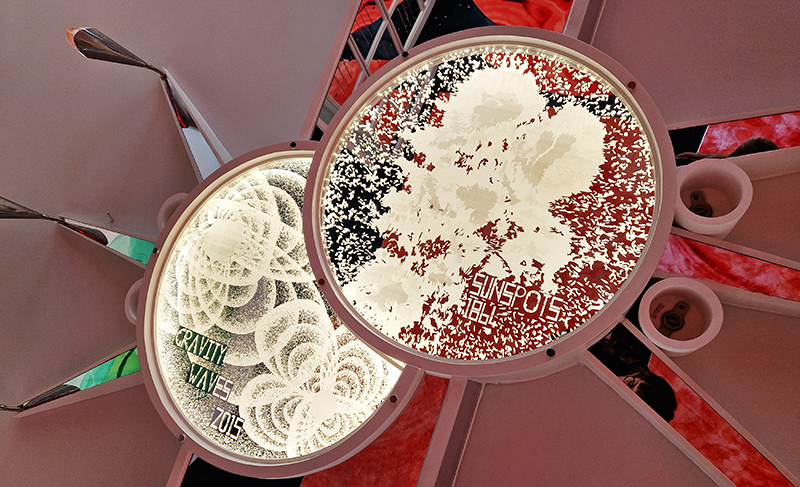
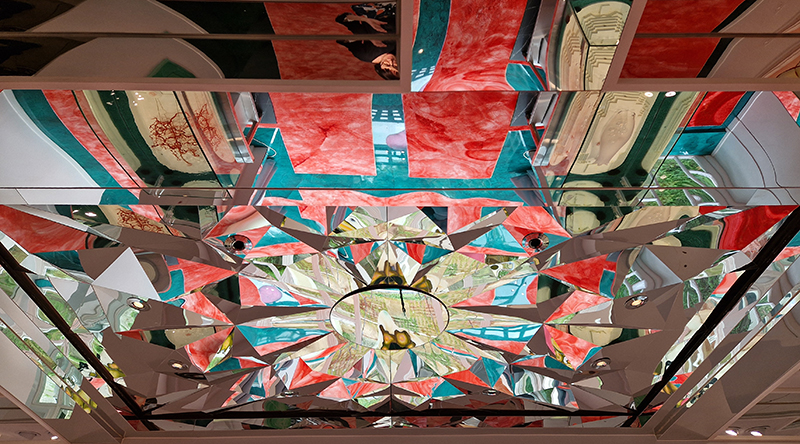
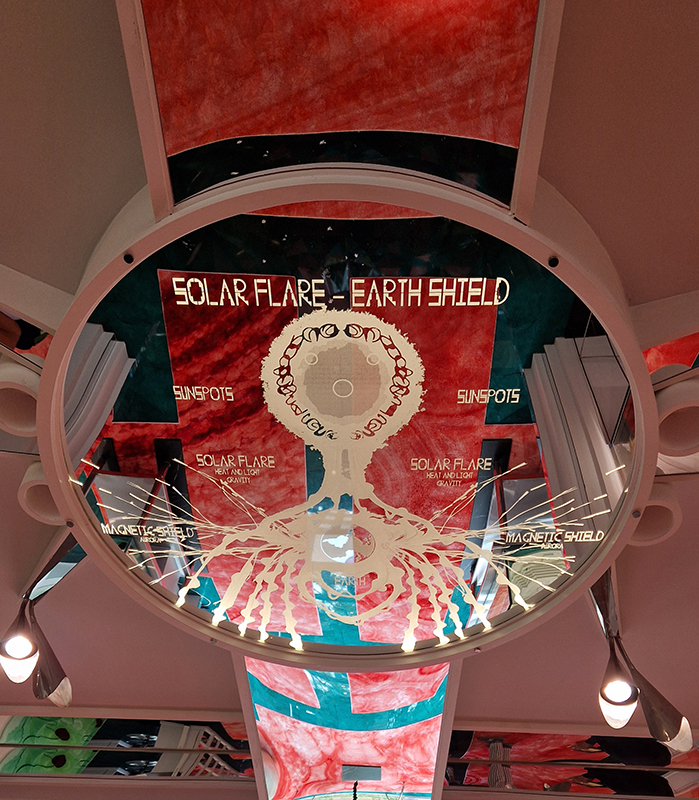
The ‘Art, Science and Creativity’ exhibition at Liverpool’s spectacular Central Library continues. The exhibition is inspired by statements from Albert Einstein, highlighting the fact that creativity is central to explorations in both art and science. As we wonder, and attempt to understand the universe and ourselves, categories can, and perhaps should, become blurred. Distinctions can be both valuable and problematic: ‘art’ versus ‘science’, ‘nature’ versus ‘human’, ‘natural’ versus ‘supernatural’, ‘material’ versus ‘spiritual’, ‘secular’ versus ‘religious’ and so on. And as the great science-fiction writer Arthur C Clarke said “Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic”.
I am very happy to have two unique books included in the exhibition. In/Out and Unbound.
Liverpool Book Art and Fevered Imagination are collaborating to create a video loop of all the artworks, enabling audiences to get a fuller appreciation of the artists’ creativity than allowed by the use only of display cases. Fevered Imagination is a website dedicated to Artists Books, through which works from the exhibition can be bought.







I am delighted to be invited by Serendipity Arts Foundation to show Cosmic Chiasmus: crossing the universe at Serendipity Arts Festival in Goa later this year.

Serendipity Arts Foundation is an organisation that facilitates pluralistic cultural expressions, sparking conversations around the arts across the South Asian region. Committed to innovation and creativity, the aim of the Foundation is to support practice and research in the arts, as well as to promote sustainability and education in the field through a range of cultural and collaborative initiatives. The Foundation hosts projects throughout the year, which include institutional partnerships with artists and arts organisations, educational initiatives, grants, and outreach programs across India.
Serendipity Arts Festival is one of the largest multi-disciplinary arts initiatives in the South Asian region. It spans the visual, performing, and culinary arts, whilst exploring genres with film, live arts, and literature. Besides the core content, which is conceptualised by an eminent curatorial panel, the Festival has various layers of programming, in the form of educational initiatives, workshops, special projects, and institutional engagements. Through active conversations between the artistic community and the urban, social landscape, the Festival continues to evolve around the mandate of making the arts visible and accessible. The Festival is driven by a spirit of collaboration, hoping to inspire new perspectives and fresh aesthetic encounters. This labour of love is a cultural experiment that also addresses issues such as arts education, patronage culture, interdisciplinary discourse, inclusivity, and accessibility in the arts.
Other exciting news is that Julie F. Hill and myself are working together again on a new project. Following on from our ambitious duo show A Stone Sky at Thames-side Studios Gallery (Nov 23), we will be curating and participating in an exhibition next spring, exploring themes of stone consciousness and human-mineral encounters.

In the studio I have been working on a proposal for the Moon Gallery. Moon Gallery is an international collaborative artwork and a gallery of ideas which aims to set up the first permanent museum on the Moon. Moon Gallery will launch 100 artefacts to the Moon within the compact format of a 10 x 10 x 1cm plate on a lunar lander exterior panelling as early as 2025.
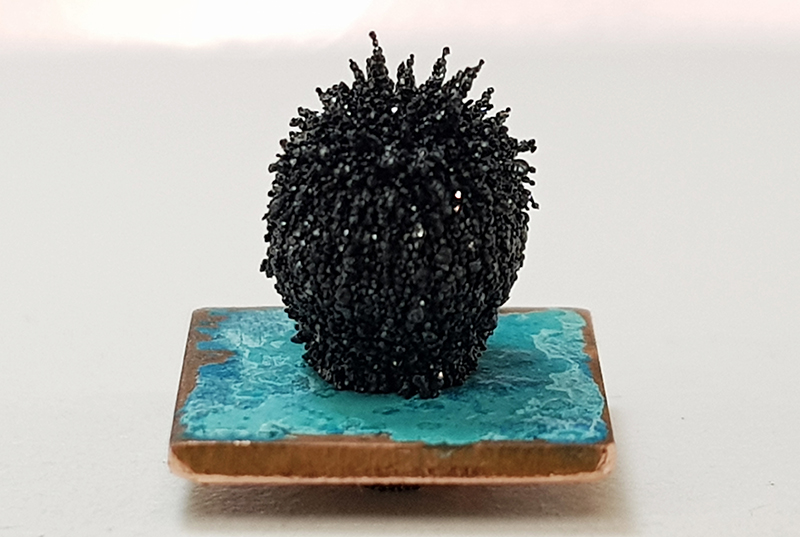


Each sculpture has to fit within a 1cm cube, which is quite challenging. My proposal is a 5mm spherical magnet sparkling with black volcanic sand on a 1cm square of patinated copper. Space exploration means leaving the protective shield of Earth’s magnetic field, placing astronauts and technology at risk from increased levels of harmful high energy particles. This artwork is a small realization of a magnetic field offered as a symbol of safe passage to those venturing beyond our home planet and protection of Earth’s magnetosphere. The black volcanic sand used in this work is naturally magnetic, making visible the force that emanates from the core of the magnet. The patination colour reflects on the astonishing view of our blue planet from the moon and the importance of water to sustain life. The title Core Values, makes reference to the molten core necessary for a planet to generate a magnetic field as well as the ethical principles and beliefs that guide humanity in a positive spirit of peaceful cooperation for the benefit of all. The work operates as a motif for what is in the heart of a body, rocky or otherwise. It also celebrates the beauty of the elements and natural forces that together inspire the human imagination and makes the cosmos so exciting to explore.
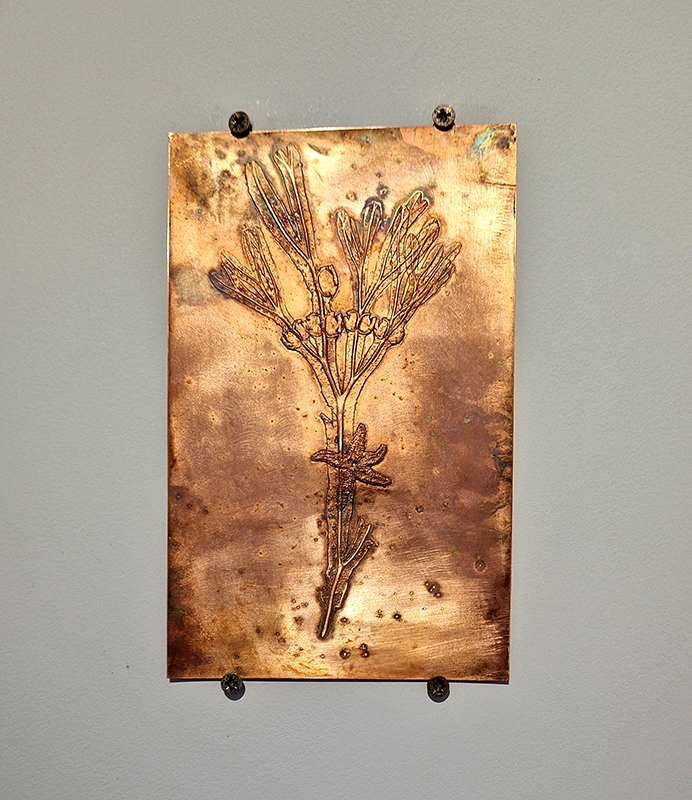
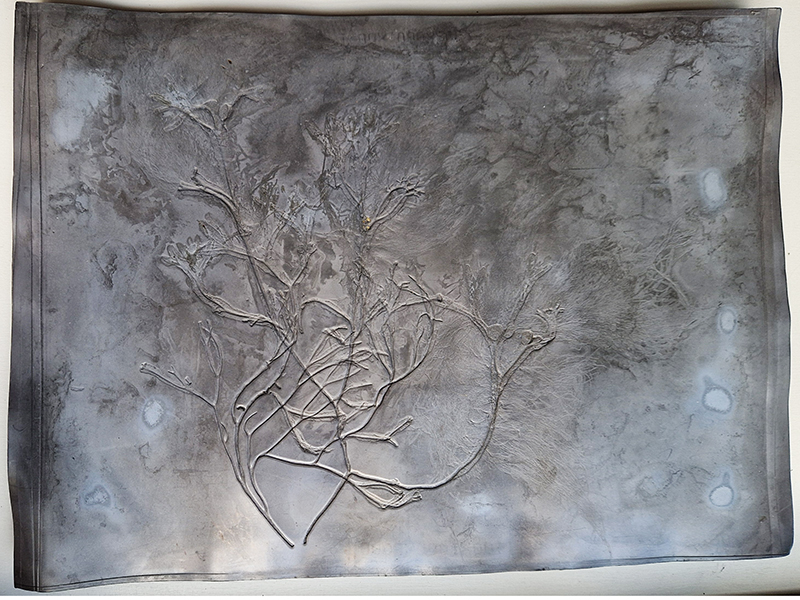
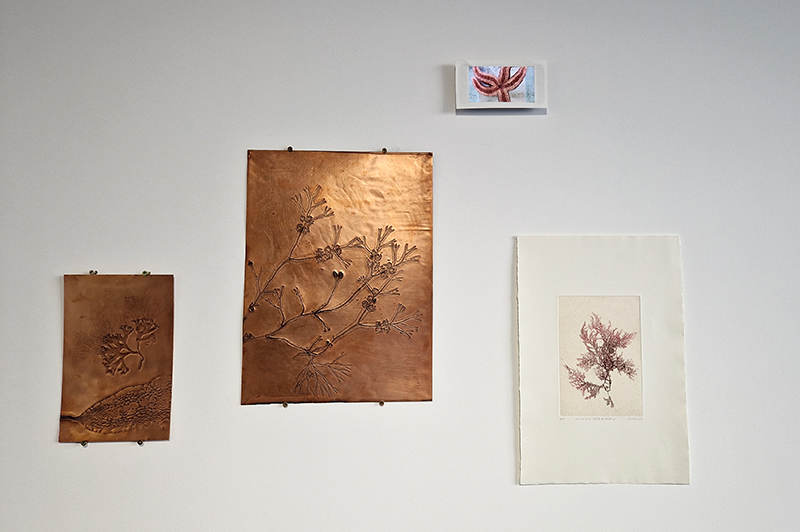
I have been sorting out the copper contours from The Absolute Hut (of action potential) as I couldn’t store this work, it had to be dismantled. The copper will be reused in future work.
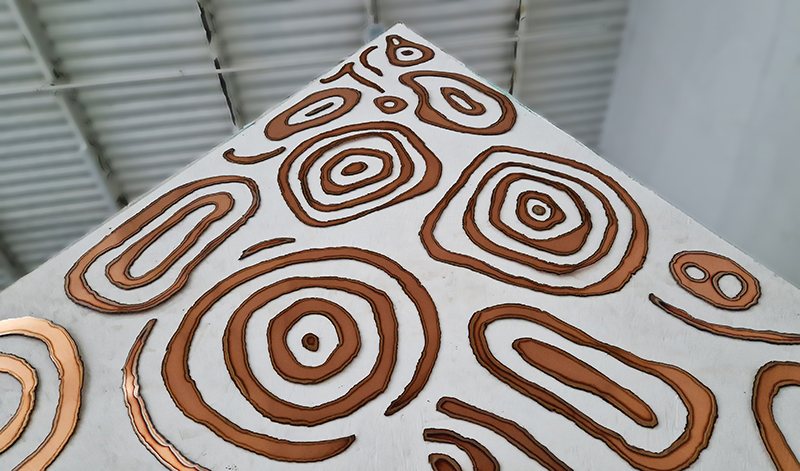


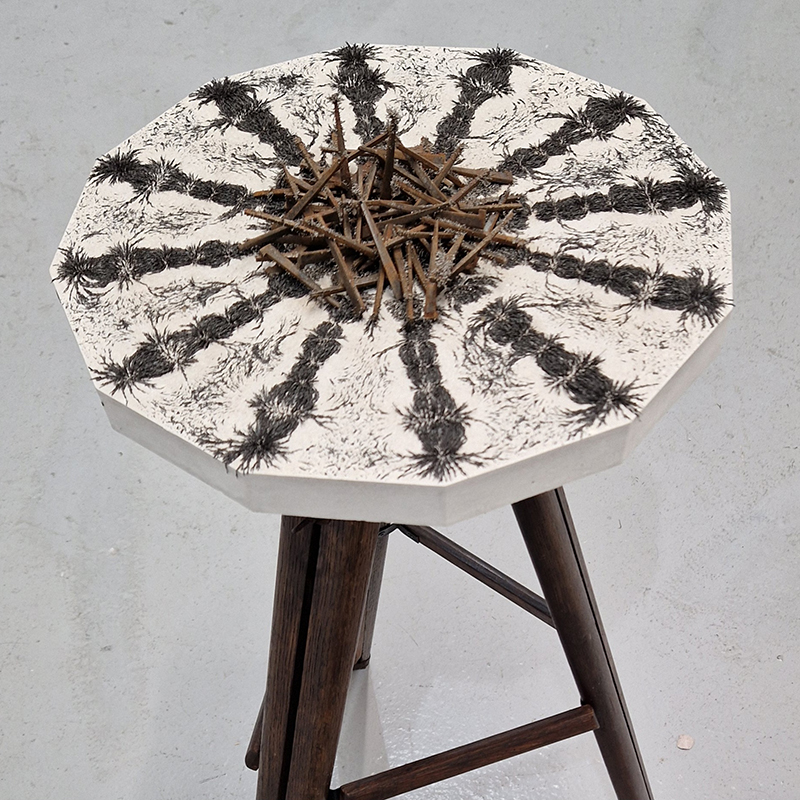
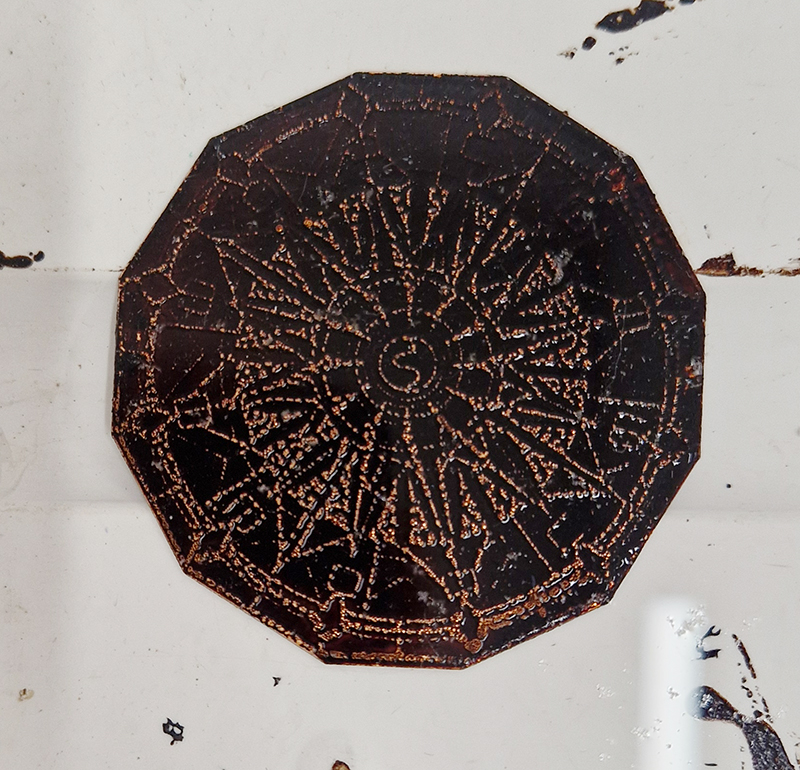
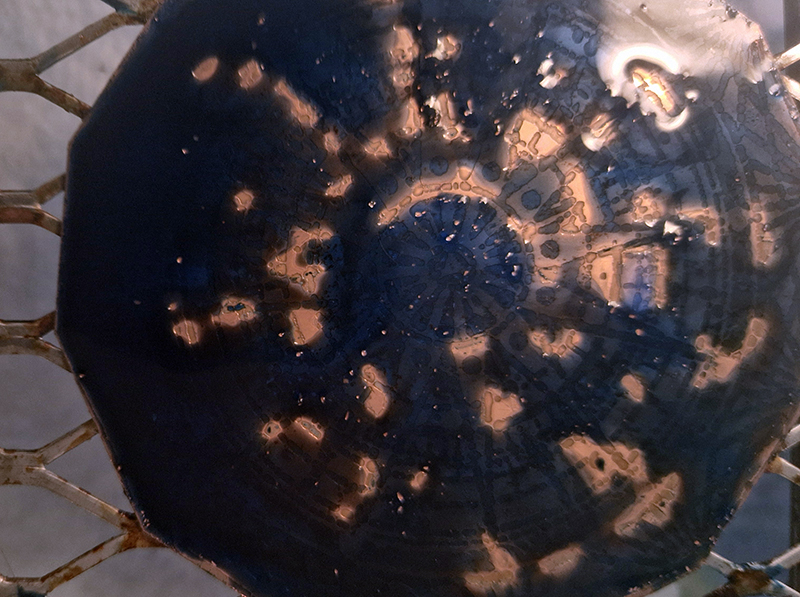
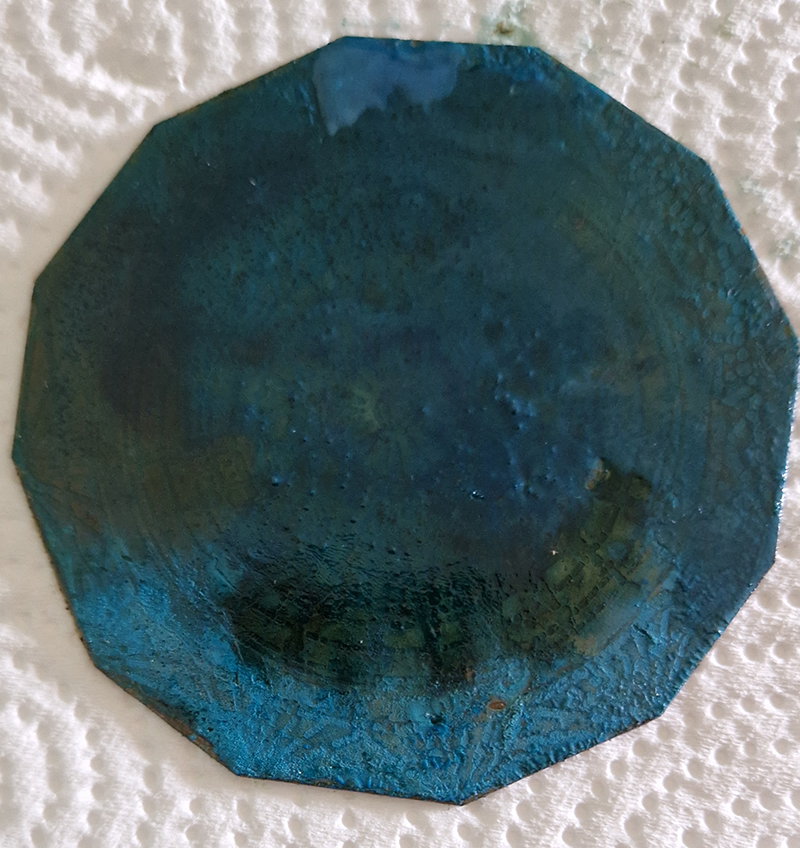
I am making a new concrete tablet for Instruments of the Anemoi series with more detailed compass rose inspired copper insets. The copper is guillotined to shape and screen printed with a sugarlift solution.
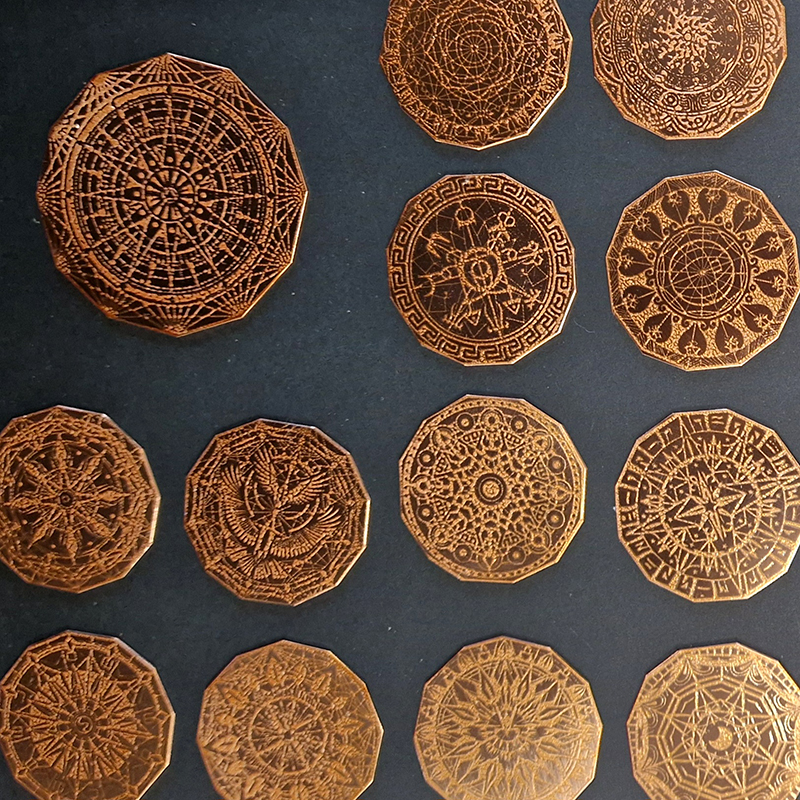
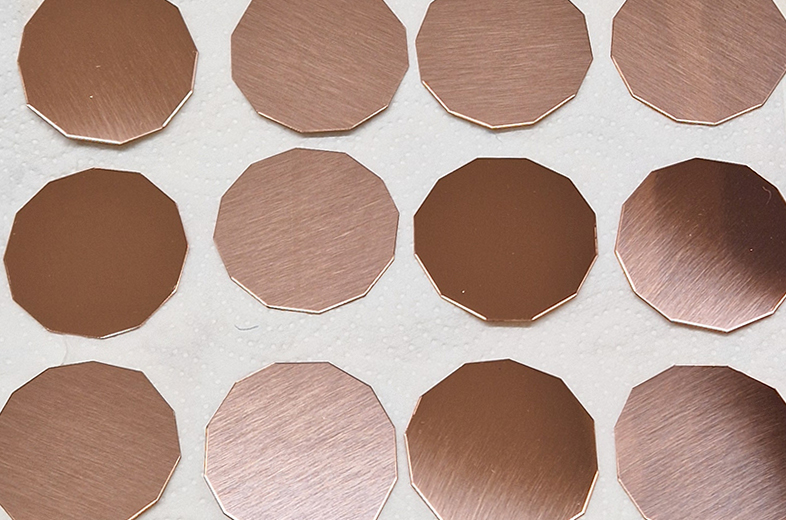
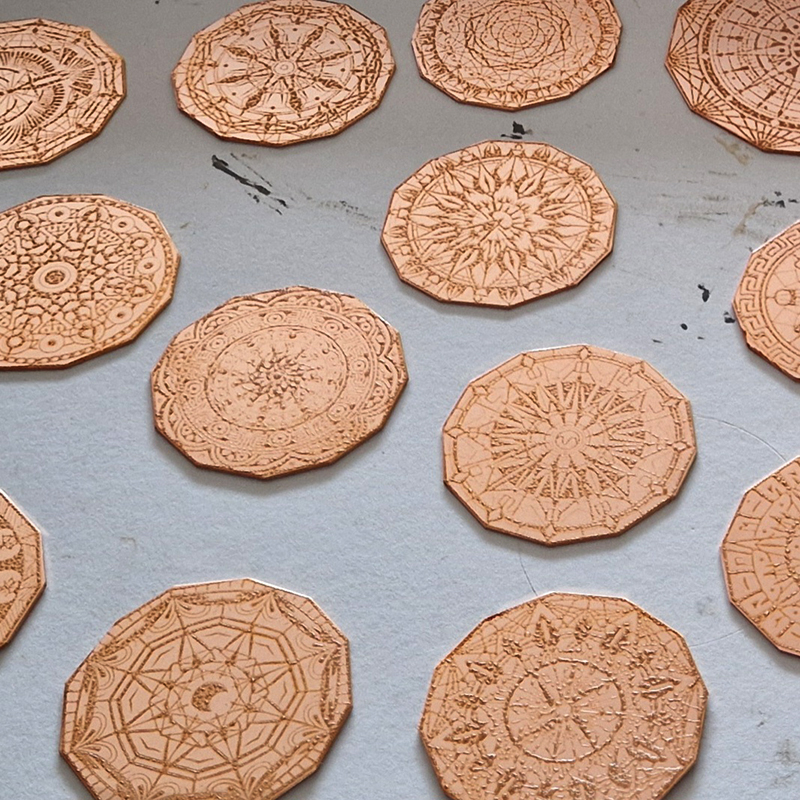



The pieces are then dipped in bitumen and left to dry before putting in a bath of warm water to dissolve the sugar solution, leaving the design ready to be etched.
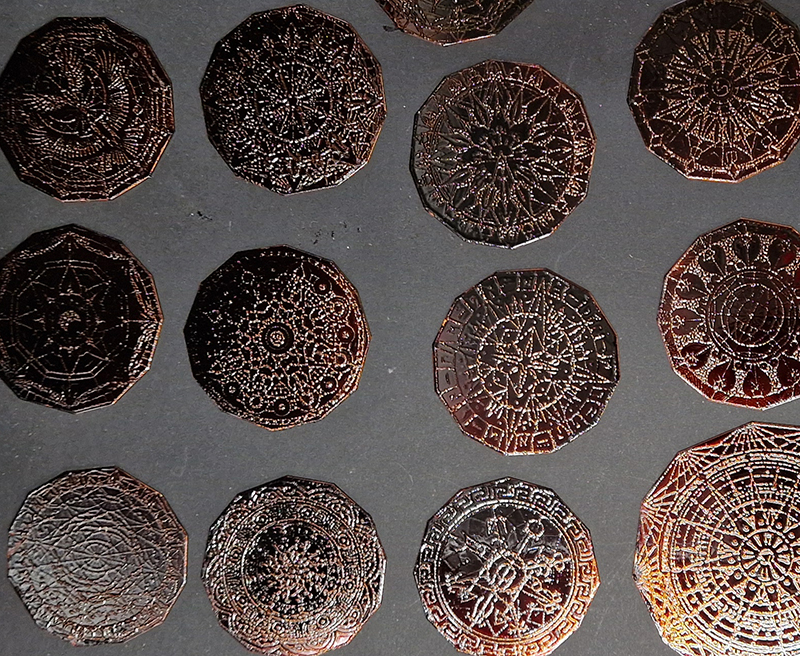
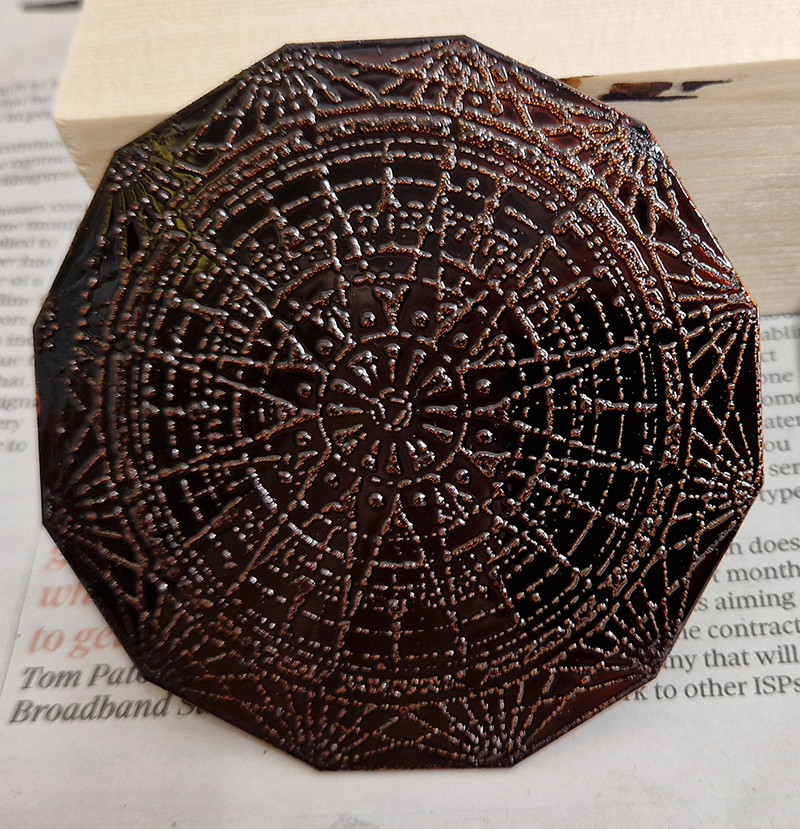
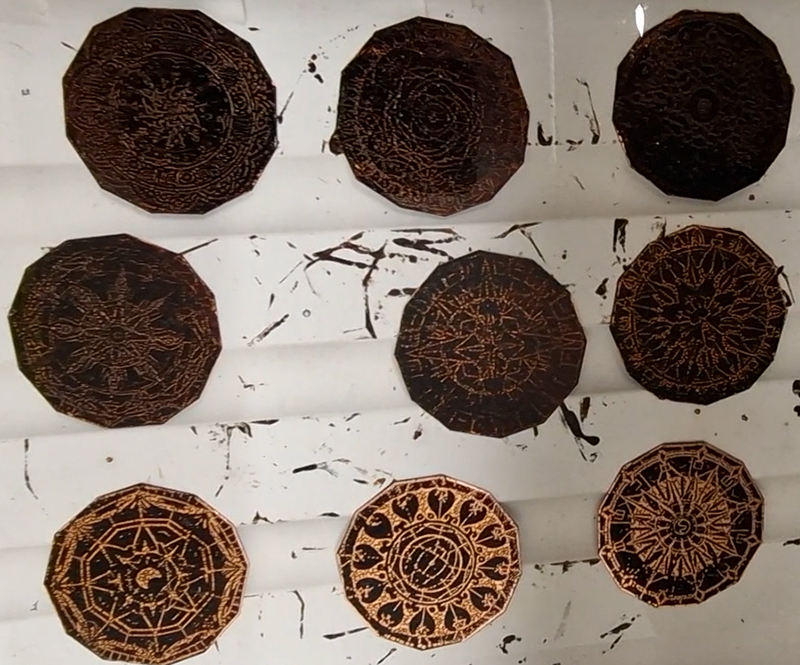






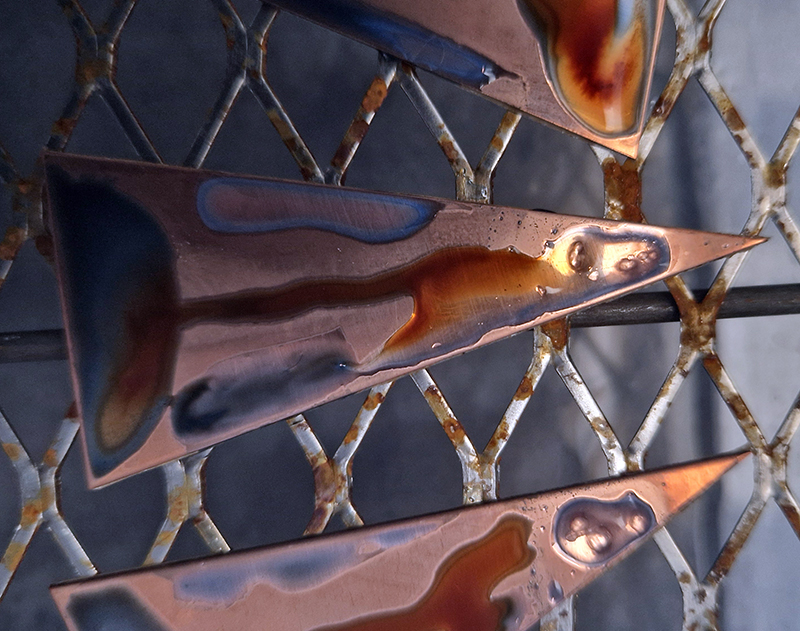
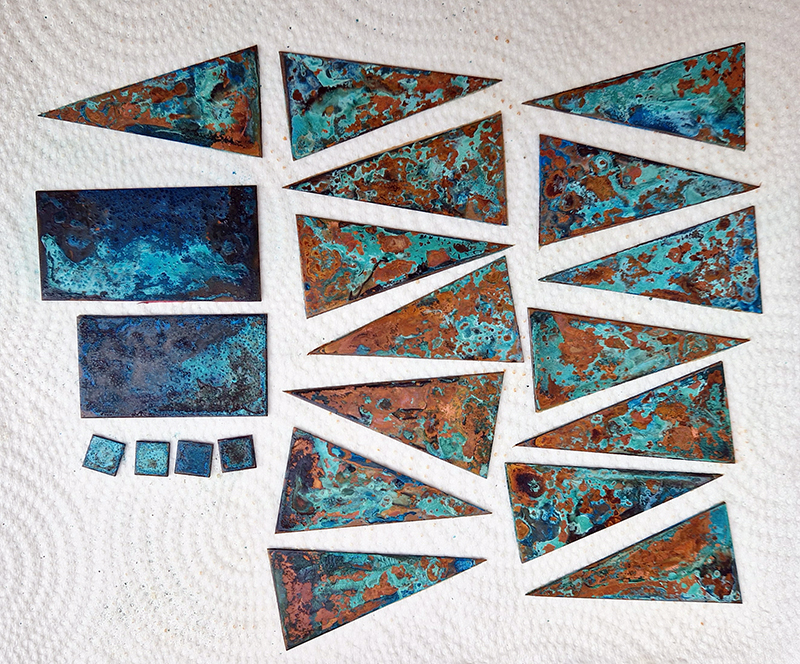
I also cut some copper shapes to patinate, painting the copper with salt and vinegar and soy sauce before fuming in an ammonia bath. I love how the colours change throughout the process.





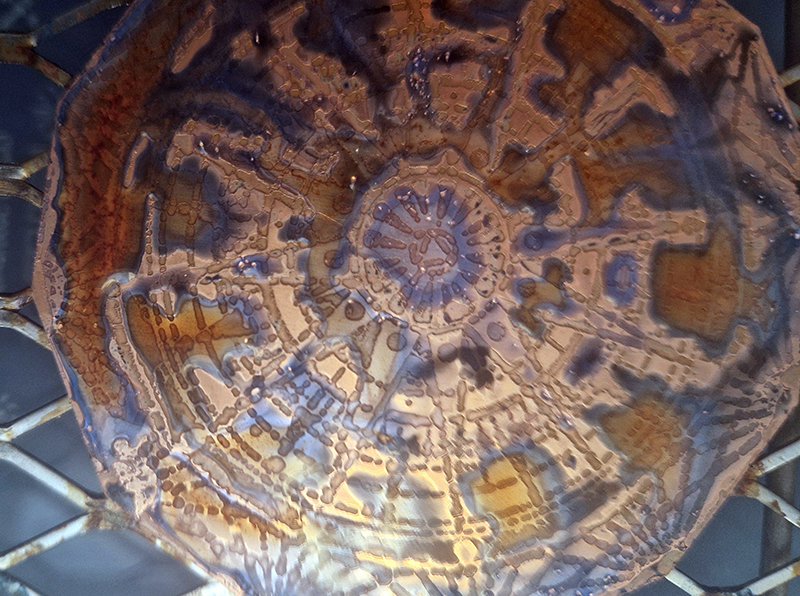
I was going to patinate the dodecagon shapes as well but in the test I did, I lost a lot of detail, so these will just be inked and left.



Gallery Visits
Charmaine Watkiss showing her beautiful drawings full of symbolism in Hard Graft at Wellcome Collection. The exhibition explores the impact of work on health and her works celebrate the ancestral herbal knowledge of medicinal and edible plants and fruits that carry powerful healing properties.
These were used to secretly cure illnesses and prevent diseases as an act of survival and self-dependency, distinct from Western medicine. The connection between herbal healing and African spiritual practices is represented by cosmological symbols discreetly tattooed on the women’s bodies. Natural dyes – such as Jamaica’s Blue Mountain coffee and indigo – and materials such as brass and raffia palm embed historical knowledge in the fabric of the works. This knowledge is preserved, yet concealed, by the figures who avoid the viewer’s gaze.

The London Group Stillness in Movement at Bermondsey Project Space. Taking three evocative lines from Four Quartets by T S Eliot as a starting point for this group show. Images – Carol Wyss, Sandra Crisp, Genetic Moo and Beverley Duckworth.
‘Not known, because not looked for
But heard, half heard in the stillness
Between two waves of the sea’




Rona Lee Lithic Entanglements at Sedgewick Museum of Earth Sciences. A considered intervention in the Whewell Mineral Gallery to ‘bring the dirt back in’, making evident the scarred landscapes, physical extraction processes as well as the social strata of those involved in procuring such a collection. There is no denying the allure of minerals and gemstones and the work here captures the beauty of the rocks while also reminding us of the ravaged Earth left scarred and depleted.
‘A Modern Lapidary a video work, back projected through one of the free-standing cases, animates mid-century scientific photographs of minerals, altering our perception of the samples within as ‘dead’ matter. Elsewhere, in An Extractive Index, digitally collaged photographs of geological field trips are laminated on to the glass, inviting reflection on the social and environmental relationships which these reveal.’
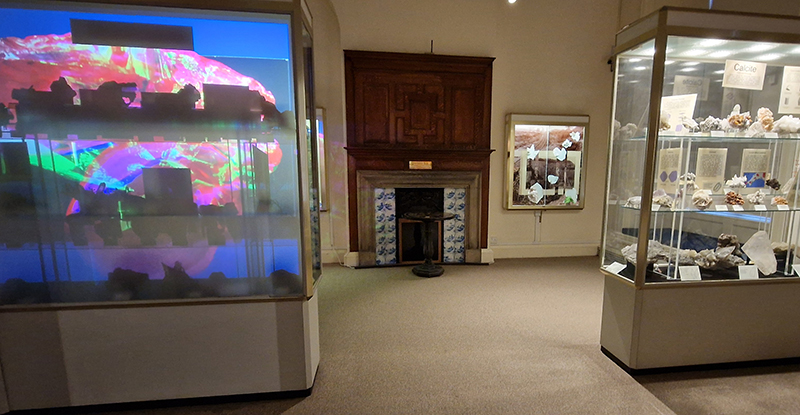
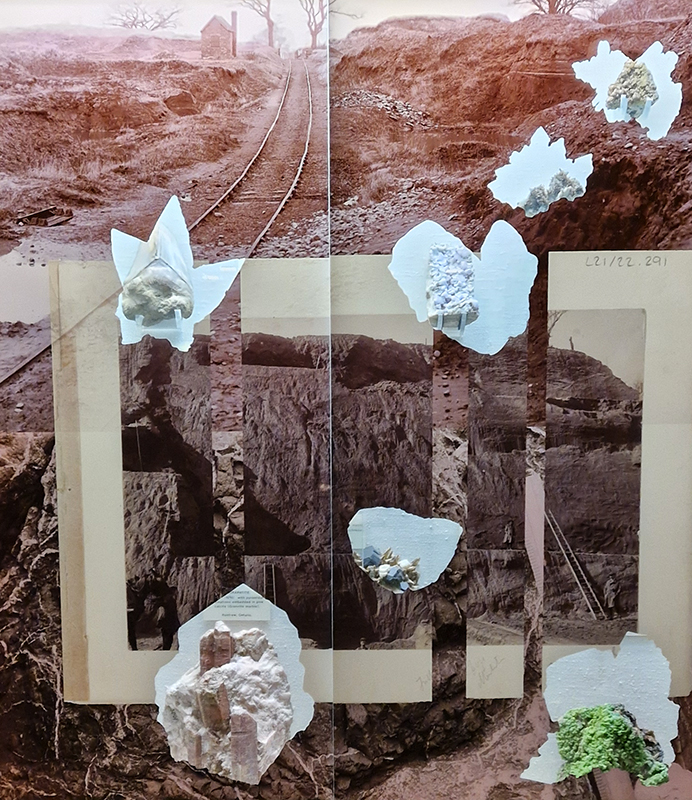






The Museum itself was also fascinating to look round and after Rona’s artist talk we were treated to tea in the The John Watson Building Stones Gallery which houses the most complete collection of stones used in construction.







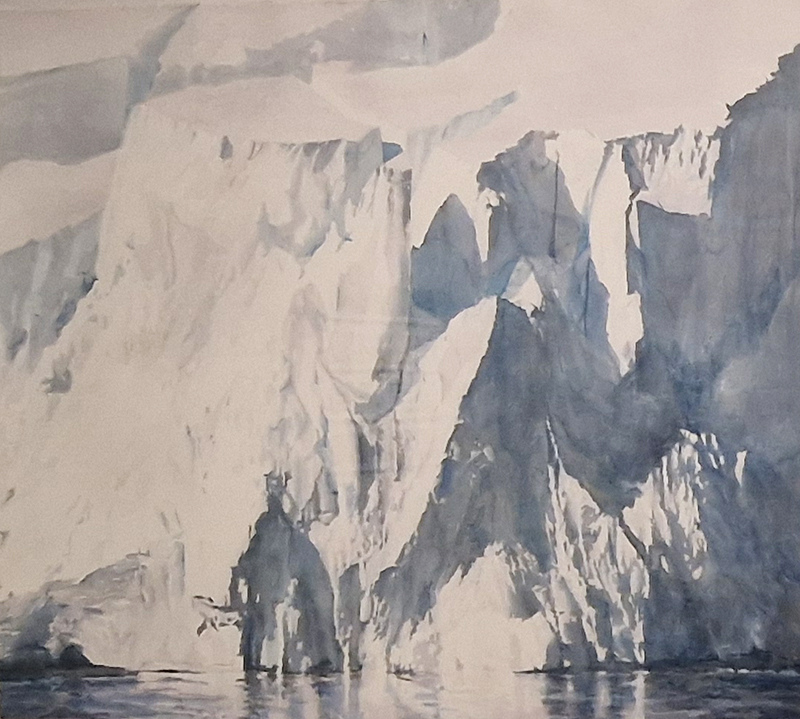
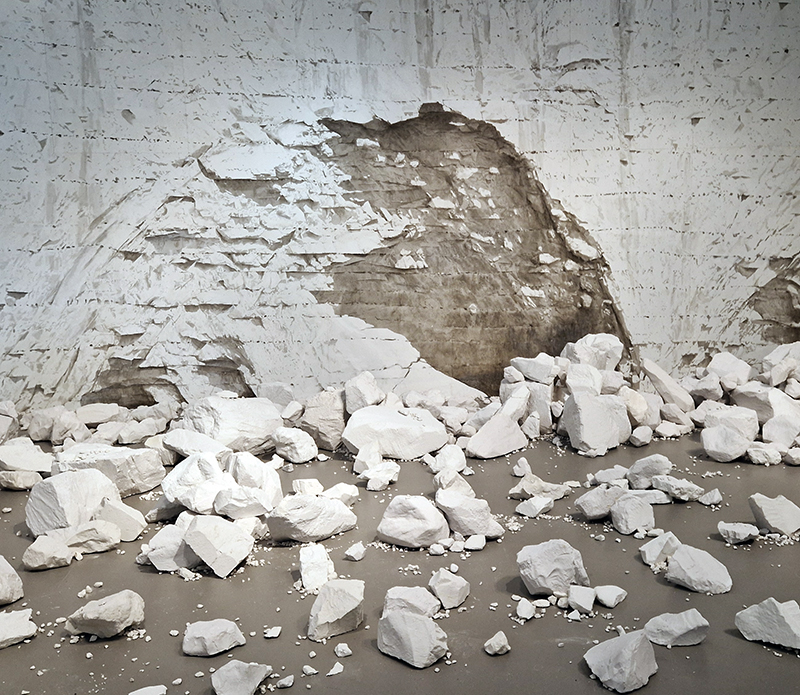
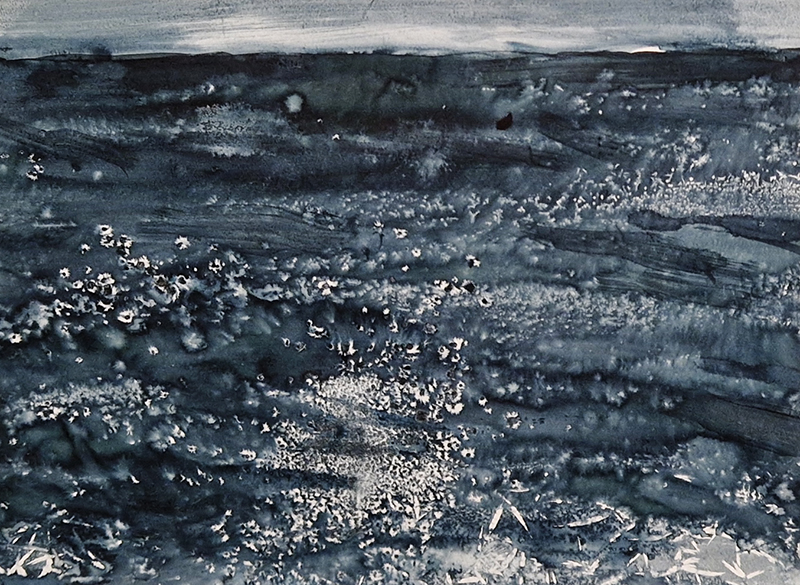
Emma Stibbon Melting Ice | Rising Tides at Towner Eastbourne. A day trip to the see this remarkable body of work so thoughtfully curated. The pale majesty of ice or chalk cliff faces, fragile against pounding seas that Emma witnesses in both the polar and local Sussex coastlines are captured so poignantly. These are portraits of great bodies under stress. Close up, edges and lines break down into fluid, watery strokes, a diaphanous translation of the fast painterly sketches made in often gruelling conditions. Wonderfully immersive, through scale and placement, and the understated palette of deep muted greens and blues, almost blacks and luminous whites which draw the viewer into the landscapes.
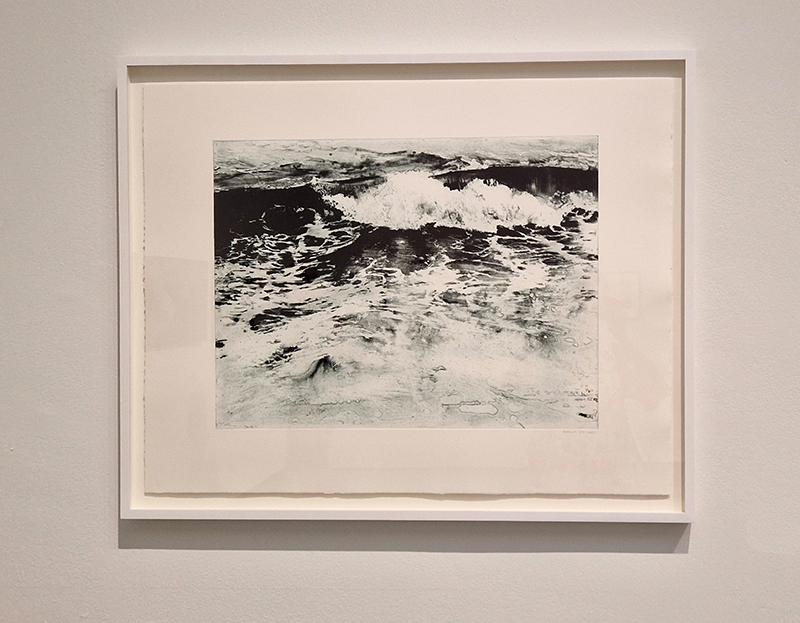
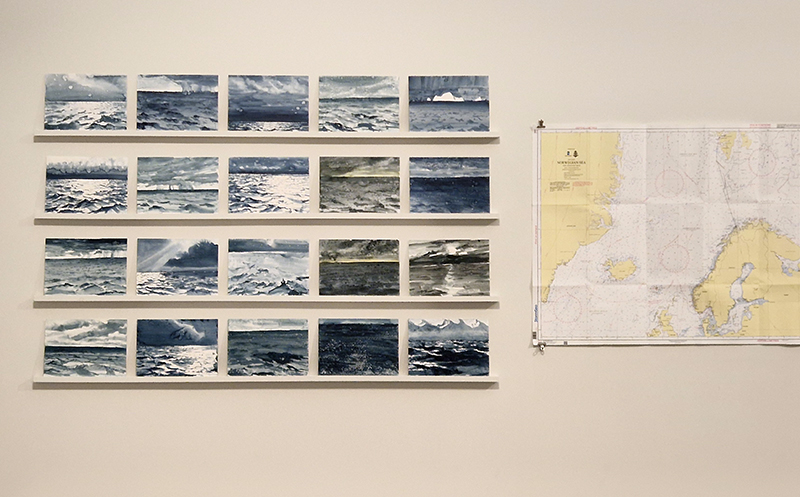
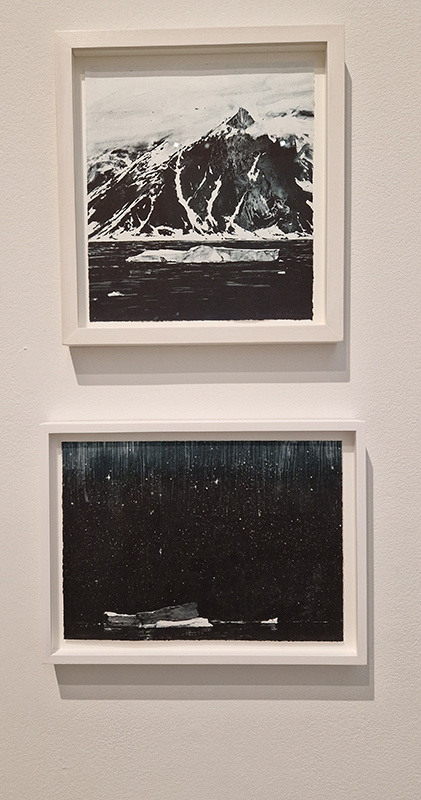










Listening
Sideways – A New Frontier. A four-part podcast about the ethics of space exploration with former NASA astronaut Nicole Stott, new astronaut Ed Dwight, Space Philosopher and author Frank White, Anthropologist of Space and Religion, Deana Weibel, Professor of Religion at Knox College Robert Geraci and former ISRO scientist, Jijith Nadumari Ravi.
Astronauts and space tourists often cite the overview effect as a transformative experience offering the perspective to see a shared planet with no borders. Some however, experience the ‘ultraview’ effect which is the overwhelming and disorienting knowledge of the magnitude of the universe.
BBC Inside Science Podcast. How much of a risk is space junk? As we send more and more metal in the form of satellites up into space, scientists are warning it is becoming more of a risk both here – and up there.
Much space junk comes from defunct satellites. There are plans to launch 60,000 more satellites by 2030. It is estimated there is currently 12, 400 tons of space junk orbiting Earth – 2,500 discarded satellites and 130 million fragments that travel at 10 times the speed of a bullet. Because of the orbiting junk, Space X satellites must make around 275 collision avoidance manoeuvres every day. It is not only dangerous in space but large debris is falling to Earth and not burning up in the atmosphere. It is predicted life will be lost in the next decade as a result of falling space junk, there have already been some near misses. The satellites and launch debris that does burn up in the atmosphere releases large amounts of metal into the atmosphere with unknown consequences.