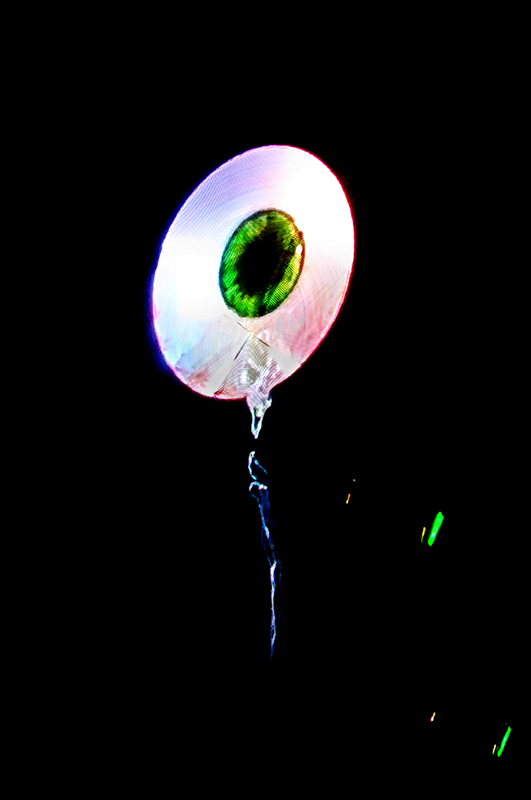Delighted to share the news that I have been longlisted for The Aesthetica Art Prize 2024. A live recording of The Breath of Stars will be included in the digital showcase at York Gallery. The Aesthetica Art Prize celebrates contemporary art across a range of media and I’m looking forward to joining the Future Now conference for critical and cultural debate running alongside the art prize exhibition.

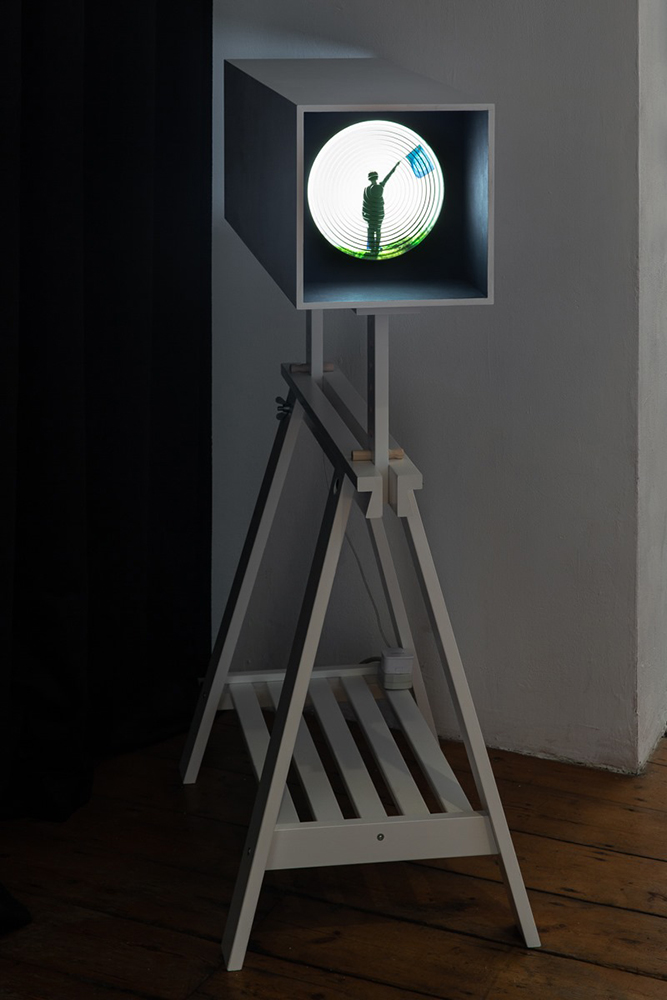
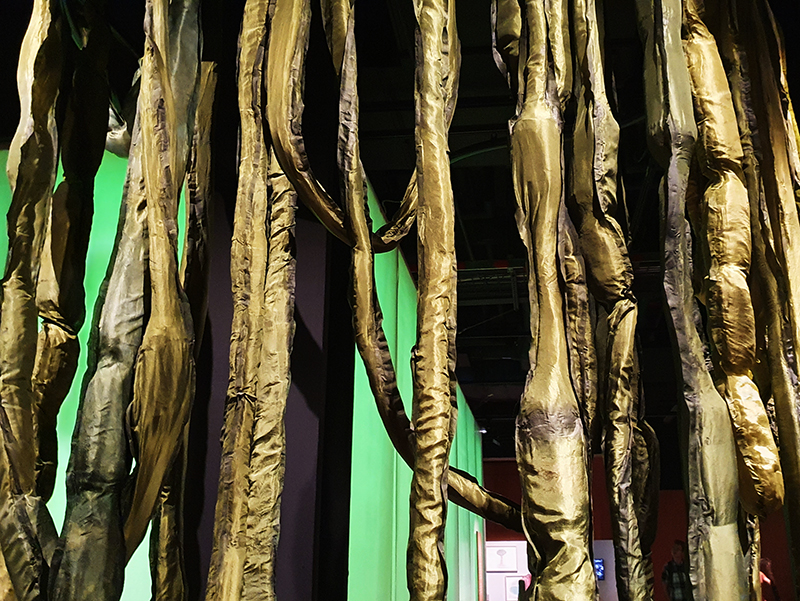
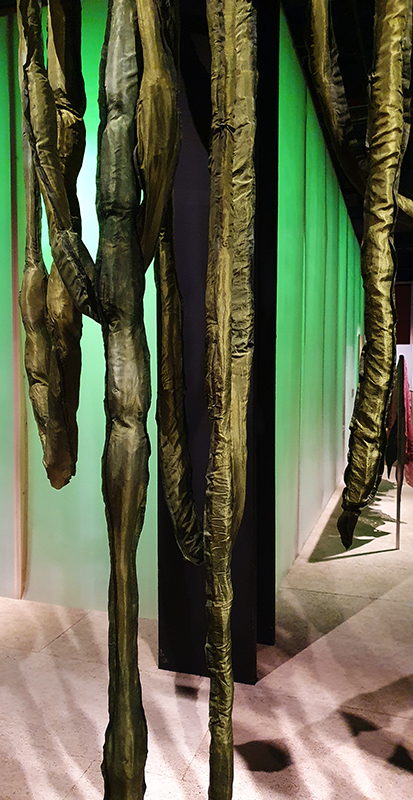
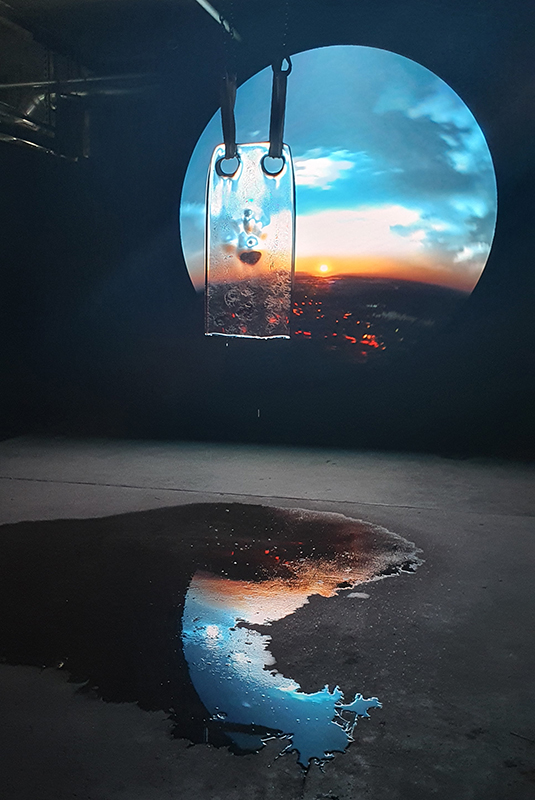
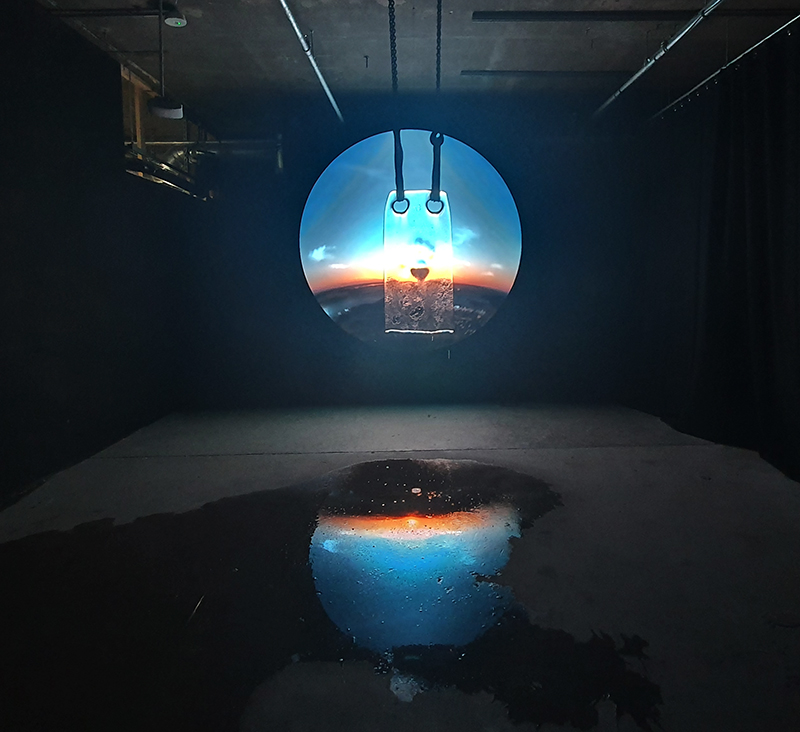
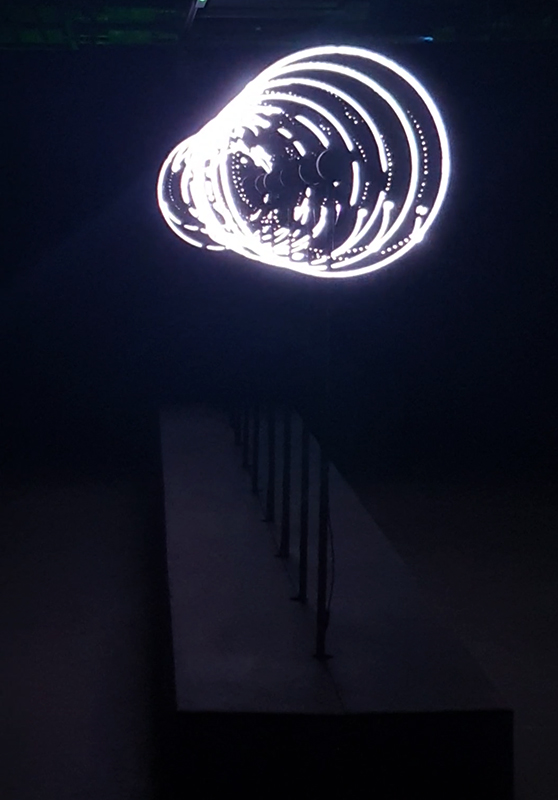
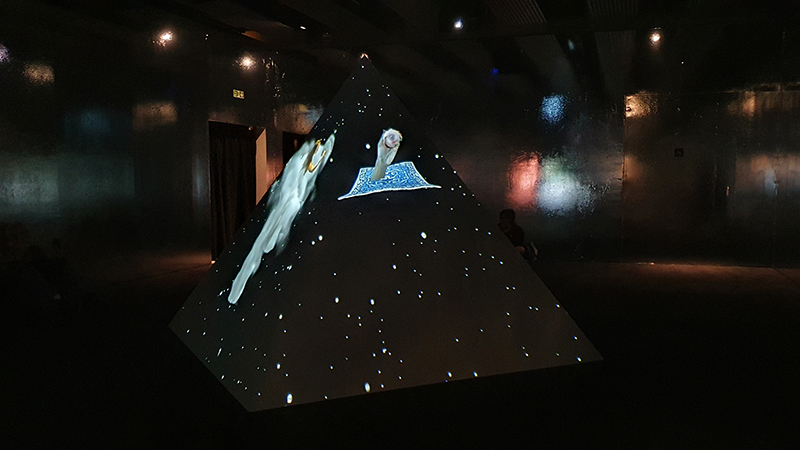
The Breath of Stars (Cosmic ray detectors, mini computers, wooden box (20×20 cm), video projection; live duration) is a digital video work activated in real time by the passage of cosmic rays through a pair of scintillator detectors. Cosmic rays from exploding stars or other extreme events, power across the universe, collide with atoms in the Earth’s atmosphere, break apart, and shower down upon us. Some particles silently interact technology on Earth. In this work, particle detectors and mini computers are connected to a projector. Every time a cosmic ray passes through the plastic scintillator blocks inside the detectors, its energy is recorded, and a starburst video is displayed.
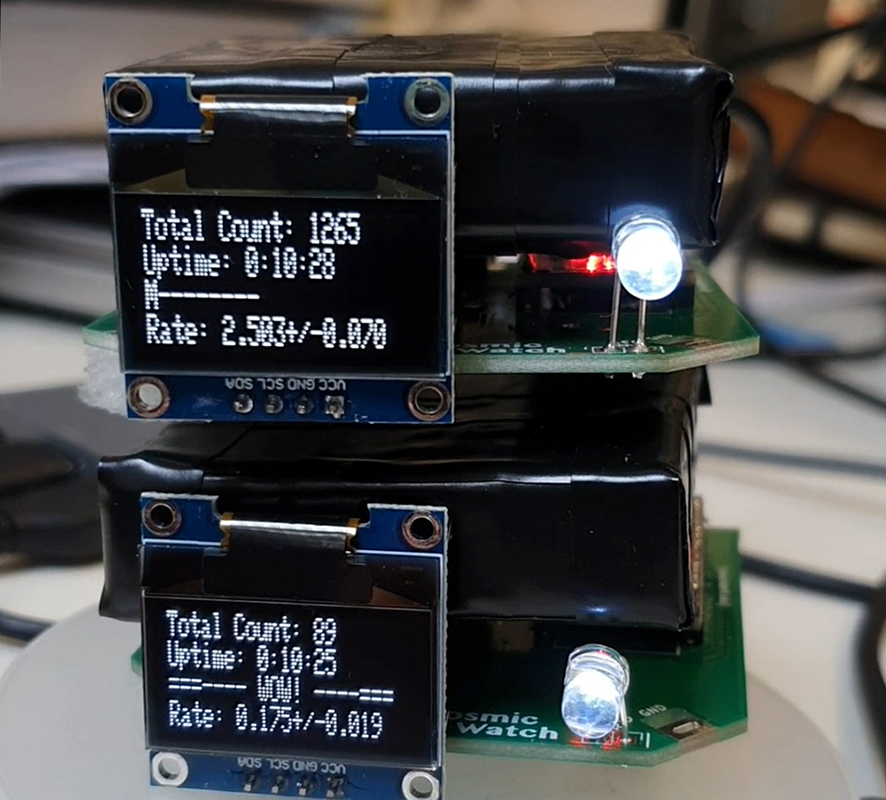
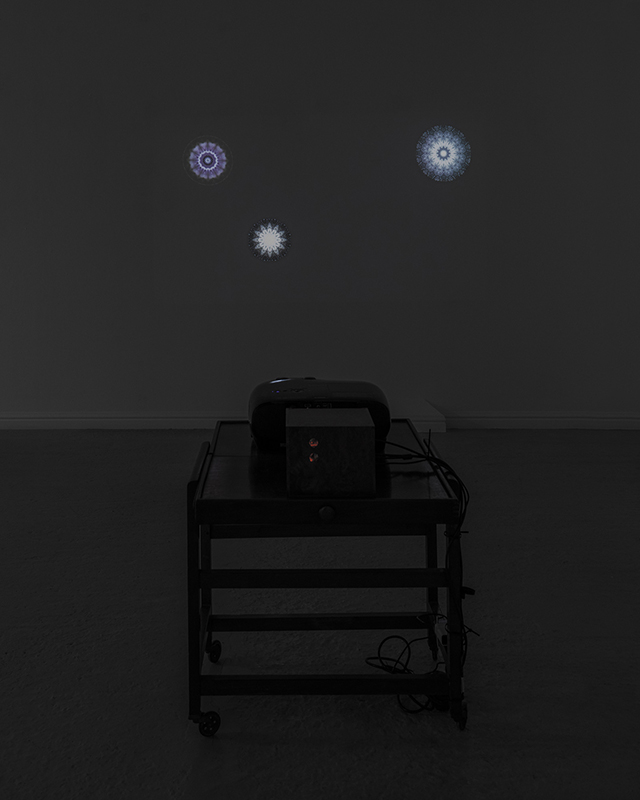


The kaleidoscopic video images that appear are created from mirrored footage of cosmic ray trails filmed during my cloud chamber experiments. Cosmic rays are subatomic – smaller than an atom – they are protons or the nuclei of an atom which has had its electrons ripped away. We can’t see the actual particles but we can see the trails of condensation they leave behind as they whizz through a cloud chamber.

Cosmic rays arrive at Earth randomly, and this can be witnessed by the sudden flurries and silent gaps of the video imagery. The kinetic energy in just one particle can be equivalent to the energy of a cricket ball bowled by the fastest bowler on the planet – so much energy squeezed into one tiny particle gives it a huge velocity. Light travels a thousand billion kilometres in one year – a light year – no object with mass can travel at the speed of light but an ultra-high energy cosmic ray would only lag behind the photon by 100th of the diameter of human hair. Most cosmic rays heading for Earth are deflected by the planet’s magnetic field – without this protection, life on Earth, as we experience it, could not survive this bombardment of radioactive matter.
Around 95% of the universe is ‘dark’ to us, formed of unknown and possibly unknowable matter. Phenomenon such as dark matter may be inaccessible to us, but cosmic rays offer a more tangible contact with outer space as they have mass. Although too small to see, we can witness their effects via technology, such as that used in The Breath of Stars, which affords us the opportunity to gaze beyond and between the stars to gain an insight into the structures of the cosmos and imagine what might be hidden in those dark spaces.
I am very excited that Cosmic Chiasmus: crossing the universe is showing at the super brand new Science Gallery Bengaluru in their inaugural exhibition CARBON: under pressure.
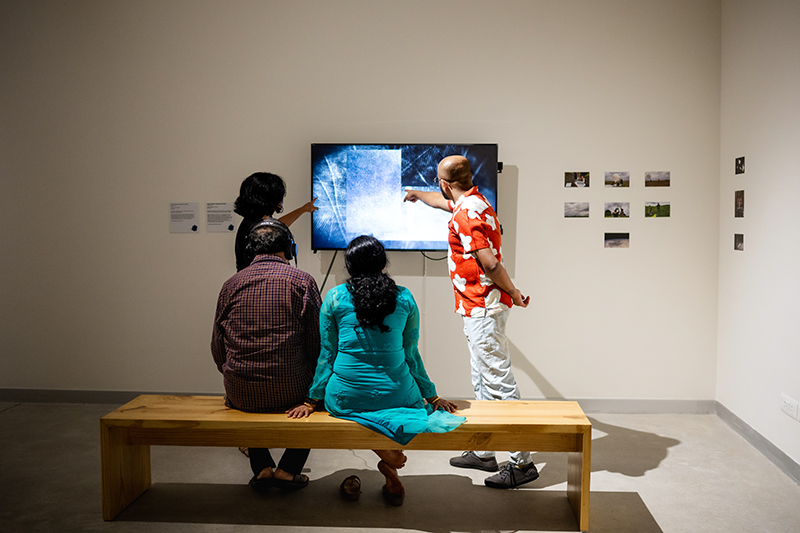


Science Gallery Bengaluru (SGB) is part of the Science Gallery International Network pioneered by Trinity College Dublin. The exhibition explores the ubiquitous nature of carbon, its energy history and the potential futures it enables. Given its unique capability to form bonds and compounds carbon is a foundational element of both life and non-organic matter and its properties have been harnessed as fullerenes, graphene, nanobuds, nanotori, nanocones, and nanohorns, enabling the creation of new screens, batteries, ultra-fast computers, ultra-thin sensors and cables of braided nanotubes. Carbon-14 in organic materials serves as the basis for radiocarbon dating, and Carbon-12 was the standard Dmitri Mendeleev used to determine the atomic weights—and now mass—of all other elements. Carbon dioxide is used as the standard to understand and regulate the flow of exchanges between ecology and economy. Industry driven by coal and oil-fired productivity have triggered alarming climatic effects and created a chasm between geo-biological time as shaped by the material memories of the planet and historical time—that shaped by human action. Carbon is an archive of buried sunshine, bridging the divide between substance and phenomena; caught between the finitude of nature’s resources and the near infinite wonderous potential it holds.


Cosmic Chiasmus: crossing the universe offers a glimpse into a subatomic world where cosmic rays travel from distant galaxies to collide and silently interact with atoms and technology on Earth. Cosmic rays are particles that move extremely fast. They are raining down on planet Earth all the time. Although they are called rays they are not like photons, as light is made of, because they have mass, but they do travel at nearly the speed of light. Cosmic rays go through a violent process of creation, transformation and decay. From the heart of stars or the depths of black holes these particles power across the universe with unimaginable energy colliding with life on Earth and triggering other processes such as cell mutation, computer data corruption and carbon-14 formation. Above our heads where cosmic rays collide with atoms in Earth’s atmosphere radioactive carbon-14 is formed. This radioactive carbon-dioxide in our atmosphere is absorbed by plants and enters the food chain. The radiocarbon decays while an organism is alive but is continually replenished as long as the organism takes in air or food. When an organism dies no more Carbon-14 is absorbed and that which is present starts to decay at a constant rate. By measuring the radioactivity of dead organic matter, the carbon-14 content can be determined and the time of death established. Cosmic ray activity gives us carbon dating techniques. It is an incredible journey that cosmic rays make, blasted across space, spiralling along magnetic field lines to end up entangled with carbon in our bodies.
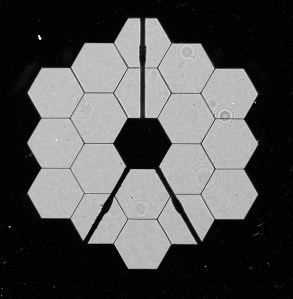
The James Webb Space Telescope selfies of its own light searching mirrors shows cosmic ray activity impact. Space weather can have serious implications for technology. Satellites are particularly vulnerable. and can be sent off-orbit or suffer electrical interference. The satellite population orbiting Earth has more than doubled since 2020, and with more satellites launched in the past year than during the first thirty years of the Space Age, reliance on this technology is increasing at a rapid rate.
I am making new work looking at information insecurity caused by space weather for an upcoming group show at APT Gallery which takes the lifeboat as a metaphor for precarity. Participating artists: Rachael Allain / Caroline AreskogJones / Beverley Duckworth / Liz Elton / Susan Eyre / Kathleen Herbert / Kaori Homma / Anne Krinsky.

Life Boat brings together artists with a shared interest in exploring precarity as a site of dynamic transition. Each takes an investigative approach to the environmental, social and historical themes evoked by the lifeboat, as a means of addressing ecological crisis, liminal landscapes, close and distant horizons, boundaries and displacement, lines of rescue, navigation and transformation.
The gallery location in Deptford, once a major departure point for maritime trade and scientific expeditions from Deptford Dockyard, resonates with the exhibition’s concept of being ‘at sea’, in the sense of negotiating the unknown. Research into local histories and ecologies informs work created for the exhibition and is further expanded upon in the accompanying events programme. There will be a low tide river walk led by Creekside Discovery Centre in collaboration with artist Anne Krinsky who has an ongoing project looking at wetland vulnerability. A group discussion – Fieldwork as Practice hosted by artist Caroline AreskogJones who has invited a skipper from Sail Britain, a principal curator from The Natural History Museum and an environmental historian to join the conversation. Artist Kaori Homma will lead a hands on workshop to reveal the secrets of invisible ink and fire etching, links to espionage and the geopolitical nature of the meridian line explored via her Homma Meridian Project.
In tackling concepts of the perilous, the vulnerable and the lost, Life Boat raises the alarm on the passive position of waiting for rescue and encourages urgent action in troubled waters.
“How do you calculate upon the unforeseen? It seems to be an art of recognizing the role of the unforeseen, of keeping your balance amid surprises, of collaborating with chance, of recognizing that there are some essential mysteries in the world and thereby a limit to calculation, to plan, to control.” Rebecca Solnit, A Field Guide to Getting Lost
Gallery Visits
Tania Kovats as above so below at Parafin. She says: ‘I make drawings more than I draw drawings.’ There is something captured in the simplicity of her work, a haptic viscerallity that is very emotionally stirring.
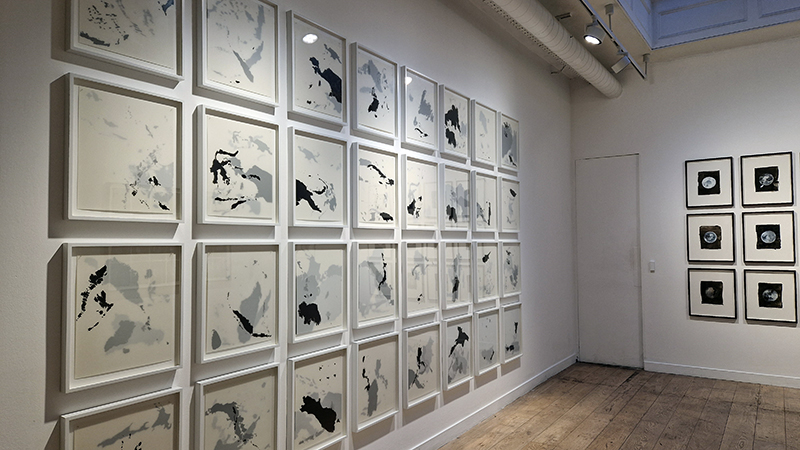
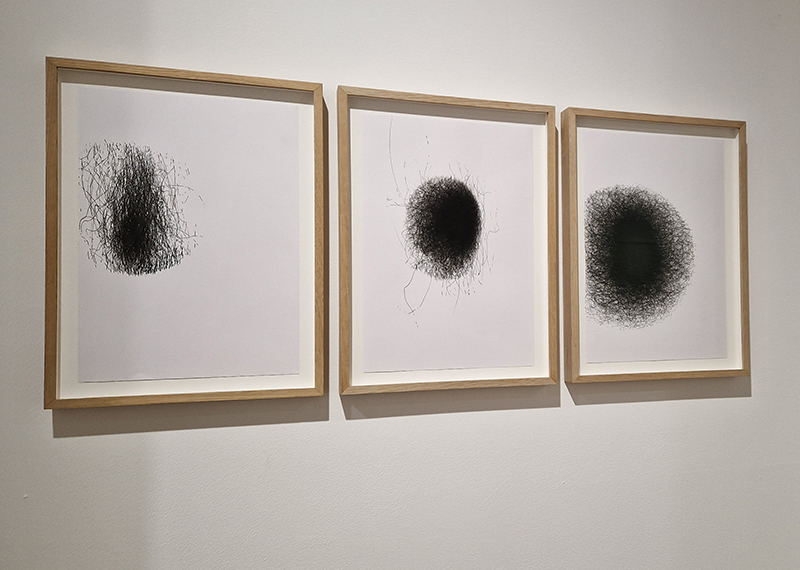
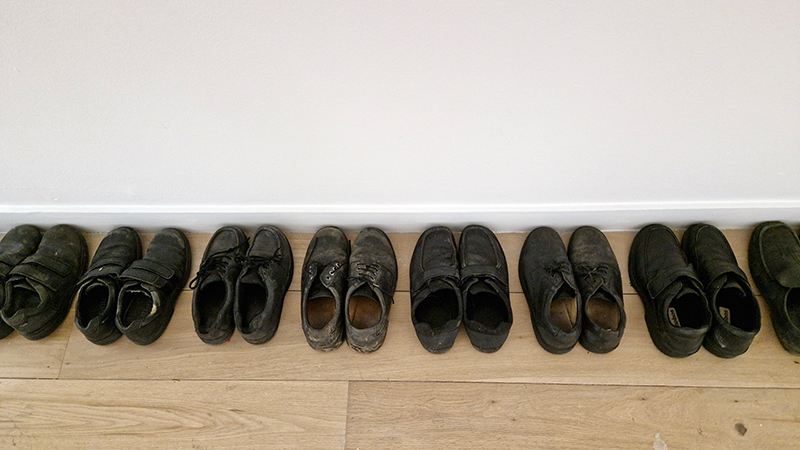
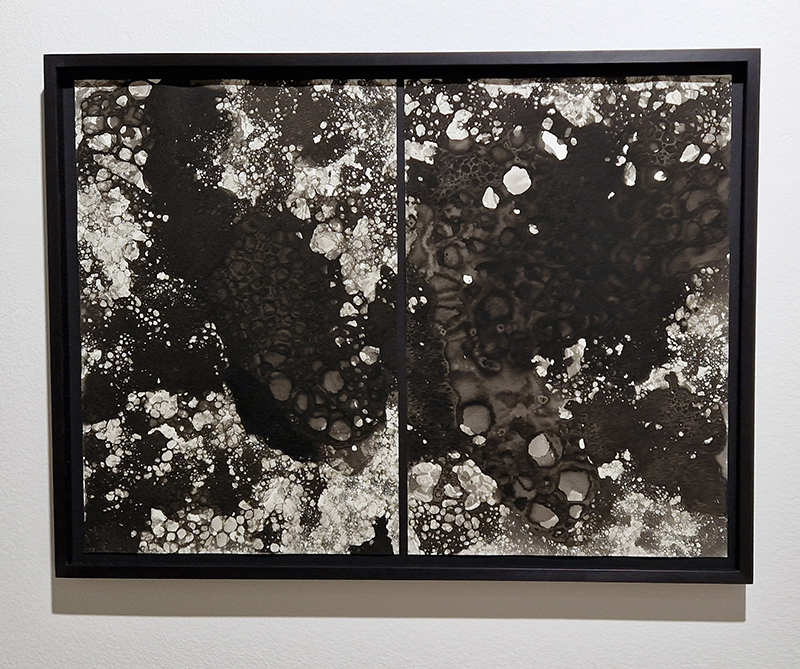
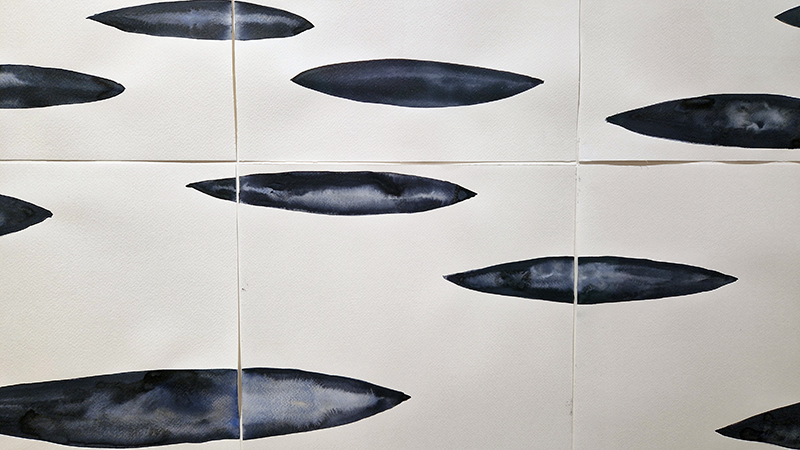










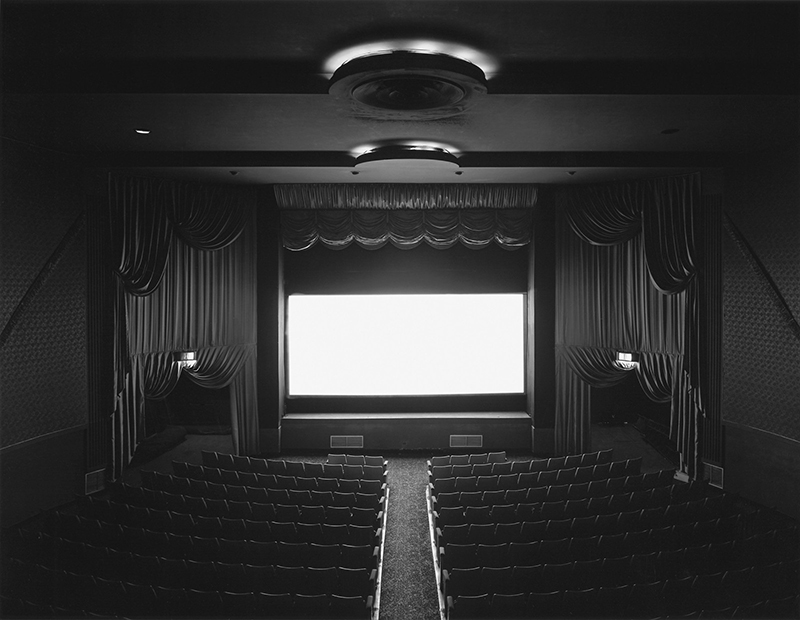
Hiroshi Sugimoto: Time Machine at Hayward Gallery. Beautifully crafted, astonishing work. Hard to believe his models are waxworks or museum taxidermy dioramas, not living subjects and that it is his studied use of light that so cleverly activates his images. I particularly like the Theatres series where he set his camera on an exposure equal to the length of the film being projected into an otherwise dark and empty cinema. The resulting images of a blinding white screen bleeding light like an opening to heaven are remarkable records of passing time. I also loved the work stemming from his interest in mathematics and optical sciences and his experiments with different electrical discharge tools. Sugimoto discovered that he could produce shapes that looked like amoeboid organisms, so he set out to recreate the conditions of the ocean from the time that life began. Using rock salt from the Himalayas (today’s mountain range was once the ocean floor), he mixed his own primaeval seawater. Submerging electrically charged film into the water, the artist was amazed to see light particles move across the surface like microorganisms.




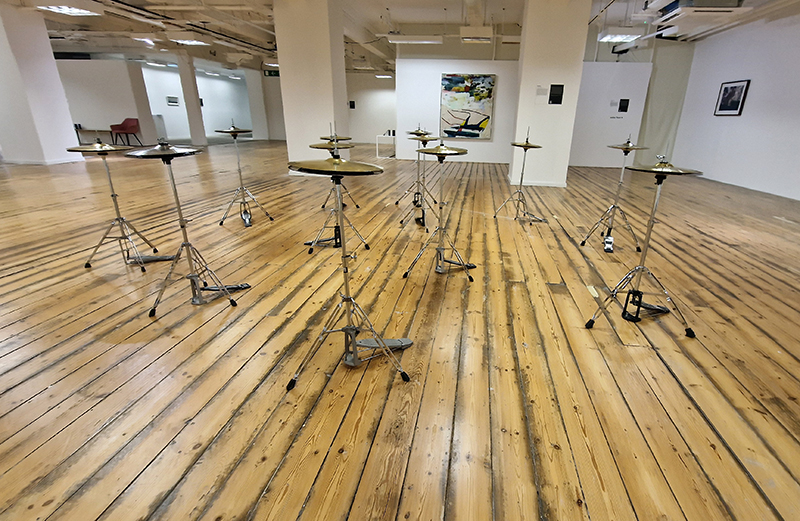
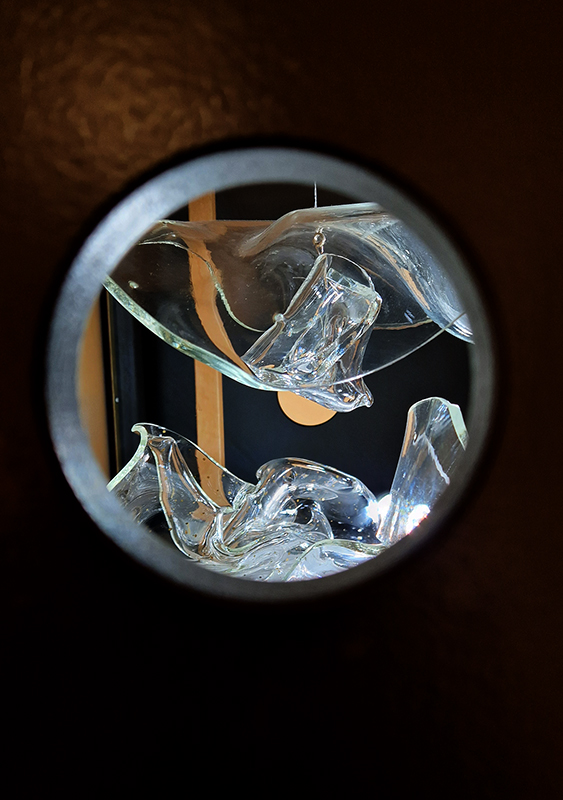
SEISMIC: ART MEETS SCIENCE at GIANT Gallery, Bournemouth, a collaboration with SEISMA Magazine curated by Paul Carey-Kent who was leading a tour of the works when I visited. Artists: Uli Ap, Edward Burtynsky, 0rphan Drift, Peter Matthews, Claire Morgan, Elpida Hadzi-Vasileva, Lisa Pettibone, Shuster + Moseley, David Rickard, Troika. Scientists from corresponding fields of interest are called upon to comment on the work of the curated artists. I was curious to see David Rickards Cosmic Field (3.7mHZ) – a commission by Seisma magazine – which sees cymbals clash when a cosmic rays passes through a hidden Geiger counter. Unfortunately, I didn’t get to witness the full effect as the detector mechanisms hadn’t been charged up, and so only one cymbal was responding with an occasional clash. There are some clever maths in the title and references to John Cages silent composition and the oscillations of the sun. I would like to have learnt more about how the Geiger counters can be sure they are recoding cosmic rays and not just background radiation. It was interesting to read about how stars have sound trapped within and resonate at natural frequencies, like waves inside a wind instrument. Astrophysicist Dr William Chaplin refers to this process as gentle breathing which can be seen in periodic changes in brightness as the stars breathe in ( compressed and bright ) breathe out (relaxed and darker). Other work in the show included Lisa Pettibone’s Truth to Illusion a screen that appears to show a digital undulating image is revealed through a peep hole to be caused by a rotating light and glass mechanism. Light can reveal and mislead in the quest for an understanding of reality. Jewell of Space by Claudia Moseley and Edward Shuster is a mesmerising moving sculpture of light refracting and scattering across a constellation of glass, shadowing the lensing effects of light across the galaxy. Clare Morgan’s Heart of Darkness – a grid of bluebottle flies – a comment on complexity in a system and the importance of each individual to create a whole. Elpida Hadzi-Vasileva’s animal organs given new context – the body turned inside out (cow’s stomach) – the unseen revealed (lamb intestine).
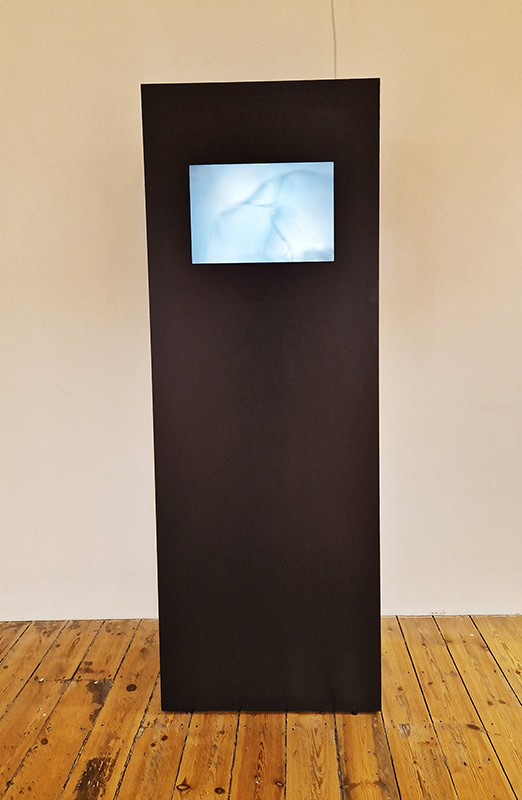
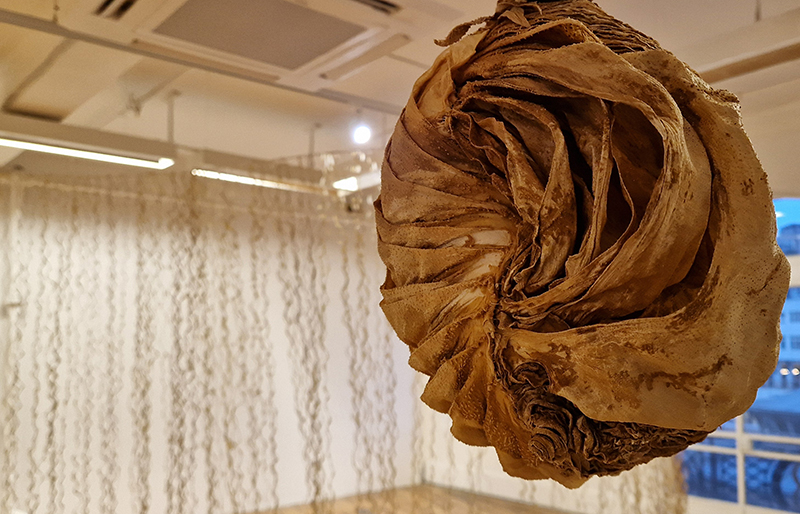
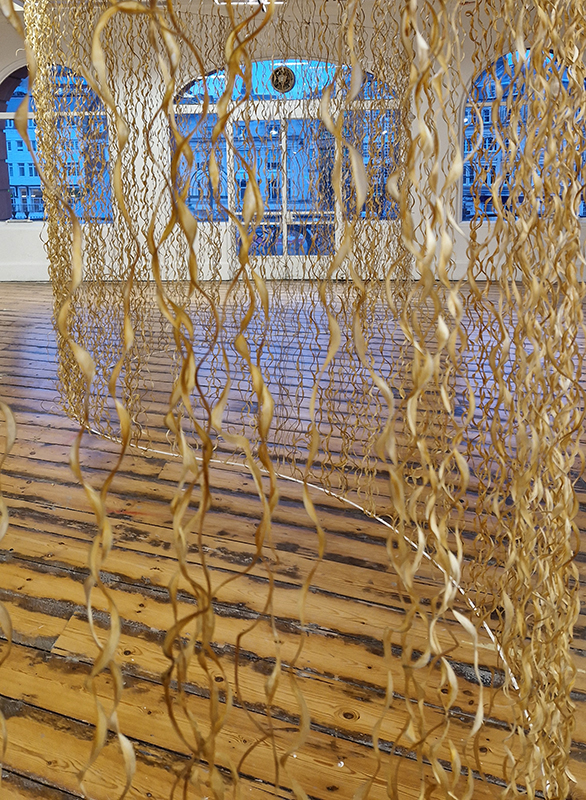
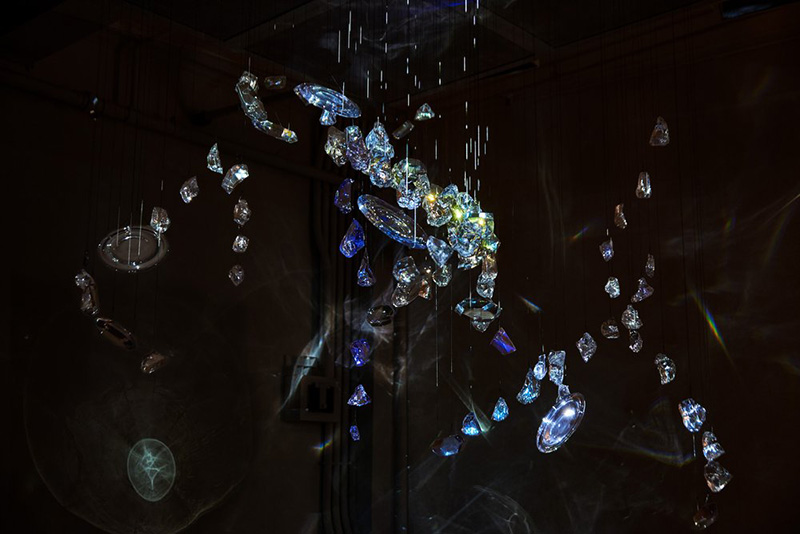









The Accurate Perception Available When Our Eye Becomes Single at The Cut, Halesworth, Suffolk. A lucky chance to see another iteration of this impressive collaboration between Richard Ducker (video) and Ian Thompson (sound). This atmospheric multi-screen installation transports you to the remote otherness of Orford Ness with its innate aura gained from status as a top secret military site and atomic development centre of the 1950’s.
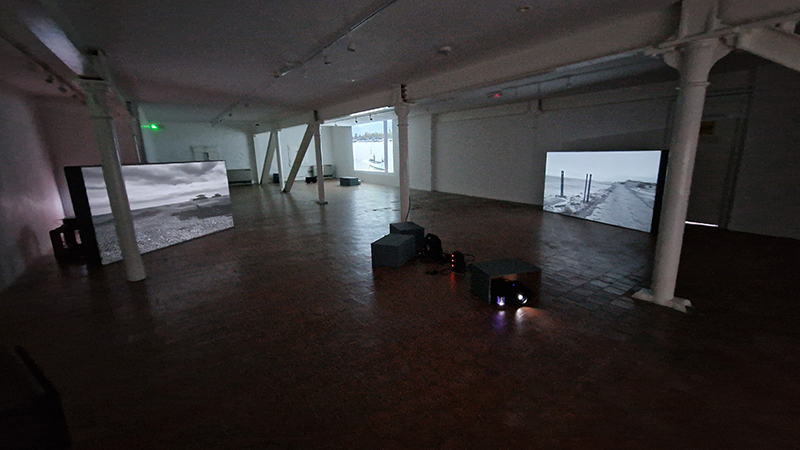
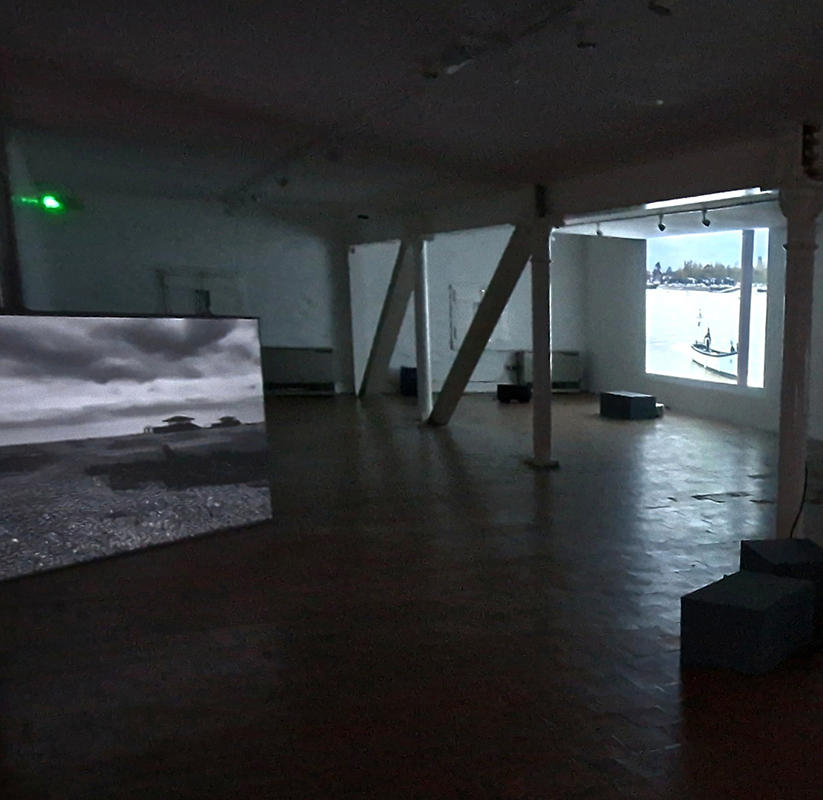


Holding Cosmic Dust: An Almanac, a video installation at The Swiss Church in London by Hot Desque. I enjoyed their previous theatrical inspired installation at Thames-side Studios Gallery where lighting played a key role in creating atmosphere. Again lighting was key, this time very low lighting meant identifying friends at the event was unpredictable. This installation is partnered with an intervention within the permanent, archaeological collection of the Corinium Museum, in Cirencester, positing a speculative archaeological dig in which a matriarchal society is uncovered. The installation draws out connections between archaeology, history and fantasy. There was in conversation with historian Frederika Tevebring about the speculative nature of archeology and evidence of matriarchal societies, but due to challenging acoustics and lighting much of this fascinating talk was lost. I would have liked to hear about the cosmic ray connections. Was it to do with Carbon dating? Participating artists: Holly Graham, Rubie Green, Rebeca Romero, Amba Sayal-Bennett, Abel Shah and Suzanne Treister.
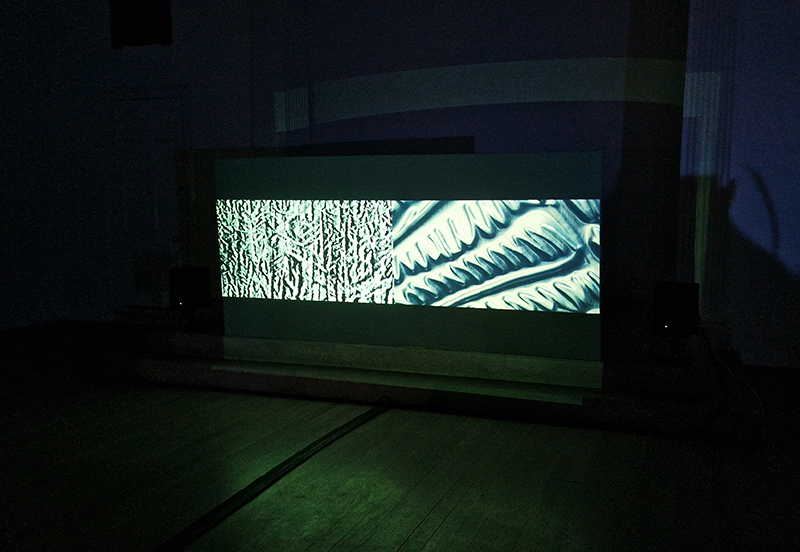
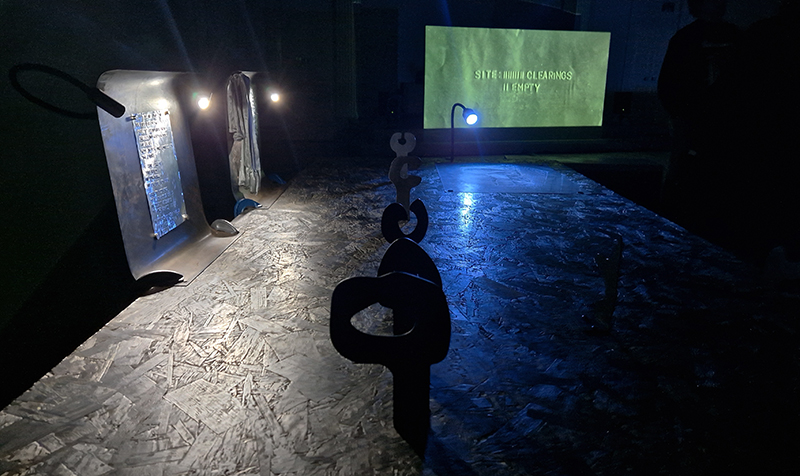






Reading
All The Light We Cannot See by Anthoney Doerr. An extraordinary evocation of the depths of human tenderness and cruelty and the power of knowledge. This is a beautifully written fiction spanning the decades from the 1930’s into the 21st century when advances in radio technology went from a being a source of public information and enlightenment to a weapon of war. Through the wonder of the young protagonists in discovering the magic of radio transmissions, the author also stirs in the reader a reminder that it is invisible waves crisscrossing our world, carrying information vast distances, across political and geographic boundaries. I loved this book.
The Future of Geography: how power and politics in space will change our world by Tim Marshall. Clear and accessible writing takes the reader through the history of the space race to the ubiquity of orbiting satellites and on to the era of astropolitics, military strategy and the battle for future resources. The stakes are high.
Entangle: Physics and the Artistic Imagination edited by Ariane Koek, written in conjunction with an exhibition at Bildmuseet in Sweden. The book is filled with fascinating essays from both artists and scientists giving personal perspectives on their interest in and interaction with particle physics. The importance of an open imagination, the thrill of the unknown, the quest for knowledge that may never be accessible, are relevant to all participants. The common ground between art and science, and the benefits to both fields of joint conversations, is increasingly being acknowledged. Scientists offer the abstract theories, controlled experiments or new technologies that feed artists imaginations, throwing up new questions for both to consider and relate to the human experience.
Watched the deeply moving film by Werner Herzog, The Enigma of Kaspar Hauser – a fictionalised documentary of a teenager suddenly released from an existence of inexplicable confinement chained in a cellar with no human contact other than his captor. The film follows the internal struggle of Kaspar as he is subjected to the demands of society, and take on the current belief systems of the Church. His confusion at the world and despair at how much he doesn’t understand is an allegory for the limitations of human knowledge. The film spotlights the failure of logic and science to provide answers to the human condition.