I am very grateful to a-n The Artists Information Co for awarding me a professional practice and creative development bursary to expand on my research and respond to the many ways Earth’s magnetic field impacts life on earth. The award will be used for a research trip to the remote location of Eskdalemuir Magnetic Observatory and Kielder Dark Skies Observatory. Fingers crossed for an Aurora experience. I will also gain expert tuition in concrete casting and mould making from Anna Hughes and make use of the facilities at The London Sculpture Workshop.
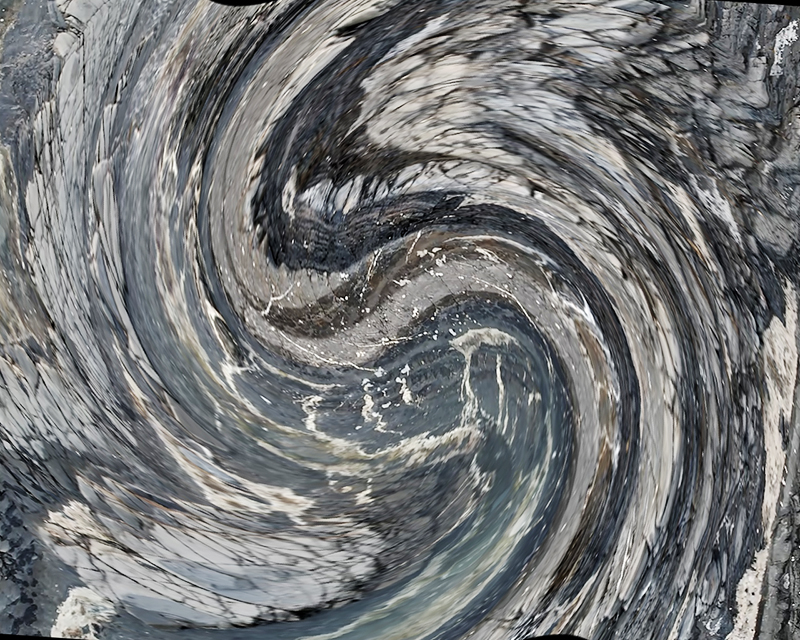
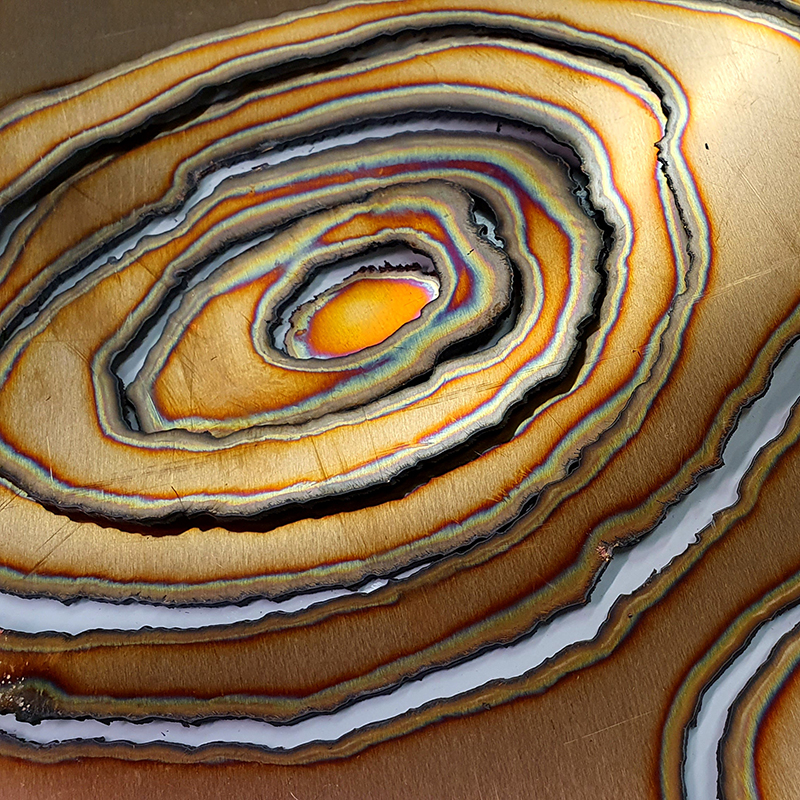






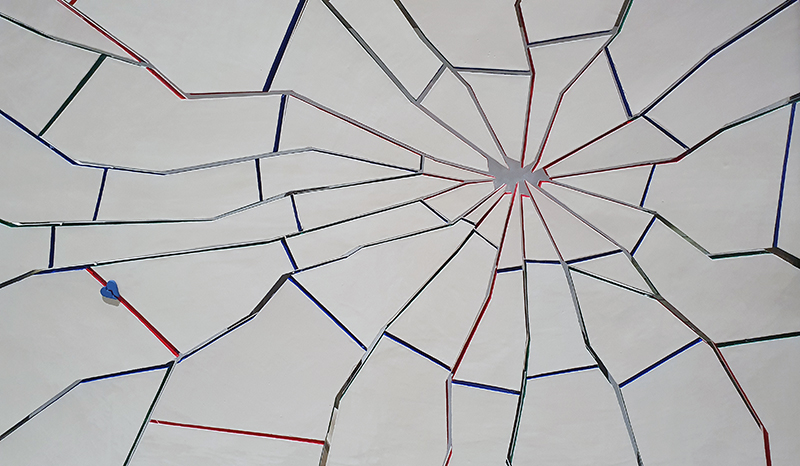
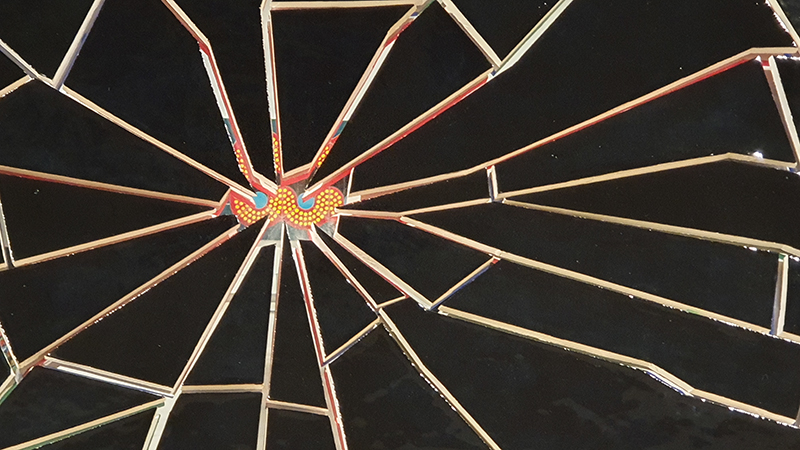
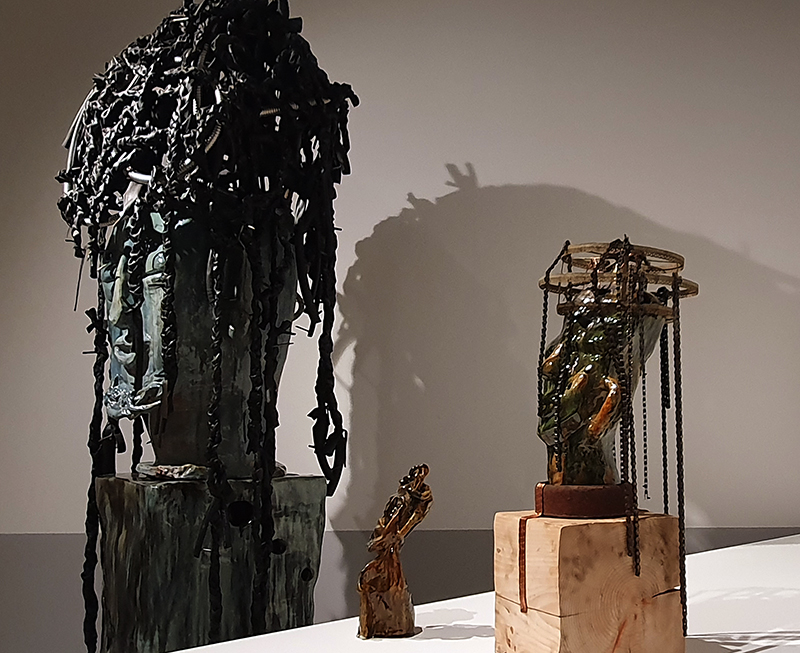
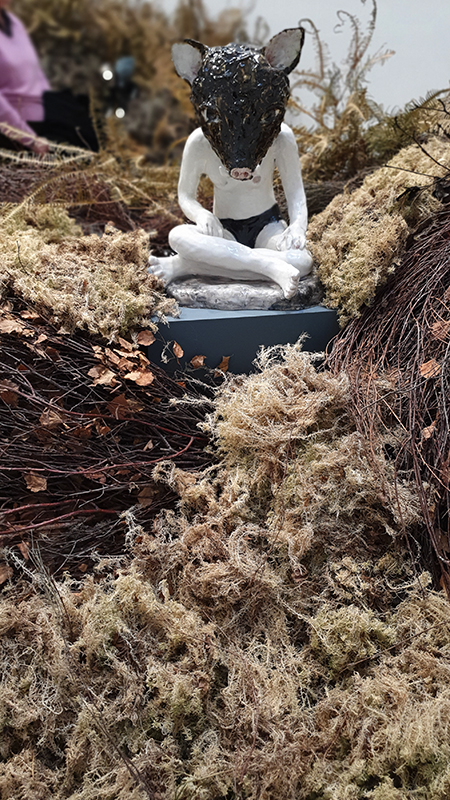
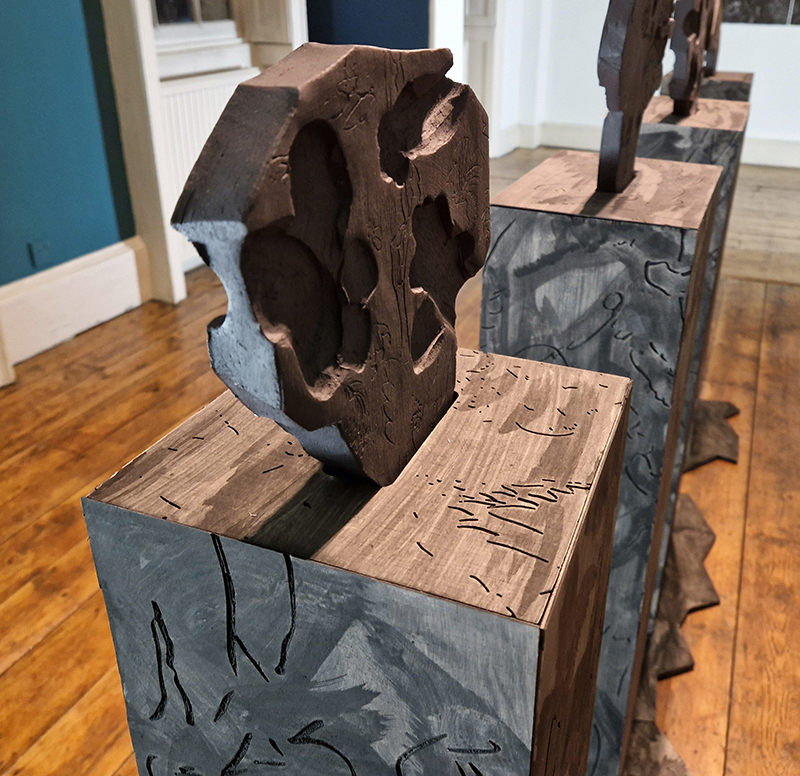
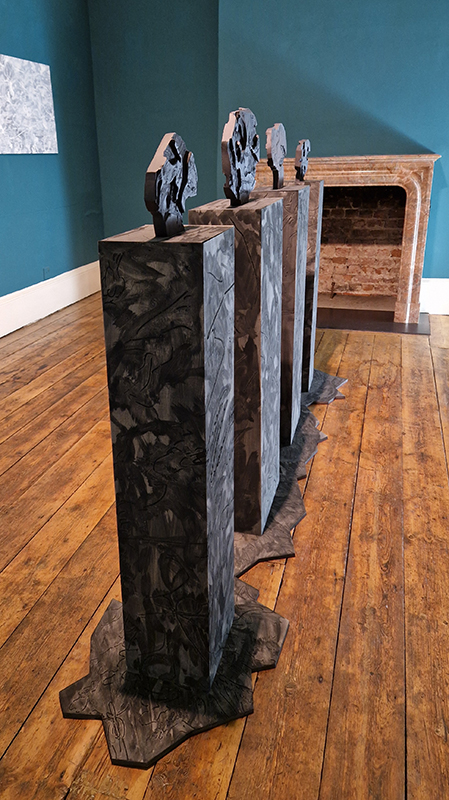
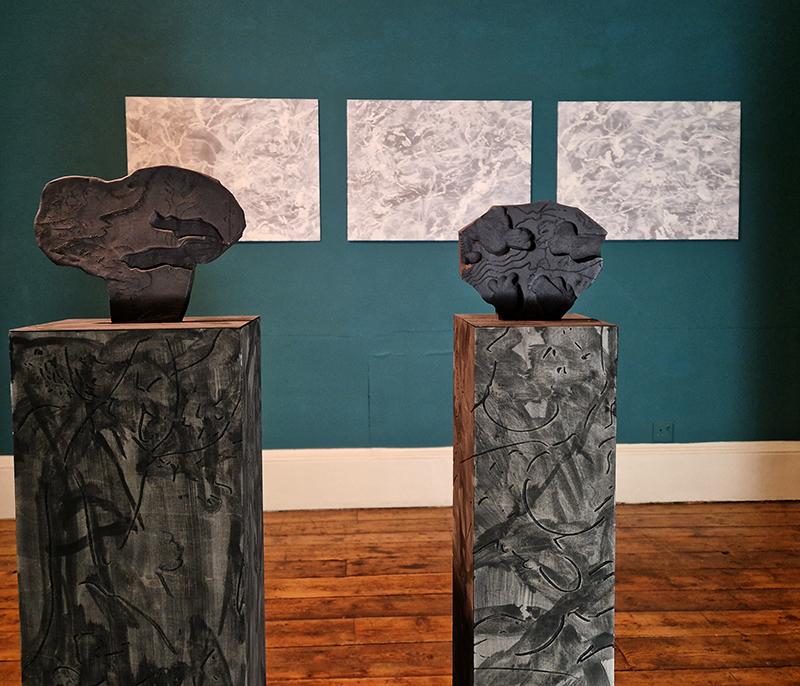
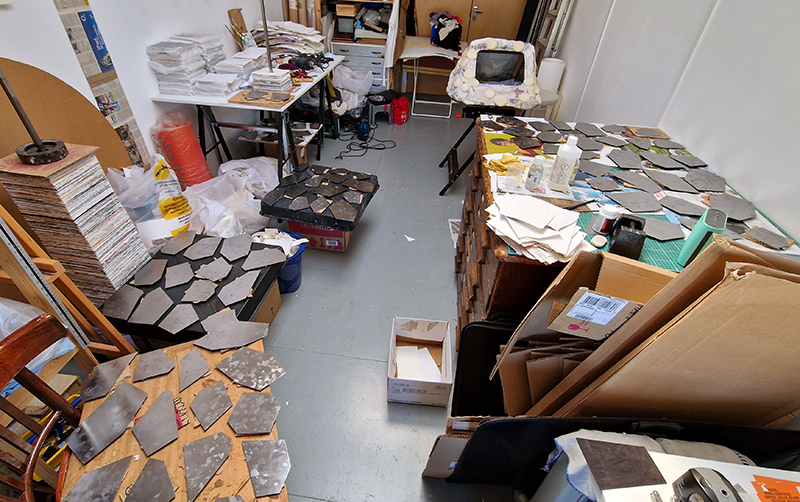
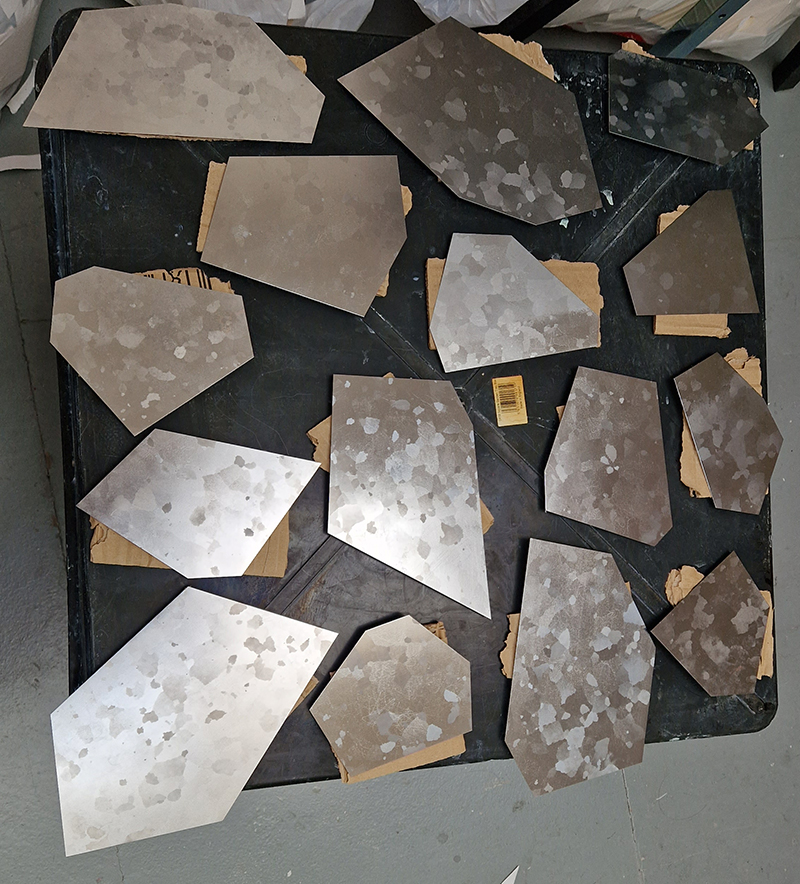
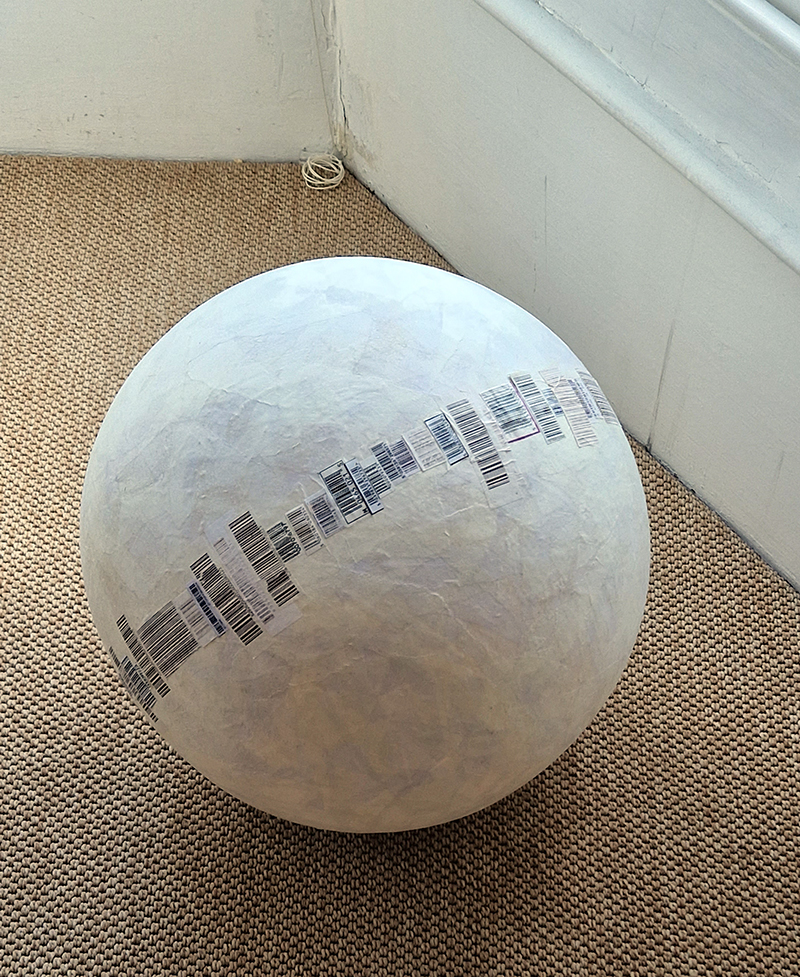
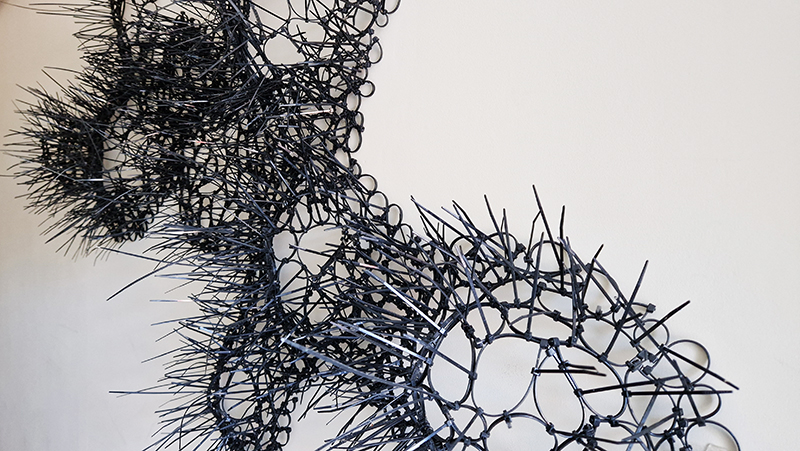
Domain of the Devil Valley Master – work in progress. It is likely that compasses were first used in China to divine an alignment of order and harmony for important sites and rituals. Jade hunters discovered they could also help to keep them from getting lost long before Europeans used them for navigation. The first mention of a south-pointer is in a fourth-century BCE text – The Book of the Devil Valley Master, and it is this that I am referencing in the title of this sculpture. Other references in the work are the rotation of the Earth’s core and geological formations of polygonal prisms. A magnetic domain is a region within a magnetic material in which the individual magnetic strength and orientation of the atoms are aligned with one another and they point in the same direction. The work uses directional magnetic steel stripped of its industrial coating to reveal the jigsaw pattern which comes from rolling single crystals of an iron silicon alloy into thin sheets to minimise magnetic losses for use in industry. The sheets have been sanded, etched, guillotined, treated for rust and sealed.





The Earth’s core is made almost entirely of iron and nickel. Siderophiles are elements that form alloys easily with iron and are concentrated in the Earth’s core. When the Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago from the collision, accretion and compression of matter it was rock all the way through. Heat from the massive violence of formation and radioactive decay caused the planet to get hotter and hotter. After about 500 million years of heating up it finally reached the melting point of iron. As the iron liquified lighter material rose to the surface becoming the mantle and crust and the heavy metals like iron and nickel fell towards the centre becoming the core. The siderophiles that descended into the core are gold, platinum, and cobalt along with around 90% of the Earth’s sulphur. Hence the smelly sulphur vents around the volcanic regions.


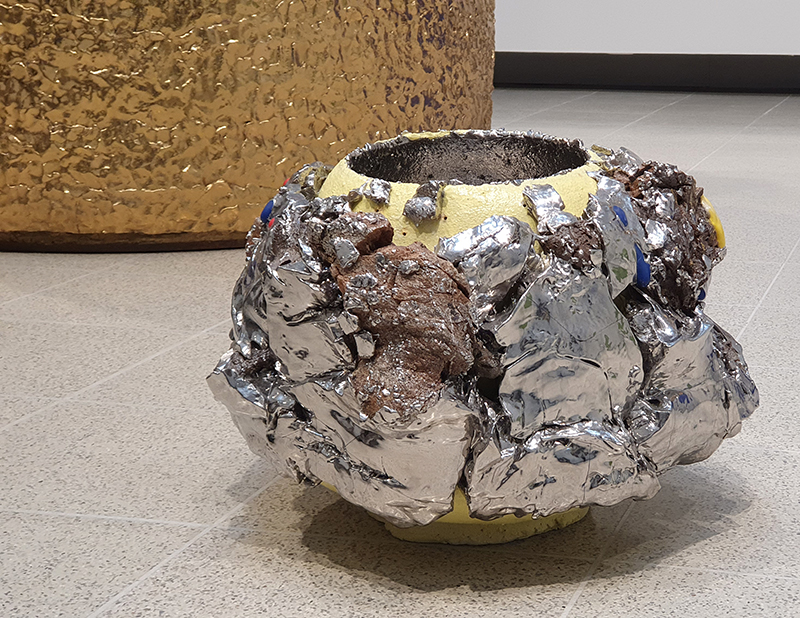
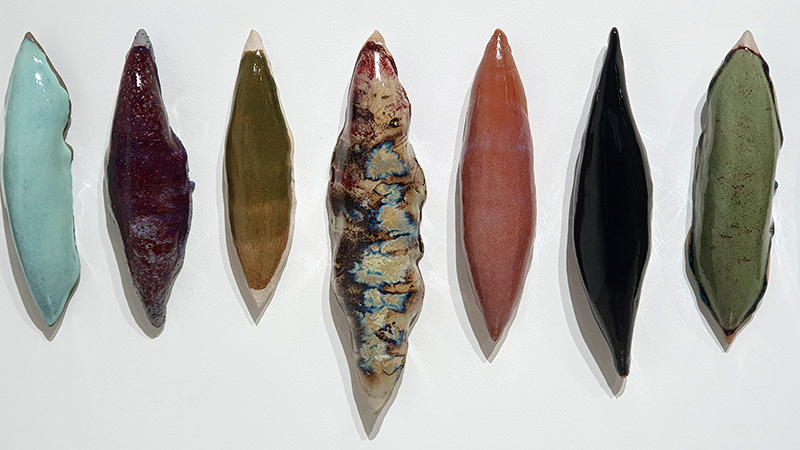
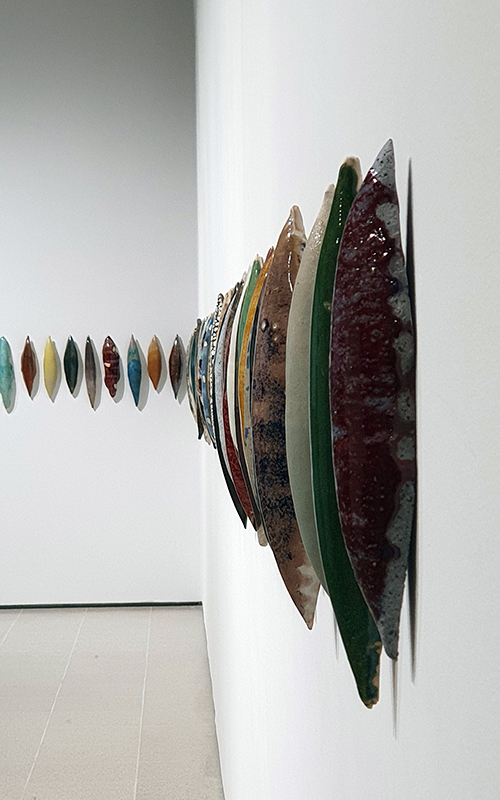
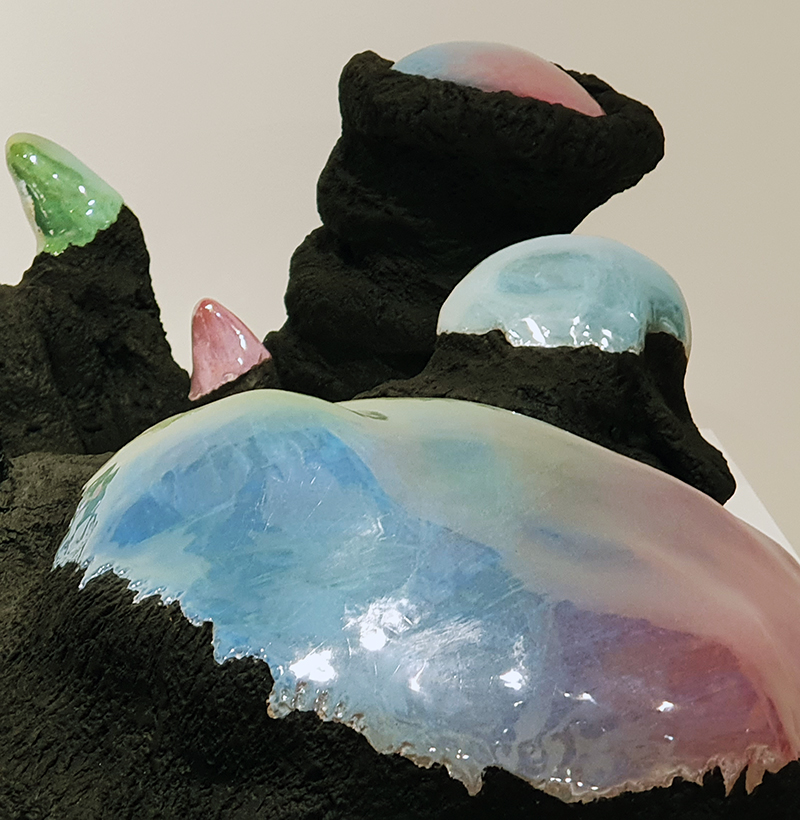
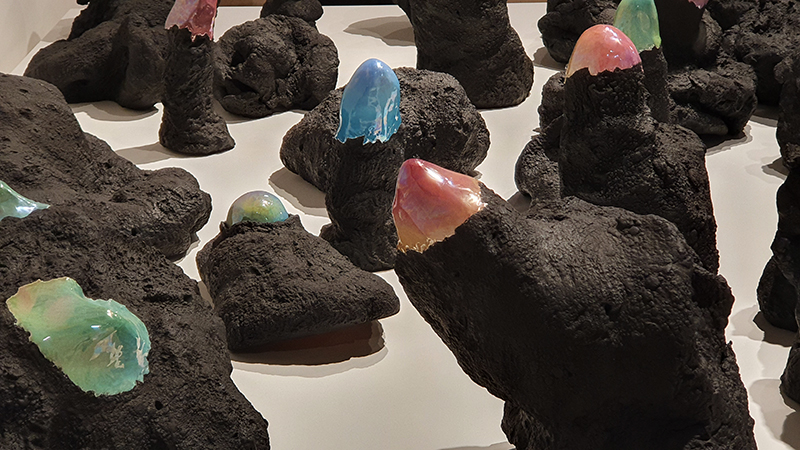
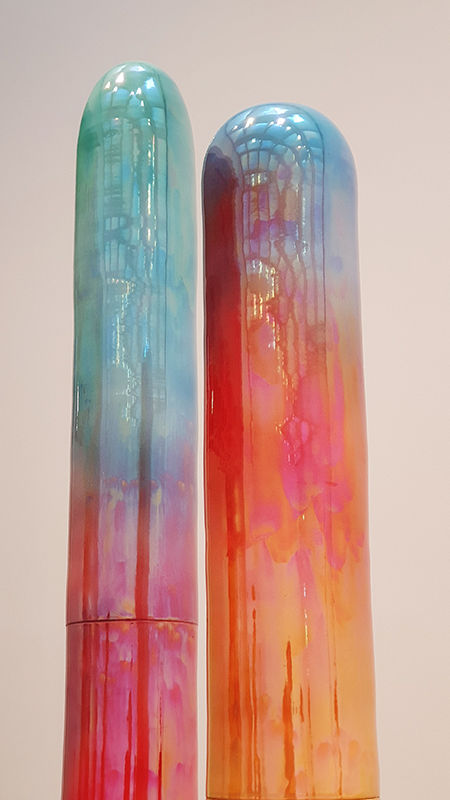
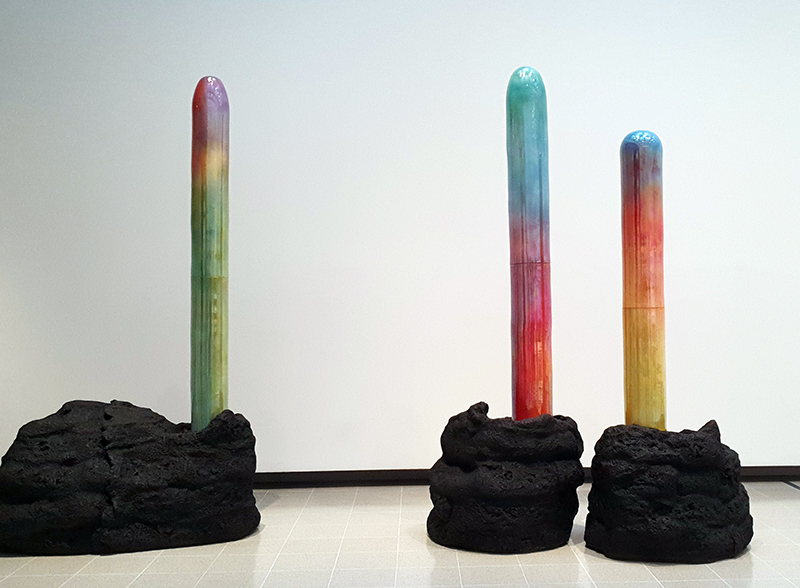
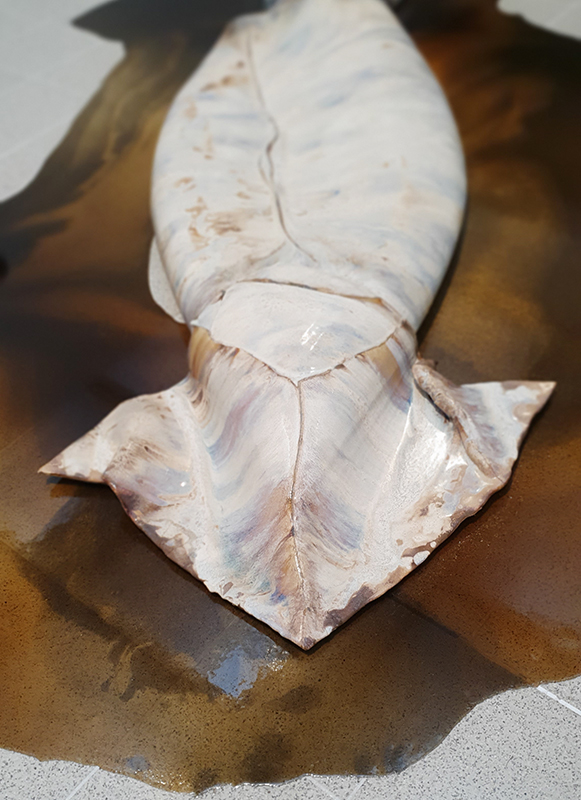
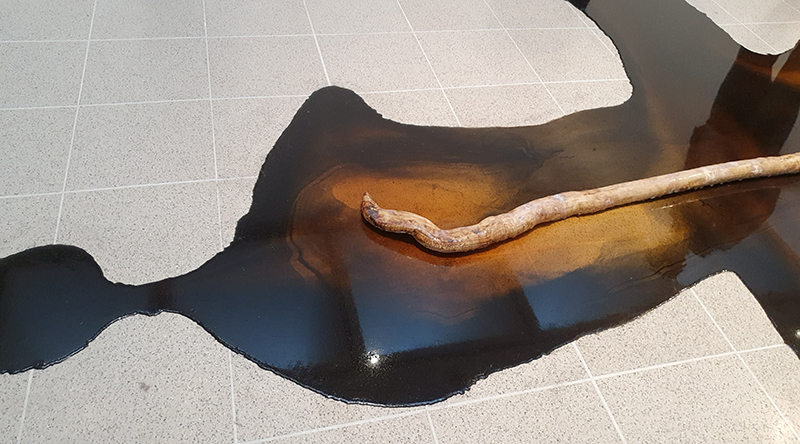
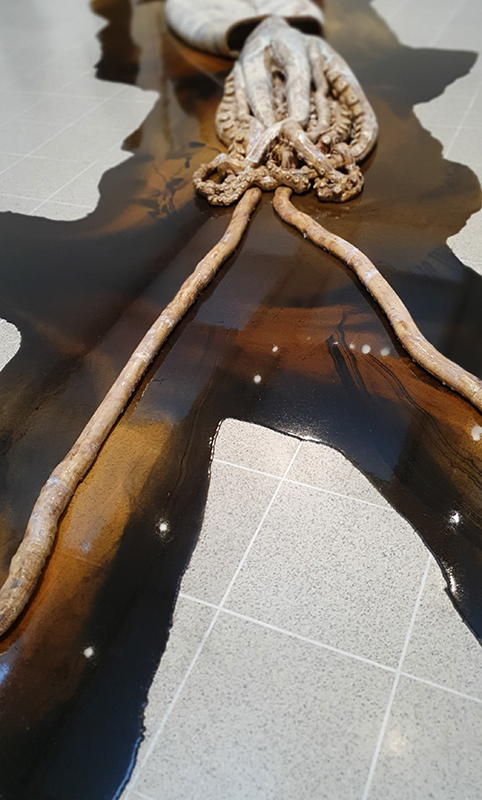
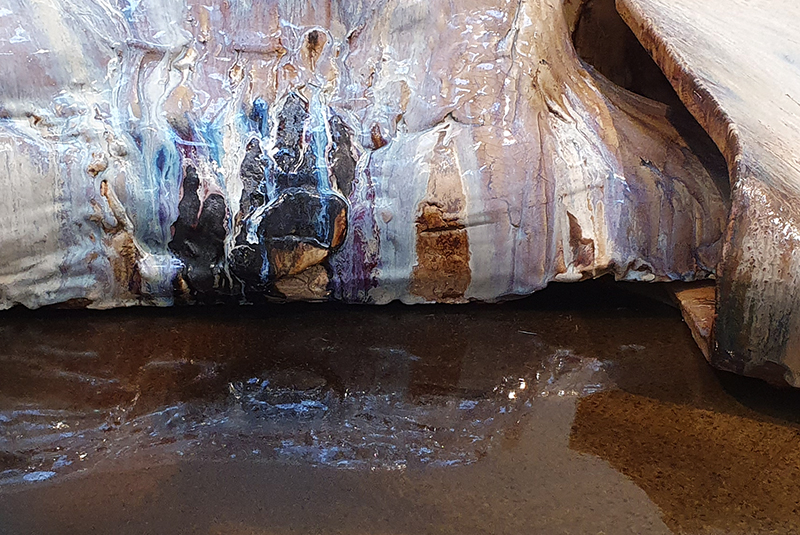
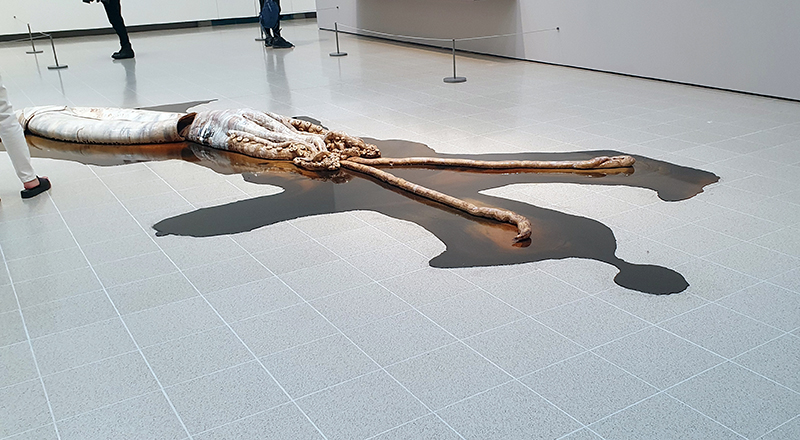
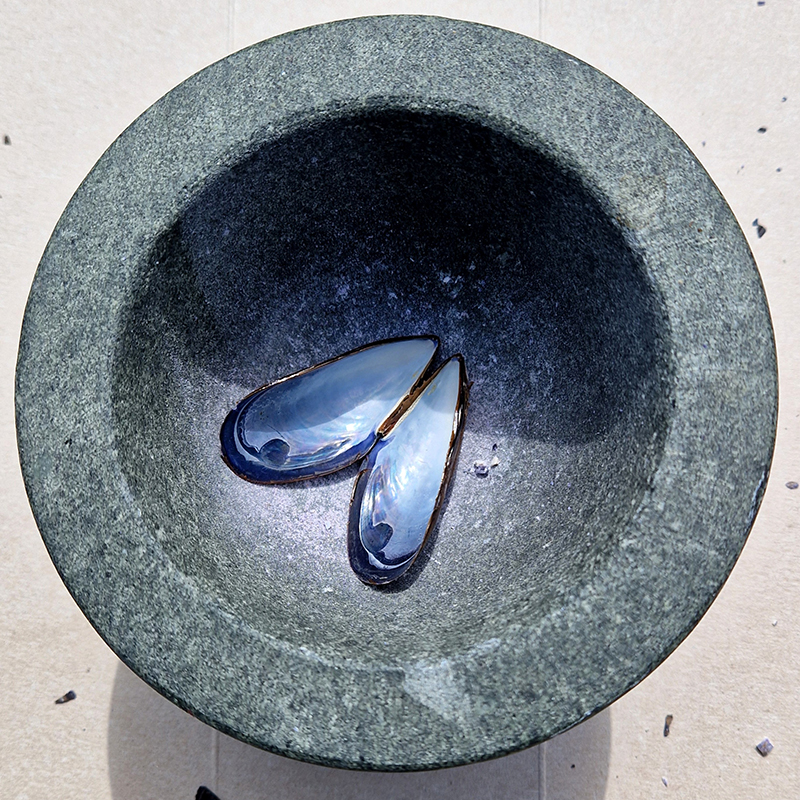
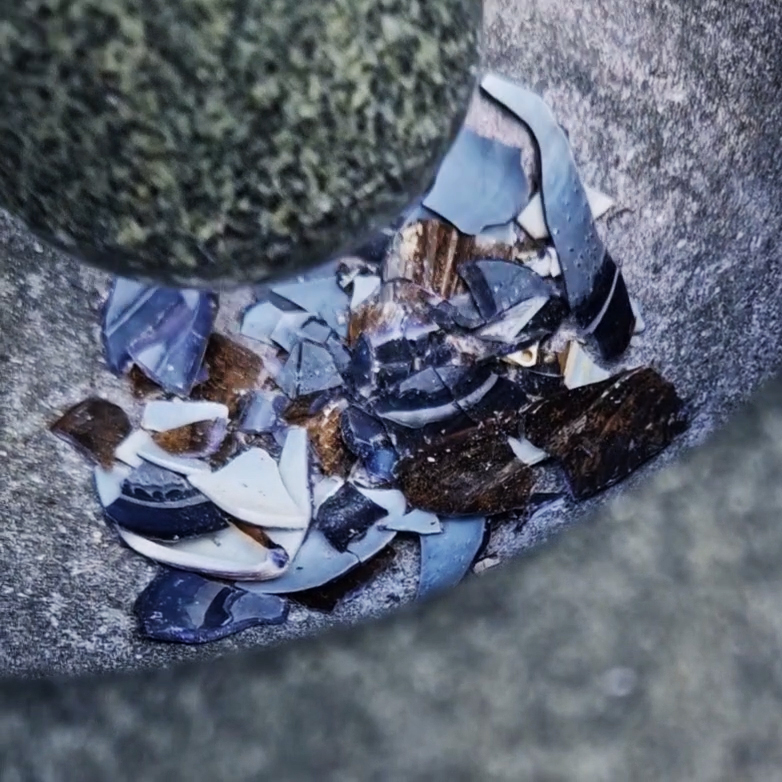
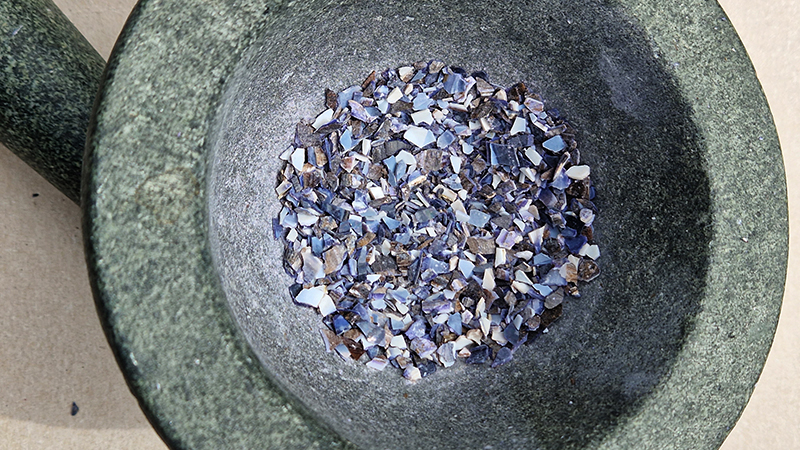
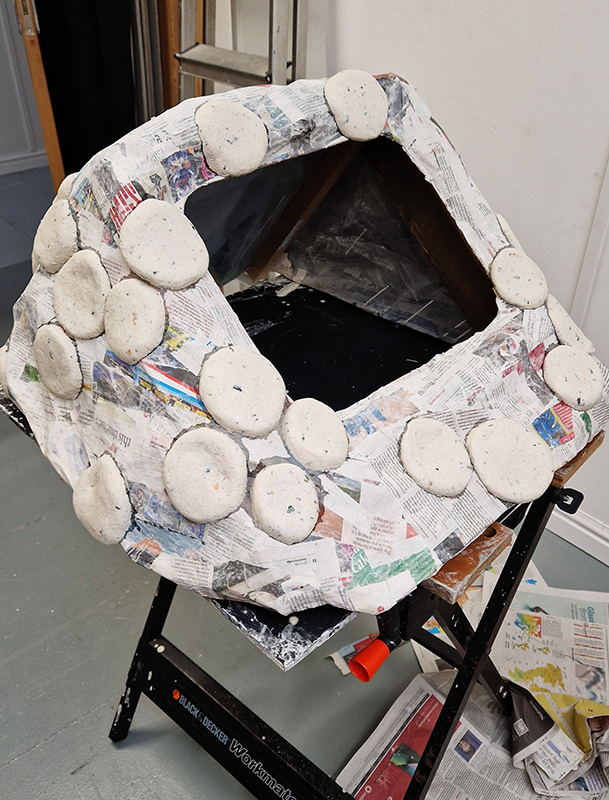
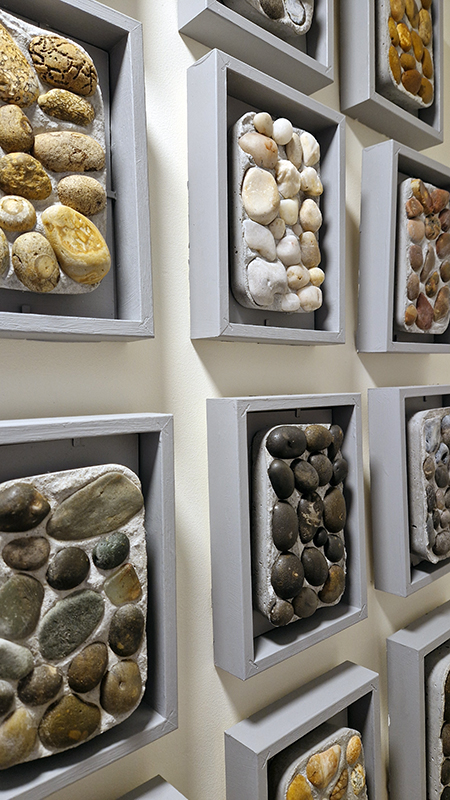
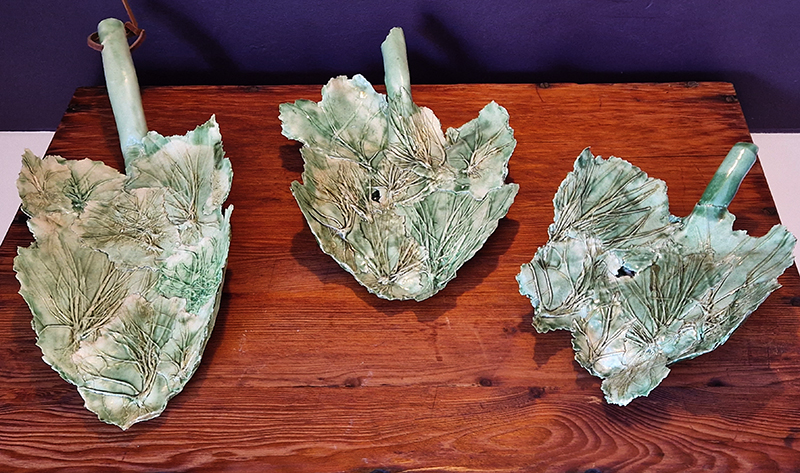
Belly of a Rock – work in progress. Making paper clay discs to build the surface of this hybrid sculpture and crushing mussel and oyster shells to use as texture.




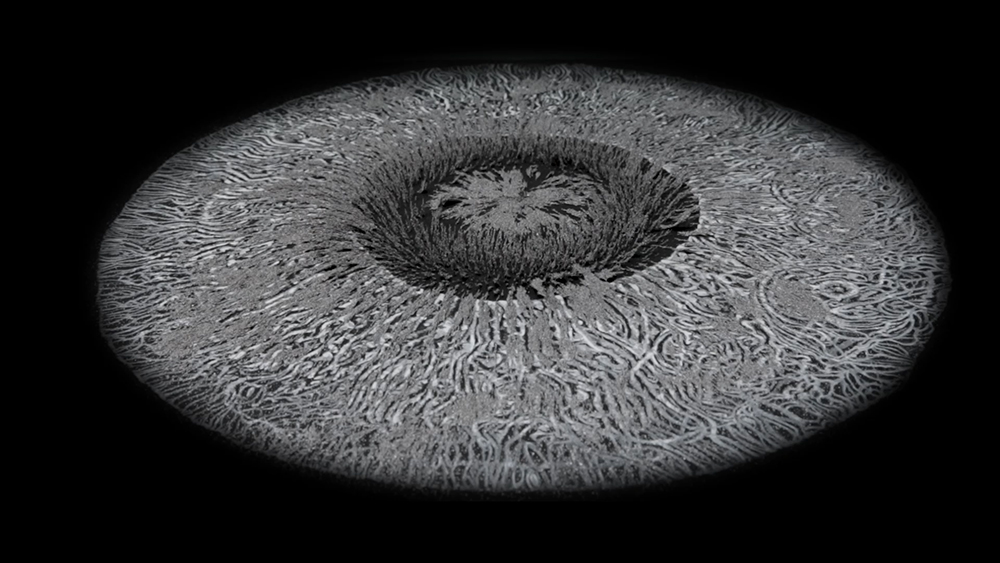
The geographic north pole lies in the middle of the Arctic Ocean, covered in shifting sea ice, where the sun rises and sets only once per year. All lines of longitude converge here and hence all time zones. It is known as true north to distinguish it from the magnetic north pole. However, as the Earth’s axis of rotation wobbles slightly in an irregular circle, even this pole is not fixed. The magnetic north pole, also called the magnetic dip pole, is where the planet’s magnetic field is vertical and a compass needle here would dip and try to point straight down. The north and south dip poles are not found directly opposite each other. These dip poles are located by experiment in the field but as they are found in the most remote and harsh regions of the planet they are not easy to track. Also they can move around over considerable distances during each day, tracing out oval shapes as they are acted upon by dynamic electrical current systems of the magnetosphere, which are in turn defined by the activity of the solar wind. There is an equivalent (but fictional) magnetic dipole at the centre of the Earth assigned from global modelling of the geomagnetic field. These geomagnetic poles are an approximation arrived at by reducing Earth’s complex and varied magnetic field to that of a simple bar magnet. The north dip pole lies in Northern Canada, the northern dipole is roughly off the northwest coast of Greenland.
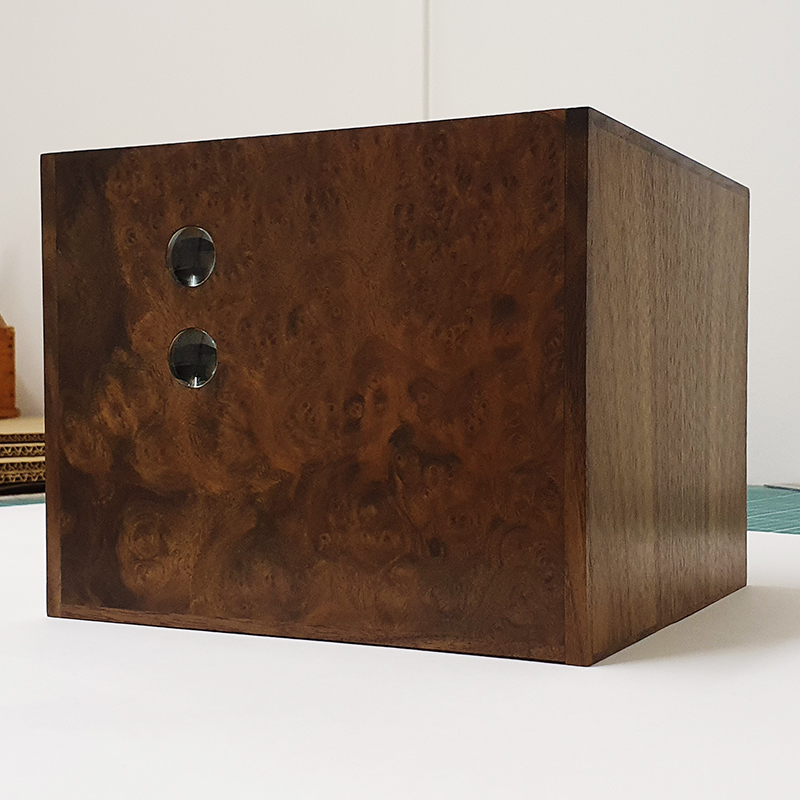
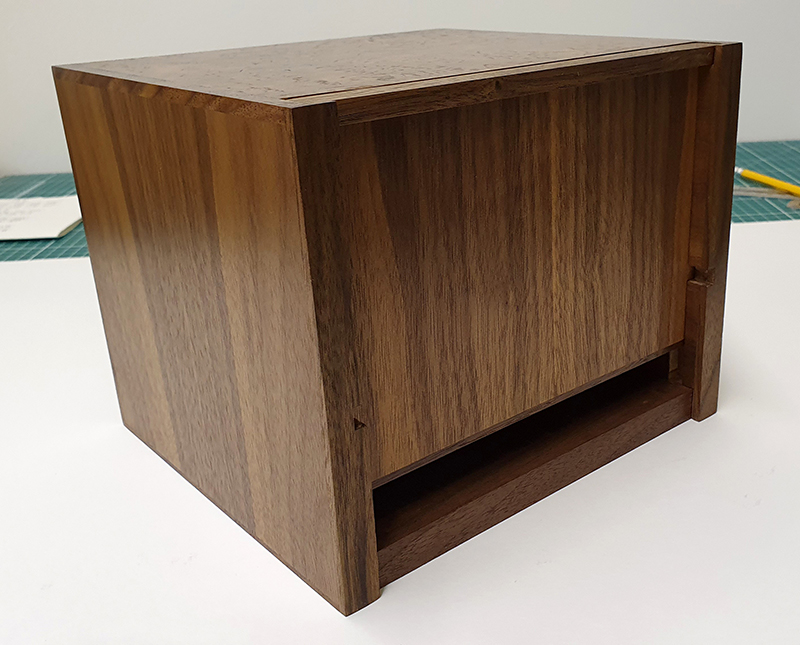
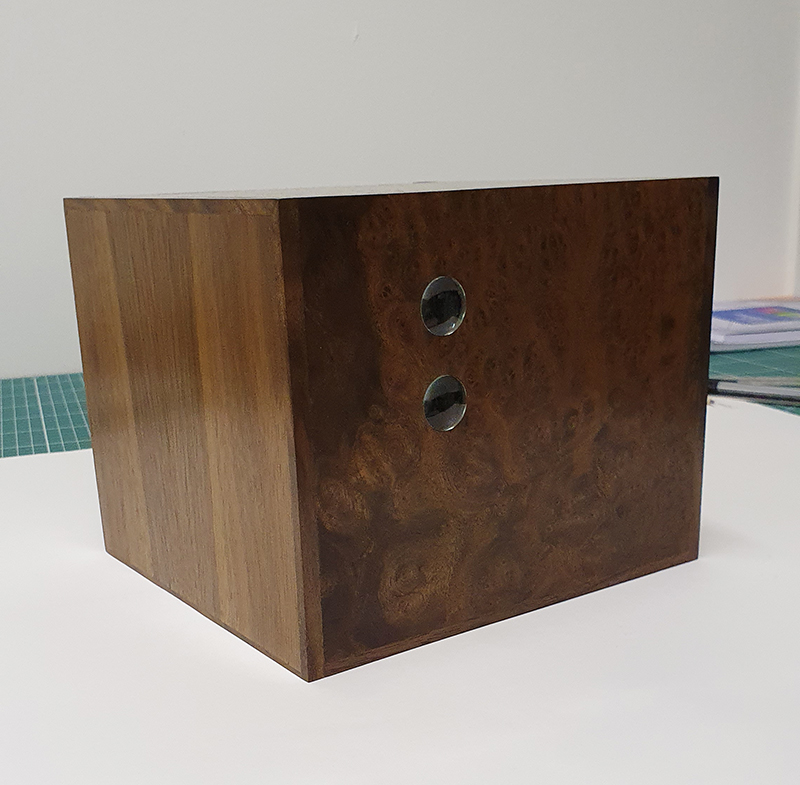
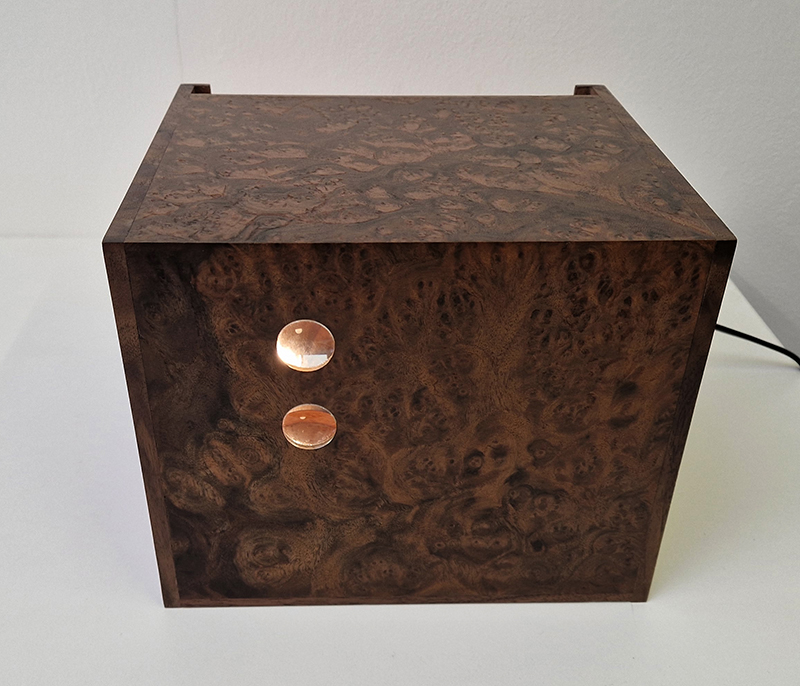
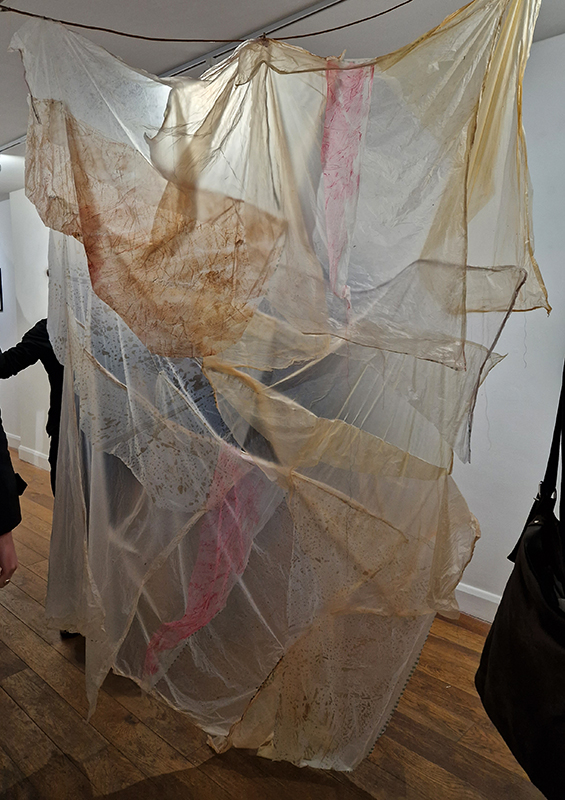
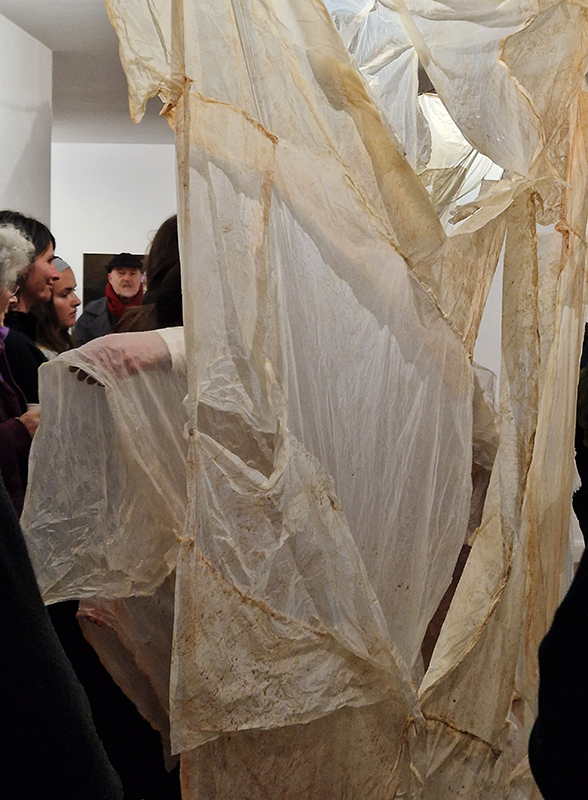
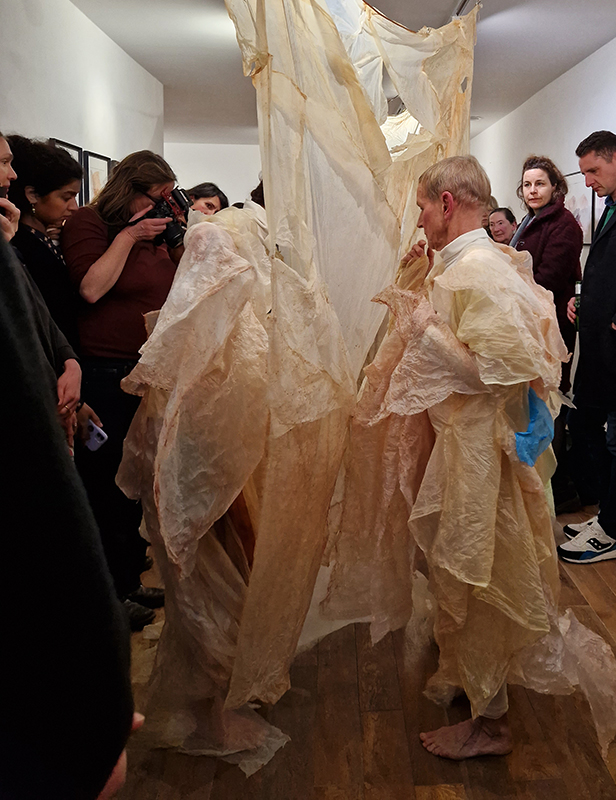
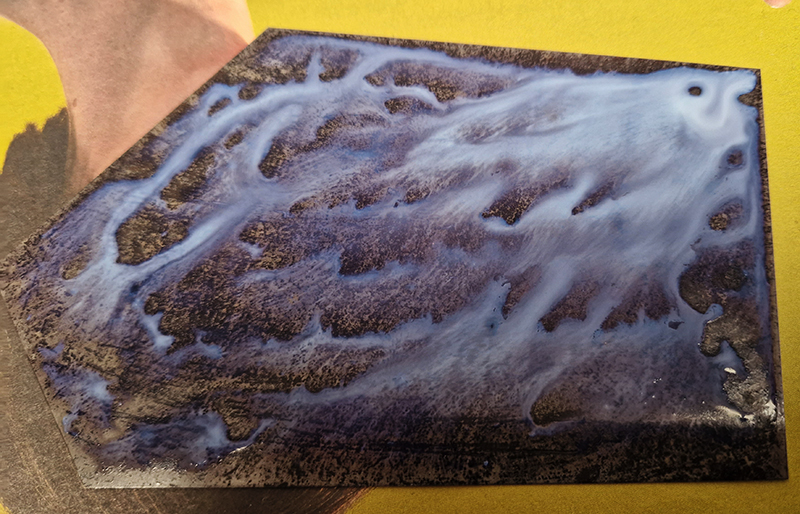
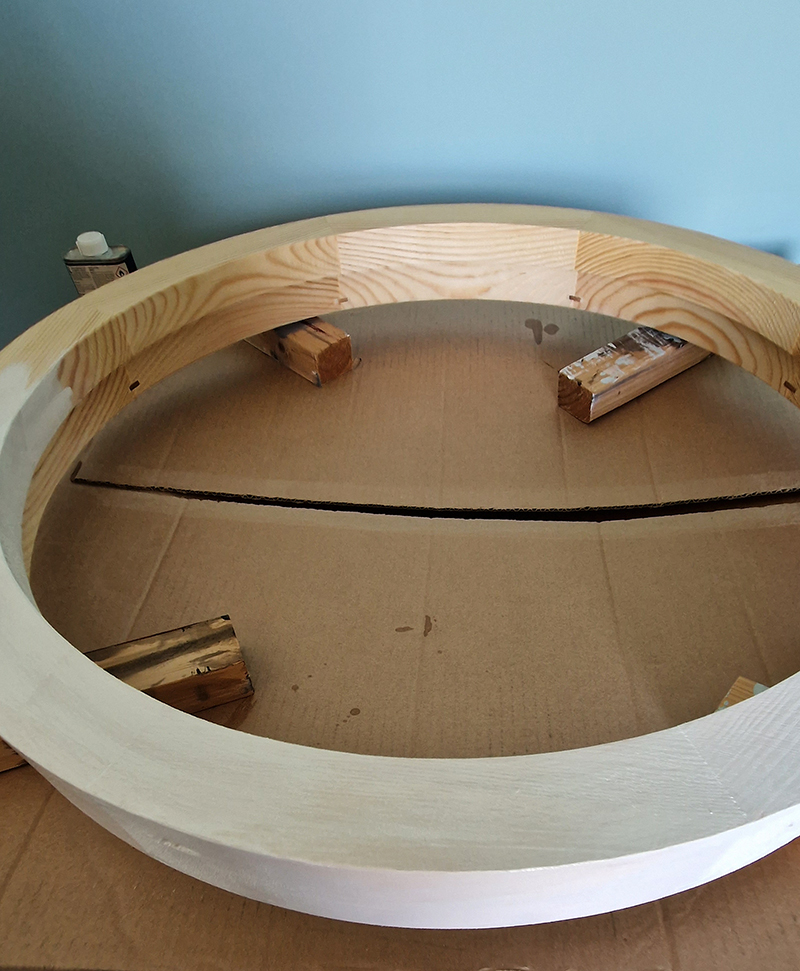
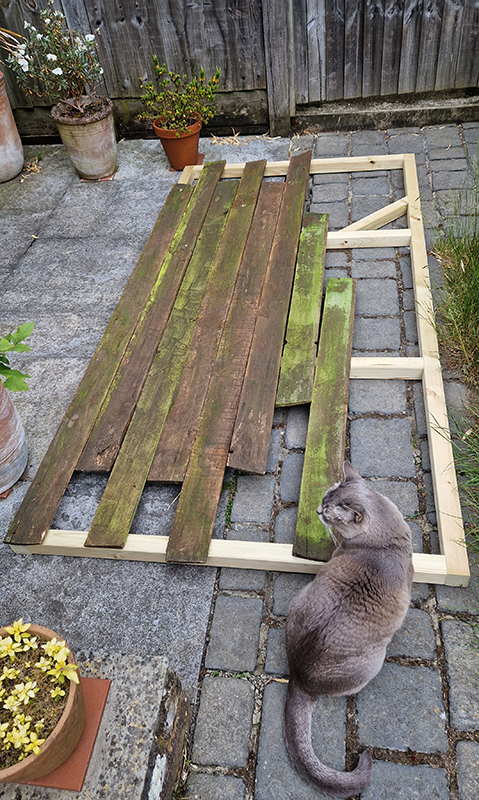
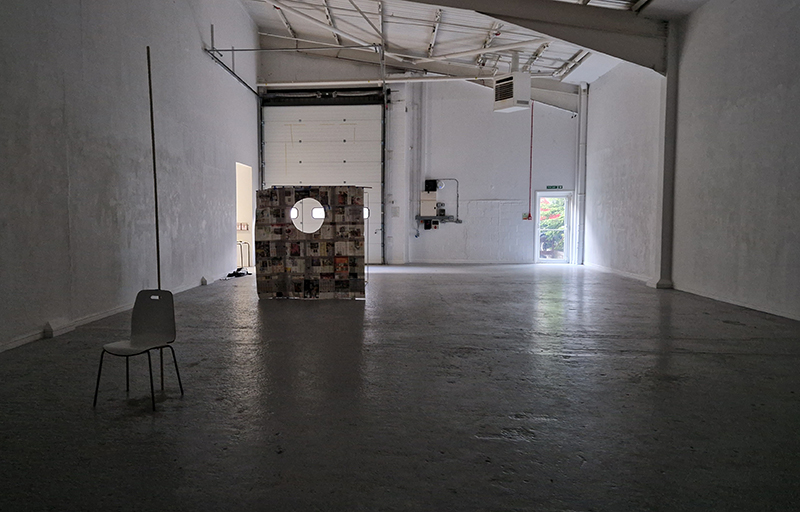
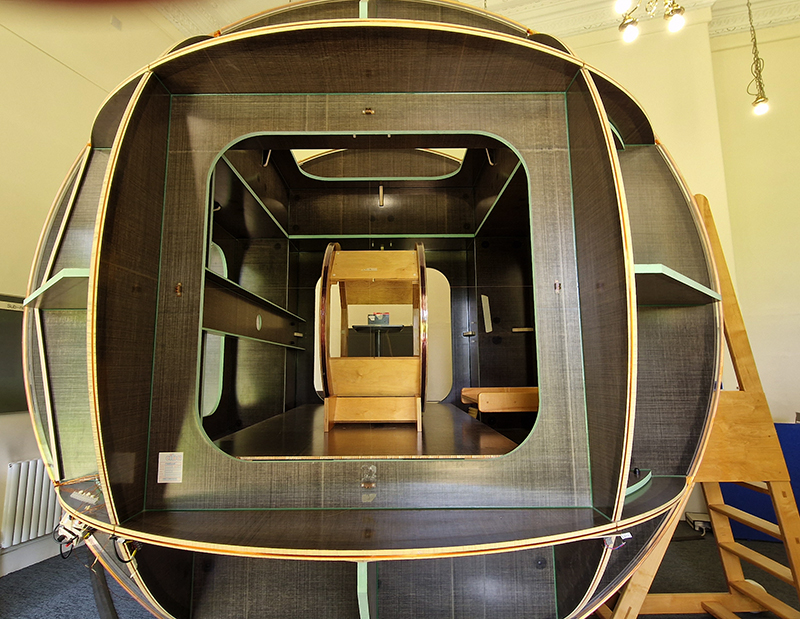
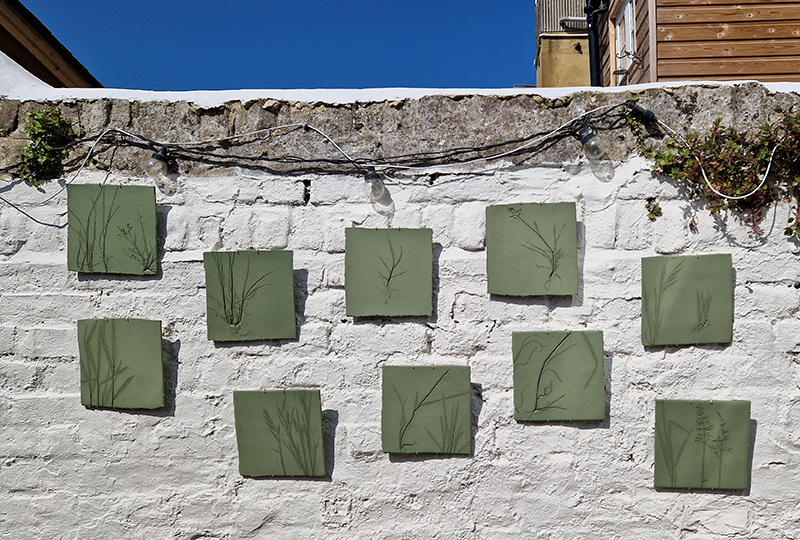
The Absolute Hut – work in progress. This installation is a reimagining of the Absolute Hut at Hartland Magnetic Observatory where monitoring of the Earth’s magnetic field takes place. Topological contours of suminagashi marbling also echo fluid magnetic field lines. Testing scale and alignment in the gallery space. Collecting planks for the north facing wall. Prepping the round window. Suminagashi experiments on different Japanese papers. I want to consider the hut as a sensory hub.








Other exciting news is that APT Gallery have selected a proposal for an exhibition which will take place in March 2024. The exhibition will consider the lifeboat as a metaphor in relation to uncertain times, ecological and social change and shifting landscapes as viewed from the land and the sea. The artists in this group show share an interest in exploring precarity as a site of dynamic transition. I am so happy to be working with these wonderful artists – Rachael Allain, Caroline AreskogJones, Beverley Duckworth, Liz Elton, Kathleen Herbert, Kaori Homma, Anne Krinsky.






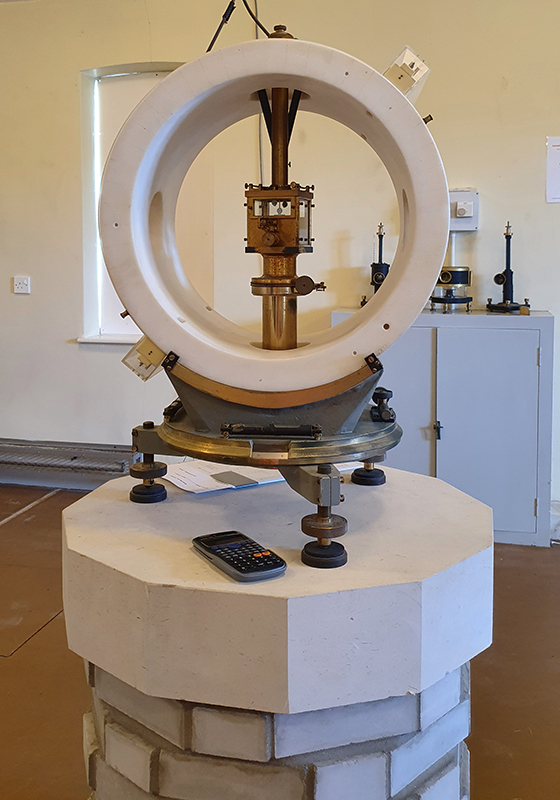
In celebration of World Metrology Day, NPL opened Bushy House and gardens to the public. A chance to see and hear about ever more accurate ways of measuring the physical world. Bushy House was the residence of William, Duke of Clarence (William IV) and his mistress Dora Jordan from 1797, and was offered to the Royal Society by Queen Victoria in 1900 as a location to establish The National Physical Laboratory. The impressive apple tree is from an offcut of one from Newton’s home estate. The magnetic laboratory here is concerned with devising and standardising the instruments used by magnetic observatories such as the one at Hartland that I visited last summer. I saw the 1kg sphere of single crystal silicon, with the smoothest polished surface of any made object and notoriously hard to photograph. The application of a strong magnetic field during the crystal growth process reduces contaminants giving a purer silicon crystal. Developments in technology bring new units and definitions of measurements.







From early concepts of number, patterns in nature (symmetry, branching, spirals, cracks, spots, stripes, chaos, flows, meanders, waves, dunes, bubbles, foam, arrays, crystals, and tilings) magnitude, and form came mathematics, meaning subject of instruction. This has evolved into complex theory from an understanding of negative numbers to imaginary numbers which combined with real numbers have been found necessary to describe quantum mechanics.
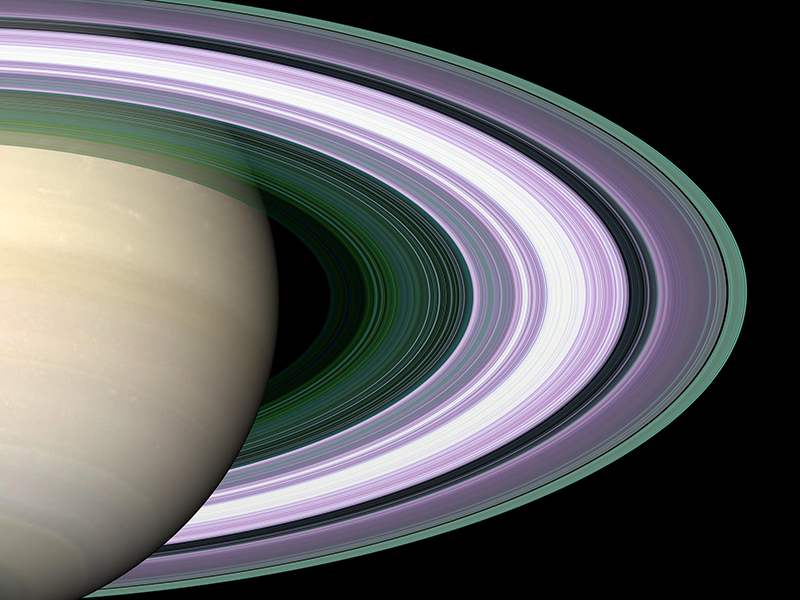
The colour coding of Saturn’s rings according to particle size used radio occultation to determine the different regions. Radio signals were sent from the Cassini spacecraft during orbits which placed Earth and Cassini on opposite sides of Saturn’s rings. This remote sensing technique measures how the radio waves bend around the matter they encounter to assess the physical properties of a planetary atmosphere or ring system. The purple colour indicates regions where most particles are larger than 5 centimeters. Green and blue shades indicate regions where there are mostly particles smaller than 5 centimeters and 1 centimeter. The white band is the densest region where radio signals were blocked preventing accurate representation in this area. The radio observations showed that all rings appear to have a mix of particle size distribution right up to boulder sizes, with several many meters across.
Gallery Visits
It’s Coming From Inside at Bell House, Dulwich. Curated by Sarah Sparkes and Jane Millar. In their thinking about the Impressionist Berthe Morisot, and the exhibitions broader theme of ‘Windows and Thresholds’, the curators see the two different domestic spaces, and the liminal corridors between them, as places expressive of dialogues in both Morisot’s and their invited artists’ works: of confines, dreams of escape, of external inscrutability and internal passion. Exhibiting artists: Fran Burden | Ruth Calland | Helen Carr | Mikey Cuddihy | Janet Currier | Robert Dawson | Andrew Ekins | Liz Elton | Lisa Fielding-Smith | Deborah Gardner | Caroline Gregory | Birgitta Hosea | Mindy Lee | Wayne Lucas | Julia Maddison | Jane Millar | Darren O’Brien | Kim Pace | Sarah Sparkes | Geraldine Swayne
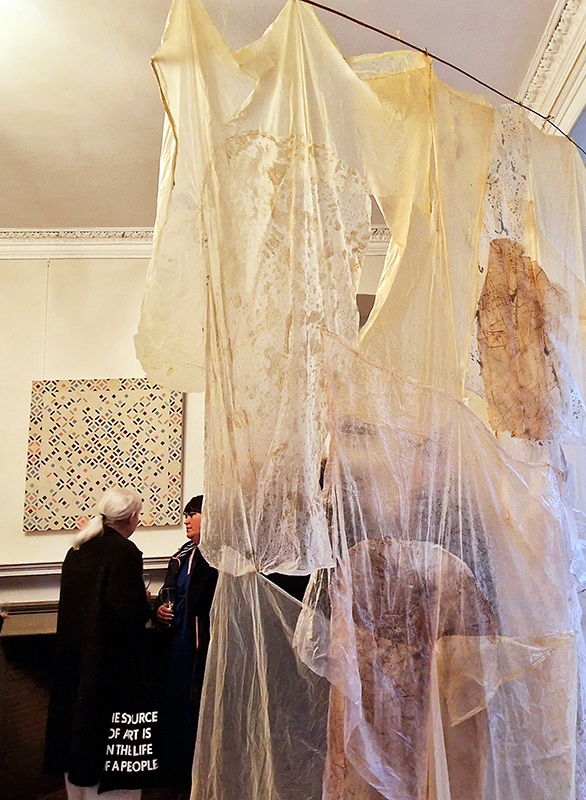
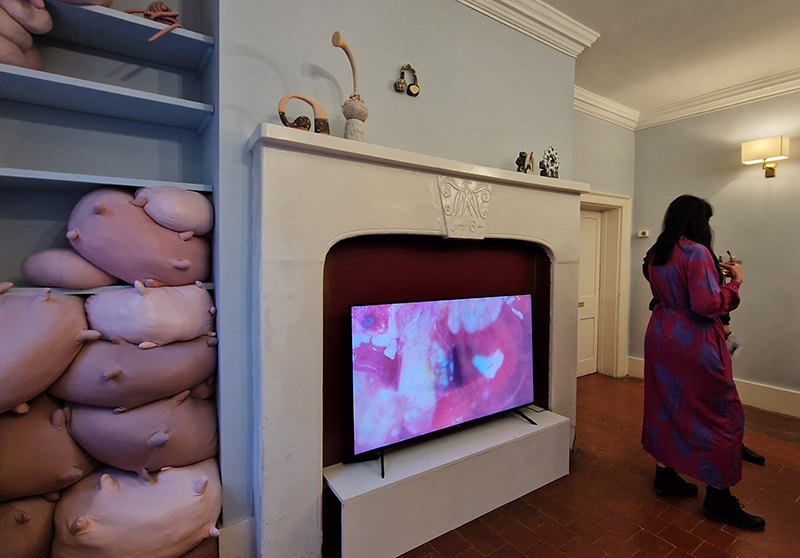
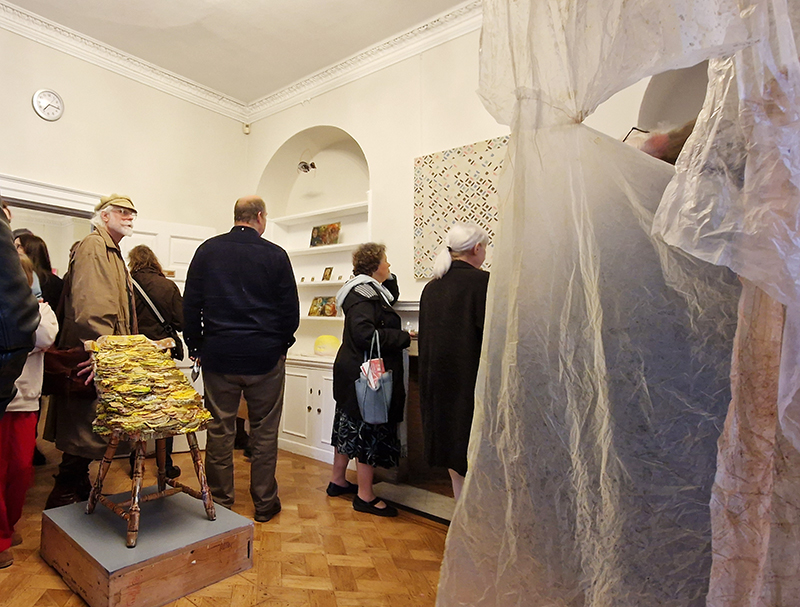





Georgina Sleap Now and here and there together at Cable Depot. A residency undertaken in collaboration with Neil Cheshire, Olive Hardy, Mercedes Melchor, Agnieszka Szczotka, Derek Horton, Farida Youssef and Niamh Riordan. A wonderful installation conjured from simple materials and experimental technology, both analogue and digital that blur the here and there of time and space. Sounds of everyday street noise live from the artist’s Cairo balcony are streamed into the gallery where suspended torches project still slide images onto the wall or inside elongated sculptural forms. A loom for weaving a plain coffin shaped carpet hangs like a hammock next to CCTV recordings of yogic performance while a camera obscura style intervention casts shadows, bringing the local outside in.
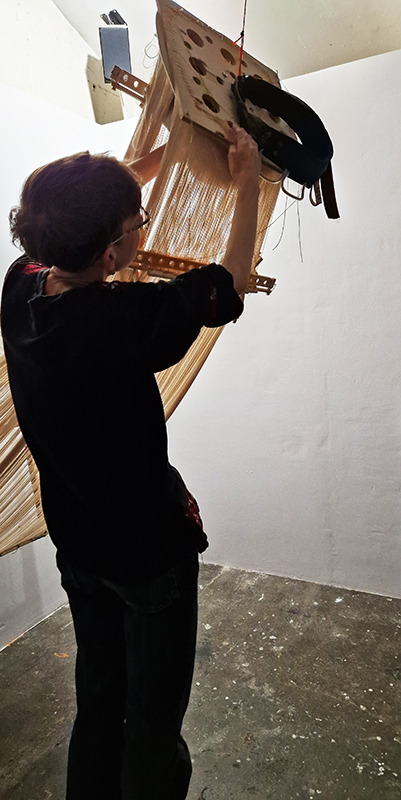
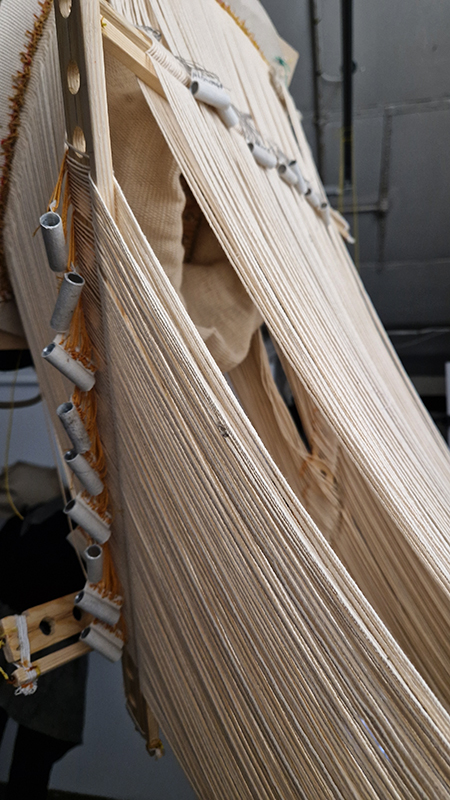
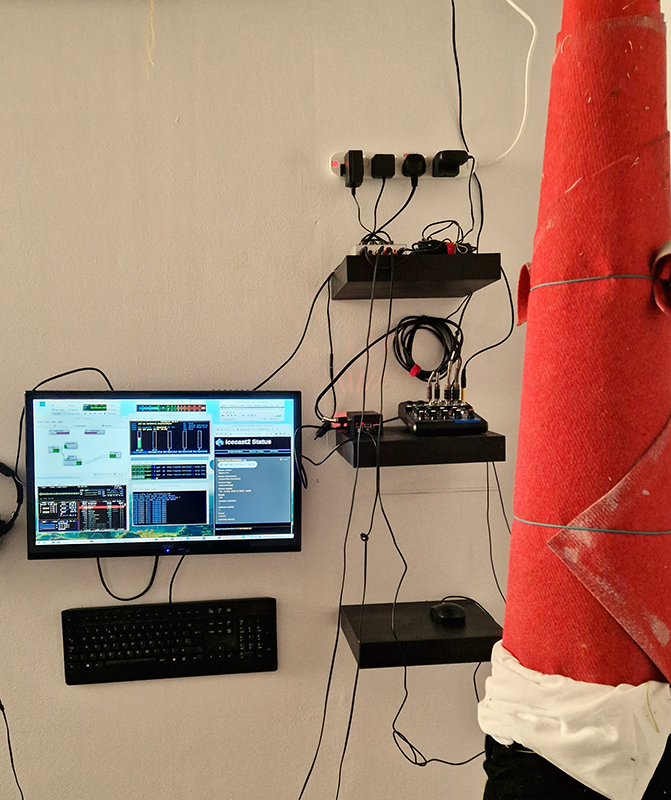
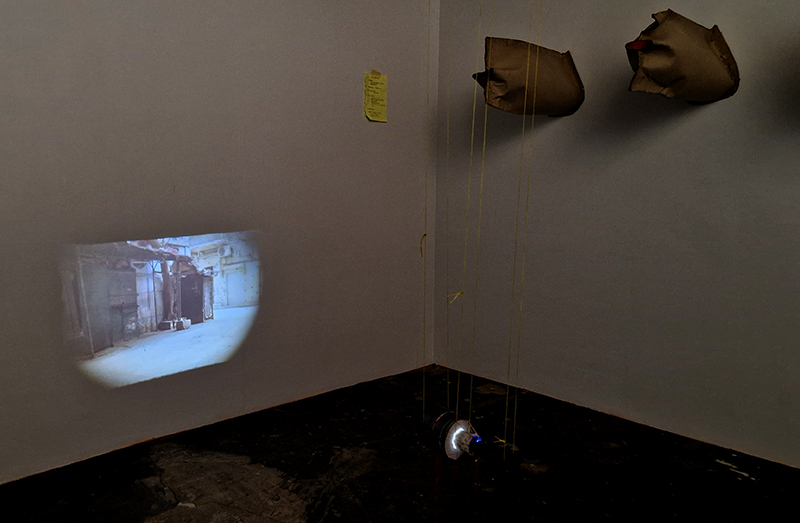







The Shape of Things by Clan, a collective of multidisciplinary artists – Caroline Penn, Liz Lowe, Ashley Goldman, Nicky O’Donnell at Gallery 3, a delightful Georgian property in Margate. The artists examine issues of loss, both personal and environmental, that are balanced by ideas of hope and regeneration. A nice use of recycled and sustainable materials including netting from fruit and cable ties.






Beatriz Milhazes at Turner Contemporary. Perfect for a summer’s day at the seaside. Exuberant.





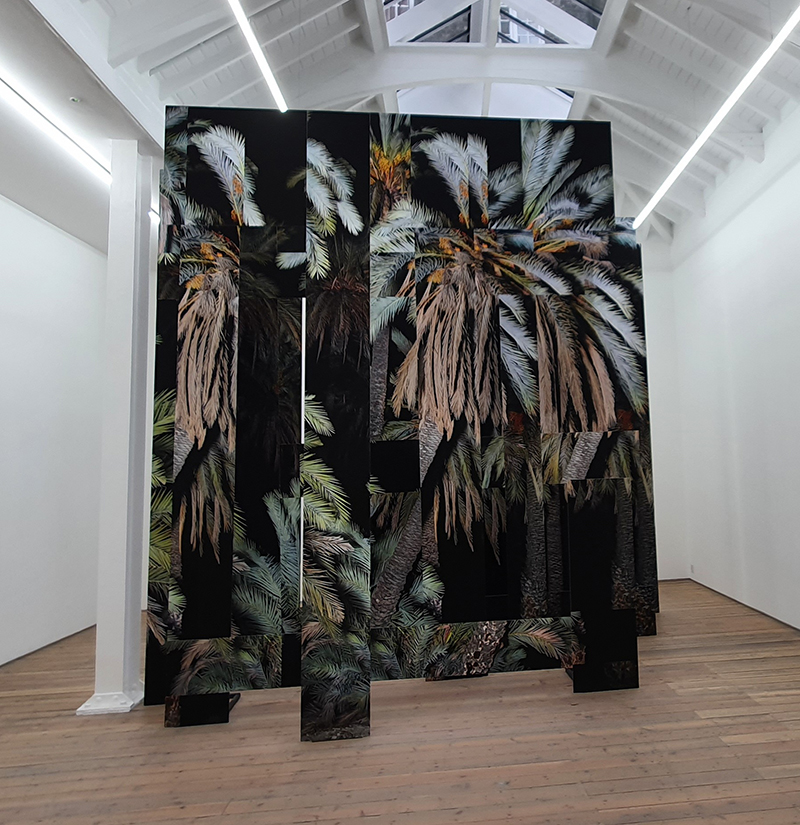
Opening event for the new photography centre at the Victoria and Albert Museum. Interesting to hear about the process Noémie Goudal undertakes to create her ambitious illusionist photographic sculptures such as Giant Phoenix VI from the series ‘Post Atlantica’ which has been acquired by the Victoria and Albert Museum for their photography collection, housed in a new dedicated gallery. This work was inspired by her interest in shifting landscapes, the movement of tectonic plates and how landmasses join and separate over millennia. There was also the chance to see her video Inhale Exhale along with behind the scenes footage of her technical team and the scale of the resources involved. Tarrah Krajnak has also had work acquired by the museum and read some of her poetry at the event. Her interests are also in discontinuity, severance and cataclysmic events but on a human scale. Being born from an act of violence she puts her own identity forward to explore power relationships.




Reading
I have really enjoyed the breadth of information delivered so beautifully by Hettie Judah in her book Lapidarium – The Secret Lives of Stones. The character described and stories told of each geological layer, formation, rock and gem brings to life a world often perceived as static, perpetual and dry. This book is a great resource and has been particularly appropriate for me in the run up to the exhibition A Stone Sky with Julie F. Hill as we explore the intimate connections between the rocky planet earth and space.