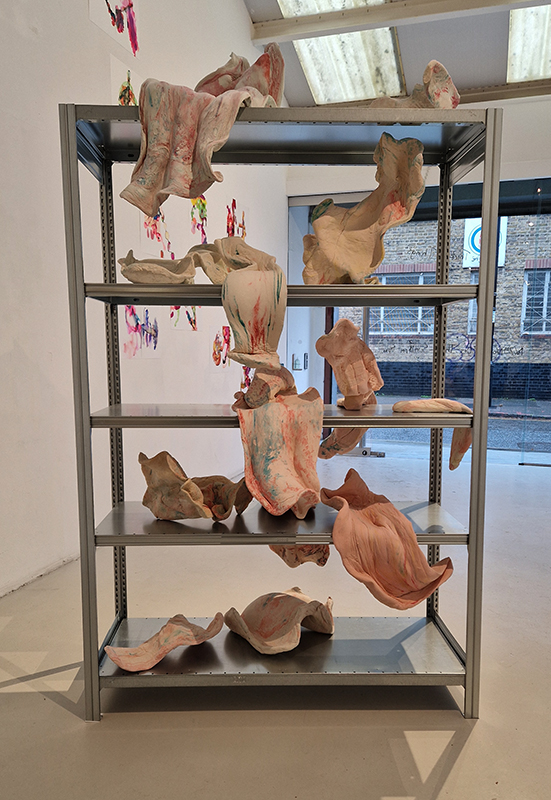
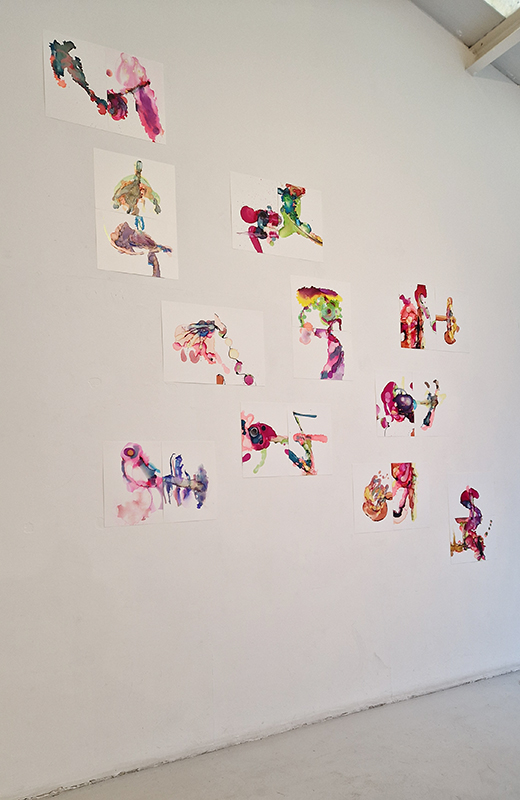
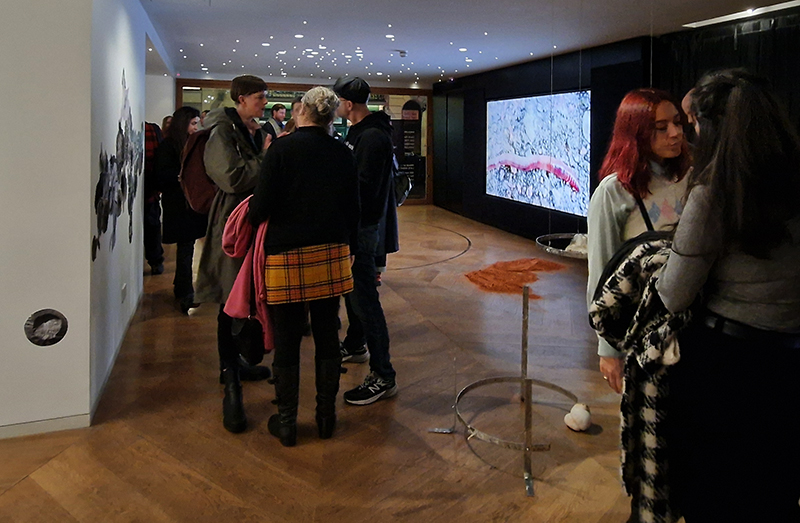
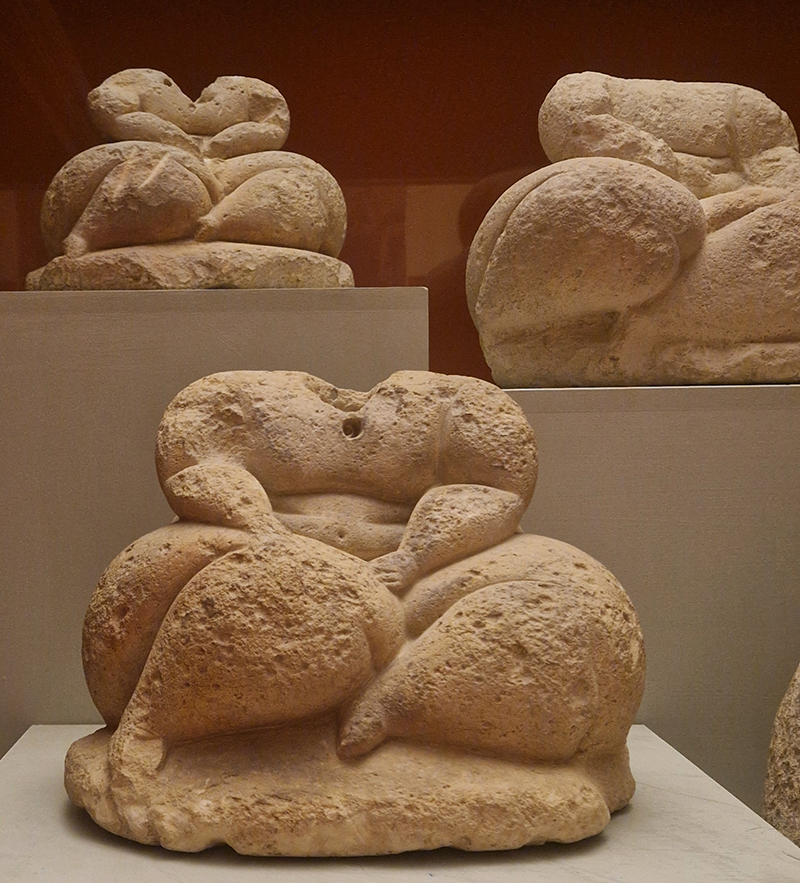
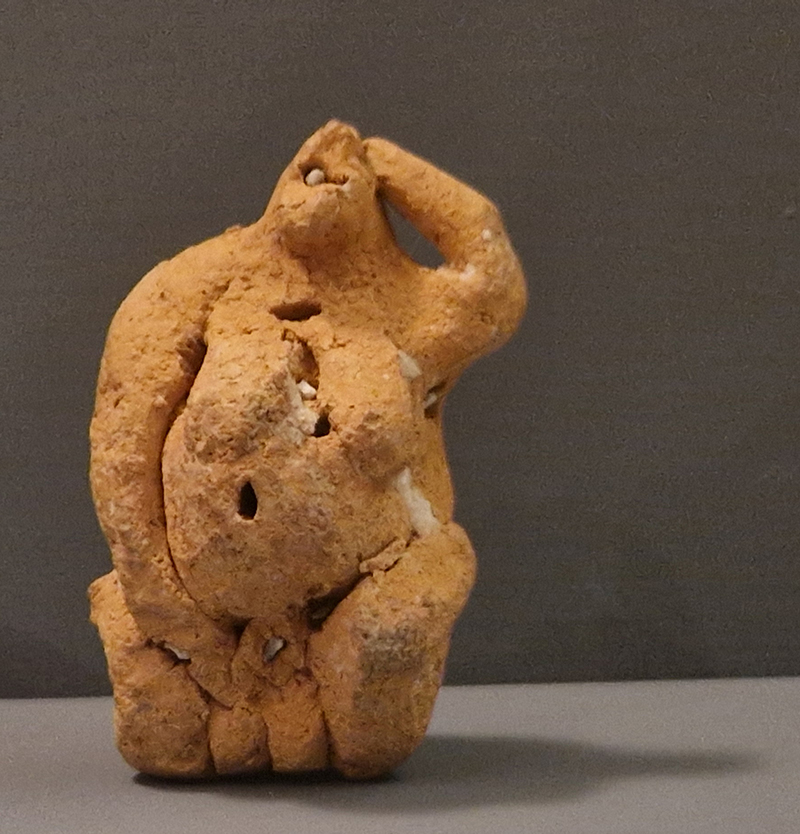
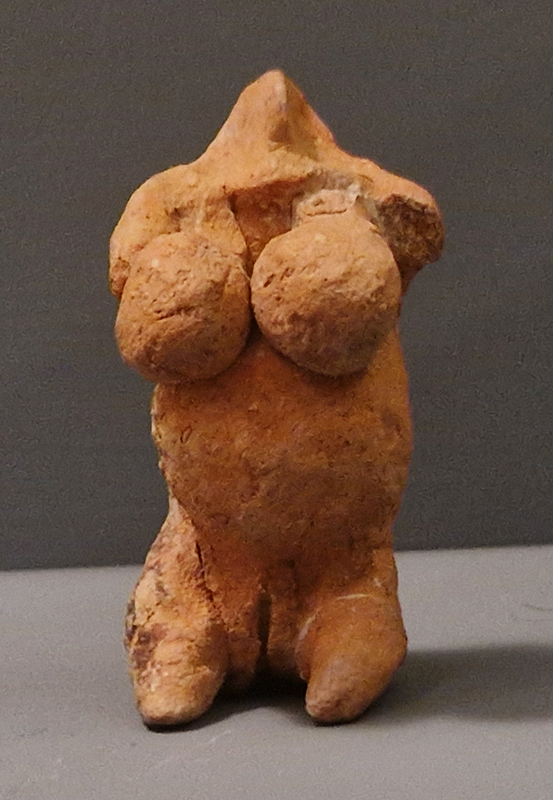
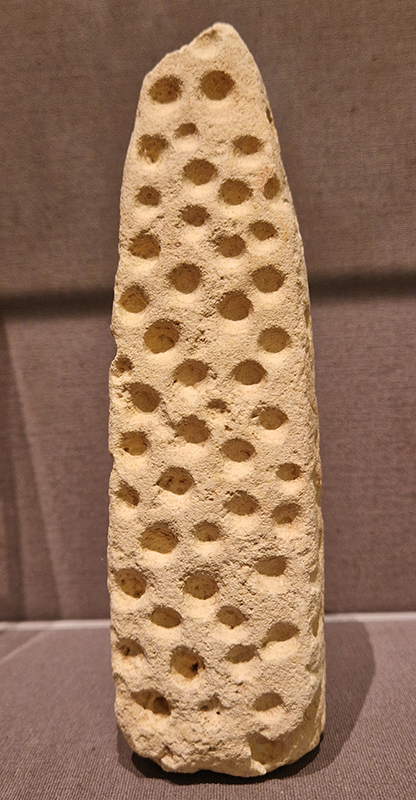
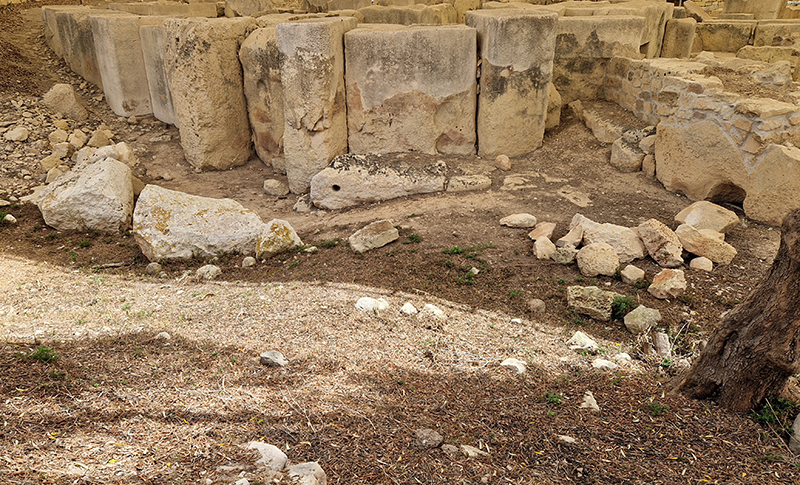
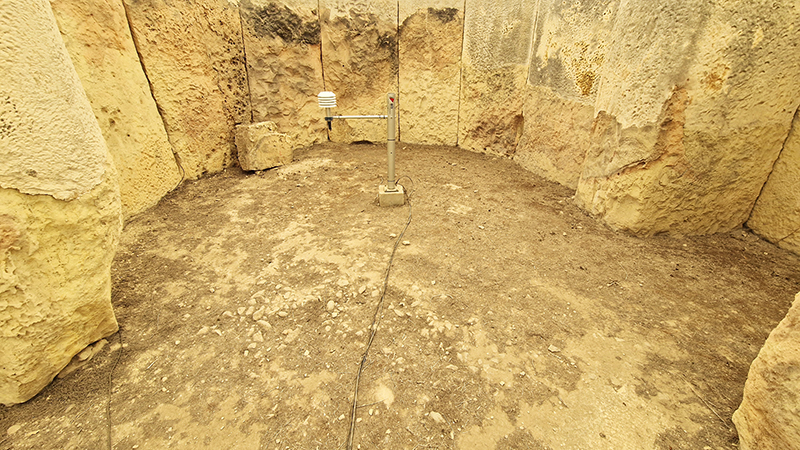
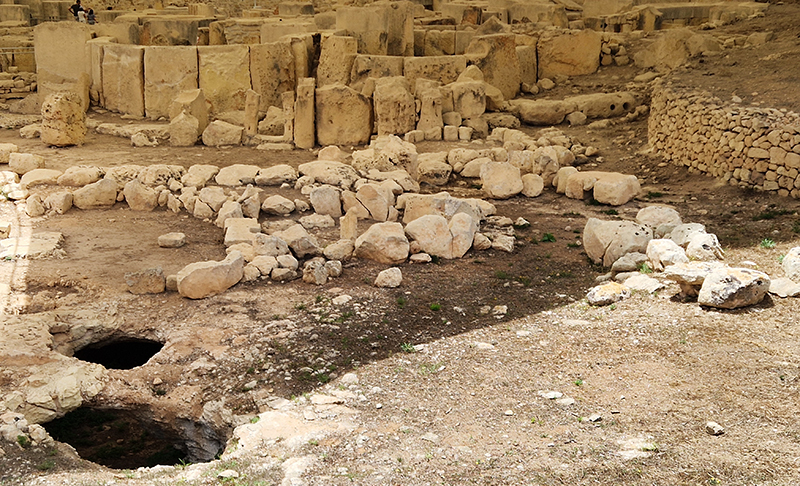
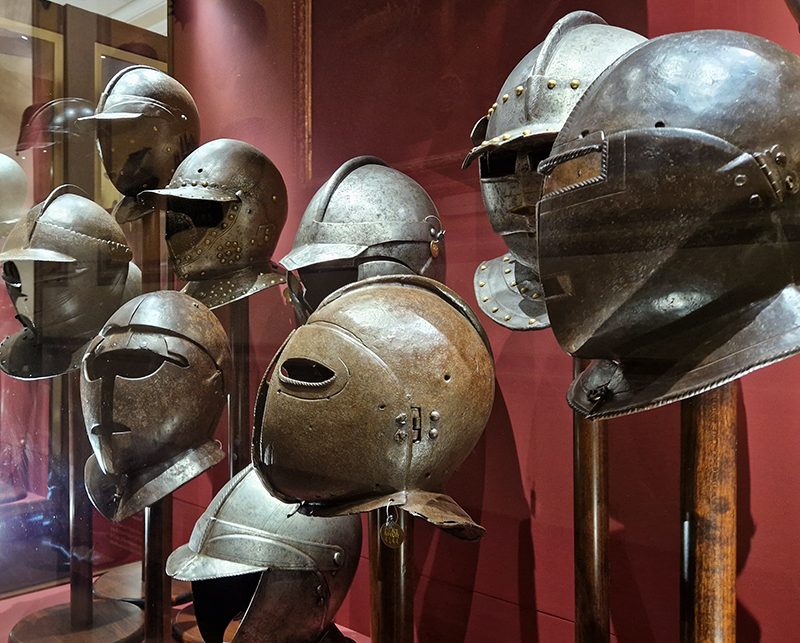
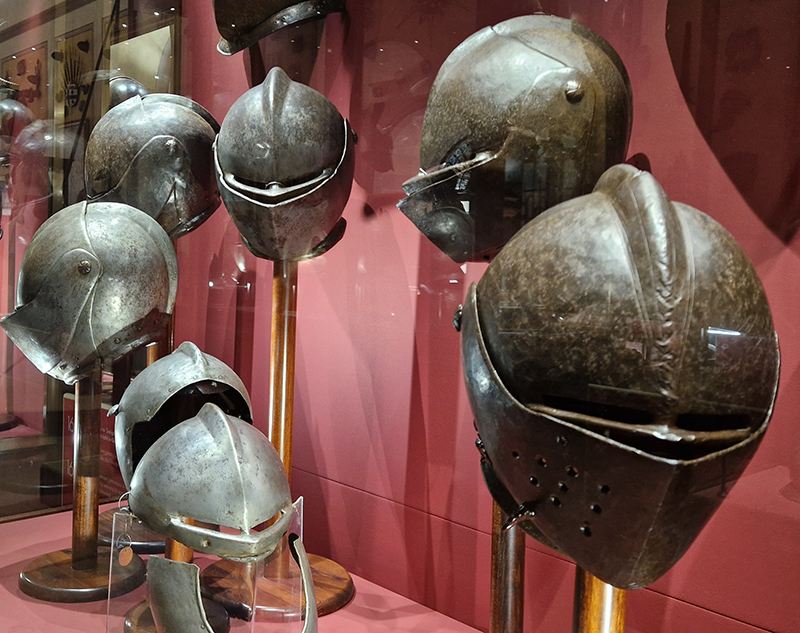
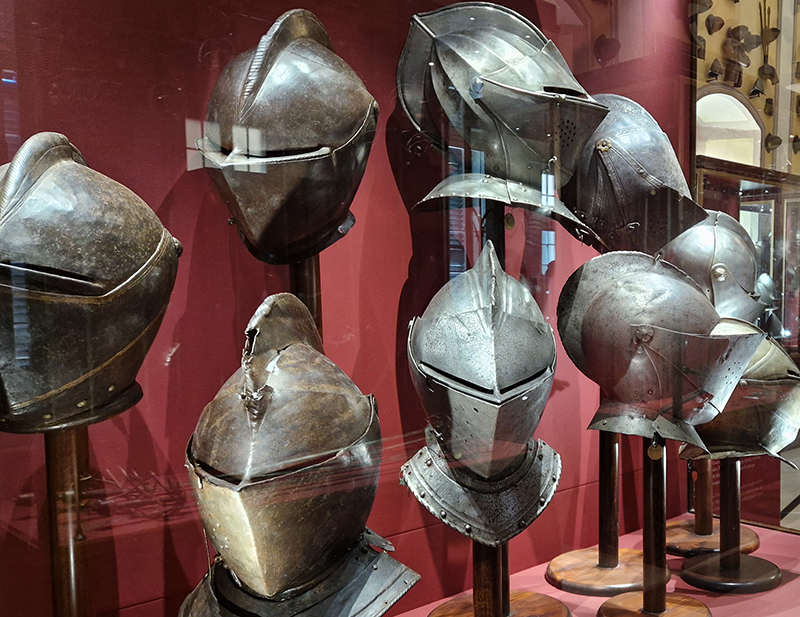
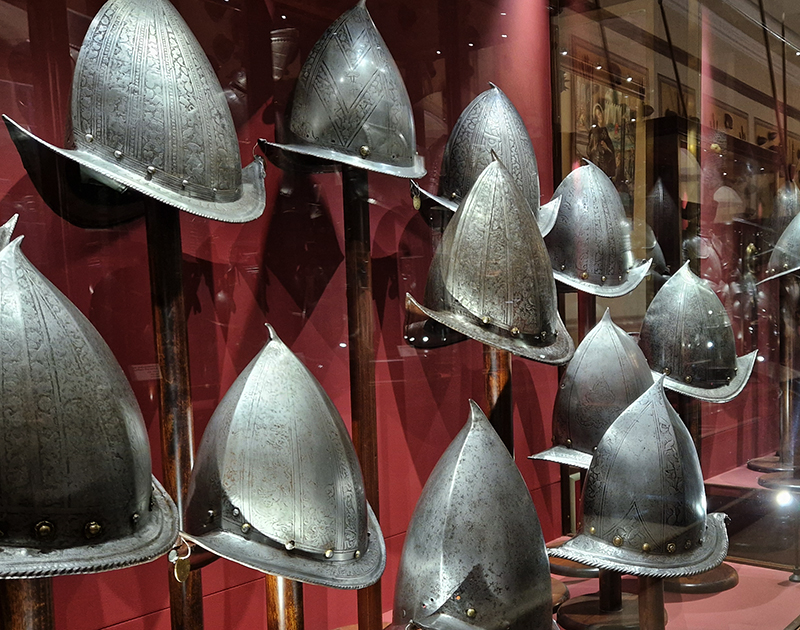
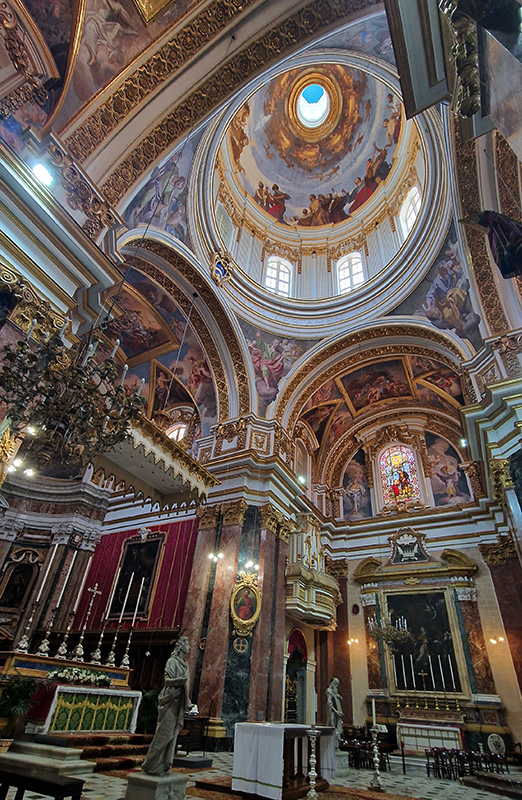
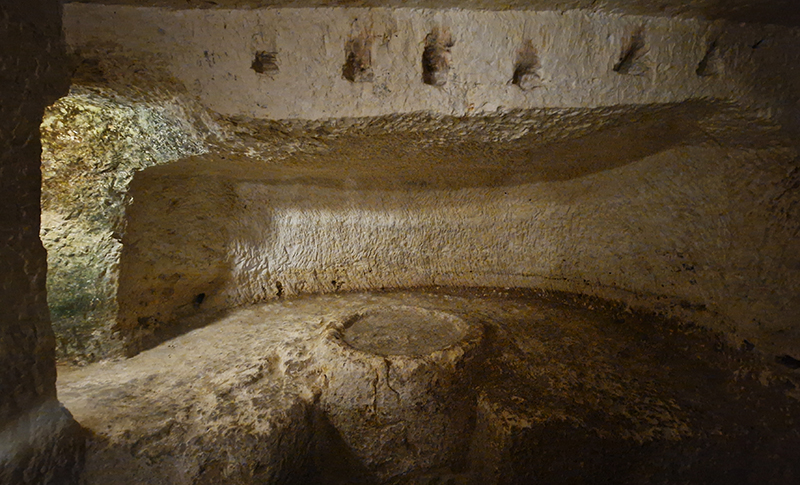
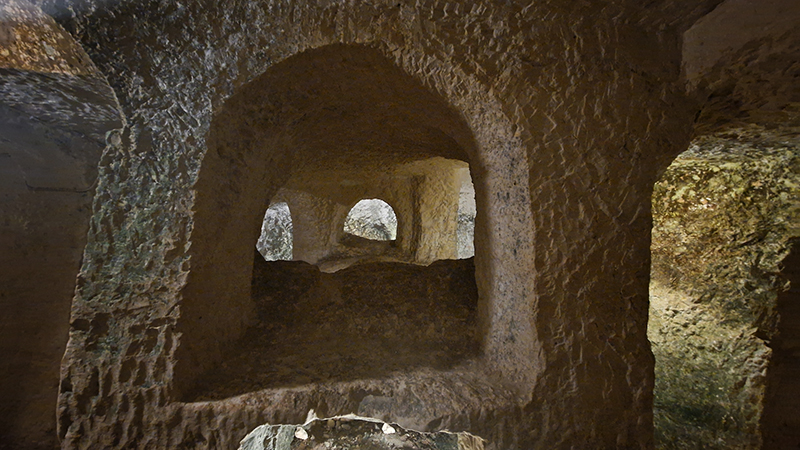
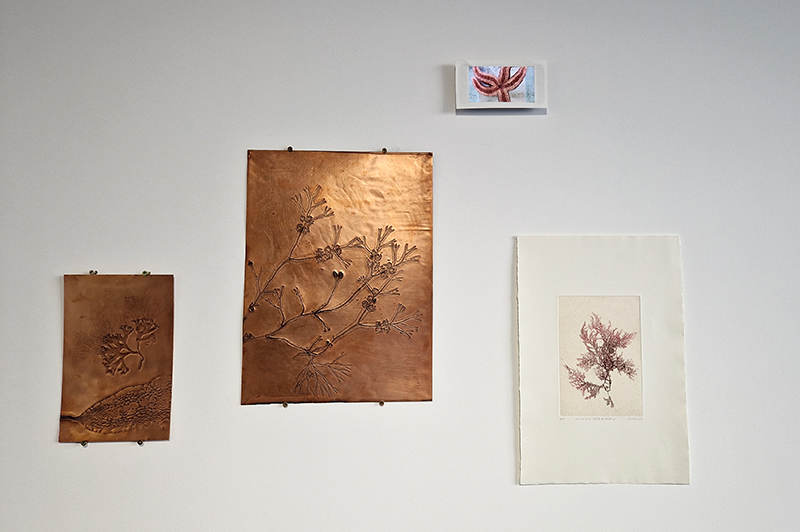
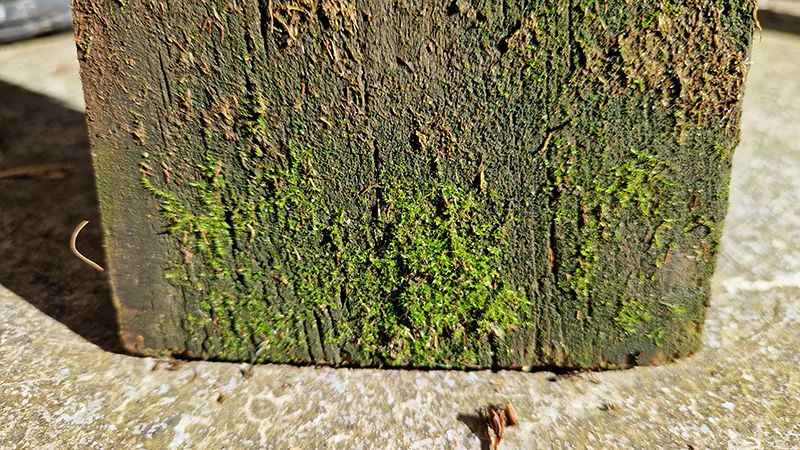
The Geological Unconscious had a wonderful six week run at Hypha HQ, Euston. Responding to Jason Groves’ inquiry into the mineral imaginary in his eponymous book, as well as the ‘Writing of Stones’ as proposed by writer and mineral collector Roger Caillois, the exhibition exposes the complex entanglements between the organic and the inorganic; the human and the lithic.
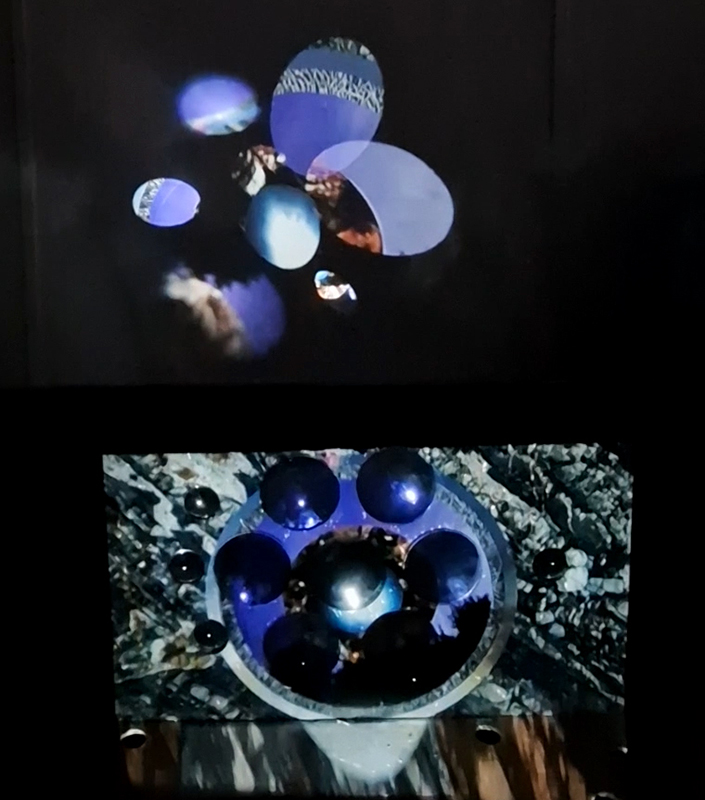
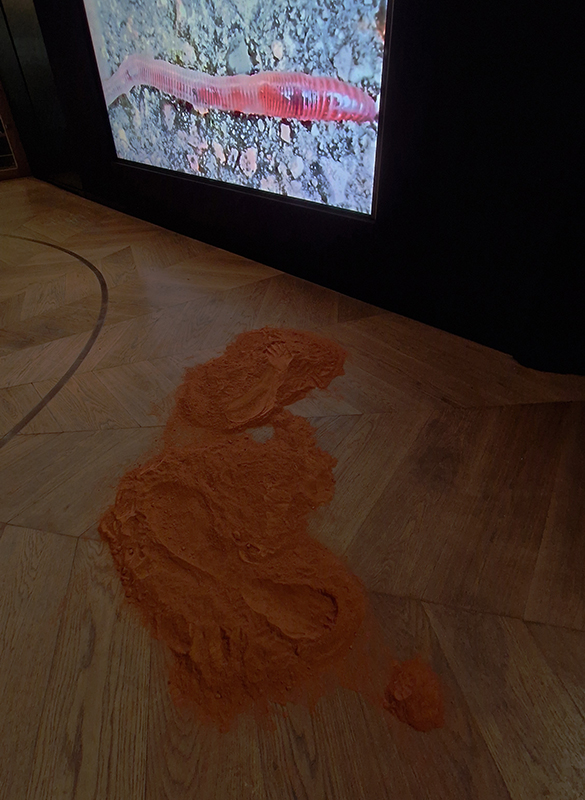
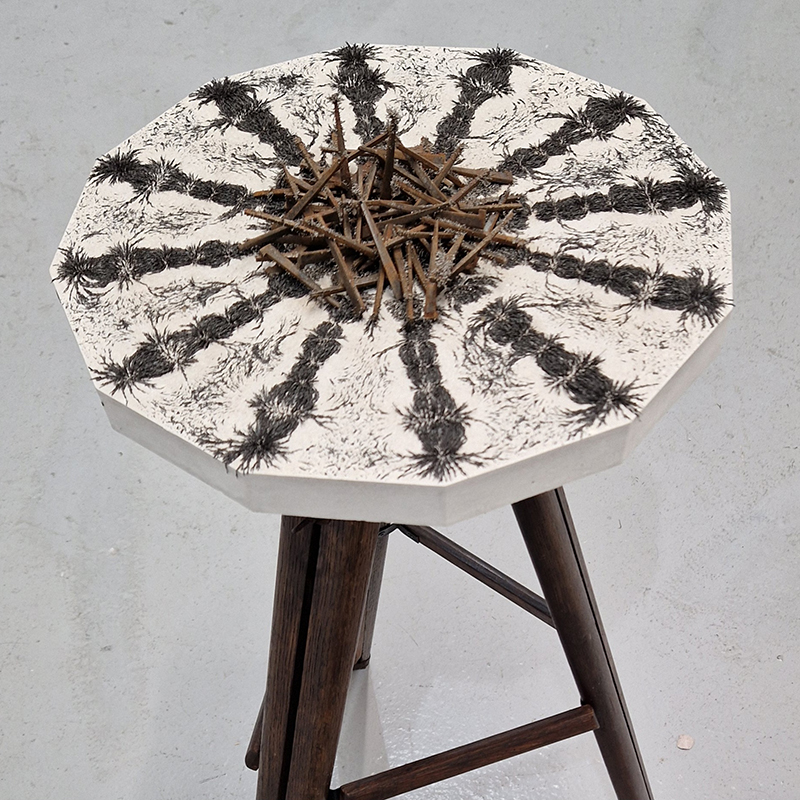
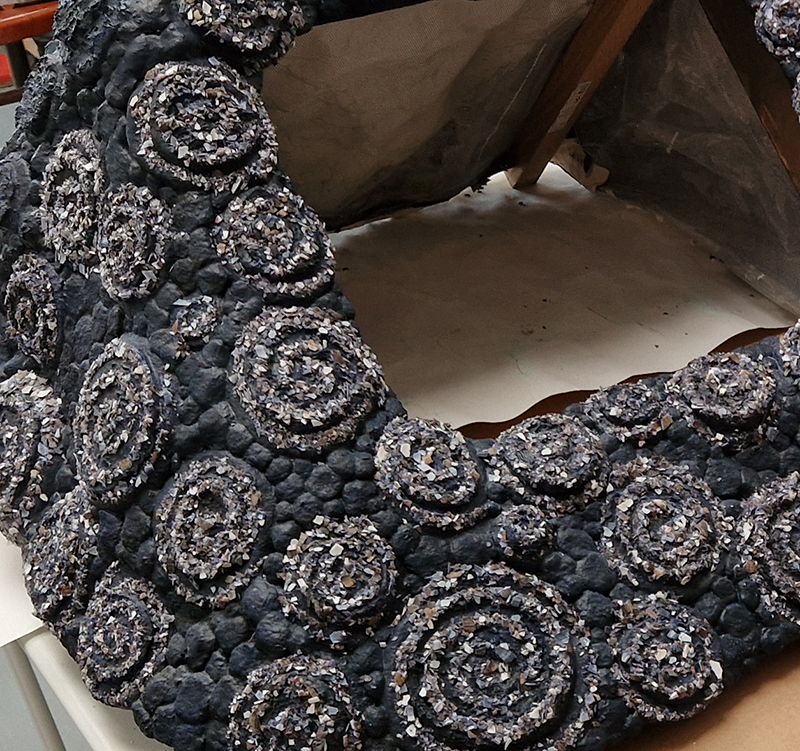
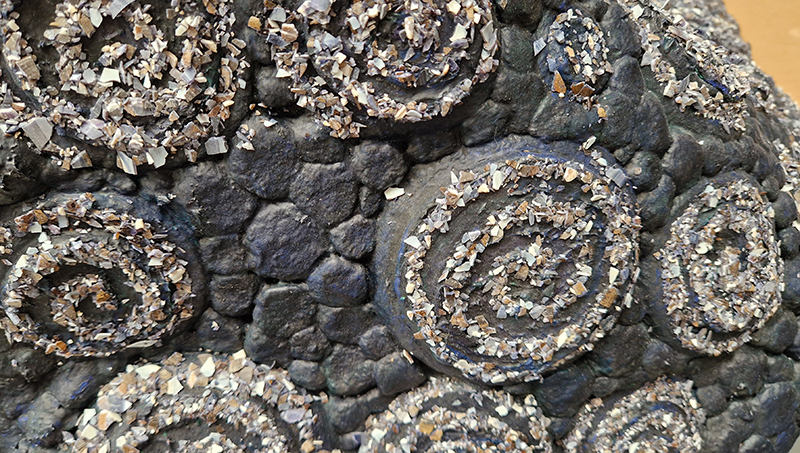
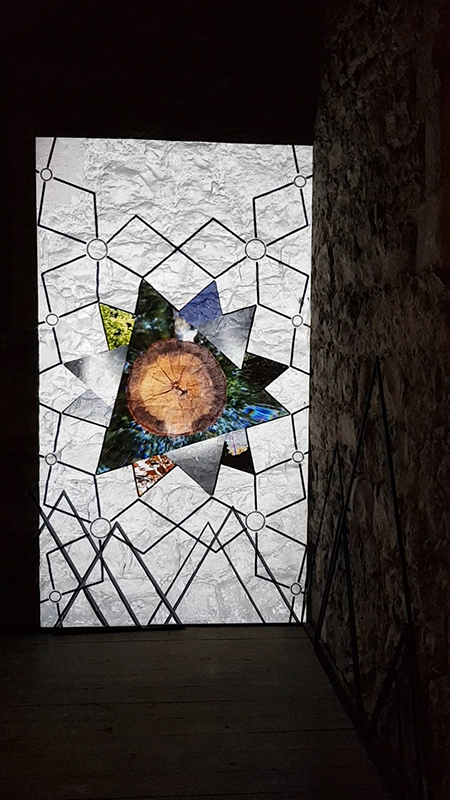
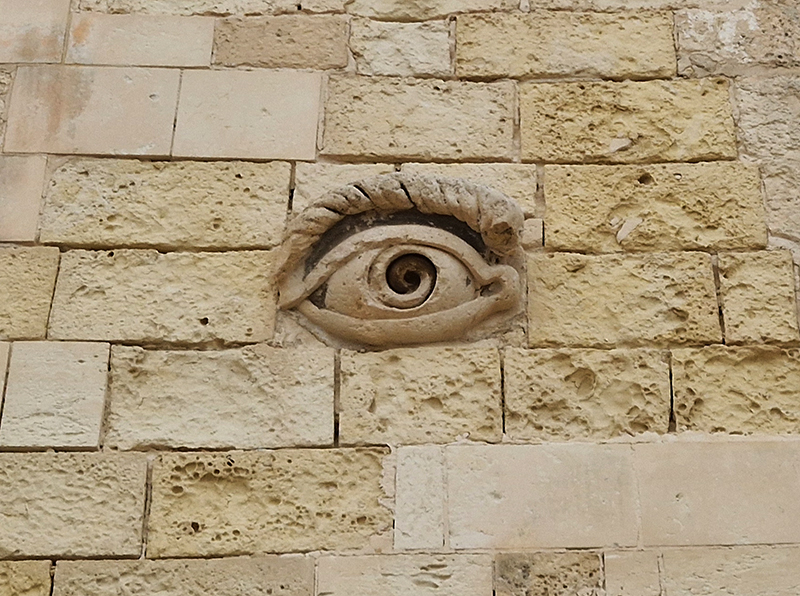
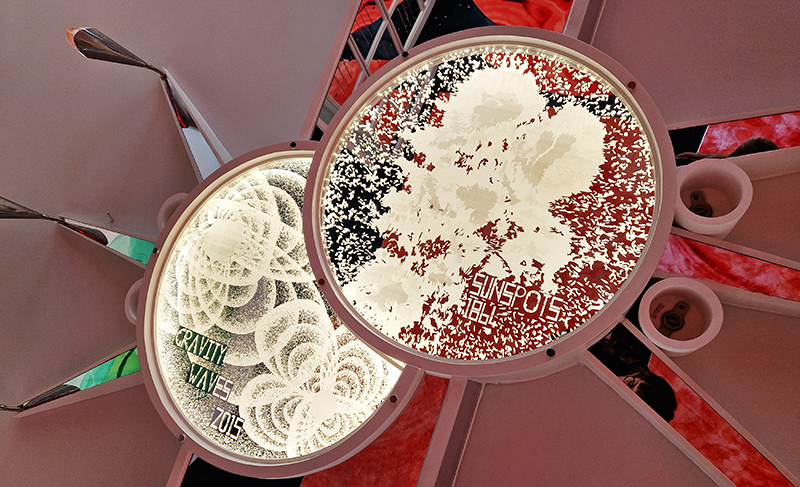
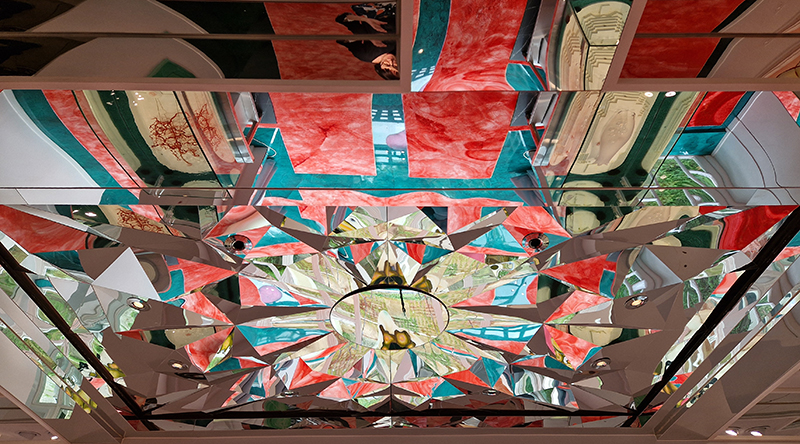
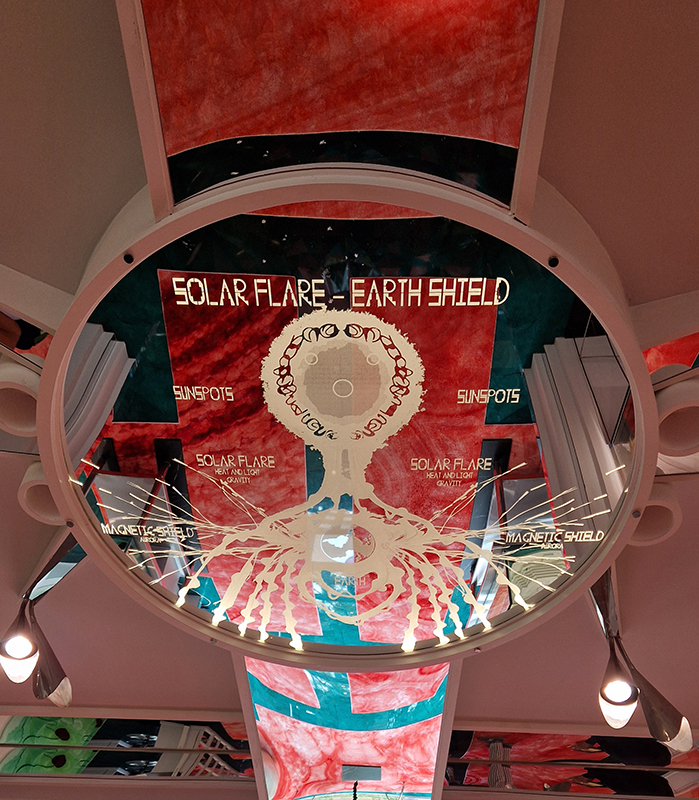
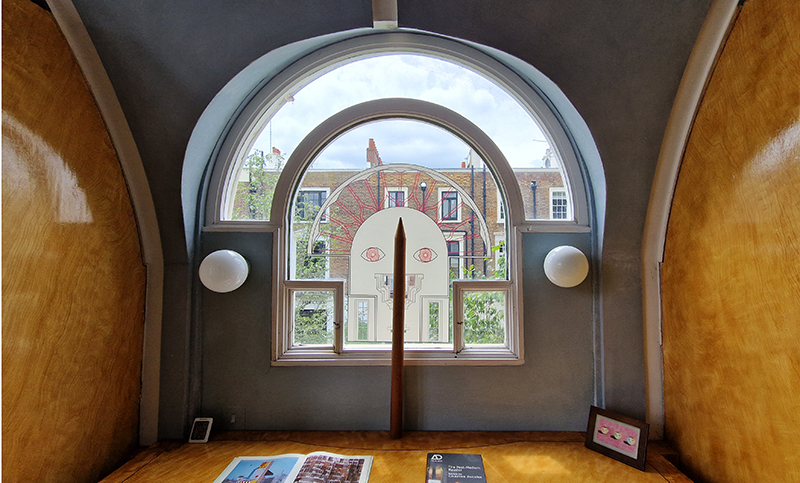
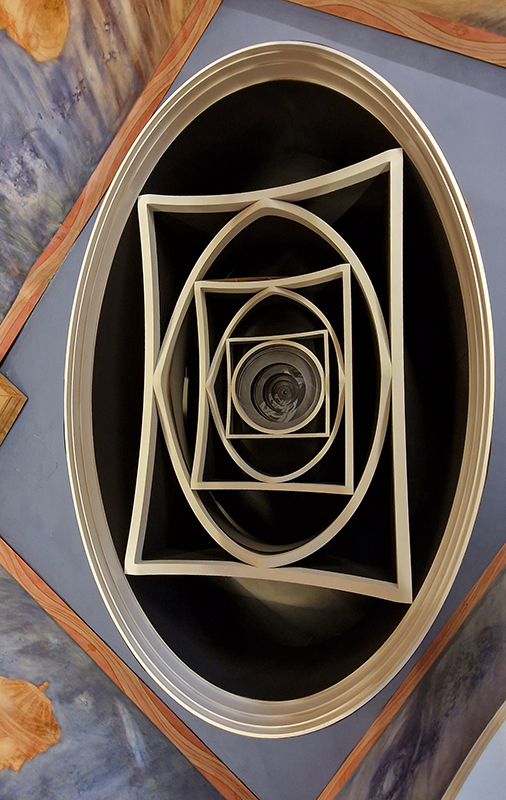
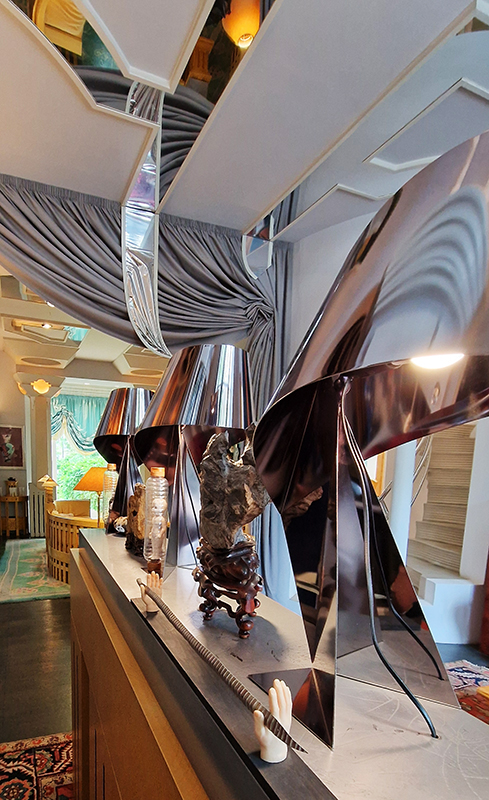
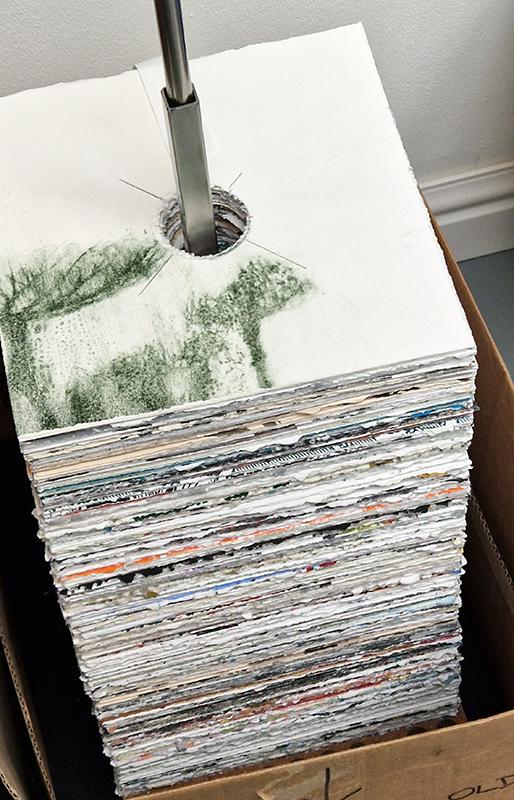
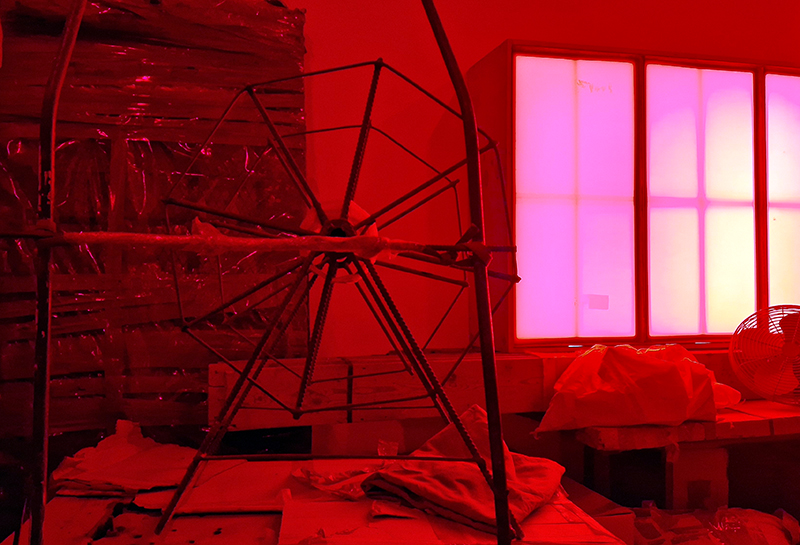
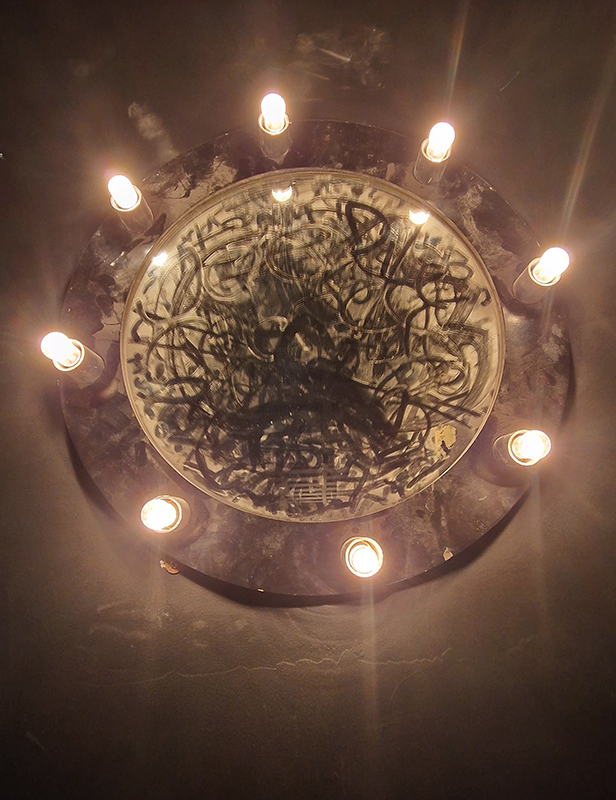
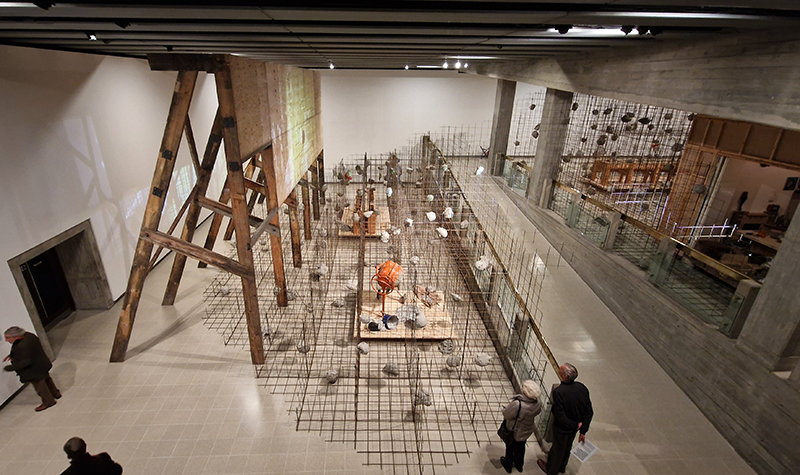
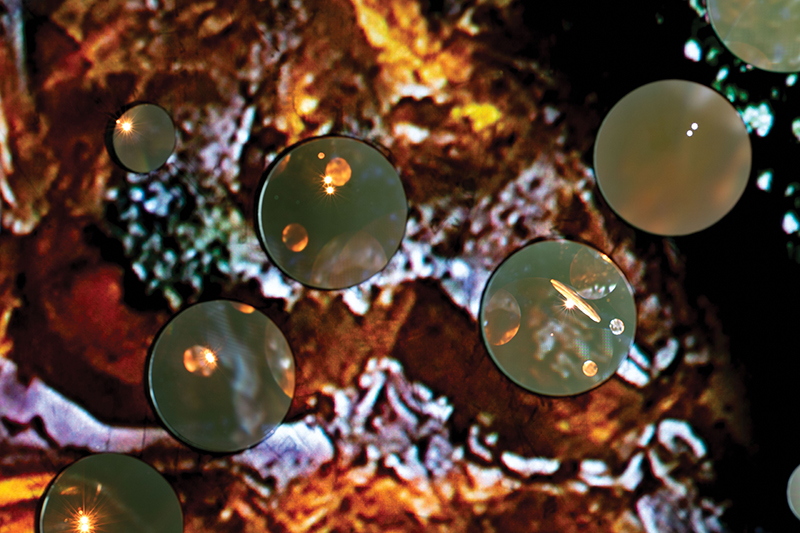
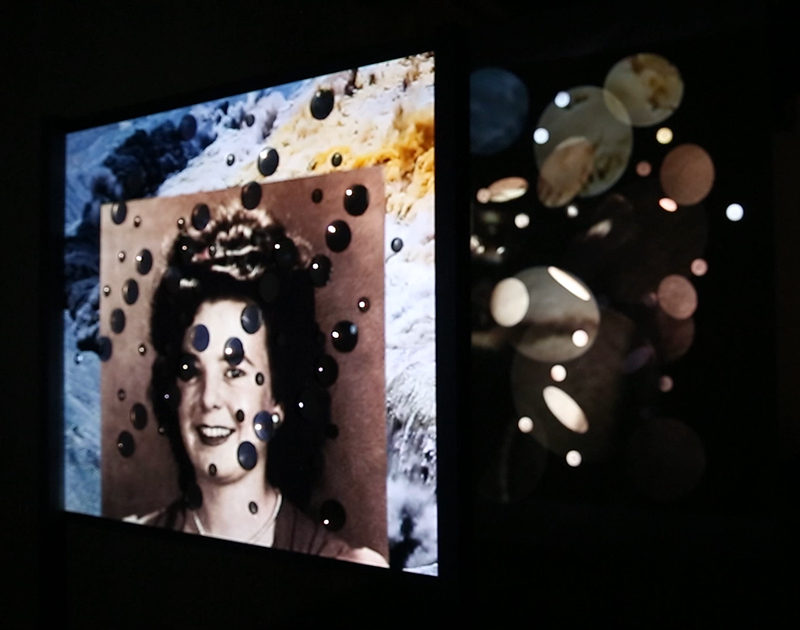
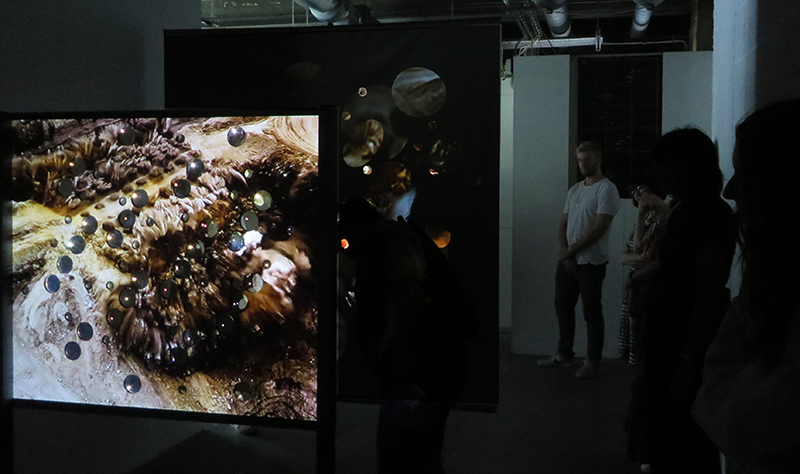
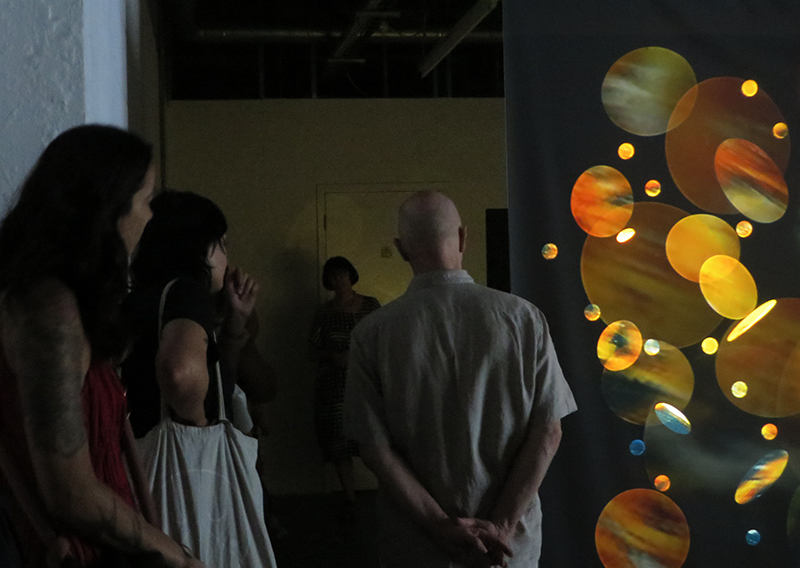
Very happy to receive lots of positive feedback for my video installation Lithos Panoptes. People were very engaged with how the work reveals itself in stages, from the kaleidoscopic imagery displaying on the two way suspended screen to discovering the board of distorting lenses behind the screen and finally stepping back to see the original film from the human perspective before it is transformed by the lenses.
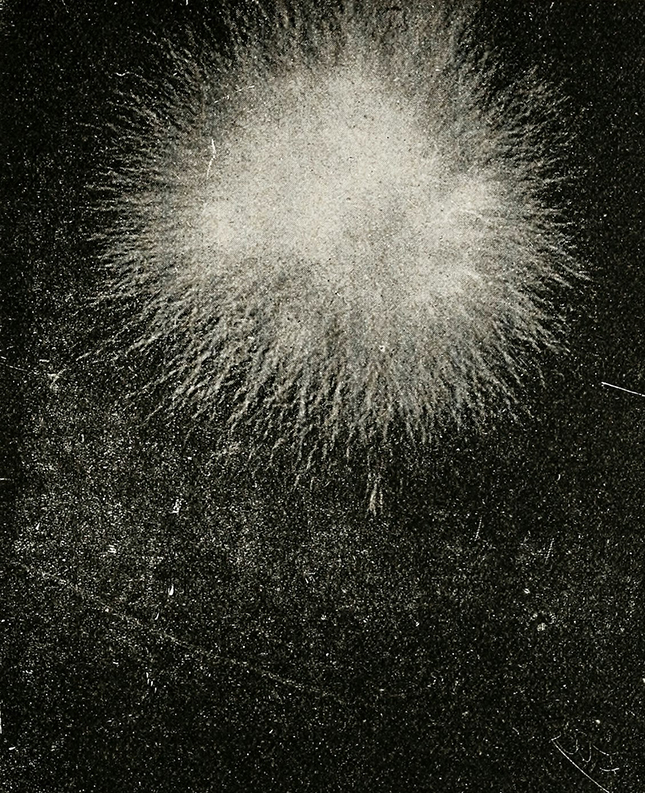
Referencing a many-eyed giant of Greek mythology, Argos Panoptes (always eyes still awake), the work considers the perpetual vigilance of rock as record keeper and witness. Video of human activity projected through distorting optical lenses transforms the anthropocentric position to imagine the perspective of the rock.
The pattern of lenses is informed by the molecular structure of magnetite, a mineral found in magma and metamorphic rock in Earth’s crust as well as in meteorites and the cells of organisms.
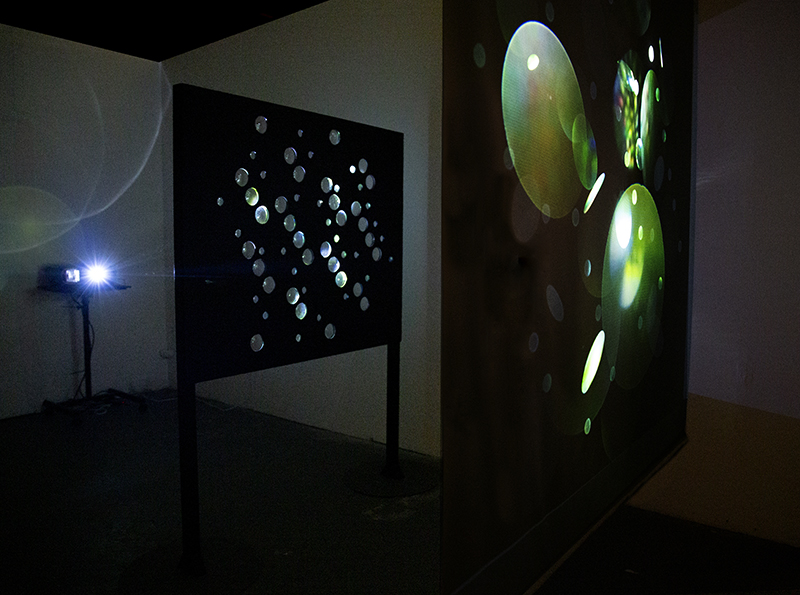


Through actual and metaphoric lenses, the relationship between the organic and non-organic is explored.
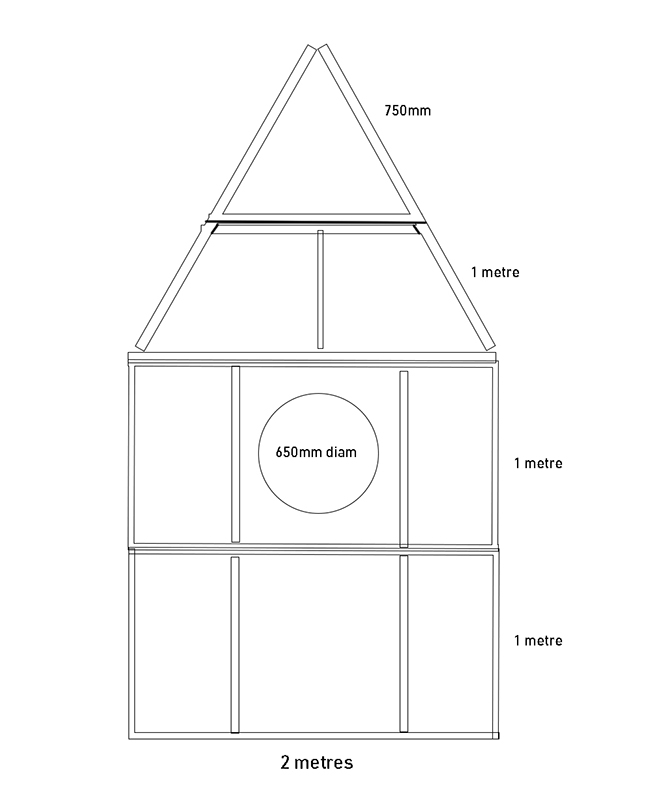
Lithos Panoptes 2025, Optical lenses, wood, steel, projector. Video 09:27 min Sculpture: H172 × W170 × D50 cm, Rear projection screen: H180 × W180 cm.
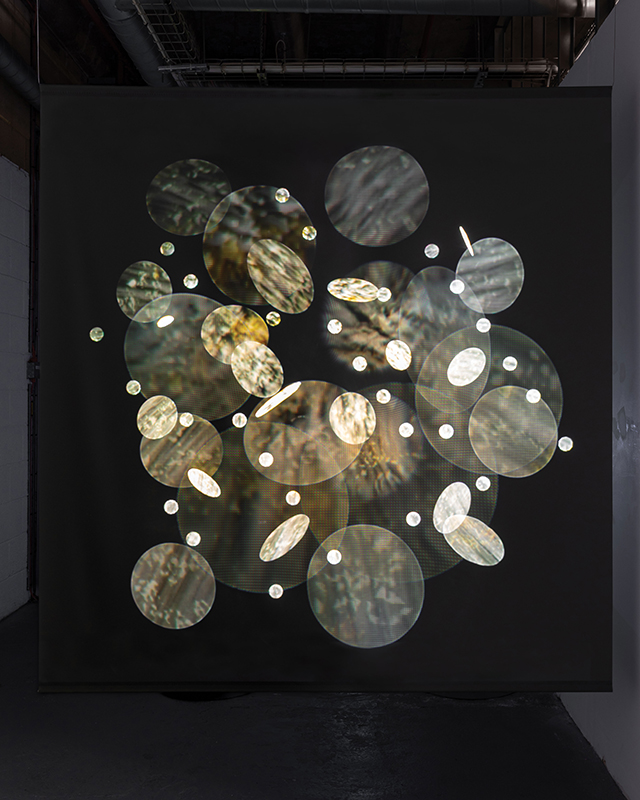
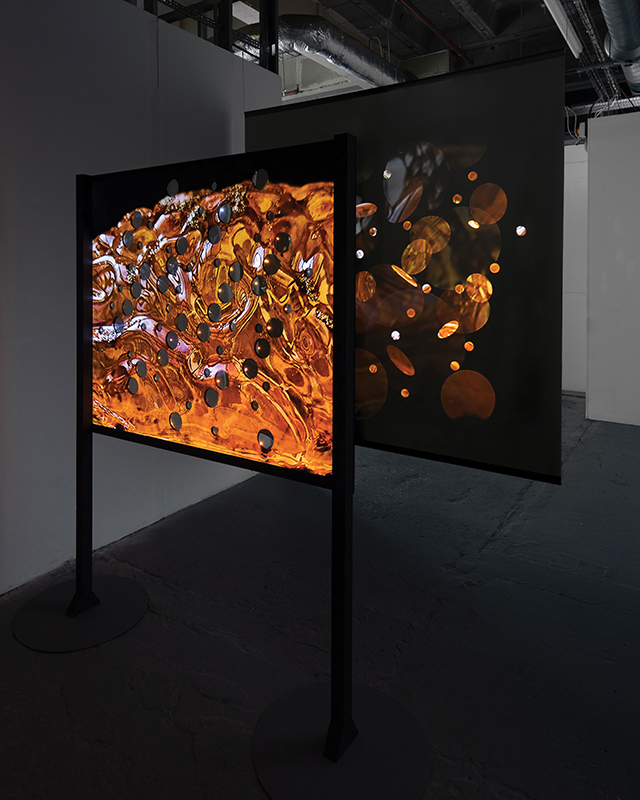


Photography by Benjamin Deakin
Mined magnetite is used in industrial and mechanical processes and its use in combustion engines and vehicle braking systems is releasing nanoscale pollutant particles into the air which are finding their way into human brain cells, vastly overwhelming the innate magnetite present, causing concerns linked to the development of degenerative brain diseases.
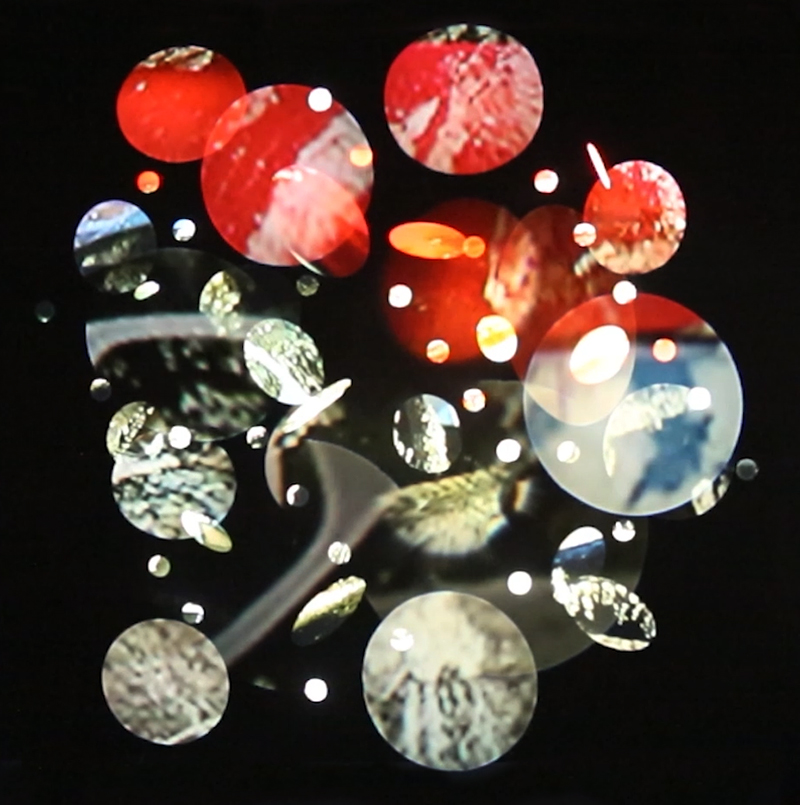
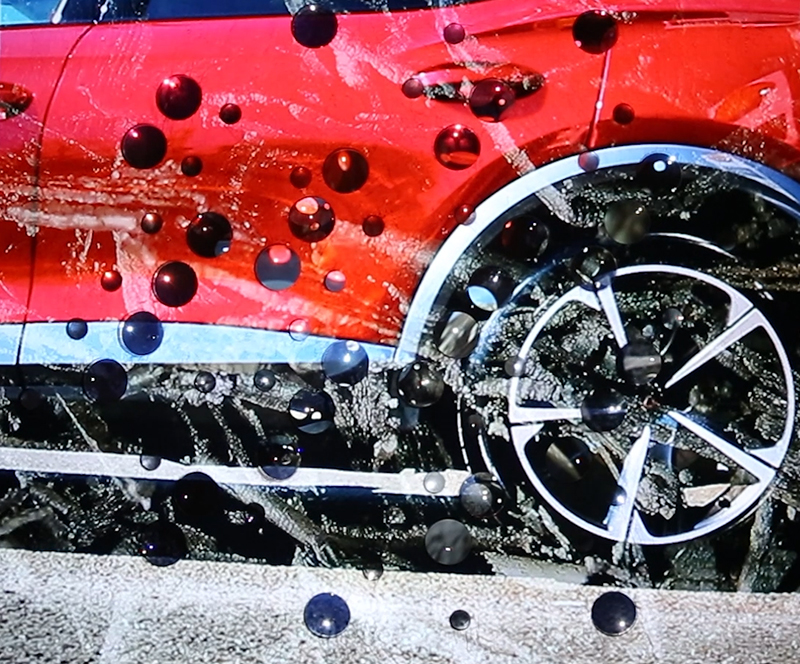


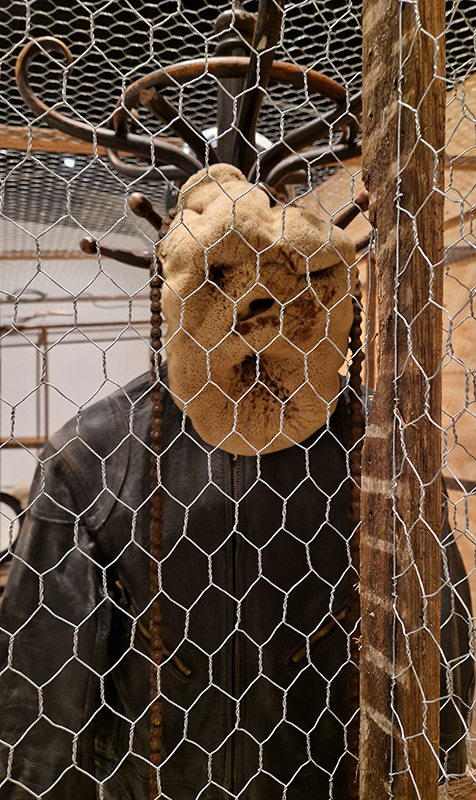
As well as referencing an ever watchful, many-eyed giant of Greek mythology, Lithos Panoptes also considers the numerous eyes (ocelli) of the chiton (a species of mollusc) whose rock crystal lenses have evolved over many millions of years to keep watch along rocky coastlines across the globe.
The only creature with eye lenses made of mineral and not protein, the chiton is also unique in having rows of teeth primed with magnetite which allow chomping on the hard rock surfaces it clings to. Some chiton’s teeth also contain the recently discovered mineral santabarbaraite, named after the mining district Santa Barbara in Italy where it was found – it is one of the few minerals named after a woman.
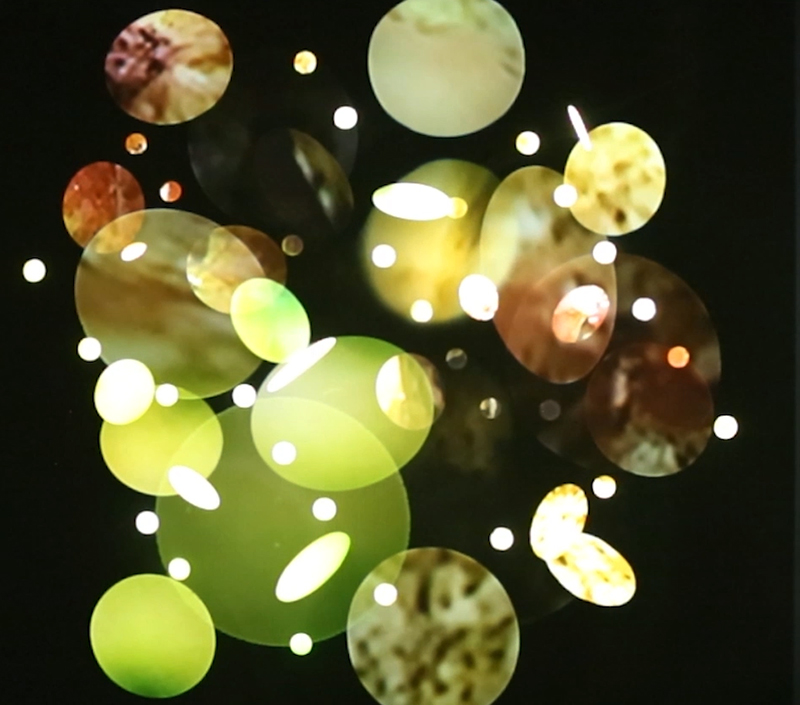


I was surprised to discover that the benedictions of Saint Barbara are still sought today, with shrines installed at tunnel entrances at Crossrail and even at CERN, the epicentre of scientific rigour. Before the boring machines were set in motion, services seeking her blessings were performed by local priests, with some even being winched down excavation shafts to carry out their duties.
Saint Barbara, who is associated with sudden death from fire, lightning and explosions, including military armaments, was adopted as patron saint of miners and tunnellers when the use of explosives in mining escalated during the 1600’s.
As the statues of Saint Barbara installed at these tunnel entrances are now buried, I have substituted images of my mother Barbara, coincidently born within hours of this Saint’s Day, in my video installation Lithos Panoptes.

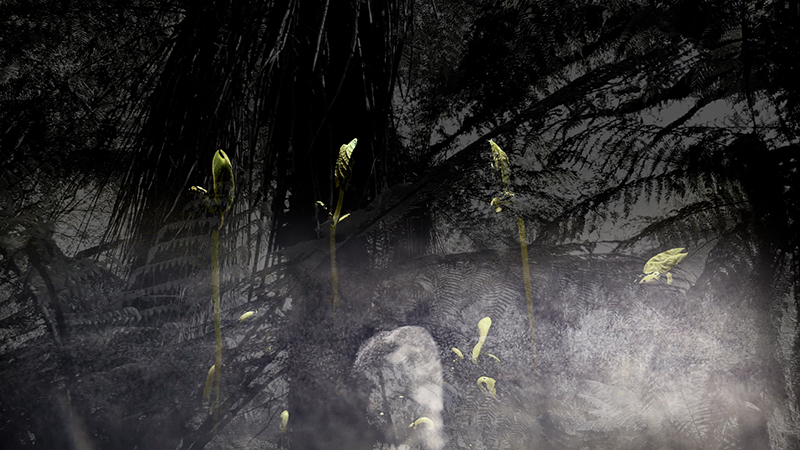
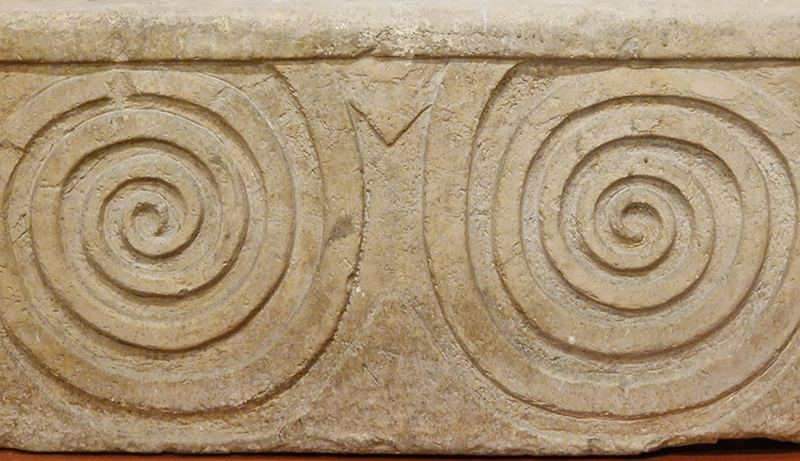
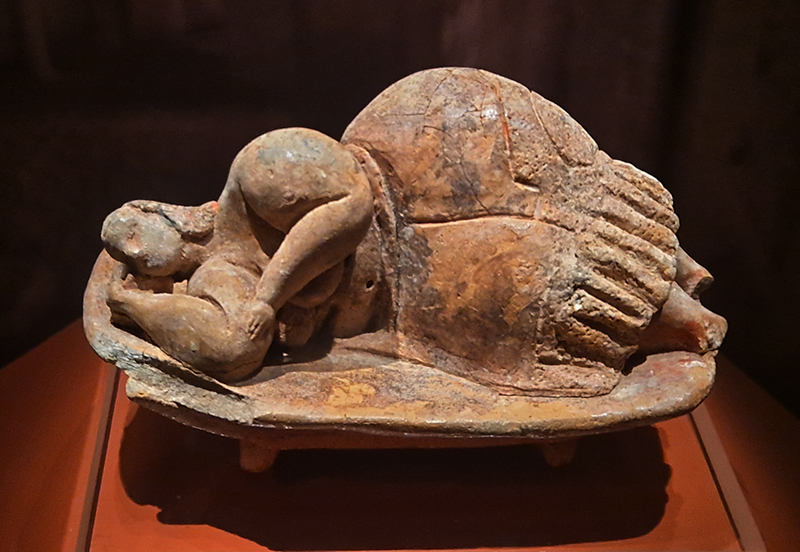
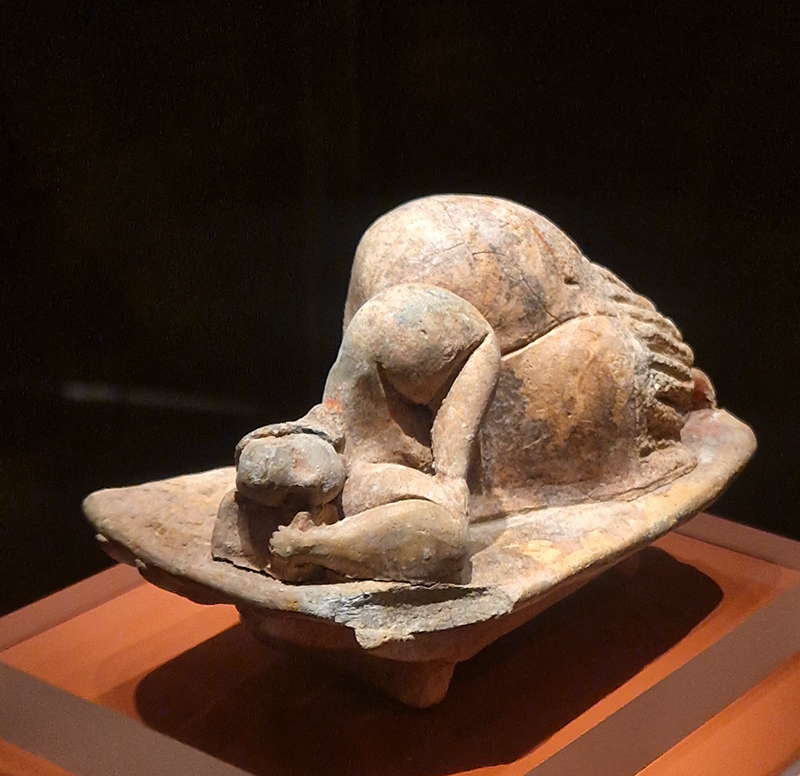
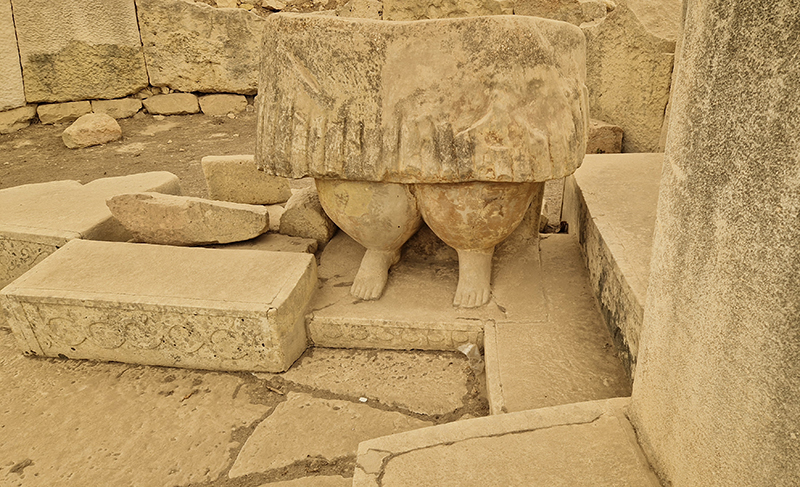
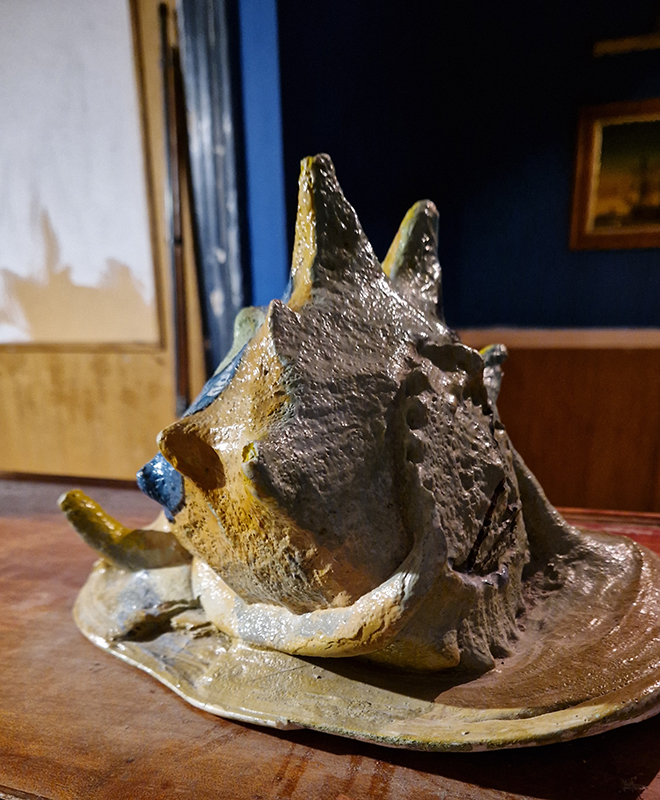
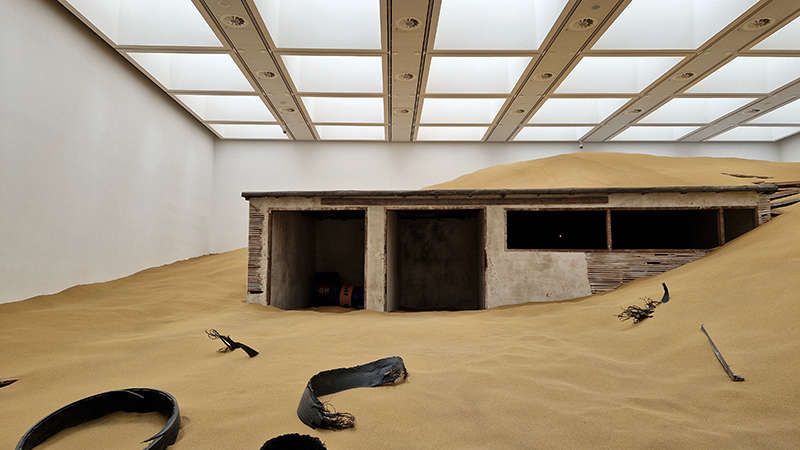
Tucked into a dark recess of the gallery, Belly of a Rock suggests an imagined place of chemical conversations at the intersection of the organic and inorganic. A hybrid between rock, mollusc and technology this video sculpture responds to an early lifeform’s emerging self-awareness, desire to communicate and urge to create as described by Italo Calvino in his story ‘The Spiral’. We don’t always know what we are creating.

Thrilled to show these works alongside Julie F Hill @juliefhill, Rona Lee @ronaleeartist, Charlie Franklin @charlie__franklin and Deborah Tchoudjinoff @deboraht_ff
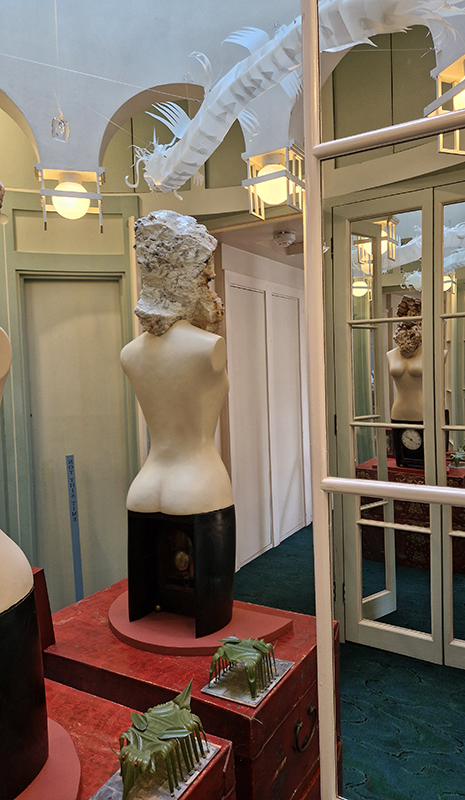
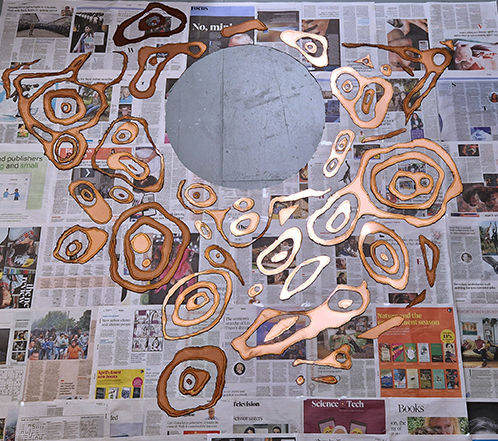
Julie F Hill’s sculptural print installation Parent Body uses scanning electron microscope imagery of samples recently returned from asteroid Bennu. The cave-like entrance, provides an embodied experience of the data and invites intimate contemplation of expanded scales. The ambiguous rock-like yet flowing forms echo the words of Jeffrey Jerome Cohen ‘stone is fluid when viewed within its proper duration’. Hill’s miniature work Return, considers the chemical and molecular cross exchanges between earth and space and in a gesture of reverse sample return (scientific missions and human extractive processes both take), a bead of Iridium is returned to the belly of asteroid Itokawa. Her small-scale embroidery work Water and Night, is based on observational studies of moonlight on water, continuing her explorations of water as the eye of landscape as proposed by Gaston Bachelard.
Julie F Hill, Parent Body, physically manipulated soy-ink print on tissue, chalk and clay pigments, chrome metal, water, clamp, funnel. c. W3 × H2.2 × D2.5m. 2025. Return, 3d print of asteroid Itokawa cast in plaster-of-paris, Iridium, 20 ×11× 8mm. 2024. Water and Night, silver metalized embroidery thread, 5.3 ×11 cm. 2025



Photography Julie F Hill (1+3) Benjamin Deakin (2)
Deborah Tchoudjinoff’s moving image installation work The City of Gold (with sound in collaboration with Joe Farley) considers vast, beyond human, geological timescales when continents have once again become as one. Starting as a short fiction text, Deborah began to form an imagined world of cities in a future Amasia. The fictional cities are named after minerals that are heavily sought – rare earths, copper, uranium, gold, and coal – hinting at a narrative of an Earth depleted of the resources we rely on. The City of Gold is one of the five imagined cities. In a world where these natural resources are no longer, she questions what it would look like and who would be the inhabitants.
Deborah Tchoudjinoff, The City of Gold, video with sound, sculptural installation, 2m × 4m × 2m. 2025.



Photography B J Deakin (1) Julie F Hill (3)
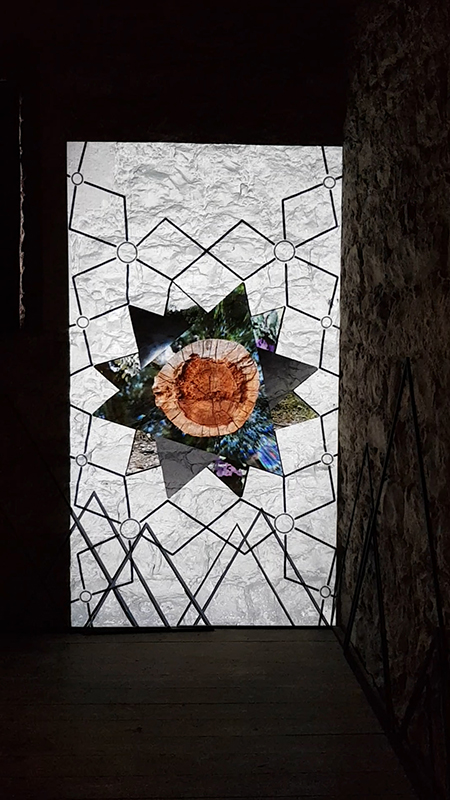
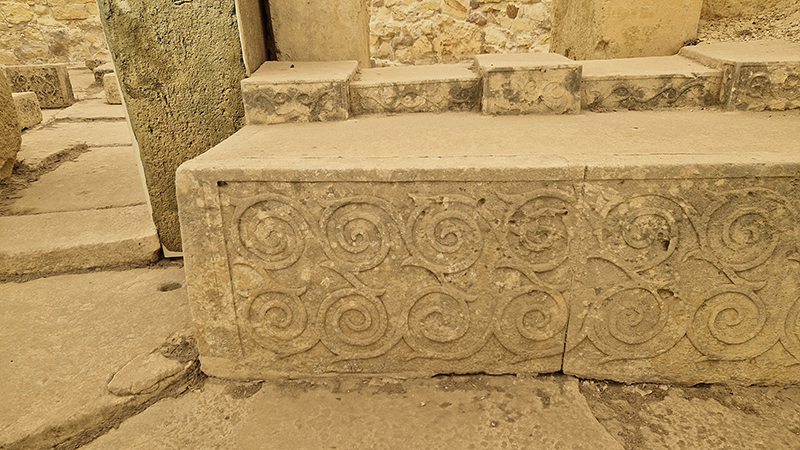
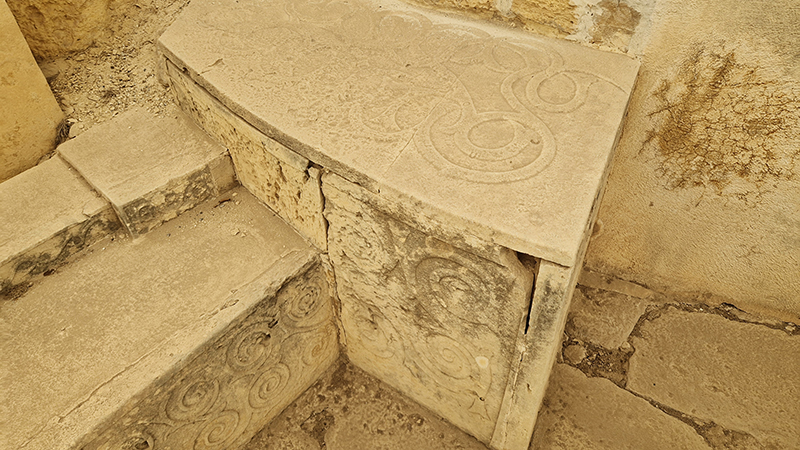
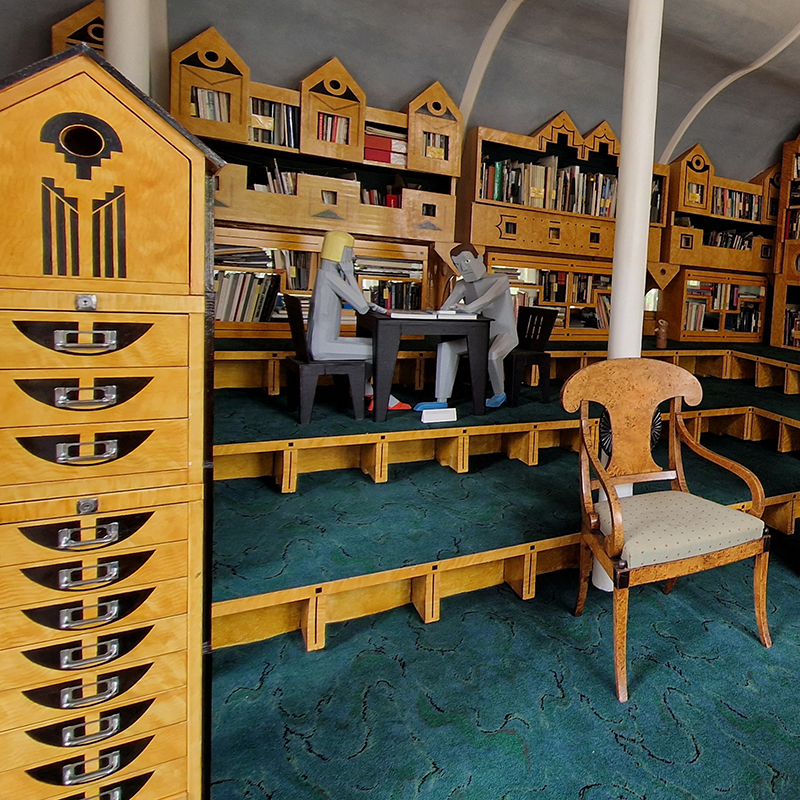
For Litho/Domous Rona Lee has chosen to work with book plates originating in the post-war period of the ‘great acceleration’ – a time in which population numbers, use of natural resources, popular consumerism, technological dependency and environmental degeneration burgeoned. Unified in their varying representations of the geologic but broking no contradiction between their celebration of extractive processes such as tourism and industrialisation and idealisation of the ‘wild’, the images selected by Lee conjure a pre-fall world in which imaginaries of lithic instability are firmly suppressed.
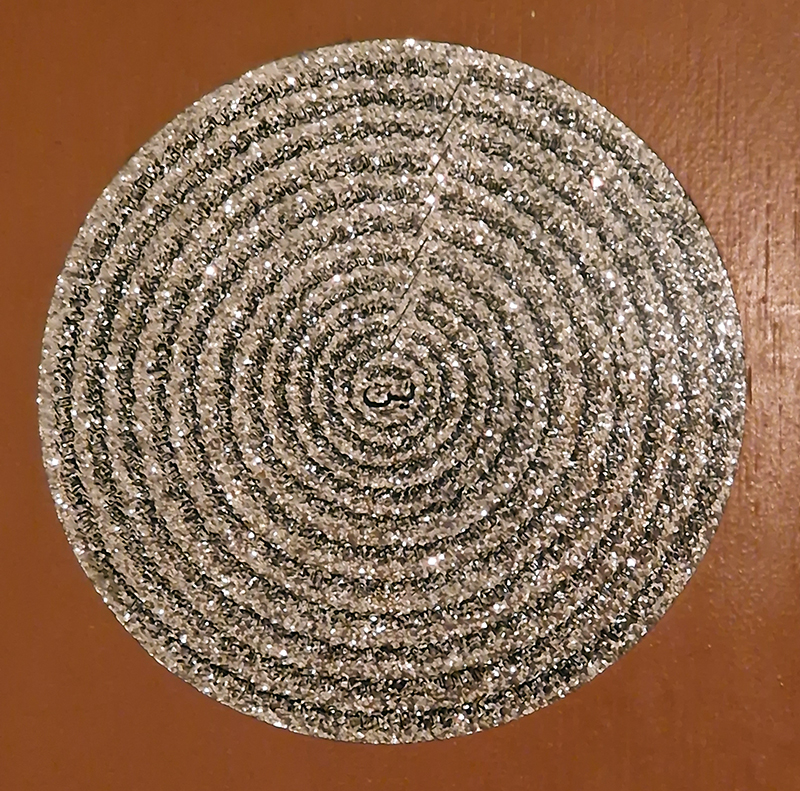
Two handfuls of silt (the residue of scientific samples collected at a depth of 4,000 meters), squeezed into the artist’s hands, fired and then gilded, form Rona Lee’s I want, I want, I want (2012), the title of which references William Blake’s engraving of the same name, wryly conjures the possibility of reaching down into the ocean’s depth, as though into a rock pool, while simultaneously cautioning against the folly and voracity of such ambitions.
Rona Lee, Litho/Domous, light panels, bookplates. 2025. I want, I want, I want, fired and chromed handfuls of sediment, 2012.


Photography B J Deakin
The sculptures presented by Charlie Franklin, Landform and FRAGS, are lumpy, solid looking forms that speak of geological debris or ruins. All three pieces were soaked in the waters of the North Sea, on the easterly edge of the UK. This process allowed the natural elements to determine their individual patination or colouring, along with indentations and scuffs, where materials have been worn away by salt and stone. Cave Drawings (Aladdin’s Cave, Series of Grottos, Marble Curtain, Fairy Grotto, and Solomon’s Temple) are a series of five found postcards depicting the caves at Cheddar Gorge in Somerset, UK which have been hand coloured by the artist. Franklin is interested in how the addition of colour can provoke a personality or aura within each cave interior, allowing for grand experiments to be realised on an intimate scale.
Charlie Franklin, Landform, Cardboard, found fabric, gaffer tape, gouache, scrim, plaster, adhesive, acrylic paint, copper leaf, sea water residue, 87 × 26 × 30cm. 2025. Cave Drawings, felt tip on found postcards, 14 × 9cm. 2025. FRAGS, cardboard, rope, gaffer tape, scrim, oil paint, aluminium leaf, plaster, adhesive, acrylic paint, copper leaf, seawater residue, work in two parts, 29 × 22 × 28cm / 12 × 29 × 23cm. 2025.


Photography B J Deakin, Julie F Hill
A highlight of our events was an Urban Geology Walk led by geologist Ruth Siddall.
“The gravel pit, like other mining holes, is the reverse image of the cityscape it creates — extraction in the aid of erection.” Lucy Lippard
Ruth lead a group walk to explore the geology of the local built environment around Regent’s Place and Fitzrovia. Her knowledge of geology is astounding and her passion for stone infectious. Everyone came away incredulous, having their eyes opened to the deep time history of the rocks that build our city. The deep, black, Archaean dolerite from Mashonaland in Zimbabwe that Ruth points to is 2.2 billion years old. The large block of polished stone shaped like a giant pebble, itself crammed with pebbles of other rocks, is a sculpture by John Aiken, Monolith & Shadow. A patchwork of Jurassic limestone from southern Spain is crowded with the spire-shaped fossil shells of the gastropod Nerinea, stained red and yellow with ochres.
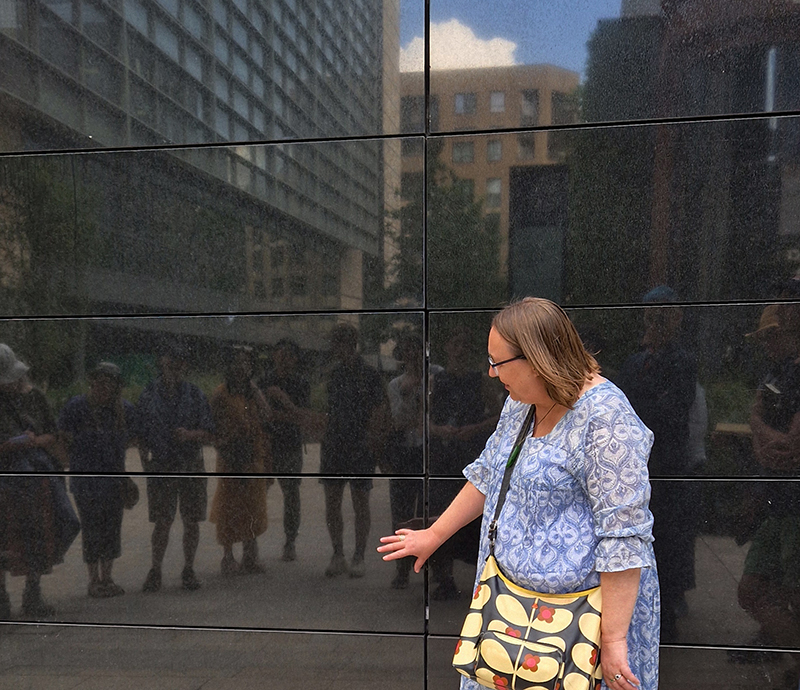





After the walk Ruth joined us for a tour of the gallery – it was fantastic to hear her insight and corroboration on some of the research that fed into the artworks.
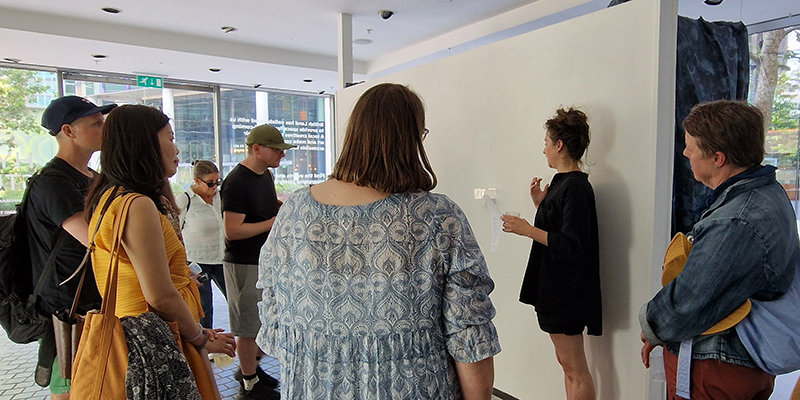

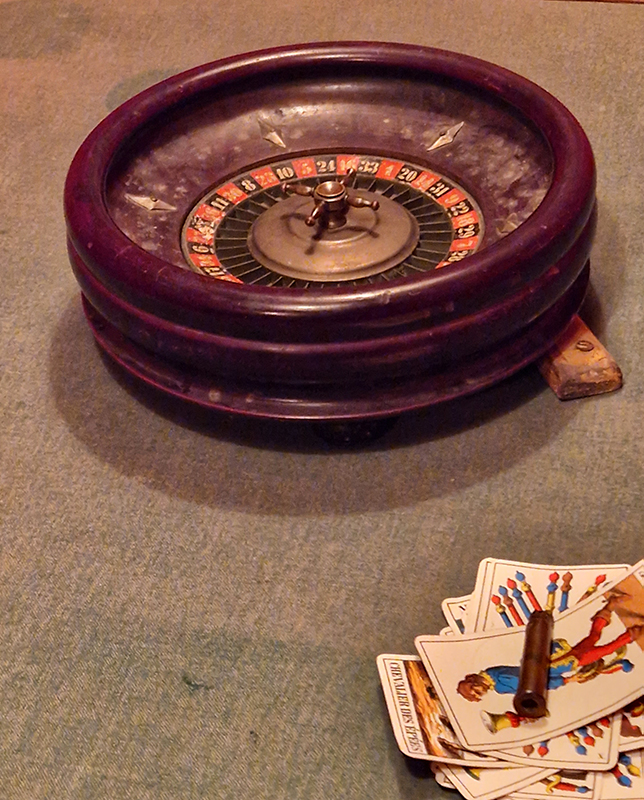
I offered Lithomancy drop-in sessions on Friday afternoons as part of a programme of events for The Geological Unconscious. Visitors were invited to throw gemstones with specially assigned characteristics onto a wooden board divided into geologically themed sections. They are then given personal interpretations based on the position of the cast stones by drawing from the esoteric ritual of lithomancy which seeks to divine the future from the reading of stones.
This performative experience proposes insights into the power and allure of stones emanating from the symbolic meanings attributed to them and exposes the entangled relations between the human and the geologic found in our language and desire to align the human condition with the lithic.
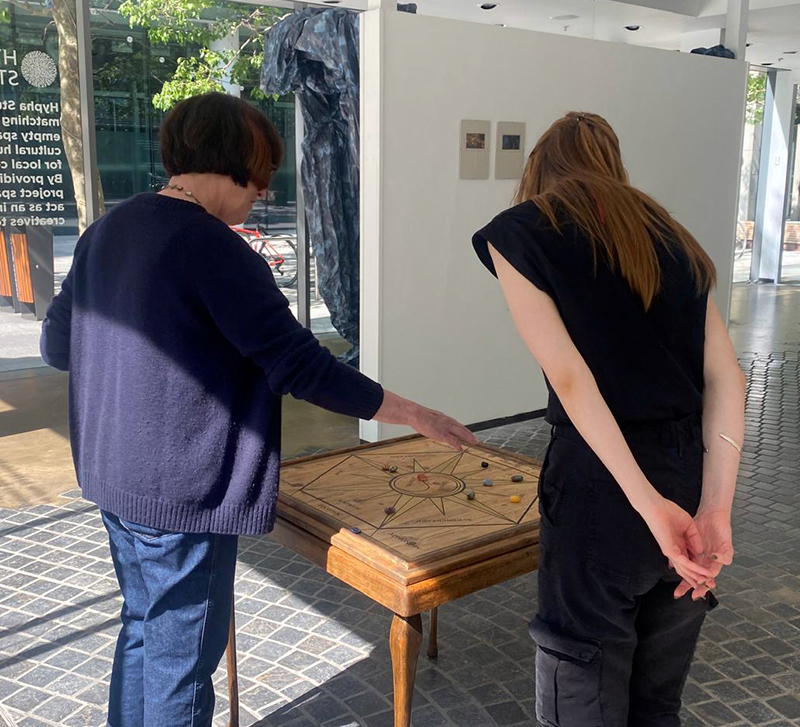
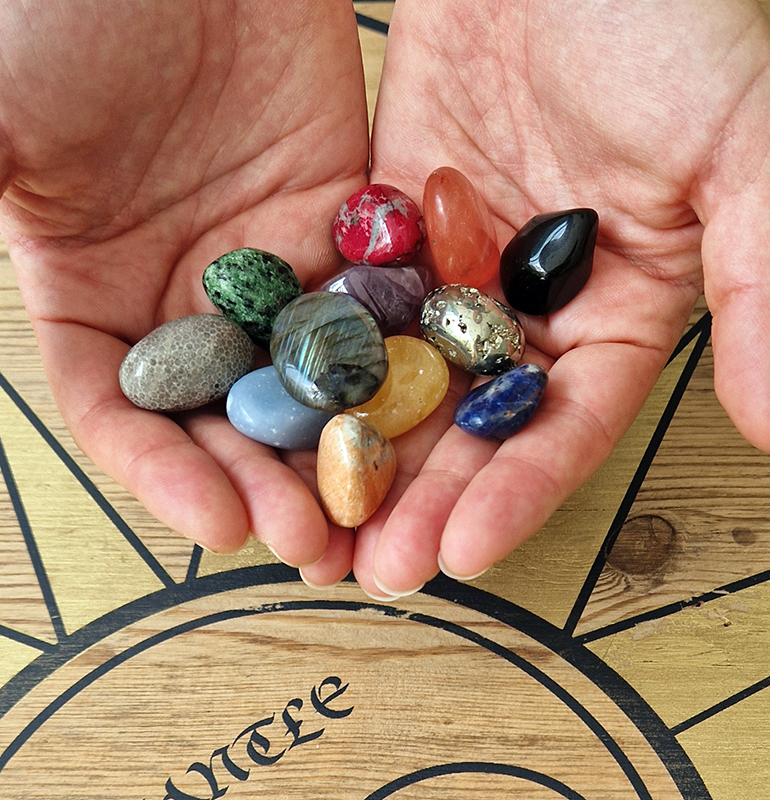






We had many interesting visitors to The Geological Unconscious and have made some wonderful new contacts. Not least among these was meeting Melanie Wheeler who has recently completed a residency in the UCL Geology Department where she worked with the technician to re-curate the rock room. Julie and I were lucky to be taken on a tour of the newly curated collection and receive gifts. So excited to have a beautiful sample of magnetite.
In ancient Greek, magnetite was known as “magnes lithos,” meaning “stone from Magnesia” – the region in Thessaly, Greece, where magnetite was first discovered, supposedly by a shepherd who noticed the nails in his boots were sticking to the rock under his feet.

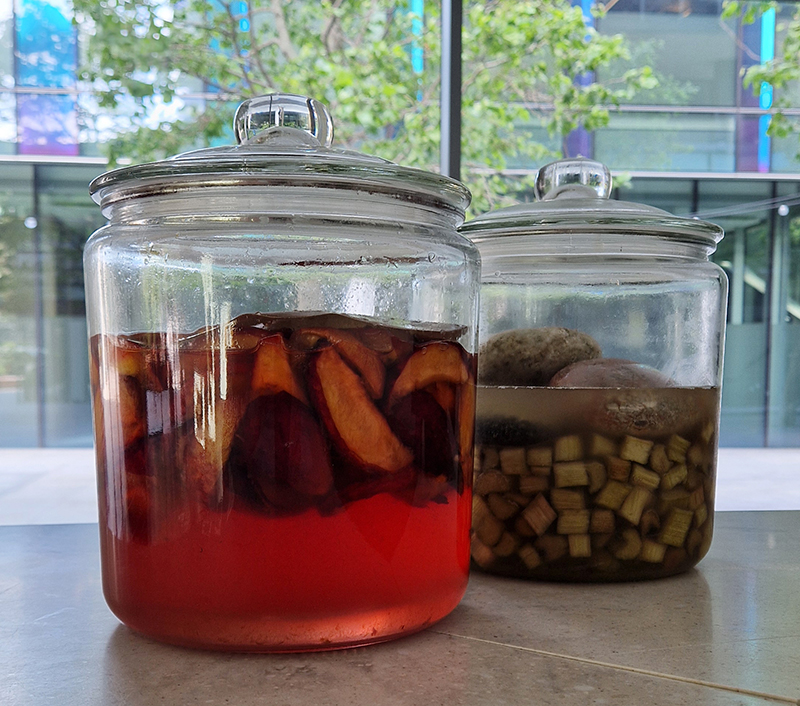
As an additional daily drop in activity during The Geological Unconscious we offered cheong tasting. Chef Moonhyung Lee explored human-mineral entanglements through digestion using stones to create cheong (Korean fermented syrup). The use of weighing stones helps create the environment for preservation, a process which amplifies the bioavailability of minerals in food. Moonhyung Lee is a food designer with a background in graphics. She is currently based in London and works at zero waste restaurant Silo.


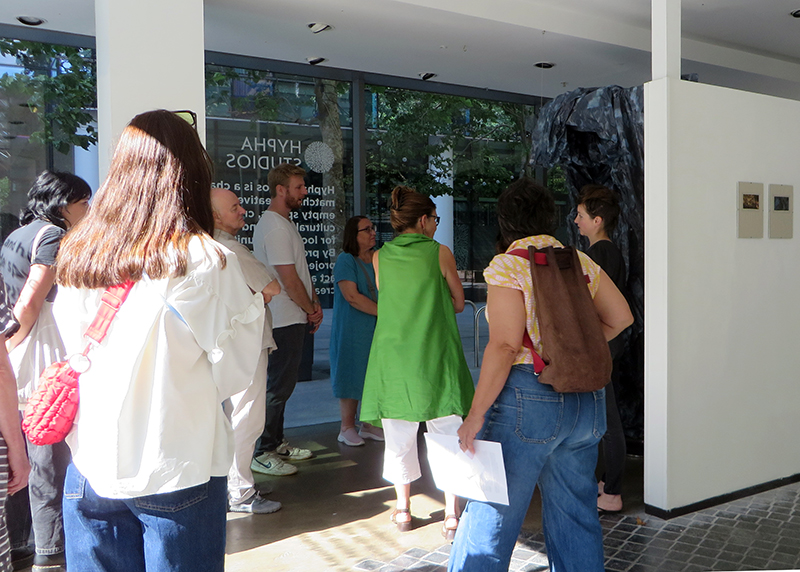
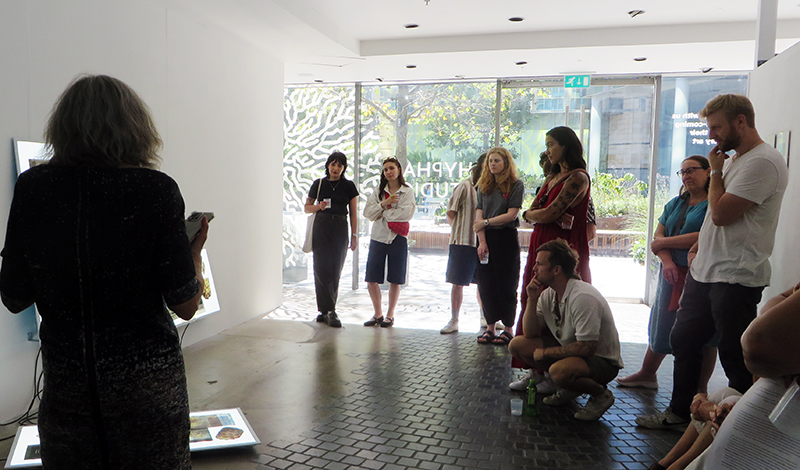
It was great to have so many people join us for our Closing Event artist talks and the launch of the exhibition publication with preface by Jason Groves and short essay by Ruth Siddall.
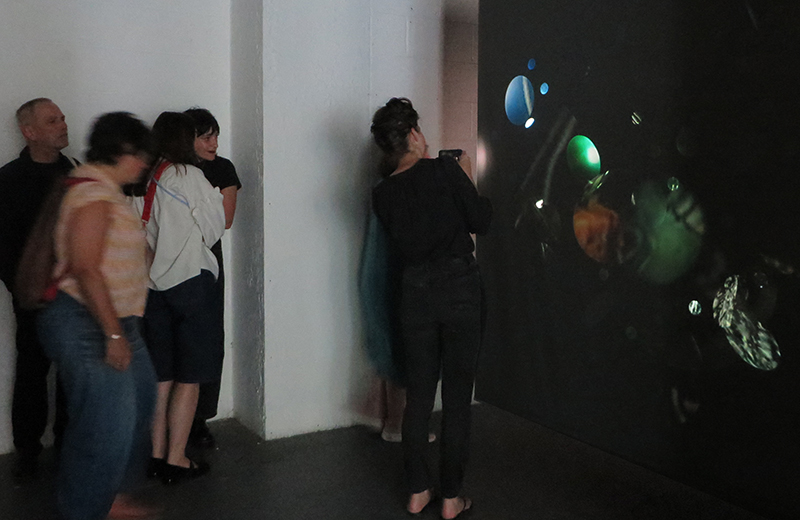












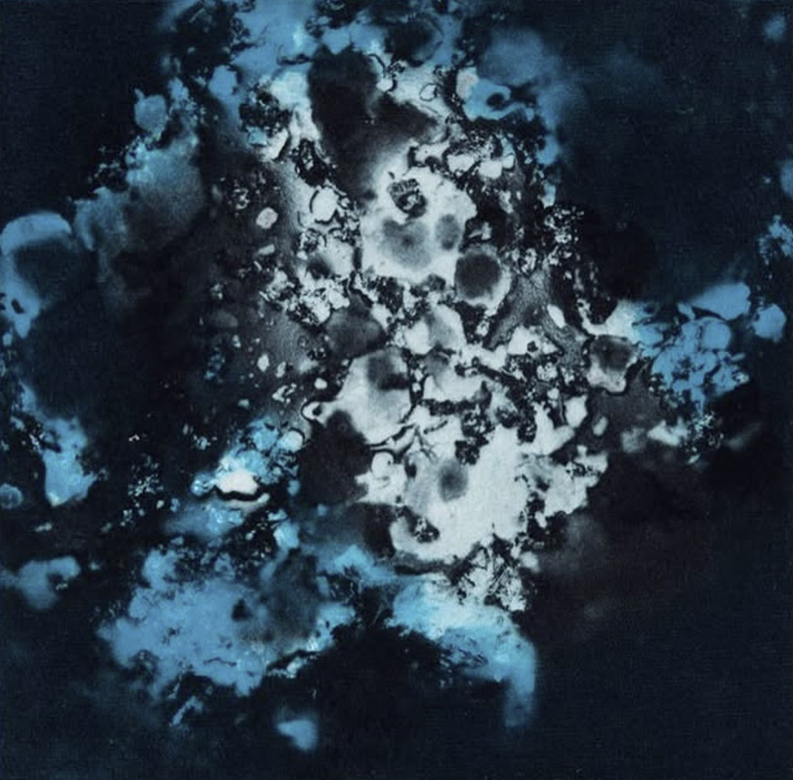
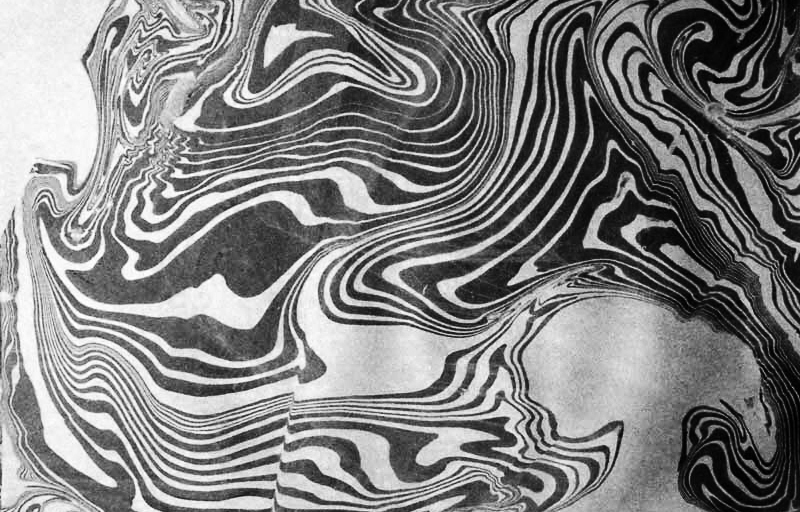
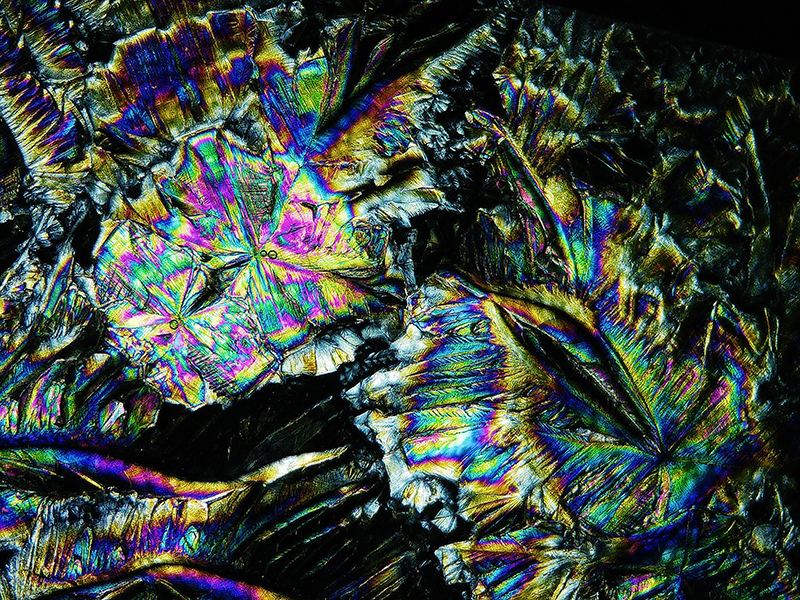
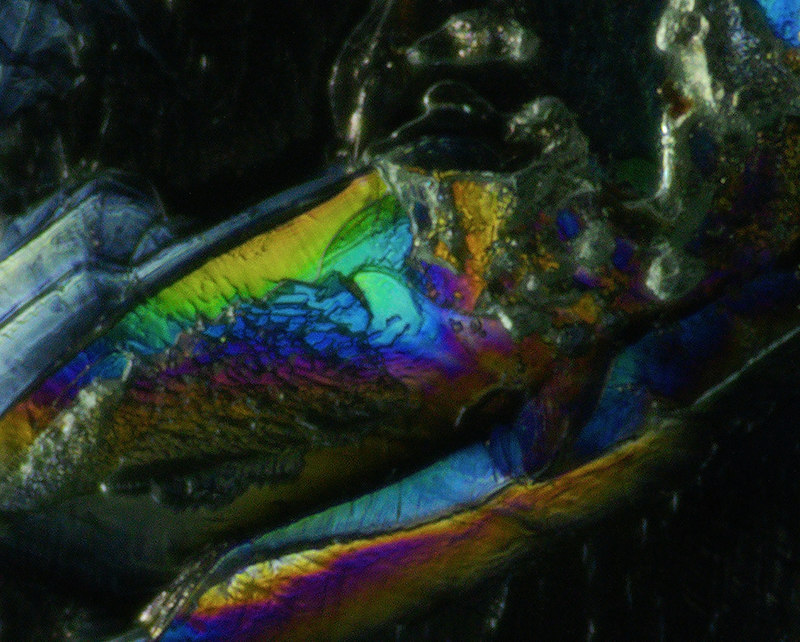
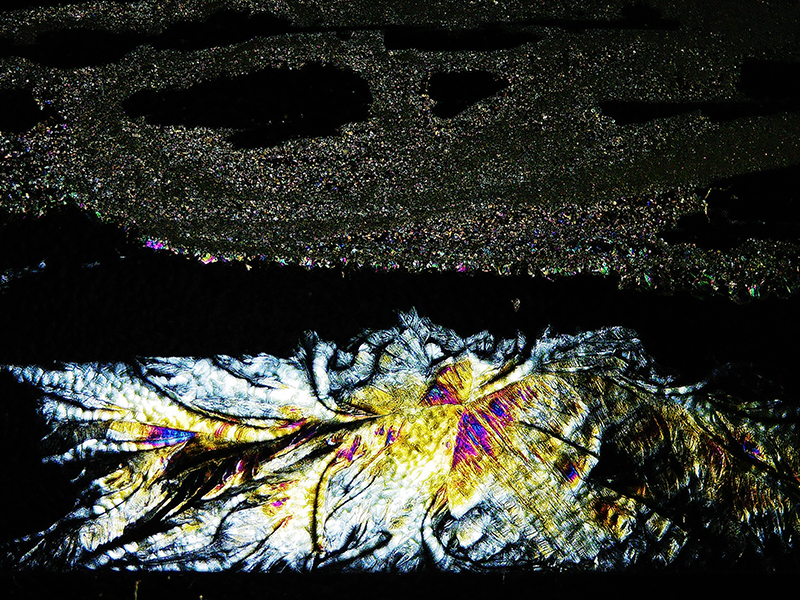
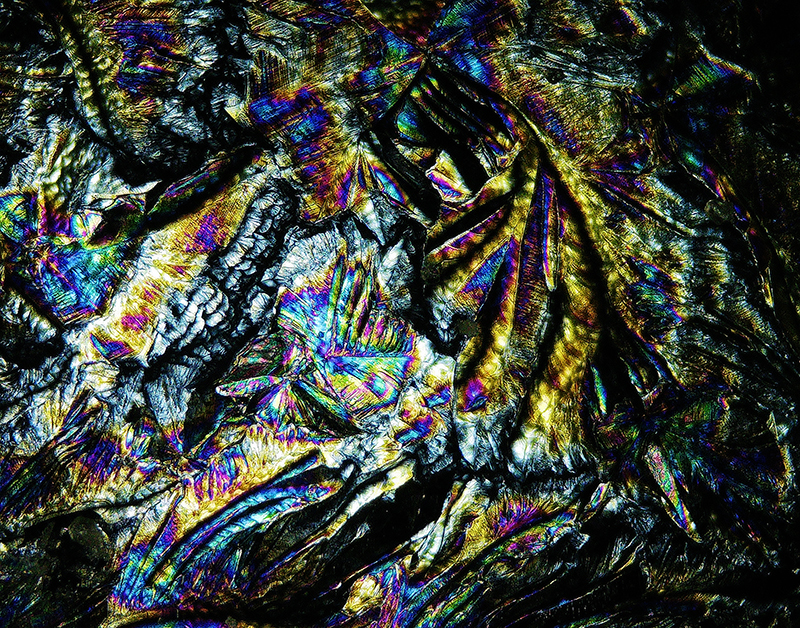
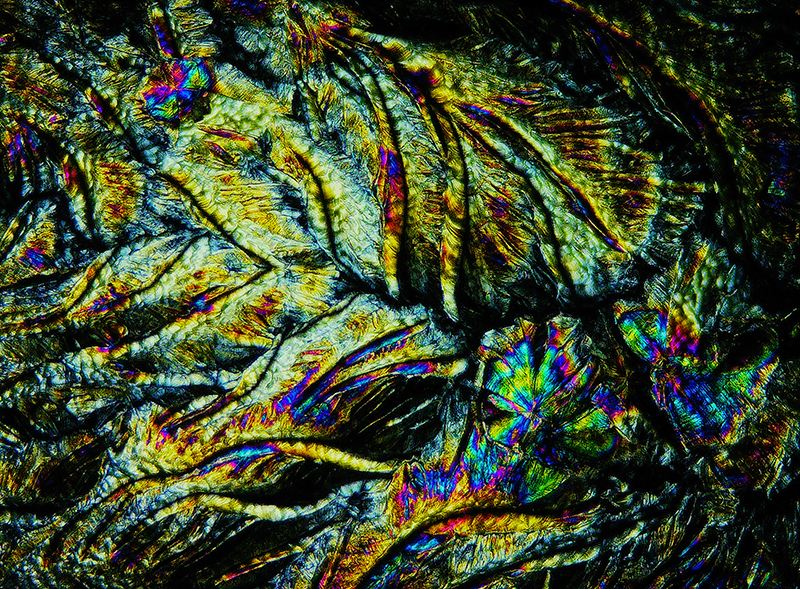
We also had the microscope set up at the closing event to look at some crystal growth in solutions prepared by Julie who works extensively with crystals.
I had tried some ‘Vitamin C’ crystal growing microscopy experiments at home. These images use a polarising filter under the microscope to reveal the vibrant colours. Next step will be to set up a timelapse of the crystals growing.
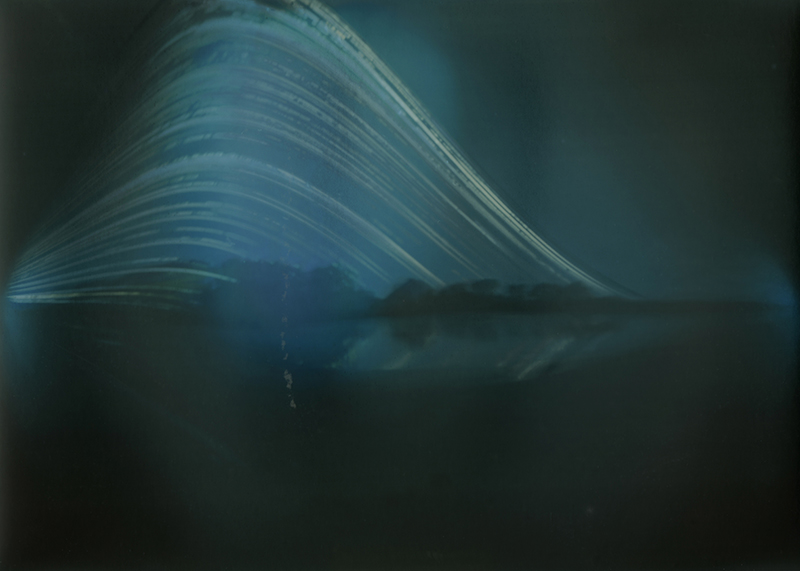
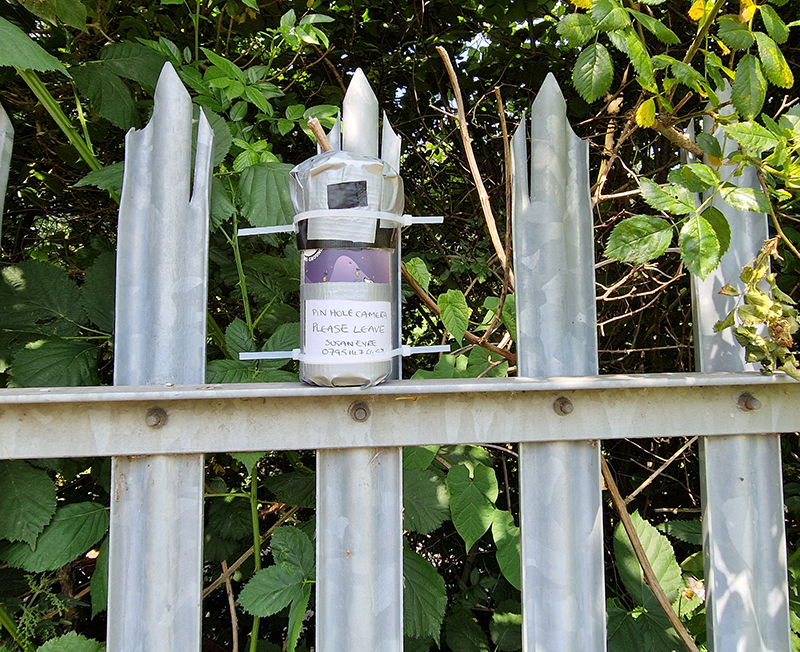
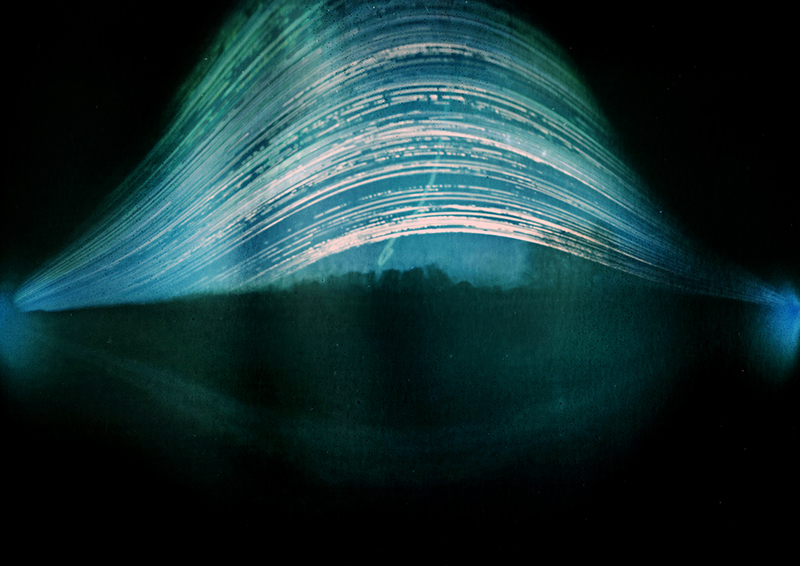
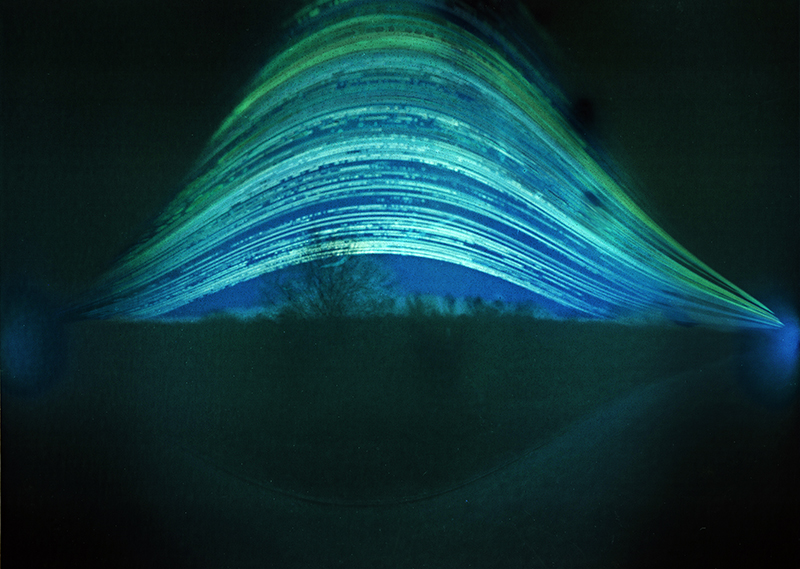
Summer Solstice 2025. The shortest night of the longest day brought an awful darkness. Collected the last two solargraphs I had installed at the Hogsmill Nature Reserve. These have been collecting light from the sun for a whole year, recording every sunrise and sunset. May the light shine through.
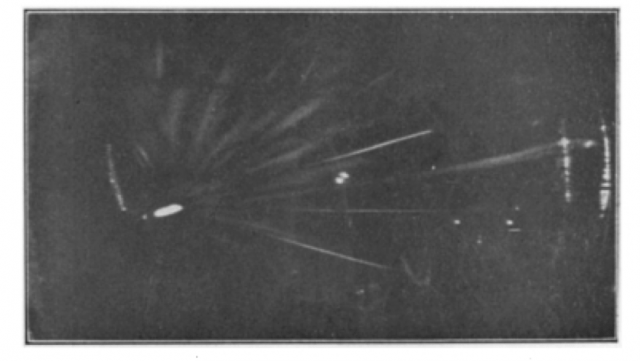
I was delighted that my video Cosmic Chiasmus: crossing the universe was included in CARBON: Under Pressure, at the Mazumdar-Shaw Advanced Research Centre as part of Glasgow Science Festival 2025, in a special exhibition partnership with Science Gallery Bengaluru.
The video offers a glimpse into a subatomic world where cosmic rays travel from distant galaxies to collide and silently interact with atoms and technology on Earth. Alongside the screening of the video I was also invited to give an artist talk and cloud chamber demonstration. It was great to share the wonders of the cloud chamber with visitors who were able to see cosmic ray trails for themselves.
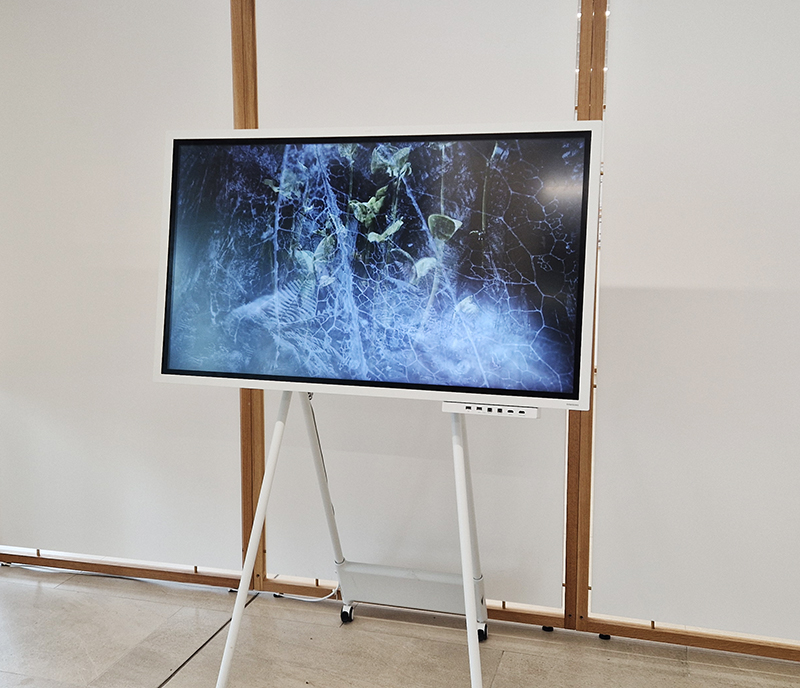






It is an incredible journey that cosmic rays make, blasted across space, spiralling along magnetic field lines to end up entangled with carbon in our bodies.
Not only is all life physically permeated by cosmic rays with the potential for nuclei collisions, but some cascading particles smash into atoms of nitrogen and combine with oxygen to create radioactive carbon-14 which enters our atmosphere. Plants absorb it during photosynthesis, and it is incorporated into their carbon skeleton, which we then eat. While plants and animals are alive, carbon-14 is continually replenished as the organism takes in air or food. But when an organism dies no more carbon-14 is absorbed and that which is present starts to decay at a constant rate. By measuring the radioactivity of dead organic matter, the current carbon-14 content can be determined and the time of death established. Cosmic ray activity gives us carbon dating techniques.

Reading
The Geological Unconscious – Jason Groves. Returning to this book that sparked the ideas we explored in our exhibition. A redirection of geology to consider a type of connection between things that are not in themselves geologic. Stones that stare, stones that speak. An image of the human could develop through geologic processes, becoming part of the mineral consciousness. Quoting Heather Sullivan ‘There is a difficulty for biology and philosophy to maintain a reliable distinction between life and non-life.’
The Writing of Stones – Roger Caillois. A paean to the capacity of minerals to form images within the imagination, which in turn is considered to be nothing more than an extension of matter.
The Performances of Sacred Places: crossing, breathing, resisting – edited by Silvia Battista. I read this for some background research while thinking about how I might make work responding to the abandoned sites of the cosmic ray detector huts at Haverah Park on the North Yorkshire Moors.
‘An horizon stands, in modern hermeneutics, for what is possible to see from the position of a specific observer. That is, not only a location in space but also a position in the cultural and historical apprehension of the world.’ Silvia Battista
The book opens by questioning relationships between the site and its ascribed attributes, which may be mercurial qualities not easy to define or quantify. It reflects on the performativity theories of Karen Barad which argue that matter, in its complexity, is an active participant in our relationship to the world and Jane Bennet’s call to recognise the ‘vitality of matter’ that crosses the human non human divide. In the section on ‘crossing’ the sensitive work of Louise Ann Wilson explores ritual around death, grief and loss through walking in rural locations echoing walking an interior landscape of memory. Walking the labyrinth and the pilgrimage are also considered as journeys that take place in physical and metaphysical space.