In Pliny’s Natural History (published after his death in the AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius, when, ever curious, he had gone to investigate the strange cloud rising), he marvels at the powers of the magnet ‘For what, in fact, is there endowed with more marvellous properties than this?’; ‘What is there in existence more inert than a piece of rigid stone? And yet, behold! Nature has endowed stone with both sense and hands! He goes on to assert that ‘it received its name “magnes”, Nicander informs us, by the person who was the first to discover it, upon Ida’. ‘Magnes, it is said, made this discovery, when, upon taking his herds to pasture, he found that the nails of his shoes and the iron ferrel of his staff adhered to the ground.’

Nicander was a 2nd century BC Greek poet, physician, and grammarian and there is no surviving record of his claim. Gillian Turner, in her book North Pole, South Pole, admits that this story will have been embellished over time but acknowledges that if an electrical storm took place on Mount Ida and the naturally magnetic magnetite was struck by lightning, it would be permanently magnetised into lodestone and would therefore attract the nails of Magnes’s shoes.
The legend is not impossible but it is also possible the stone is named after the region where it was first found. In ancient Greek, magnetite was known as magnes lithos. There were two ancient regions called Magnesia and so the true provenance of the first discovery of the lodestone is hard to determine. In Greece, ancient Magnesia was a long and narrow slip of country in Thessaly between Mounts Ossa and Pelion. Around the 4th Century BC, the people known as Magnetes, migrated and settled in Ionian cities which were named after them as Magnesia on the Maeander and the neighbouring Magnesia ad Sipylum, currently in Aydın Province near Ephesus, Turkey.
I decided to follow the footsteps of Magnes.
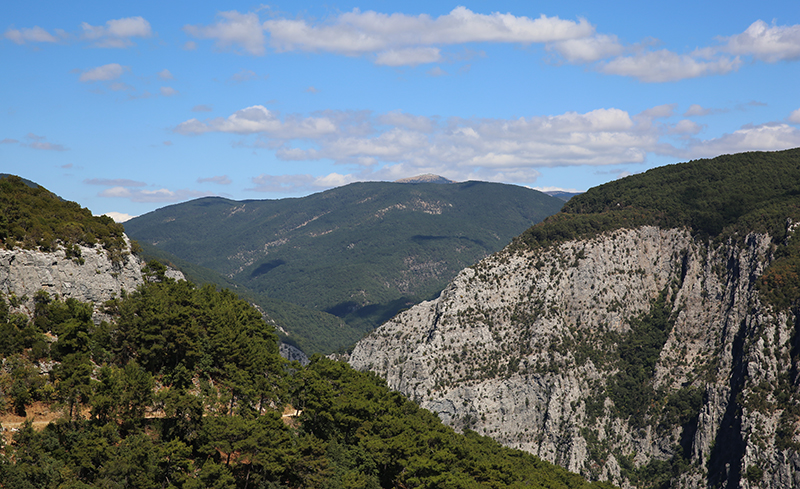
Mount Ida is famous in Greek Mythology as the location for the Judgement of Paris, where he fatefully chose Aphrodite as the most beautiful goddess, setting in motion the events of the Trojan War which the gods watched from its summit while its fir trees were felled to build the Trojan Horse. It was also an ancient sacred site for worship of the mother goddess Cybele, an embodiment of a universal Mother Earth. Its name was changed to Kazdağı (Goose Mountain) as the goose holds sacred significance in Turkish mythology. The landscape is literally breath-taking with very high oxygen levels due to the extensive pine forests and unique geographic features that funnel ionised air up from the sea to mix with the clear mountain air.
Setting out on the first evening the walk to view the mountain brought home the vastness of the landscape to negotiate.
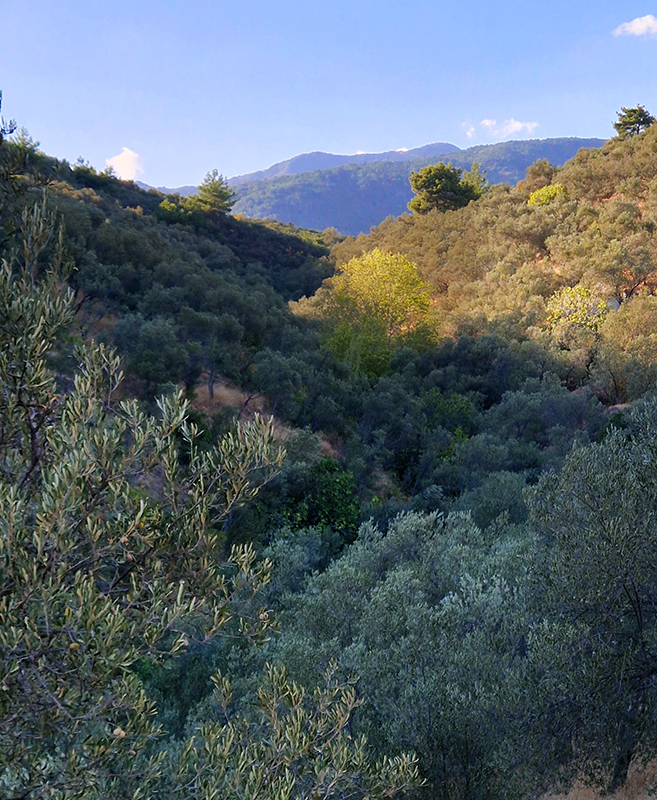

After dinner, the owner of our hotel in Zeytinli said he would find a guide to the area if we gave him 5 minutes. Thinking he would come back with a book of hiking trails, I was surprised when he returned with a Kazdağı National Park Ranger. We arranged to meet the next day when he led us up the dusty mountain tracks with his old school friend as driver.
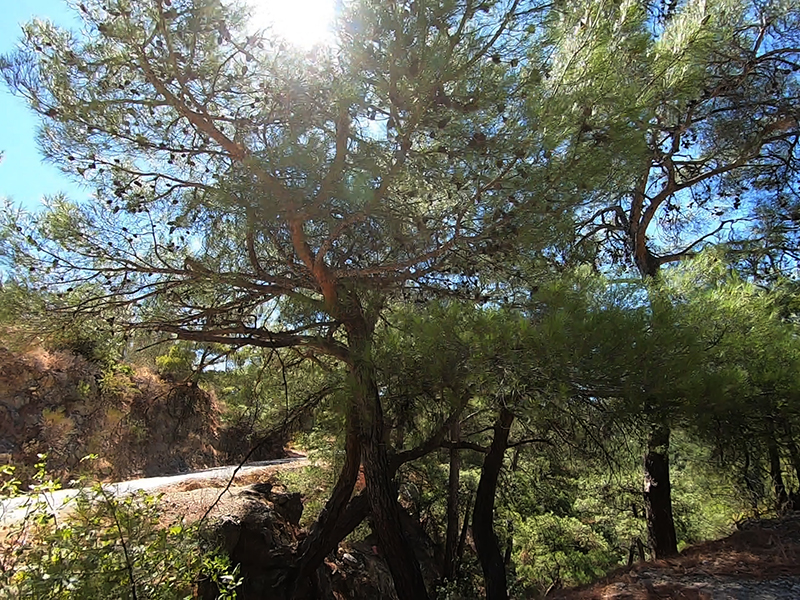



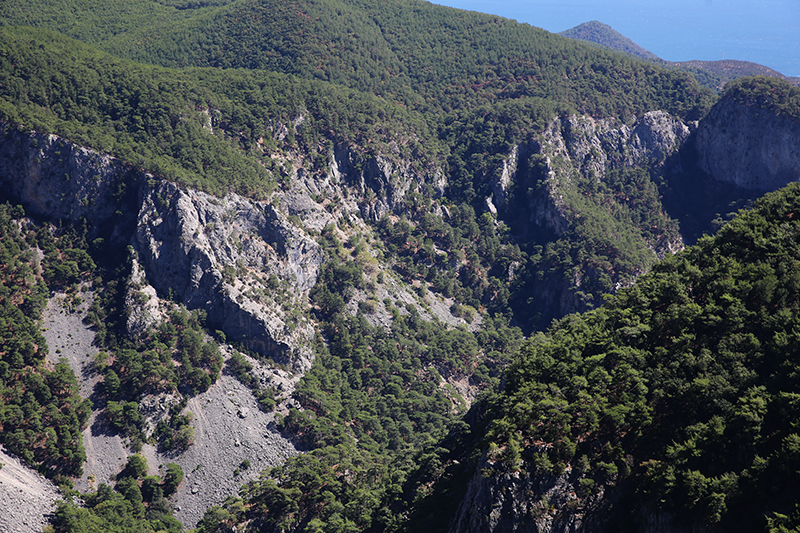
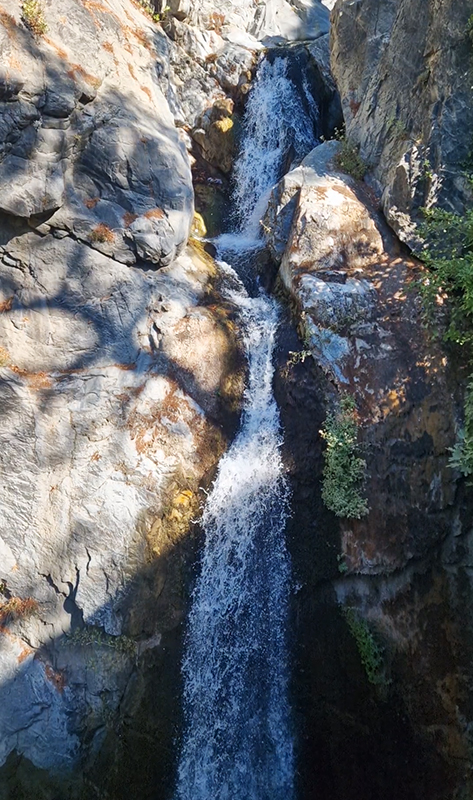
The summit of Mount Ida was always in the distance and it is not possible to walk unaccompanied in the National Park during the summer season. We drove up to a height of 800m to view the spectacular Sahinderesi Canyon.

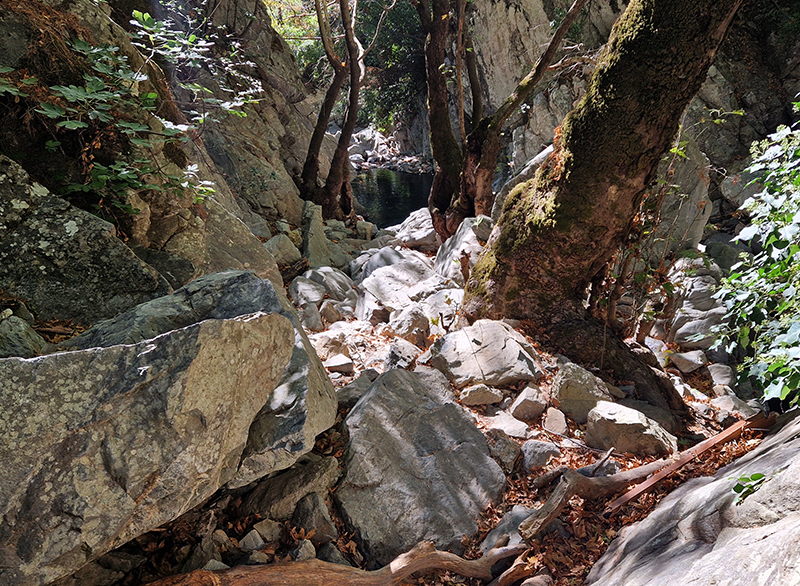
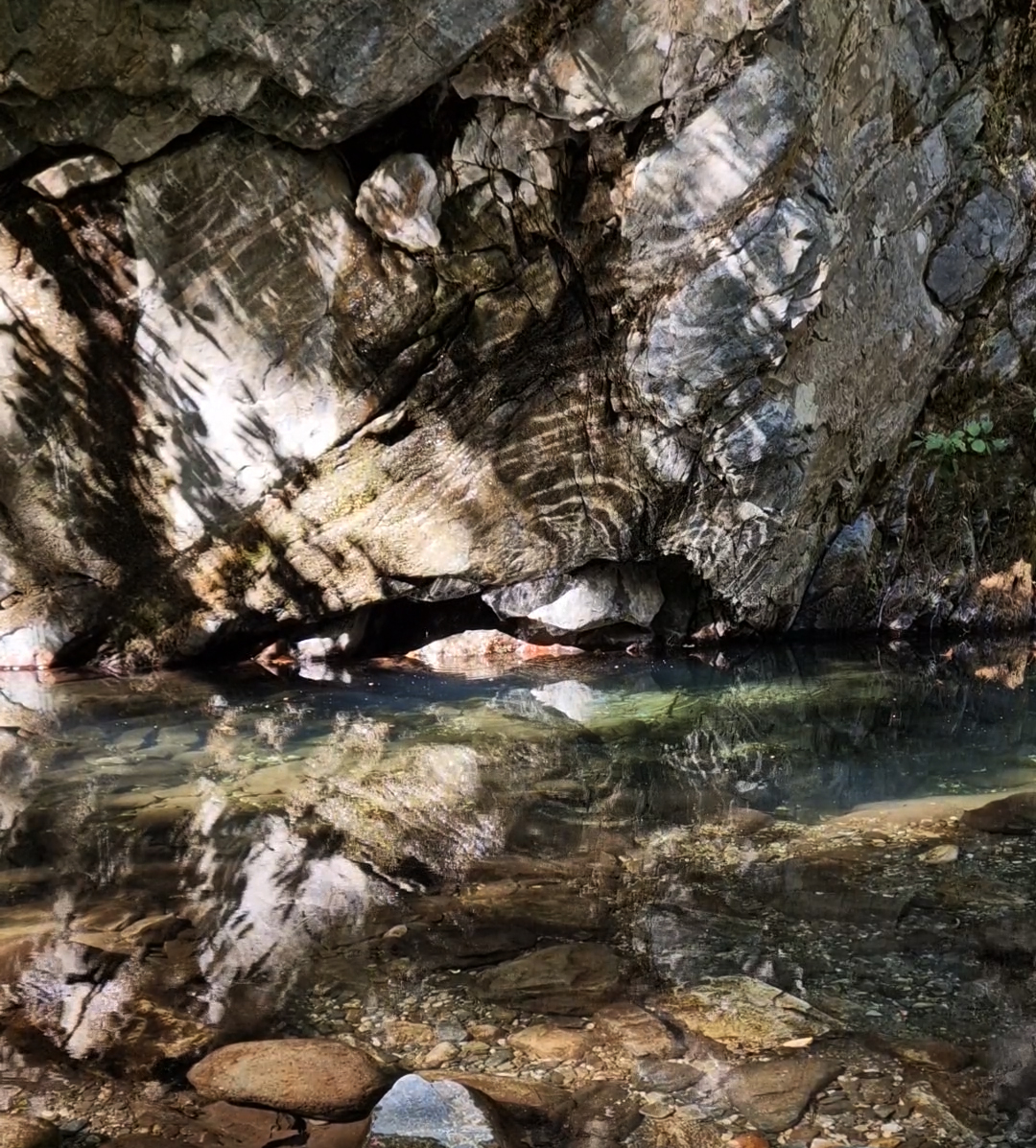
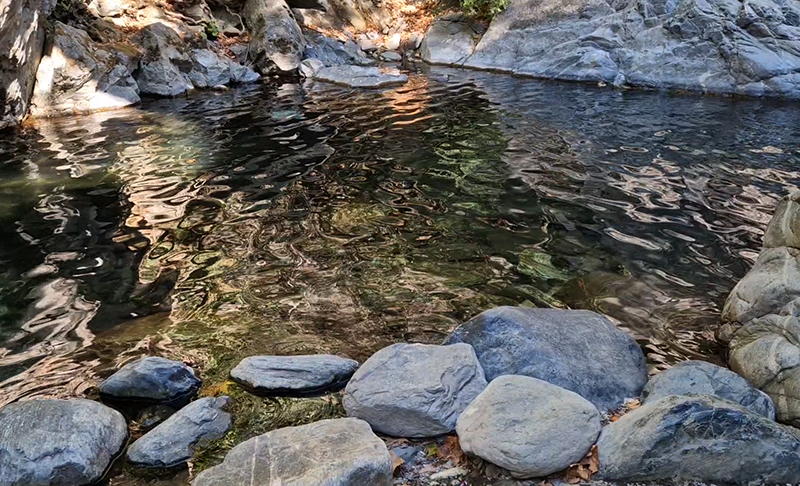
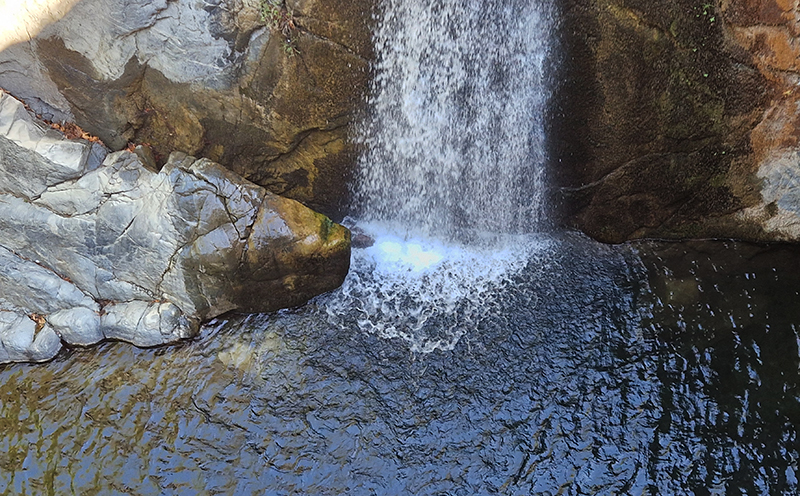
Mount Ida abounds with fresh water springs, rivers, ponds and waterfalls including the Sütüven Waterfall which we visited.





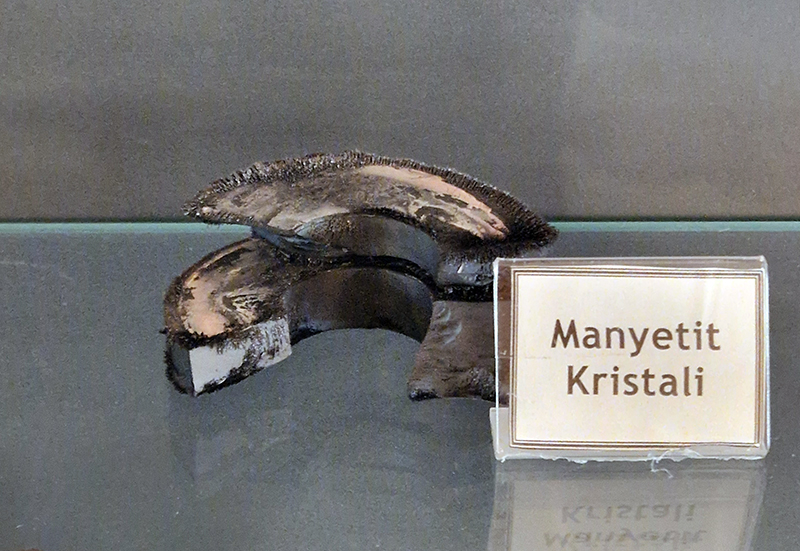
We visited the Ida Madra Geopark Museum which displayed tantalising exhibits of magnetite crystal and volcanic rock but there was only a security guard on duty who could offer no information about the collection or the local geology. The magnetite crystal does look like a broken magnet rather than raw crystal.


Fascinating choice of sentence to describe magnetite in the Turkish-English online dictionary – ‘Category, Turkish, English. Technical. 1, Technical, manyetit · magnetite n. The enzyme dissolved the brain tissue and left the magnetite particles intact.‘
Outside the museum was a tomb that our guide told us is called ‘the man eating stone’. Pliny also talks about a stone called sarcophagus (stone of Assos) of which he says ‘It is a well-known fact, that dead bodies, when buried in this stone, are consumed in the course of forty days, which the sole exception of the teeth.’ There was also a magnificent Oriental Plane Tree, over 570 years old.
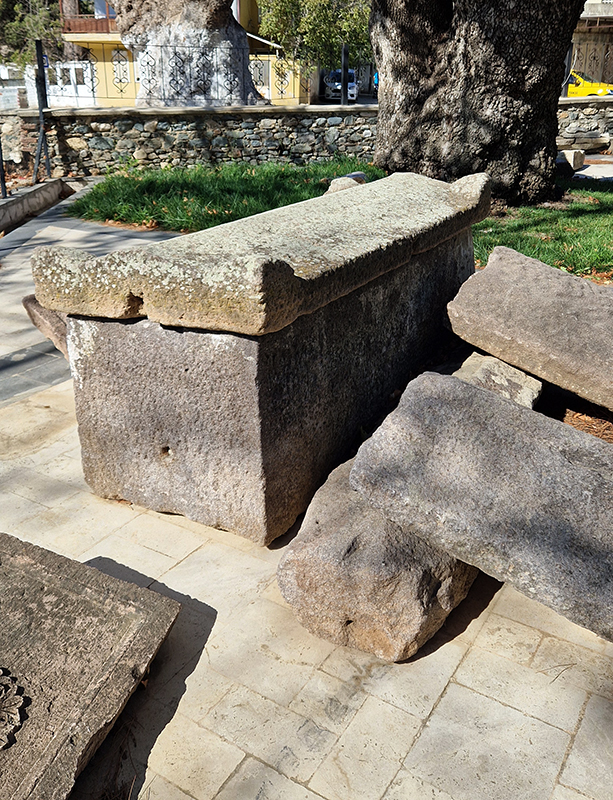


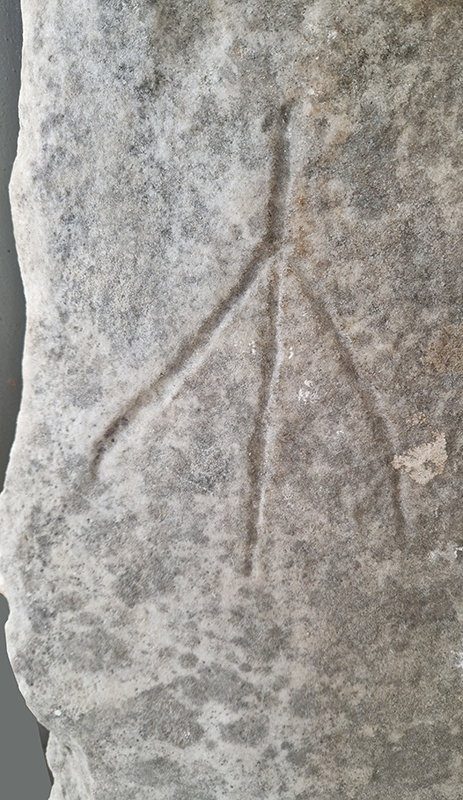
We visited the wonderfully eccentric Tahtakuşlar Ethnographic Museum which celebrates the cultural heritage of nomadic Turkish tribes and displays a stone tablet inscribed with the symbol of a goose foot reflecting the veneration of the goose by the Turkmen people. There is a rather faded model of Mount Ida which apparently shows the line of a mysterious ancient structure that circles the summit.


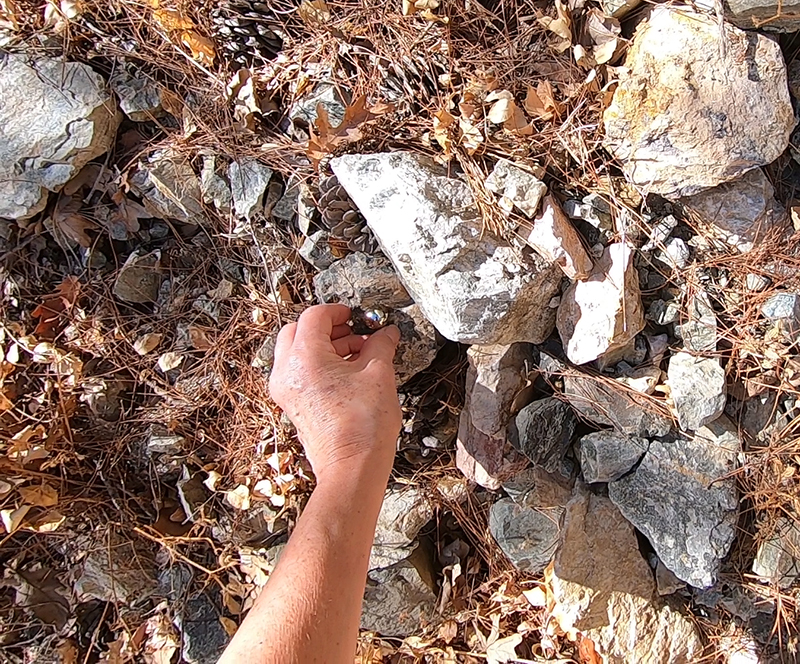
The next day we made another winding ascent. Equipped with my own magnet sphere (terrella) I went in search of magnetite on the foothills of Mount Ida. I was thrilled to discover some rocks that were magnetic.
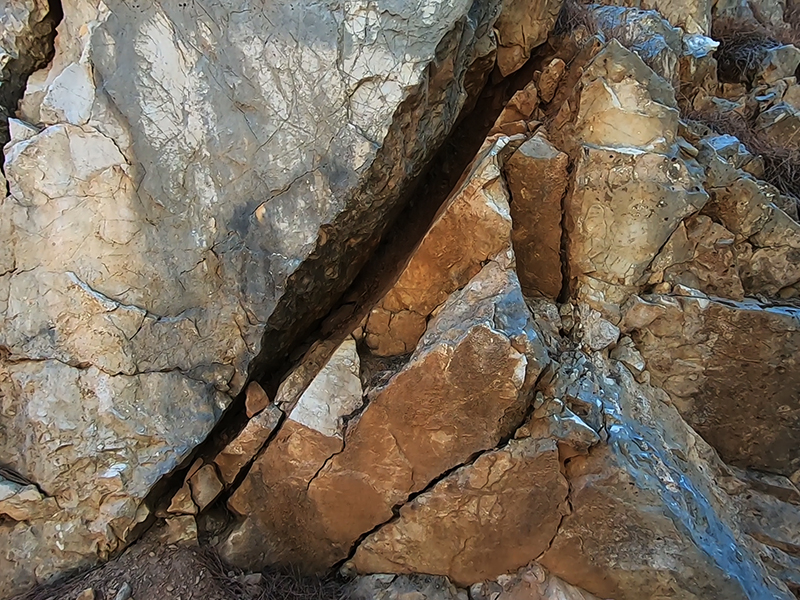
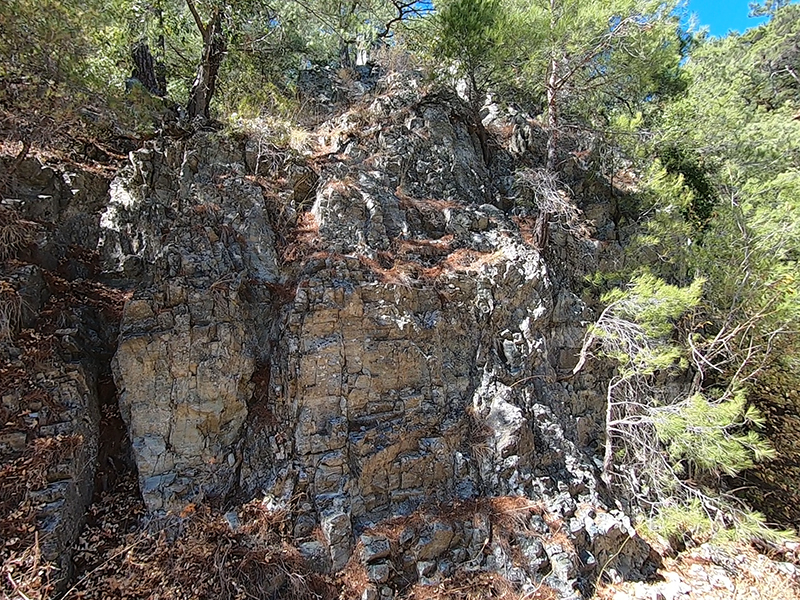









The final evening in northwest Turkey was spent watching the light fade over Mount Ida as bats and hedgehogs made an appearance along with quite a lot of street dogs that were thankfully more interested in barking at each other.


On to the urban geology of Istanbul and a number of monolithic erections. In the Hippodrome, once a vast public arena for chariot races, imperial ceremonies, and public events, there are several examples of phallic architecture.

The towering red granite Obelisk of Theodosius, originally 30m tall, is an ancient Egyptian obelisk of Pharaoh Thutmose III (1479–1425 BC), first erected at Karnak to celebrate victory in battle. It was removed from Karnak and transported along the river Nile to Alexandria by the Roman emperor Constantias II in 357 and just 33 years later Theodosius I had it transported to Constantinople and erected on the spina of the Hippodrome, the relocation upheavals having reduced its height by a number of metres.

It is not known exactly when The Walled Obelisk was constructed but was probably built to mirror the Obelisk of Theodosius in the Hippodrome. Obelisks were often erected in symmetrical pairs. It was originally decorated with gilded bronze plaques (maybe to hide the fact that it wasn’t a true obelisk which should be hewn from a single piece of rock) but these were removed and melted down by Christian crusaders in 1204.

The Serpent Column is the remains of an ancient bronze column that was part of a Greek sacrificial tripod originally built in Delphi 478 BC as an offering to Apollo but relocated to Constantinople in 324.
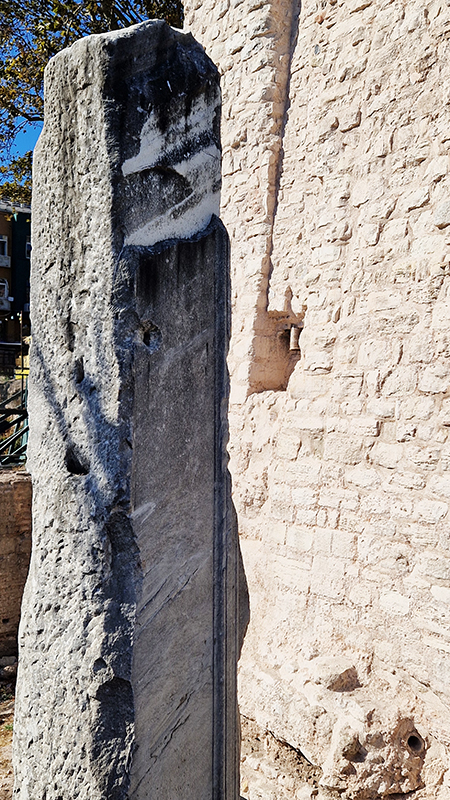

The stone Milion was a marker from which all distances across the Roman Empire were measured. Erected by Septimius Severus upon the re-founding of Byzantium as Constantinople in 330 AD it became the starting-place for the measurement of distances for all roads leading to the cities of the Eastern Roman Empire.
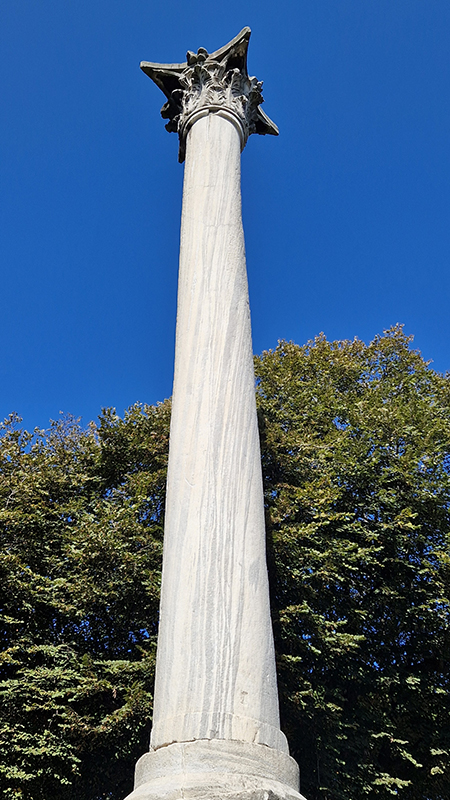

The Column of the Goths, a single block of marble 18.5 metres high, erected in Gulhane Park, is the oldest monument still standing from Roman times.
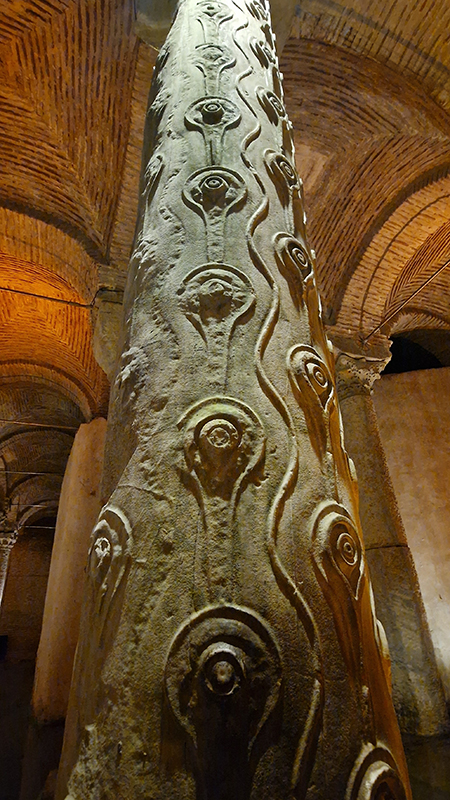

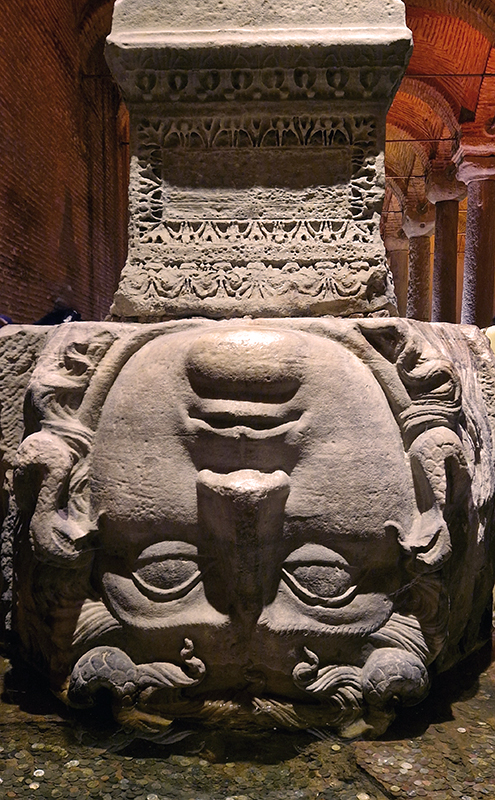
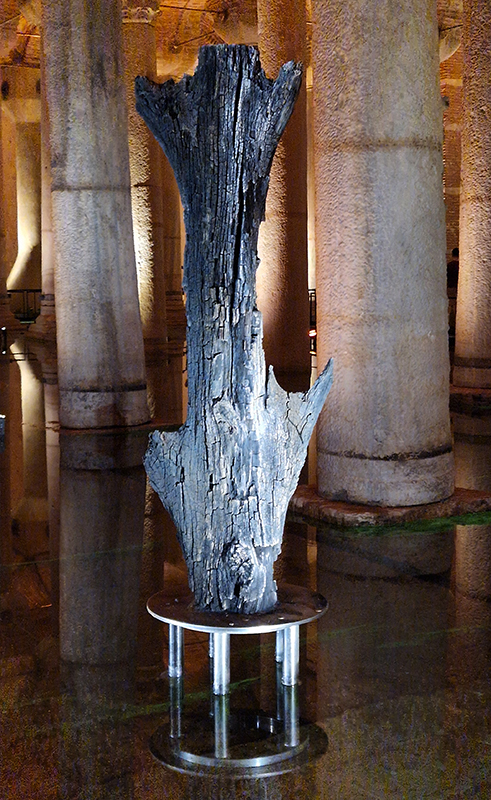
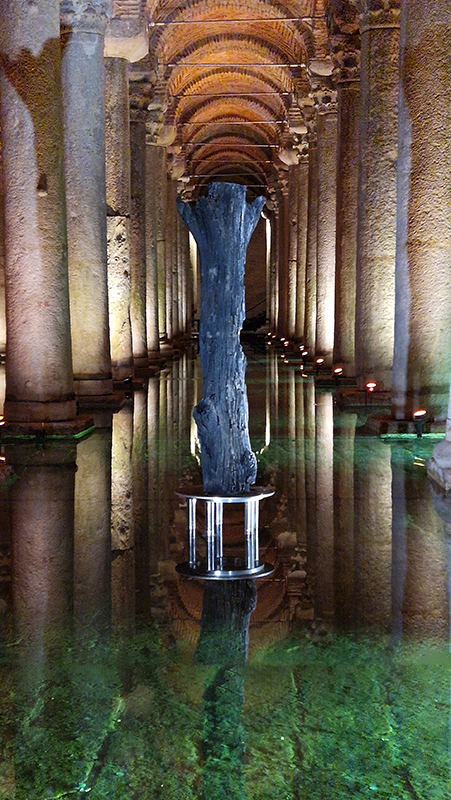
The Basilica Cistern is a vast subterranean forest of columns with the 4th Century ‘Tear Column’ standing out for its unique patterns which are often thought of as tears but may actually be a stylised representation of a tree.
The Basilica Cistern is the largest of several hundred ancient cisterns that lie beneath Istanbul, built in the 6th century during the reign of Byzantine emperor Justinian I to supply the city with drinking water. The ceiling is supported by a 336 marble columns, each 9 metres high which appear to have been recycled from the ruins of older buildings and are carved out of different types of marble and granite.


Two columns reuse blocks carved with the face of Medusa. Tradition has it that the blocks are oriented sideways and inverted in order to negate the power of the Gorgon which held that anyone who looked upon her was turned to stone.
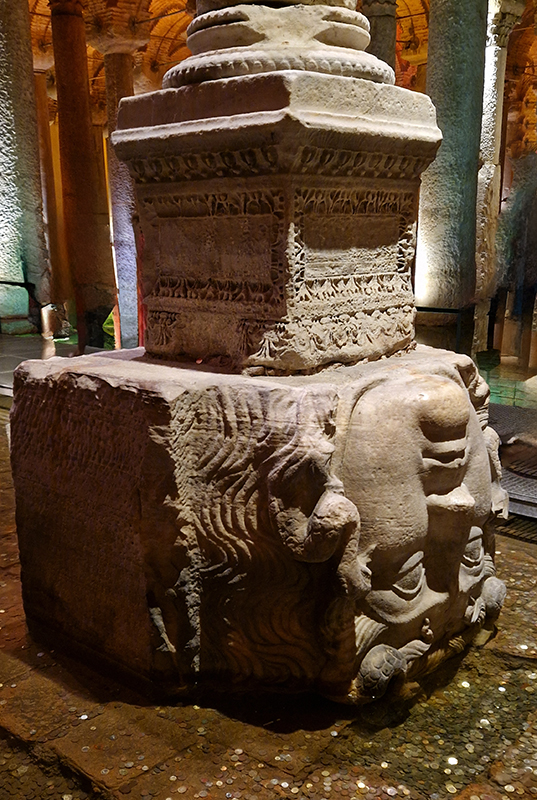




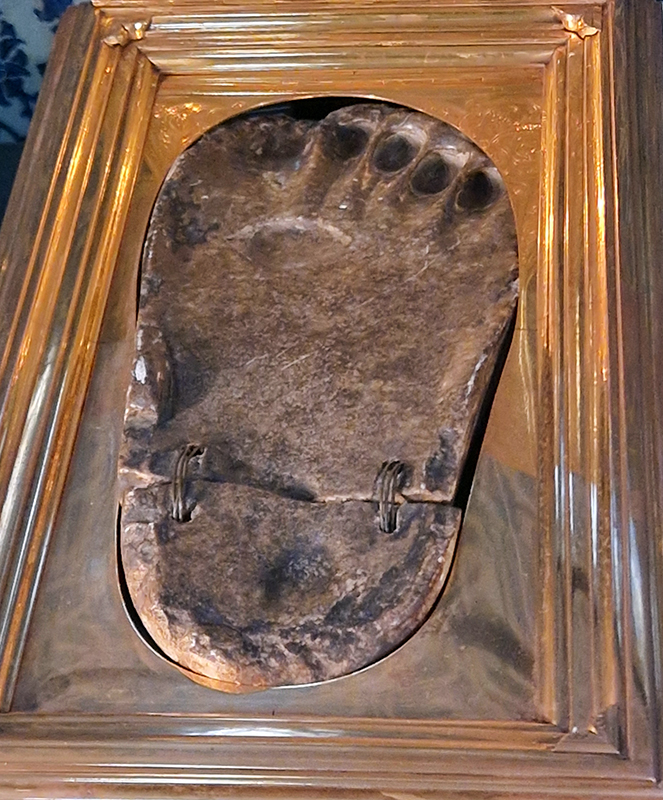
The Sacred Trust, of Islamic religious relics kept at the Topkapi Palace includes the Casing for the Black Stone, a rock set into the eastern corner of the Kaaba, in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. Revered by Muslims as an relic which, according to tradition, was set intact into the Kaaba’s wall by Muhammad before he became a prophet. It has had a turbulent history, being stolen, taken hostage and smashed. Today its fragments can be seen set in cement, encased in a silver frame on the side of the Kaaba, polished smooth by the hands and kisses of pilgrims. Although idolatry is forbidden in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran the use of aniconic stones, or baetyls, which are sacred stones stones venerated for their connection to the divine, without needing human-crafted images, were permitted. There has been speculation The Black Stone is a meteorite, but it has never been scientifically analysed to ascertain its physical origin. Also on display are footprints in stone (Kadem-i Şerif) attributed to the prophet Muhammad. An Ottoman scholar, Mehmed Münib Ayıntâbî (d. 1823) wrote a treatise to explain that this footprint was one of the miracles of the Prophet for otherwise how could it be possible to leave the impression of a foot on hard ground like stones. This was reiterated by a guide at the palace. There are six Kadem-i Şerif of the Prophet four of which are on stone and two of which are on brick, the most significant is the one in a gold frame believed to be left on his ascension to heaven from the Dome of the Rock.



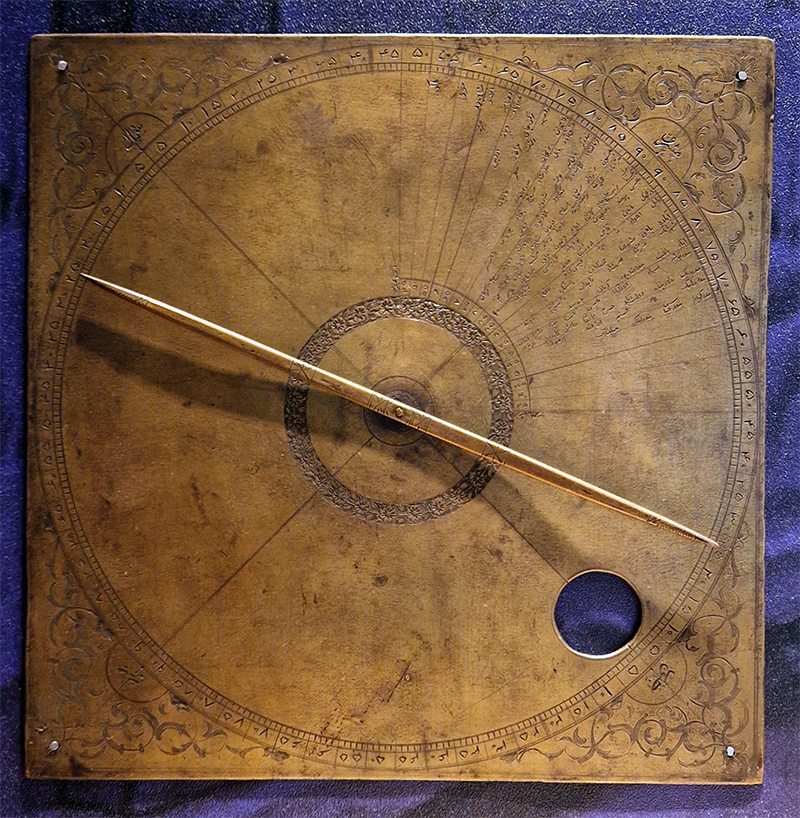
Mechanical clocks didn’t arrive in Ottoman lands until the 15th Century, 200 years after their initial invention. Chief astronomer to Sultan Selim II, Taqi al-Din, bemoaned the new instruments as ‘the most burdensome to construct, which demanded modest workers’. The qibla compass was used to determine the direction for prayer. This Ottoman marble sundial is from 1526.


‘Were man to look up from the ground, he’d see a starry sky, were he to look down from the heavens – a wavy sea’ Tursun Beg. (15th century Ottoman historian who wrote a detailed account of Mehmed the Conqueror’s reign.)
The 1513 world map made by Turkish cartographer Pîrî Reis was discovered in the Topkapı Palace Library in 1929. Pîrî Reis created an impressively accurate depiction of the newly discovered regions of the world using a circular design based on a hypothetical centre. This map is the earliest cartographic record of Columbus’s oceanic voyages and the first to show the unique fauna of Terra Australis.

Beginning new work. Learning about the symbolism of sacred geometry in the Westminster Abbey Cosmati Pavement has inspired me to think about how I could relate ancient symbolism and contemporary iconography to think about changing relationships to fire, water, earth, air and the cosmos. Plato imagined the universe was created as a living creature in the shape of a sphere, perfect and complete in itself. Patterns of Thought author Richard Foster suggests that ‘as our minds become progressively tuned to ecological and global concerns, so the Platonic image of the world as a living creature is re-awakened from its sleep.’

In the symbolism of the Cosmati Pavement, the journey from earthly materialism to spirituality is seen as a progression from multiplicity and diversity towards unity and uniformity. The tiles show a transition from a variety of patterns through to simplified regular polygons, the archetypes of form representing a perfection that we only experience as a shadow on Earth. Random patterns at the centre of the design describe the elements in an undifferentiated state of matter, the primal chaos before the division of spirit and matter when the breath of the creator swept over the ‘turbulent waters’ or ‘silva’ bringing forth the differentiation of matter into the forms of the four elements. The medieval mind never took the world at face value and always sought to see the coexistent and equally valid layers of meaning in everything.

In medieval cosmology the separation of the elements happened before the advent of time which began with the creation of the sun, the moon and the planets as astronomical time, the timelessness of eternity is alluded to by the number 60 + 1. The end of the world was imagined as a reversal of creation. All will return into the four elements which return to the primal chaos and are reabsorbed into the divine mind and eternity.
The four elements are linked by pairs of opposing qualities: Fire is dry and hot; Air is hot and moist; Water is moist and cold; Earth is cold and dry. Each element shares a quality with two others and elements with a shared quality combine more easily. Fire is sharp, tenuous and mobile, reflected in a quick tempered choleric human temperament, it gives vision and belongs to the heavenly race of gods. Earth is blunt, weighty and immobile reflected in a heavy melancholic human temperament. Earth resides with the sense of touch and those that walk on the ground. It has stability facing to the north, south, east, west, zenith and nadir. Air is sharp, mobile and weighty reflected in a breezy optimistic human temperament. Air amplifies hearing and smell, it supports the flying creatures and is synonymous with breath and spirit. Water is mobile, blunt and weighty reflected in a dissolute easy-going human temperament. Water amplifies taste and supports the creatures that swim.
I was interested to read that in the kitchens of the Topkapi Palace (1459) in Istanbul, the four humours (blood, phlegm, black bile and yellow bile) were taken into account when designing the menus. Different foods were recommended depending on their qualities to restore good health for those suffering sickness which was attributed to an imbalance of the humours. The seasons were also taken into account in relation to the humours when deciding which foods to cook.

Gallery Visits
Deeper Beneath at the stunning 1500 year old Basilica Cistern Museum includes work by Vlastimil Beranek (Aqua One- Yellow – made from Bohemian Crystal), Jaroslav Prosek ( 6500 year old subfossil oak), Ali Abayoğlu (Glass Leaves and Jellyfish) and Muzaffer Tuncer (Seclusion)
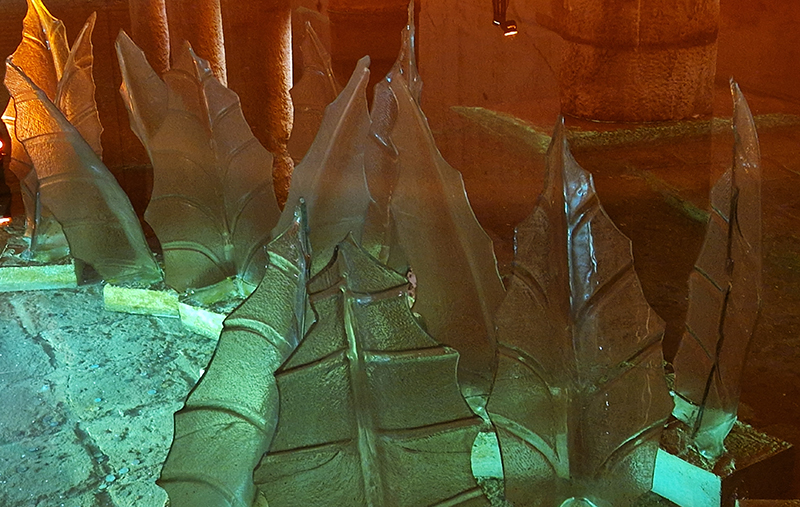
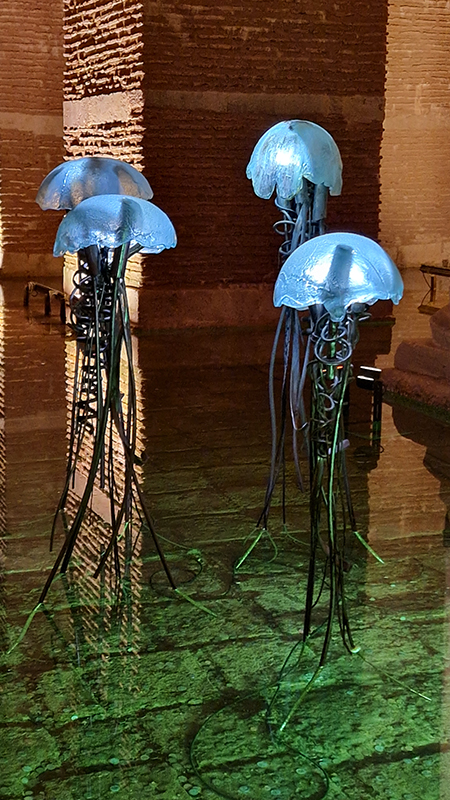
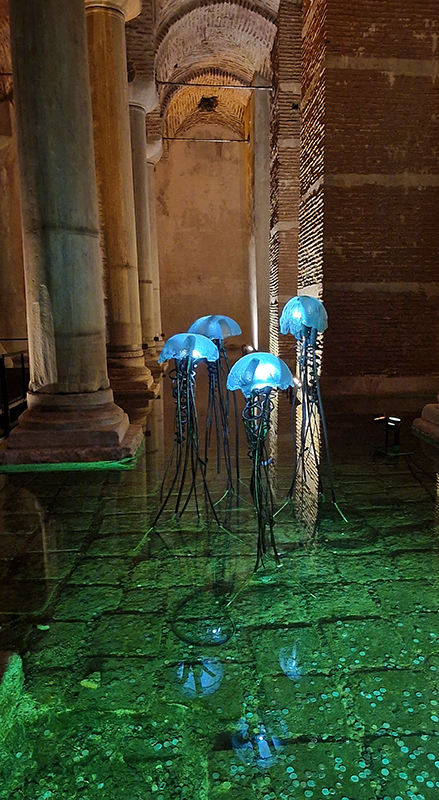








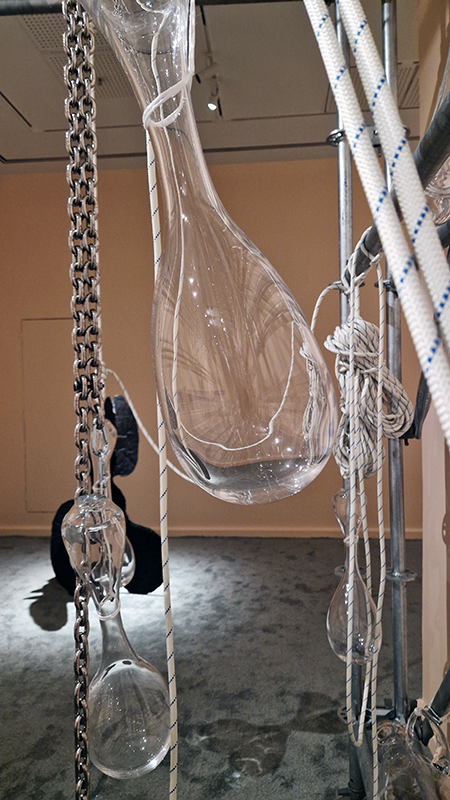
Åsa Jungnelius A Verse, Written with Earth, Fire, Water and Air at Pera Museum, Istanbul. The exhibition brings together the results of time spent in the obsidian fields of Eastern Anatolia collecting natural glass formed by the rapid cooling of volcanic lava and working in the glass furnaces of Denizli along with reflections on marble steeped in Byzantine history. Archaeological finds, glass objects, materials, and handwoven cords rooted in nomadic traditions are displayed alongside photographs by Swedish photographer Peo Olsson documenting the artist’s research. There is a strange juxtaposition of the installation scaffolding set against thick carpet in the gallery.
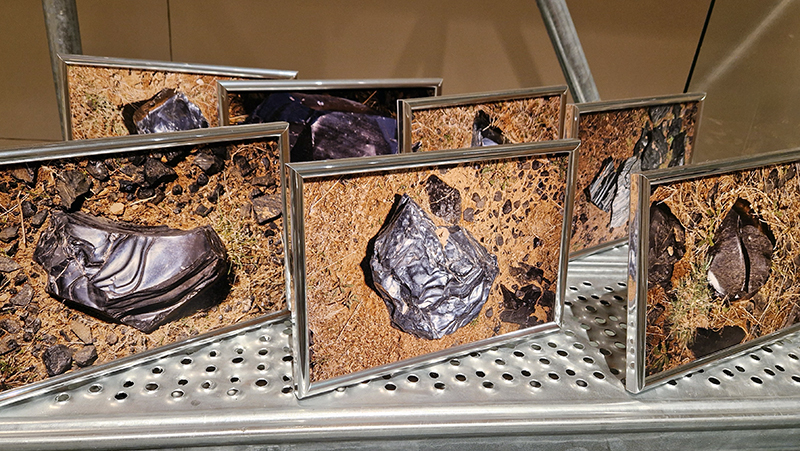
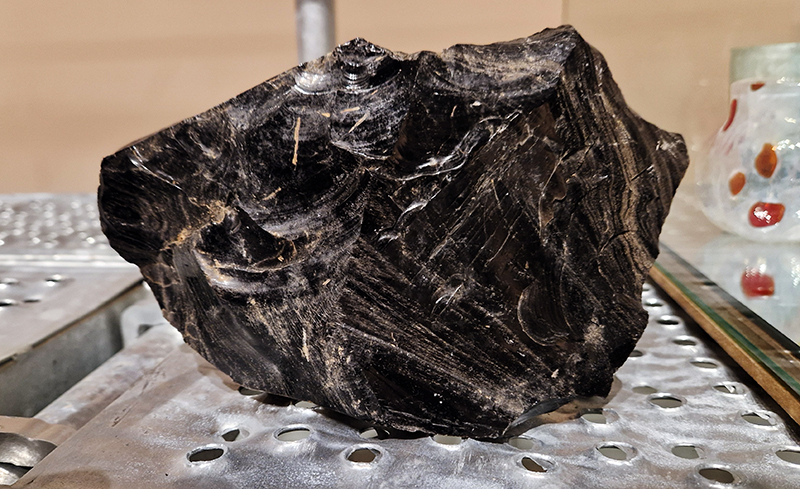
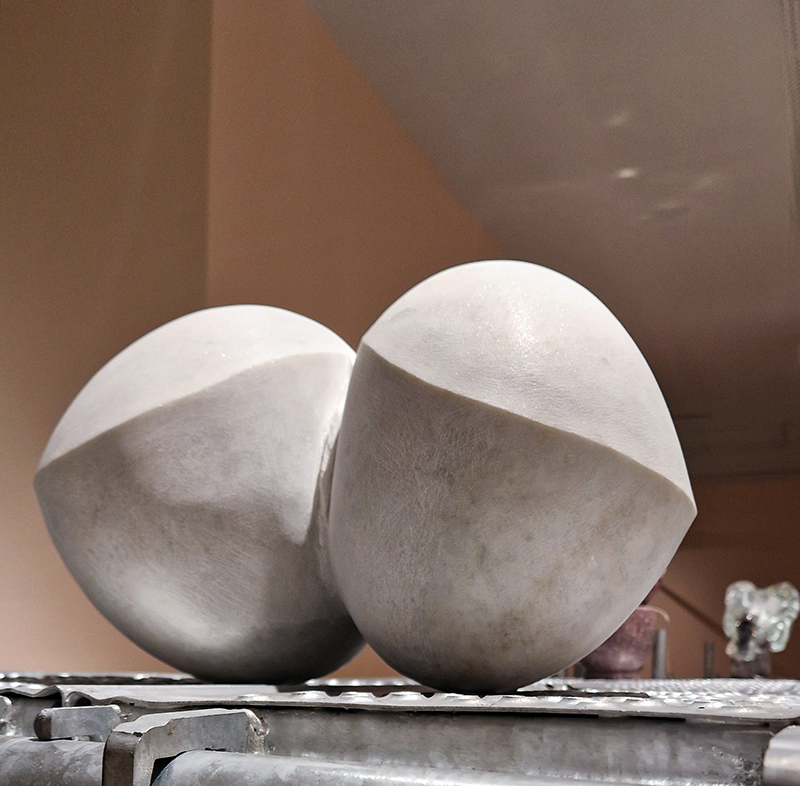







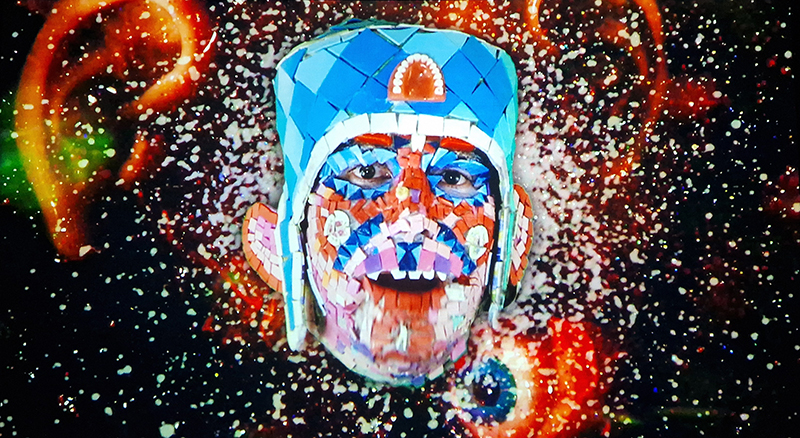
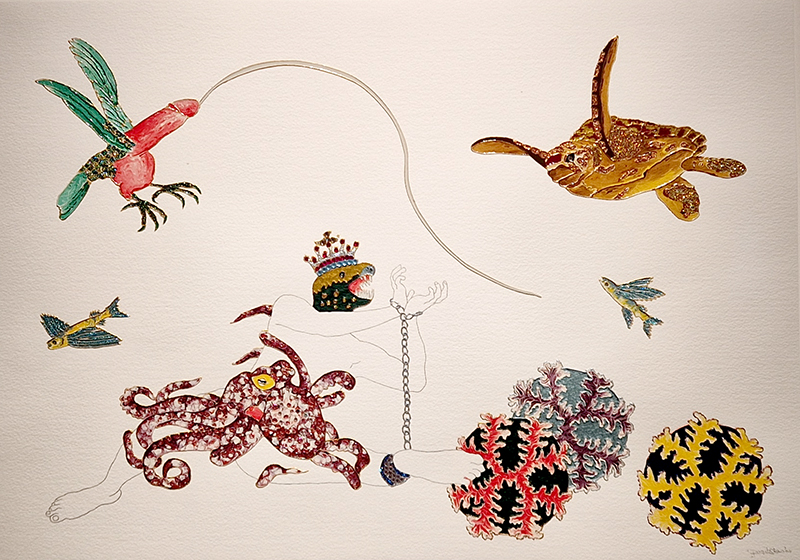
Also at the Pera Museum was Feelings in Common: Works from the British Council Collection. The exhibition is striving to form a zone where feelings in common are shared amidst uncertainties and transformations regarding the future. Happy to see Bedwyr Williams The Starry Messenger again (image 1 + 2 – the poignant geological story of a mosaic dentist which alludes to the micro macro scales of the universe ) and Larry Achiampong’s Relic 2 (an Afrofuturist exploration of postcolonial identities, imagined futures, and ancestral memory) along with a small work from Raqib Shaw from his Garden of Earthly Delights series amongst other works.




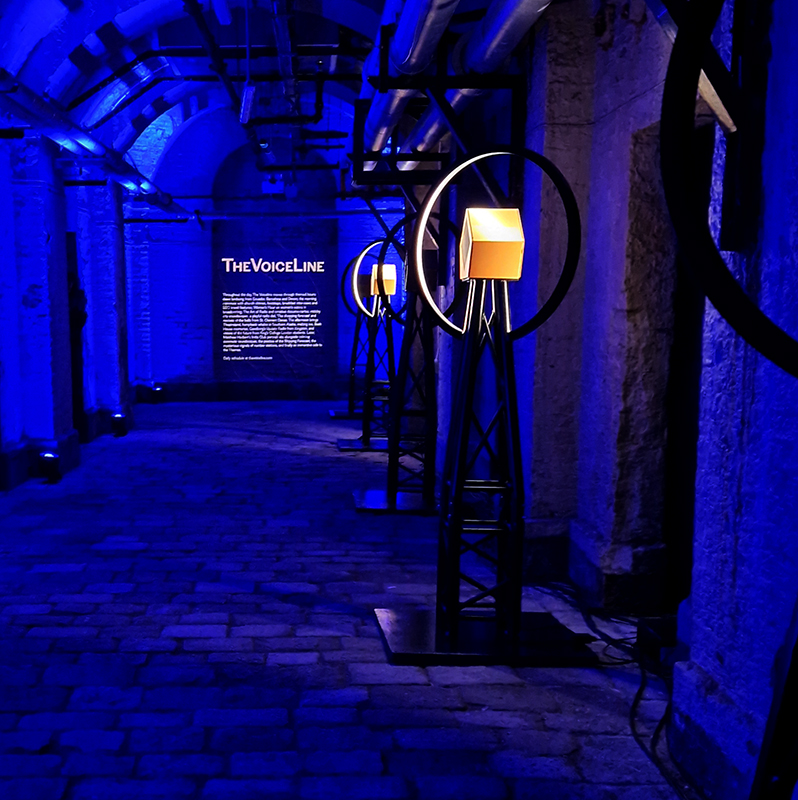
The VoiceLine by composer and sound artist Nick Ryan installed in the atmospheric Deadhouse, Somerset House. 39 precisely aligned speakers, creating an evolving pathway of sound reflecting the histories of radio and listening that began on the Strand more than a century ago.


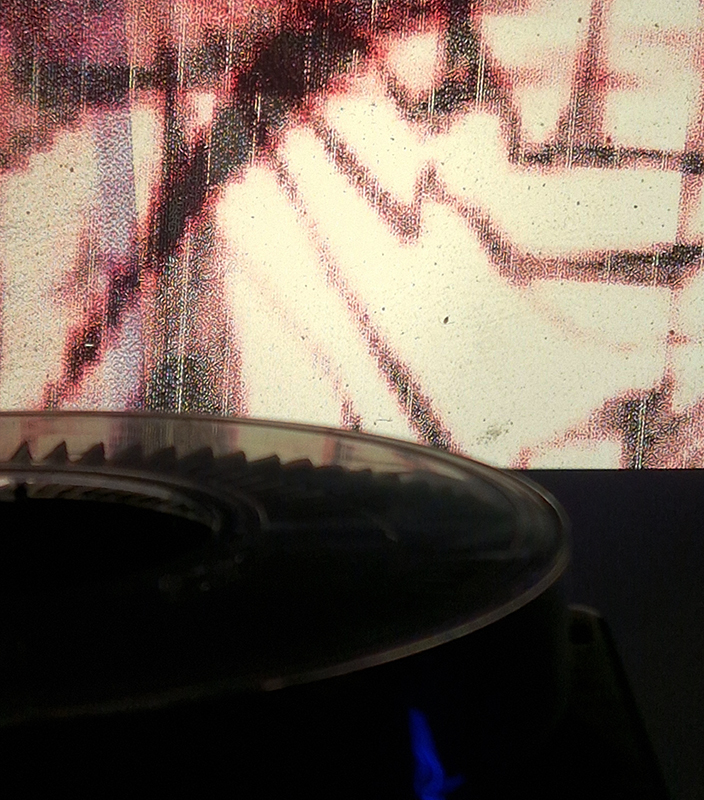
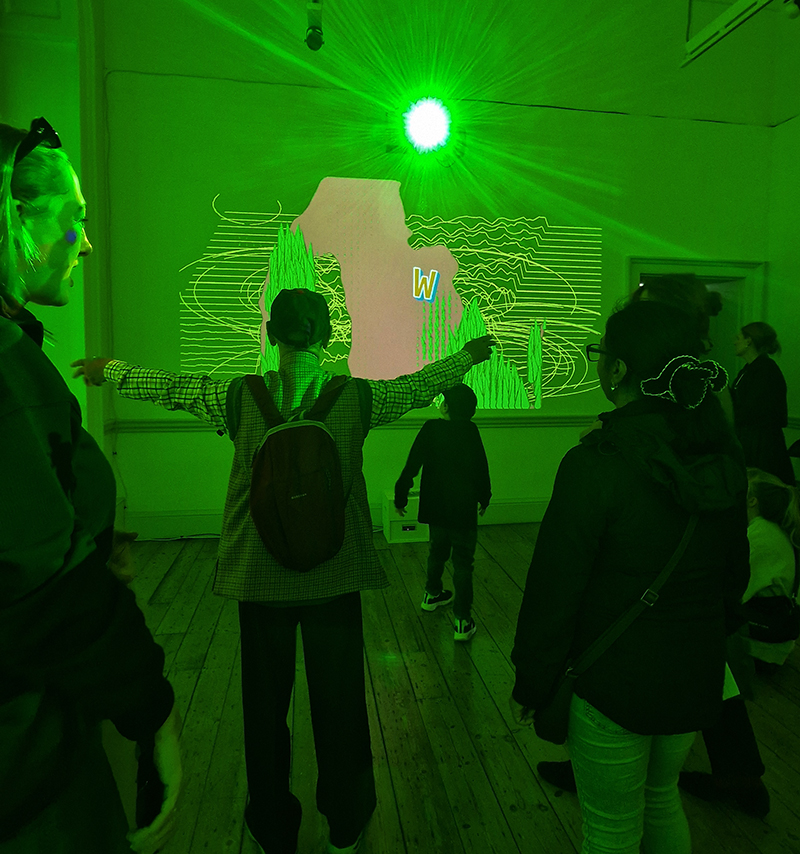
An exhibition by KitMapper, an artist led production company, Along More Latent Lines at Somerset House to showcase new and recent works of the team and creatives based here including the interactive and immersive Genetic Moo: Magic by Genetic Moo.






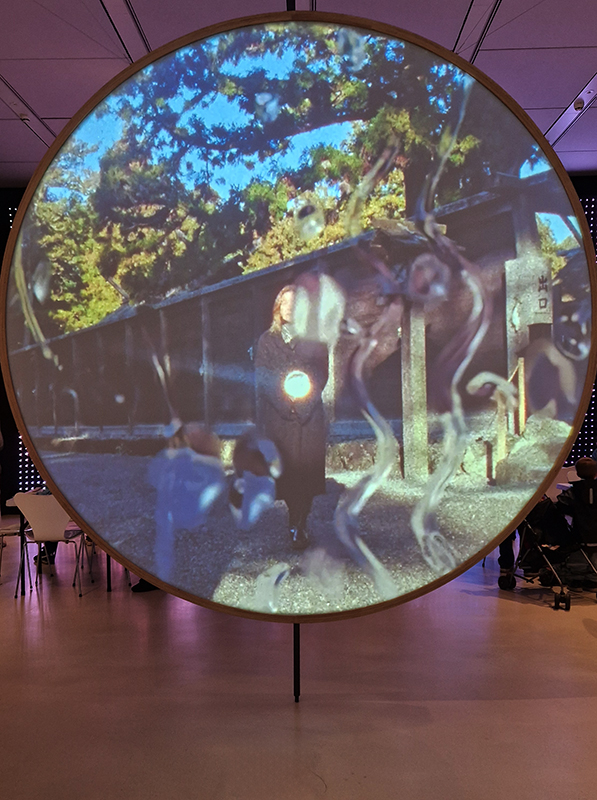
Jane and Louise Wilson Performance of Entrapment at The London Mithraeum Bloomberg Space featuring 2,000 year old oak stakes that inspired imagery looking at structure and ritual. The works investigates parallels between the sacred sites of Mithras and Japan’s Ise Jingu Shrine.
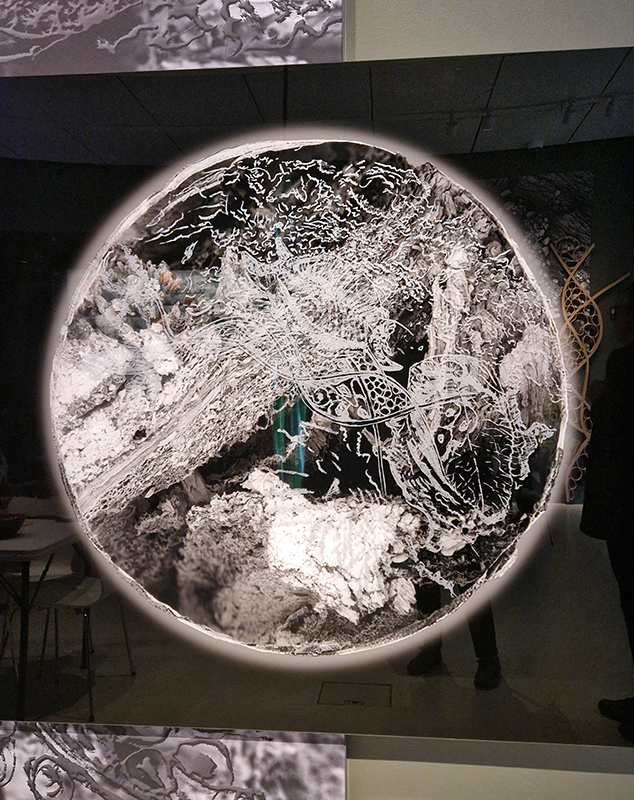
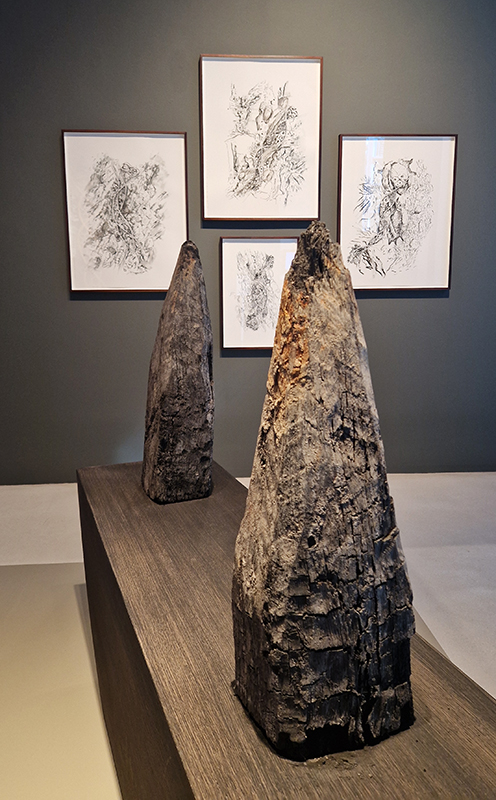



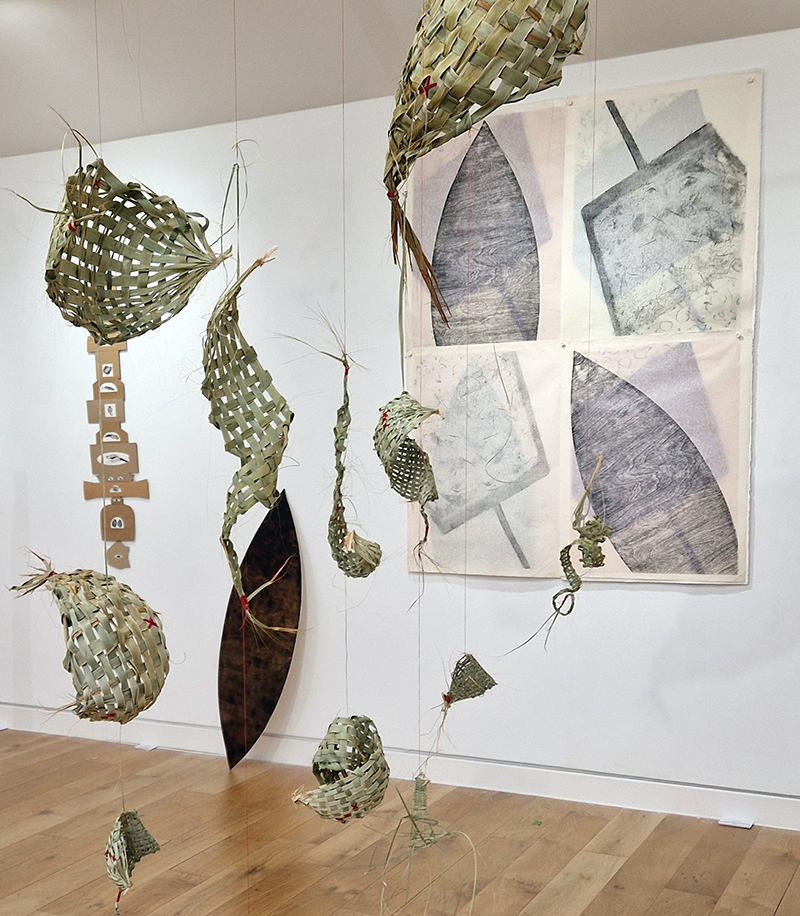
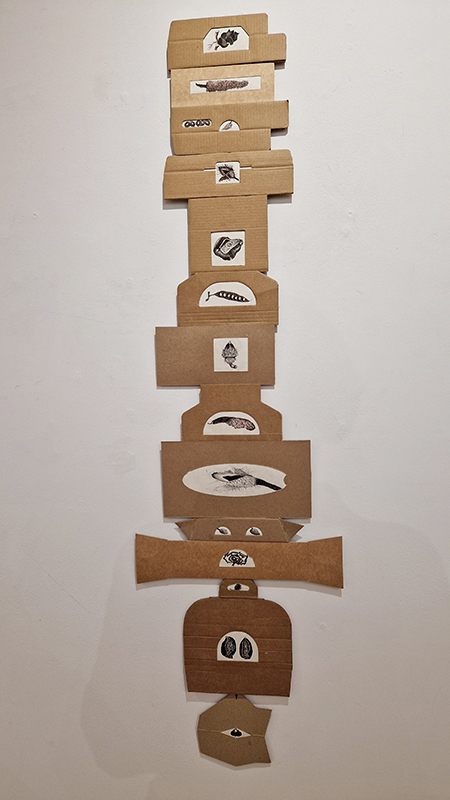
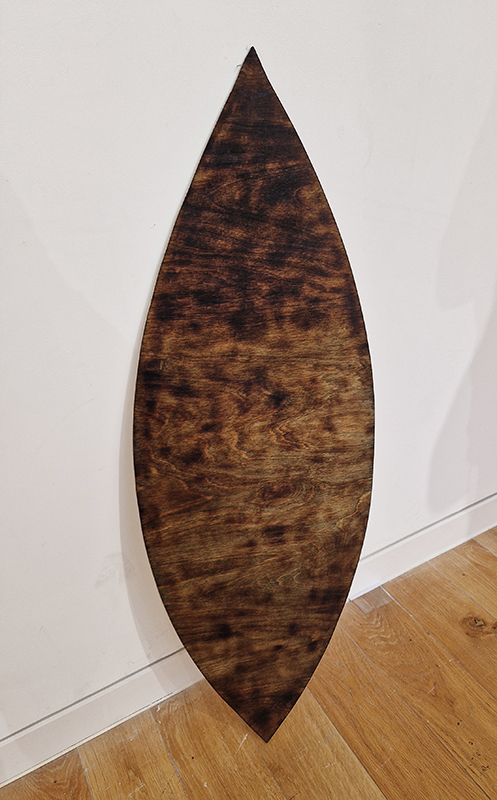
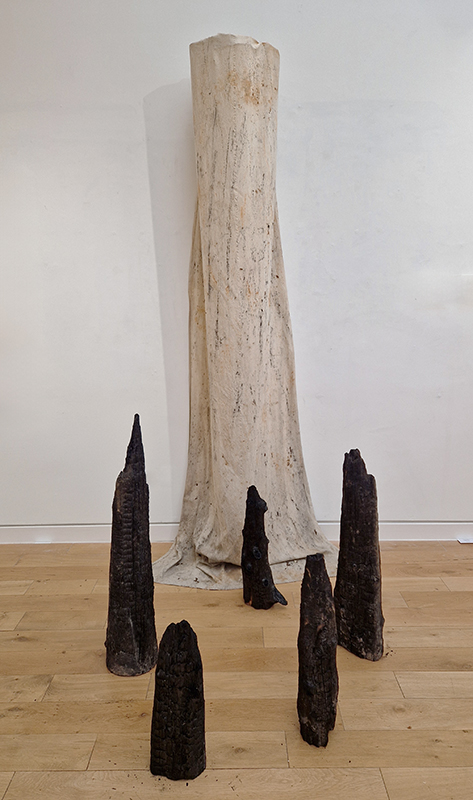
Treen (of a tree) was a collaborative event between Liz Botterill, Sevenoaks museum curator and the Kaleidoscope Gallery co-curators Rosalind Barker and Sue Evans, with the artists of Sevenoaks Visual Arts Forum. The artists were invited to respond to items in Sevenoaks Museum that are made of wood. Participating artists: Colin Anderson, Carole Aston, Jocelyn Bailey, Rosalind Barker, Susanne Beard, Sarah Cliff, Christina Crews, Louisa Crispin, Margaret Devitt, Louisa Donovan, Duncan Dwinell, Sally Eldars, Sue Evans, Deborah Farquarson, Victoria Granville, Kate Grimes, Amanda Hopkins, Marilyn Kyle, Keith Lovegrove, Venetia Nevill, Clare Revolta, Franny Swann and Irene Vaughan. Venetia Nevill worked outside the remit to create ‘Memories of a tree’ to honour a plantation of spruce trees that have been felled, because they were infected by the spruce beetle. Her process of wrapping a cloth around a tree, and rubbing the burnt soil, ash and charcoal into it, memorialises and commemorates the trees. Over a few months the cloth absorbed the sunlight, birdsong and passing of time, allowing the elements to leave their mark, and create a cloak of protection. The cloth is exhibited along with burnt remains of trees.






Reading
North Pole, South Pole: The Epic Quest to Solve the Great Mystery of Earth’s Magnetism by Gillian Turner. A very readable account of all the philosophers, explorers and scientists fascinated by the origin of Earth’s magnetism, from the earliest speculations of lodestone mountains, magnetic polar stars to seismology and deep ocean core sampling revealing the inner working of the planet.
Turning to Stone by Marcia Bjornerud. This book is the antithesis of the idiom ‘as cold as a stone’. It is a passionate and candid account of relationships between humans and rocks. Human to human, human to rock, rock to human and rock to rock. Along the way we learn a lot about geology and the human condition.
