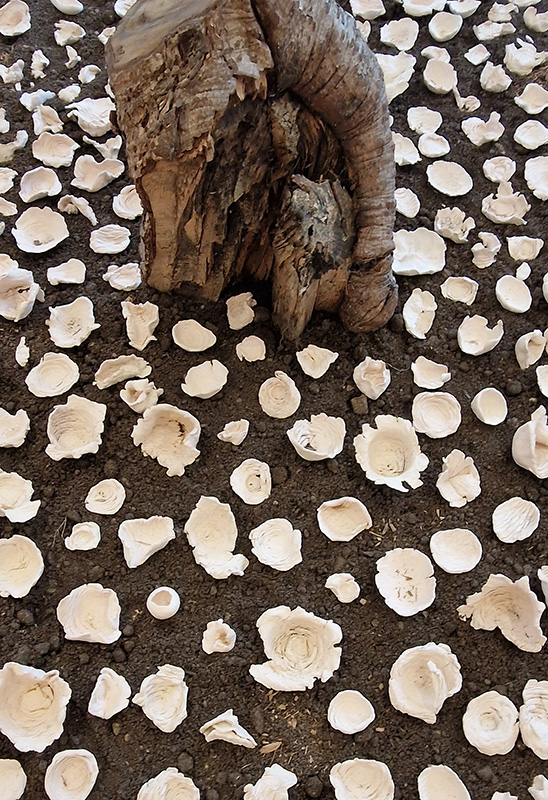




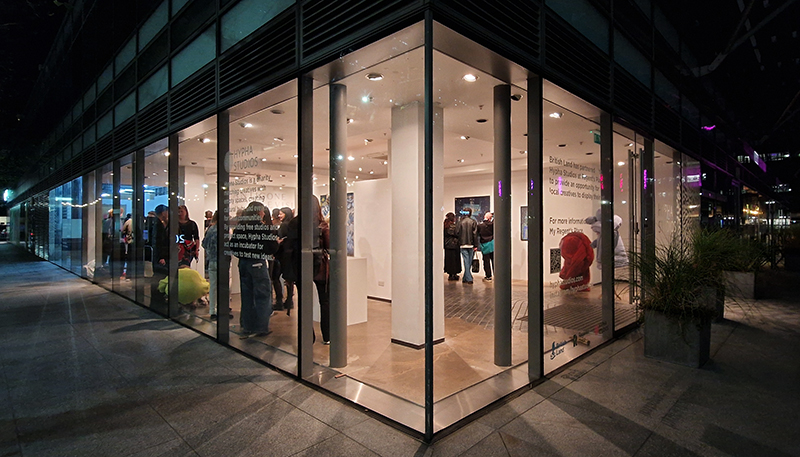
Antigone Revisited curated by Marcelle Joseph at Hypha Studios Euston. This exhibition turns to the contemporary poet Anne Carson and her interpretation of the Greek heroine of Antigone for guidance in our present era of societal crisis. It was good to see the space full and buzzing as this is the site I will be exhibiting in next year in a group show I am co-curating with Julie F. Hill. We will be discussing concepts of The Geological Unconscious taken from the book of the same name by Jason Groves.






Reading
Orbital by Samantha Harvey. This is a nourishing read. Orbital is so first person evocative, the descriptions of Earth from the ISS are so transcendent, it’s hard to believe Samantha is not an astronaut. I very much admire the Art Fictions Podcast curated by JiIlian Knipe and often wondered what book I would choose for myself in this context. I think this book would fit. Why it resonates so much with me is the sense of wonder it evokes along with an acceptance of the infinite incomprehensibility of our position in the cosmos.
‘Our lives here are inexpressively trivial and momentous at once [..] both repetitive and unprecedented. We matter greatly and not at all. To reach some pinnacle of human achievement only to discover that your achievements are next to nothing and that to understand this is the greatest achievement of any life, which itself is nothing, and also so much more than everything.’
Listening
Hannah Critchlow on the connected brain In her books Hannah Critchlow has explored the idea that much of our character and behaviour is hard-wired into us before we’re even born. Most recently she’s considered collective intelligence, asking how we can bring all our individual brains together and harness their power in one ‘super brain’.
86 billion nerve cells within the brain produce electrical currents as they pump sodium and potassium ions in and out across cell membranes and that pumping of charged ions creates an electrical current which passes from one nerve cell to the next cell in the circuit and that movement of electrical current creates our thoughts, ideas, emotions and our behaviour. An EEG machine can examine the electrical activity within the brain and the brainwaves can be read and converted to sound. Fascinating to hear that when Hannah read the brainwaves of Rowan Williams, the former Archbishop of Canterbury, as he meditated she could see an incredible burst of gamma wave activity in the brain, the fastest frequency of electrical oscillation. Scientists are exploring what happens when groups of brains start working together. In a group, brainwaves start to synchronise with each other, and that physiological alignment within the brain is linked to better learning and consensus building and problem solving ability. In a multi-person brain to brain interface – individuals across the world can be hooked up to an EEG machine and their brain oscillations can be converted into a magnetic stimulation signal which is then transmitted from one person to another person enabling them to read each others thoughts in a very rudimentary sense. Experiments have been done with isolated individuals playing games such as 20 questions and they can complete this without any other communication across the group.
Wrinkled Time The Persistence of Past Worlds on Earth by Marcia Bjornerud. Chronicling the way Earth archives Her geological history in the wrinkled strata just beneath our feet, Marcia Bjornerud orients us to the deep time-fulness of Earth—the four billion years of dynamism held in the ancient and ongoing story of rock.
Viewing
Architecton written and directed by Viktor Kossakovsky at BFI Imax as part of the 2024 London Film Festival. Fabulous to see this on the giant screen. It is an epic and poetic work meditating on humanity’s relationship with architecture. The footage of tumbling stones and rock blasts is breathtaking. An extraordinary journey through the material that makes up our habitat: concrete and its ancestor, stone.
Right In The Substance of Them a Trace of What Happened a series of short experimental films showing at ICA as part of LFF 2024. A couple of favourites were the atmospheric Hexham Heads by Chloë Delanghe and Mattijs Driesen based on a local myth of stone heads unearthed in a local garden that bring forth a chilling presence. Hemel by Danielle Dean, tapping into 1950’s science fiction of alien life and mysterious meteorites to examine lived experiences and xenophobia in Hemel Hempstead.
