In classical antiquity, a time stretching from Homer to the early middle ages, geographic orientation usually referred to landmarks or astral phenomena to determine direction. Eos, meaning dawn, and Hesperus, meaning evening, were named for sunrise and sunset with north (arctos) being marked by the constellation Ursa Major and later the Pole Star. The winds also became associated with direction and named in accordance with their qualities such as hot and humid or cold and dry.
The number of points on a wind rose began with the four cardinal points that were added to and refined over time. Aristotle designed an asymmetrical 10 point wind rose for “the study of things high in the air” (meteorology) which was later refigured by Timosthenes, a 3rd century BCE Admiral and geographer, naming a system of twelve winds and using this as a tool for navigation. The contemporary compass has its roots in the ancient classification of winds.
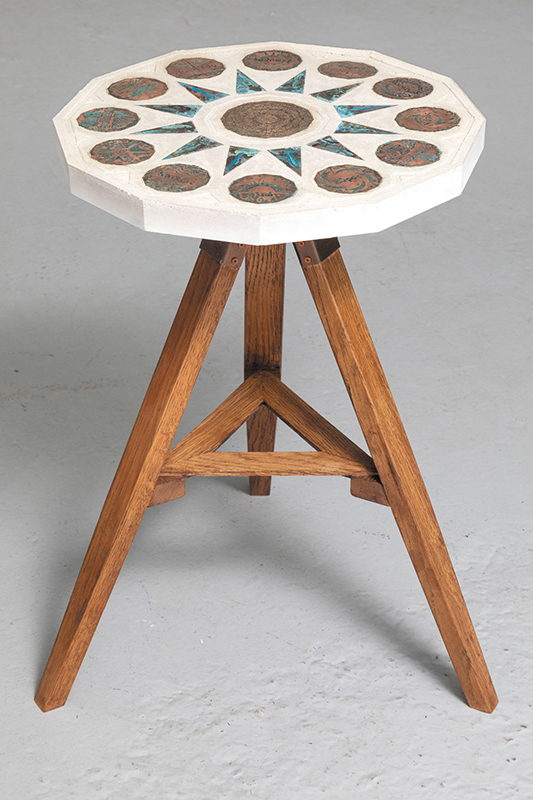
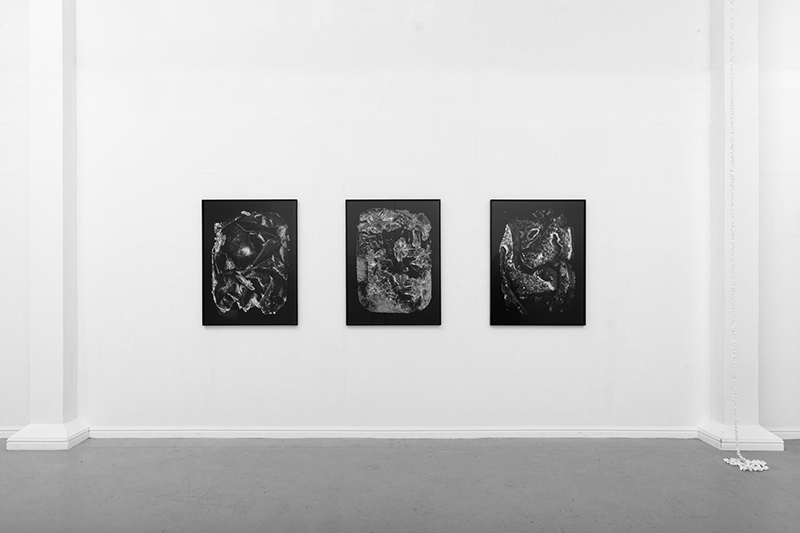
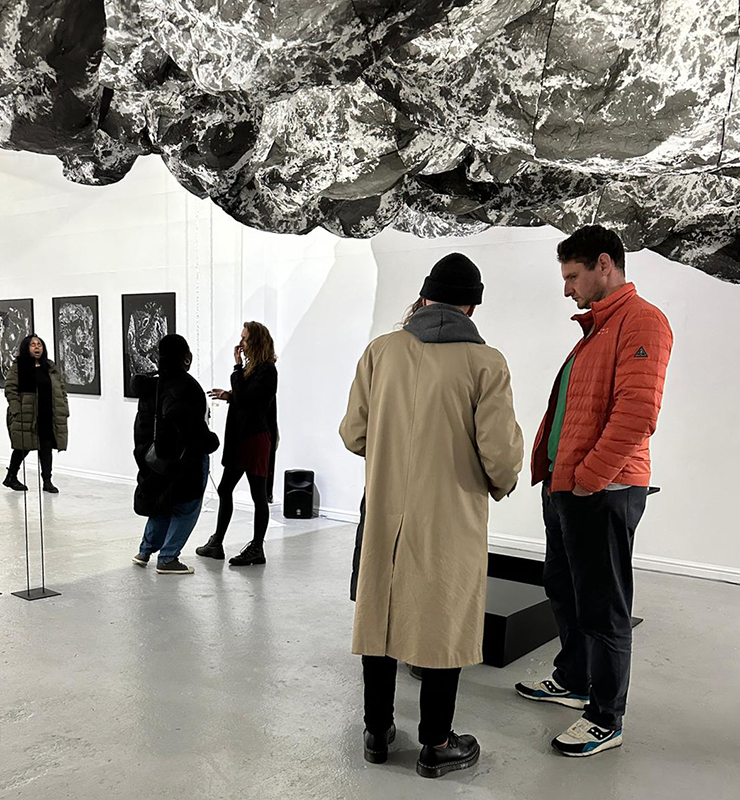
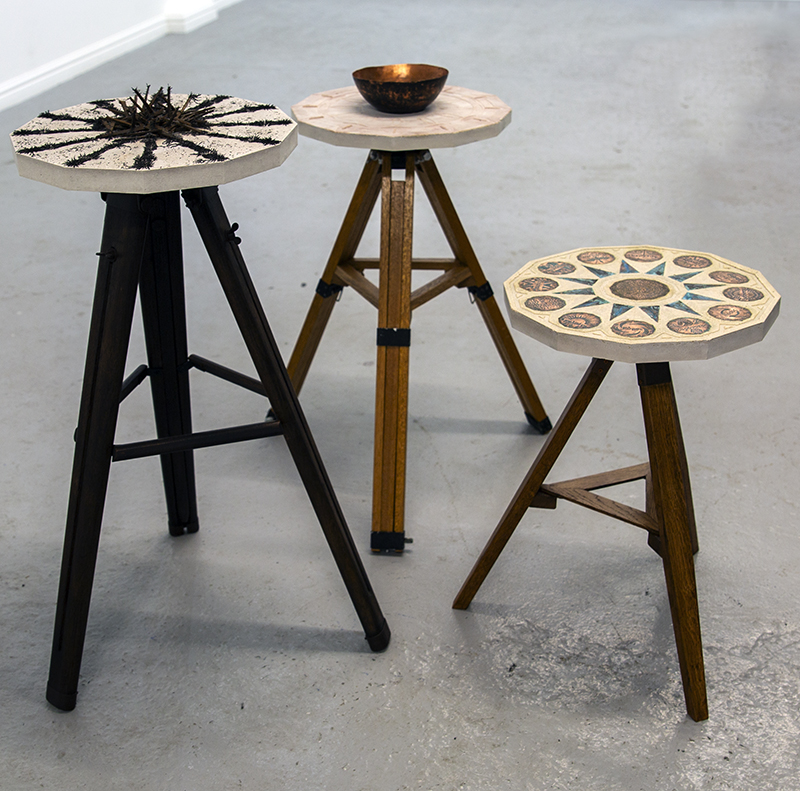
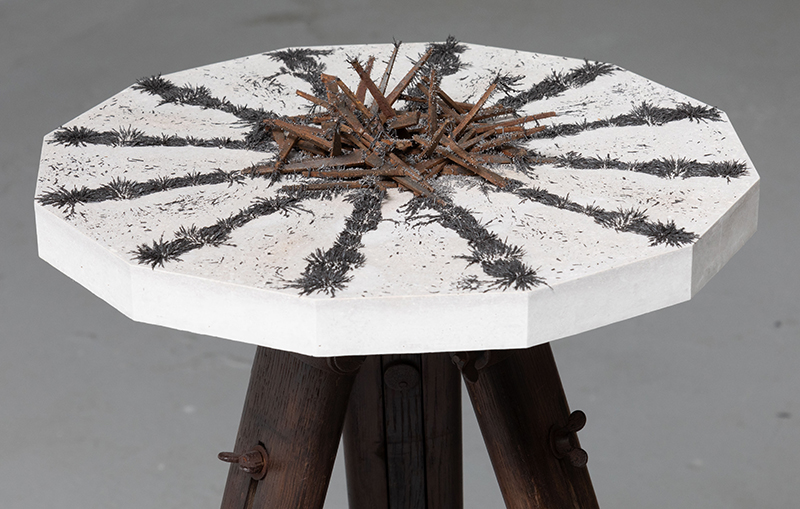
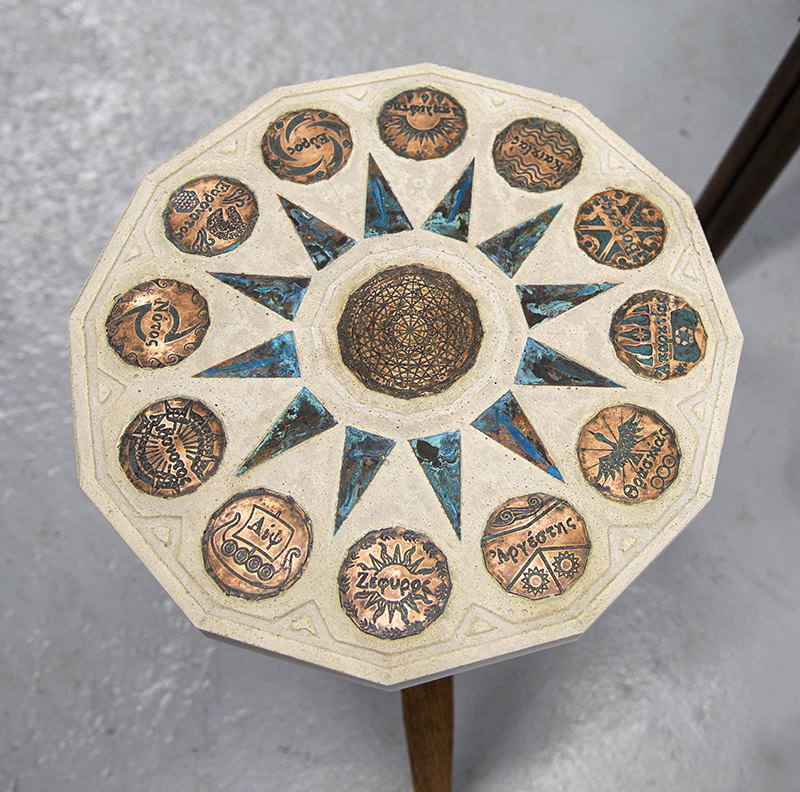
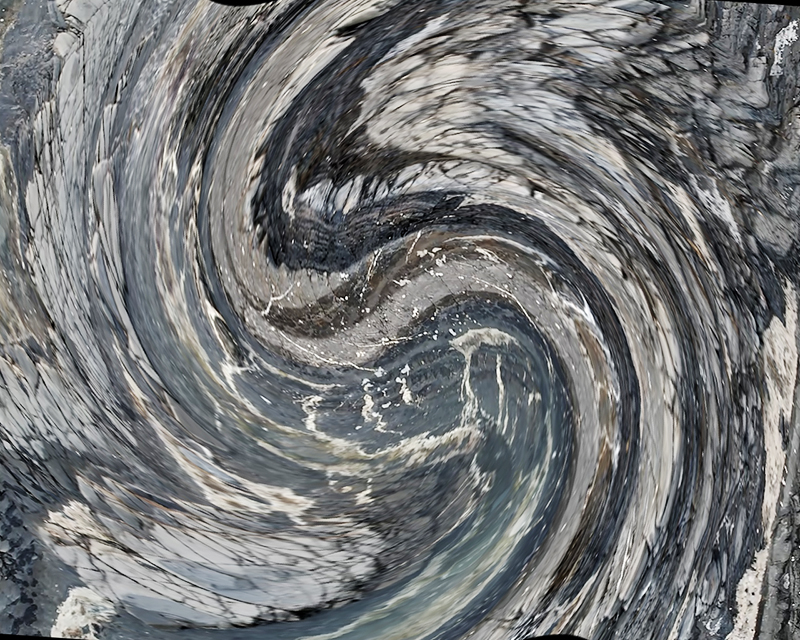
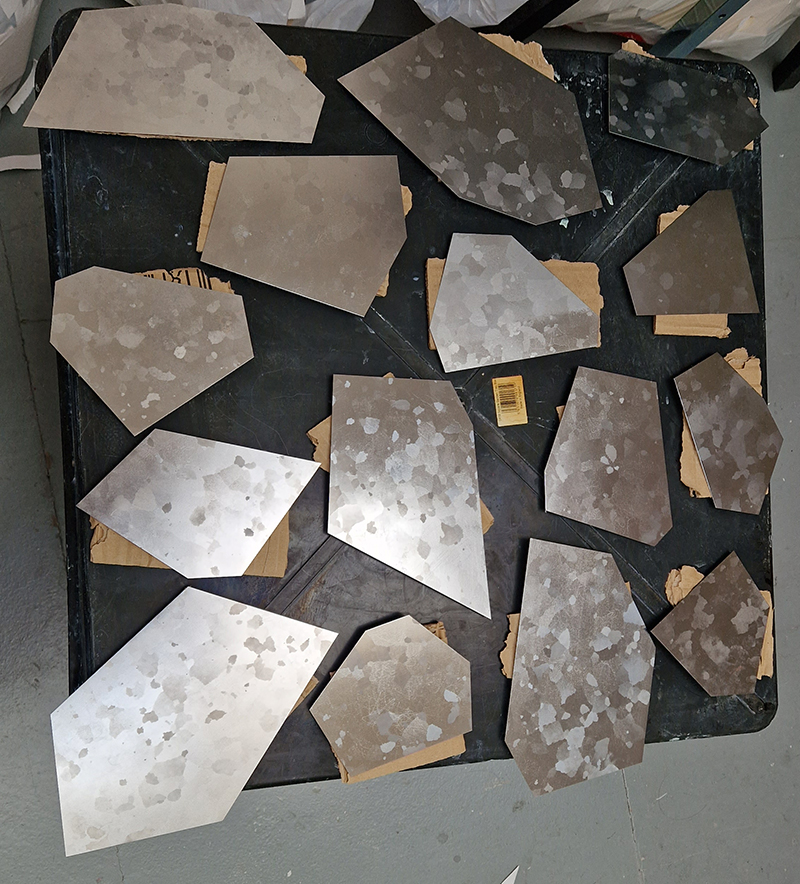
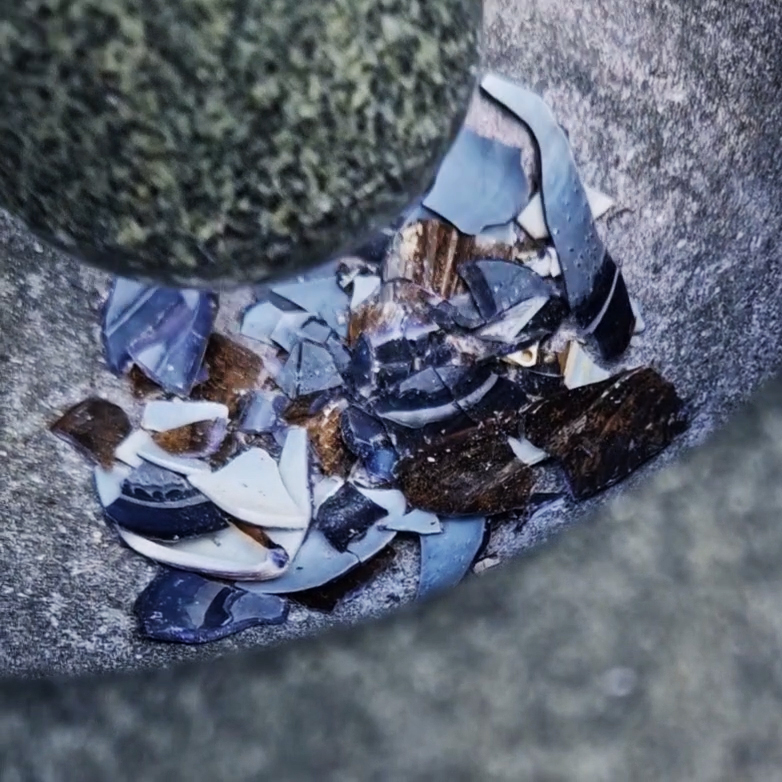
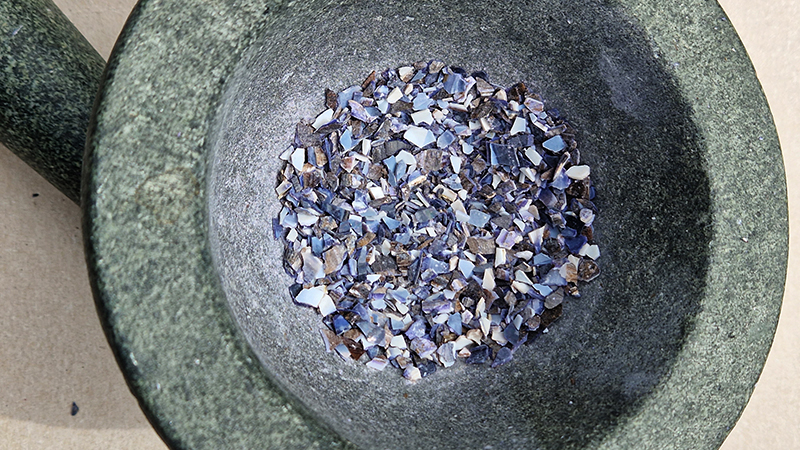
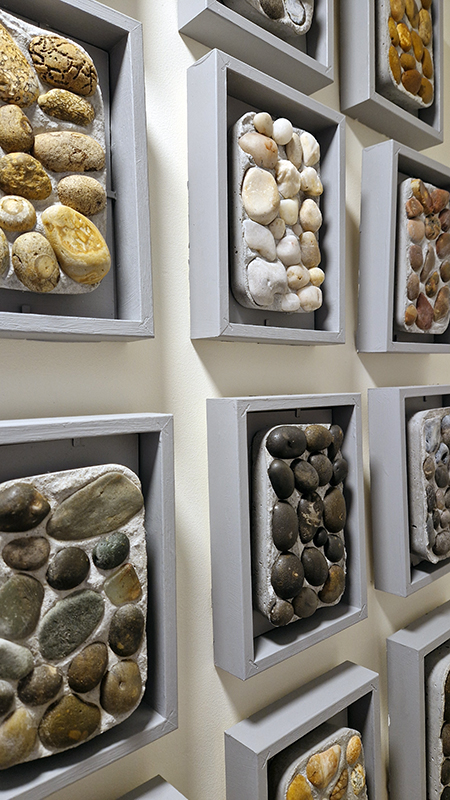
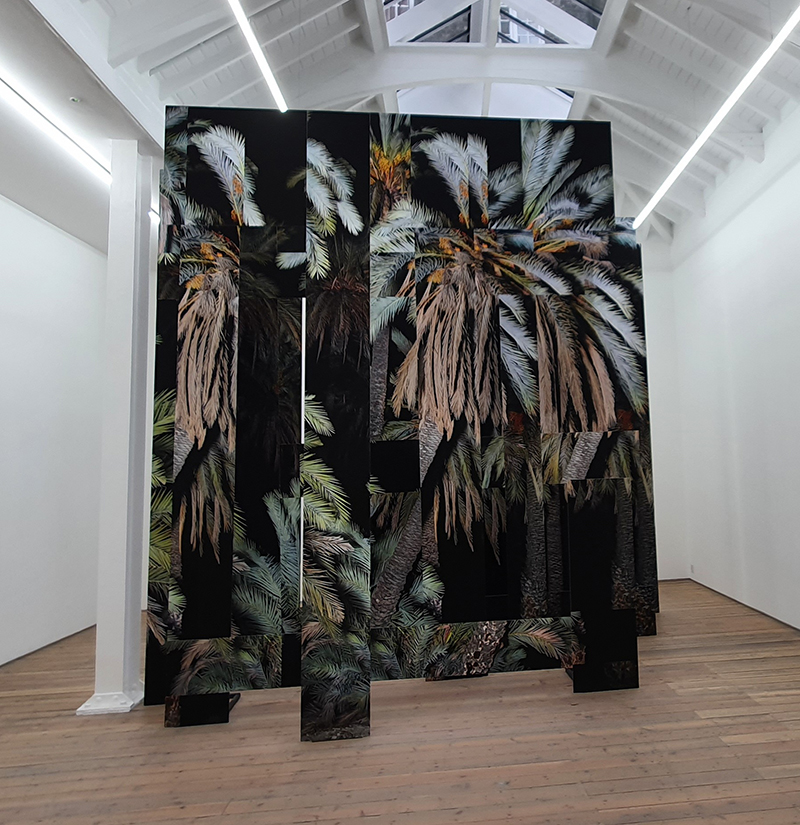
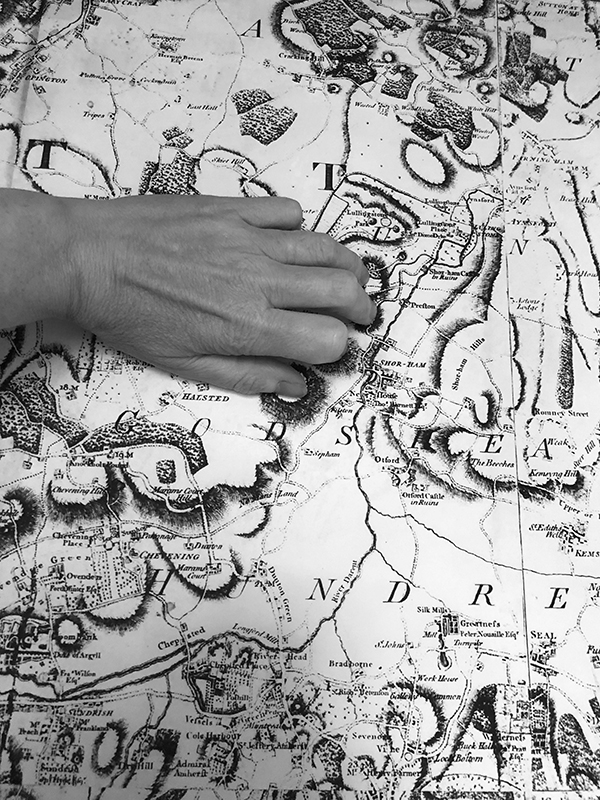
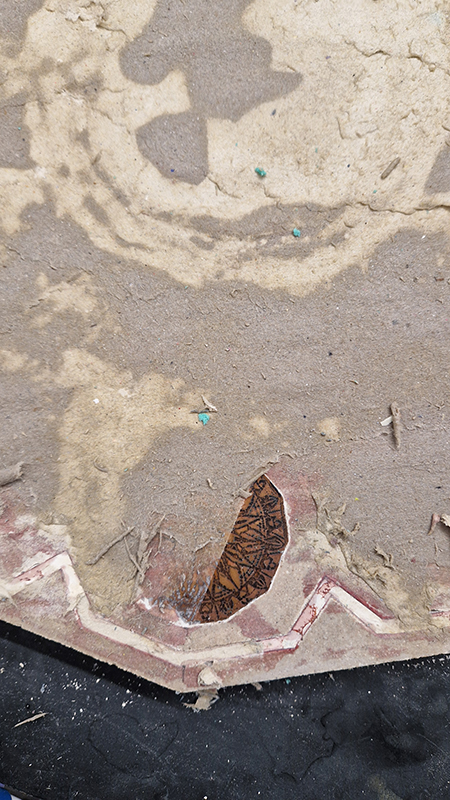
Freshly excavated. A new tablet for the series Instruments of the Anemoi, replacing a previous one based on the idea of a wind rose and set with etched copper markers, the designs of which are influenced by characteristics of the gods (anemoi) represented by each of the twelve winds.
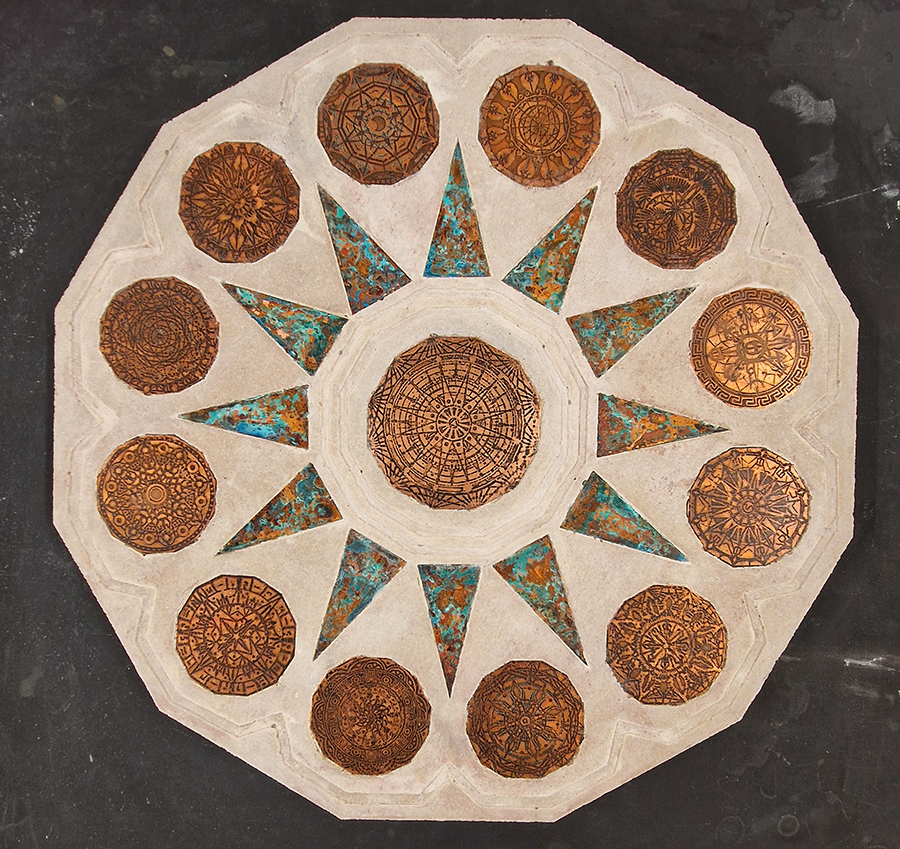

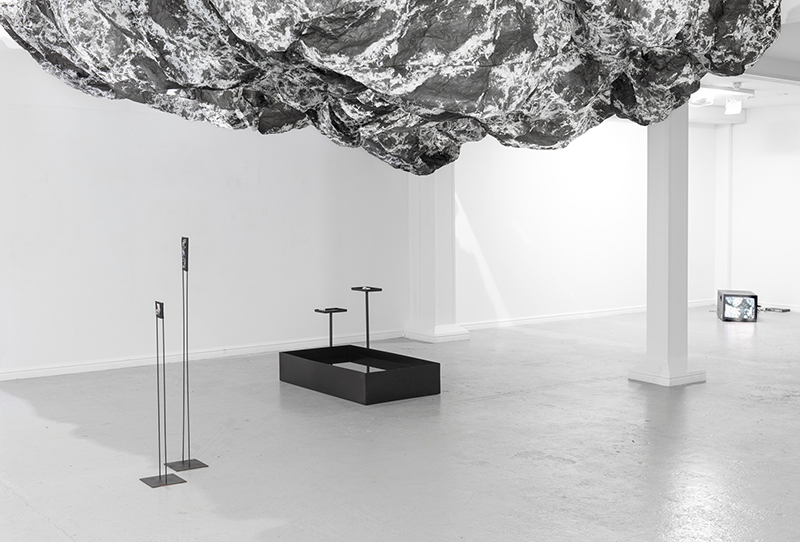
Instruments of the Anemoi are a set of dodecagon tablets cast in Snowcrete, a cement with no magnetic minerals, as is used for instrument pedestals at a magnetic observatory. They also respond to a twelve sided anemoscope “table of the winds” carved in marble around eighteen hundred years ago and held at the Vatican Museums. Releasing the cast from the mould and collagraph is a rewarding process – if all the pieces have held their position during the concrete pour and vibrating to release trapped air bubbles. Luckily this time was a success.
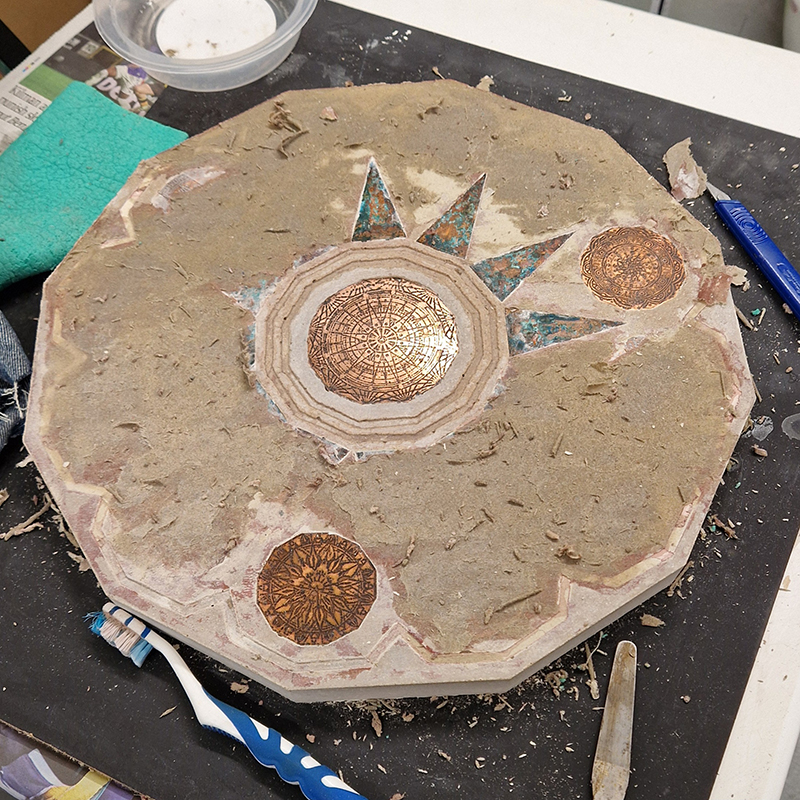





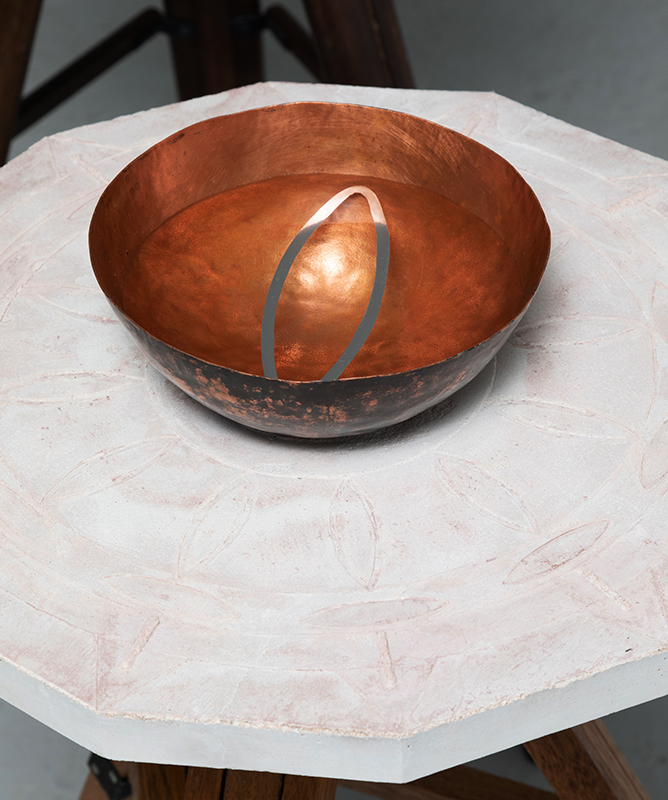
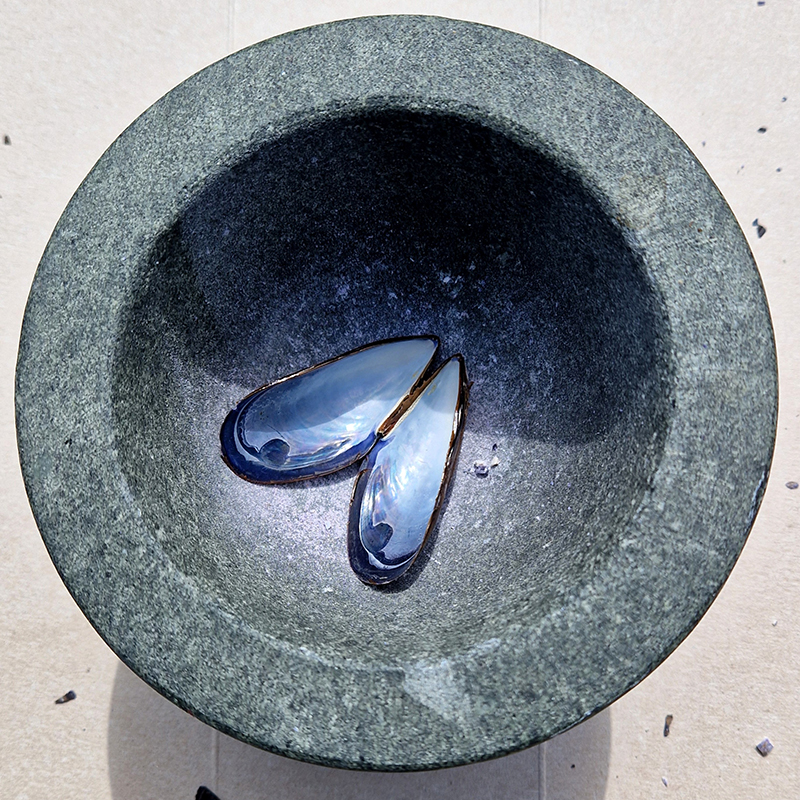
The other two sculptures in the series. A hand beaten copper bowl with a ‘silver fish’ floating in water based on the oval shaped compass needle illustrated in Breve Compendio de la Sphera de la arte Navegar by Martin Cortes 155. Wafer thin fish shaped iron leaves were also used by 11th century Chinese geomancers. Nails and iron filings reveal an embedded magnetic field and hark back to a legend on the discovery of the lodestone, a naturally magnetic mineral, which recalls a Greek shepherd who noticed the nails in his boots were attracted to the rock beneath his feet.
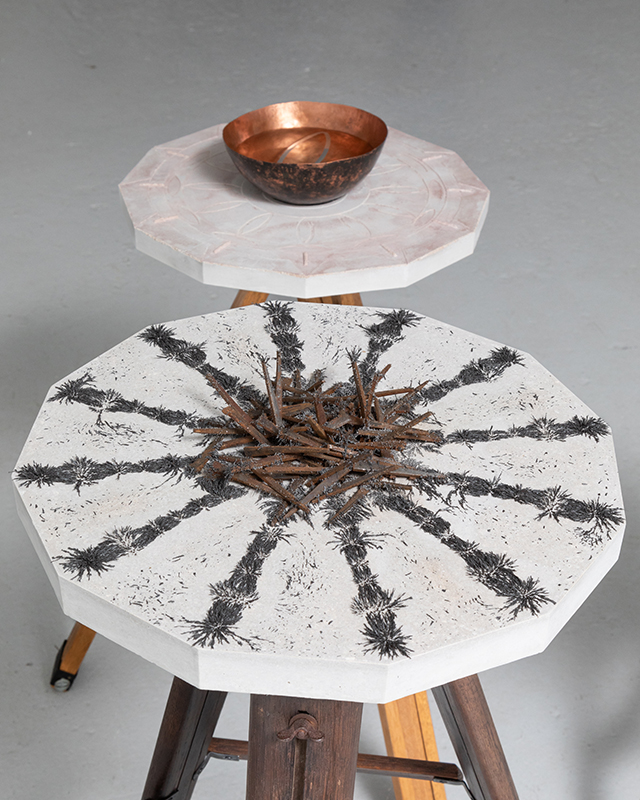

Unsettling to find it is already one year on since A Stone Sky duo exhibition with Julie F Hill opened at Thames-side Studios Gallery and this work was first shown.
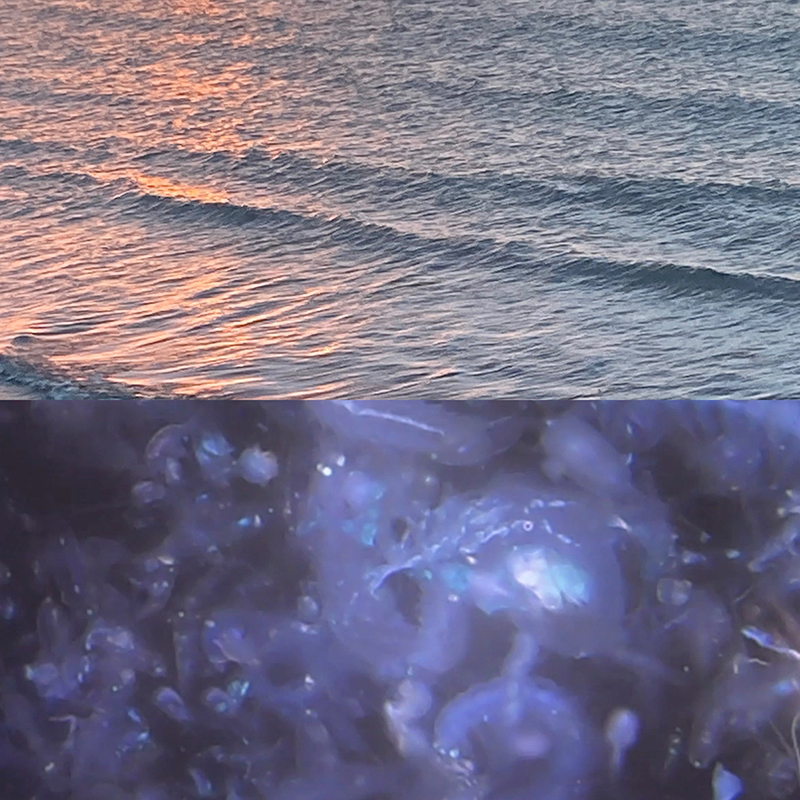
Around 95% of the universe is ‘dark’ to us, formed of unknown and possibly unknowable matter which may be inaccessible to us, but cosmic rays offer a tangible contact with outer space.
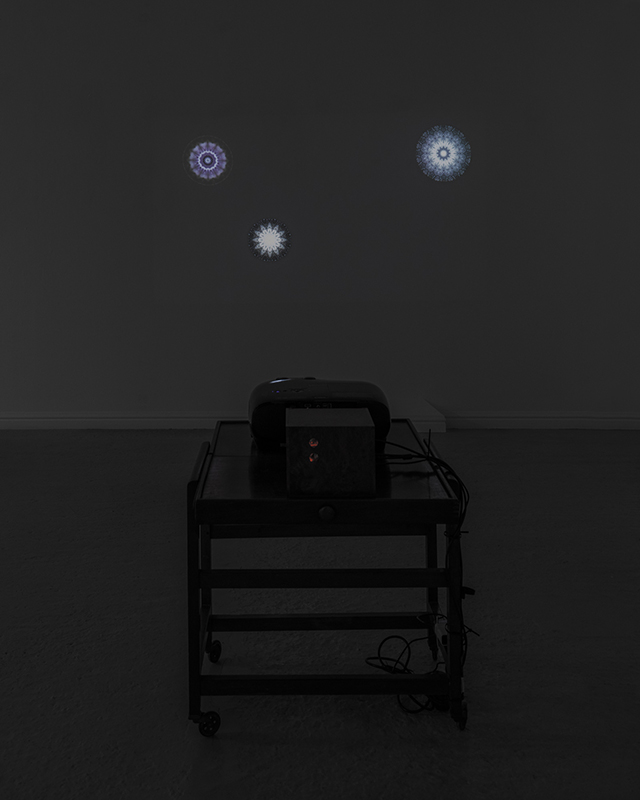
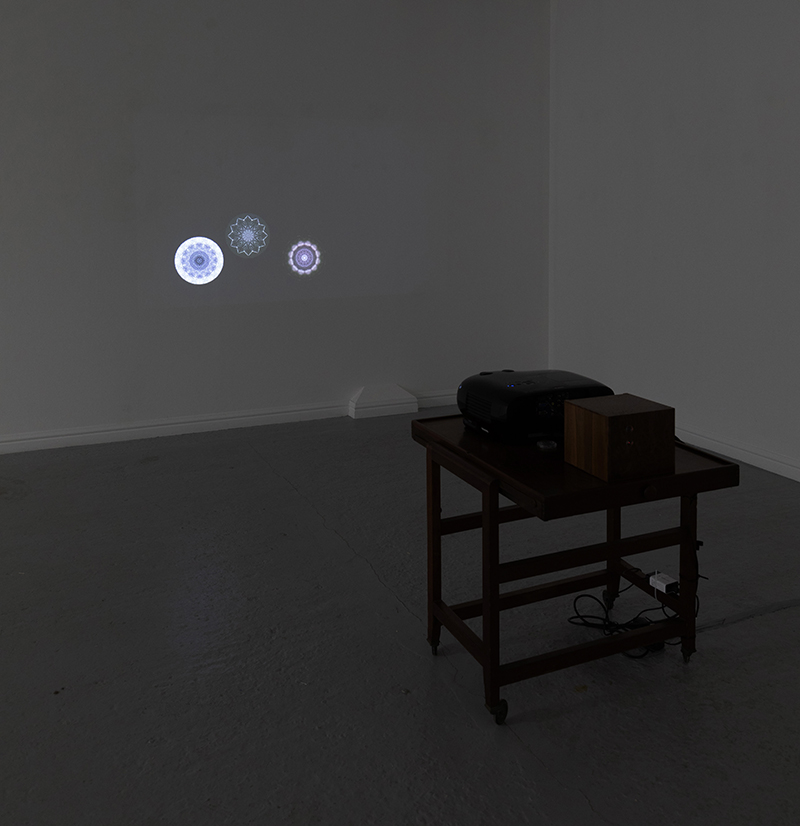
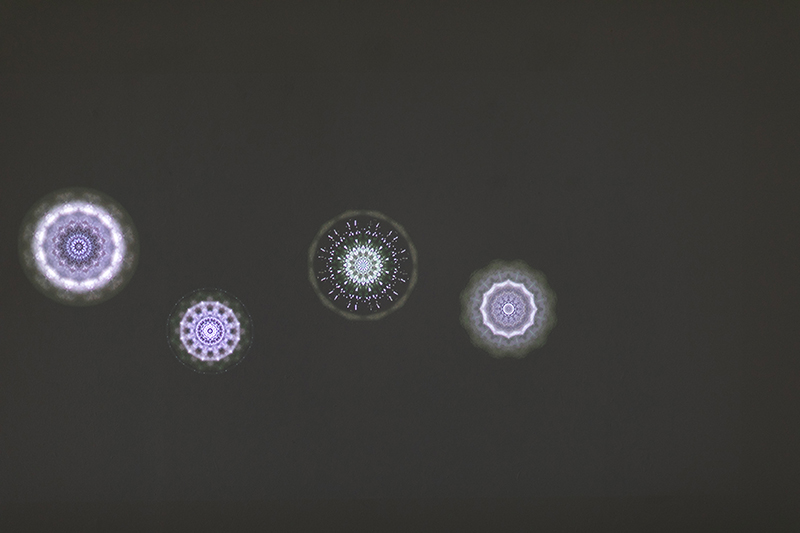
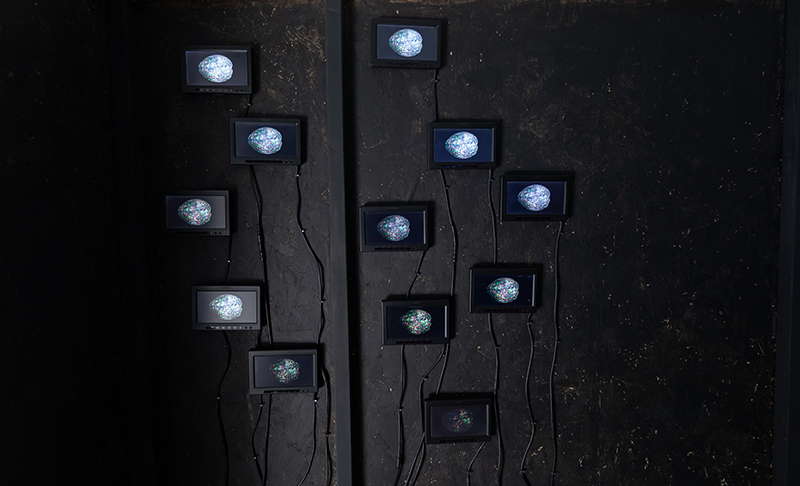
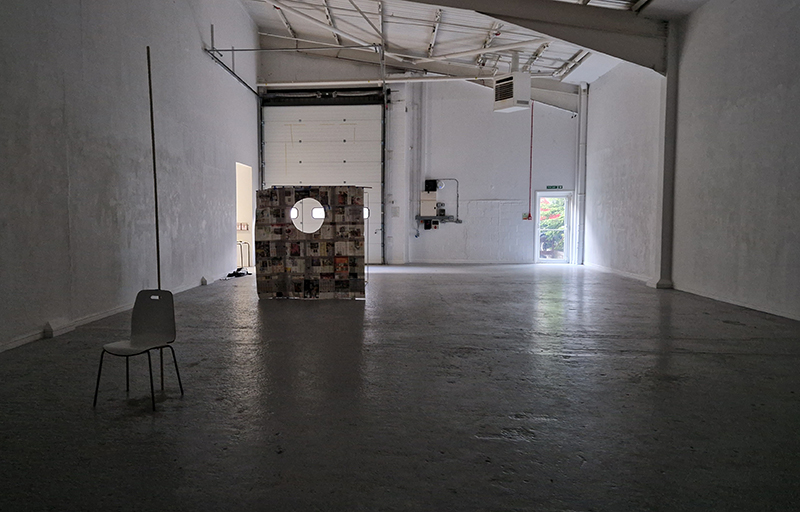
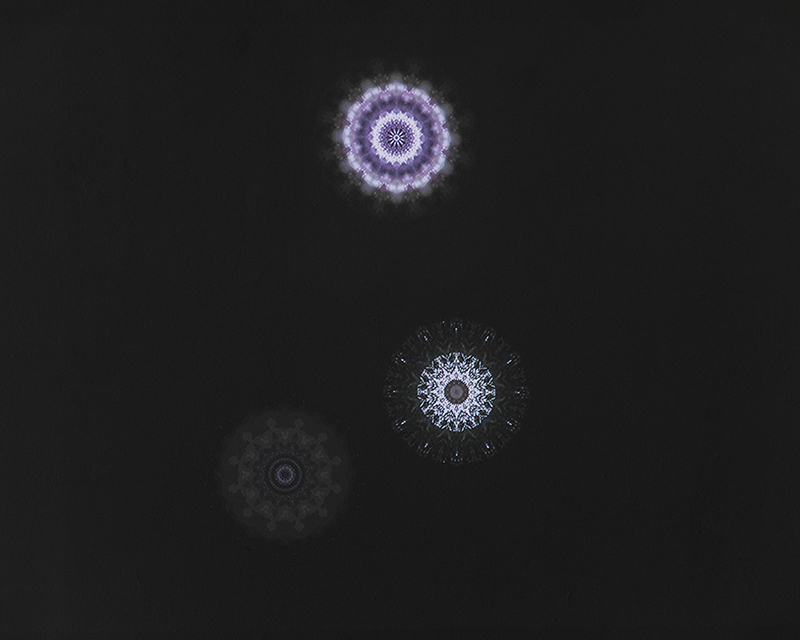
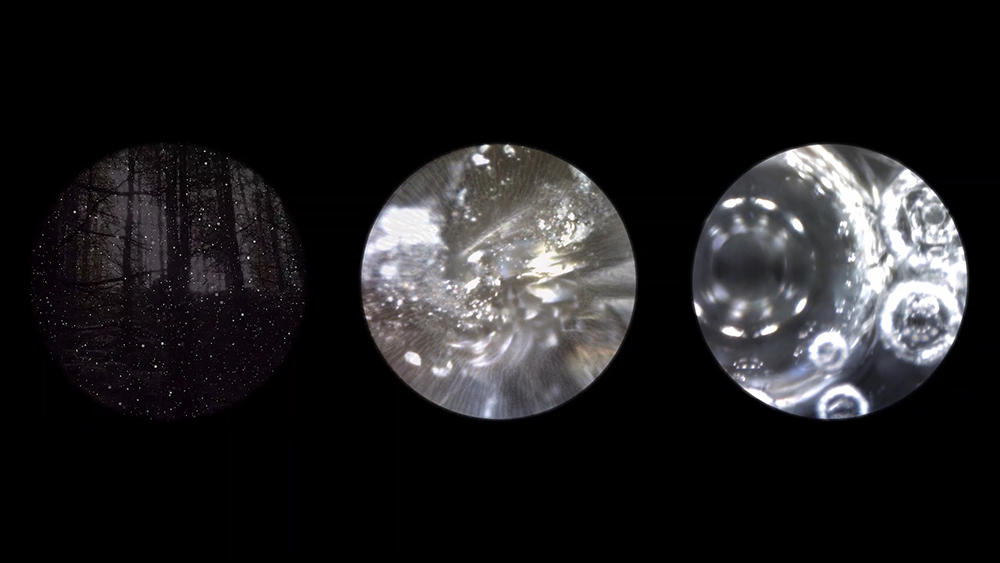
Giving The Breath of Stars a run to see if the cosmic rays are still there ![]() These images are stills of live action.
These images are stills of live action.
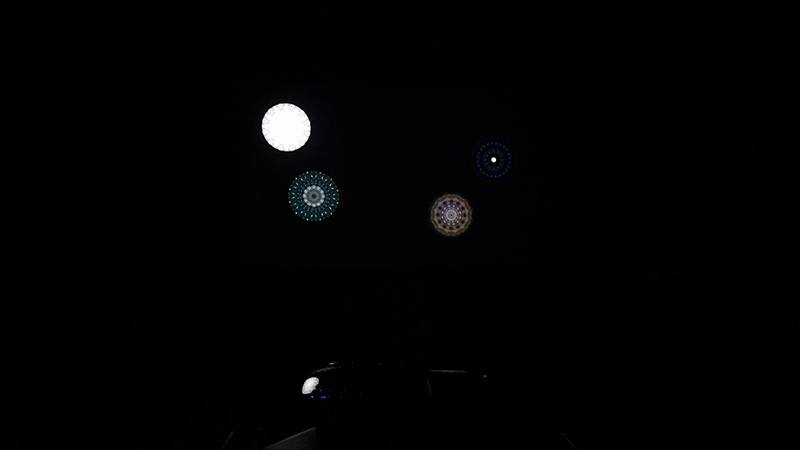
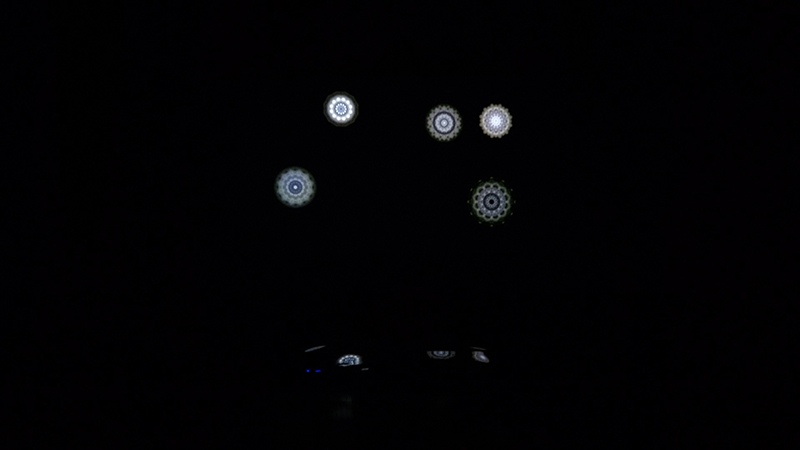
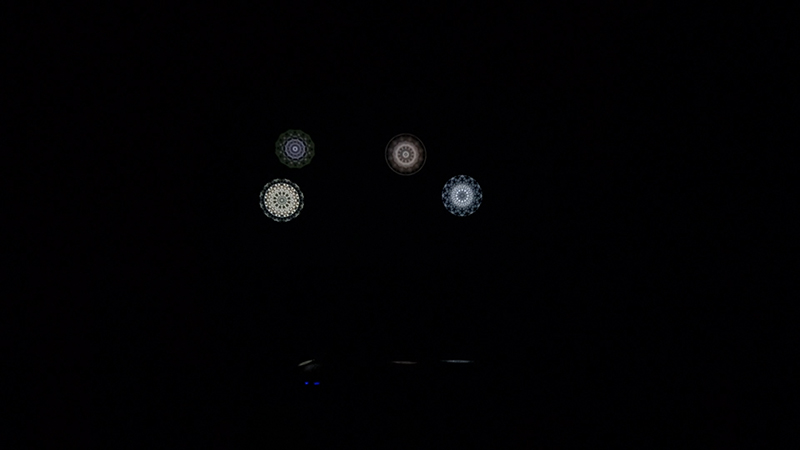






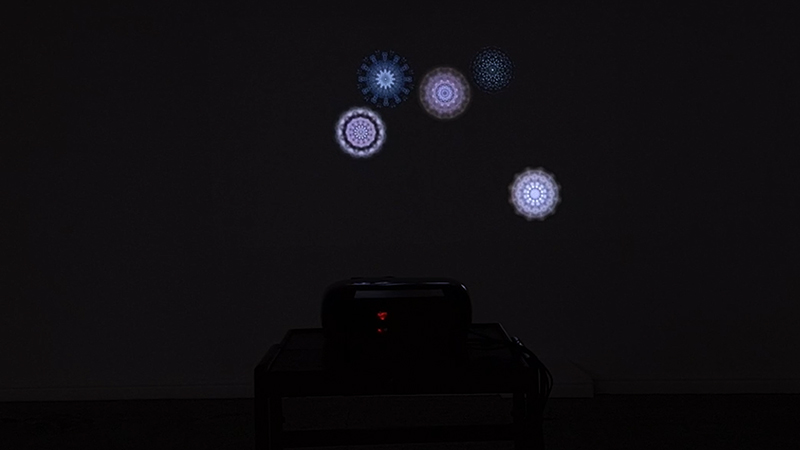
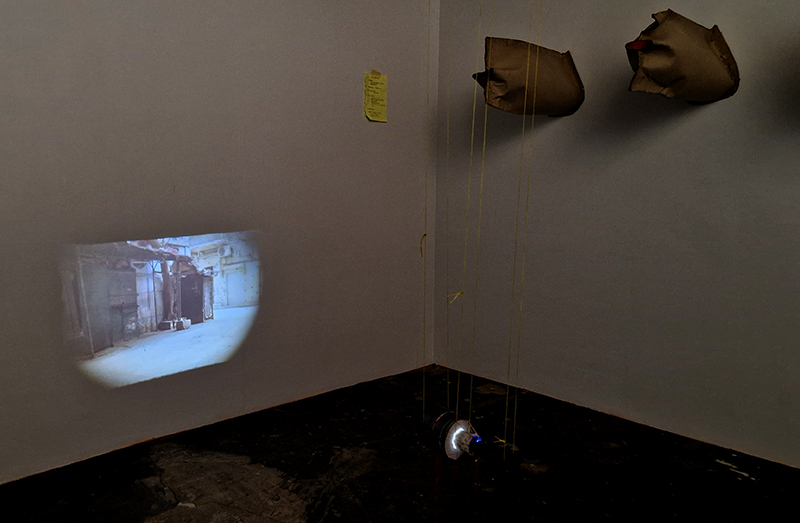
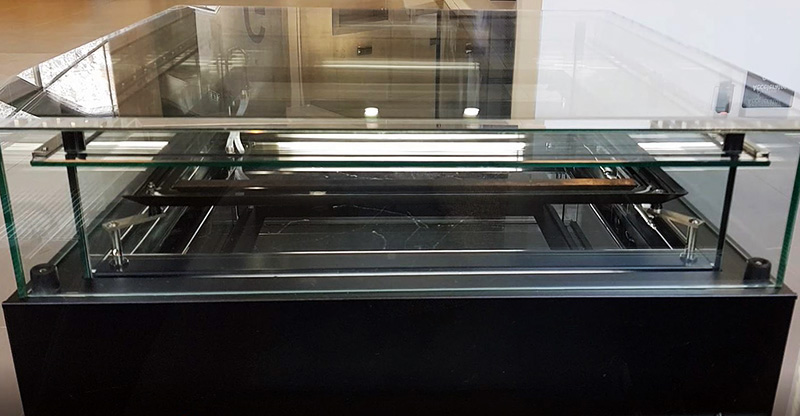
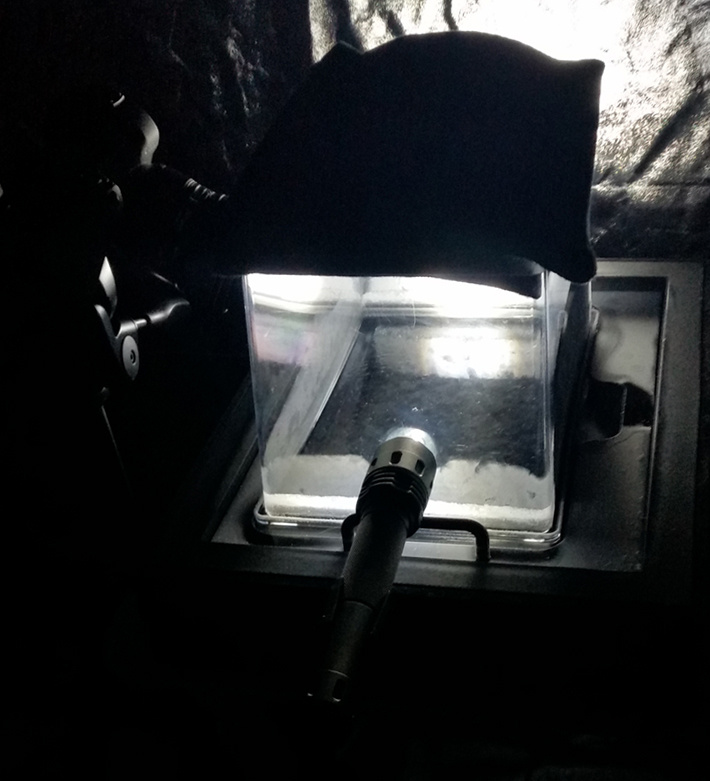
Cosmic ray detectors, mini computers, wooden box (20 x20 cm), video projection; live duration.
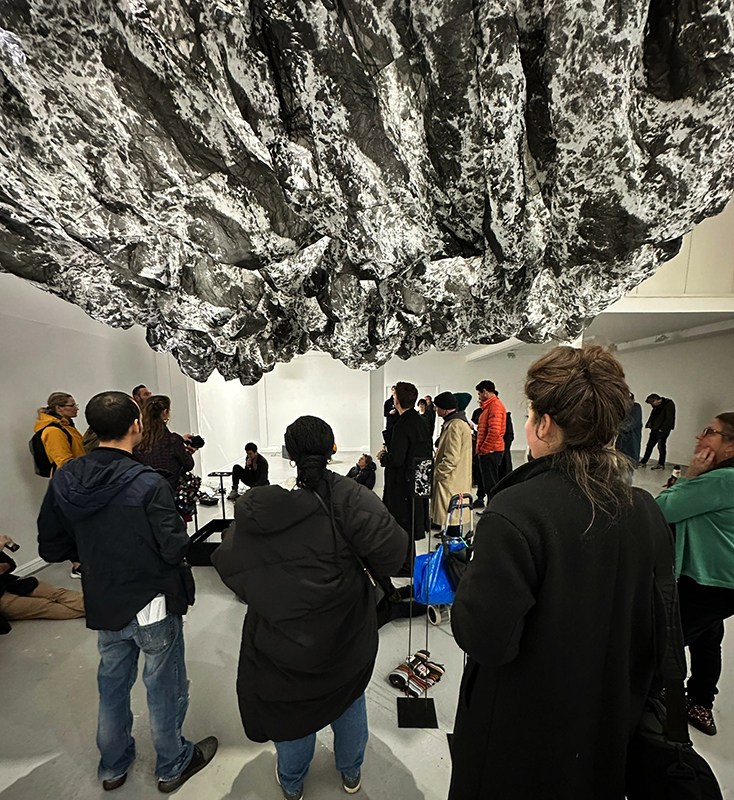
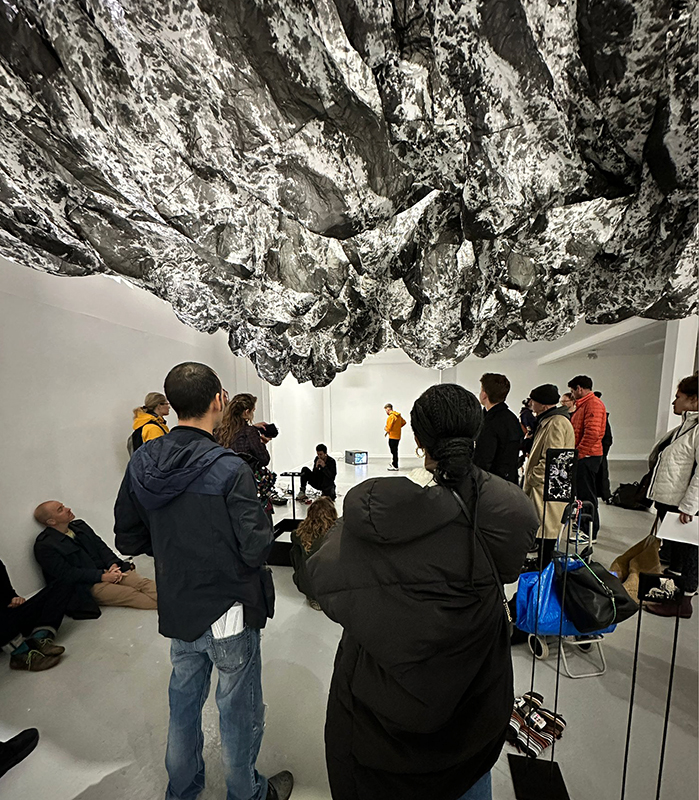
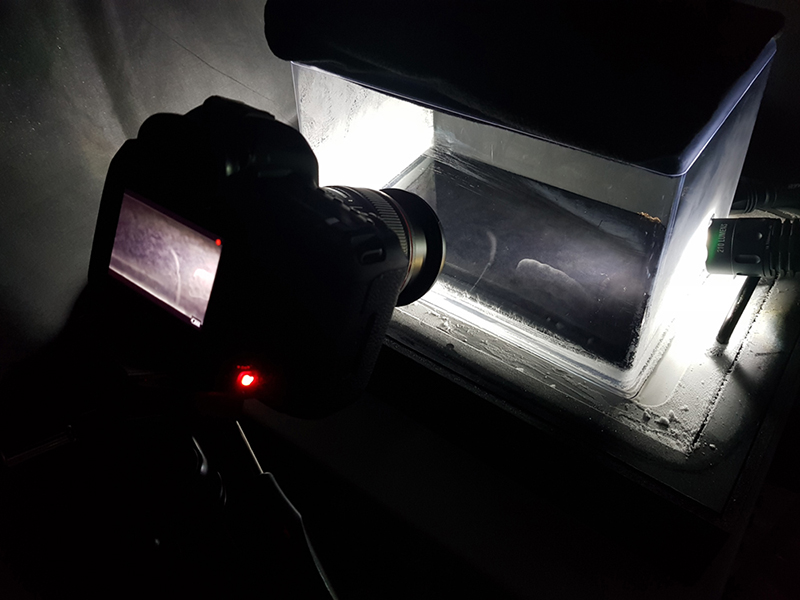
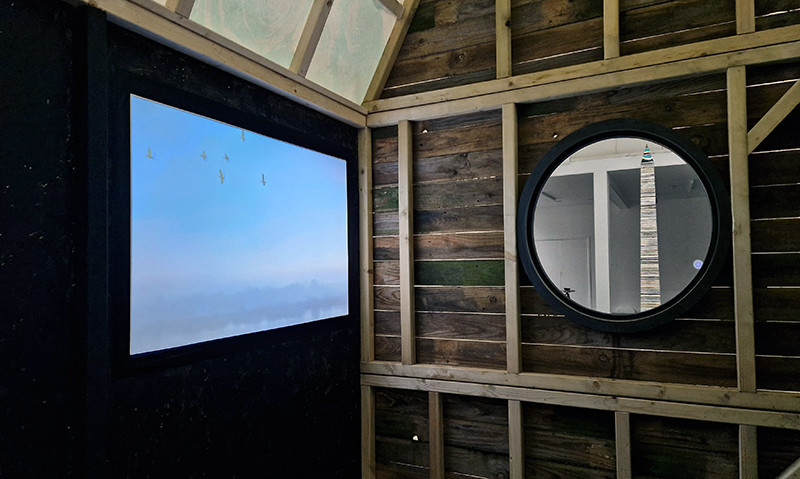
The Breath of Stars is a digital video work activated in real time by cosmic rays. These high energy particles arrive from outer space, interacting with life and technology on Earth. Coming from the heart of exploding stars or the depths of black holes, cosmic rays power across the universe with unimaginable energy. Some may come from phenomena yet to be discovered or even from other dimensions. A kaleidoscopic animation is projected every time a cosmic ray is recorded passing through the detectors. The animations are created from footage of cosmic ray trails filmed in my cloud chamber.
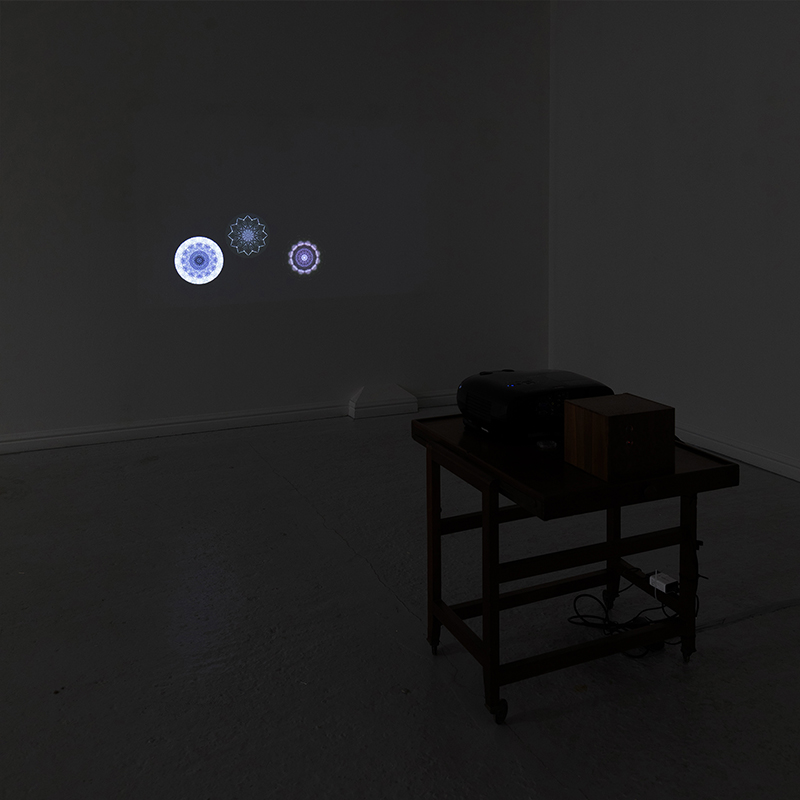
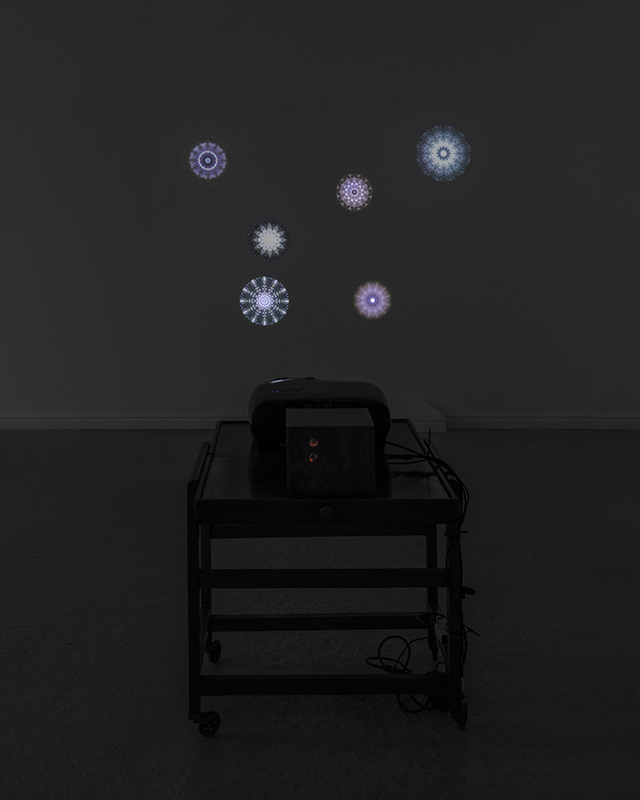


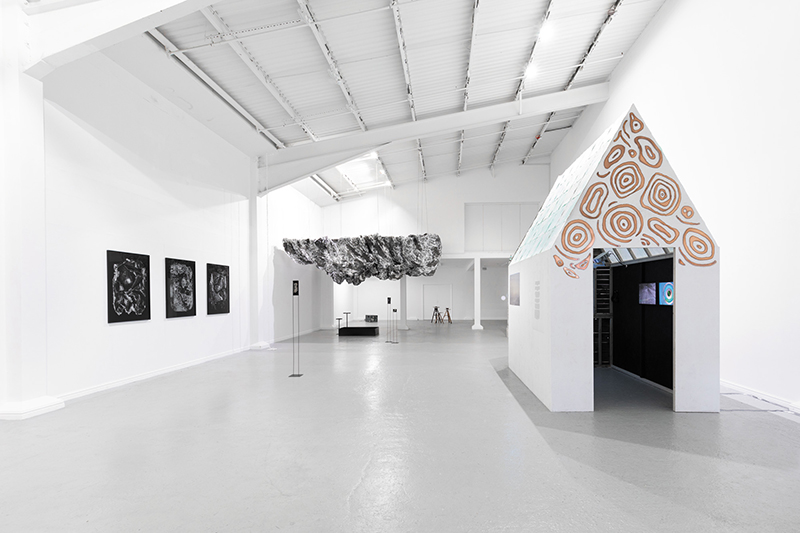
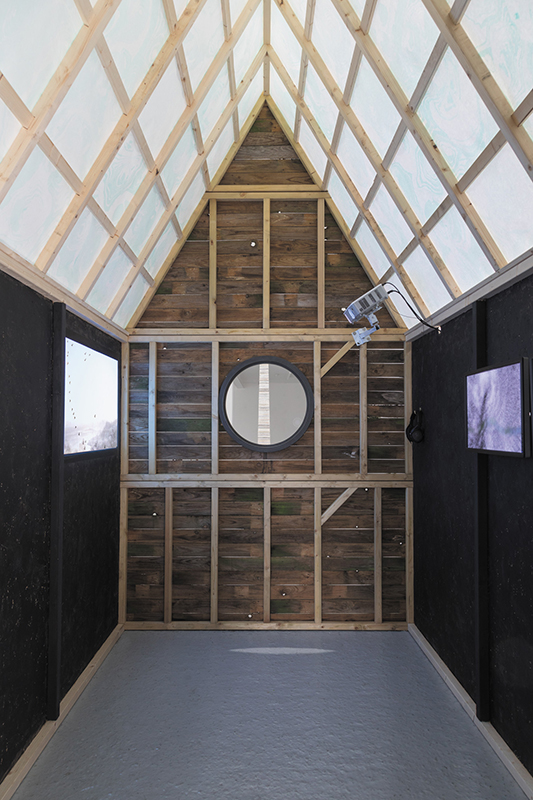
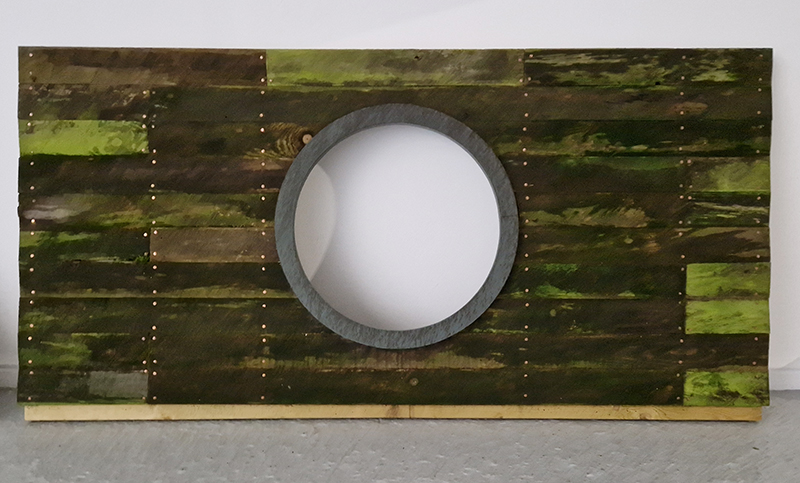
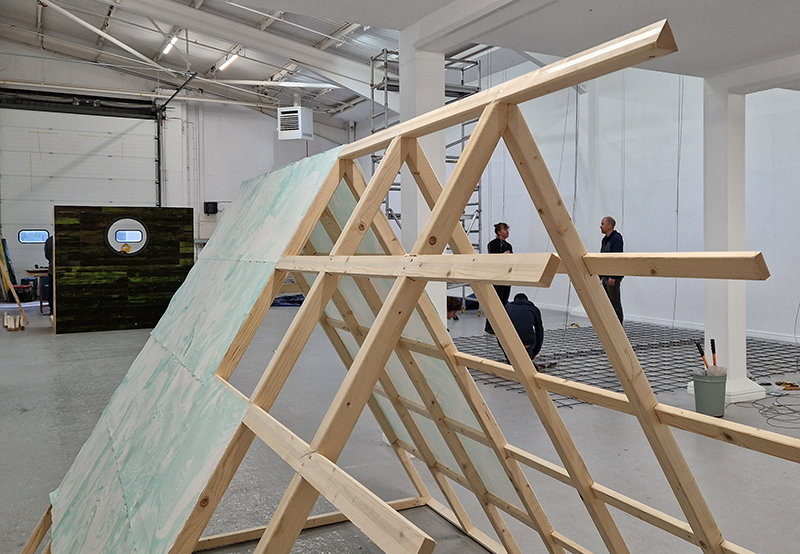
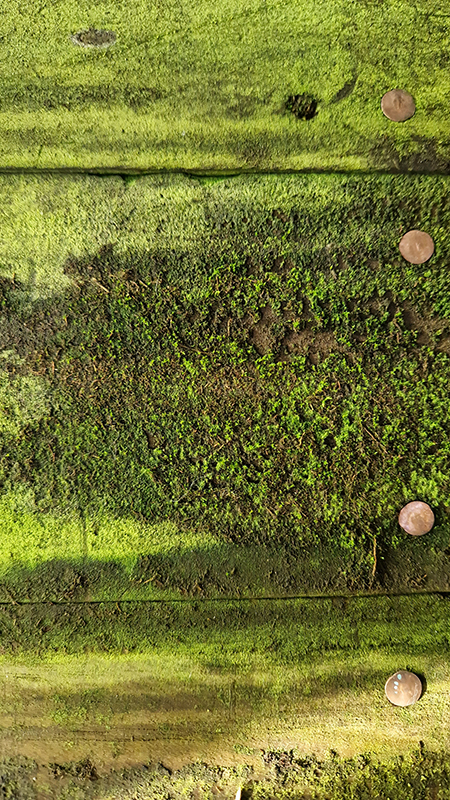
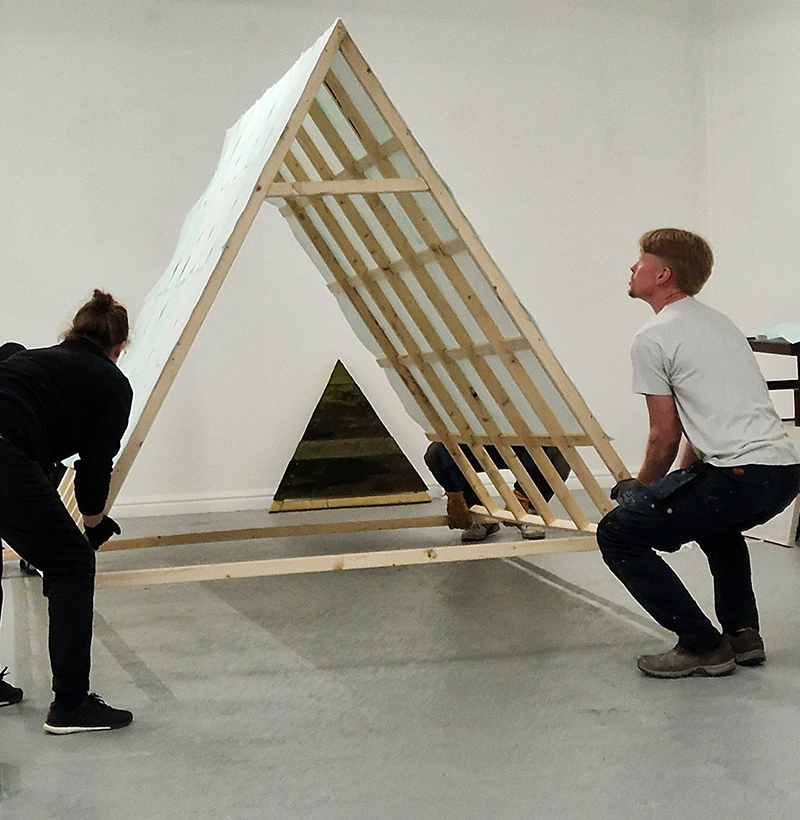
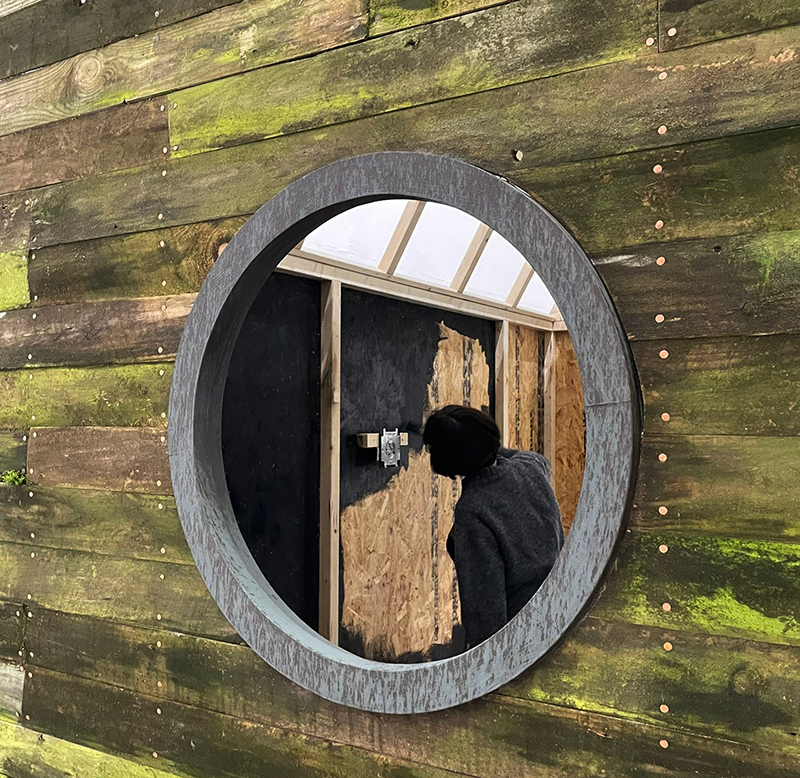
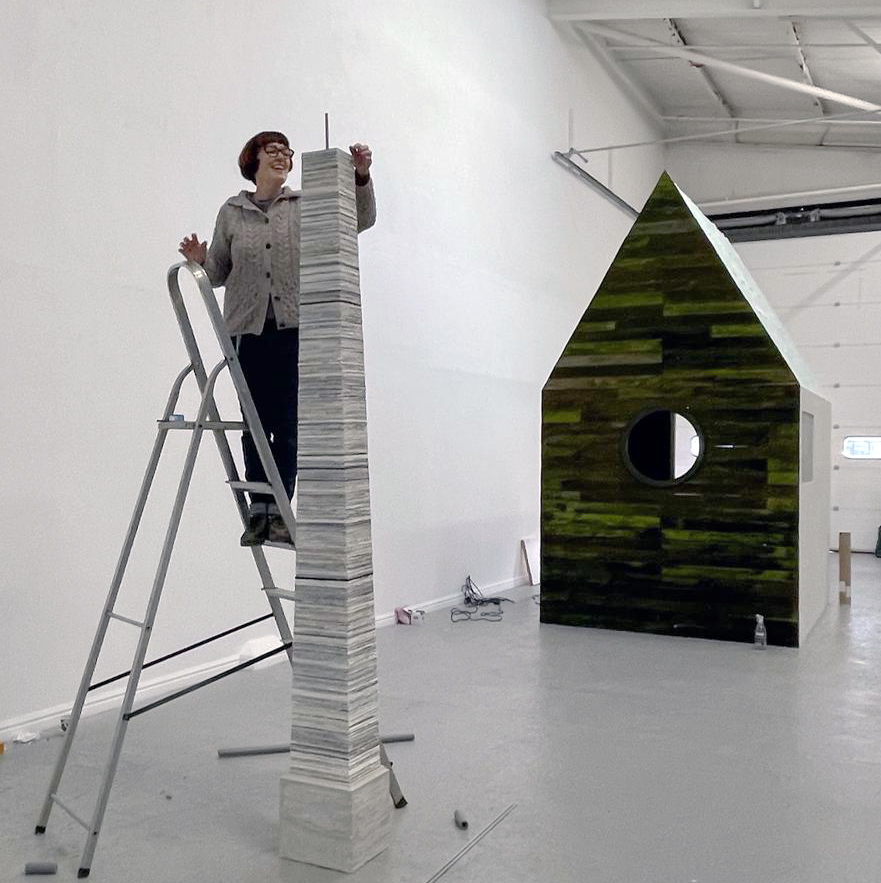
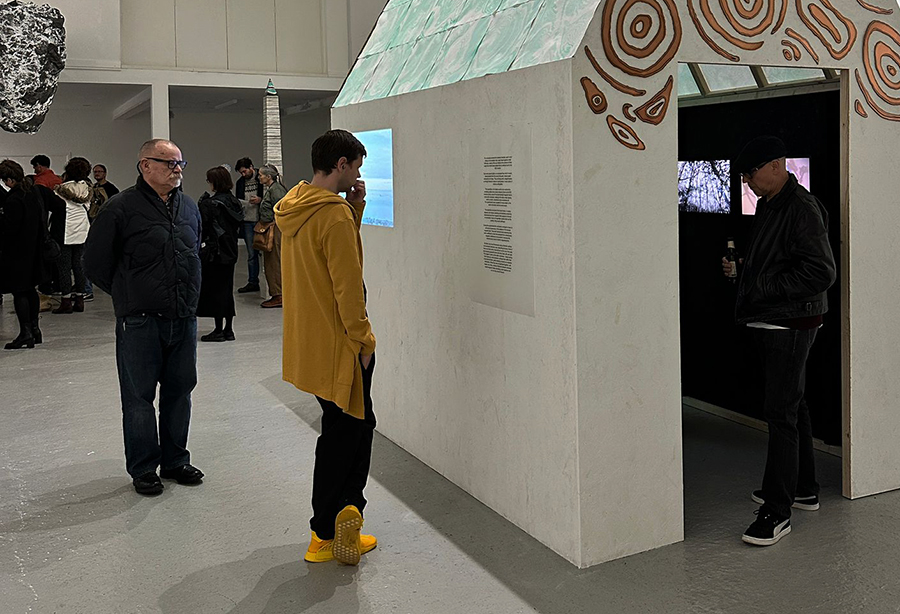
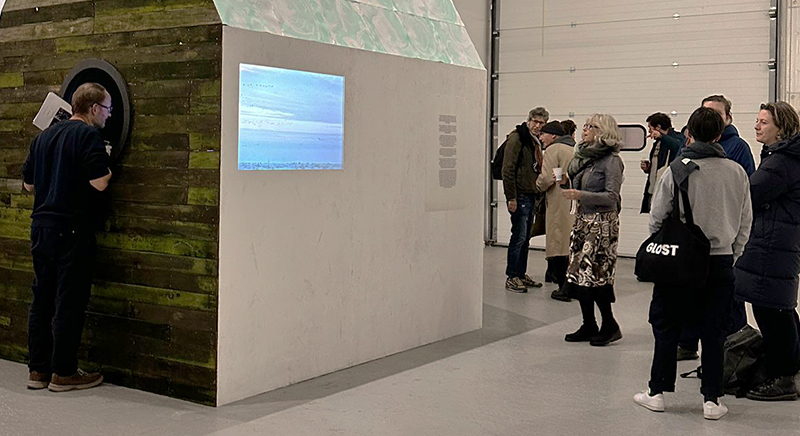
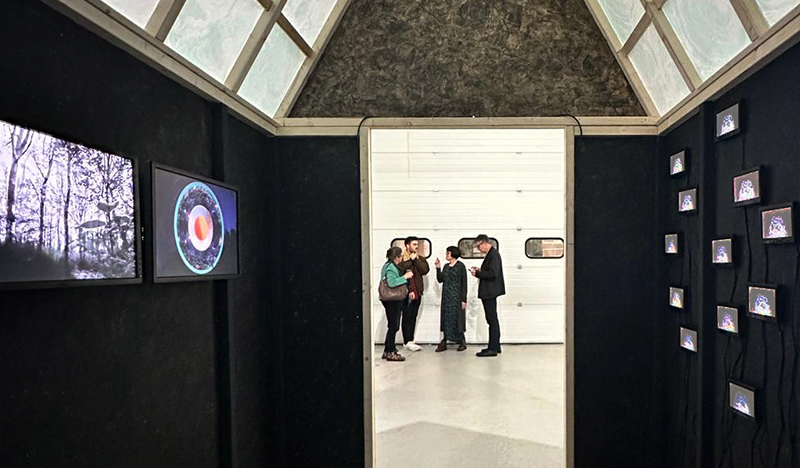
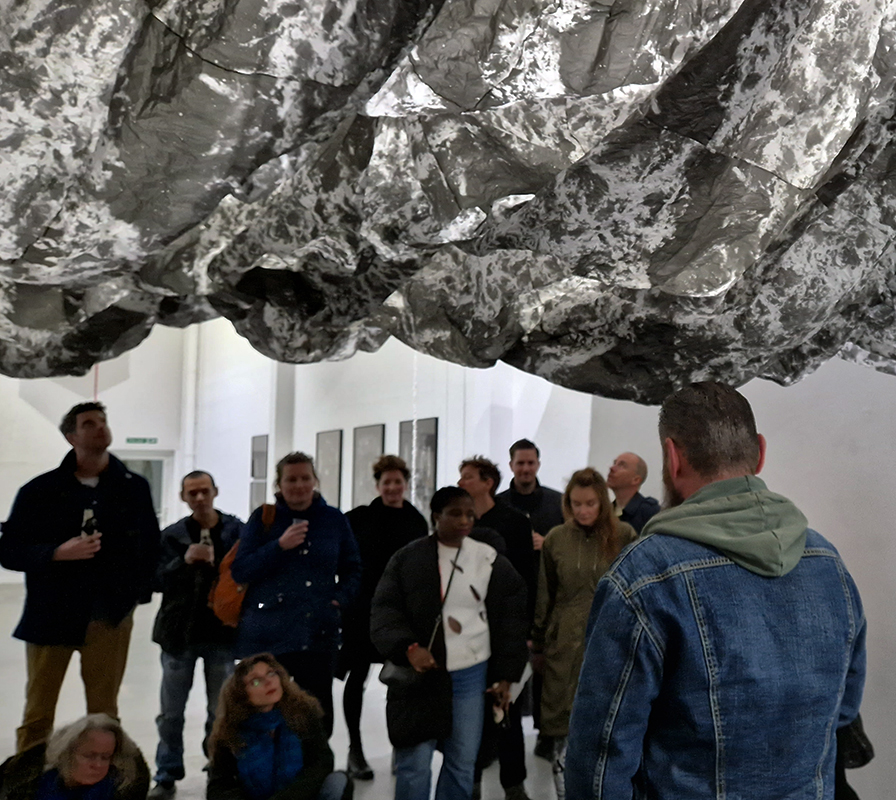
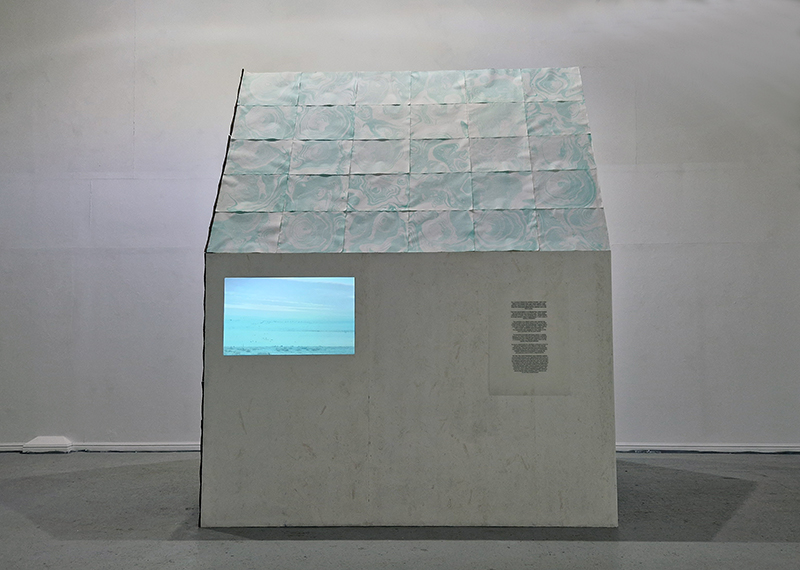
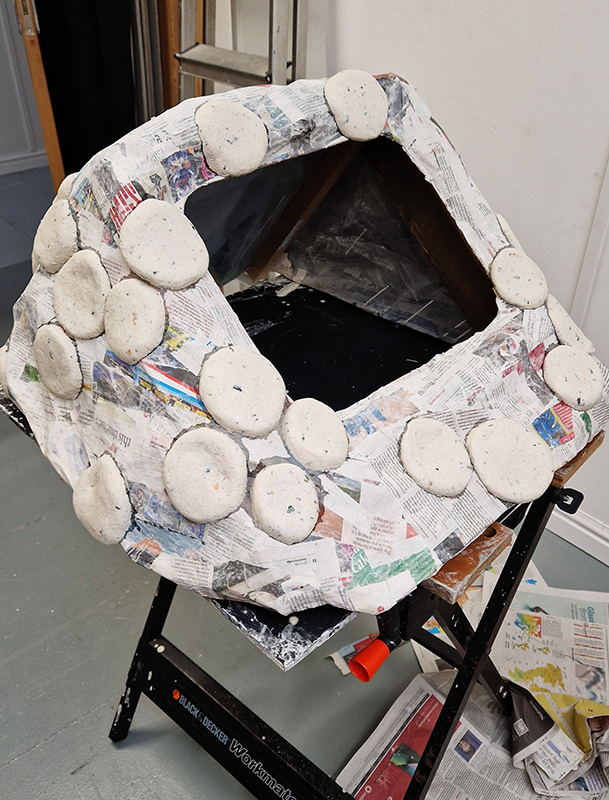
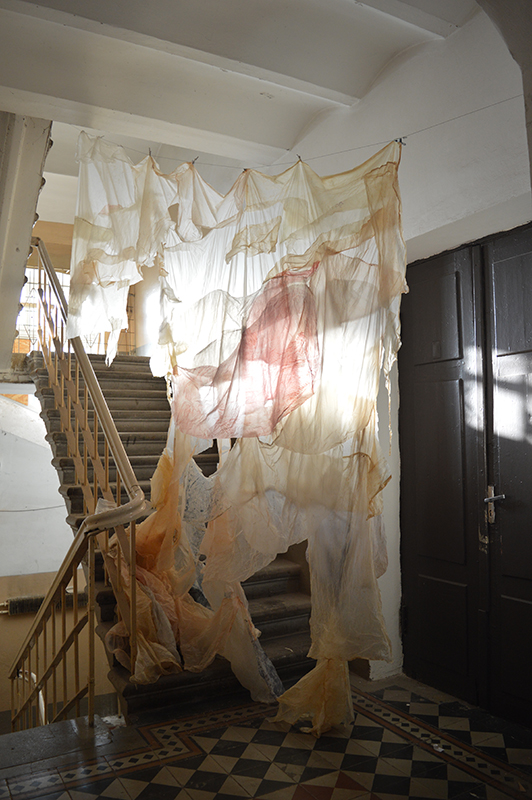
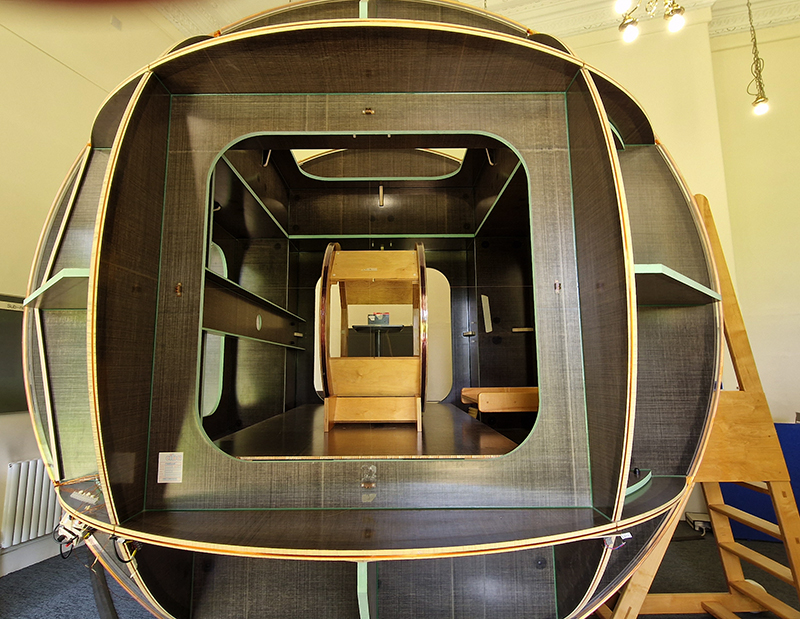
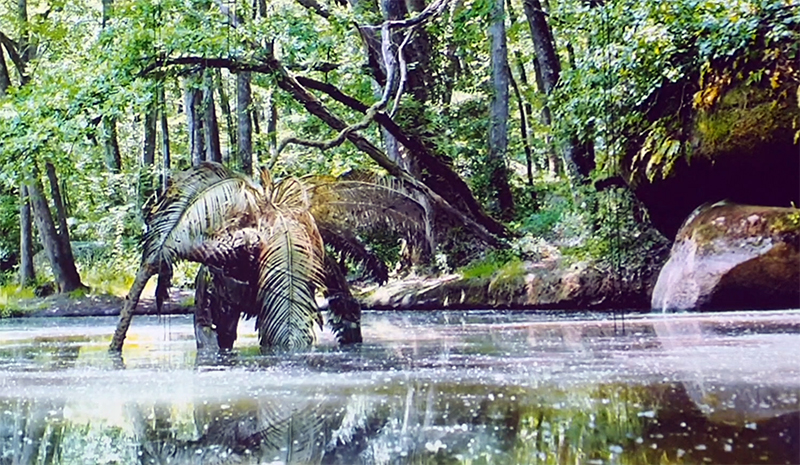
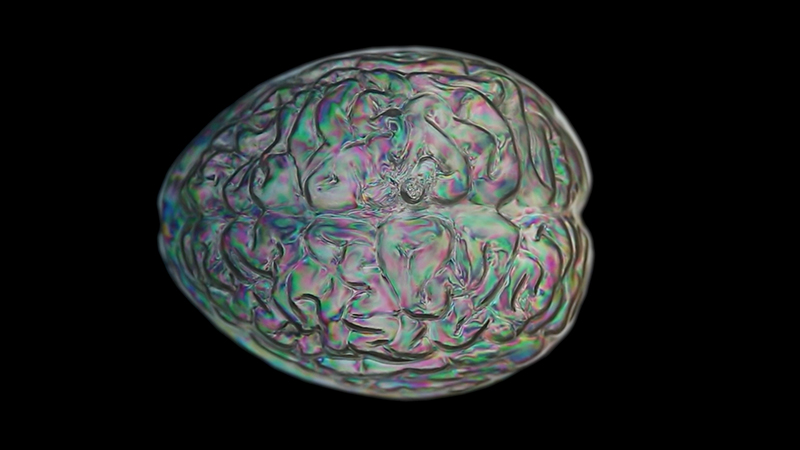
This cold damp weather is stimulating the moss regrowth on the apex pinnacle of The Absolute Hut (of action potential) that found a space in my garden after The Stone Sky exhibition this time last year. I had spent weeks preparing the recycled fence boards to make the North facing wall of the hut, painting them with various mixtures of buttermilk and yogurt blended with moss and was so excited when it began to grow. During the exhibition I would mist it every day. The beginning of my fascination with huts!
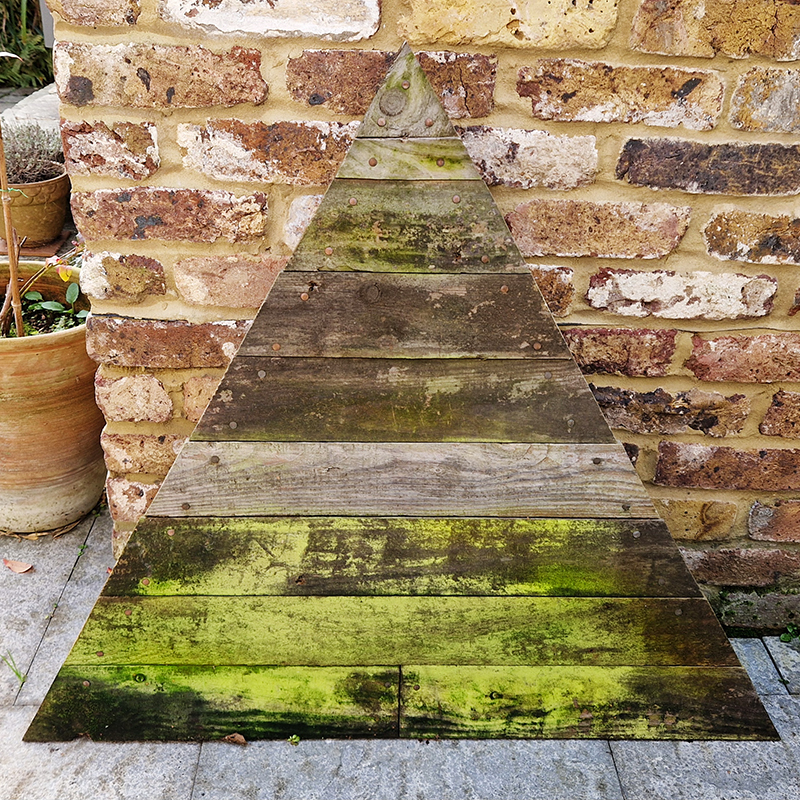



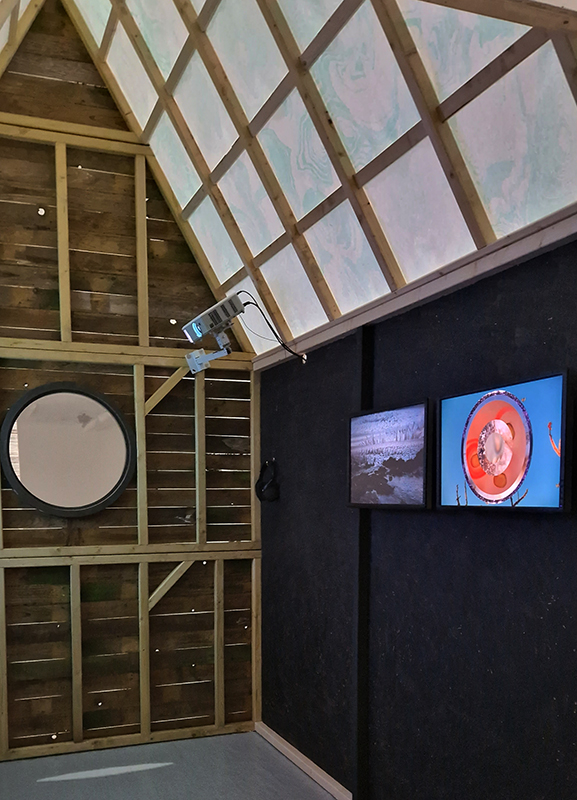
The Absolute Hut (of action potential) Wood, moss, paper, copper, video projection, video monitors ; 200 x 300 x 375 cm
Operating as a sensory hub where a range of actions and processes are running concurrently reflecting on the dynamics between the Earth’s geologic structure and navigation using the magnetic field. Neurons in the brain and nervous system send information electrochemically around the body. The signals they send are called action potentials, which is a temporary shift from negative to positive within the cell caused by certain ions entering the cell. Action potentials can be triggered by an interaction with the magnetic field, causing a reaction in the body.
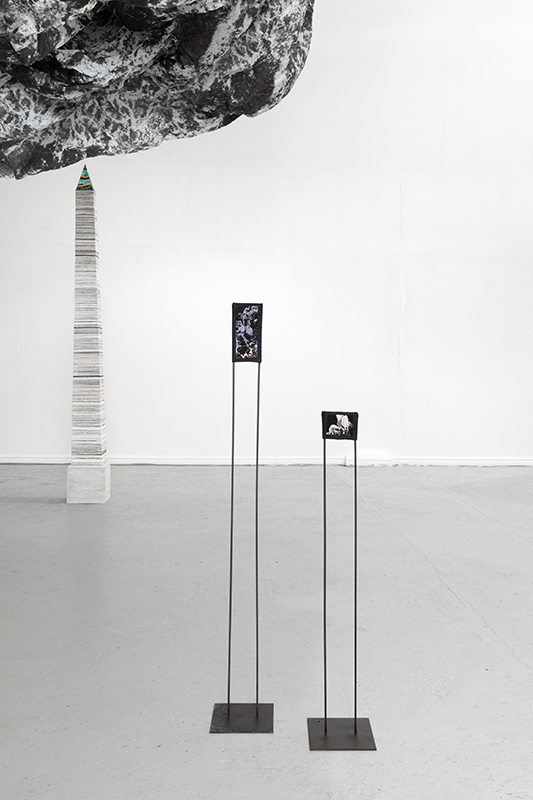
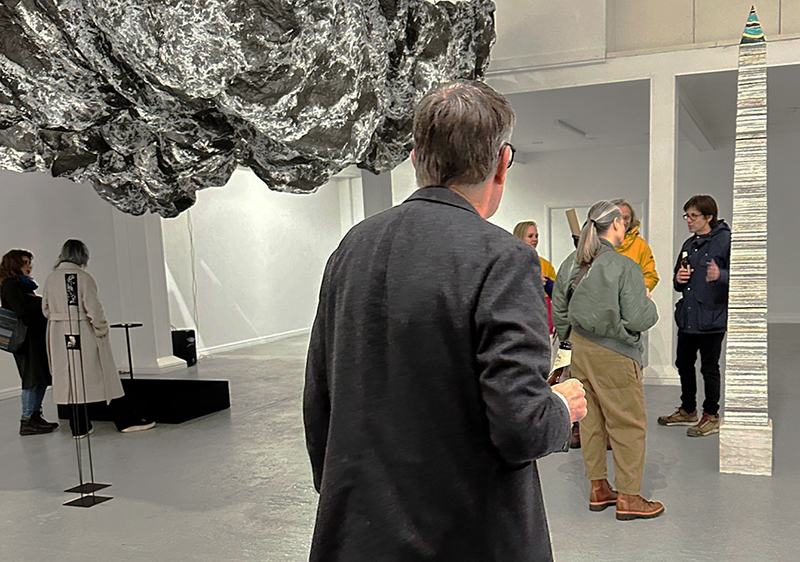
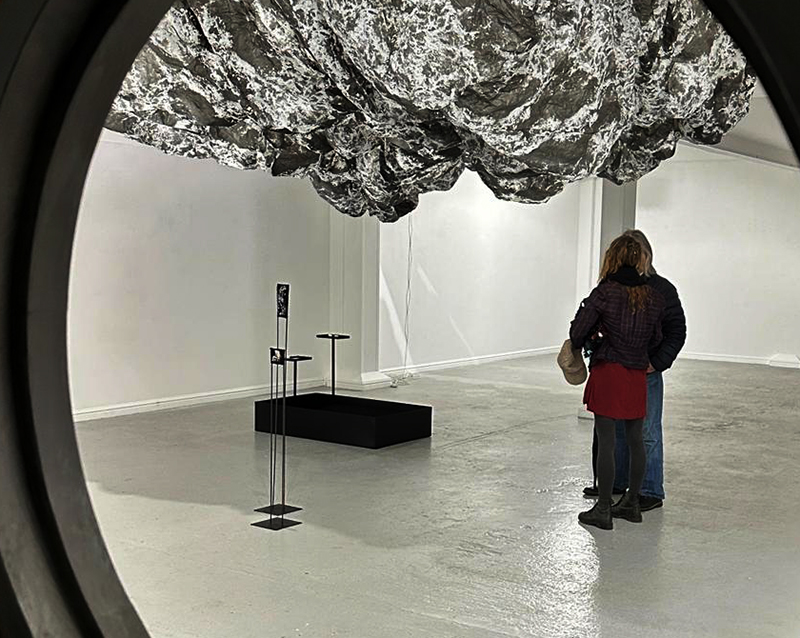
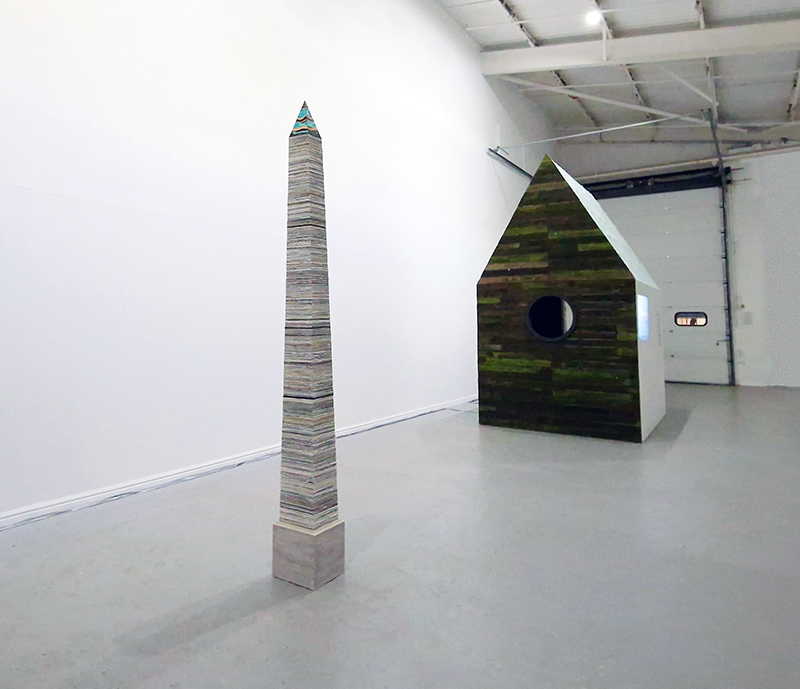
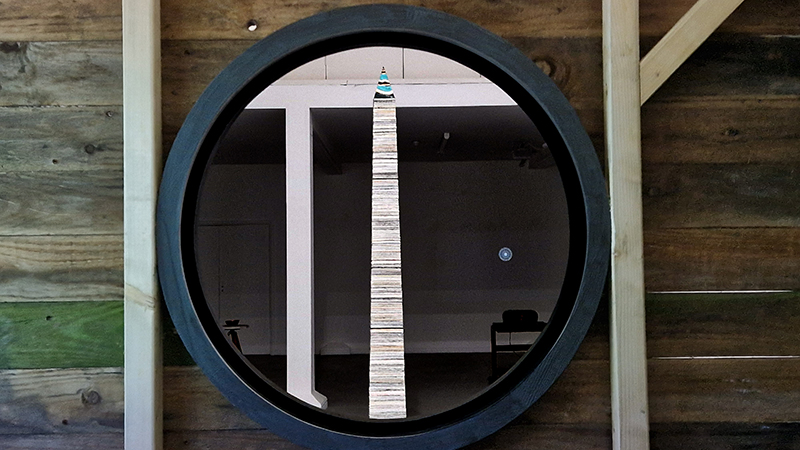
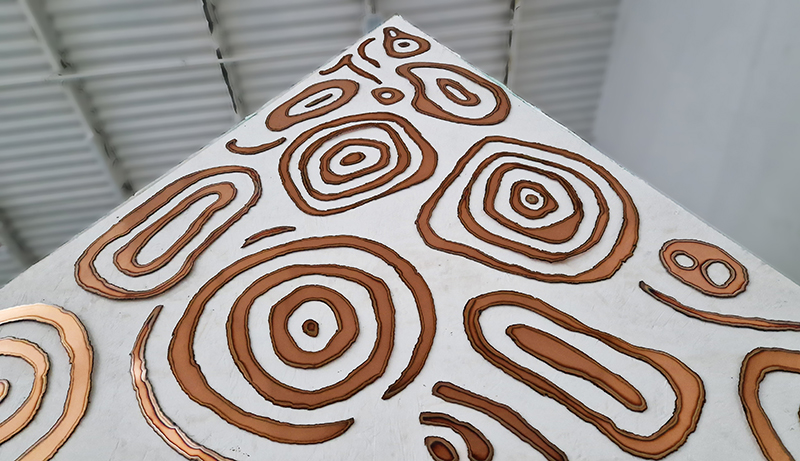
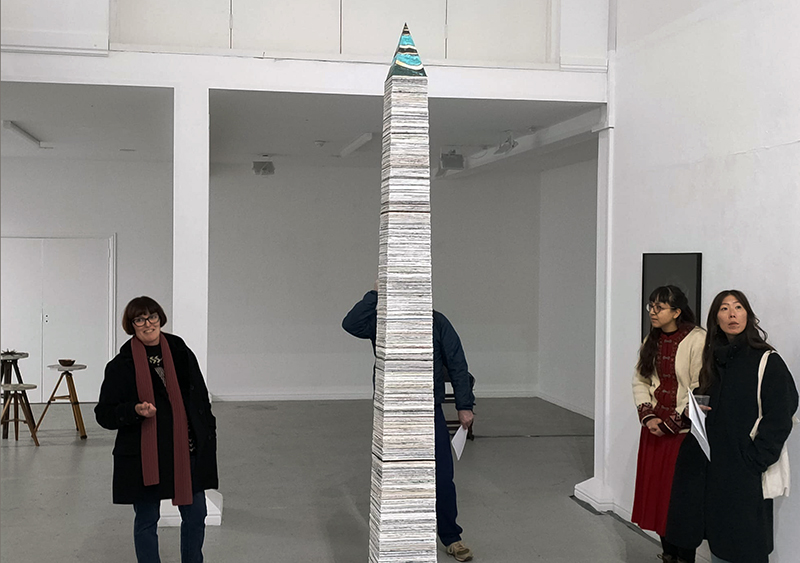
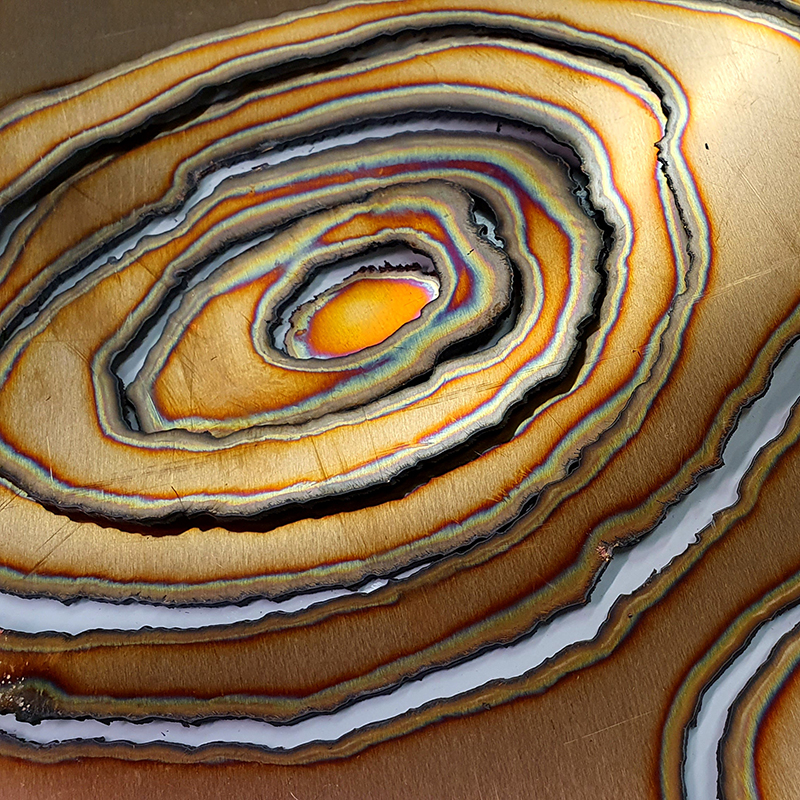
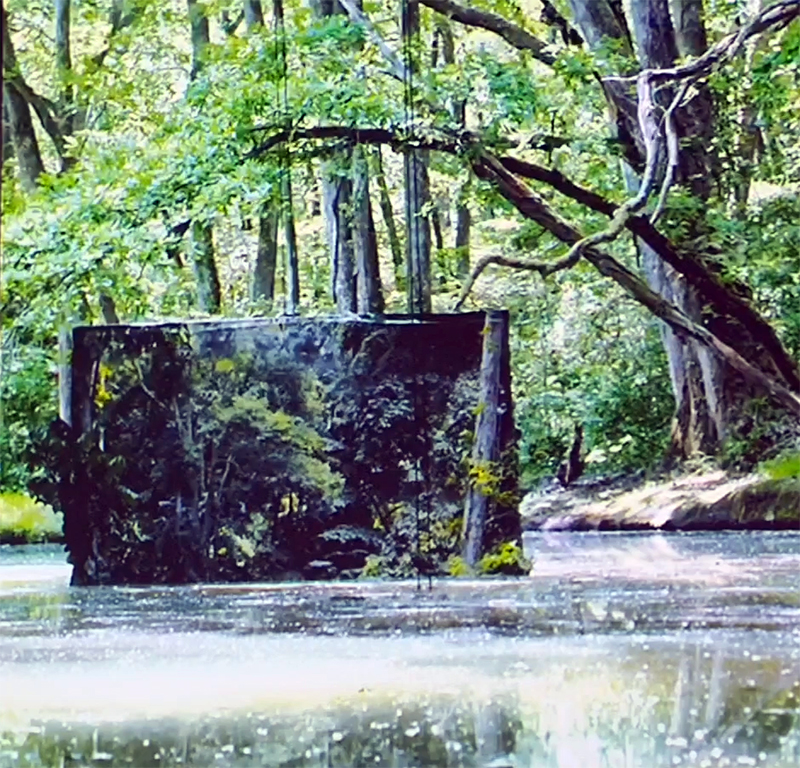
A year on and the pyramidion that sits on top of The Azimuth Obelisk (of sedimentary knowledge) is evolving. The patination, which involved a variety of chemicals being applied to the copper in layers, is an ongoing process.
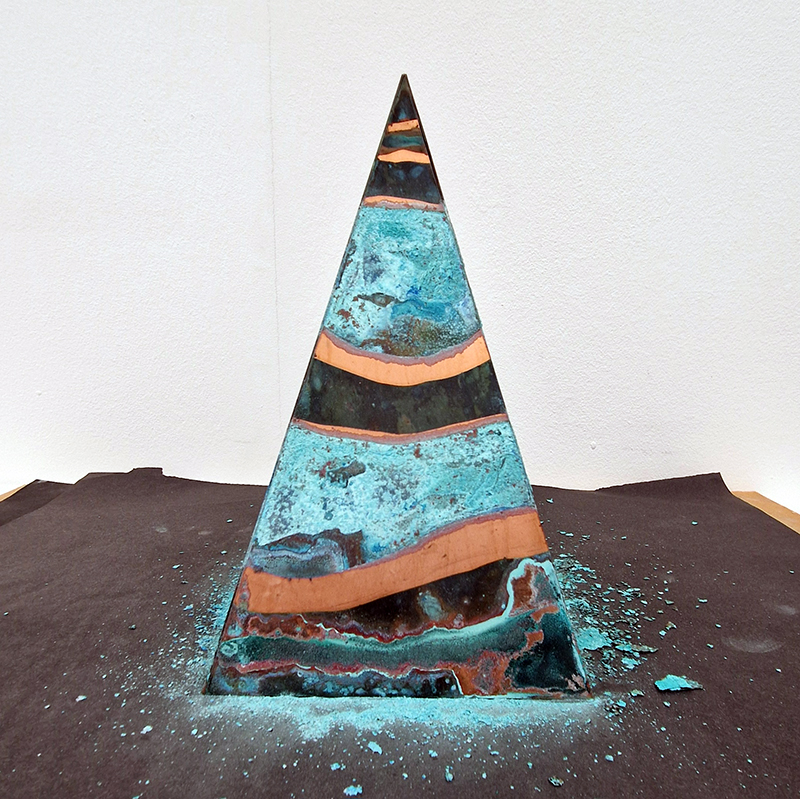
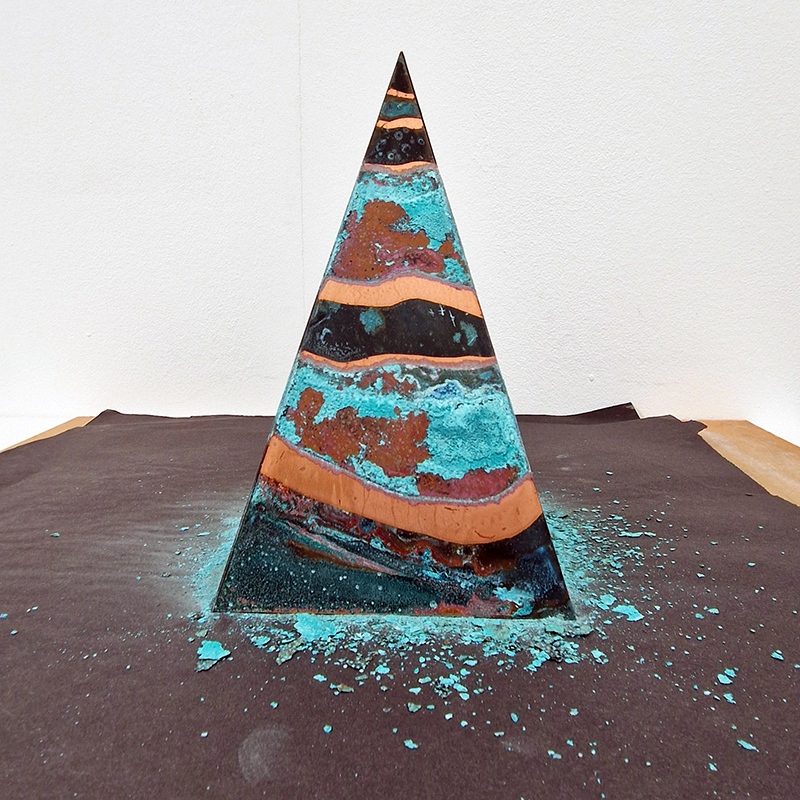
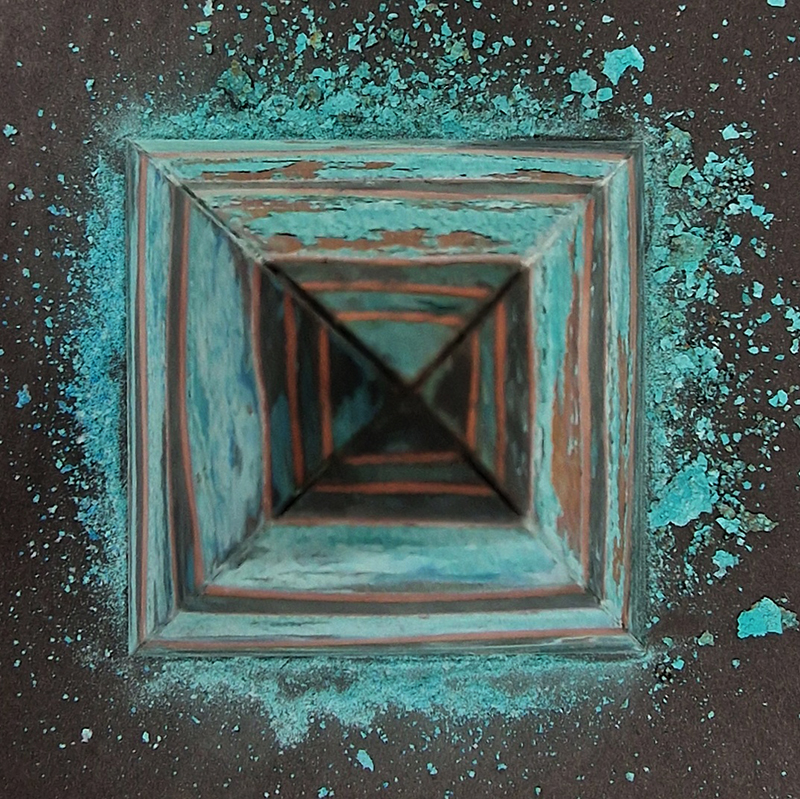



Sedimentary rock holds a geological history of the Earth’s magnetic field within its mineral components. The geomagnetic field, generated by the Earth’s molten core, varies through time; the magnetic poles migrate, go on excursions, or reverse polarity. During these periods of flux, the strength of the magnetic field changes, and this phenomenon is recorded in archaeological artefacts, volcanic rocks, and sediments. Limestone, a sedimentary rock, is often formed from crushed seashells, compressed over aeons. Crushed oyster shells were added to the obelisk base cast in Snowcrete.
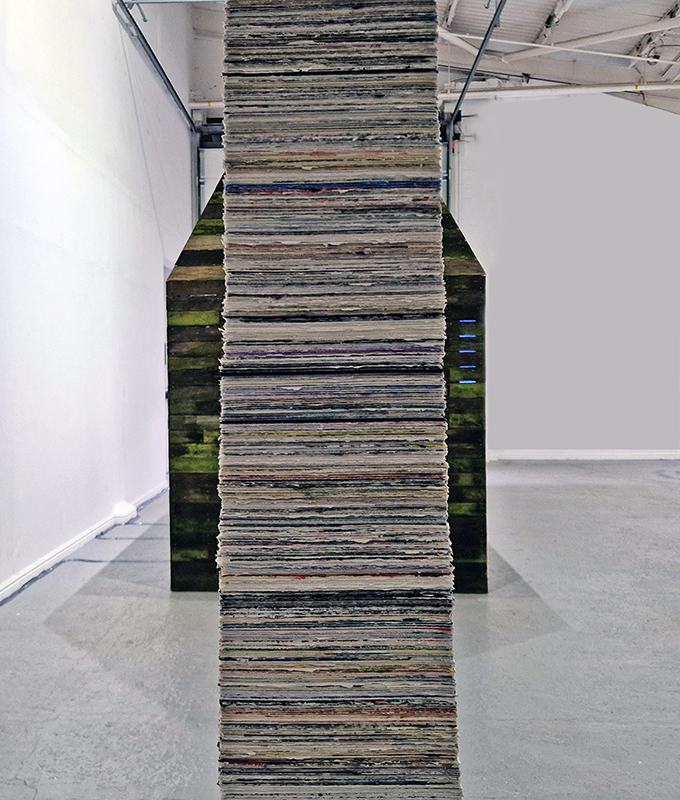



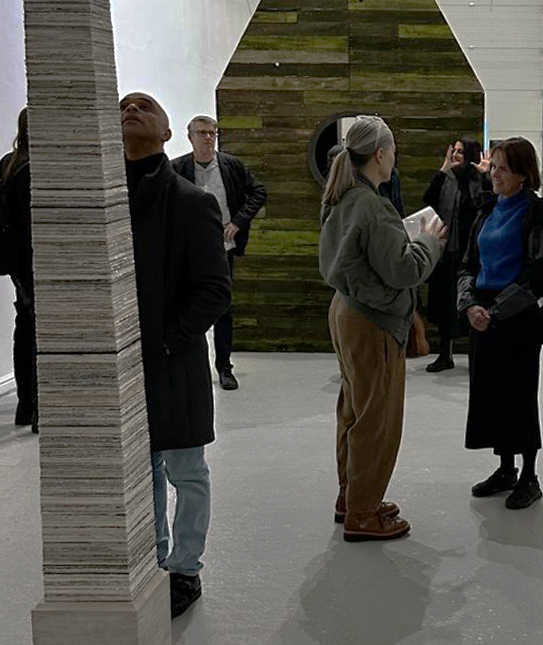
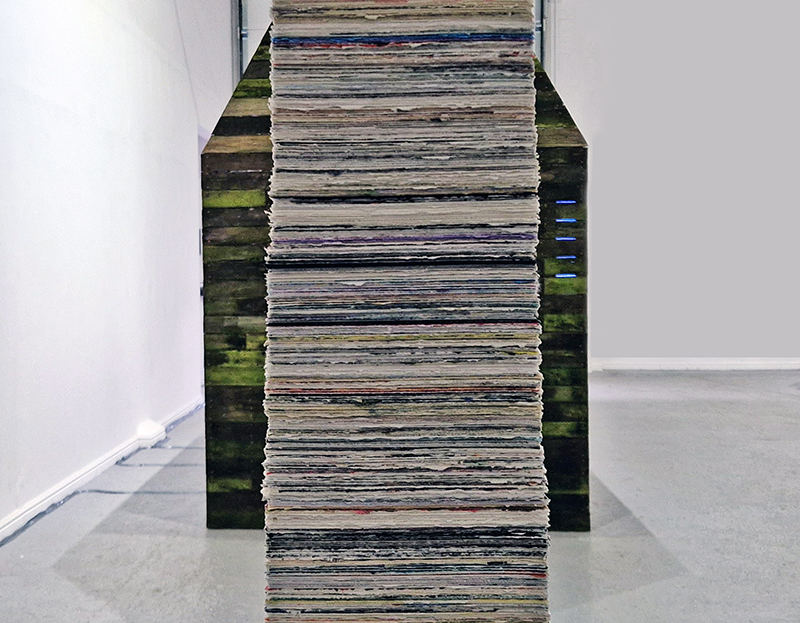
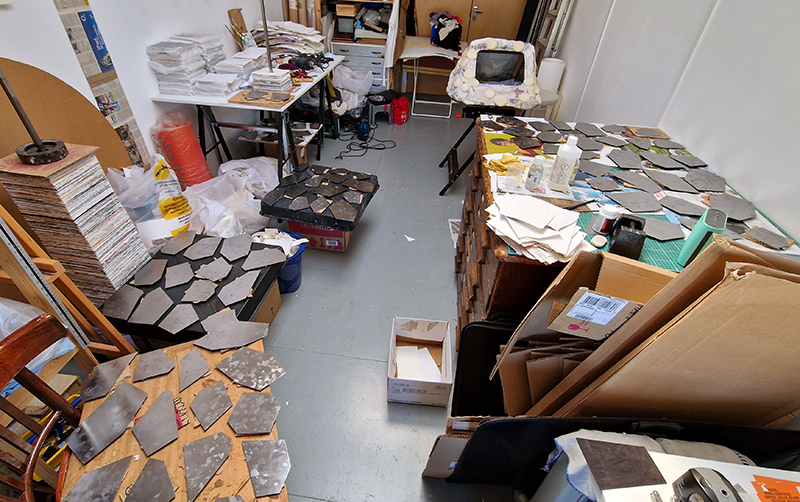
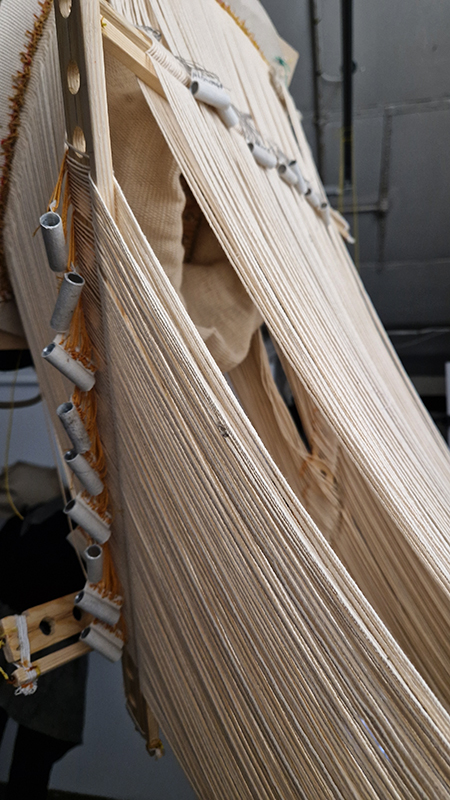
This sculpture also embodies the passage of time, and a layering of information, in the months of collecting paper donations or scavenging the recycling bins, weeks tearing down the hundreds of prints and drawings into squares decreasing by 1mm every 50 sheets, drilling holes through the centre and hours to build the almost 3m stack. I’m very grateful to everyone who donated some of their work archive. These images are now secreted within the layers of the sculpture, hinted at where edges are exposed, echoing the Earth’s sedimentary knowledge.
The Azimuth Obelisk (of sedimentary knowledge) Paper, steel, Snowcrete, oyster shells, patinated copper; 30 x 30 x 270 cm
This work is a reimagining of an ‘obelisk’ erected at Hartland Magnetic Observatory in the late 1950’s to be viewed through the north facing window of The Absolute Hut, it acts as a permanent azimuth mark from which the drift of the magnetic north pole is monitored. I am excited that this sculpture is being considered for exhibition in 2026 at the Royal West of England Academy in Cosmos: The Art of Observing Space curated by Ione Parkin with some amazing artists in the line up whose work I admire.

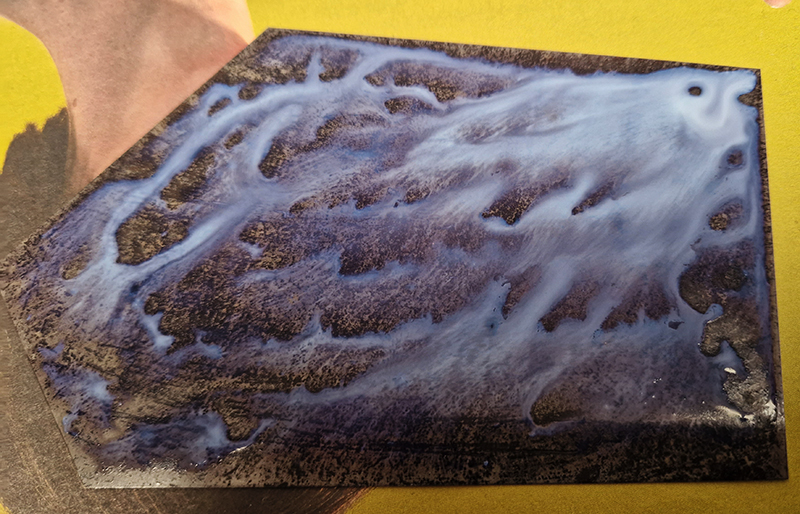
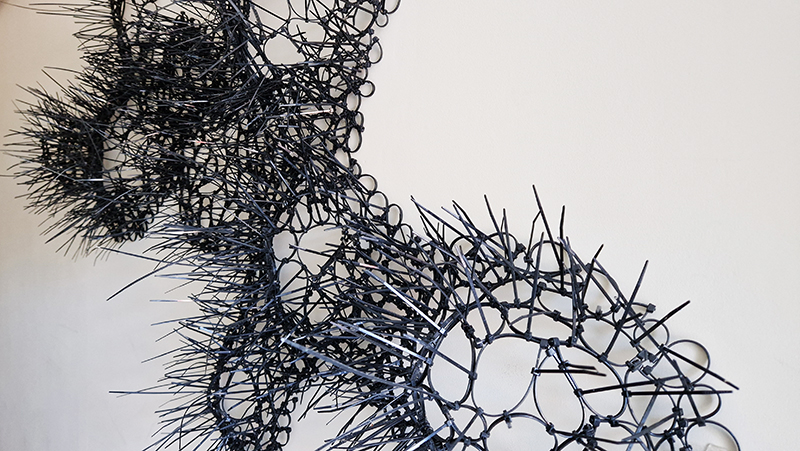
I first came across directional magnetic steel in the Electronic & Magnetic Materials Group open day at the National Physical Laboratory. Intrigued, I wanted to know if I could get hold of some to work with. I was put in touch with Union Steel Products who were very helpful in supplying a small amount (to them) of the material, but they import the product, and it arrives with an indeterminate protective matt grey coating. This was my challenge. It took many days of sanding and gently etching each sheet to reveal the pattern. It was a very temperamental material to work with, the pattern might appear but quickly tarnish and muddy over. So much of the work in the resulting sculpture was about the process of exposing an internal mechanism.
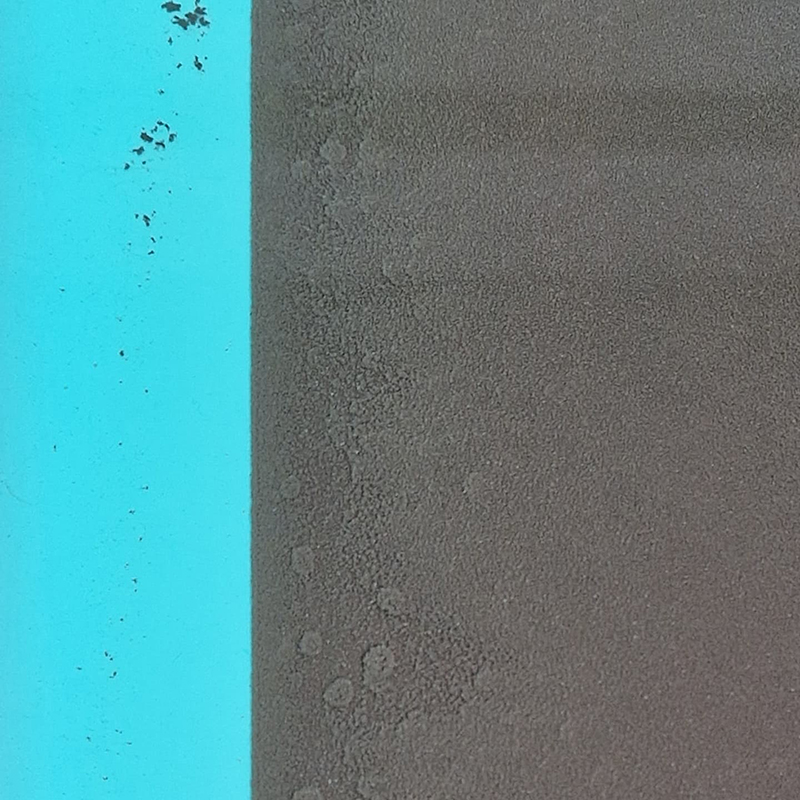



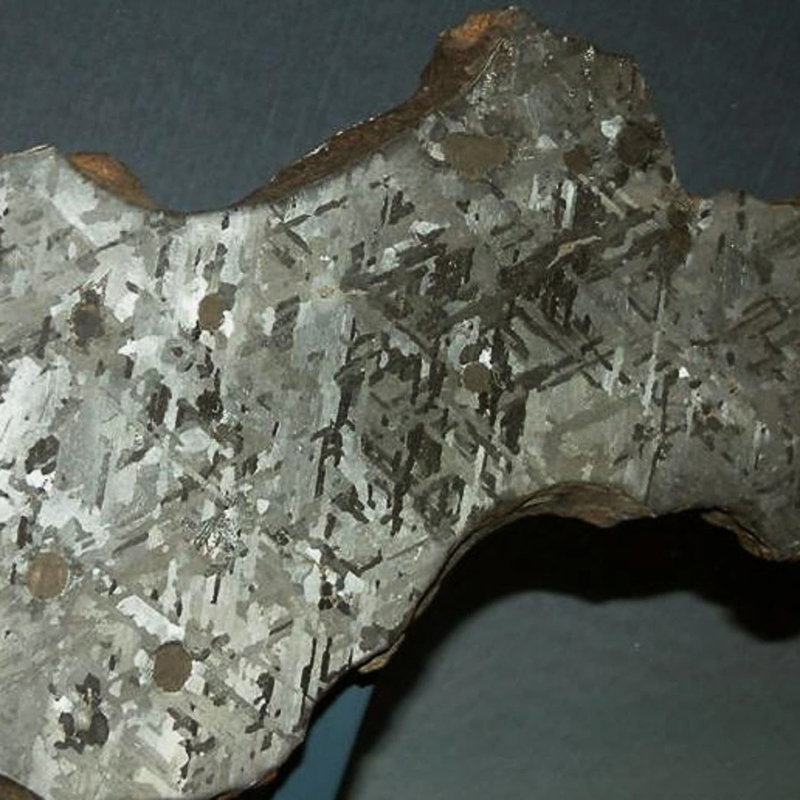
The dramatic Widmannstätten patterns found in meteorites due to their slow evolution through heat and pressure are also revealed through being cut, polished, and etched.
These secrets are not revealed lightly.
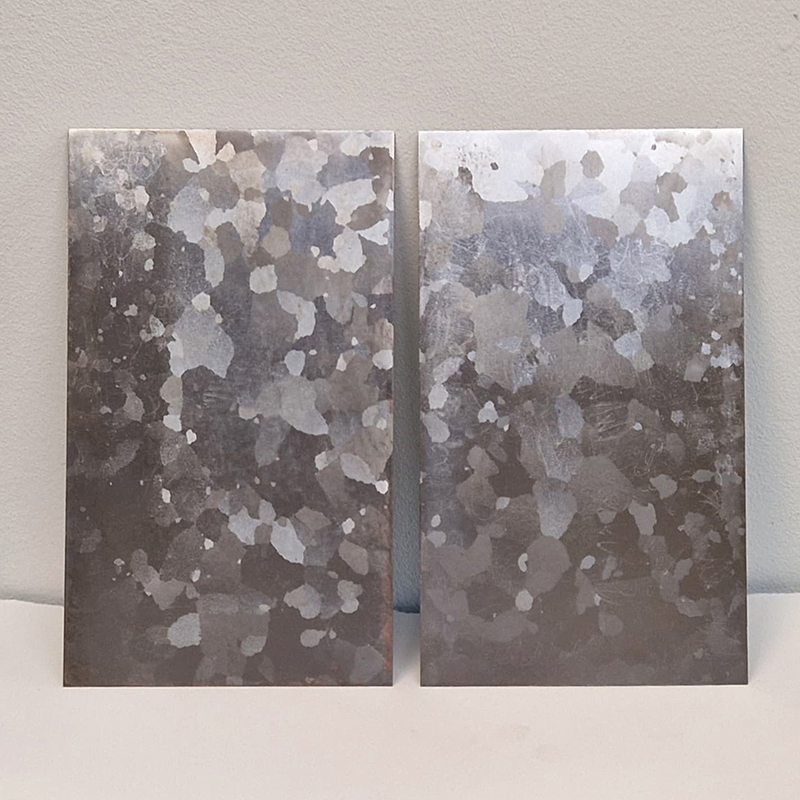


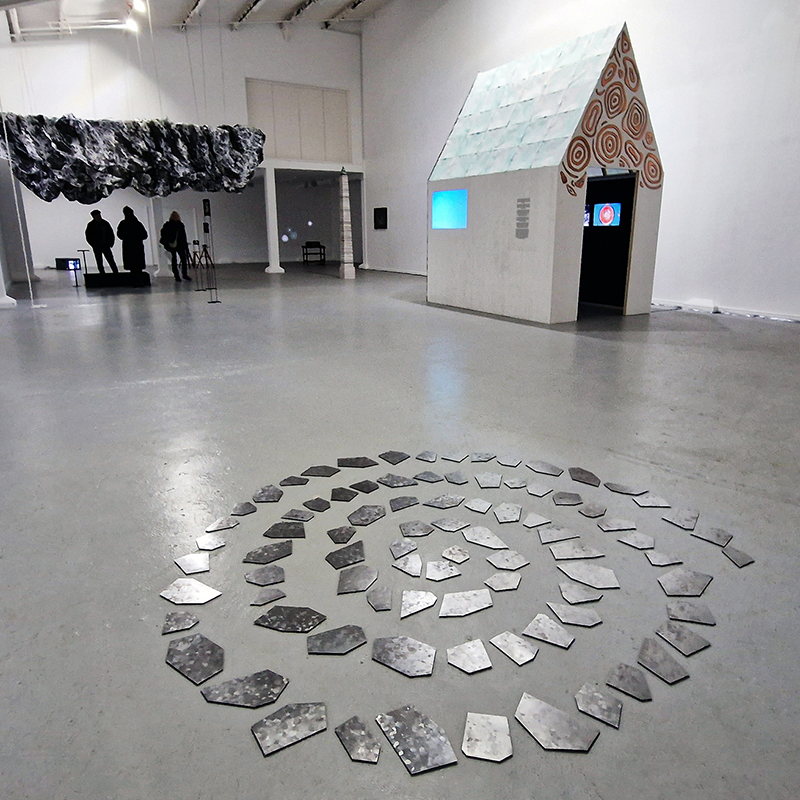
Domain of the Devil Valley Master
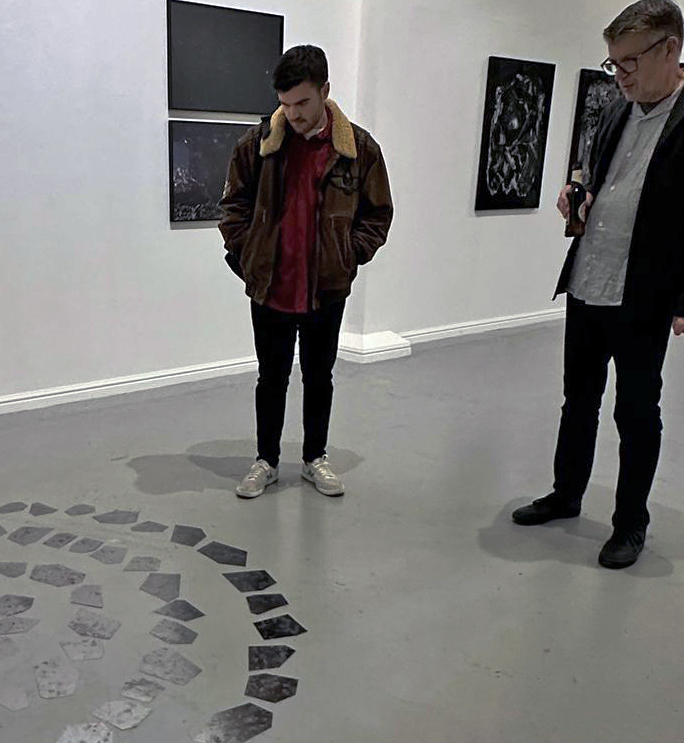
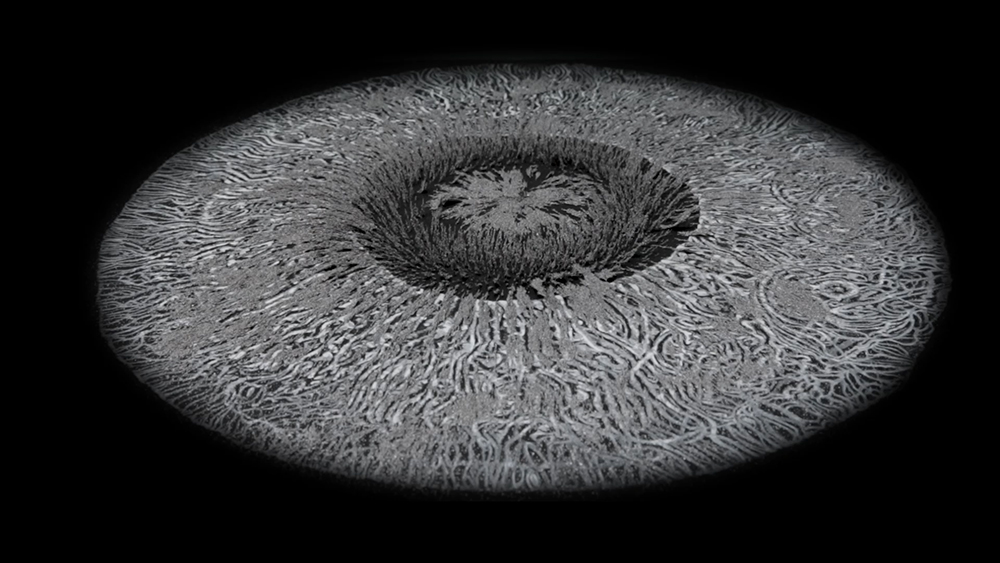
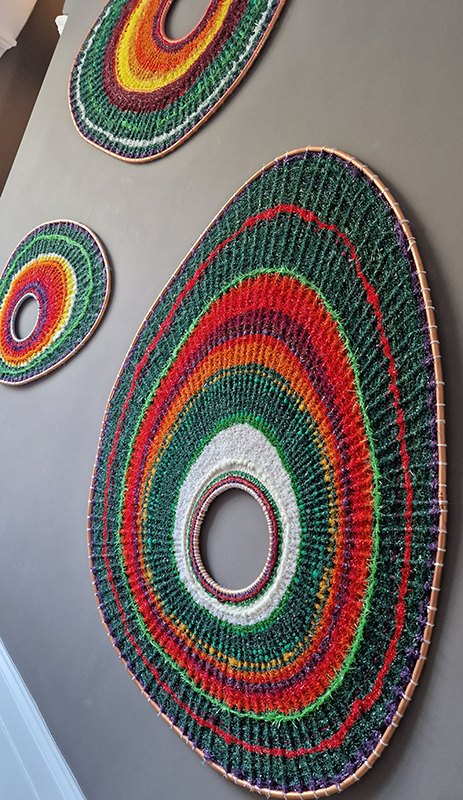
This work uses industrial directional magnetic steel, sanded and etched to reveal the Goss texture of rolled iron silicon alloy crystals. The jigsaw pattern of magnetic domains give this material exceptional magnetic properties. The simple evocation of a spiral described in geologically informed polygons draws upon many references, from the shape of our own Milky Way Galaxy sculpted by vast cosmological magnetic fields and the spiralling molten dynamo generating Earth’s magnetic field, to the inner pathway of spiritual growth and the route to the symbolic omphalos (navel) at the centre of the world where the sky entrance and the underworld meet. The title of this work originates from an ancient Chinese manual on the skills of persuasion, The Book of the Devil Valley Master, containing the first known mention of a compass, known at the time as a south-pointer.

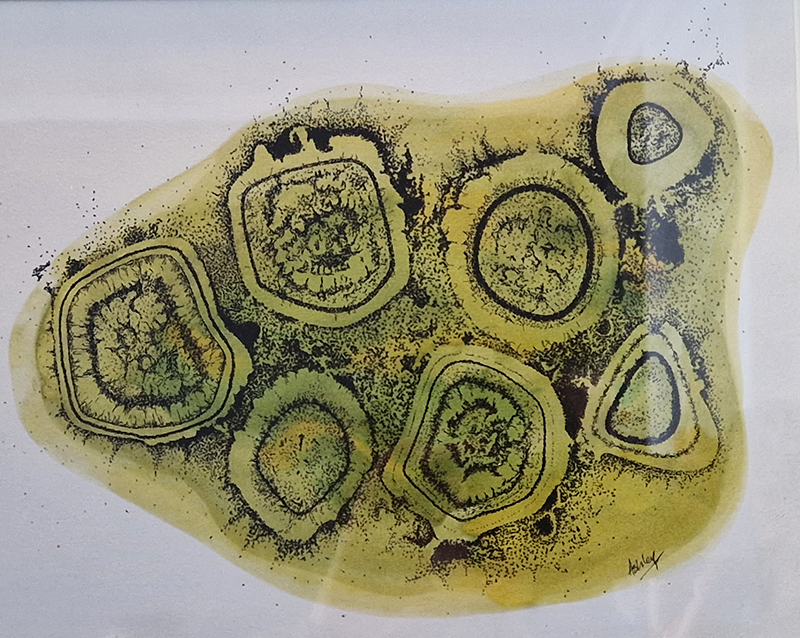
Work in progress. Mapping a response to the crystal structure of magnetite. Magnetite is the most magnetic of all the naturally occurring minerals on Earth found in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Nano-particles are also found in the human brain, heart, liver, and spleen and the cells of many other organisms, with some creatures using this for navigation techniques.
Magnetite crystals from road traffic pollution caused predominantly by vehicle frictional braking systems can outnumber natural magnetite in the human brain by 100:1 – this is a worrying trend as these crystals could be involved in our perception, transduction, and long-term storage of information in the brain.


Returning to my conversation with Alan Watson on the history of Haverah Park Extensive Air Shower Array.
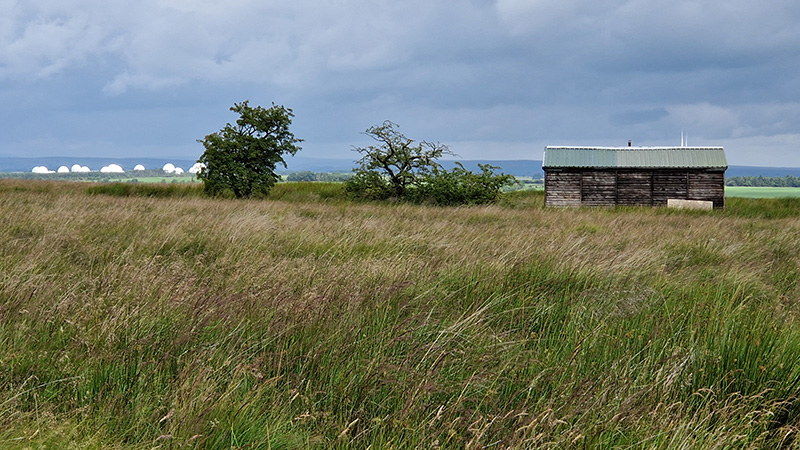

The motivation for the Haverah Park project getting off the ground came largely from the British physicist Patrick Blackett, who won the Nobel prize in 1948 for his discoveries in the field of cosmic rays. The director of The Rutherford Lab (where the British atomic bomb was being developed in the 50’s), John Cockcroft (known for splitting the atom), decided there should be fundamental science going on as well as bomb building, so outside the security wire they built an air shower array to monitor cosmic rays. When this experiment was shut down, Blackett was keen to see work with shower arrays continue, and to be within reach of a university so that scientists could combine research with teaching. Blackett was working at Cavendish Laboratory with Ernest Rutherford, but moved to Birkbeck which did all the teaching in the evening so he could do research work through the day and teach in the evening. Here he met J G Wilson, also with an interest in cosmic rays, so when J G Wilson later moved to Leeds, Blackett suggested he set up an air shower array there, which was how the Haverah Park Project came about. Land was rented from local sheep farmers to install the observation huts.


Alan Watson took a lectureship job at Leeds in 1964 and began working for J G Wilson, becoming a leading member of the UK Extensive Air Shower project until its closure in the early 1990s.
We also talked about the mesmerizing power of a cloud chamber. As well as it being considered one of the most important developments for progression in the understanding of particle physics it is also emotionally and aesthetically captivating. Alan reminisced about a time at the Royal Society Summer Exhibition when a large commercial diffusion cloud chamber drew so much attention they were asked to turn it off, as mesmerised visitors blocked the entrance to the exhibition. It’s been a few years since I visited the Institute of Physics to see the large cloud chamber in the foyer, I wonder if it’s still there. I love the fact that I can build my own cloud chamber to see these cosmic visitors.
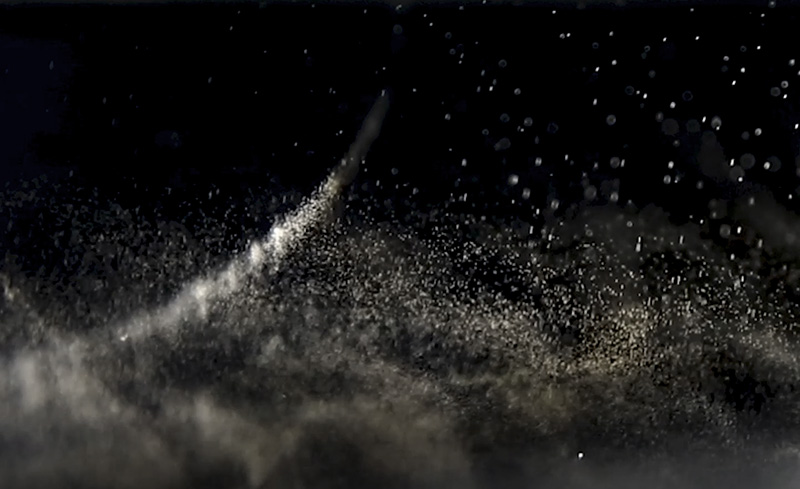



J G Wilson writing on the study of cosmic rays from his book About Cosmic Rays published in 1948, of which I have a copy:
‘It has its spectacular side, for the only laboratory which has been found big enough for its investigations is the whole of the universe to which men can win access. Most refined measurements have been made under conditions of difficulty and hazard, deep in mines and on icebound mountains, in the watses of western Greenland and cramped in the tiny gondola of a stratosphere balloon. These exploits, which are outstanding even in one of the most brilliant phases of experimental physics, are an unambiguous indication of the importance which is attached to the problems which are being studied.’
The following images from the same book show particle trails photographed in a cloud chamber -showing extensive showers and particles passing unhindered through metal plates.
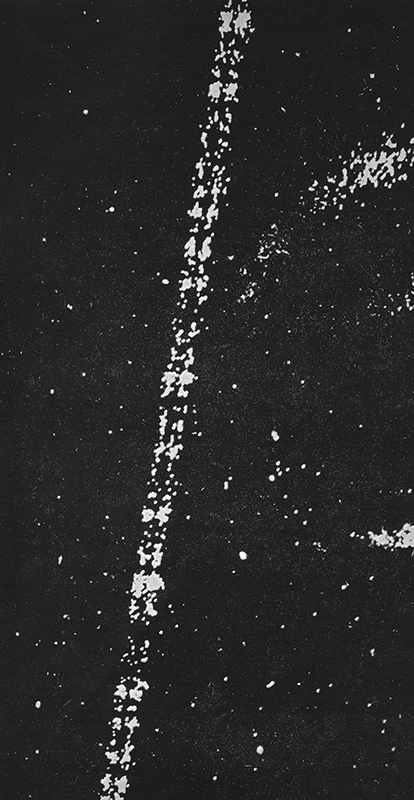
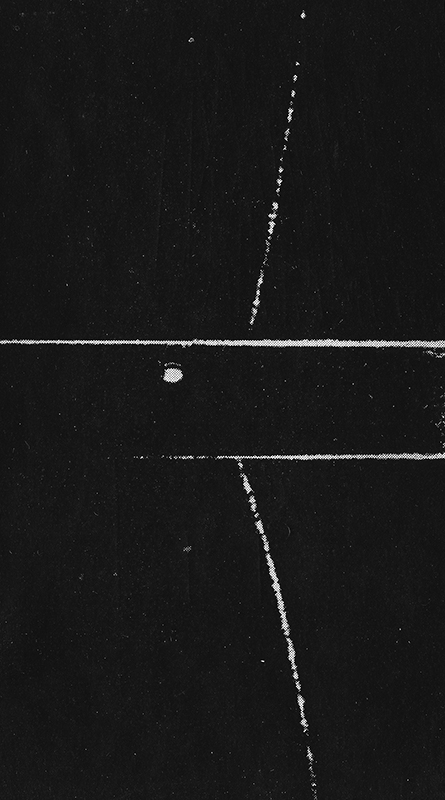




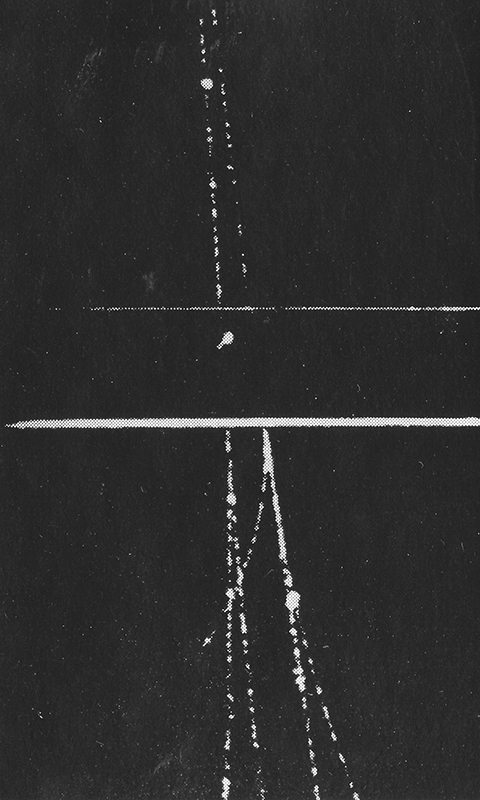

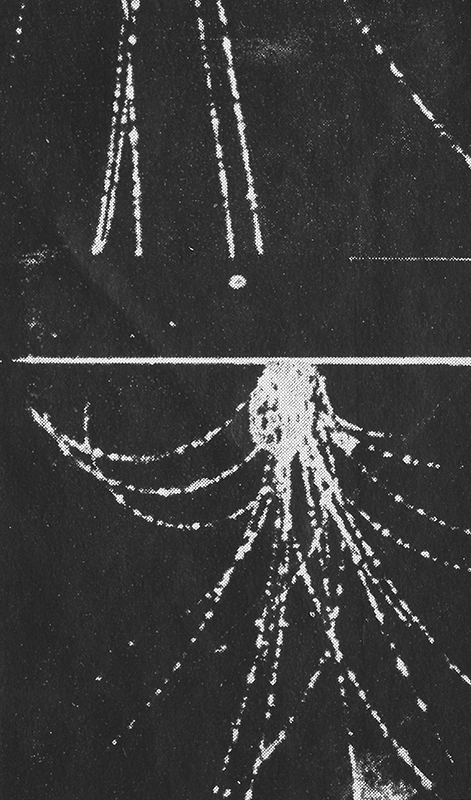


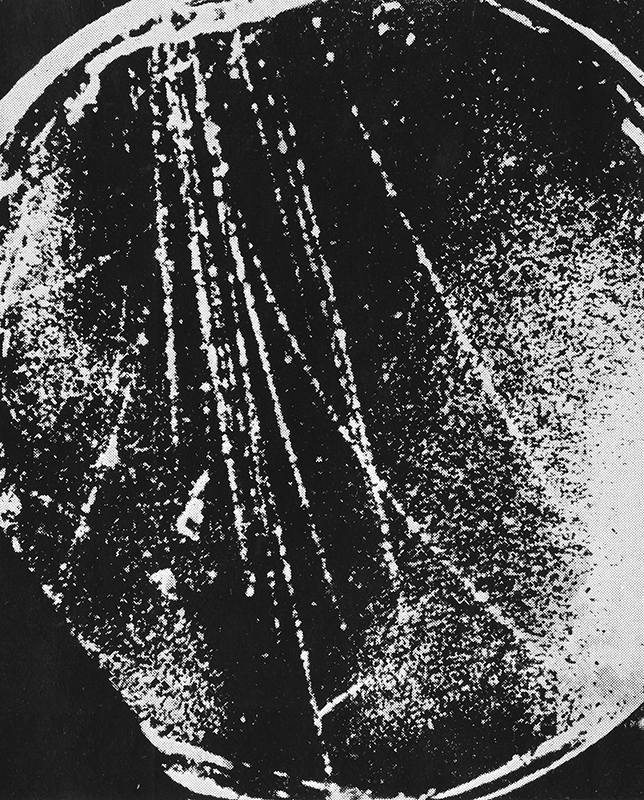

J G Wilson writes about cosmic rays ‘…it is interesting to speculate on their previous history, for before it is overtaken by the catastrophe of hitting the earth, each particle is likely to have had a placid life for years, even millions of years, cruising through the wide open spaces of the universe’.

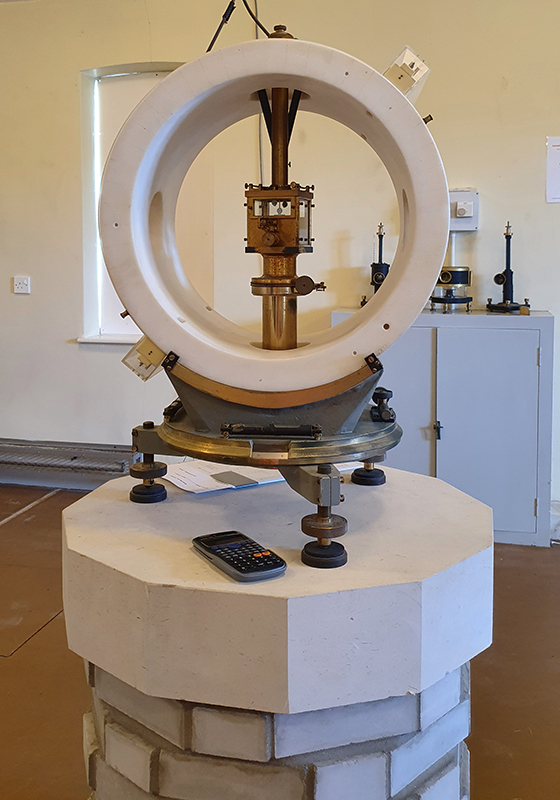
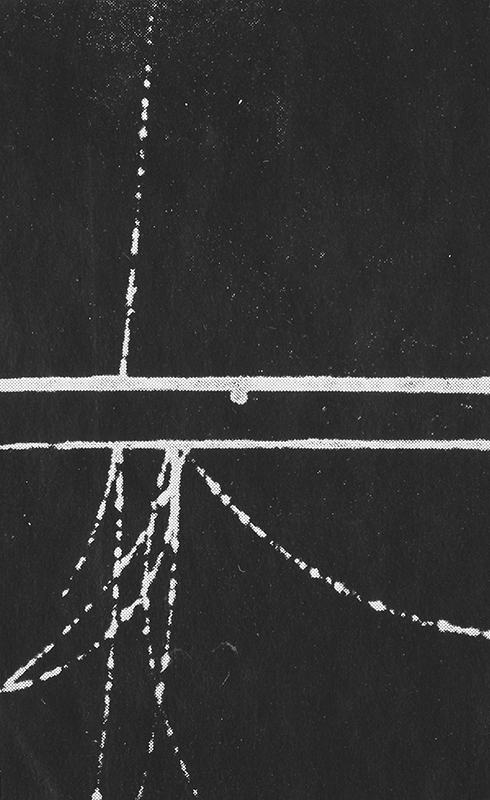
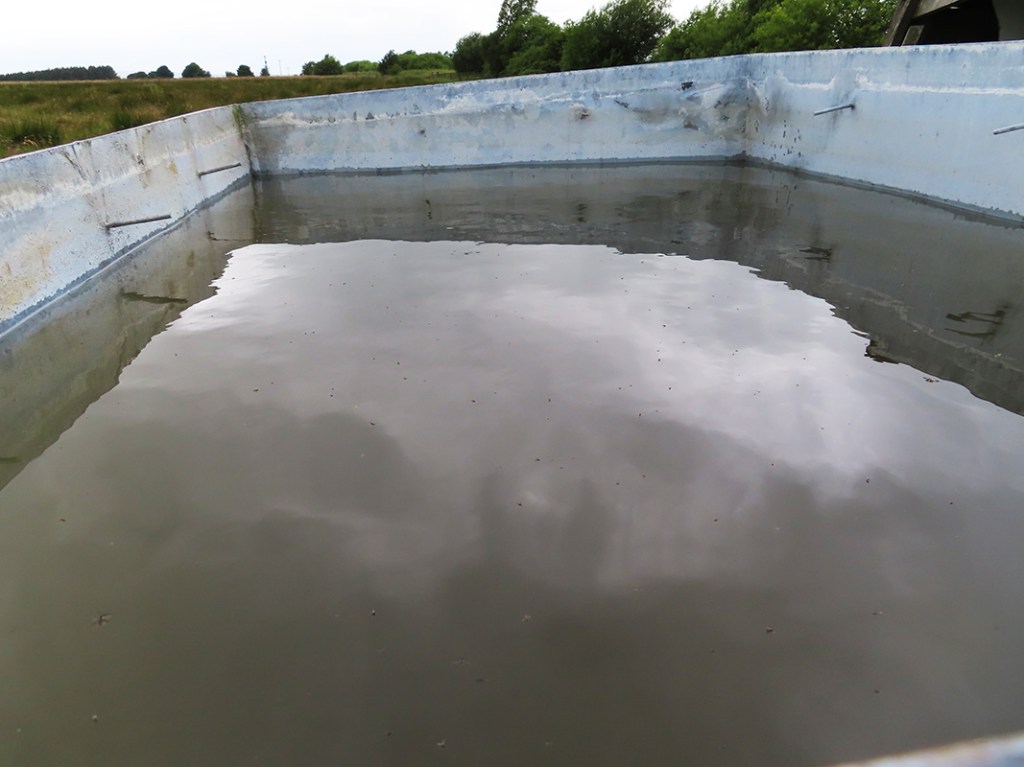
The primary detectors used at Haverah Park were water Cherenkov detectors. These are large water filled tanks filled with a photomultiplier suspended in the water to capture flashes of Cherenkov light emitted by high energy cosmic rays as they pass through. The light is emitted because the cosmic rays pass through water faster than photons of light are able to, and as they do so they lose electrons thereby emitting light. The speed of light is only a constant within a vacuum, when it passes through other materials it get slowed down.
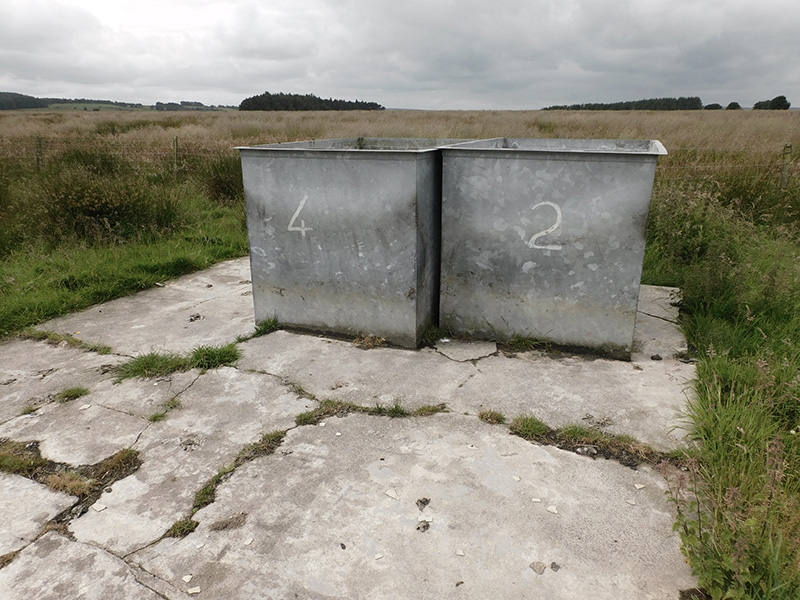


There were four 34 m2 detectors at the centre of the array in the main hut, with three detectors located 500m from the central detector. Signals from the three distant detectors were sent along buried cables to the central hut, with the signal from the central detector passing down 500 m of cable buried underground so that all signals arrived at about the same time. When signals from the central one and two of the others arrived within ~2 x 10-6 s (called a coincidence), the signals from the photomultipliers in the 34 m2 detectors were displayed on four oscilloscope screens and photographed by one camera which had its shutter permanently open. About 20 feet of film could record around 150 events. Developed and manually scanned by Alan, or a senior colleague, the film was checked for quality and to look for any large events (ultra high energy particles arriving) which were always exciting to find. The developed film was then sent to Leeds University Physics dept for measurements.



When there was a coincidence event at the centre of the array, a signal was sent by microwave to the distant detectors set across the moorlands (on average about 2km from the central hut), the signals from these distant groups of 4 x 13.5 m2 were recorded digitally with the data going onto paper tape which was collected once each week.
Along with the oscilloscope traces being photographed, the number on a counter was included which gave the time of each event to the nearest half minute. In the 1960’s when this project began the time counter was advanced by a pendulum clock. Counting time in half minutes the team found that there are roughly one million half-minutes in a year, which gave a good excuse for an annual party.


There were some brief periods in the early 1980s when a small number of scintillator detectors were also used to make cross-checks of the results from the water Cherenkov detectors against those from projects in the USA (Volcano Ranch) and Yakutsk (Siberia). The scintillators retrieved from Imperial College’s Holborn project were brought to Haverah Park for an experiment to look at much lower energy showers.
Both types of detectors register flashes of light.
Blackett was the first person to work out the details of Cherenkov light produced in the atmosphere. According to a memoir on Blackett, written by astronomer Bernard Lovell, who knew him very well, Blackett attempted to see Cherenkov light from cosmic ray showers with the naked eye but there is no mention of whether he succeeded. In 1962, physicist Neil Porter who built the first water Cherenkov tank in the UK at Harwell in the 50’s, did an experiment with some volunteers who were asked to recline on a coach in a dark room with a small Geiger telescope attached to a pair of darkened goggles and acknowledge if they saw a flash of light when a cosmic ray was known to pass through the googles. The observers did seem to experience a flash of light but results were ambiguous as to whether this was Cherenkov light being emitted as the particle passed though the crystalline lens or vitreous humour of the eye or a direct excitation of the retina. The experiment was a collaboration with the Psychology dept at the University of Dublin and published in Nature under the Psychology heading giving an impression that the lights were perhaps a figment of the imagination.
Astronauts are very aware of this phenomenon. During the 1970 Apollo 13 mission to the moon the power supply was damaged and the astronauts sat in the dark for several days waiting to return to Earth. They experienced flashes in their eyes and realized that some of this was Cherenkov light. Some flashes were caused by particles directly hitting the retina but Cherenkov light caused by high energy particles travelling through the matter of the eye faster than light, is much brighter. The energy is proportional to the square of the charge of the particle that comes through, so if you have an iron nucleus which has a charge 26 x the charge of a proton, you get 26 squared or 600 times as much light emitted. Out in space there are many more of these high energy particles and so the astronauts would become very familiar with these flashes, even using them to line up accelerator beams by putting their head in the particle beam to see the flashes.
An astronaut once told Alan that he was convinced that the very first people fired into space probably saw these flashes, but didn’t like to tell NASA in case it turned out to be a physiological defect of theirs and they would be taken off the space programme.
Recently, a professor friend of Alan’s who is aware of this phenomenon, has unfortunately had to begin radiation treatment for a brain tumour. He has found due to the position of the tumour and angle of treatment he can see Cherenkov light flashing in his eyes as the electrons bombard the tumour.

When we met, Alan was just back from a conference in Italy discussing a paper titled ‘Ultra high energy cosmic rays: The Disappointing model’. They called it the disappointing model because they believed that the Auger results with particles at the highest energy were heavy not protons. I’m not sure I understood why it was disappointing although Alan did his best to explain: ‘It’s difficult to measure the mass of the particles of a certain energy. A deduction had been made that they have a mean mass, probably the same as nitrogen but mass changes in quite a complicated way as a function of energy. It’s to do with how deep the showers develop in the atmosphere.

The techniques aren’t good enough to separate the particle’s mass on a one by one basis, we can only do averages. It looks like the average mass is much heavier than protons, which everybody had believed for a long, long time. Protons would be at a much lower energy. As the nucleus is travelling through space, it sees photons from the microwave background radiation and the photon will chip off a neutron or a proton, if it chips off a neutron, the neutron decays into a proton, so you can get protons this way, but they will be of lower energy. The energy reduces roughly by the mass of the particle, so an iron nucleus has a mass of 56, if you chip off a neutron or a proton that proton will have an energy, which a 56th of the energy that the nucleus has – so it goes down in energy.
Some particles could come from Centaurus A, which is a relatively close radio galaxy, it is thought that the jets from radio galaxies provide conditions to accelerate the particles, but the problem is, because the cosmic rays are charged, they get deflected in the magnetic field of the Galaxy so you can’t track them straight back to where they came from. In terms of heavy particles that’s more of a problem because being charged means they bend even more. So one of the disappointing things is that cosmic ray astronomy is not going to be very easy. The Pierre Auger observatory has really been very successful in changing the picture quite a bit but because there are so few ultra high energy particles recorded it is slow progress. There are hopes to expand the observatory even more and also a plan to launch a satellite with detectors to pick up fluorescence light in the shower as it passes through the atmosphere, a similar phenomenon to aurora light.

Exhibitions
The Vinyl Factory: Reverb at 180 The Strand, a multimedia exhibition exploring the intersection of art and sound with artists including Theaster Gates, Es Devlin, Julianknxx, Kahlil Joseph, Caterina Barbieri, Stan Douglas, Virgil Abloh, Cecilia Bengolea, Jeremy Deller, William Kentridge, Jenn Nkiru, Hito Steyerl, Carsten Nicolai and Gabriel Moses. Fabulous show, shame I can’t share the sounds here. Loved Jeremy Deller’s takeover of a sixth form politics class. Some of the works I had seen before but that was fine as they are worth extra viewings.












Reading
I am beginning research reading for The Geological Unconscious exhibition Julie F Hill and I are co-curating at Hypha HQ Euston opening in May 2025.
Ursula Le Guin The Winds Twelve Quarters, a collection of profound short stories each introduced by the author reflecting on the intention within.
Long after I wrote the story (The Stars Below) I came on a passage in Jung’s On the Nature of the Psyche: ‘We would do well to think of ego-consciousness as being surrounded by a multitude of little luminosities…Introspective intuitions…capture the state of the unconscious: The star-strewn heavens, stars reflected in dark water, nuggets of gold or golden sand scattered in black earth.’ And he quotes from an alchemist, ‘Seminate aurum in terrain albam foliatam’ – the precious metal strewn in the layers of white clay. Perhaps the story is not about science, or about art, but about the mind, my mind, any mind, that turns inward to itself.
Roger Caillois The Writing of Stones 1970 is a tribute to the collection of extraordinary stones Caillois acquired and which now resides in The National Museum of Natural History Paris. In these poetic chapters he describes in detail each of the stones and his fascination with the images and associations they conjure in his imagination. Questioning and celebrating the allure of the mineral and the stories hidden and revealed over millennia.
I can scarcely refrain from suspecting some ancient, diffused magnetism; a call from the centre of things; a dim, almost lost memory. or perhaps a presentiment, pointless in so puny a being, of a universal syntax.