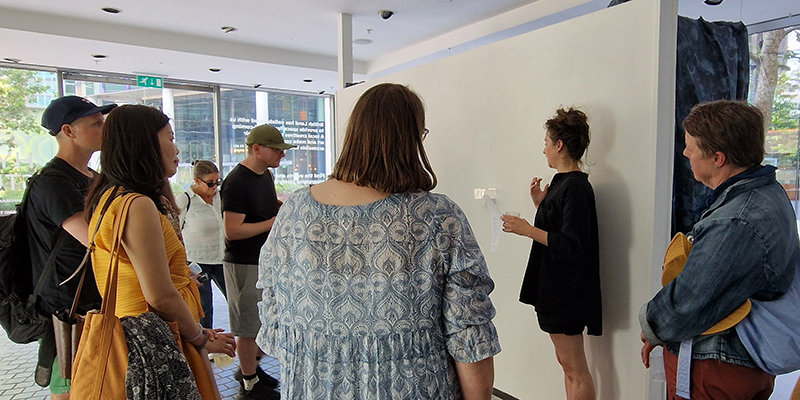
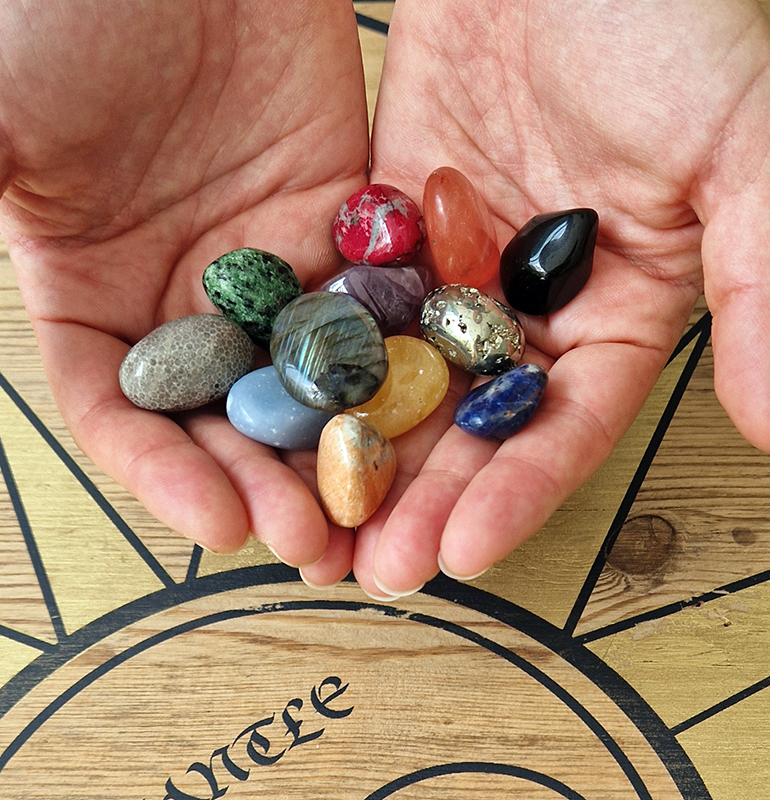
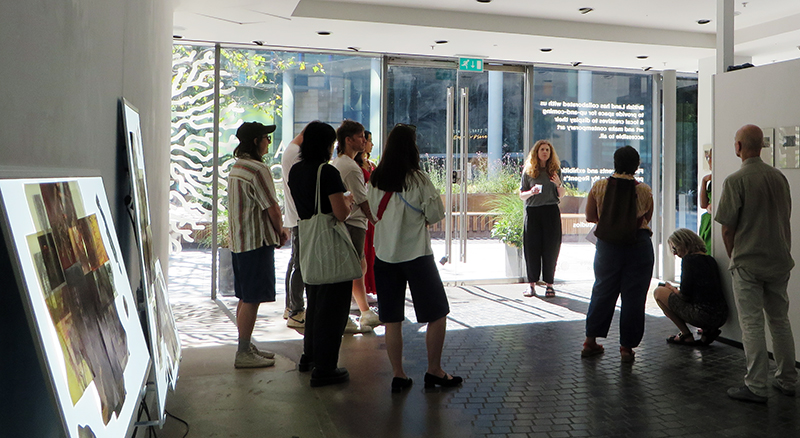
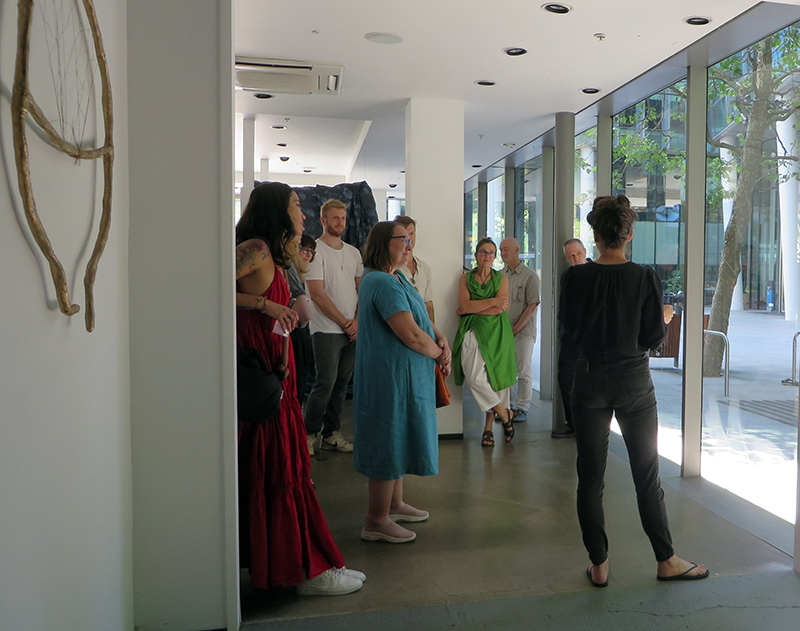
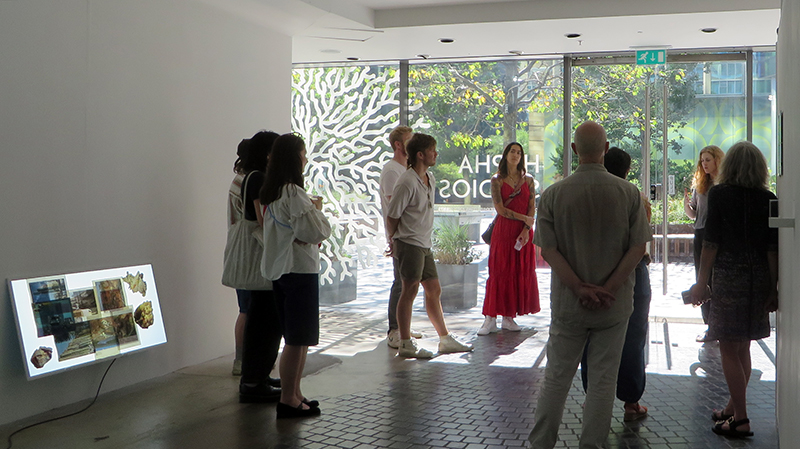
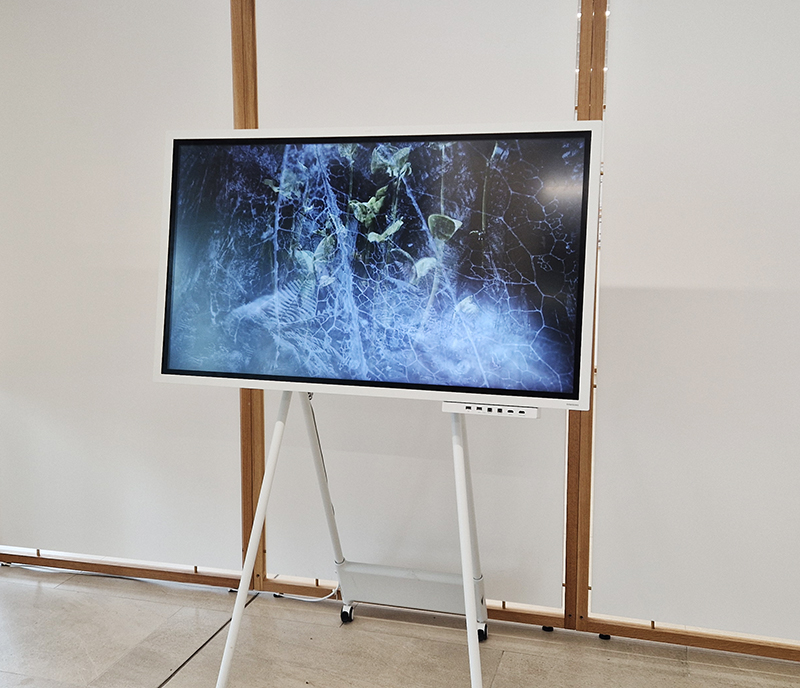
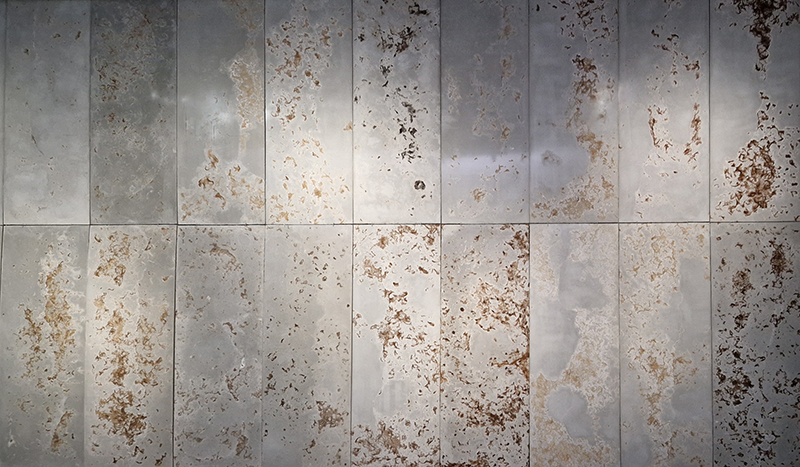
Thrilled to be invited to exhibit in Carbon, Carbon Everywhere at Hypha HQ co-curated by Indira Dyussebayeva-Ziyabek and Maria Hinel including artists Emii Alrai, Kate Daudy & Konstantin Novoselov, Simon Faithfull, Ania Mokrzycka, Nissa Nishikawa, Mariele Neudecker, Anousha Payne, Aimée Parrott, Lucia Pizzani, Lizi Sanchez, and Meng Zhou.
Integral to the constitution of our bodies, soil, air and some rocks, carbon is a highly bonding element that incessantly transmutes from state to state, each particle challenging the boundaries between life and non-life. Bringing together works by twelve international artists, Carbon, Carbon Everywhere explores the shifting states of carbon, an element that threads through organic and inorganic matter, linking bodies, environments, and temporal scales.

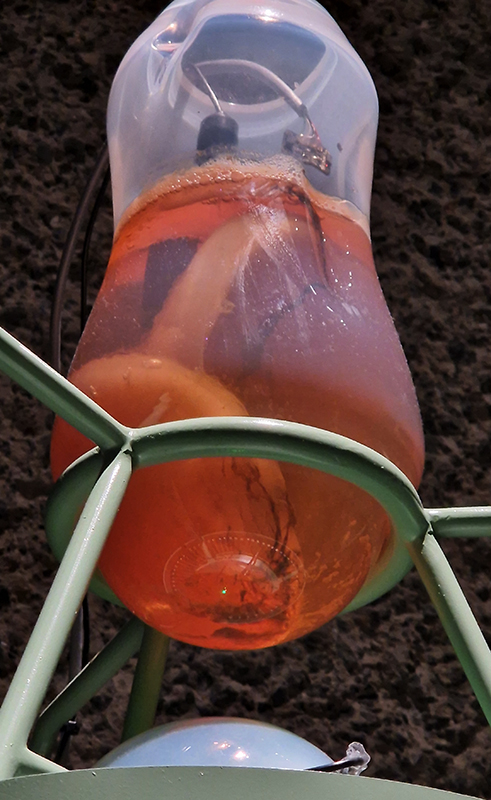
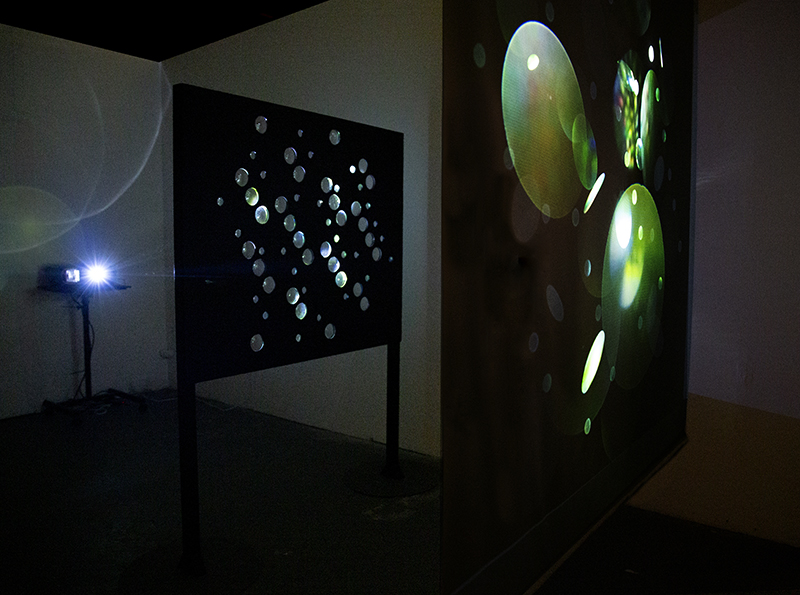
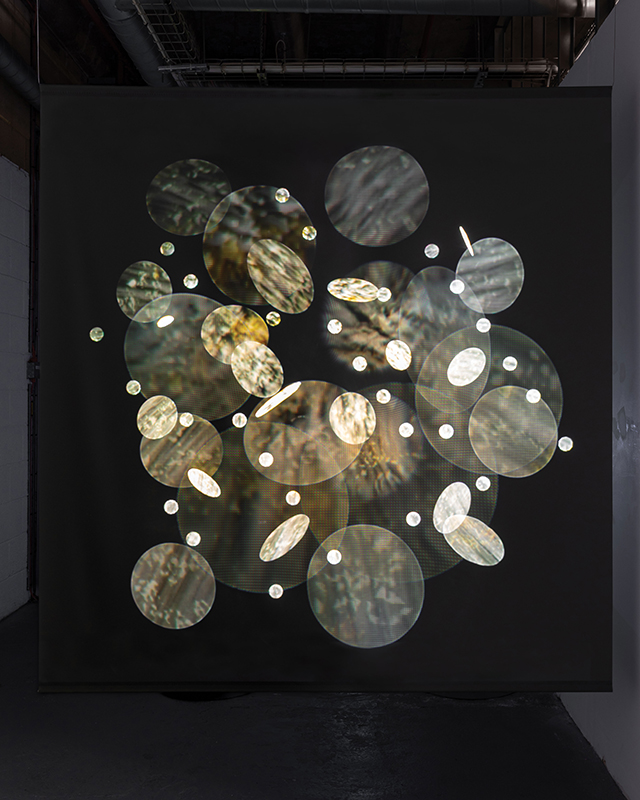
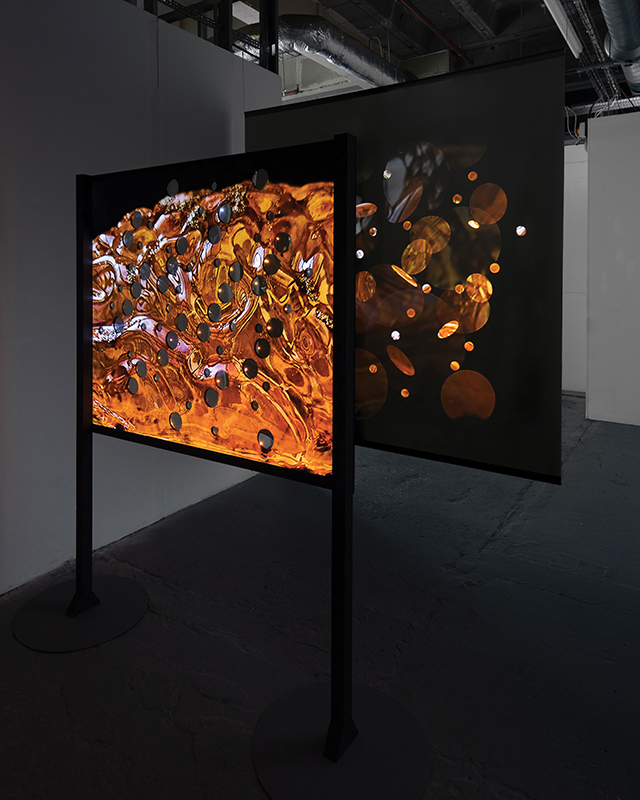
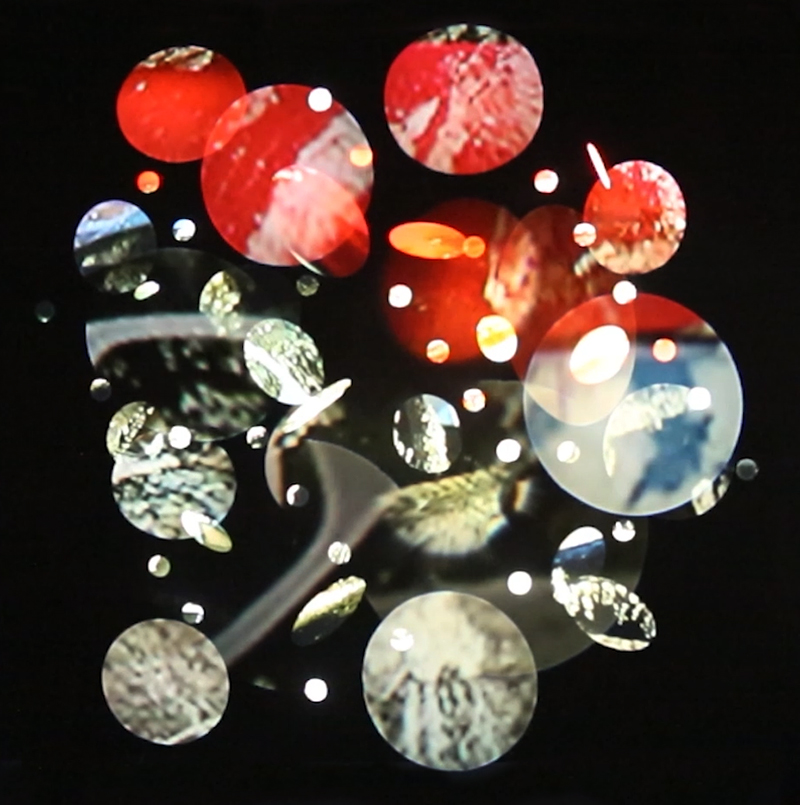
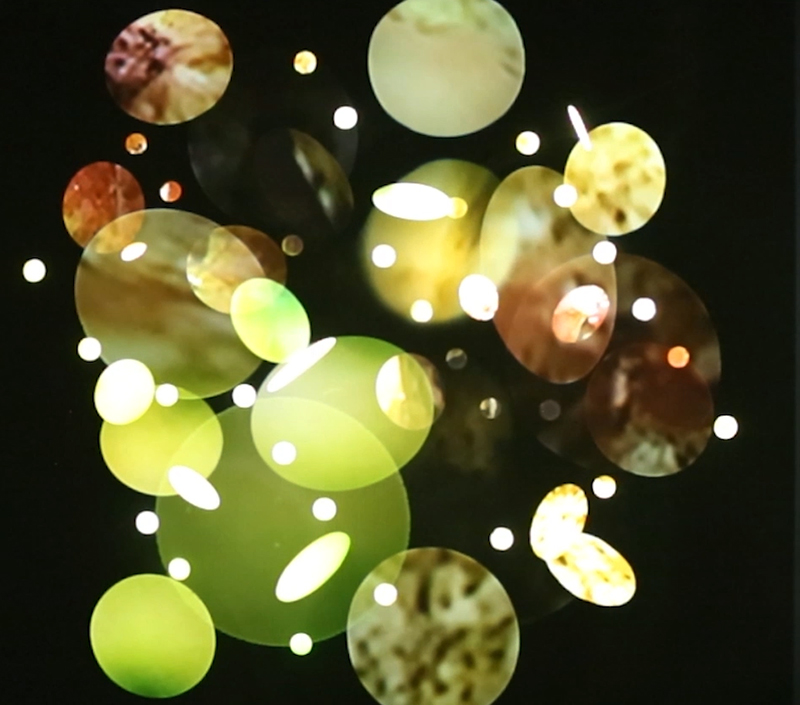
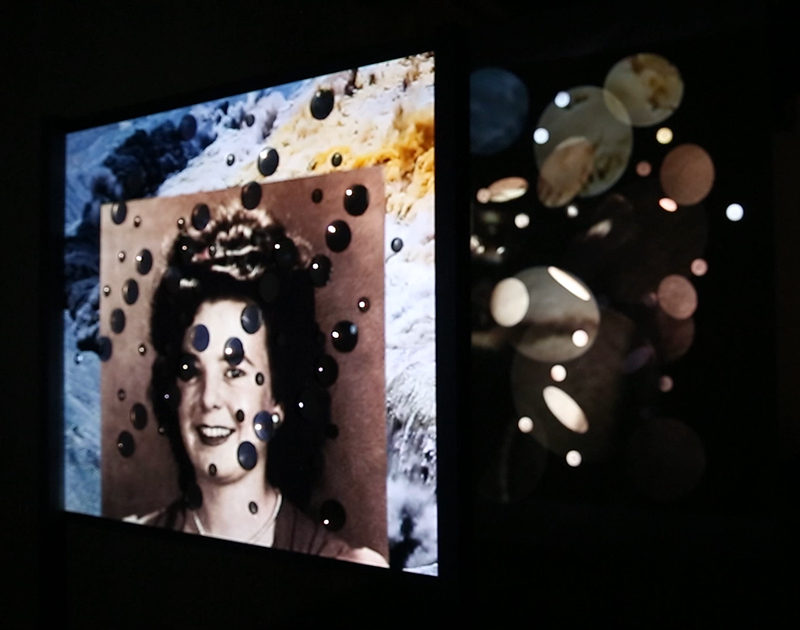
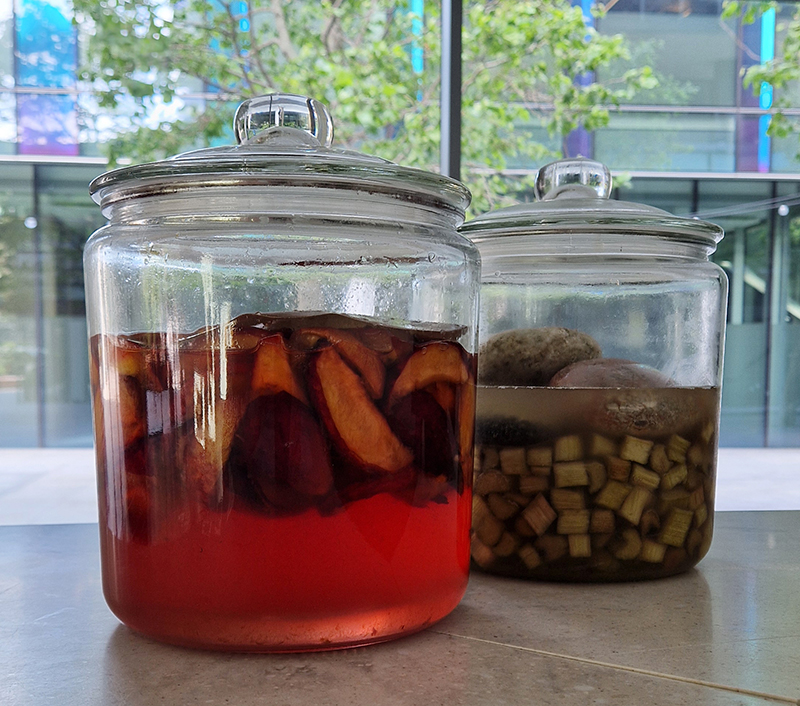
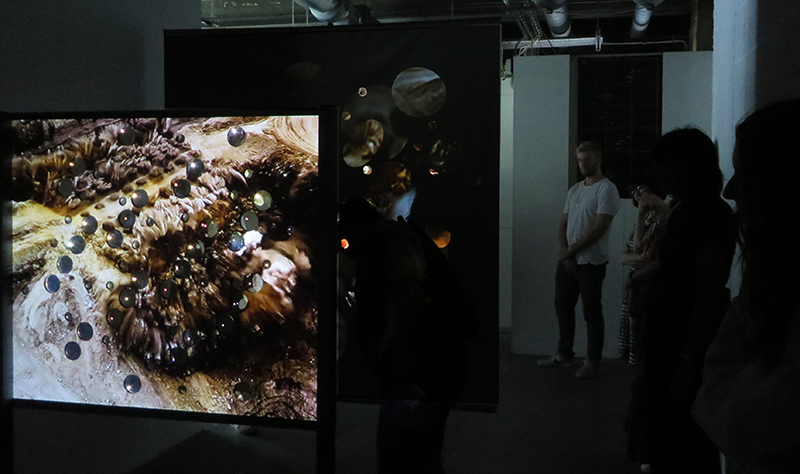
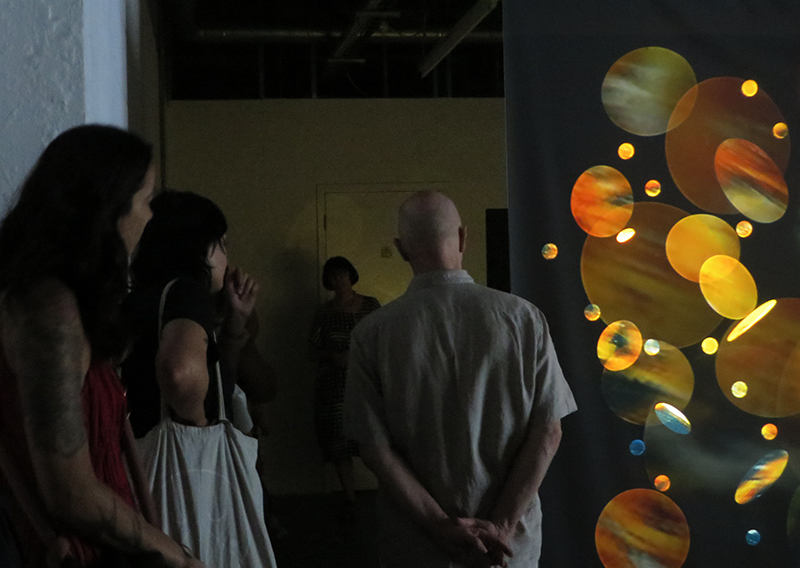
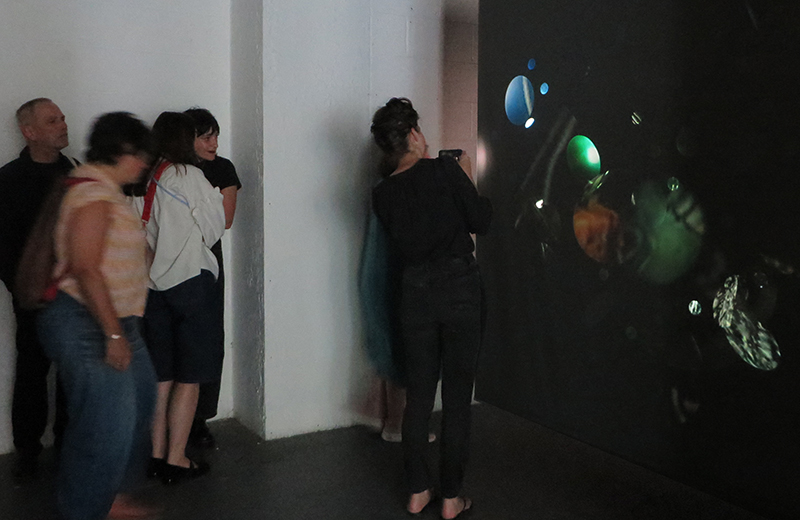
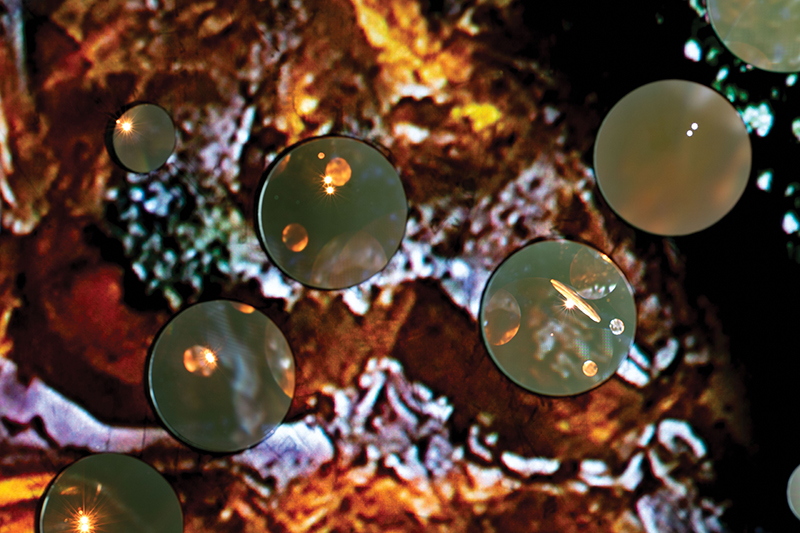
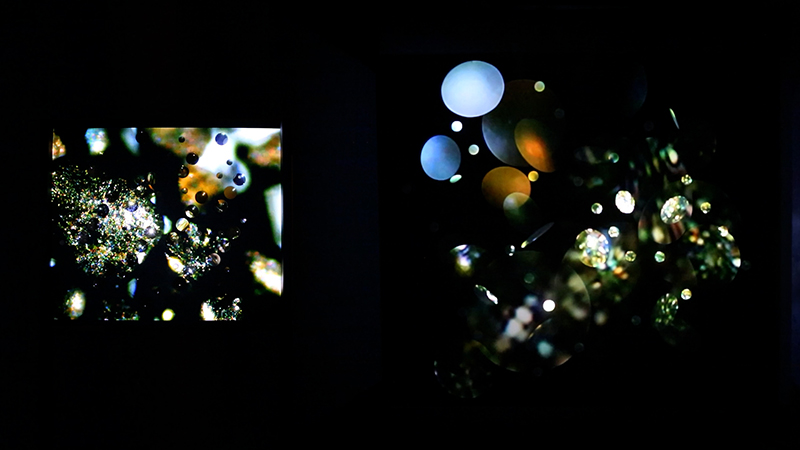
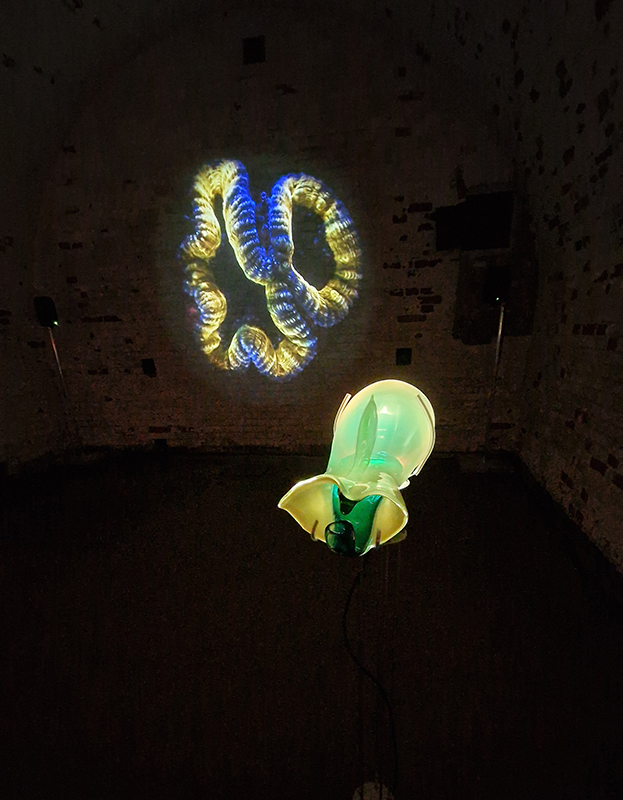
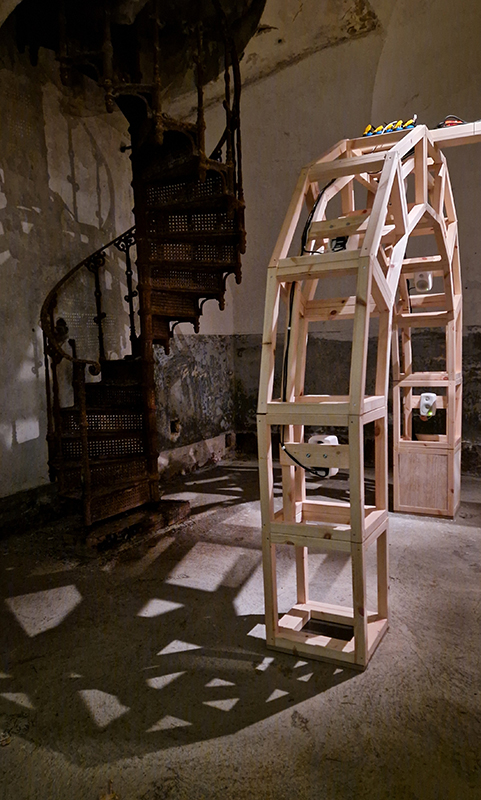
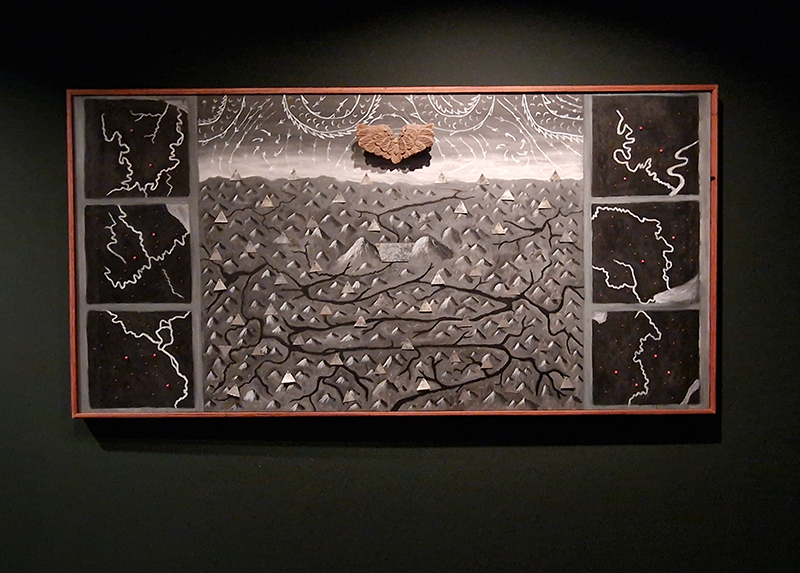
I have updated my website with documentation on the video installation Lithos Panoptes recently shown at Hypha HQ in The Geological Unconscious which can be viewed here. Referencing a many-eyed giant of Greek mythology, Argos Panoptes (always eyes still awake), the work considers the perpetual vigilance of rock as record keeper and witness.
Lithos Panoptes, optical lenses, wood, steel, two-way projection; Sculpture H172 x W170 x D50 cm, Rear projection screen H180 x W180 cm.

Great to be mentioned in an Art Newspaper article.
Magnetic News
Interesting to hear about new magnetic materials being developed that will hopefully have a less harmful ecological impact and offer more technological efficiency. The magnetic materials that are so heavily relied upon for computer memory and microelectronic devices include rare and toxic heavy elements whose energy-intensive production creates significant global carbon emissions. Previously, two primary types of magnetism had been identified, ferromagnetic (regular magnetism that we are familiar with) and antiferromagnetic (which are internally magnetic, but their opposing spin orientations make them appear non-magnetic externally). A third form known as altermagnetism has recently been confirmed with around 200 altermagnetic materials already being identified. These materials have a distinct magnetic order where tiny magnetic fields created by electrons are in anti-parallel alignment within a rotation of the host crystal structure leading to unique electronic properties. Altermagnetic materials have the potential for technological advancements offering huge increases in speed and efficiency especially in spintronics, an advanced technology that leverages both the charge and spin of electrons to store and process information.
A permanent magnet, MagNex that does not use the rare earth elements which have sustainability and supply chain issues, was developed in just three months with the help of AI analysing thousands of potential alloys. “This could have a significant future impact on our net-zero ambitions, through renewable energy and low-carbon transport, by removing the need for rare earth elements in high-performance permanent magnets.”
Recently launched, NASA’s TRACERS mission satellites fly in low Earth orbit through the polar cusps, funnel-shaped holes in the magnetic field where solar activity causes magnetic field lines to disconnect and reconnect creating disruption in the magnetosphere. By strategic placing of the twin TRACERS spacecraft in Sun-synchronous orbit, so that they always pass through the Earth’s dayside, thousands of dayside reconnection events can be observed and compared between spacecraft to see how quickly the process changes and evolves. Better understanding magnetic reconnection and its effects in Earth’s atmosphere will help prepare for impacts of solar activity on Earth. The magnetosphere protects Earth from the constant bombardment of solar particles from the Sun, but when magnetic field lines are disrupted by the solar wind, particles rain down into Earth’s atmosphere not only causing beautiful phenomena, like the aurora, but also impacting infrastructure, like satellites and GPS systems.

Out and About
I have been lucky to visit exhibitions in Finland and Norfolk to see works that interrogate human impact on the environment and other living beings that share our planet.
Helsinki Biennial 2025 Shelter: Below and Beyond, Becoming and Belonging brings together 37 artists and collectives on Vallisaari Island (which has been off-limits for human habitation for decades), in Esplanade Park, and at HAM (Helsinki Art Museum). It explores the significance of shelter and turns the gaze towards non-human nature. In the works, the focus shifts from humans to animals, water, plants, insects, minerals, and other living beings and their role as contributors to our planet’s wellbeing.
Artists with work installed in the Esplanade Park included Katie Holten (inventing a forest alphabet) and Guiseppe Penone (inseparable connections between humans and nature).
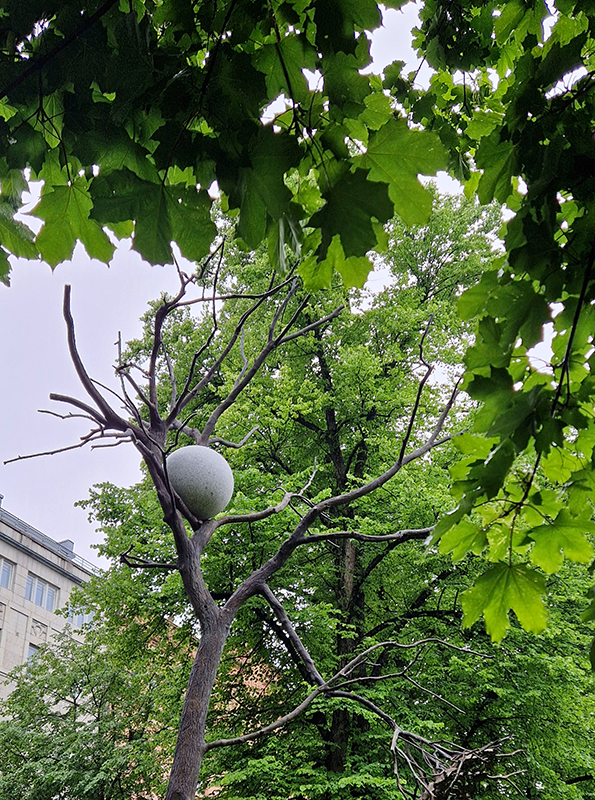


Artists at HAM (Helsinki Art Museum) included Jenni Laiti & Carl-Johan Utsi (precarity of survival), Regina de Miguel (technofossils), Aluaiy Kaumakan (displaced community), Otobong Nkanga (ownership of resources), Ingela Ihrman (invasive species), Locus/Thale Blix Fastvold & Tanja Thorjussen (eelgrass conservation), Sissel M Bergh (Sami cosmology), Edgar Calel (more than human agencies).
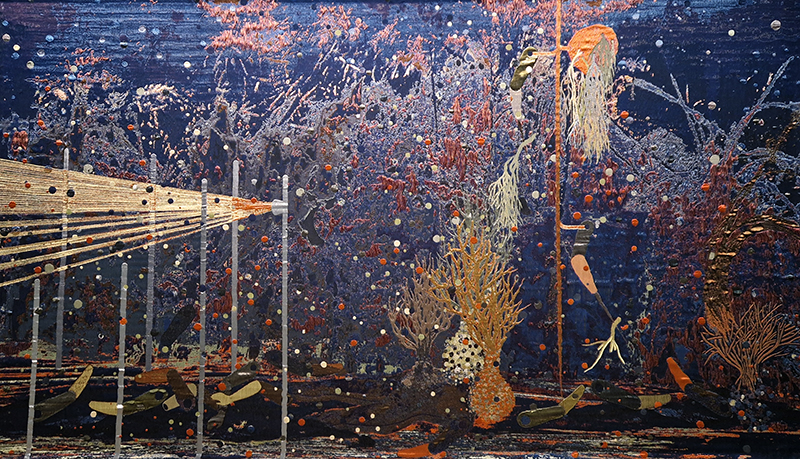
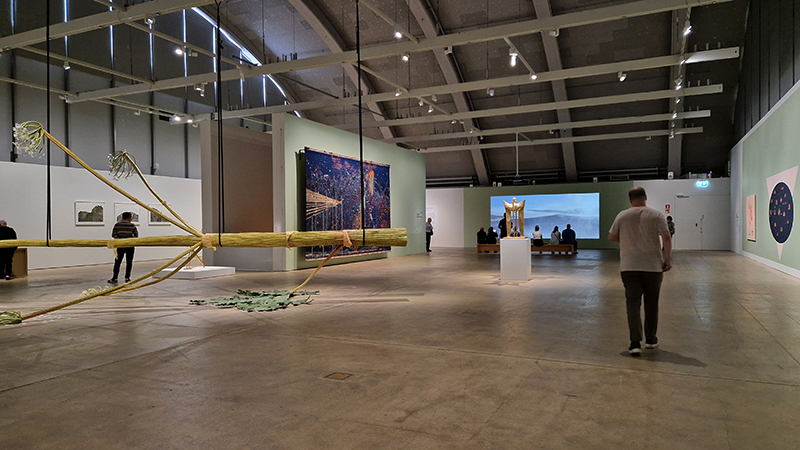
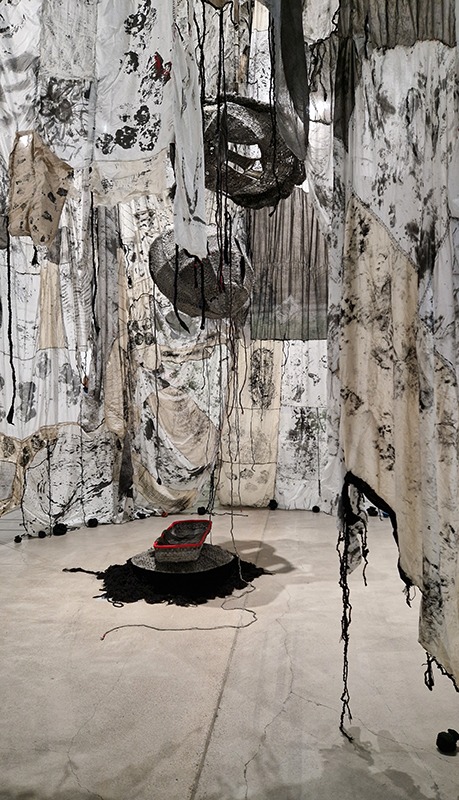
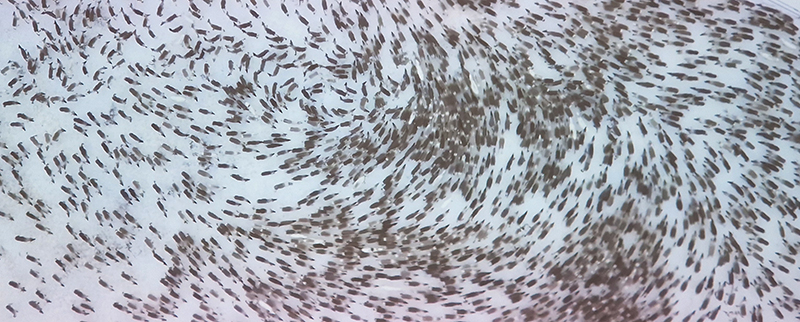




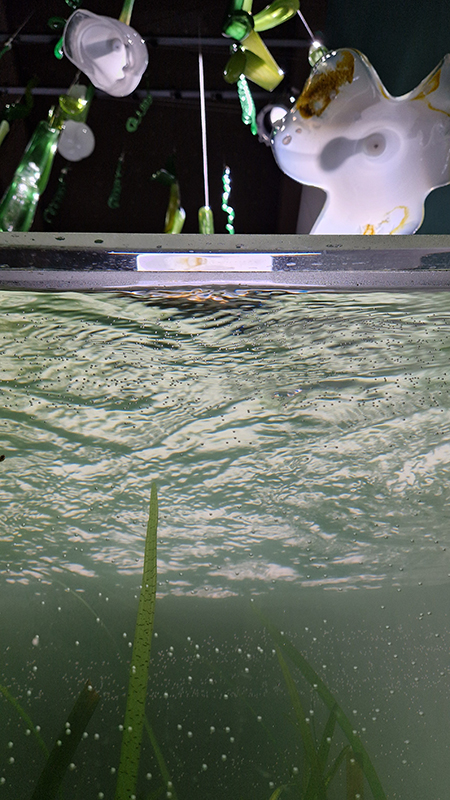



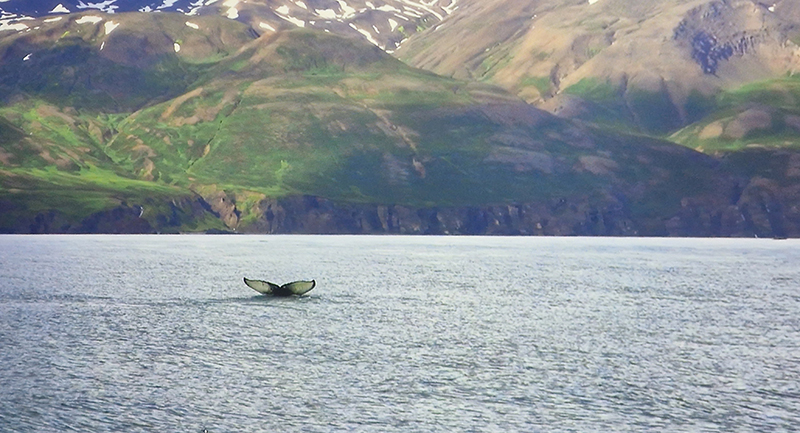
Artists with work installed around the beautiful Vallisaari Island included Hans Rosenström (petrified wood soundscape), Tue Greenfort (species evolution), Nomeda & Gediminas Urbonas (amplifying non-human voices), Pia Sirén (human modified environments), LOCUS / Thale Blix Fastvold & Tanja Thorjussen (water health), Tania Candiani (hidden networks of the forest), Sara Bjarland (discarded inflatables), Kati Roover (humans and whales), Juan Zamora (bioluminescence), Band of Weeds (vegetal distress), Kristiina Koskentola (friendship of crows), Tamara Henderson (hidden realm of worms), Ernesto Neto (shapeshifting), Theresa Traore Dahlberg (invisible frequencies), Ana Teresa Barboza (plant narratives), Carola Grahn (colonialism legacy on estrangement from nature), nabbteeri (parasitism), Olafur Eliasson (more than human ways of seeing).
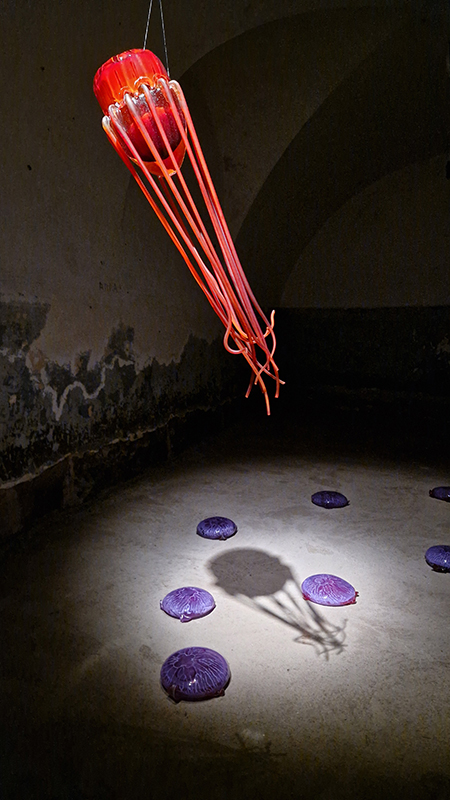
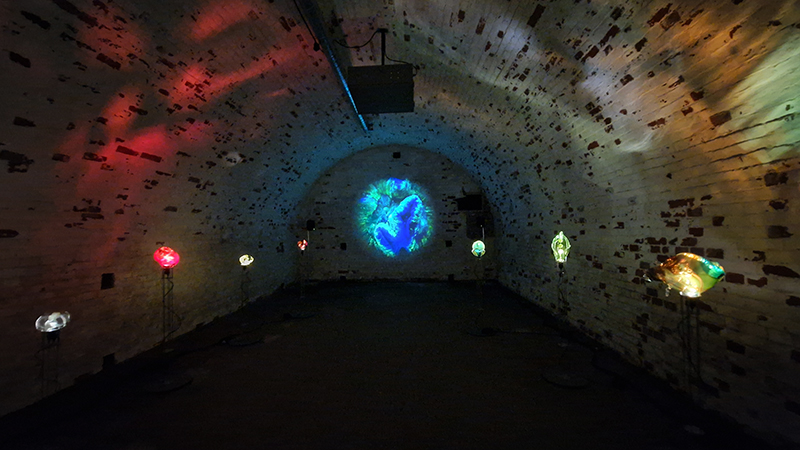
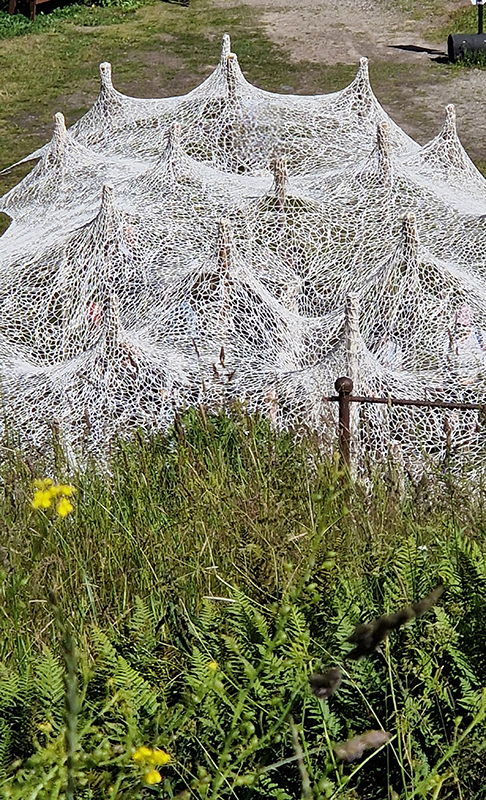
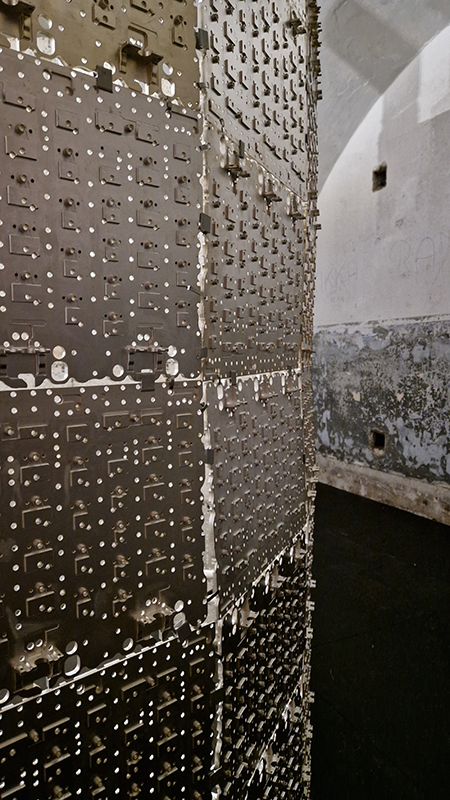
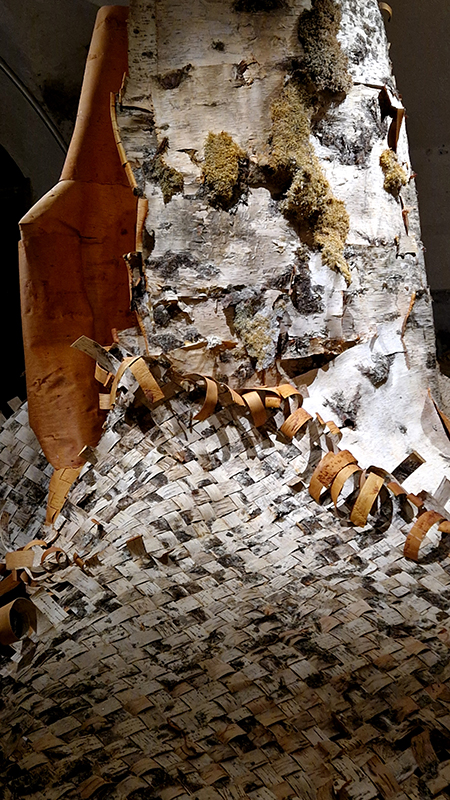
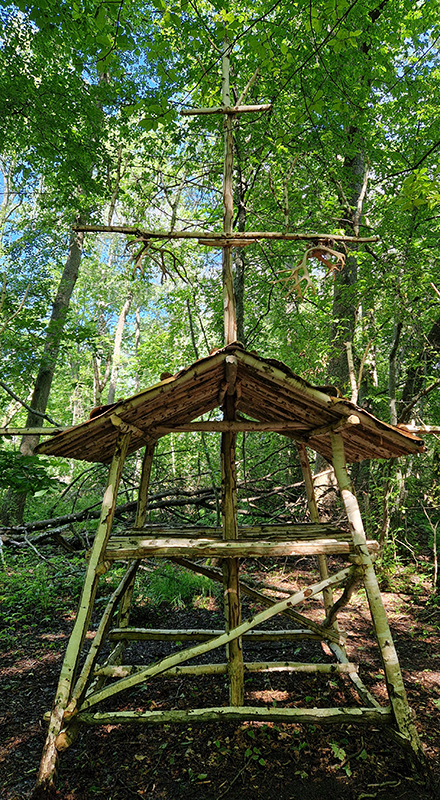
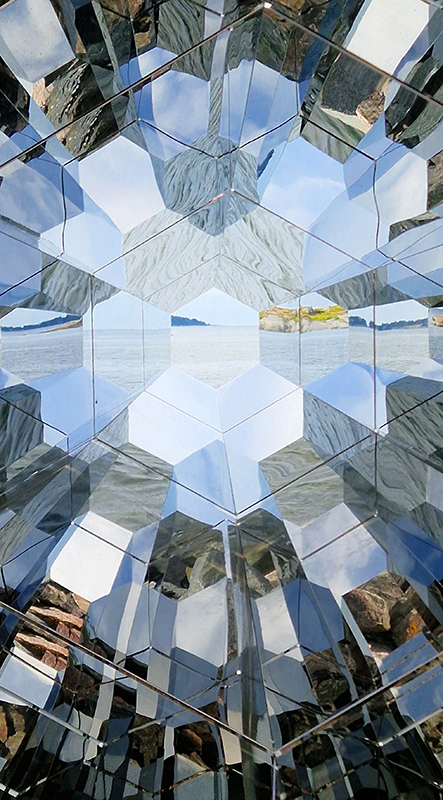




























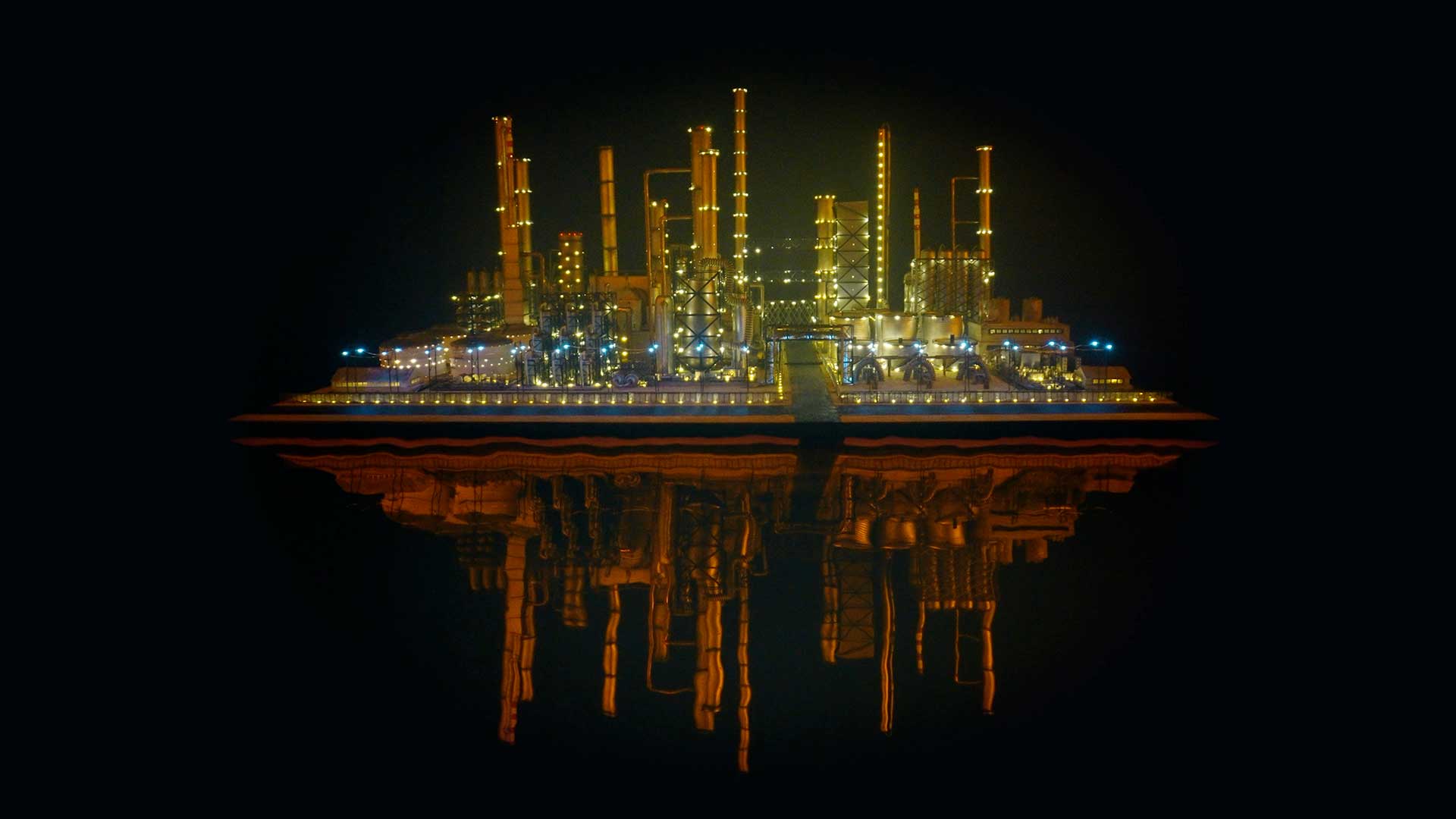
Excellent Monira Al Qadiri exhibition Deep Fate at the Museum of Contemporary Art Kiasma, Helsinki. Addressing the dichotomy of enjoying contemporary life made possible by oil during the accelerating climate crisis. Deep Fate, refers to the origins of oil deep in the earth and also to the way that dependence on oil and breaking that dependence are a matter of life and death for humankind. Al Qadiri grew up next door to oil refineries in Kuwait and experienced the Gulf War as a child. This personal experience is drawn upon in the haunting video Crude Eye which attempts to reconcile childhood memories of the oil refinery as a romantic glowing metropolis with its true nature as a site of environmental destruction. The demise of the local pearl-diving industry, a source of income superseded by the oil boom, is referenced by sculptures echoing the molecular structures of the chemicals used in oil drilling with iridescent rainbow colours that are reminiscent of oil and the shimmering surface of pearls.




Also at the Museum of Contemporary Art Kiasma was Rock, Paper, Scissors an anthology of diverse materials in contemporary art. Claes Oldenburg’s giant Extinguished Match which plays with scale brought to mind the video by David Hochgatterer Streichhölzer (Matches) where matches appear to spontaneously combust shown in the Carbon: Under Pressure exhibition recent tour to Glasgow ARC.
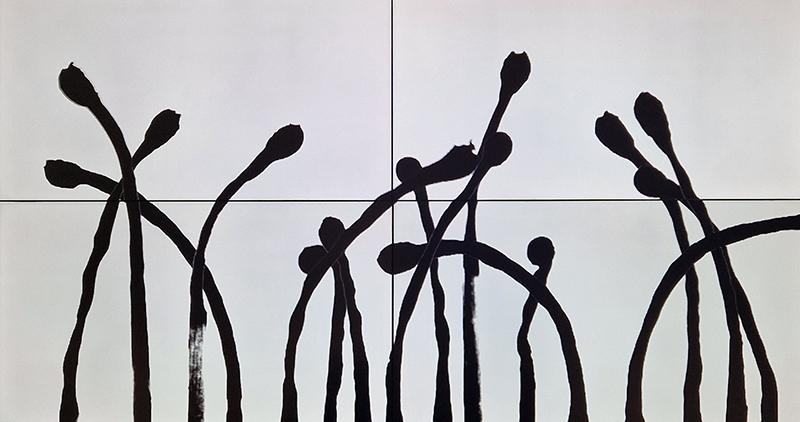


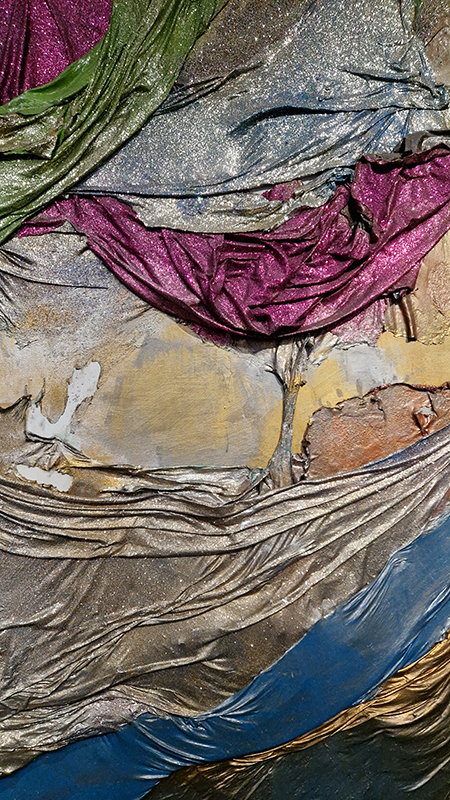
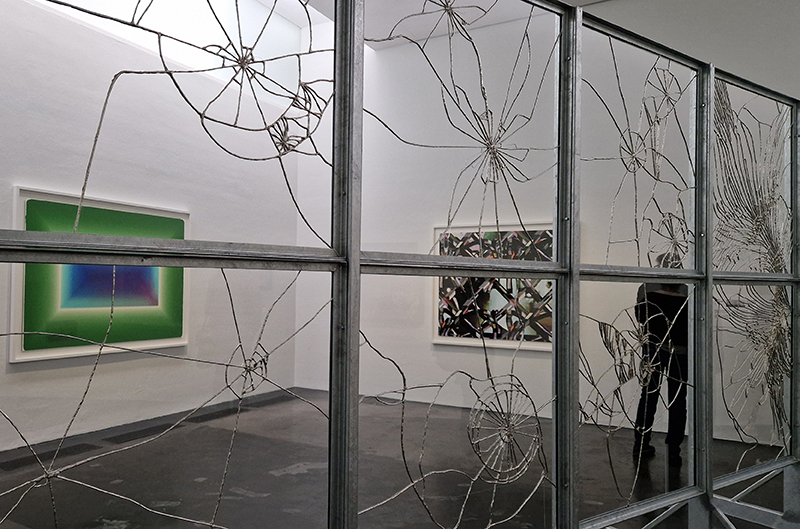
Materials celebrated through this exhibition included neural pathways stimulation of the visual system by pressure on the eyelids to see phosphenes, glittery thick folds of acrylic on canvas, leaded glass breakages, ephemeral copper wire net, faux marble that is actually hair on the barbers concrete floor.





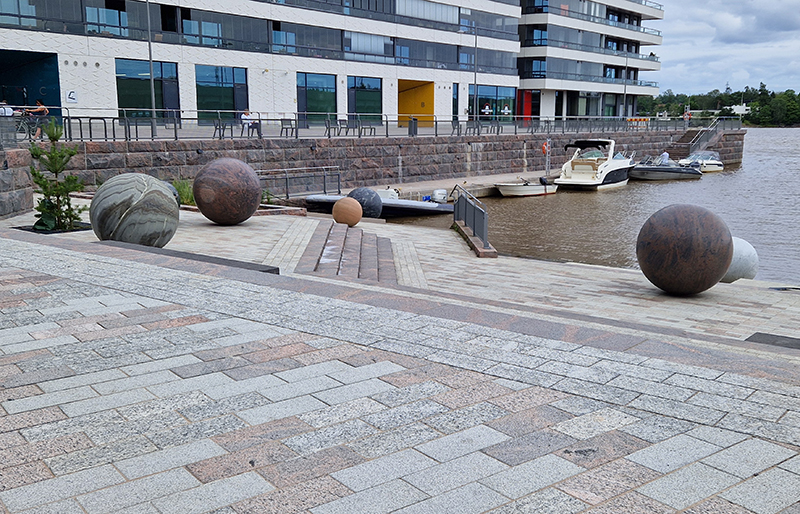
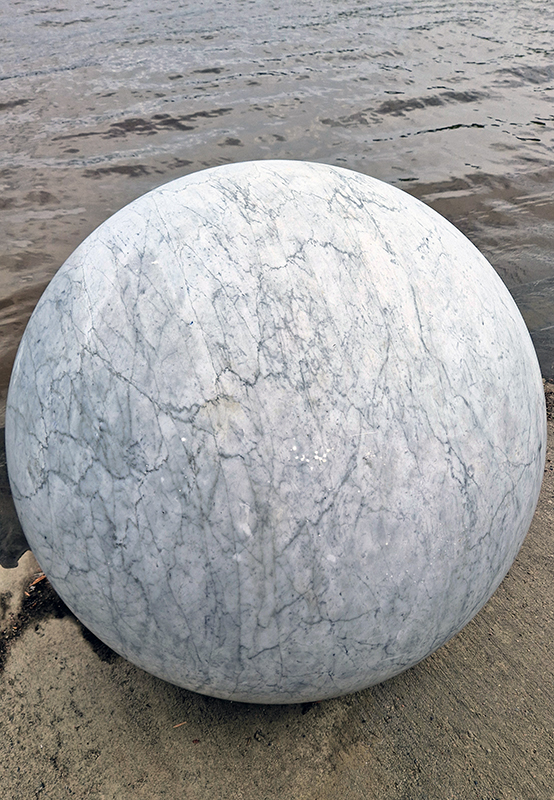
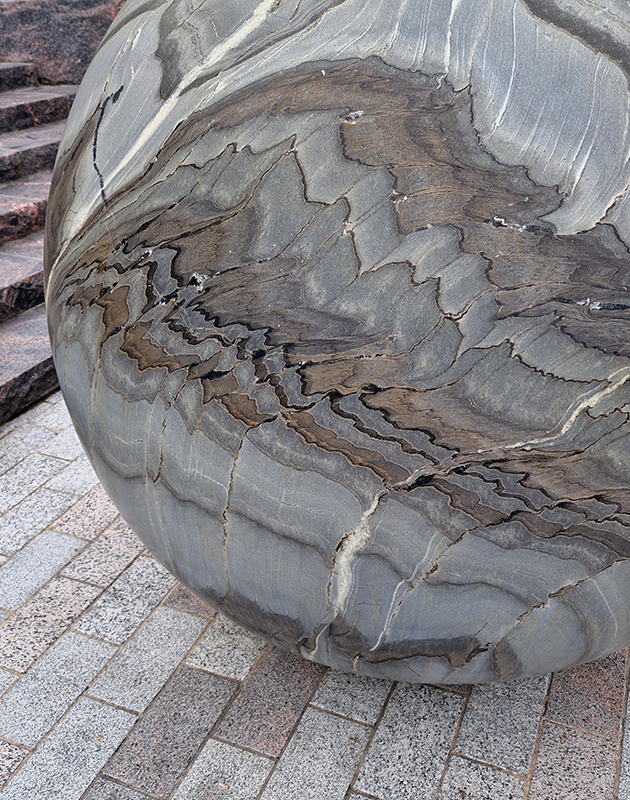
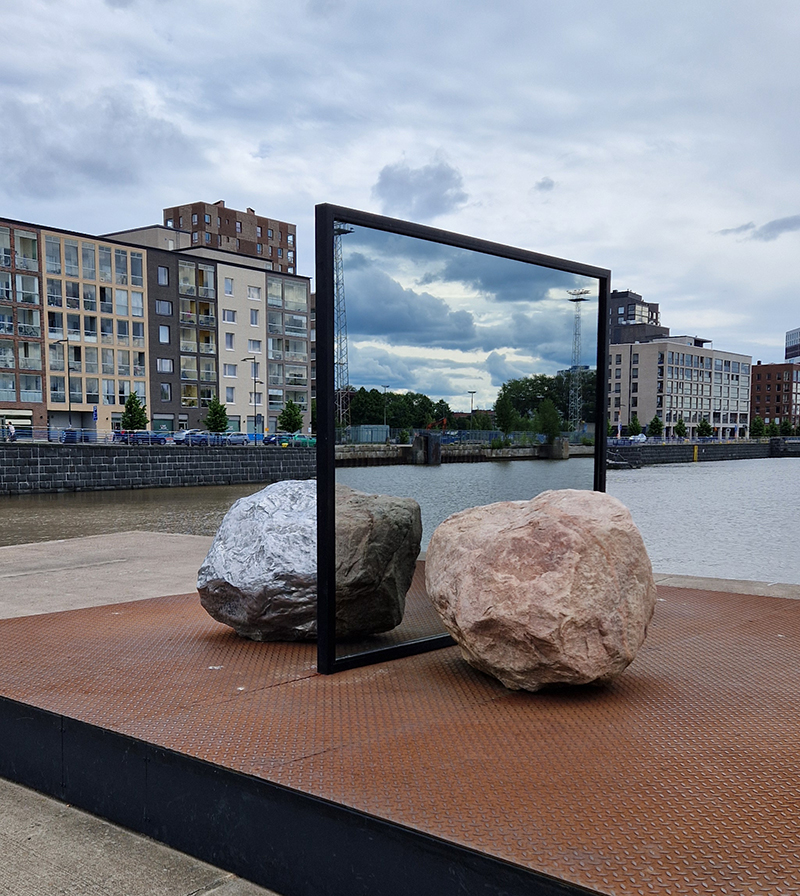
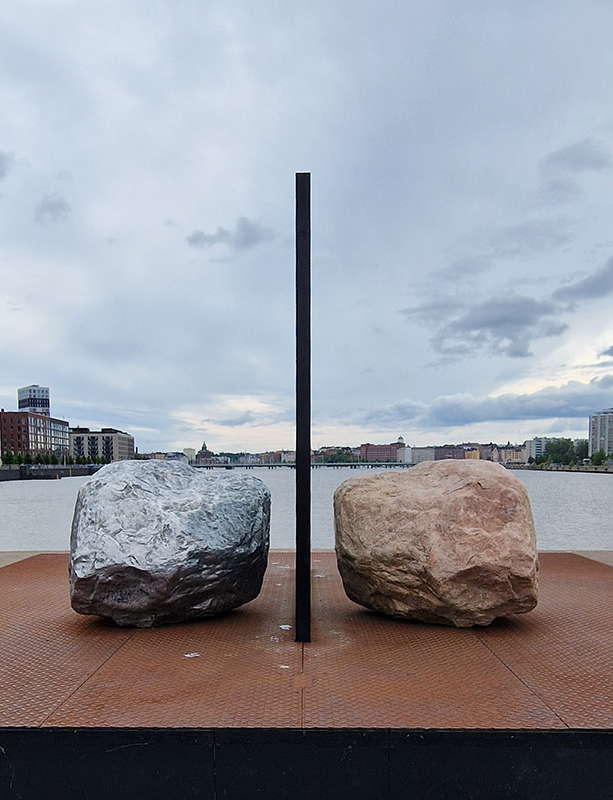
With my head still full of the geological (unconscious) it was great to see the works of Alicja Kwade, Big Be-Hide (parallel universes – natural rock and a metallic copy either side of a two-way mirror) and Pars pro Toto (a part for the whole – stone planet like spheres) from the 2021 Biennial now installed in Helsinki’s Kalasatama district.







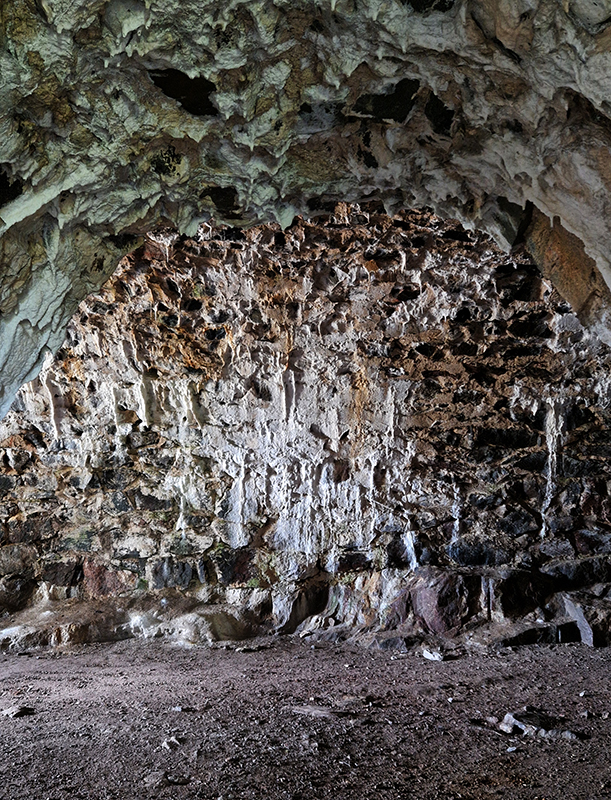
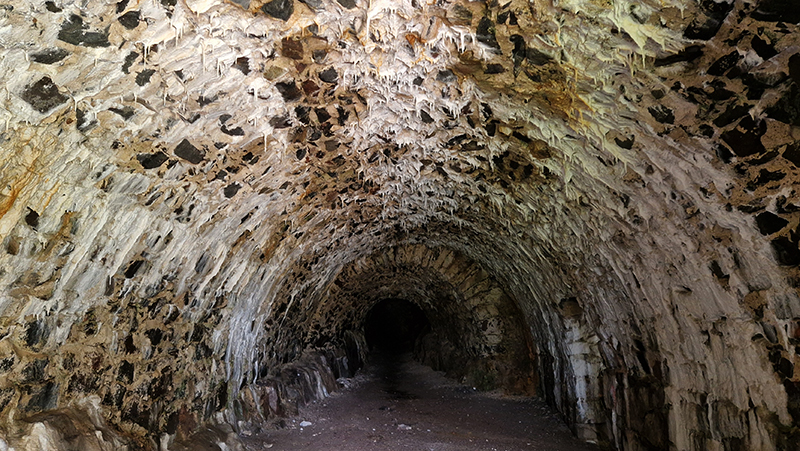
Another ‘geological’ delight was the unexpected appearance of stalactite’s forming in the tunnels of the military sea fortress built in the 1700’s on the island of Suomenlinna, a UNESCO World Heritage site.



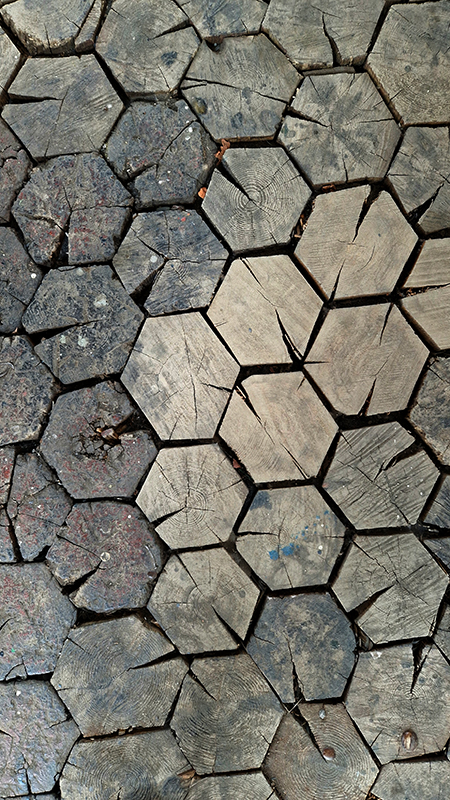
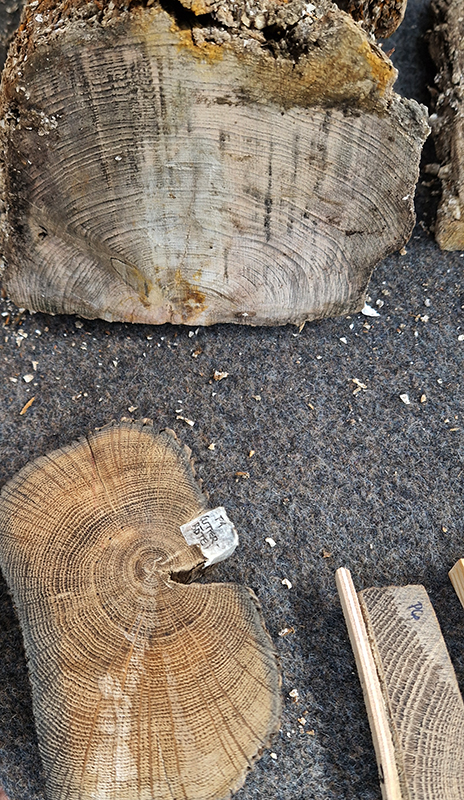
I loved the amazing hive like wood floor at Suomenlinna boatyard. Every tree carries a memory of the past, recording the weather and conditions of each season. Dendrochronologists can work out exactly when a tree was cut down which is very helpful in underwater archaeology. Around Suomenlinna there are shipwrecks beneath the sea with no identifying features except their wooden timbers which incredibly hold clues to when and where the trees used were felled. Marine archaeologists, shipbuilders and forest scientists are working together to discover the stories behind the lost ships.



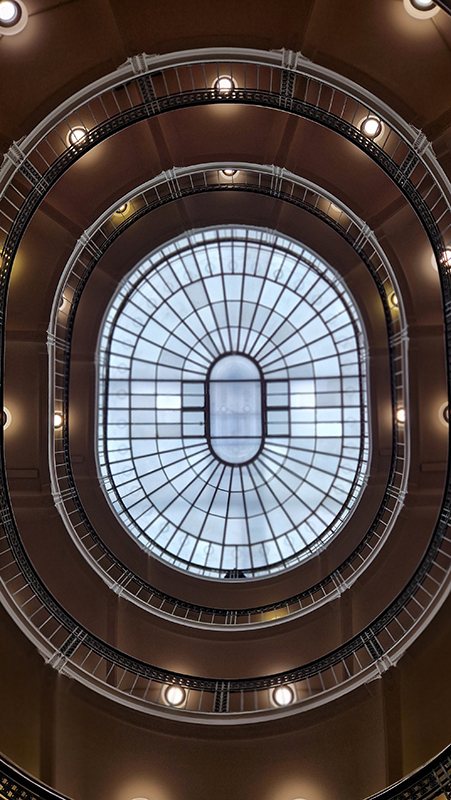
Helsinki is big on amazing libraries. The National Library of Finland is stunning and bursting with tantalizing books to explore, and the new Helsinki Central Library Oodi takes your breath away in its scale and sweeping curves.
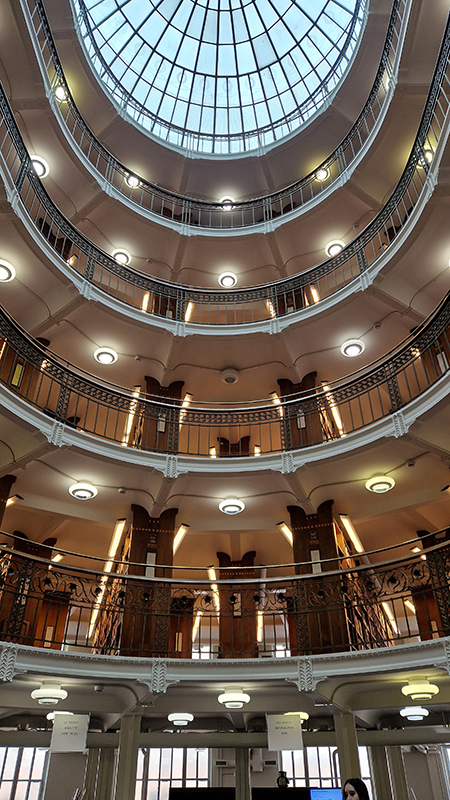





Sadly Helsinki Observatory has long since stopped functioning as a place for active astronomical research (2009) and is now a museum. It was disappointing that the electronic cloud chamber they possess wasn’t switched on but there were some interesting instruments to wonder about in the meridian room.
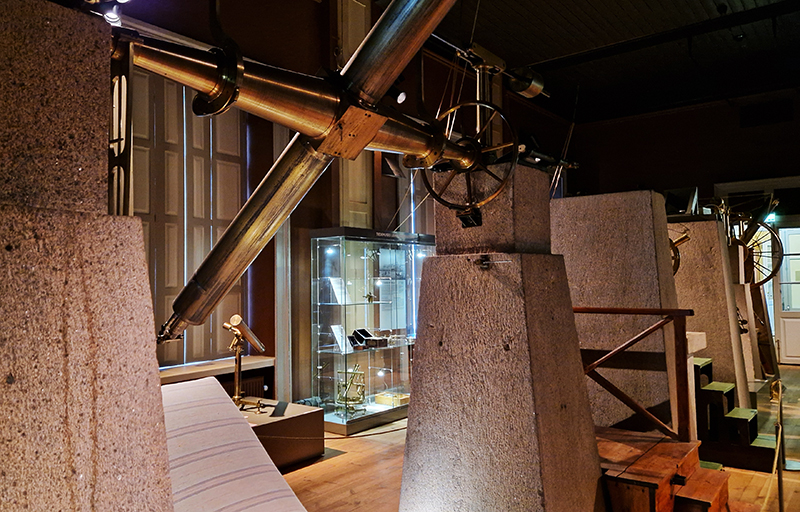
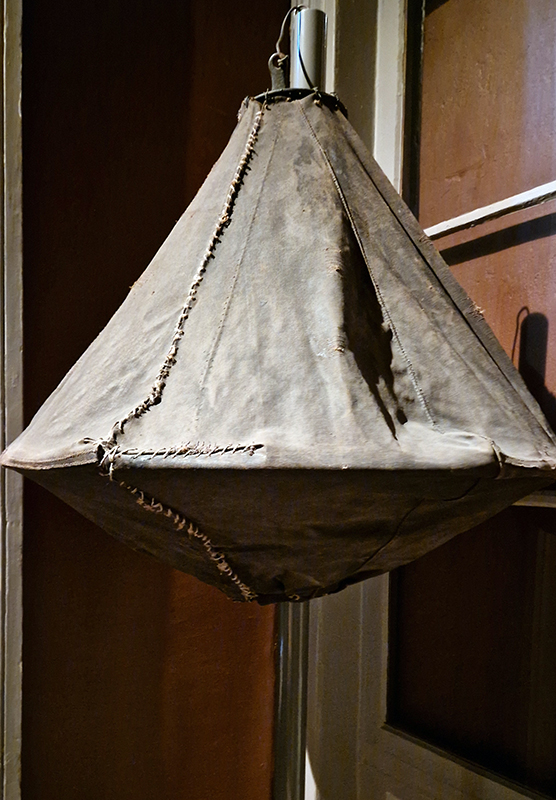




Each day the time signal bag was hoisted to the top of a mast on the roof of the observatory just before noon and dropped down exactly at noon. The correct time having been determined by an astronomer observing the stars at night. This event could be seen from Helsinki Central Railway Station where the station clock was then synchronised. This method of time keeping for Helsinki residents was in use until the 1920’s.
The future of our oceans is explored in the Sainsbury Centre’s Can The Seas Survive Us?
The sea has often been viewed as a mysterious ‘other’, with its expansive surface and seemingly infinite depths dominating marine imagery in the history of Western art. Artworks in this exhibition explore the ways the oceans have been domesticated, reimagined on a bodily scale and brought inside to be tamed, contained or better understood. Sea Inside turns our oceanic gaze towards the sea’s more intimate spaces – whether physical, psychological or imaginary – and dives into shared watery origins, Indigenous ways of life and the items we remove from the sea to display on land.
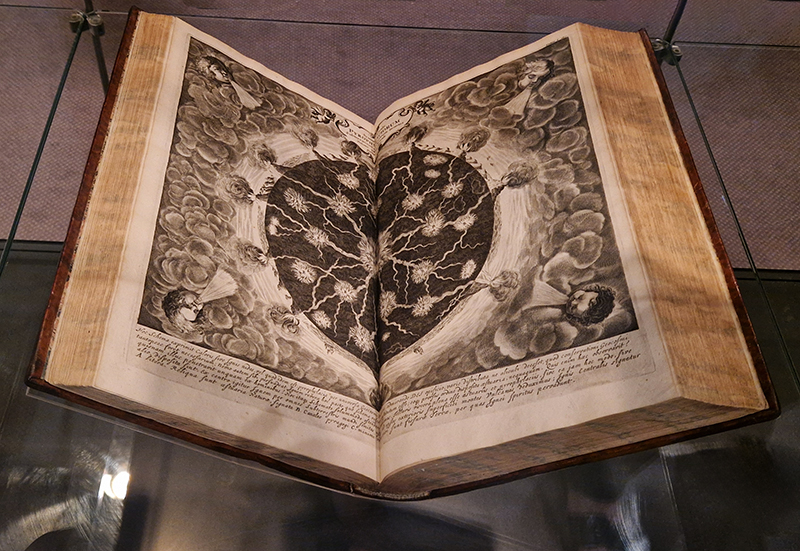
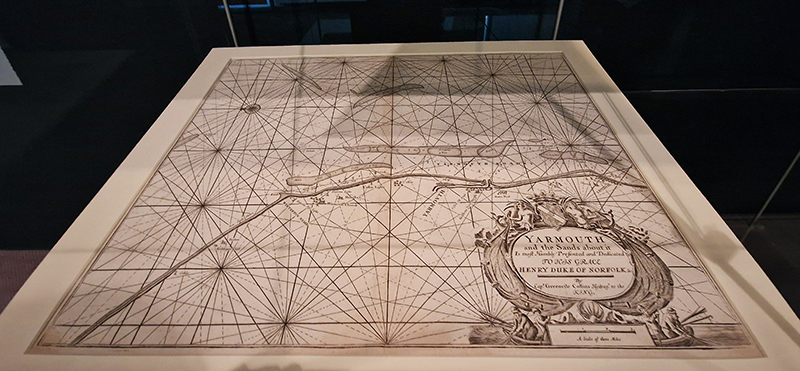
A World of Water takes the North Sea and the historical relationship between Norfolk and the Netherlands as its starting point to look at the human impact on the sea. It was wonderful to see the original book Mundus Subterraneous from 1664 by Athanasius Kirschner whose geological illustrations and speculations I have been fascinated by. Olafur Eliasson’s suspended Shore Compass uses driftwood to reflect on navigation of an uncertain world. Some great maps in this exhibition including the intriguing map of sandbanks off the coast around Great Yarmouth. I have enjoyed following Julian Charriere’s visually dramatic work on Instagram so it was good to see these images scaled up. Andrew Watkinson’s montage based on research from the Tyndall Centre for Climate Change about coastal erosion in Norfolk swerves from resignation to resistance, hope to despair and took me back to my BA dissertation (The Communication Of Ecological Concerns Through Contemporary Artistic Practice, 2007) writing about climate change warnings coming from the Tyndall Centre and the frustration of researchers about distorted media coverage that made it hard for the public to understand the facts. Suffolk too has lost a lot of land to the sea since I was a child there. Although dreams of tidal waves are common anxiety dreams I believe mine were also influenced by overheard stories of the North Sea flood of 1953 when a storm surge coincided with a high spring tide, which my parents and local villagers remembered vividly, it was the worst flood of the 20th century in England and Scotland and many lives were lost. Maggi Hambling’s sublime Wall of Water holds frozen the terrifying waves that may threaten us while Cian Dayrit’s Dam Nation examines the impact to communities and ecosystems when water is held back or re-routed.








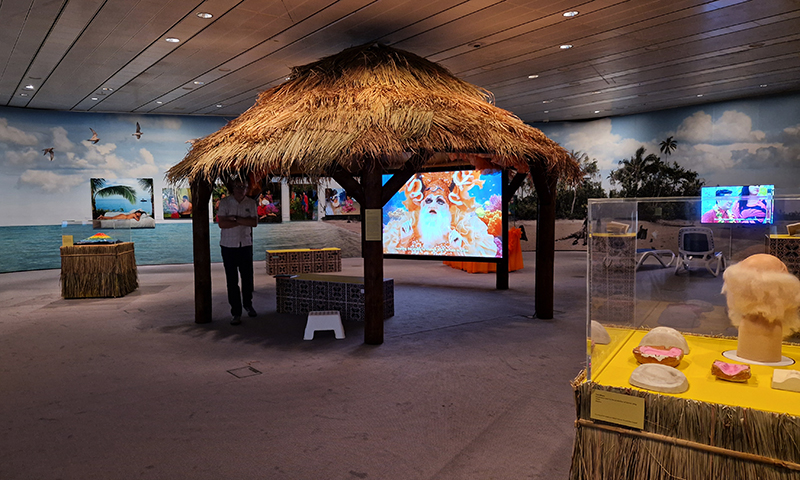
Darwin in Paradise Camp by Japanese-Sāmoan artist Yuki Kihara calls out that ” a reconsideration of what it means to be human requires a re-evaluation of the origin of the species.”

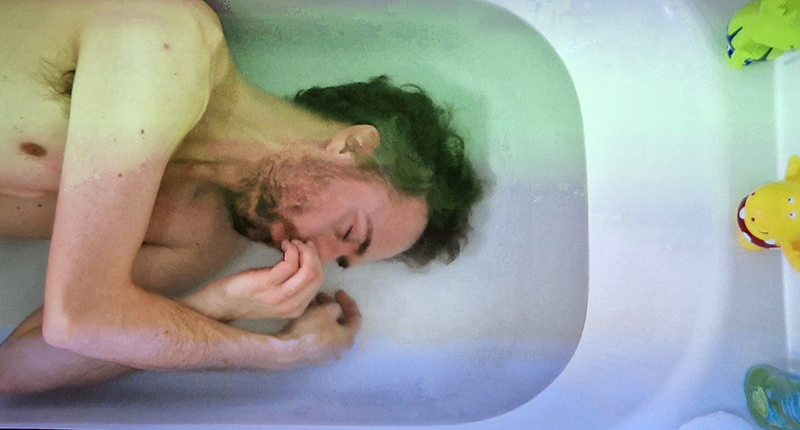
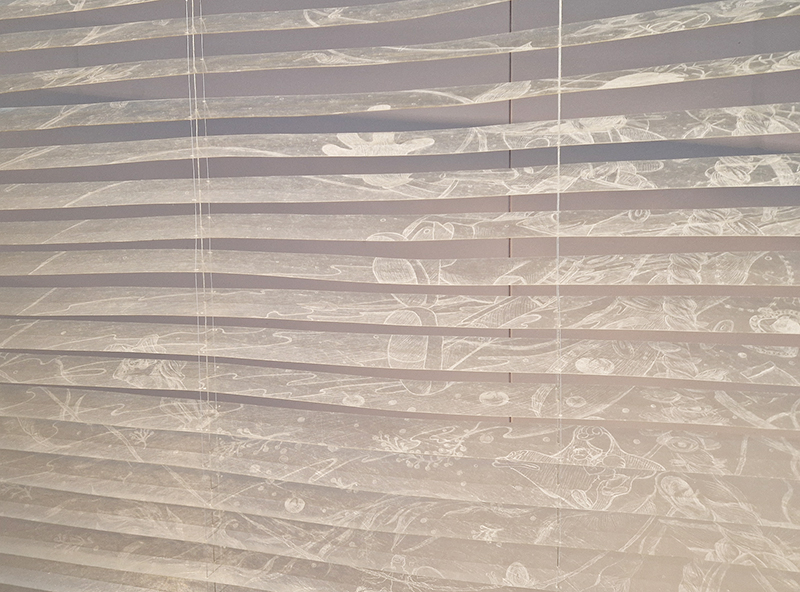
Sea Inside turns our oceanic gaze towards the sea’s more intimate spaces – whether physical, psychological or imaginary including work by Marcus Coates (attempts to create the call of the humpback whale in a bathtub), Kasia Molga (How to make an Ocean – the artist’s salt tears fill miniature glass capsules where algae is cultivated), Gabriella Hirst (ethereal images on hand etched fibreglass in a slatted structure that echoes the baleen inside a whale’s mouth).



At London galleries I saw work about tuning in to invisible forces, the importance of how we treat our fellow humans (dead or alive) and an assessment of the influence of past and present technology on hope for the future.
Islington Gallery Weekend is a great idea, just the heat while out walking that weekend meant I didn’t make it to all the galleries participating.
The Observatory at Bobinska Brownlee New River, presented abstract and textural works by Claudio del Sole, an artist and amateur astronomer who co-founded the ‘Astralist’ movement in 1959 inspired by the dawn of the space age. These cosmic inspired works are shown alongside those made in response to the Astralist manifesto by contemporary artists James Brooks, Robert Good and D J Roberts. Cocktails and an incredible performance on the piano of unique work by composer Edward Henderson were also part of the afternoon.






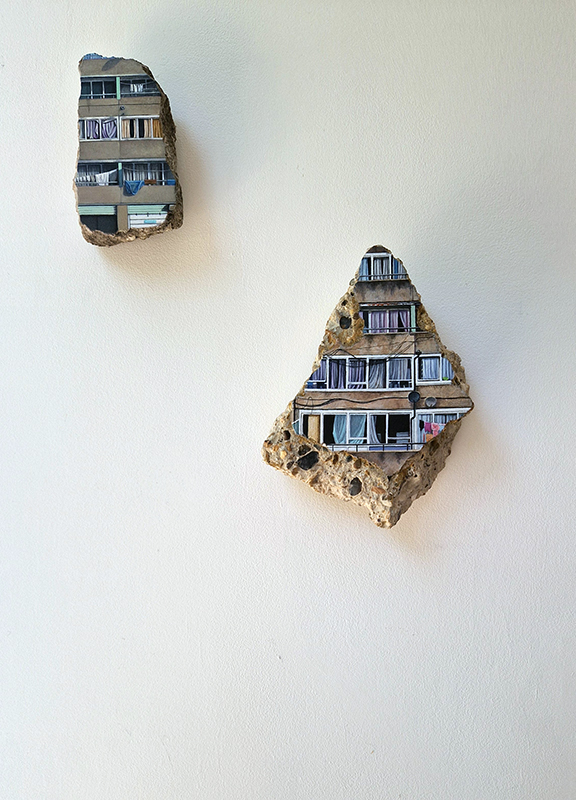
Poignant work from Harriet Mena Hill in Curtains at PostROOM Gallery. Fragments collected from demolition of the Aylesbury Estate in South East London are meticulously painted with details of the buildings that once were home to a community. An accompanying film gives voice to those who enjoyed life here before lack of maintenance and social care slowly stripped away the heart and soul.

Fascinating listening to Tracy Hill speak about her work in Natural Frequencies at White Conduit Projects which explores ways of being sensitive to invisible energies that move through us and our landscapes. Her experience of working with a water diviner feeds into her intuitive drawing processes and cut paper works.
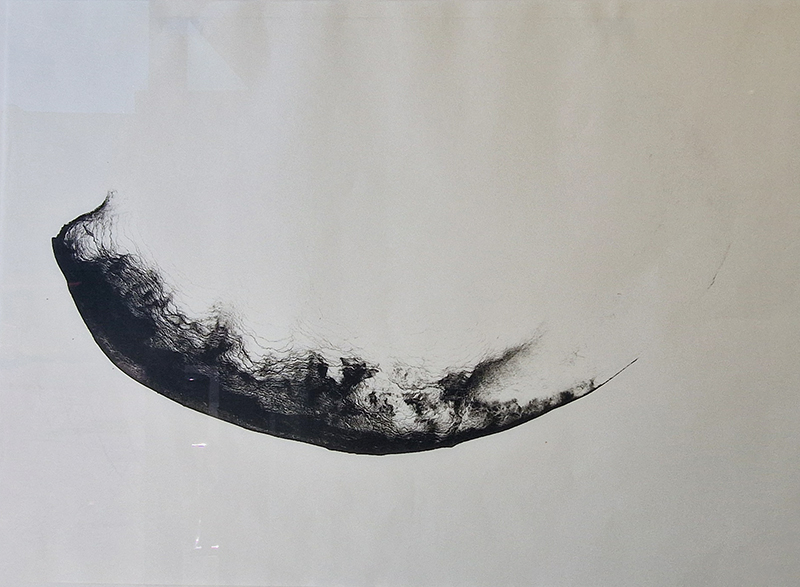


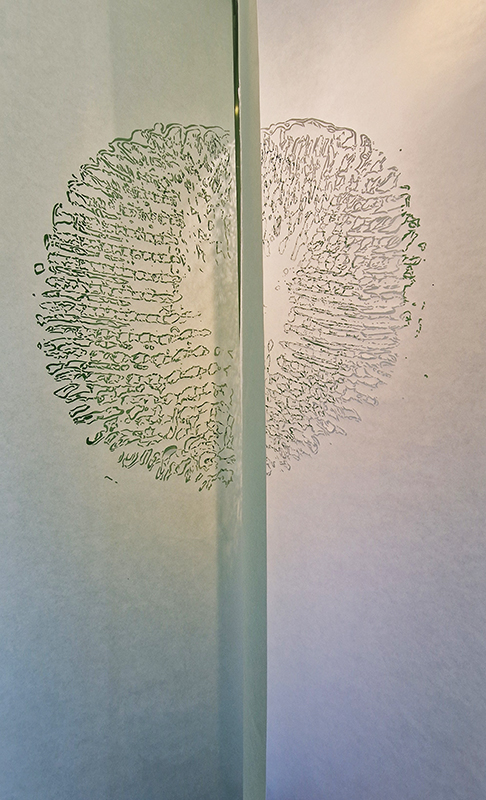


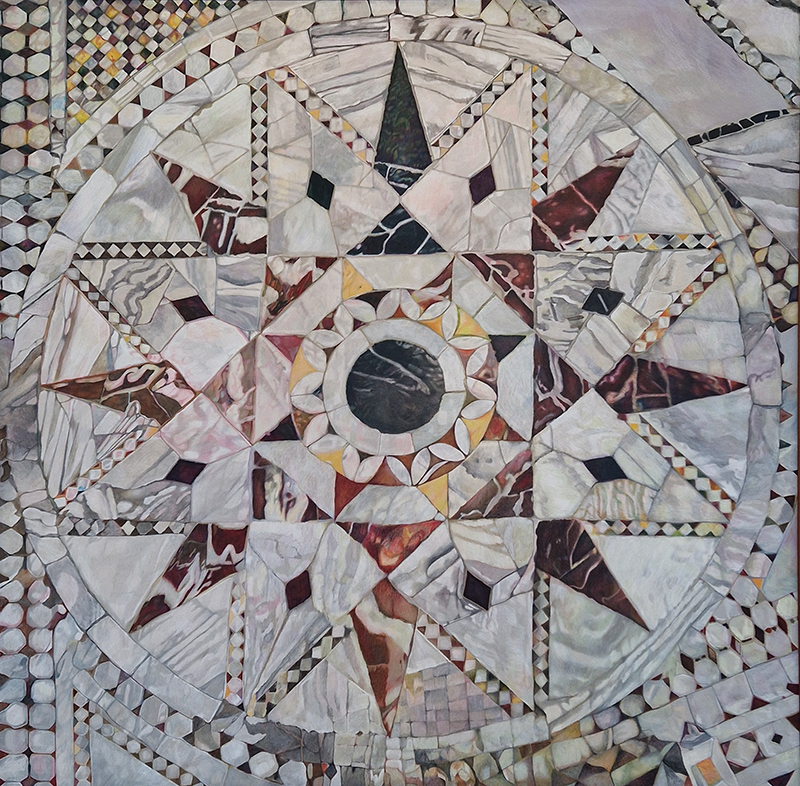
I was drawn to visit Gala Porras-Kim The categorical bind at Sprüth Magers to see these images which reminded me of the large hadron collider but made from marble. They are actually an examination of the conservation of marble tiled floors in Italy.
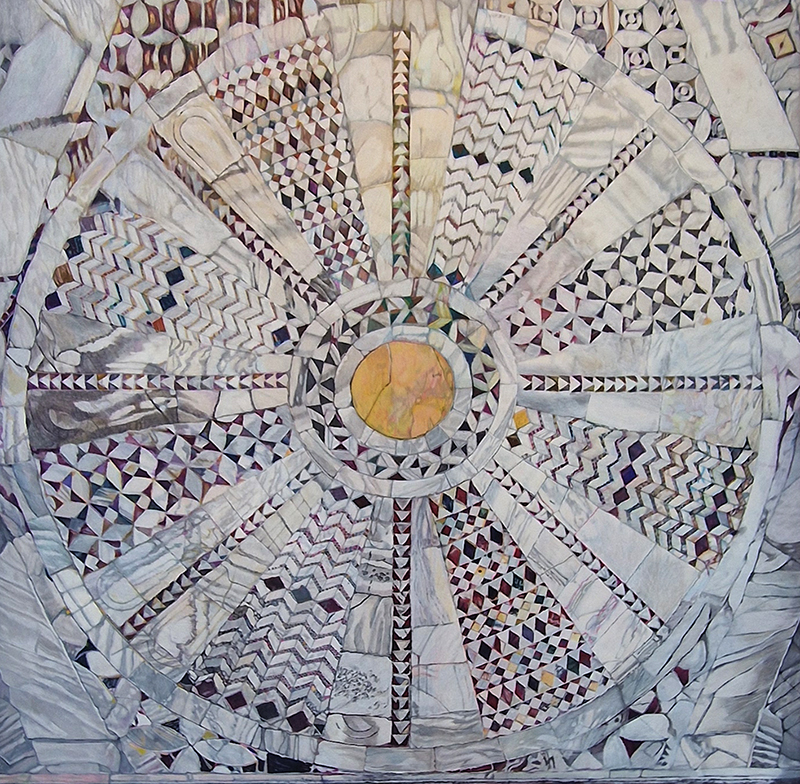


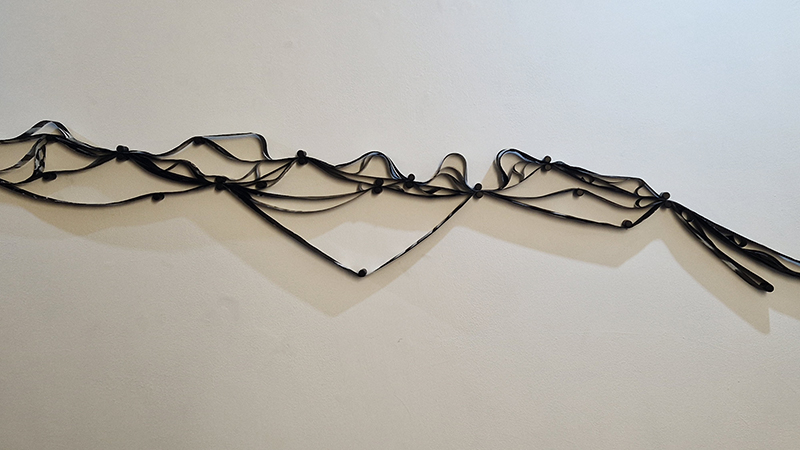
I remembered I had seen her work before at Gasworks and found it really interesting. In this piece she attempts to commune with the dead whose remains have ended up in a museum collection, possibly not where the living person had expected or would want.


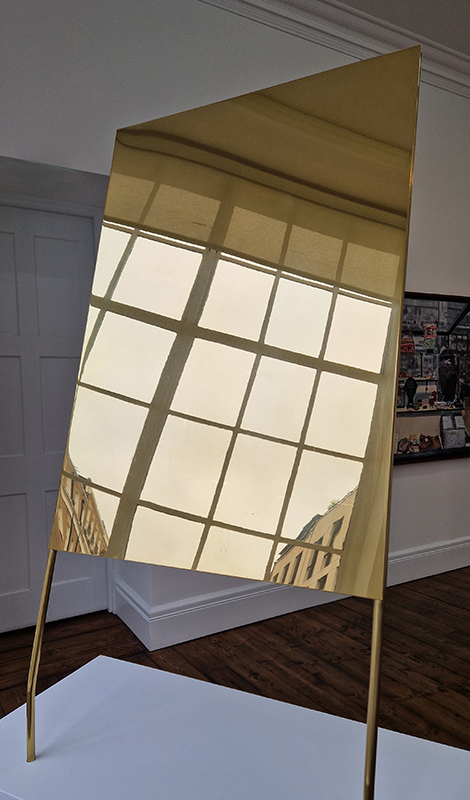
Gala Porras-Kim
All Earth energy sources are known to come from the Sun
Brass, sunlight

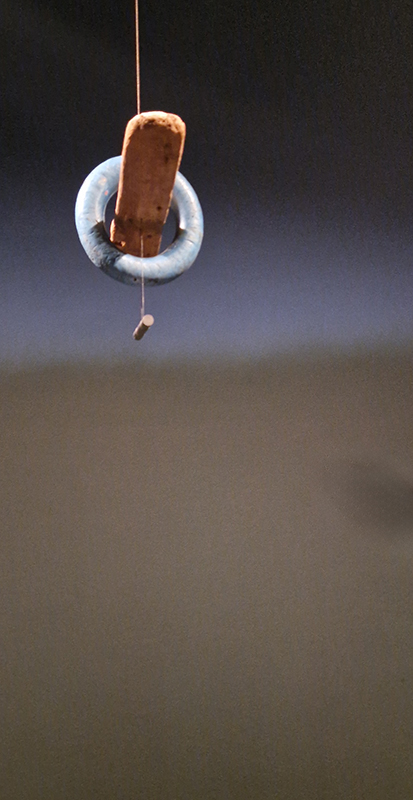
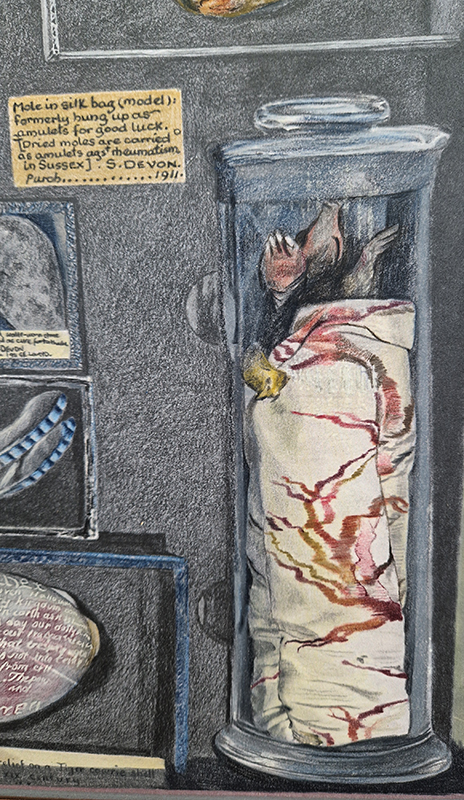
Most of the works were coloured pencil drawings of museum collections, giving agency to objects and questioning categorisation – this one of the poor mole amulet made me think of my mole killer brother who suffers from arthritis.


It is fascinating to think about how humans experience sound and consider frequencies occurring outside the human spectrum of sensitivity that other animals may be able to hear. Also to think about sound as vibrating bodily rather than auditory sensation. Barbican Feel the Sound requires a willingness for interactivity to experience most of the exhibits. The instructions weren’t always clear and so it was at times a bit of a frustrating journey through the space.