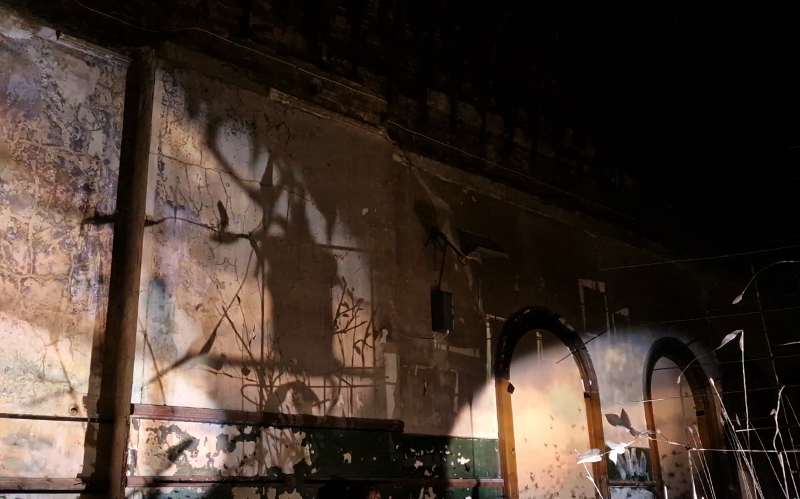‘A stone sky rotated above our heads’ – Italo Calvino, Cosmicomics
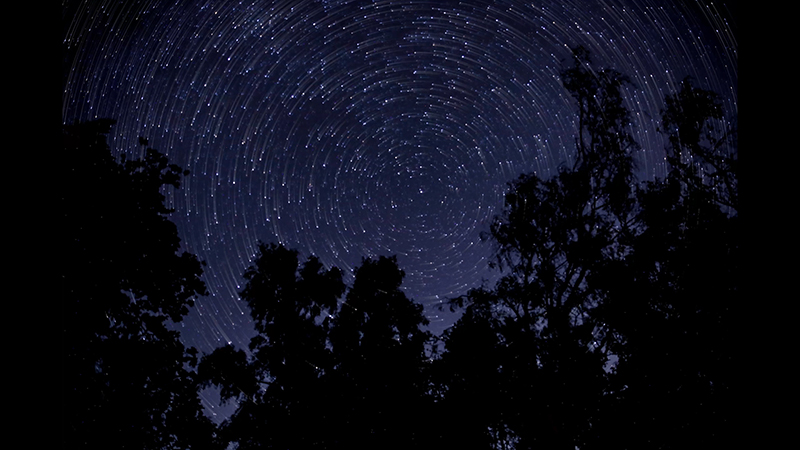
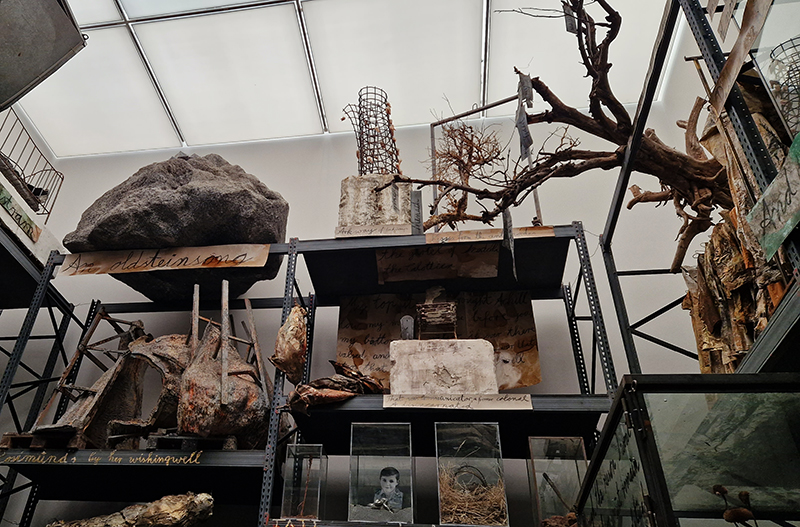
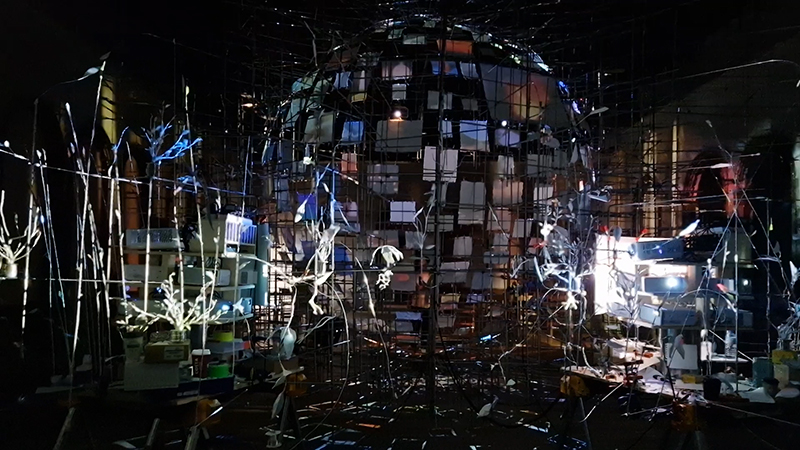
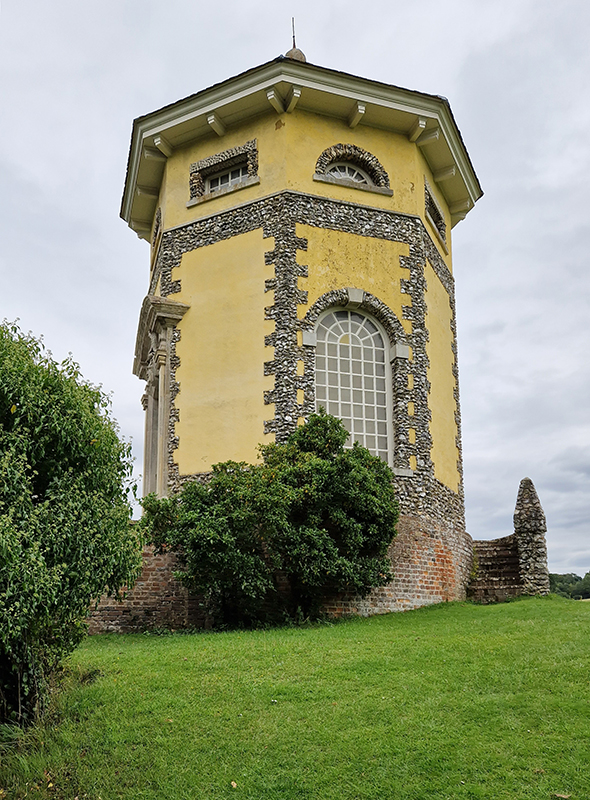
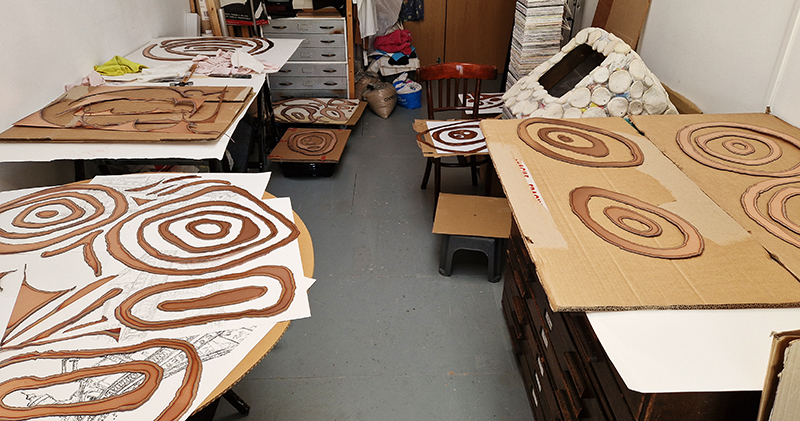
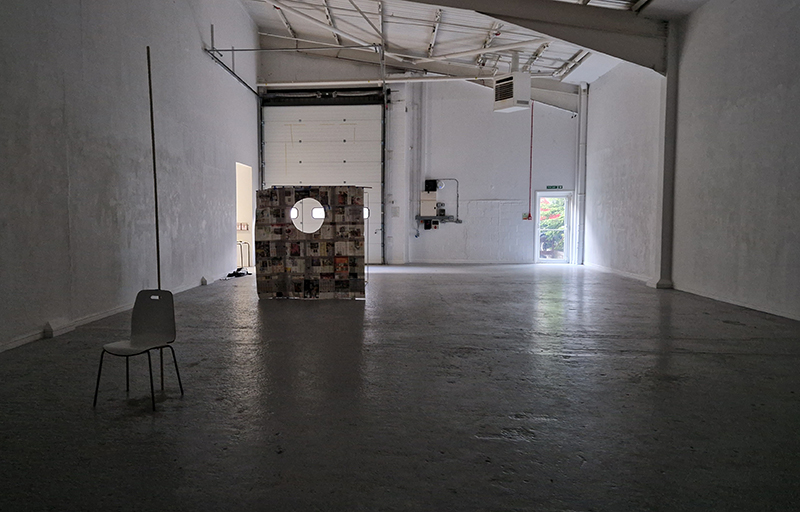
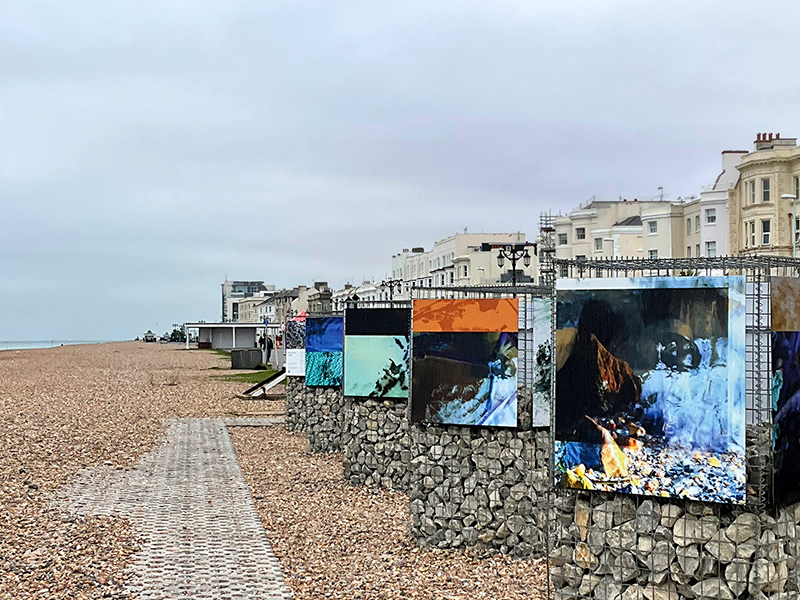
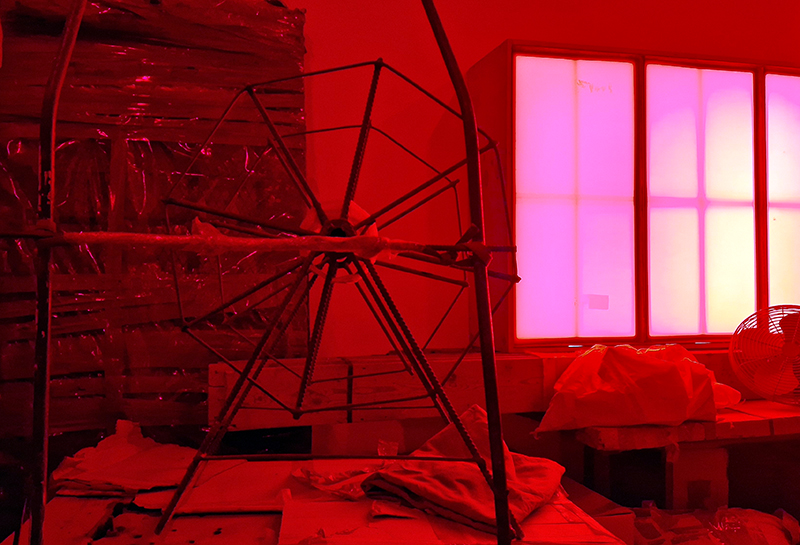
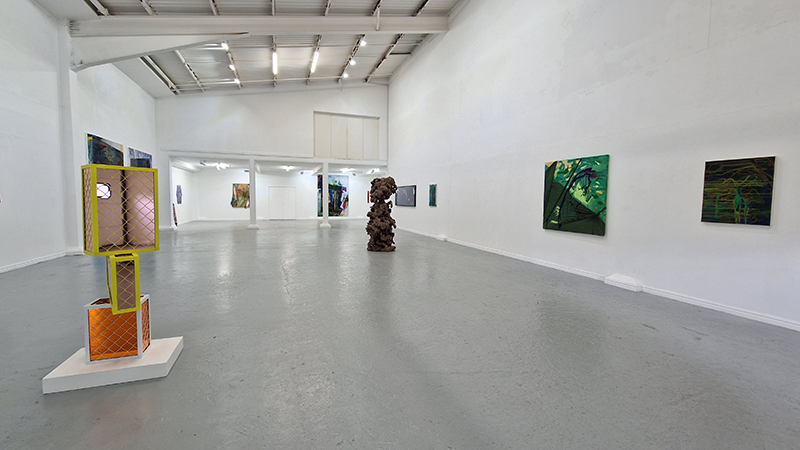
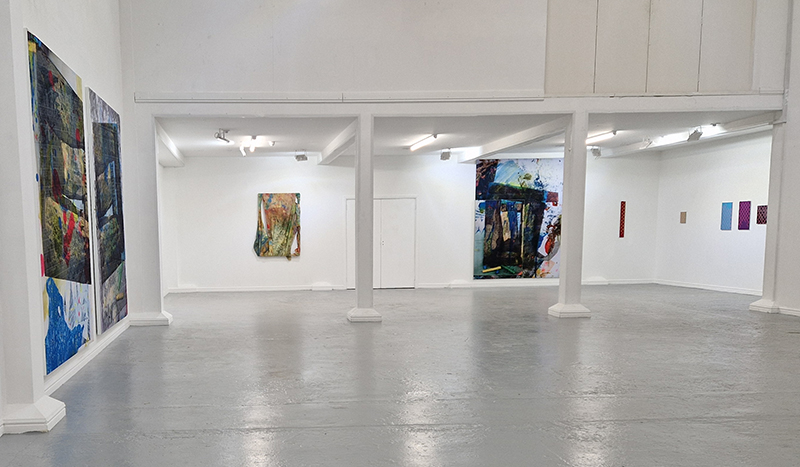
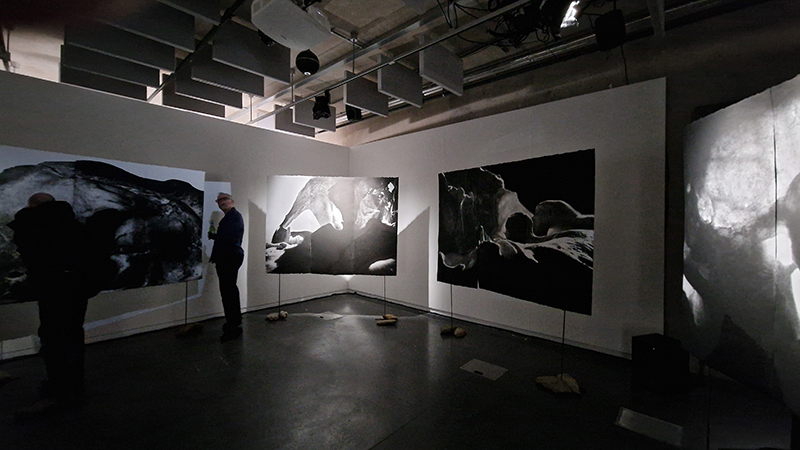
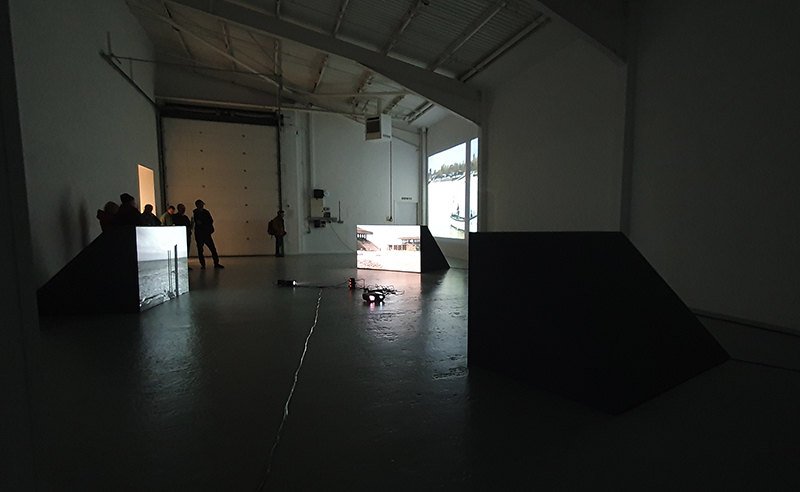
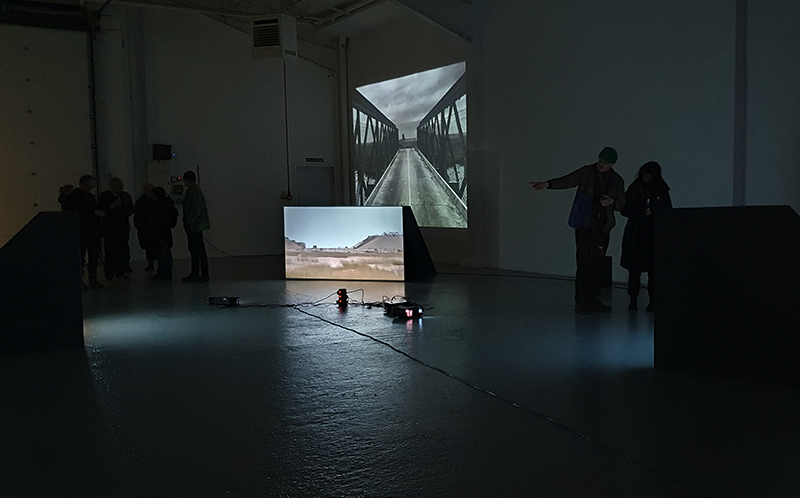
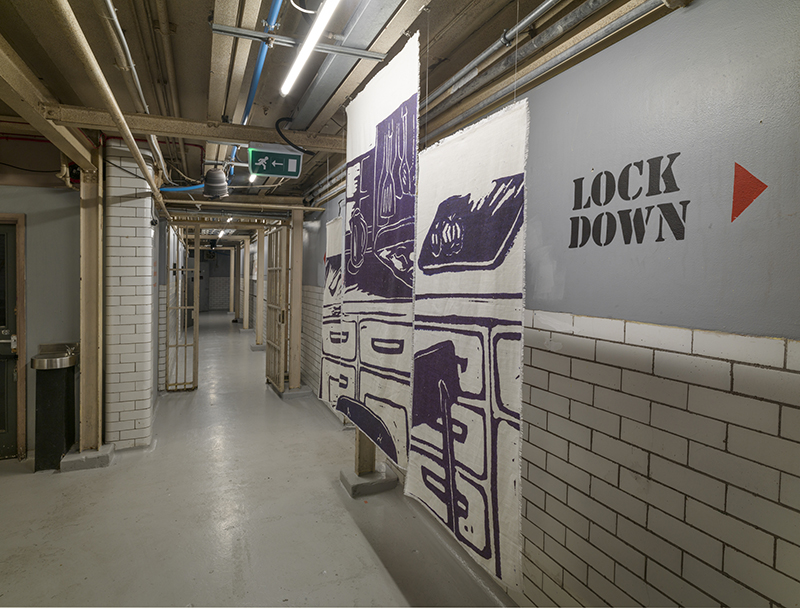
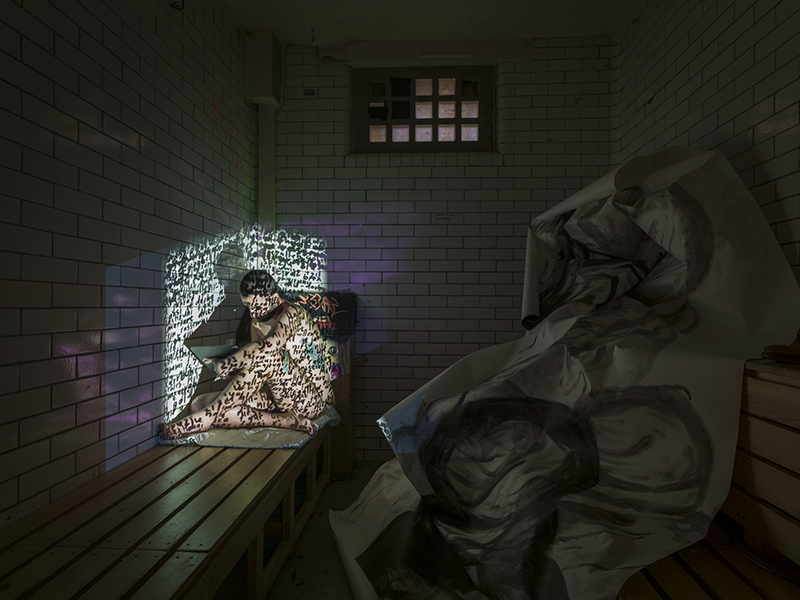
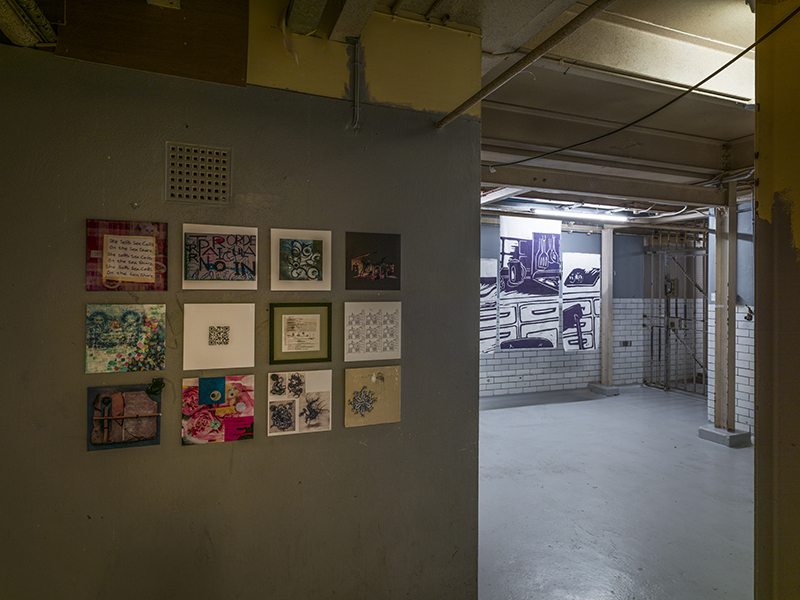
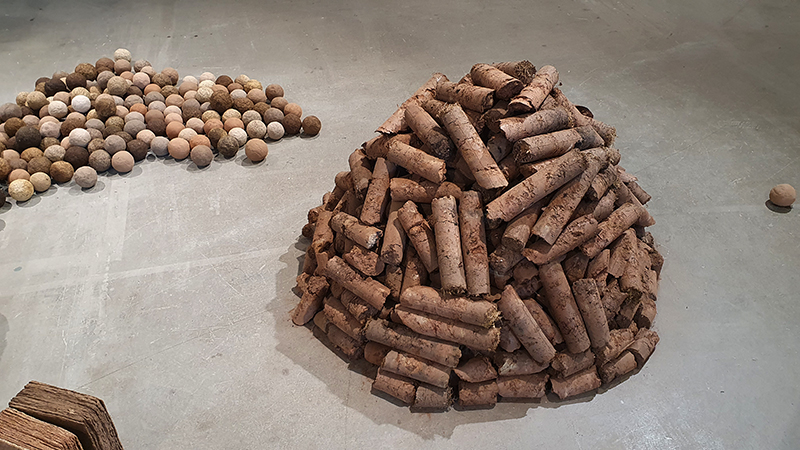
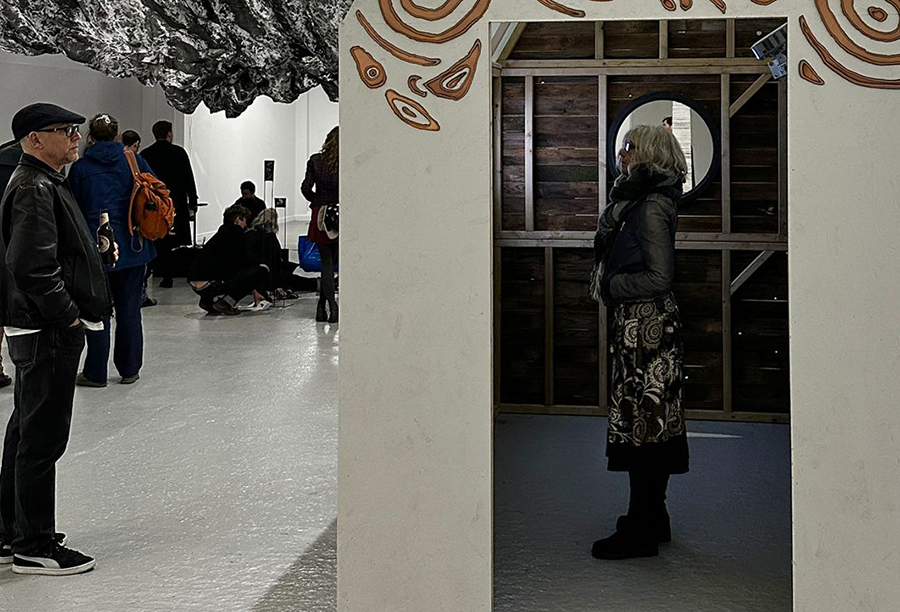
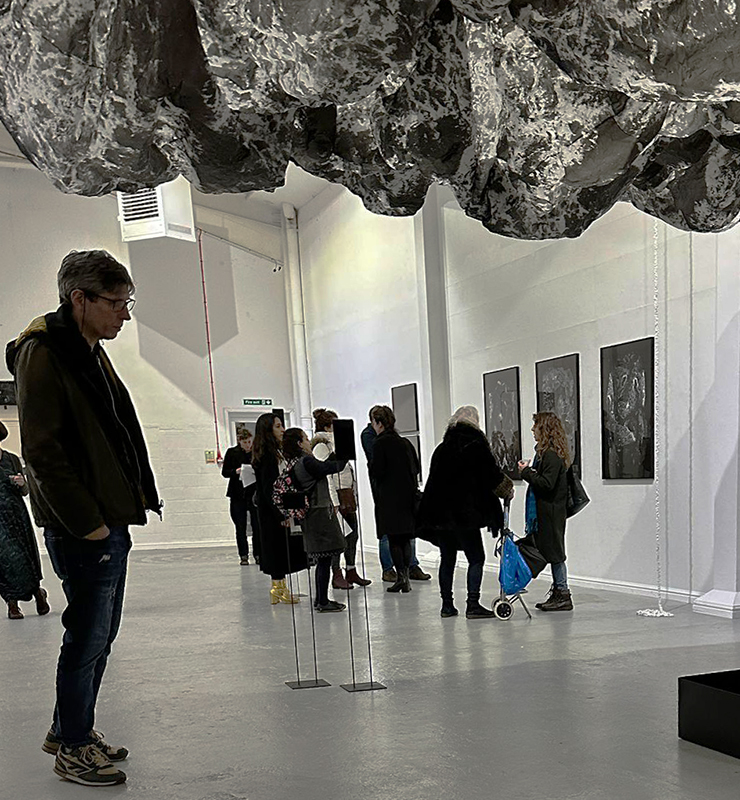
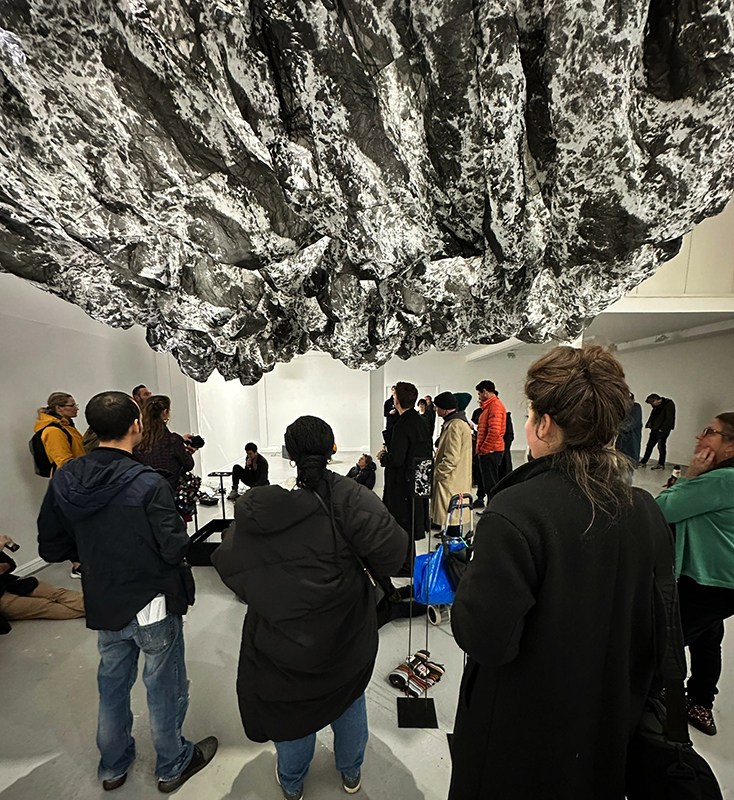
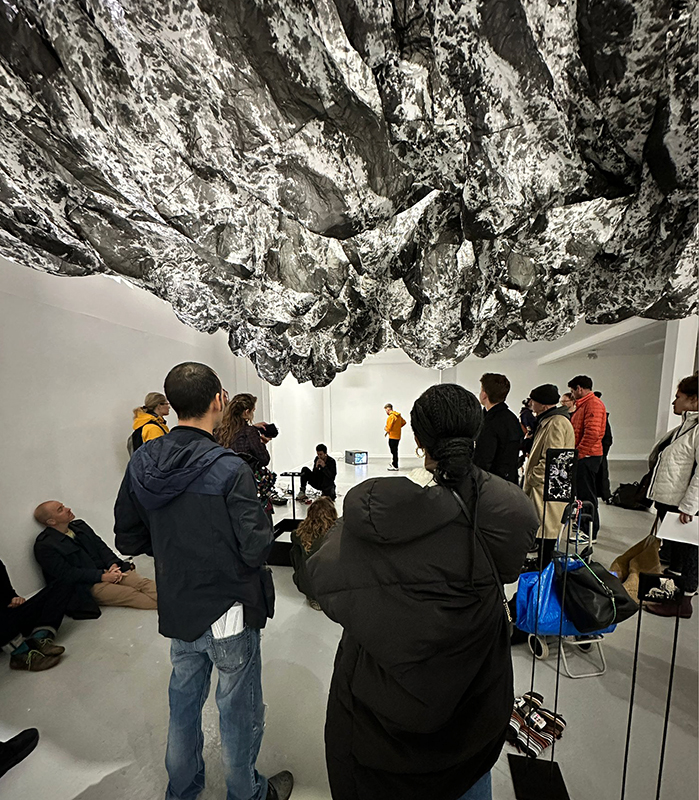
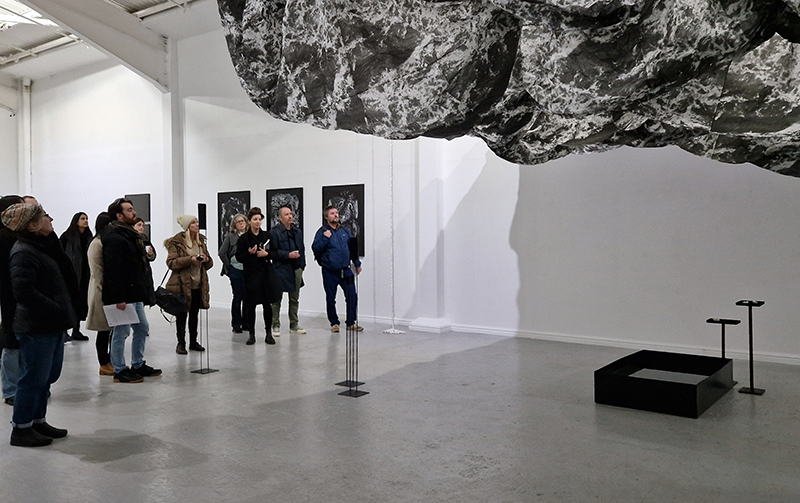
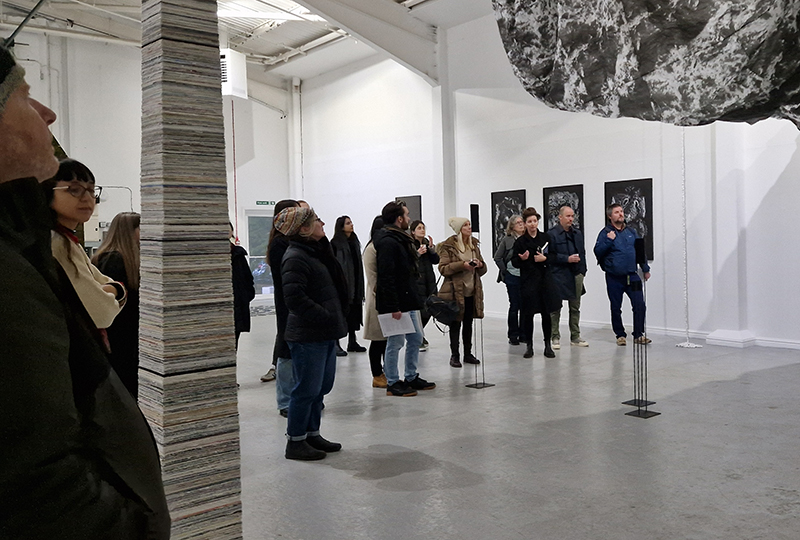
The culmination of two years work – A STONE SKY duo exhibition with Julie F Hill opened at Thames-side Studios Gallery – Reimagining the idea of an observatory – the exhibition proposes a cavernous realm of real and speculative possibilities that arise from beyond the limits of human perception. Engaging with the extended sensory range offered by technologies such as orbiting space telescopes through to the ability of birds to ‘see’ the Earth’s magnetic field, the artists’ reveal intimate connections between earth and space.
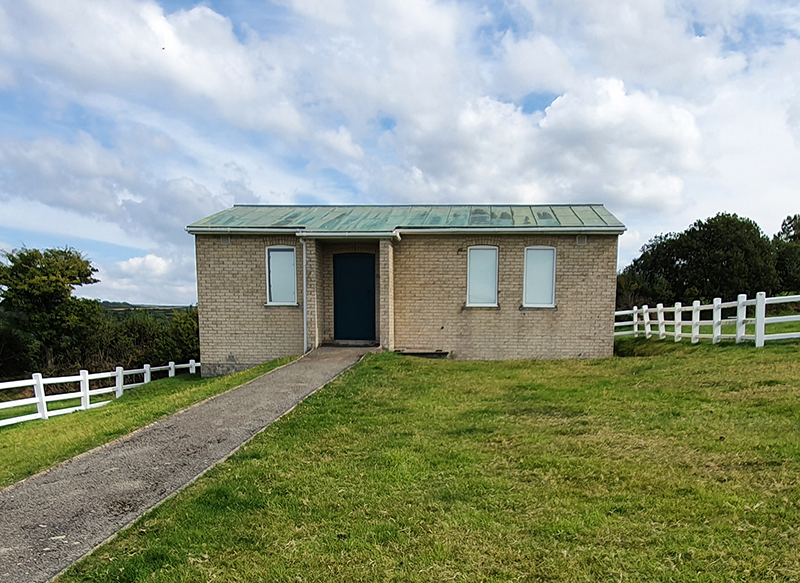
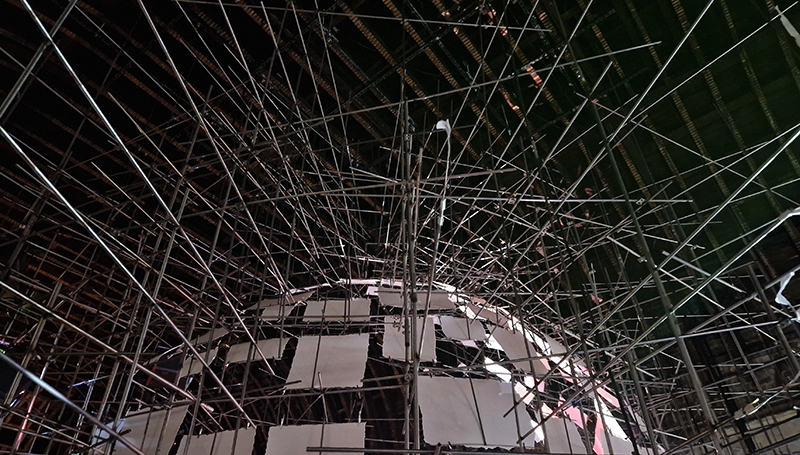
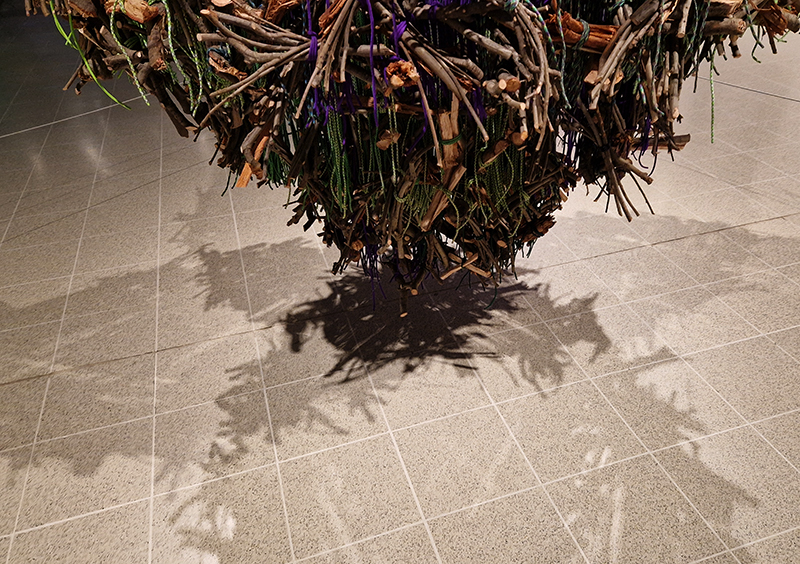
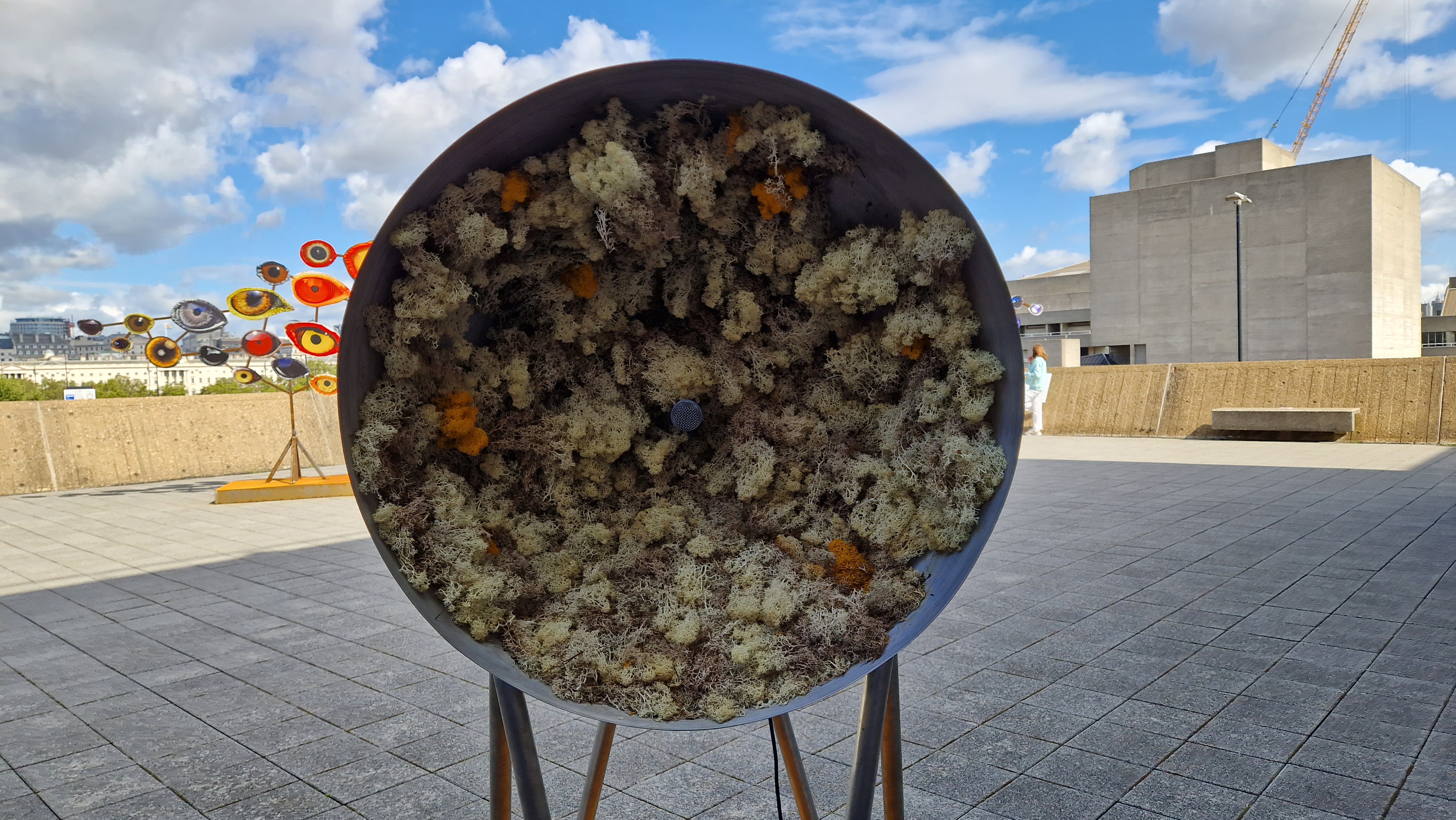
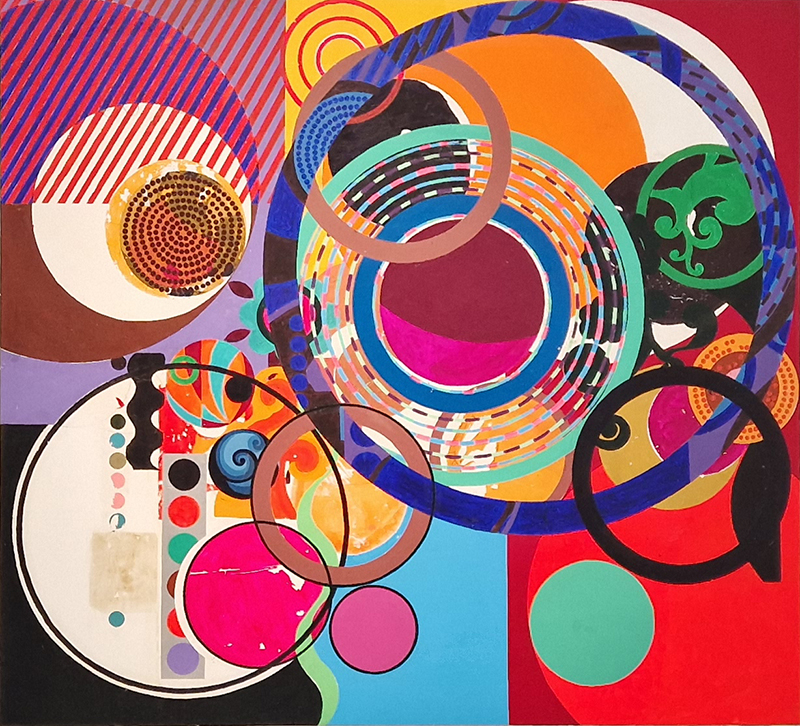
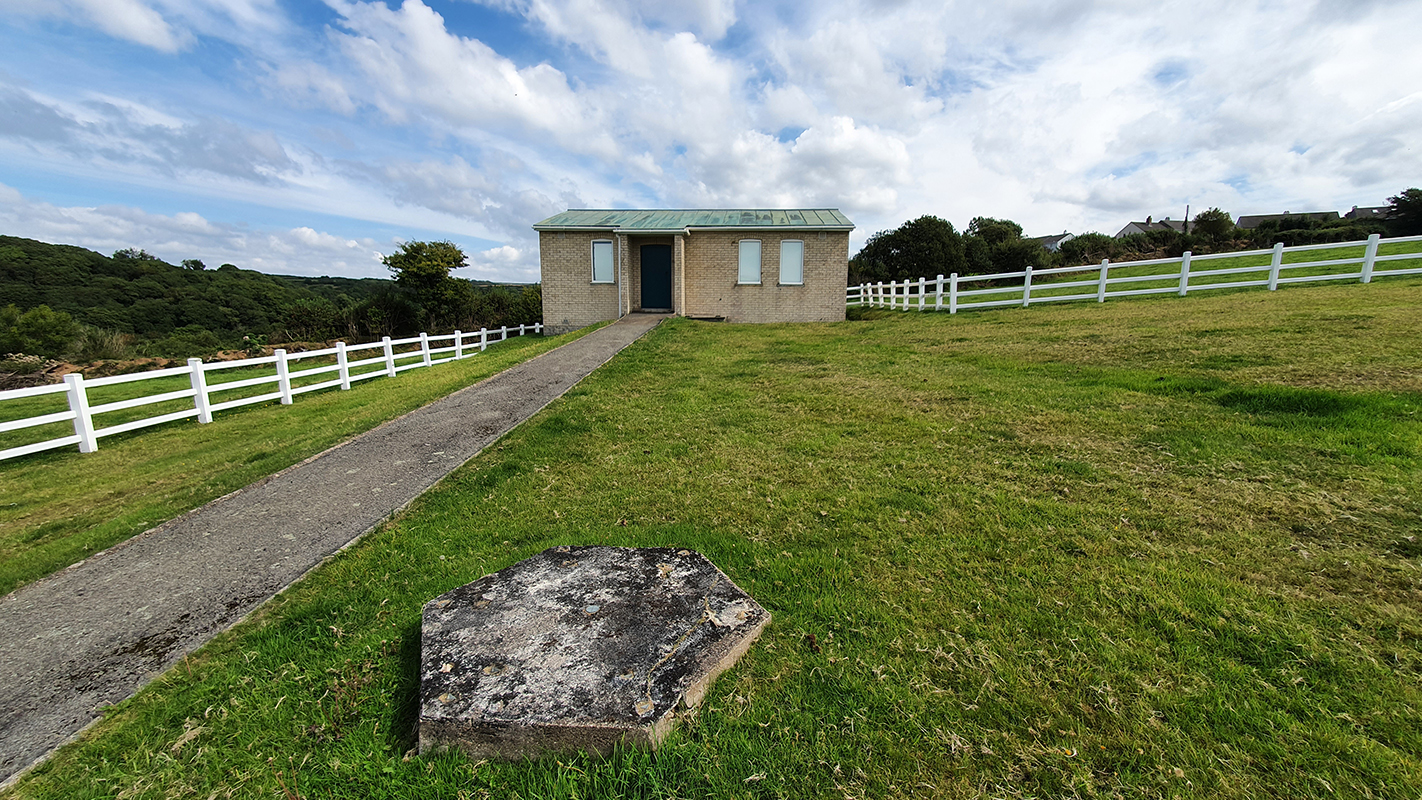
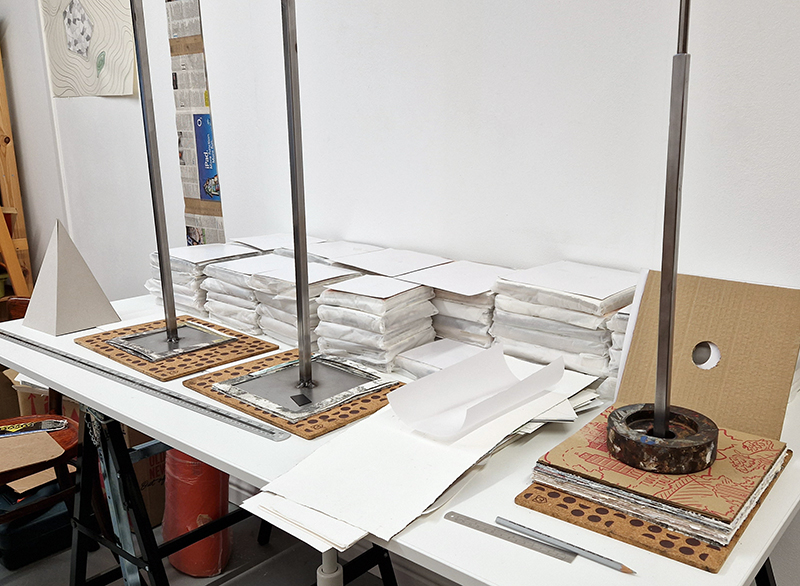
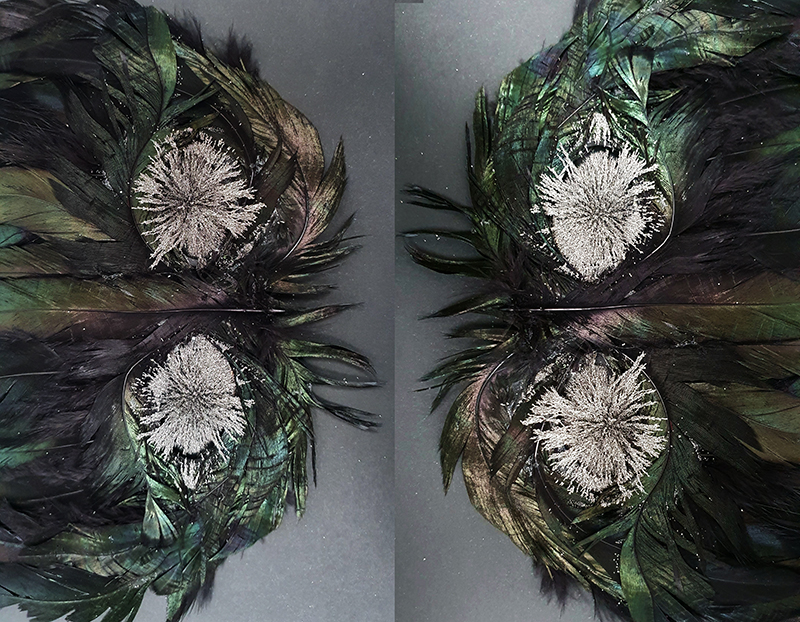
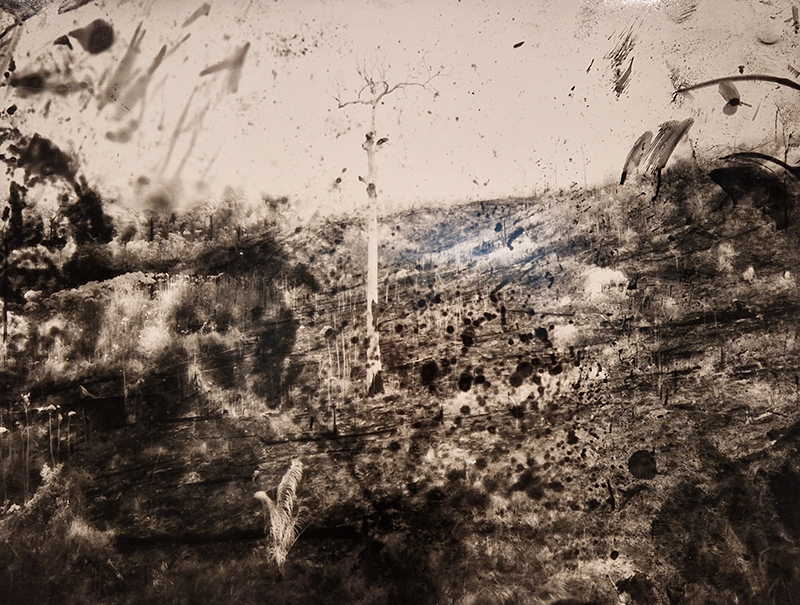
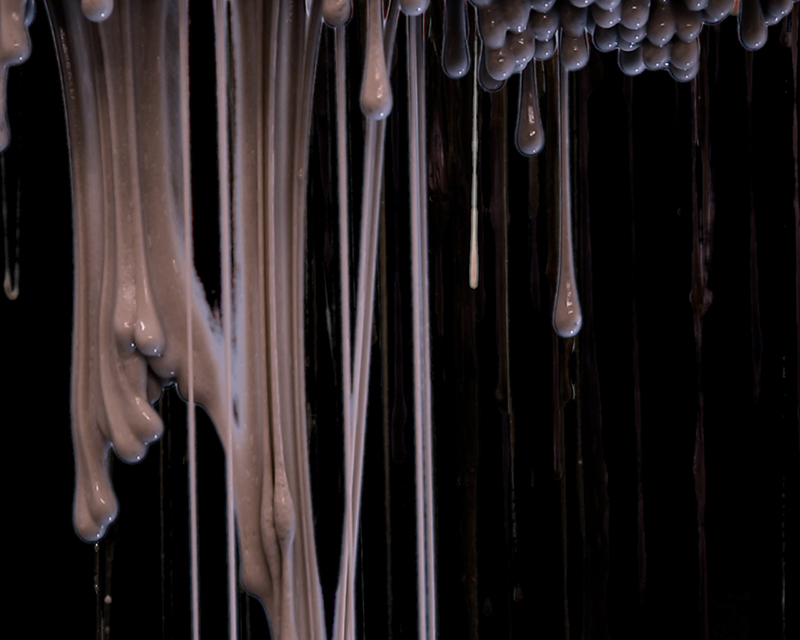
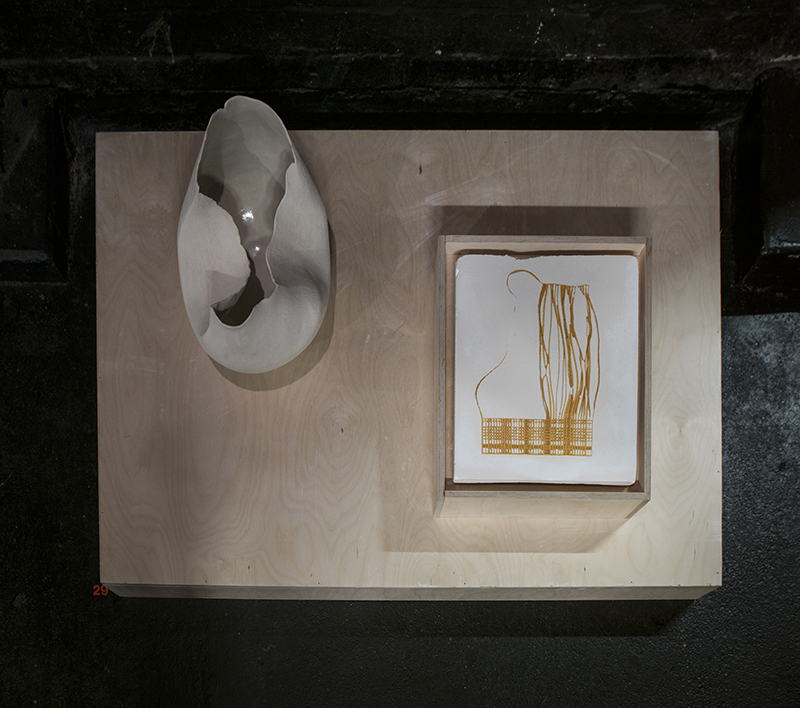
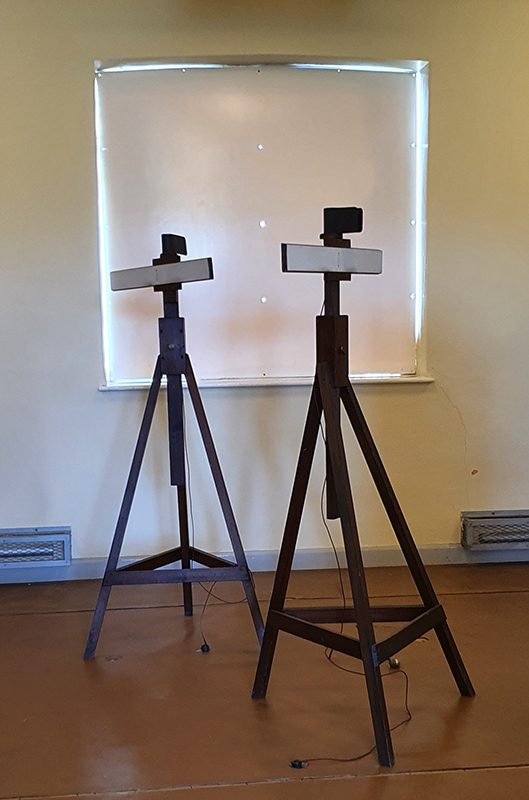
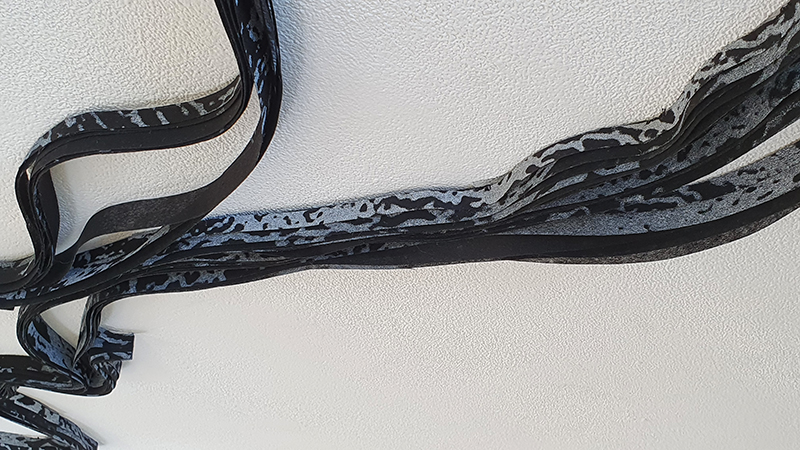
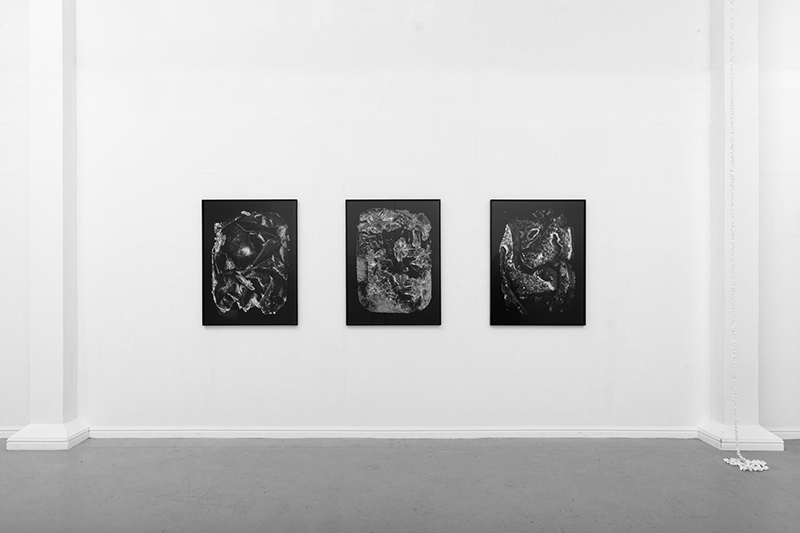
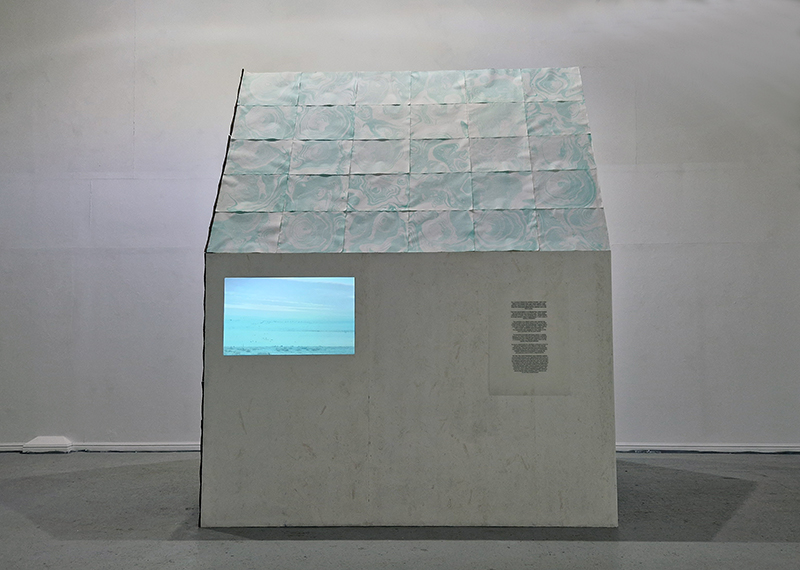
Installation shot by Ben Deakin Photography.
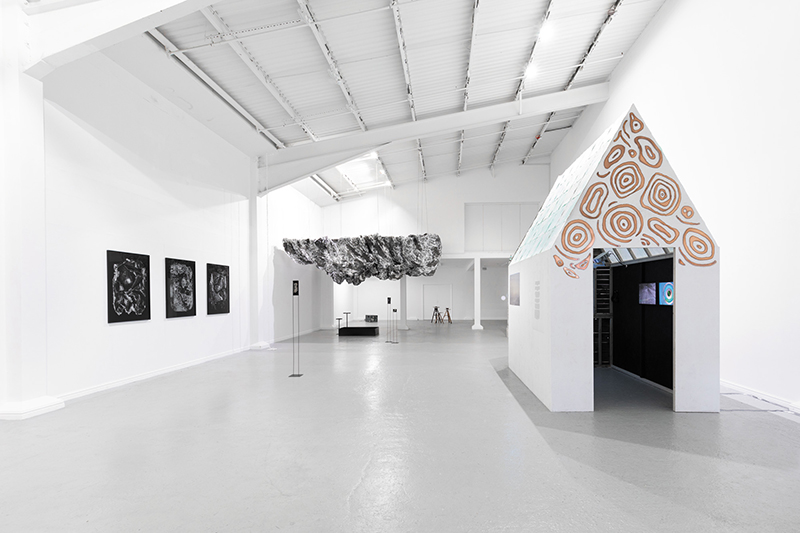

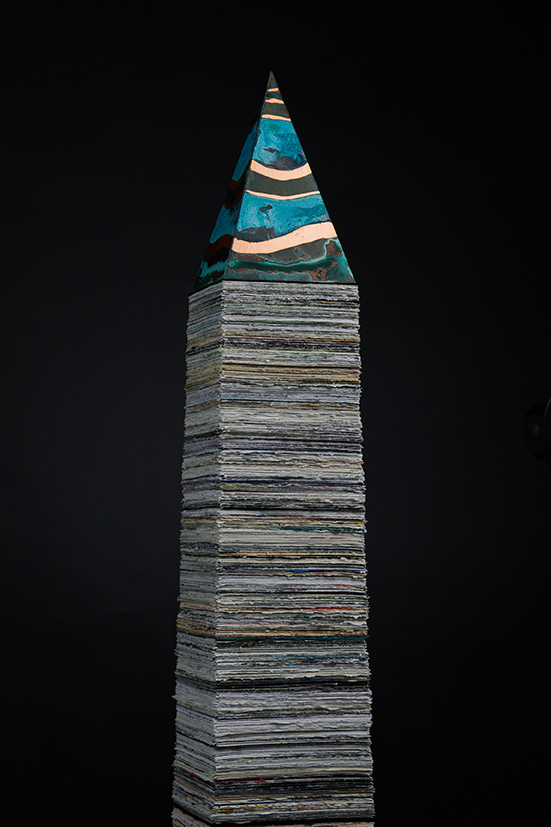
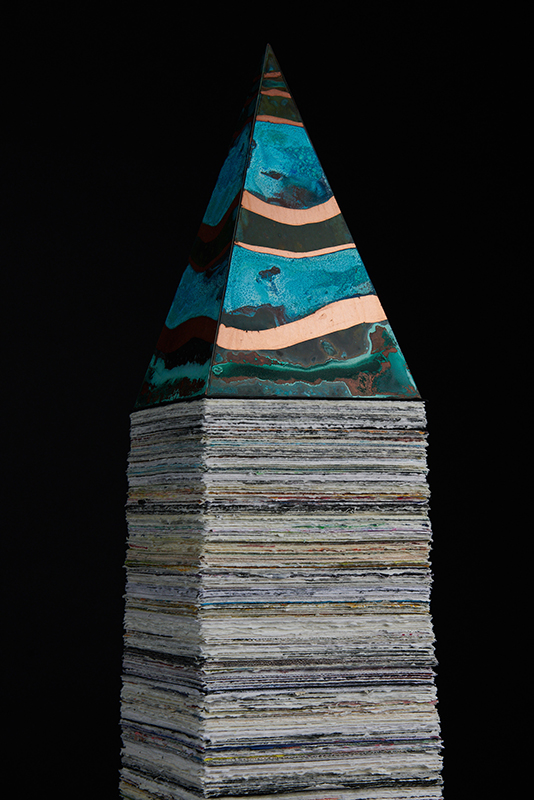
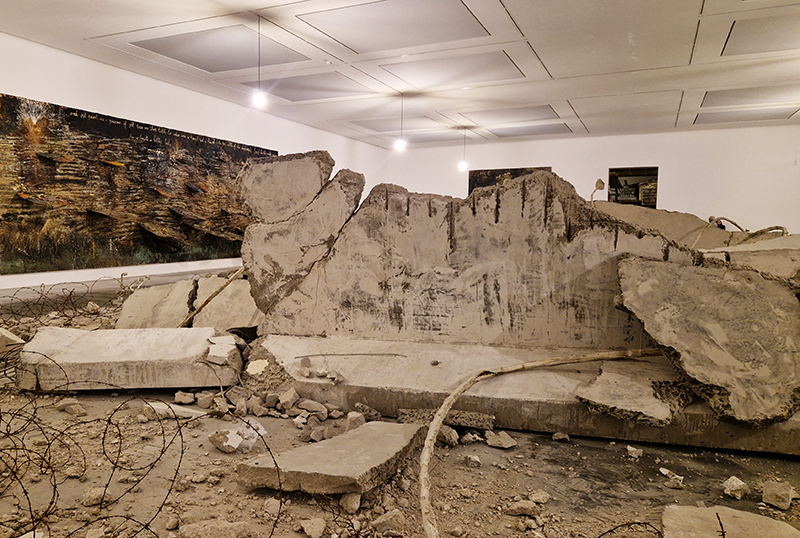
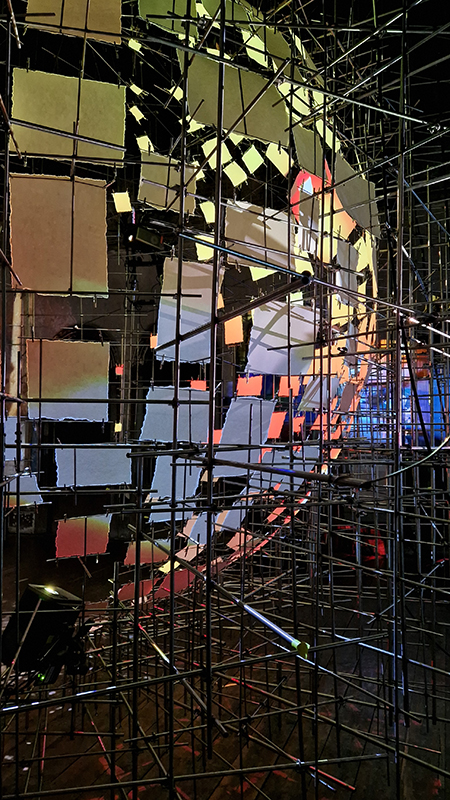
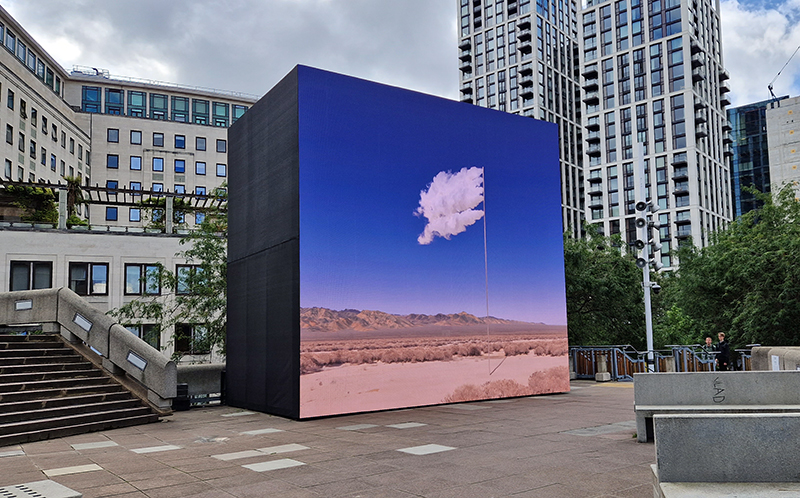
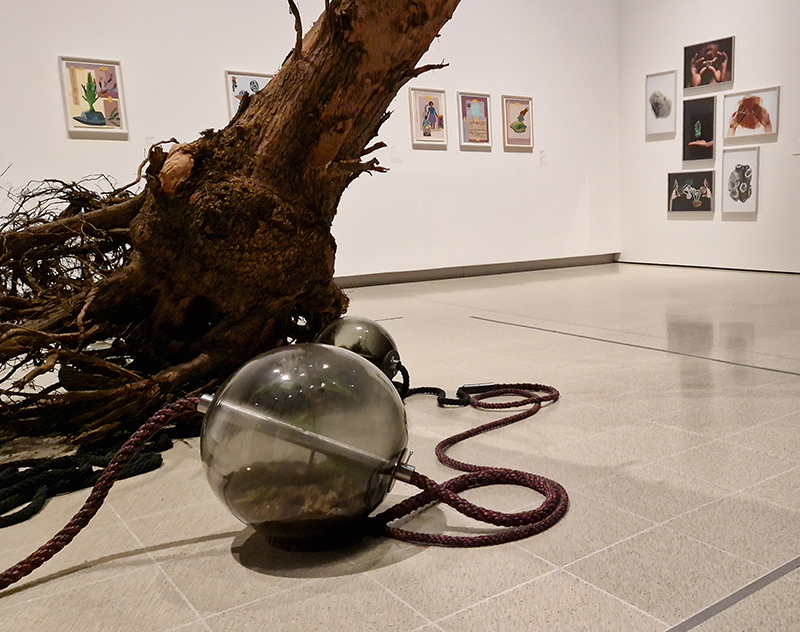
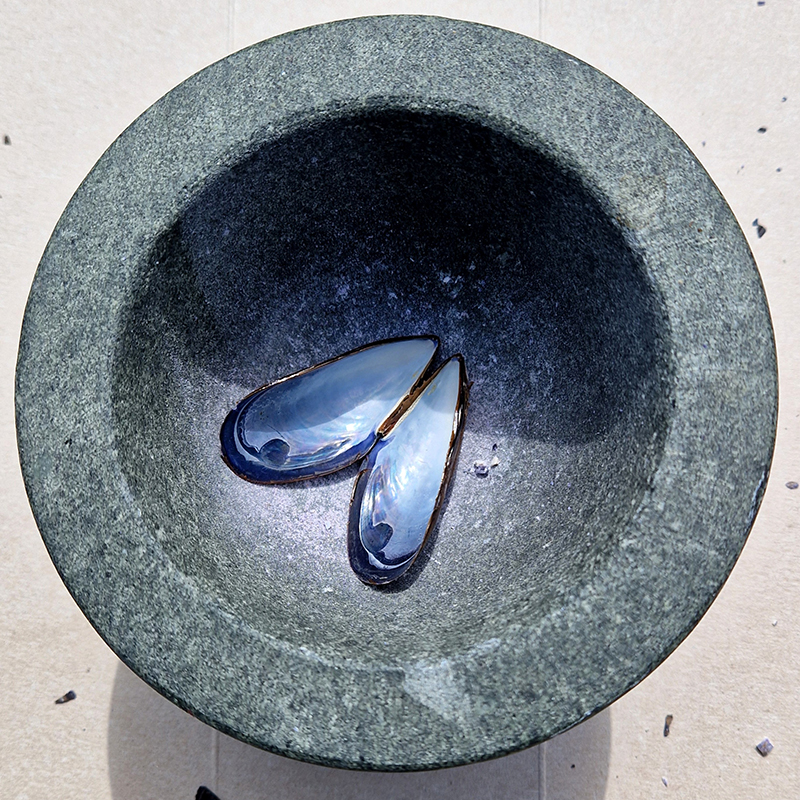
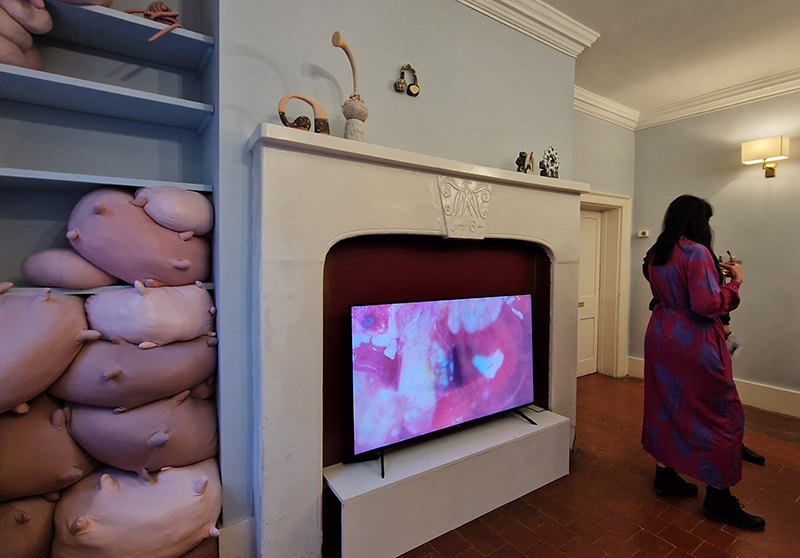
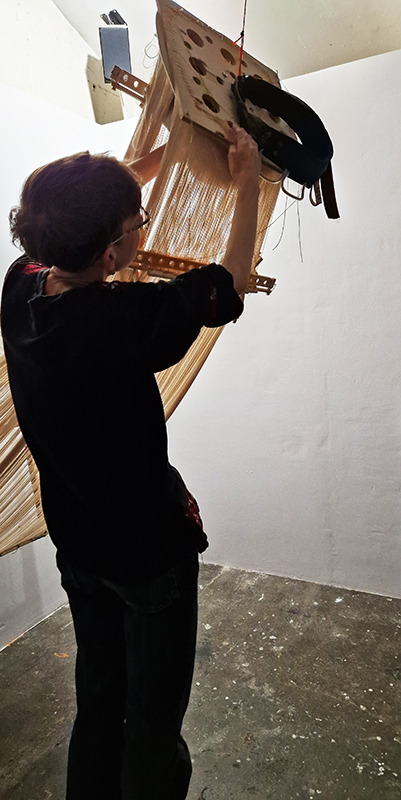
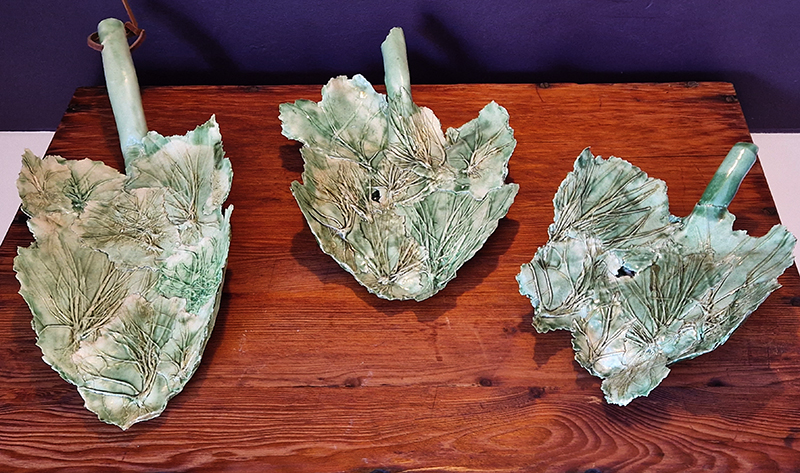
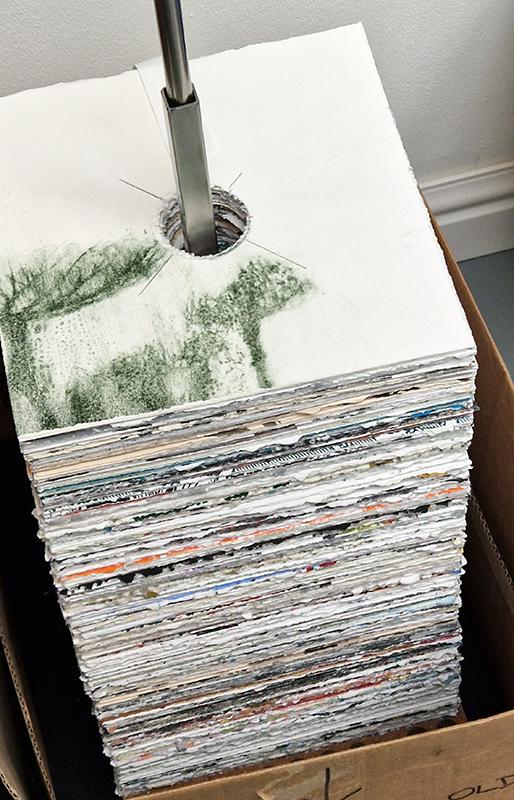
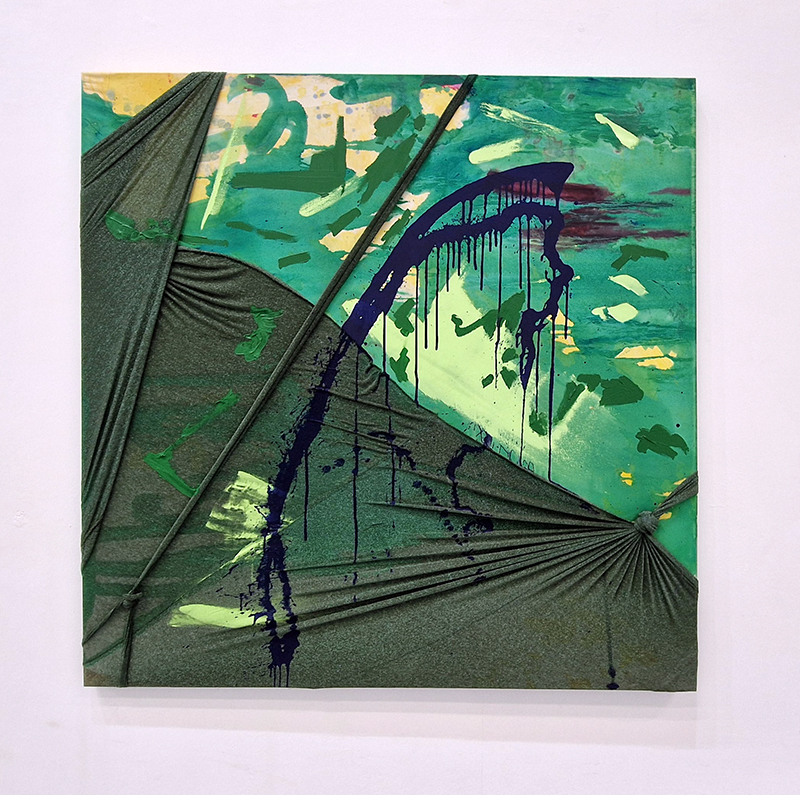
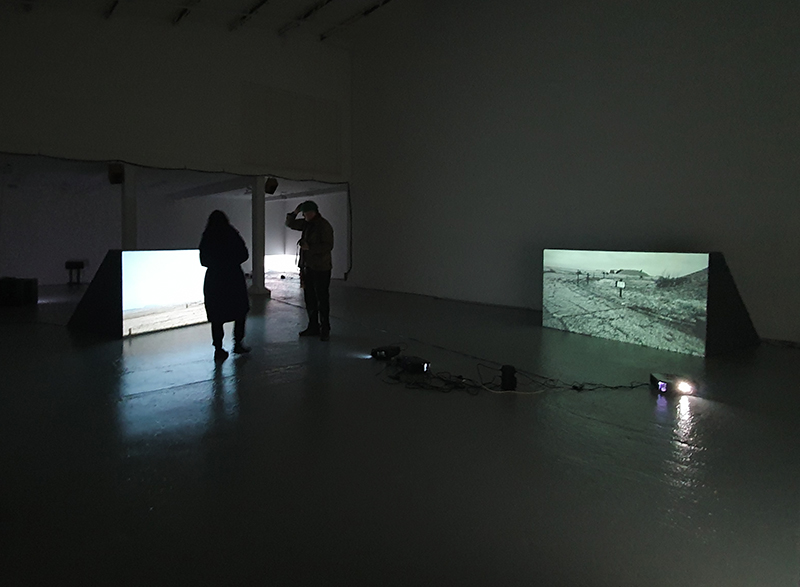
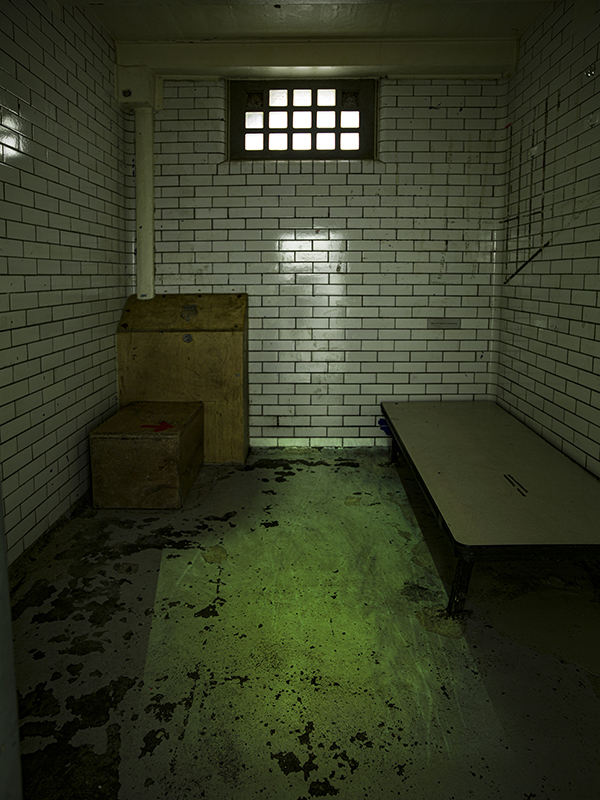
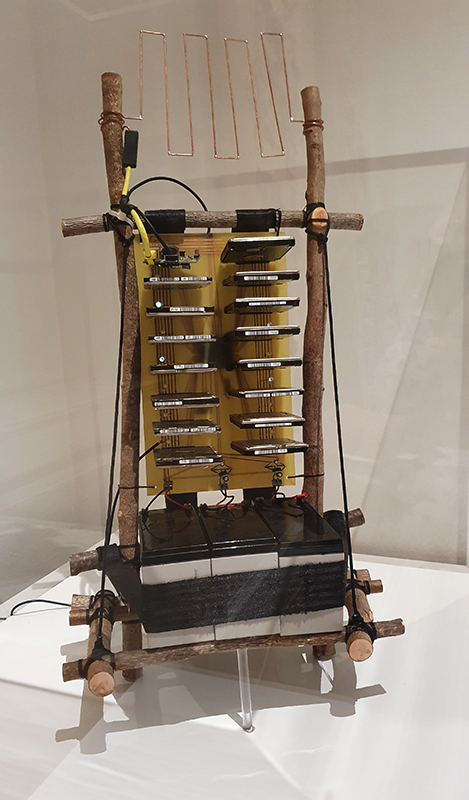
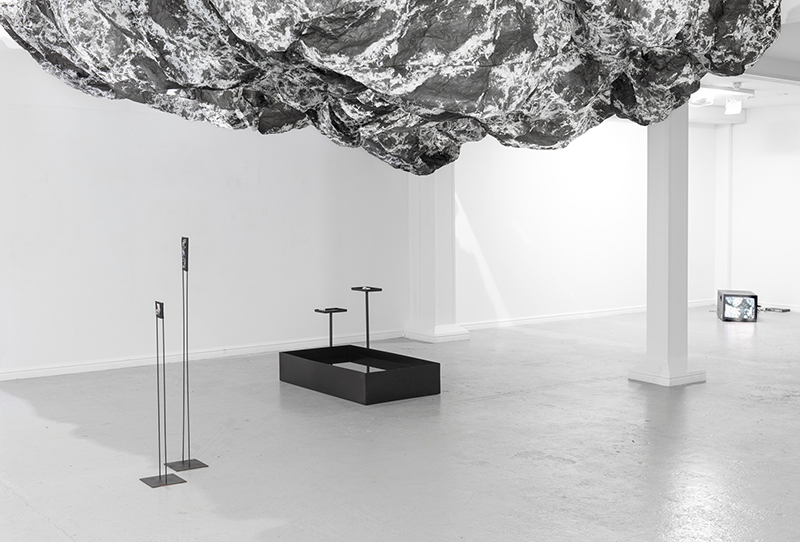
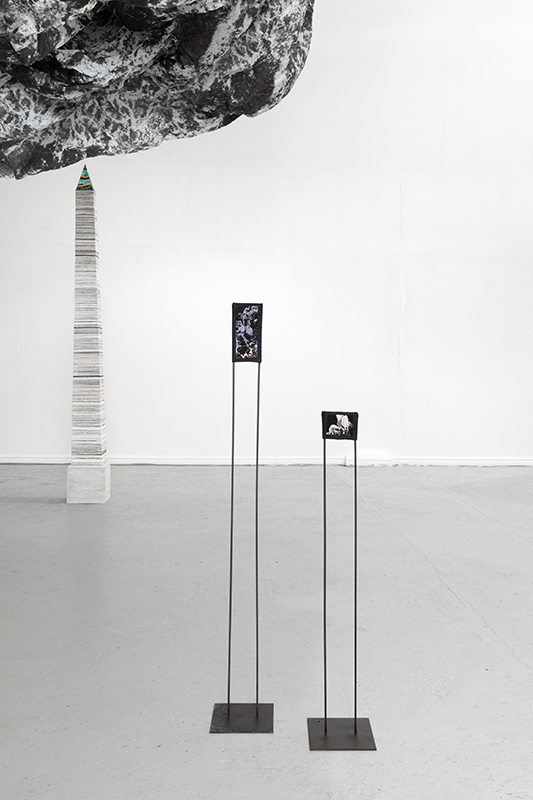
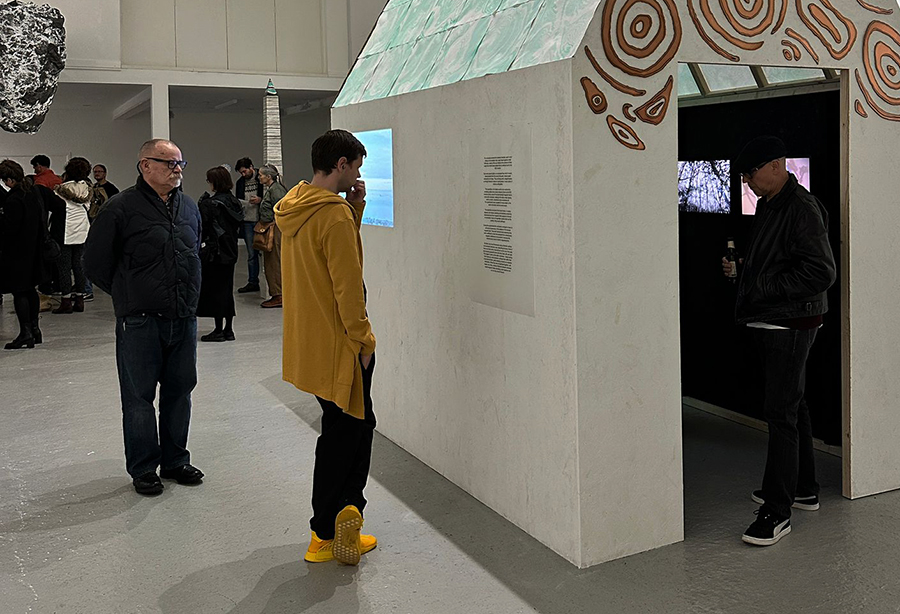
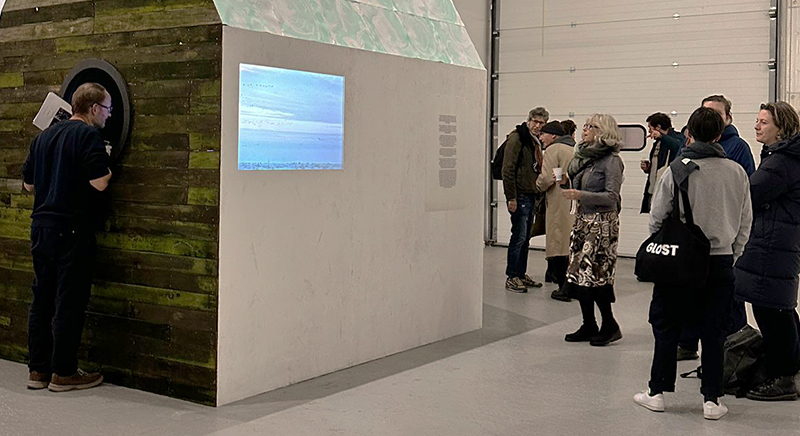
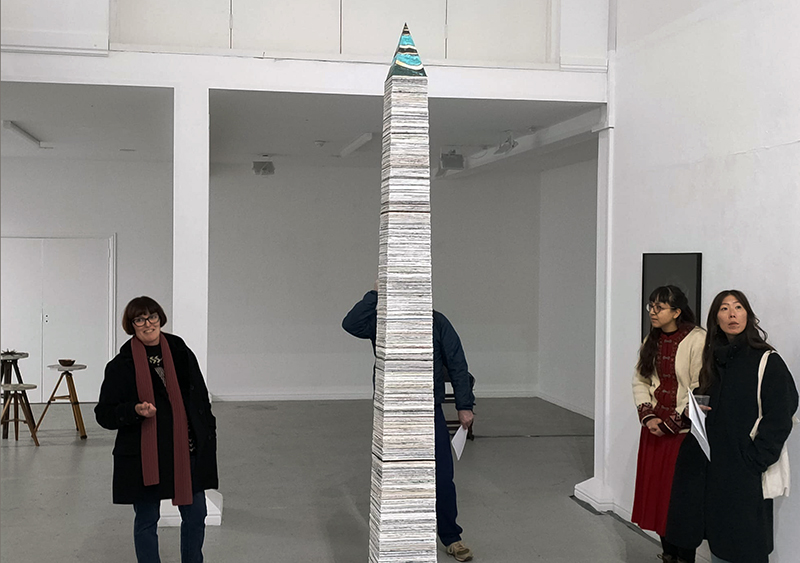
Susan Eyre seeks to navigate a path across time from the first human encounter with the magical qualities of the lodestone to current understanding of the interaction of the magnetic field with terrestrial life. Her works respond to the architecture, instruments and materials, found at a magnetic observatory while scientific objectives are expanded to include natural navigation techniques and extra-sensory methods used by the non-human realm, to form the basis of speculation as to the ability for humans to perceive the Earth’s magnetic field. Installation, sculpture and moving image works include a reimagined observation hut operating as a sensory hub with video screens suggesting portals into a web of neural pathways; an obelisk of layered recycled paper echoing Earth’s geological and magnetic history secreted in sedimentary strata of rock and a digital video work activated in real time by the passage of cosmic rays through a scintillator detector.
Images by Ben Deakin Photography







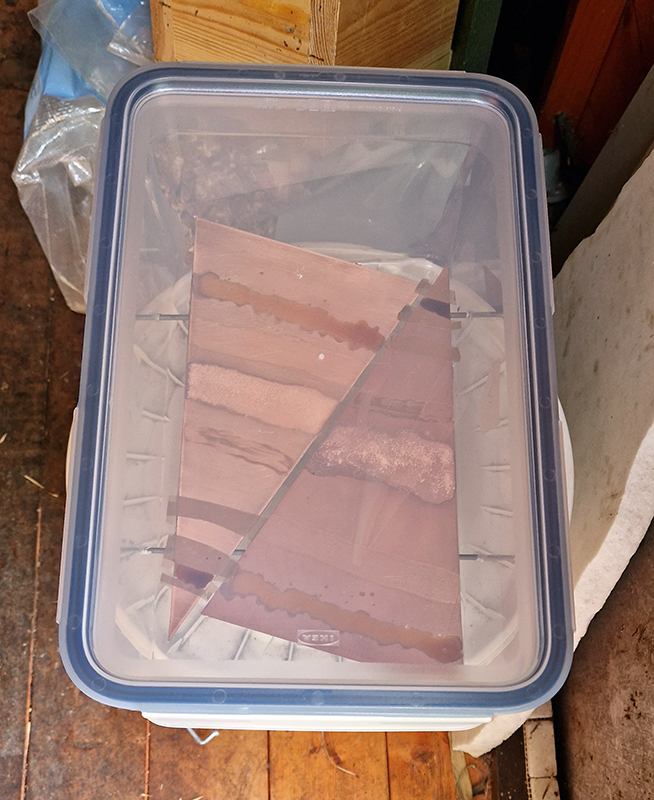
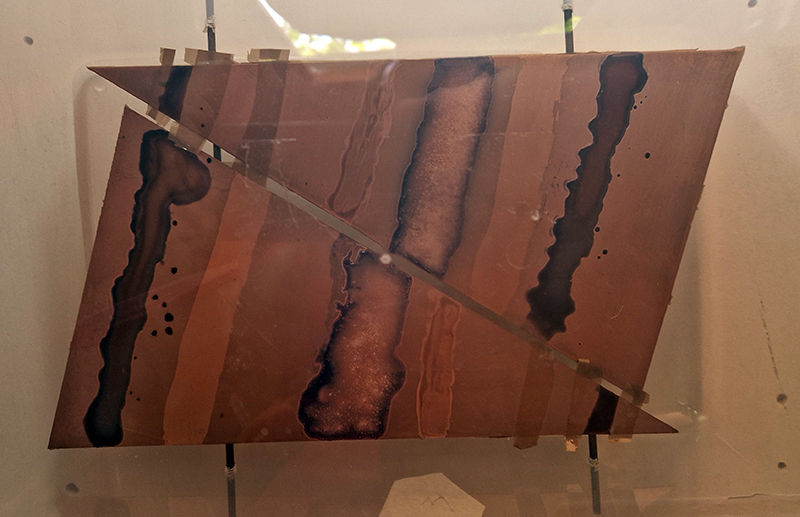
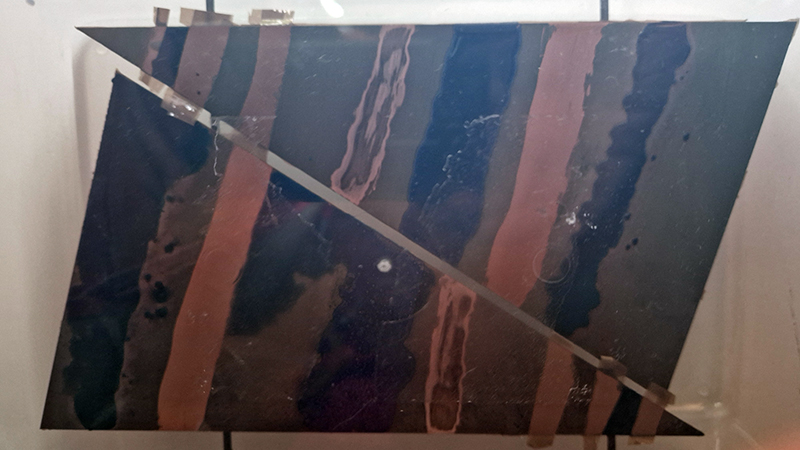
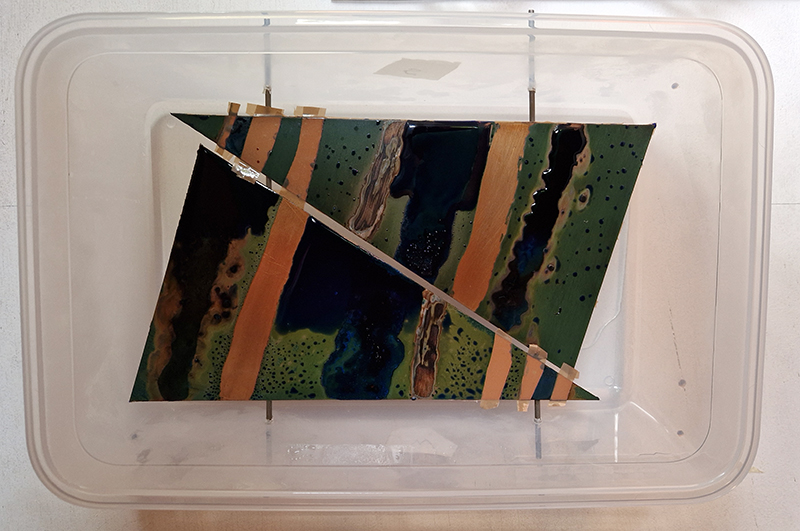
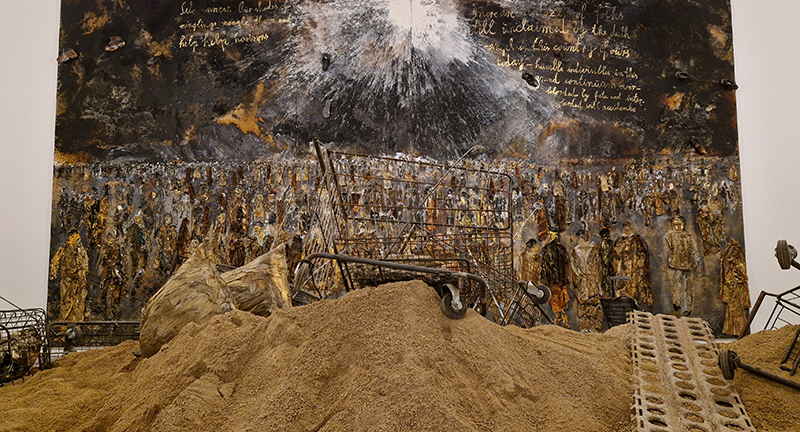
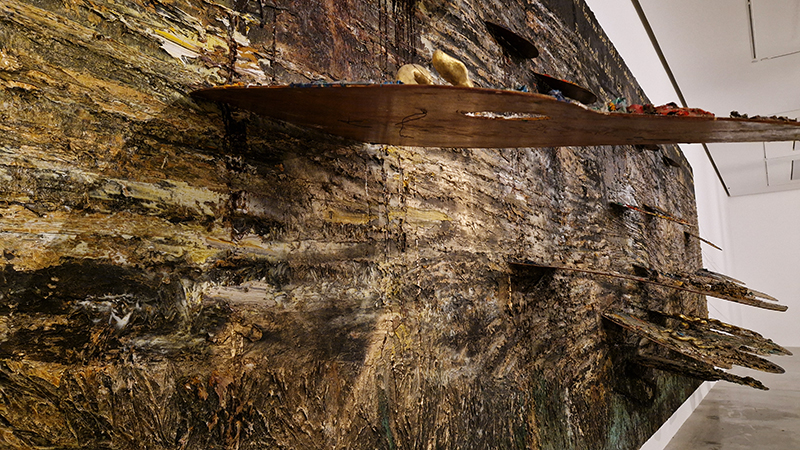
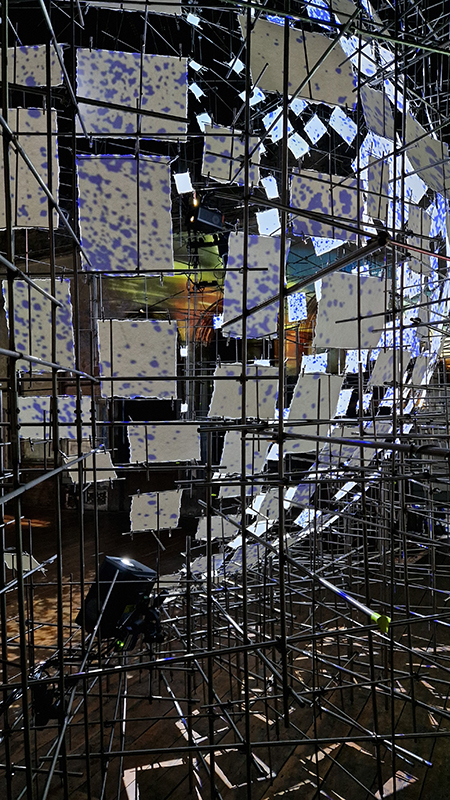
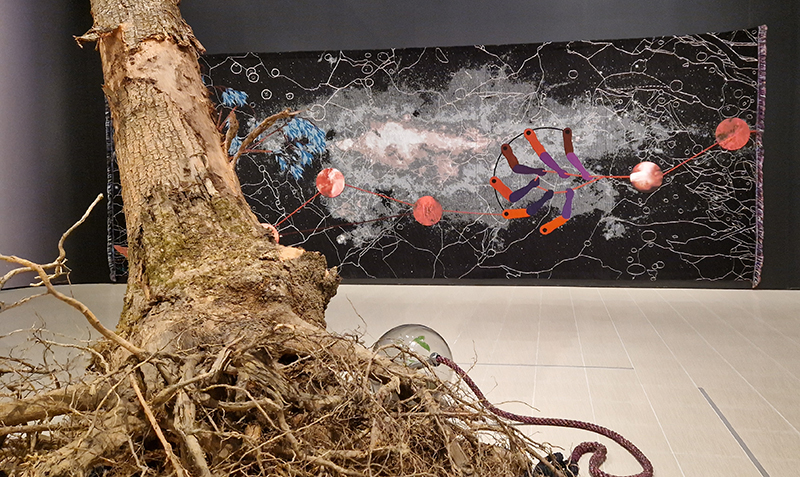
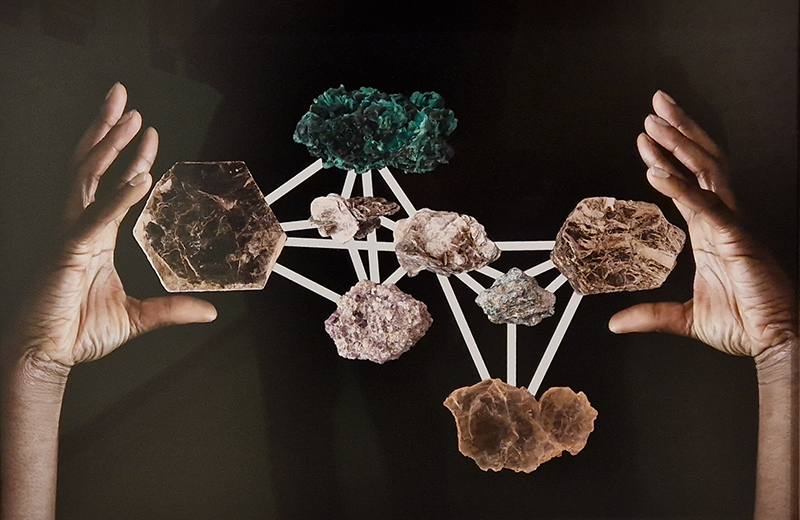
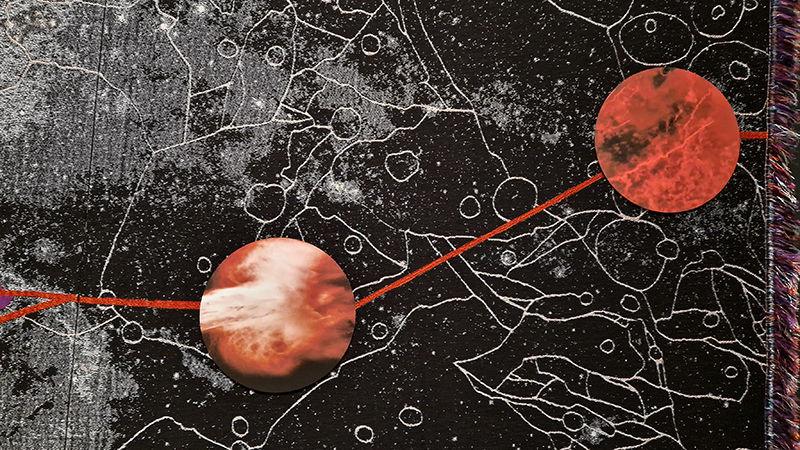
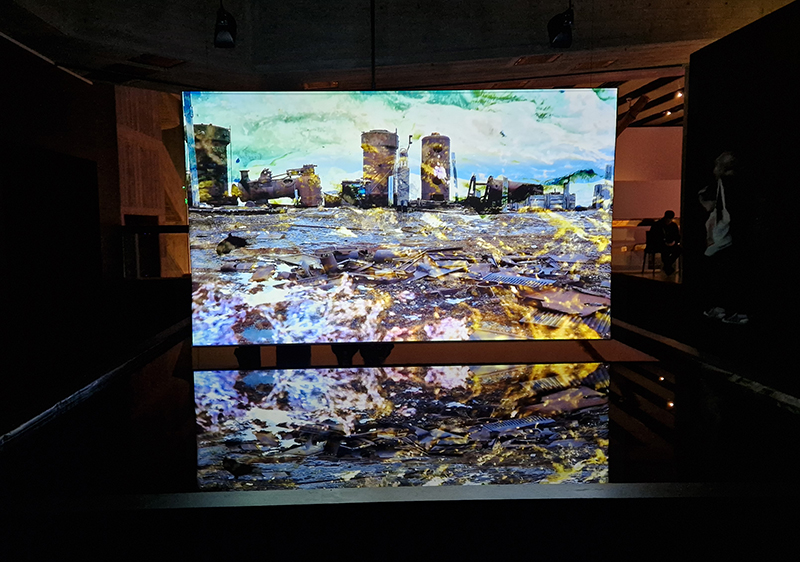
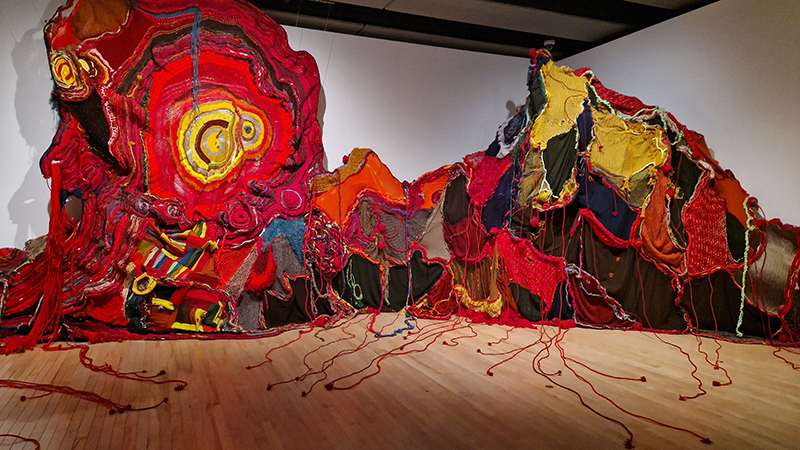
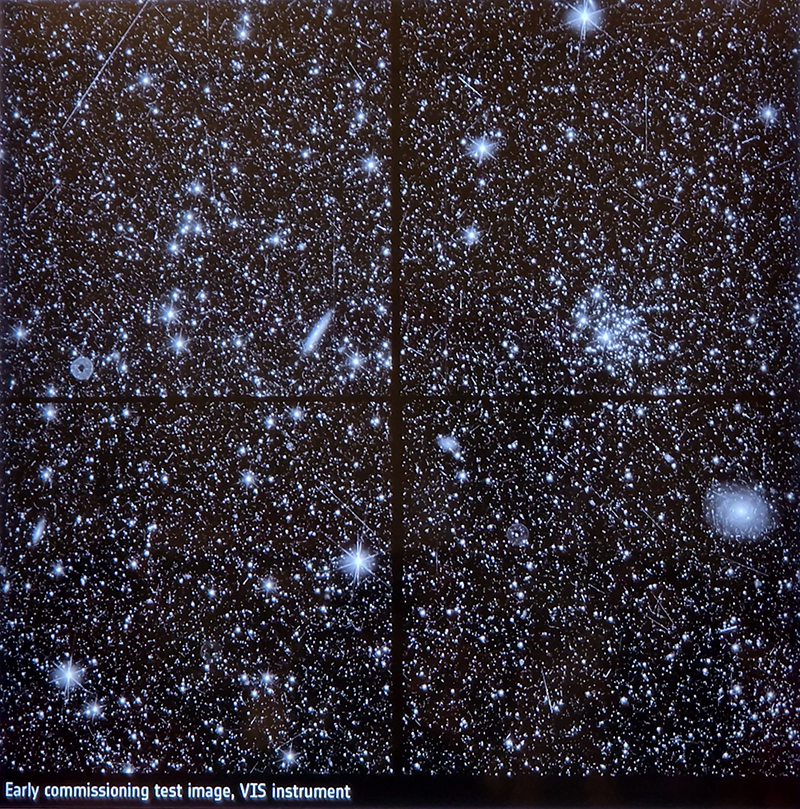
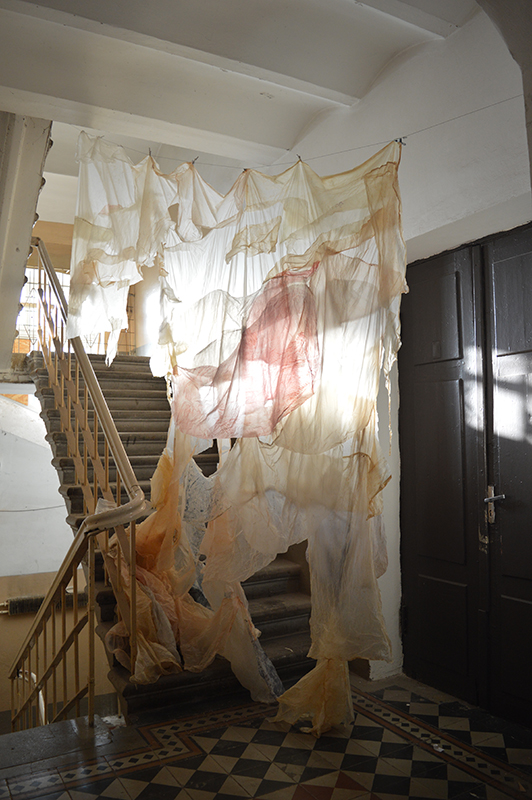
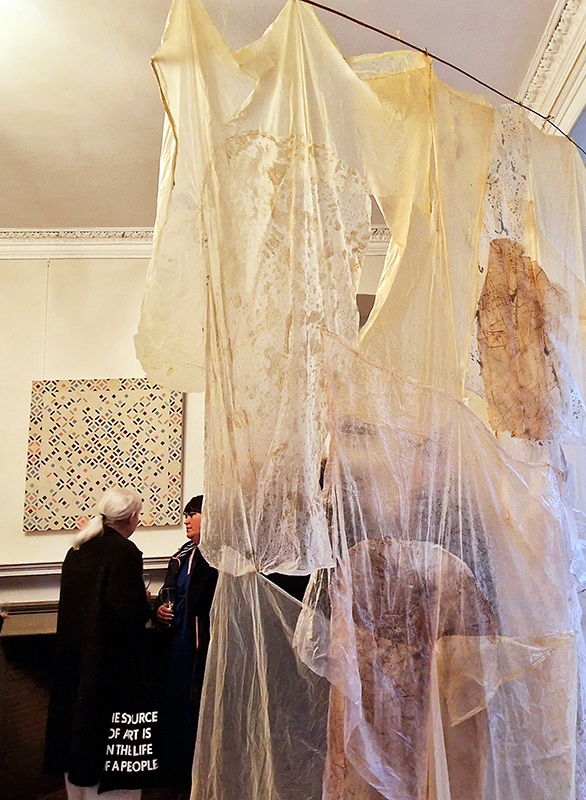
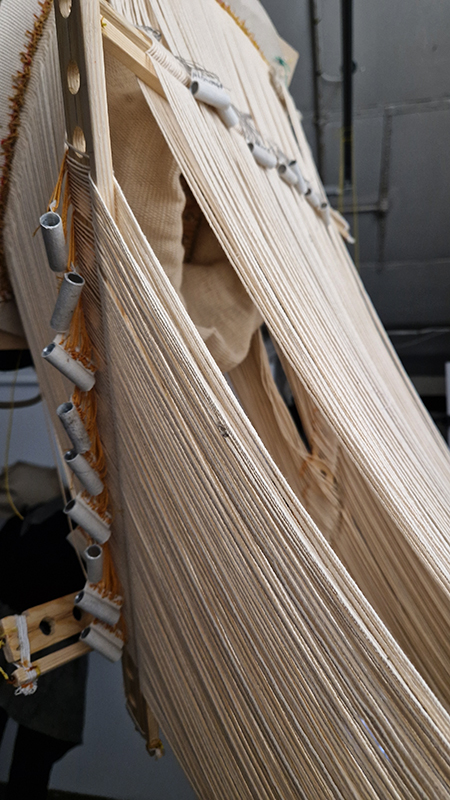
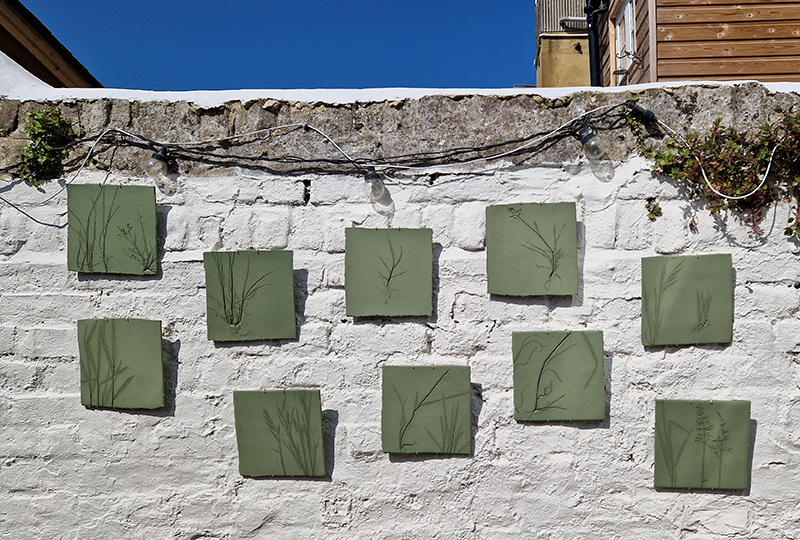
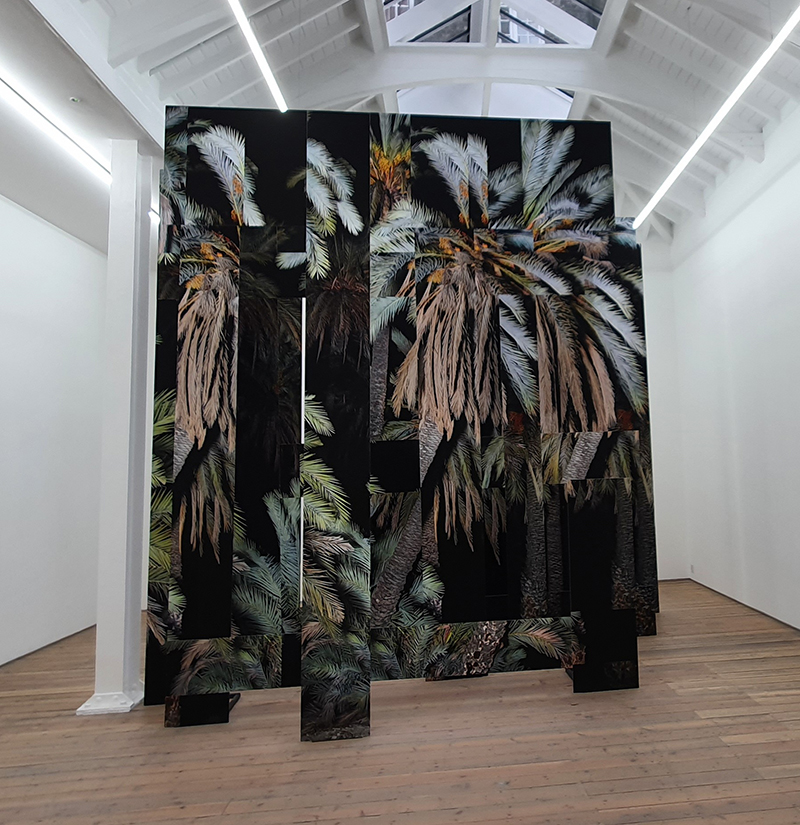
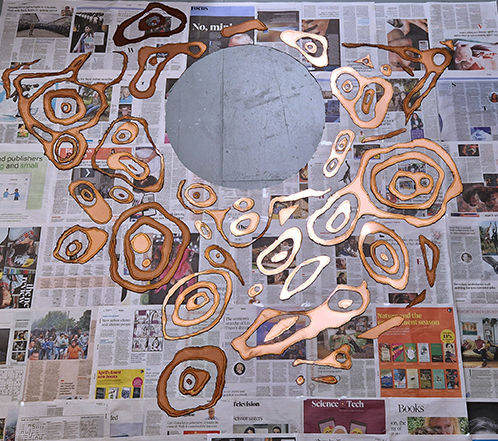
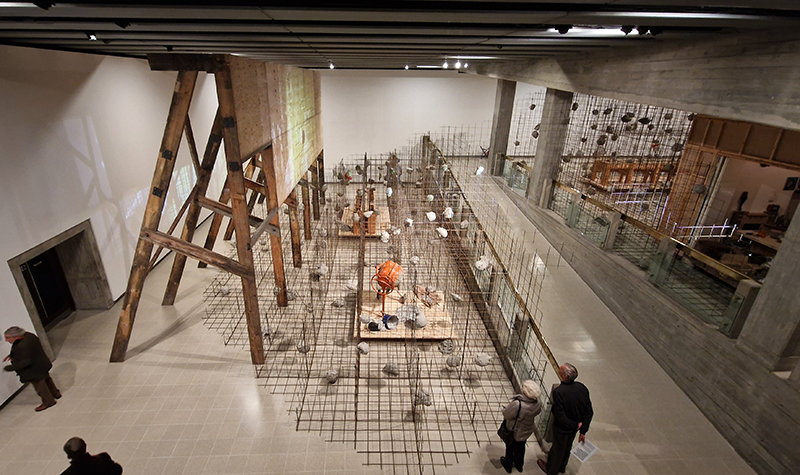
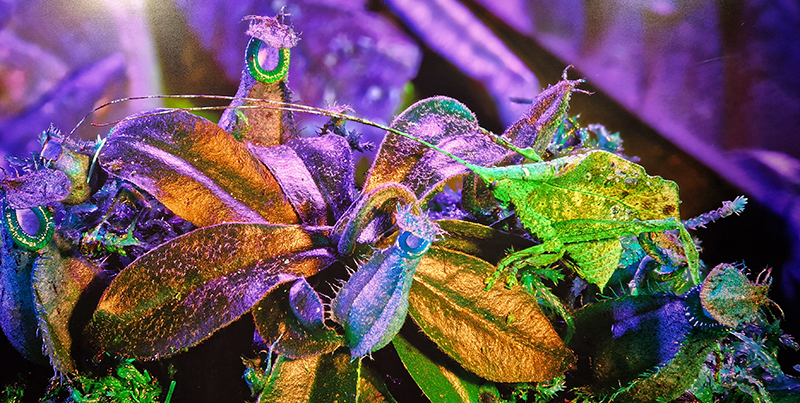
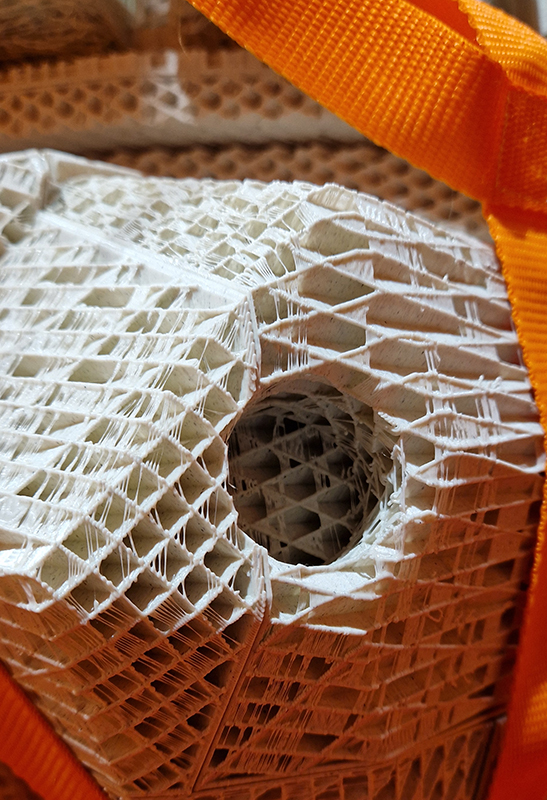
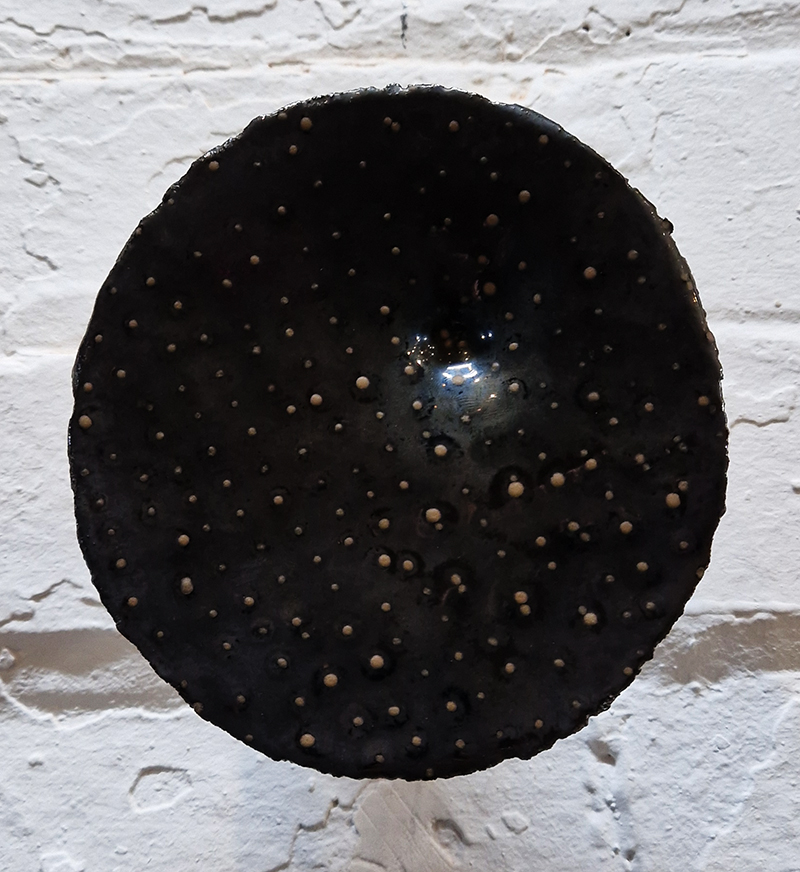
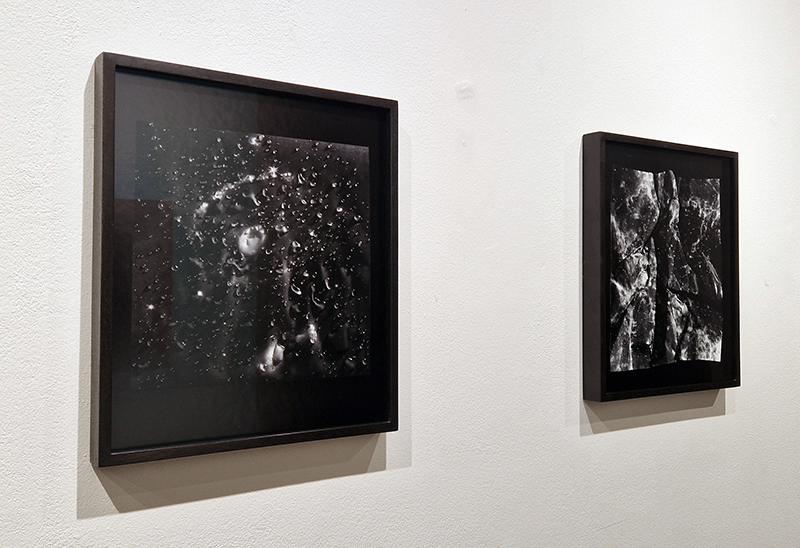
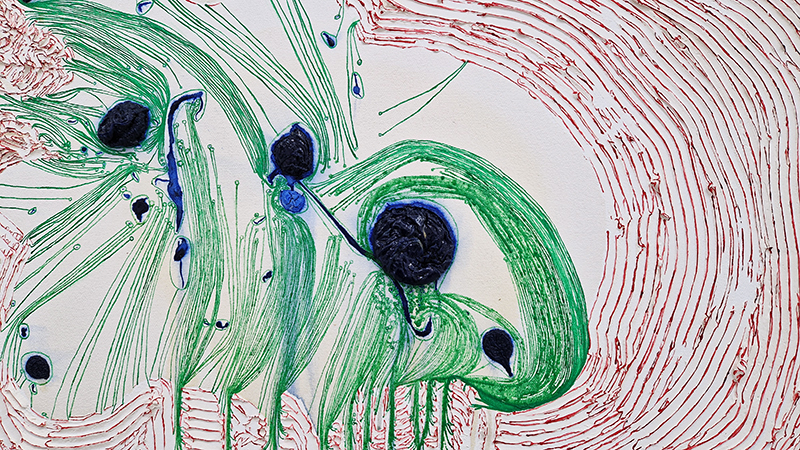
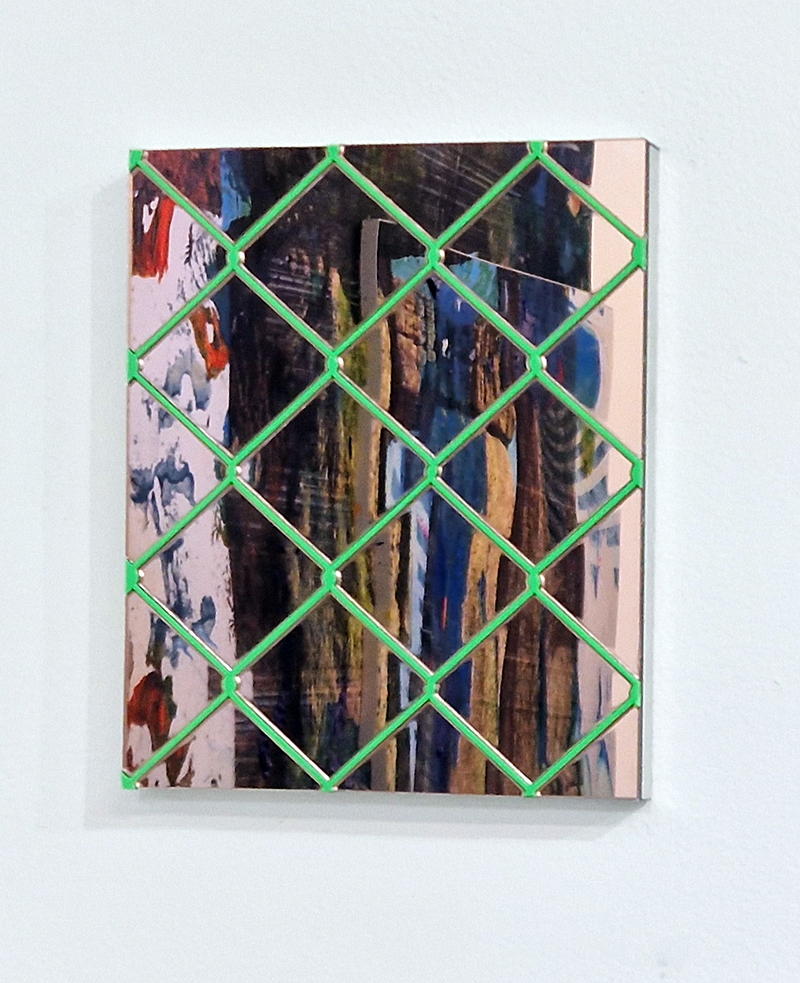
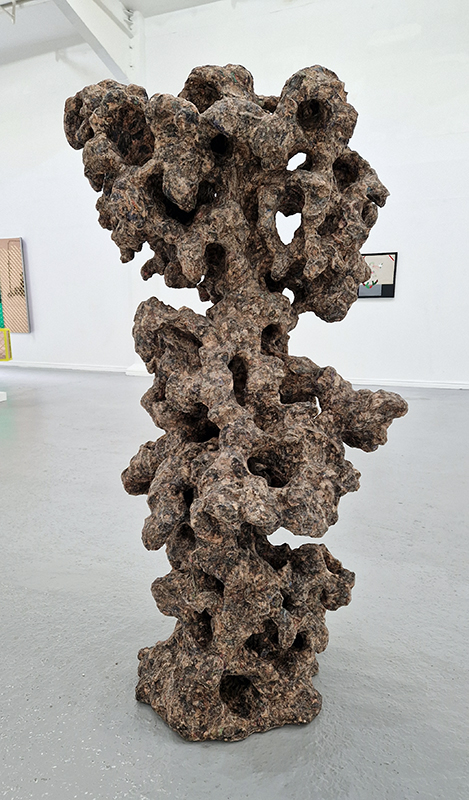
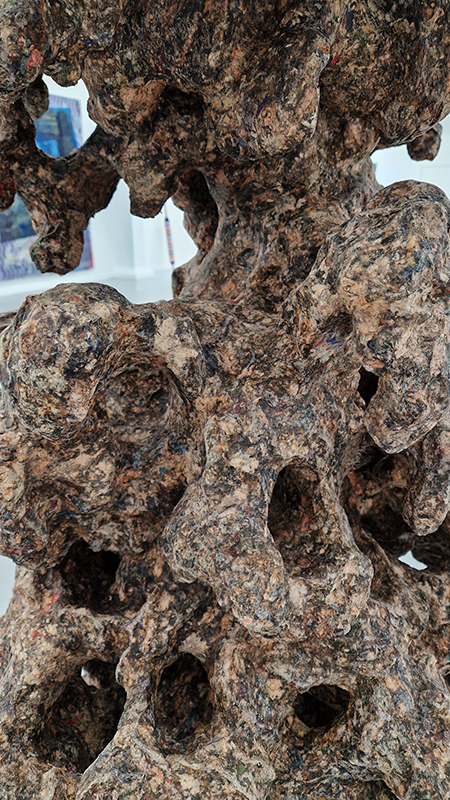
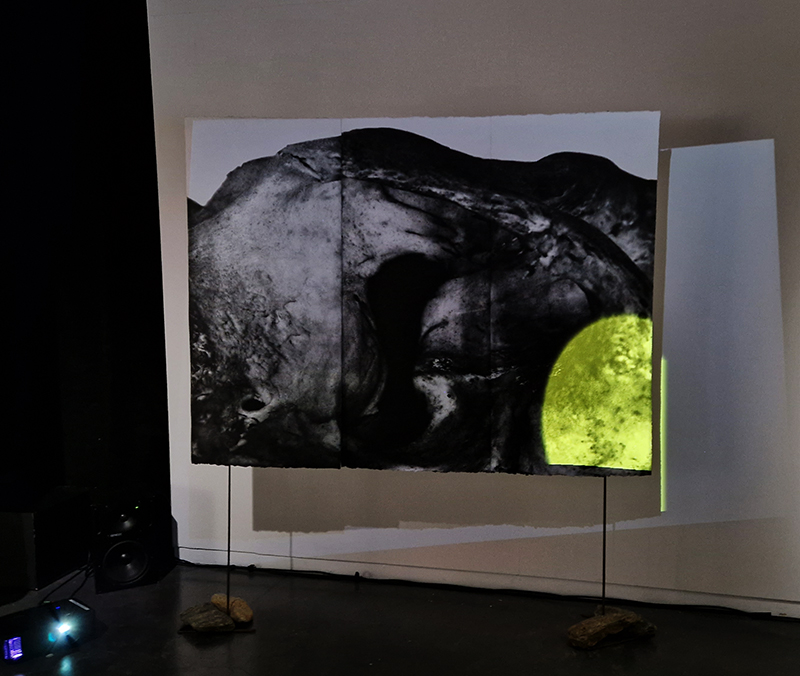
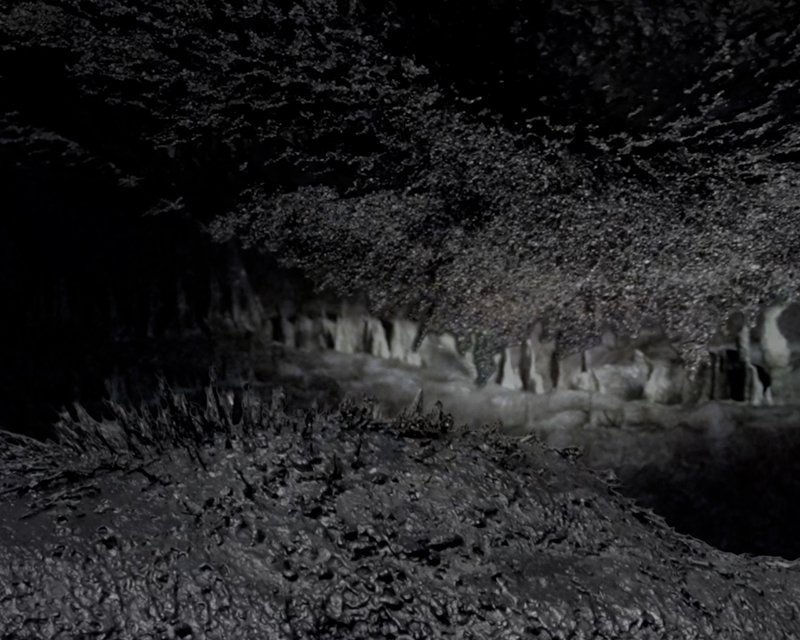
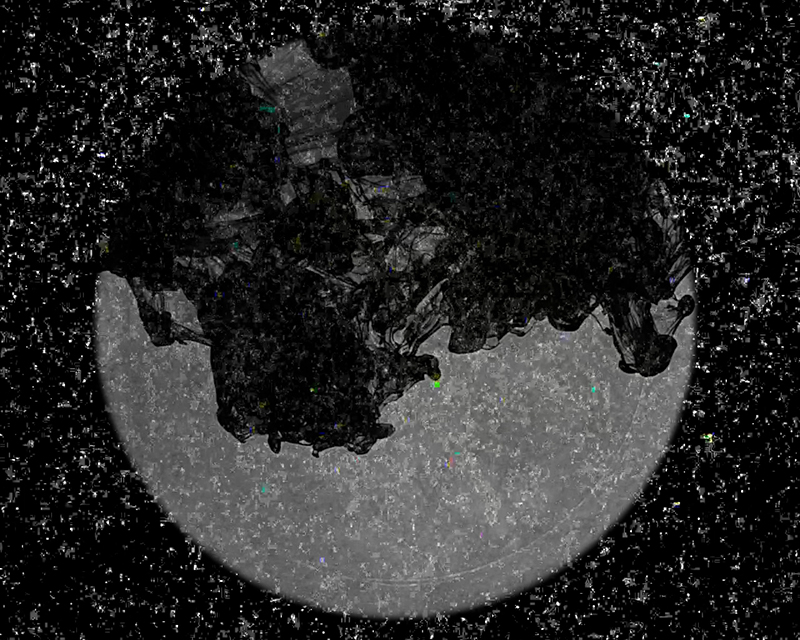
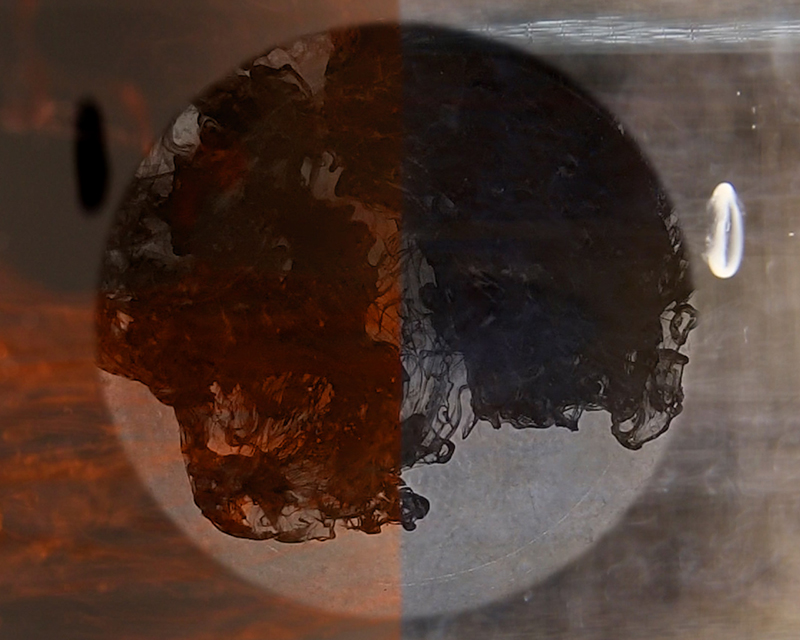
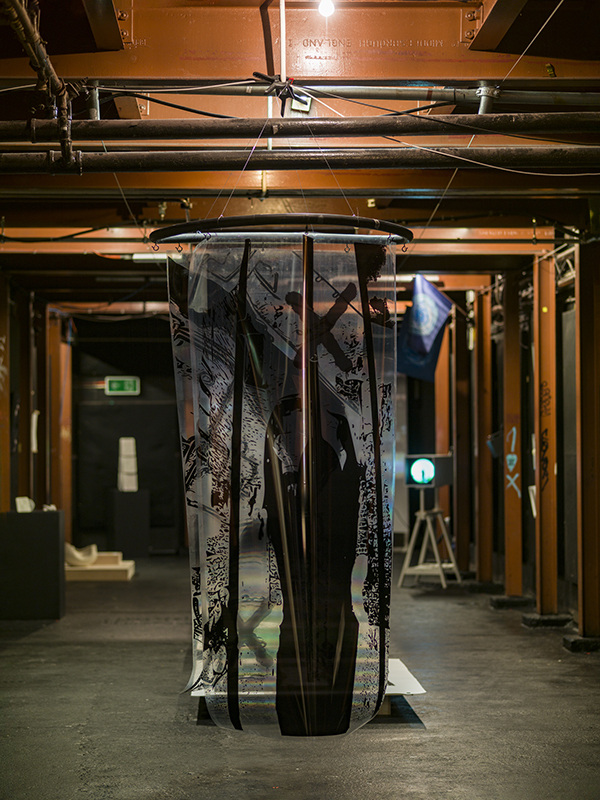
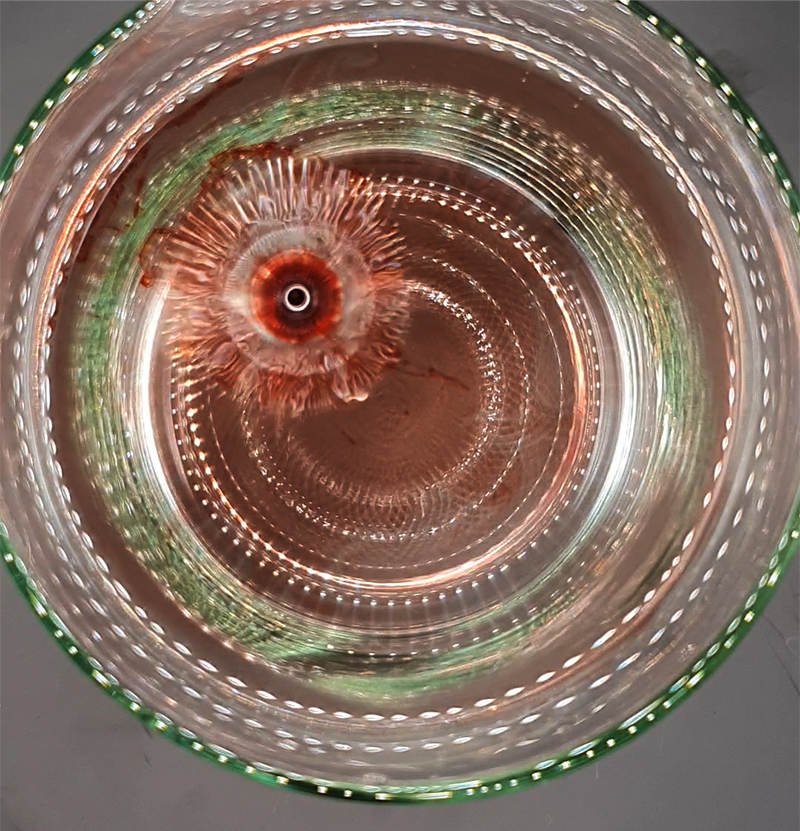
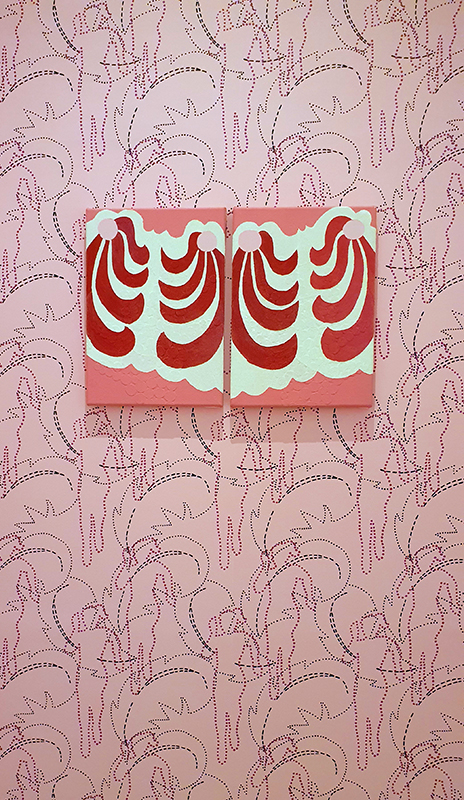
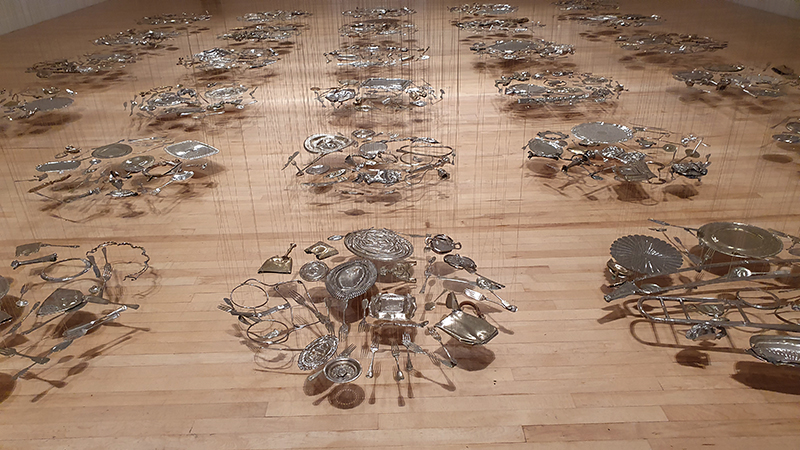
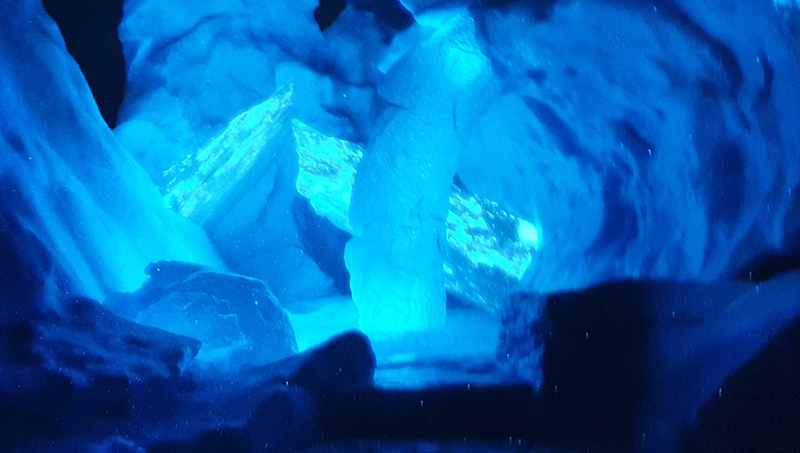
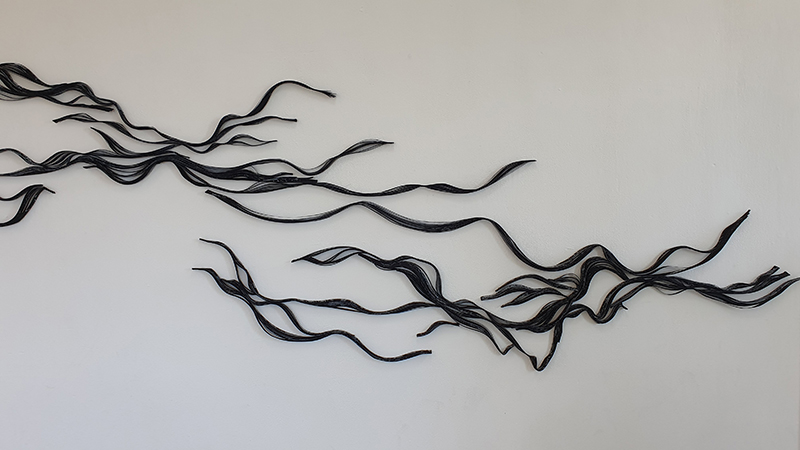
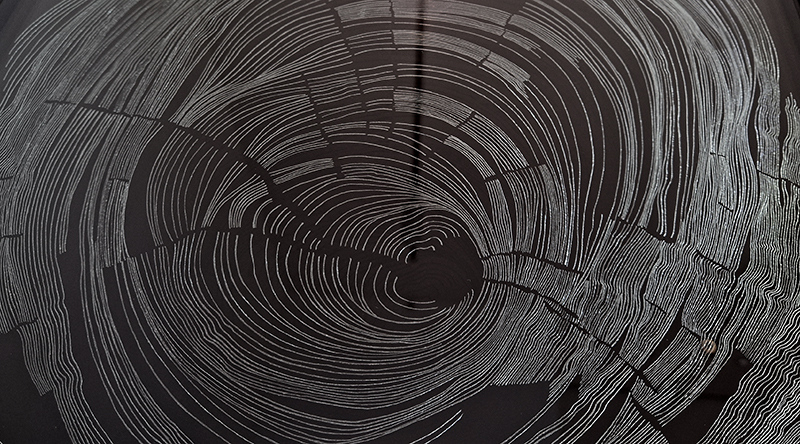
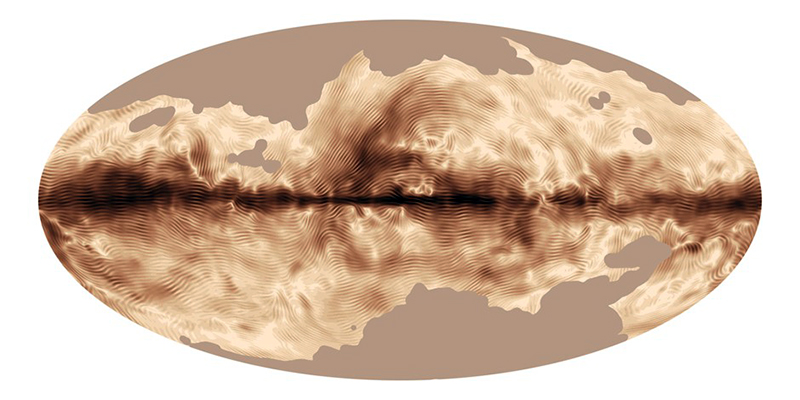
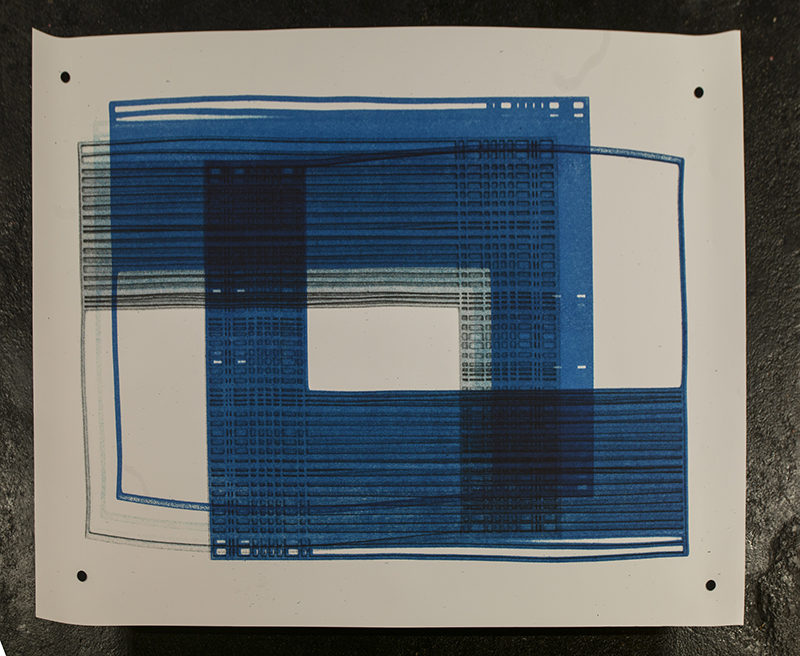
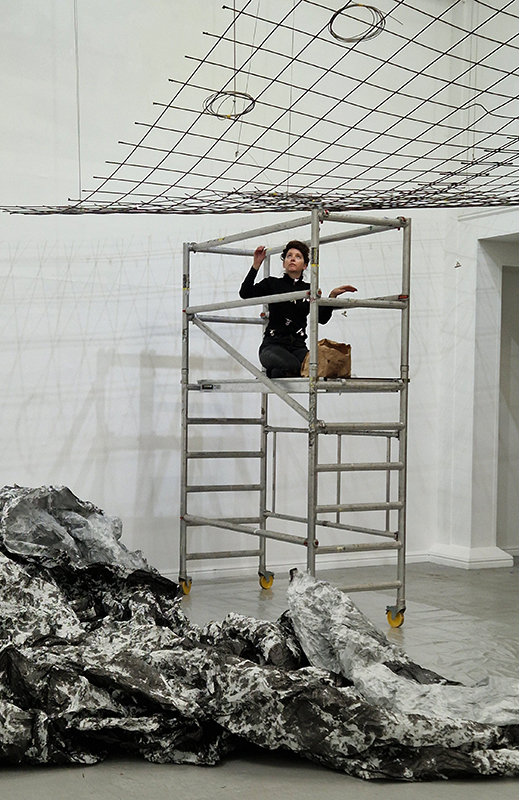
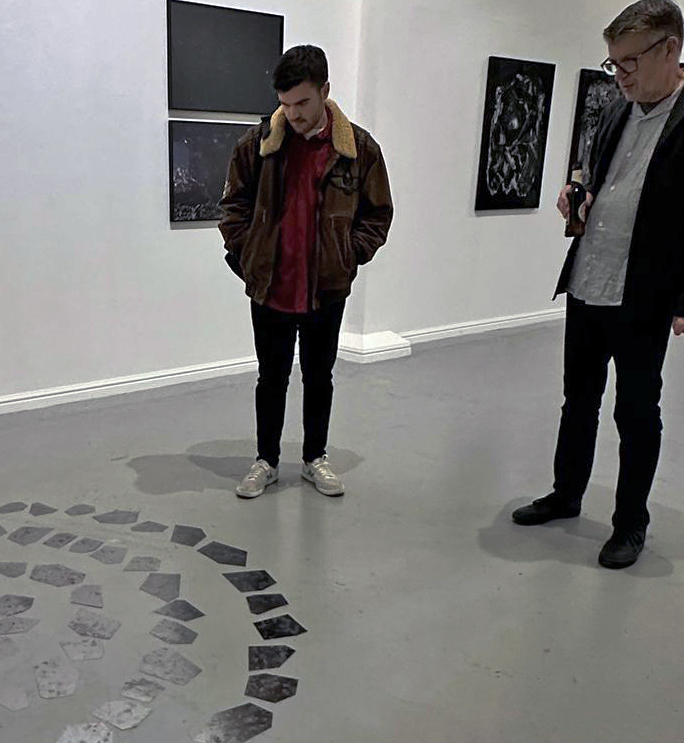
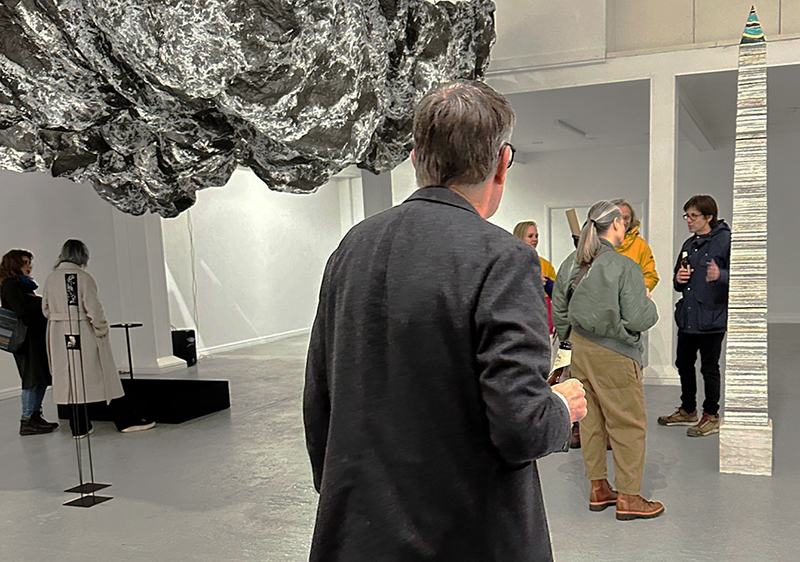
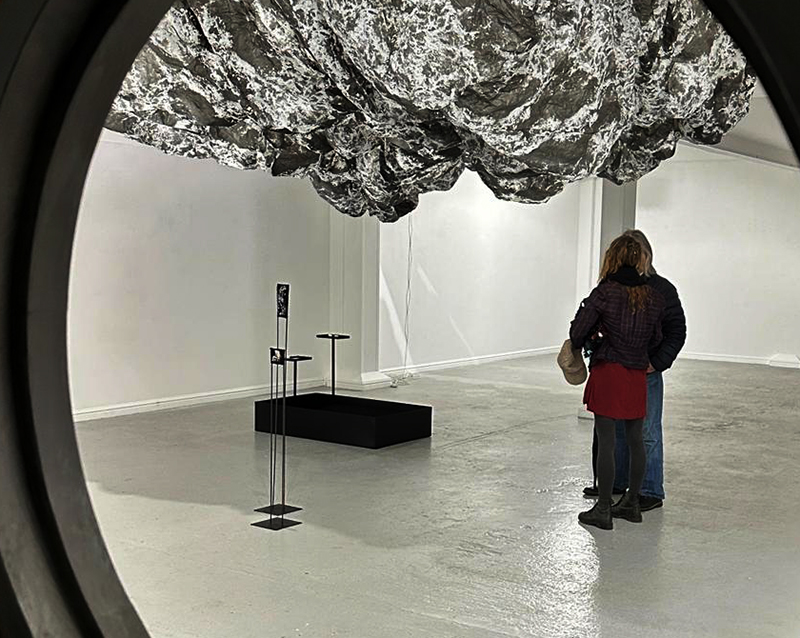
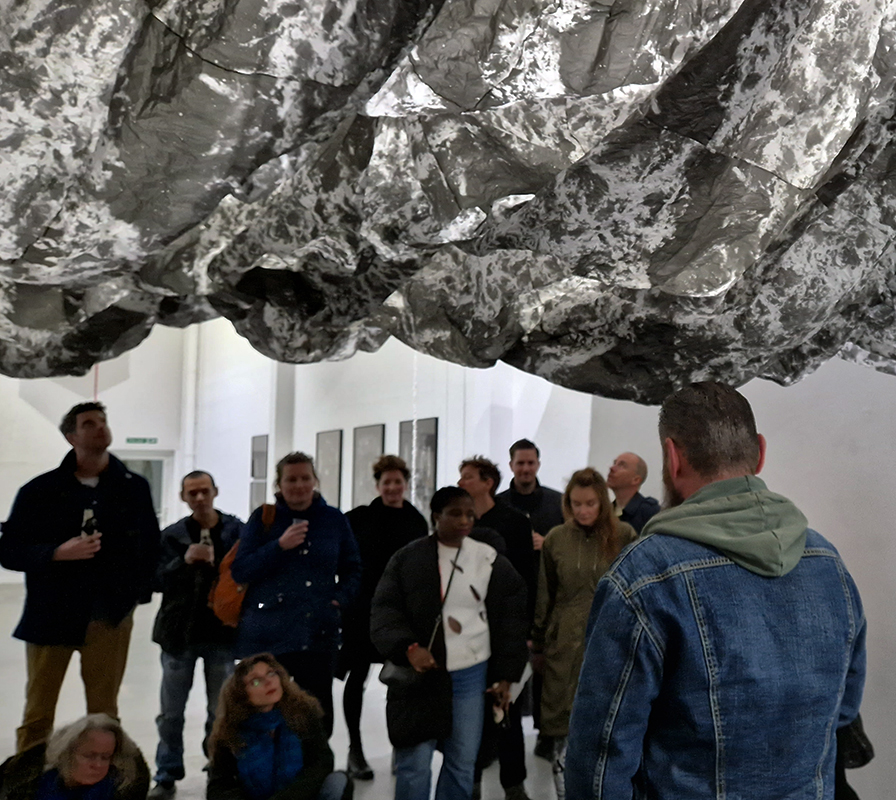
Julie F Hill explores the entwined darknesses of earth and cosmos. Crystalline and mineral substances from the deep earth fuse with astronomical data to suggest the deep-earth as an instrument for coming to know the cosmos. Crystalline and mineral substances formed in the continuum of deep earth and deep space allow us to peer back into cosmic time, both through the technologies created with them and the geological record they hold. Whilst darkness often indicates uncertainty and lack of knowledge, Hill asserts that it’s through darkness when we can be most perceptive to the interconnectedness between earth and cosmos. Through it we are able to extend our kinship with the inorganic and expand consciousness of what constitutes nature. Works include a large-scale sculptural print installation made from James Webb Space Telescope data that is reworked into a cavernous space, providing an experience of intimate immensity alongside more smaller sculptural and photographic works.
Images by Ben Deakin Photography









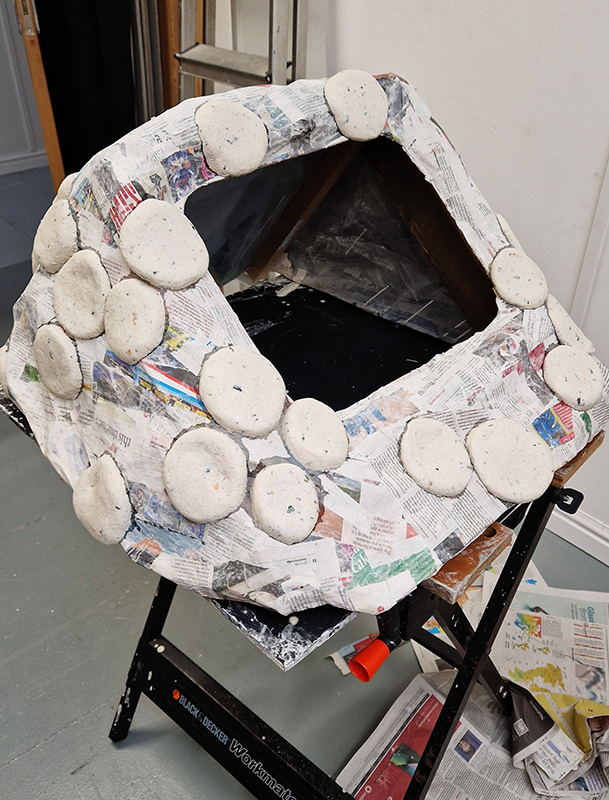
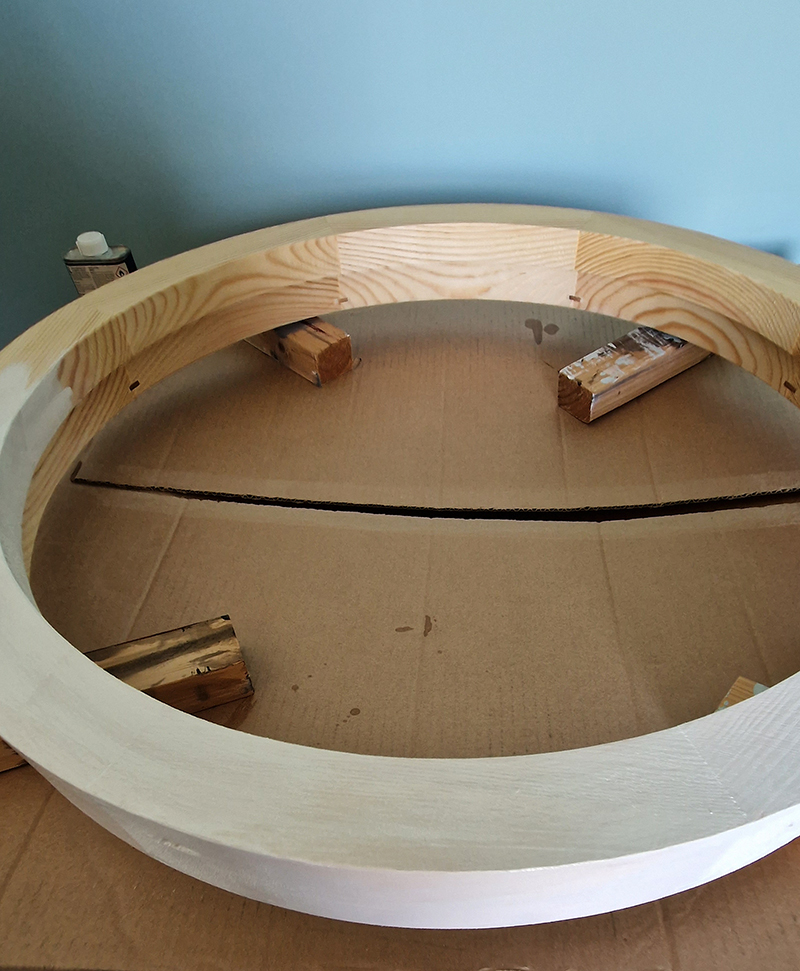
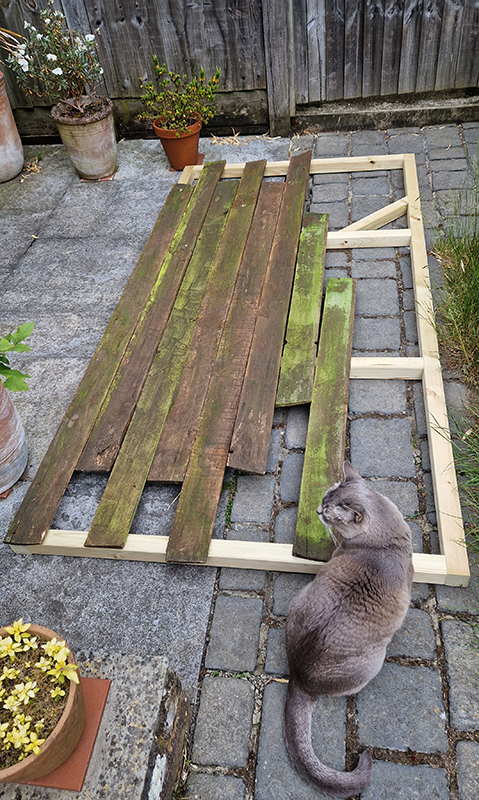
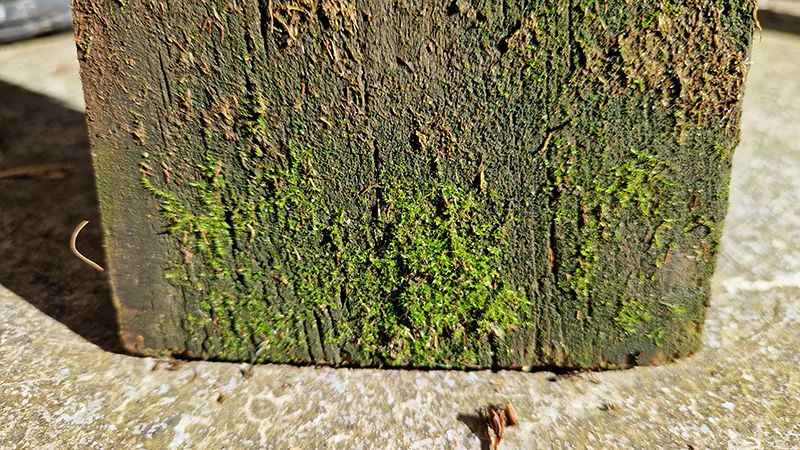
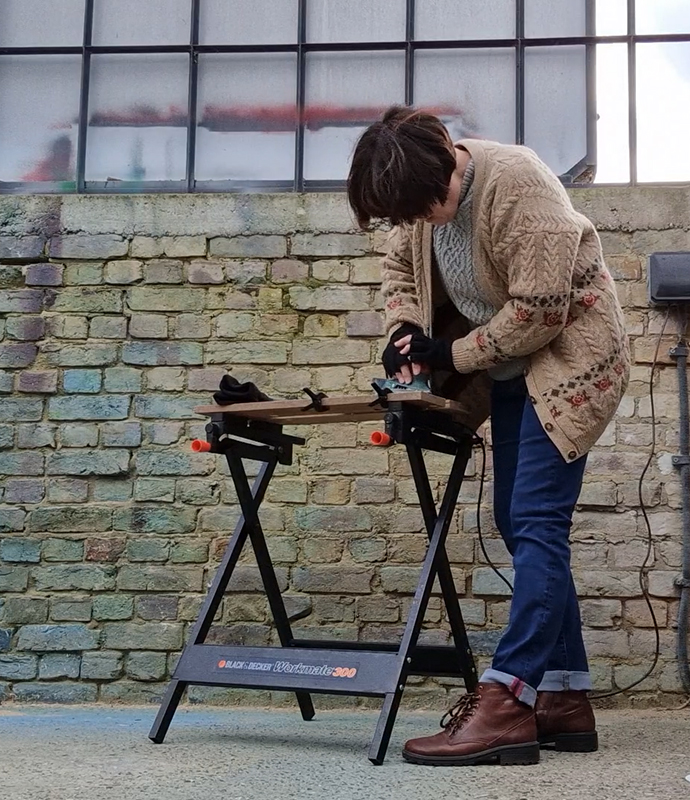
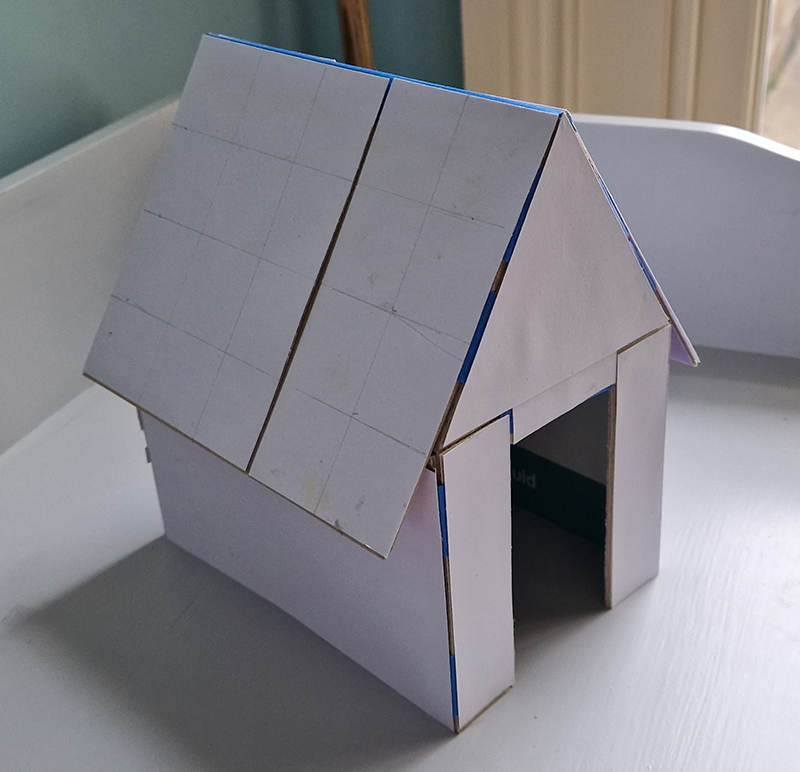
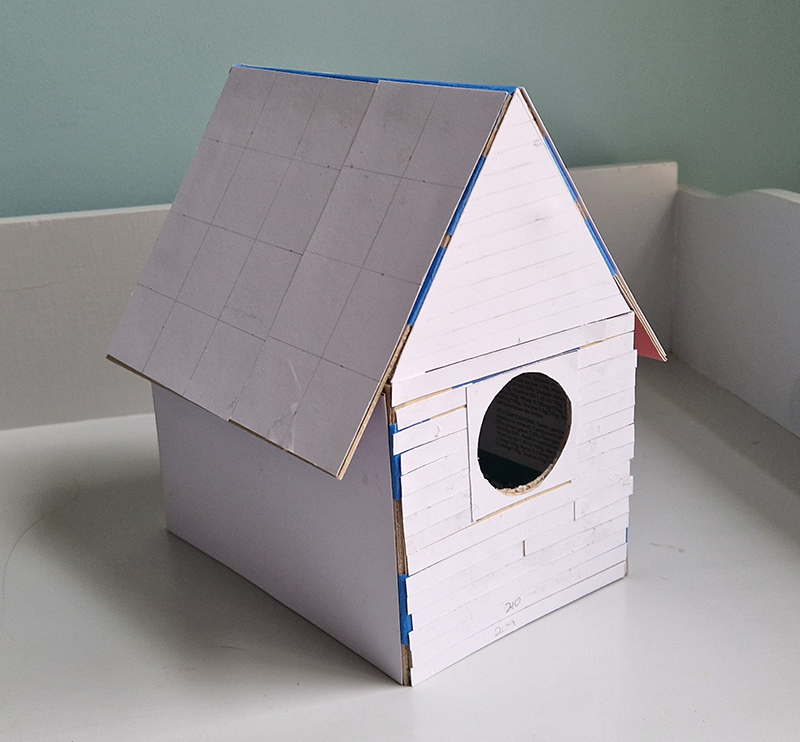
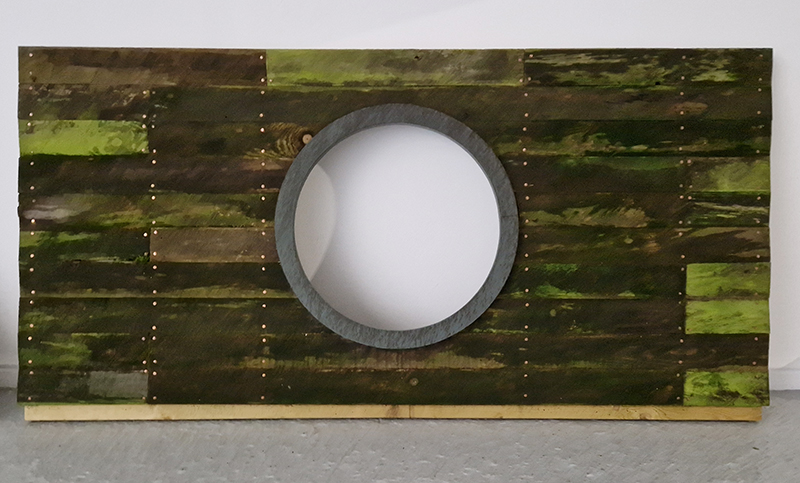
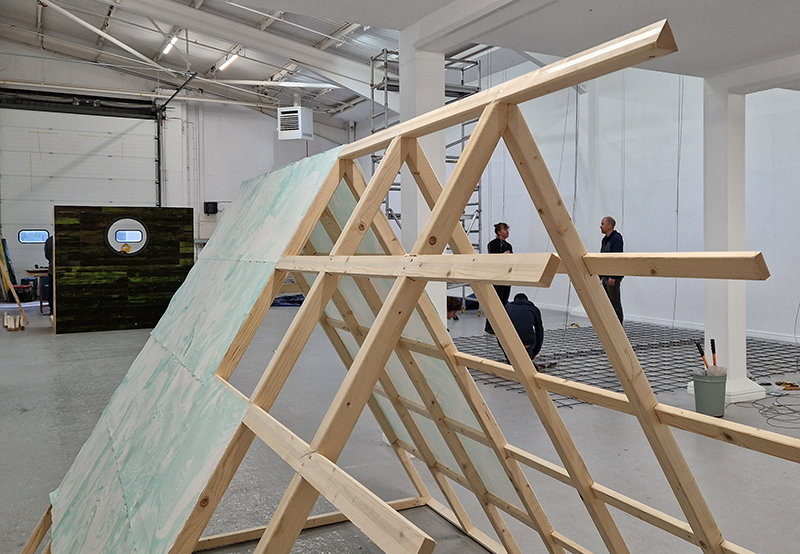
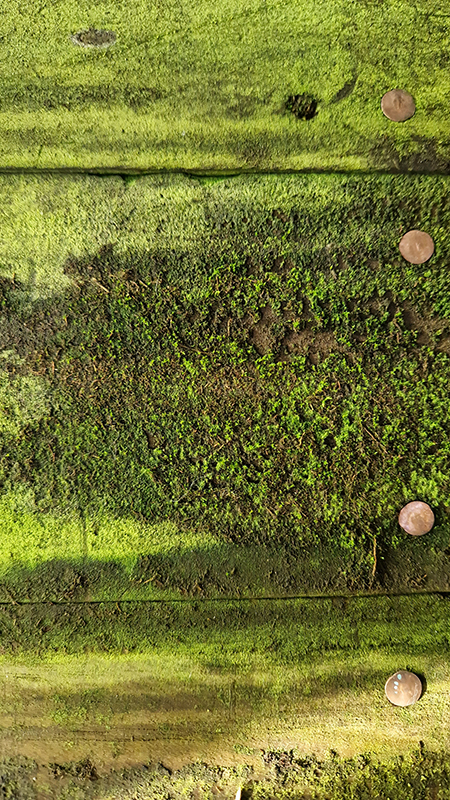
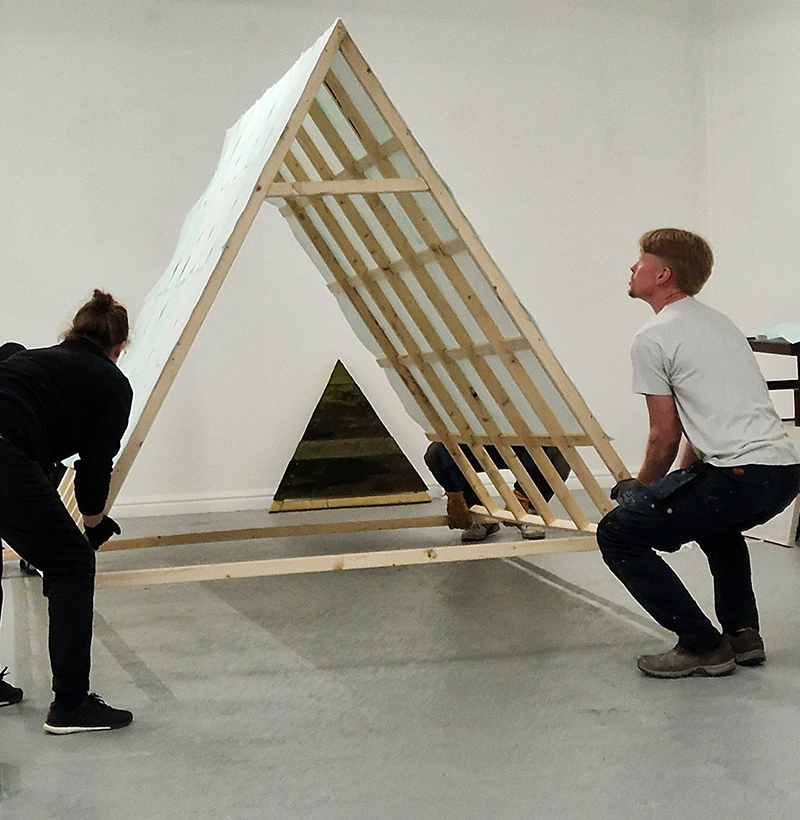
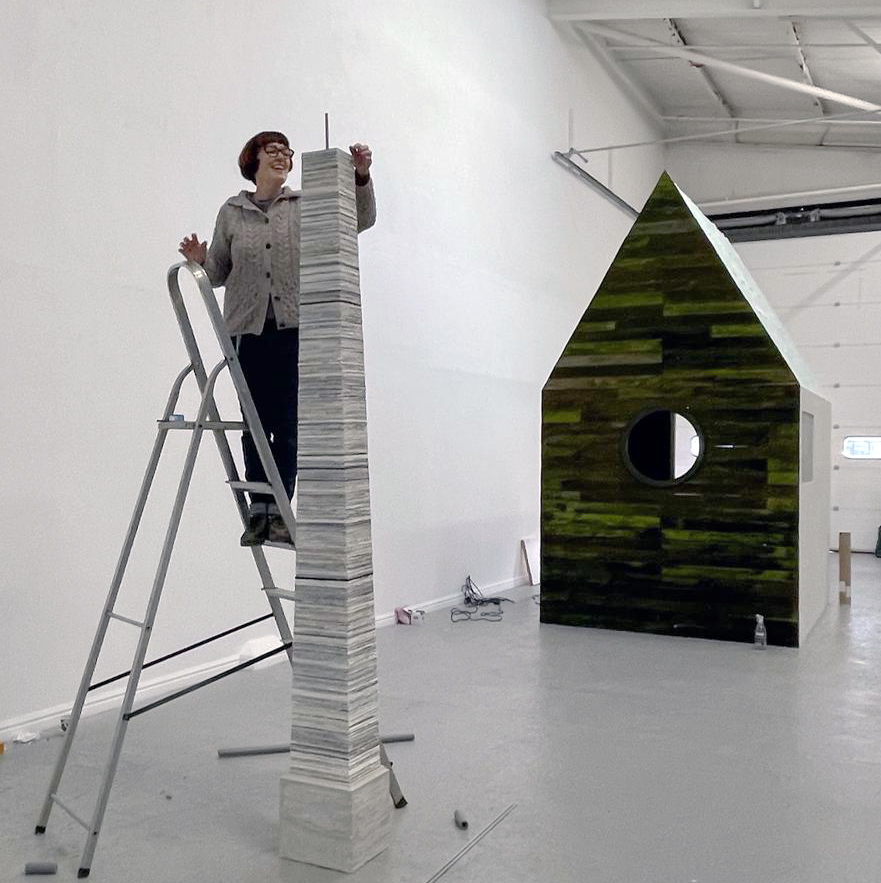
We both had ambitious large scale works to install and were grateful for the help we received from our partners (both Kevins), friends and technicians. Trevor Neale was magnificent in constructing The Absolute Hut. Anne Krinsky patiently helped apply double sided tape to the roof structure ready for the Suminagashi paper tiles and Caroline AreskogJones energetically painted the hut white and neatly edged the two way projection window. I was thrilled that, as a result of a wet few weeks, moss had started to grow on the wooden boards of the north facing wall in time for installation.




















A big thank you to everyone that made it to the opening night, we were super chuffed with the positive responses.
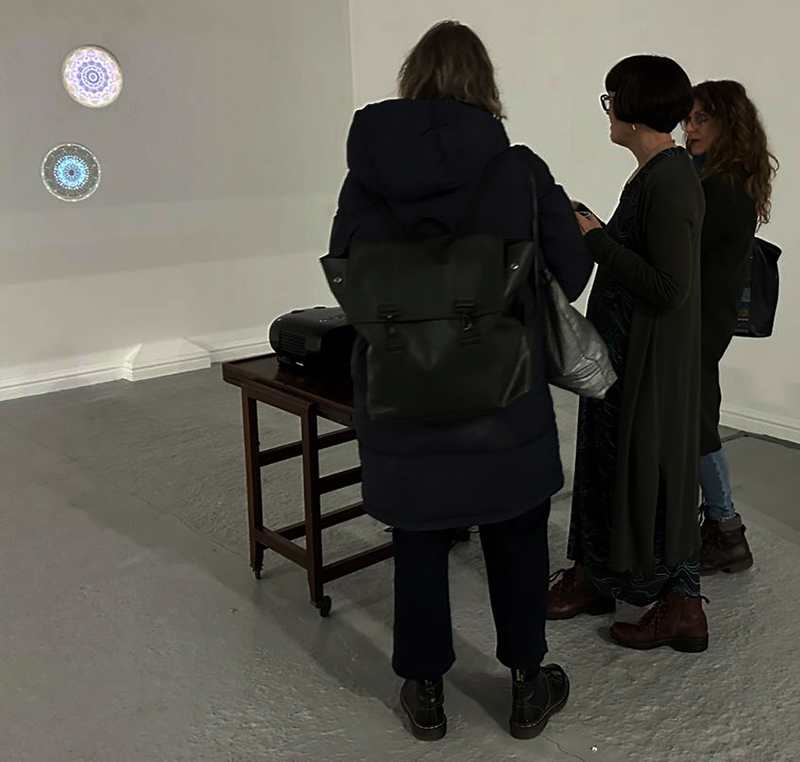
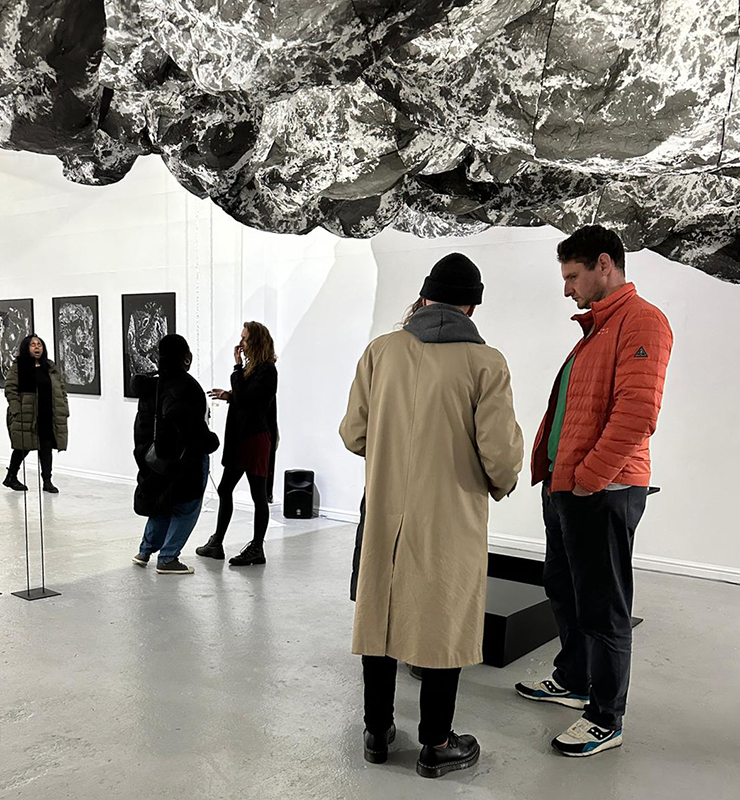
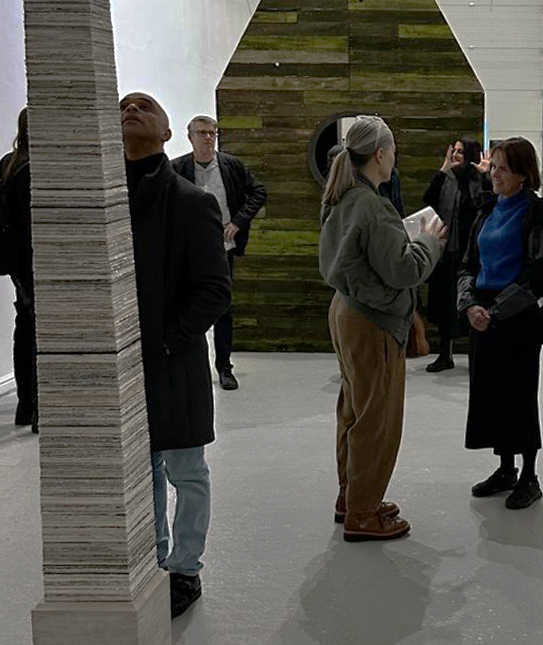
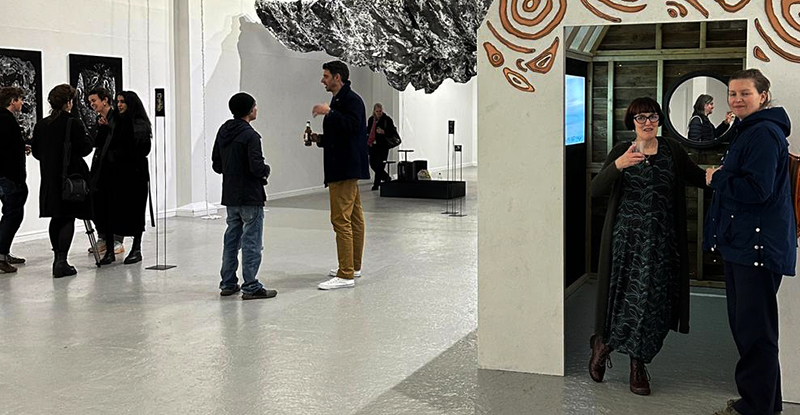



















At the private view Julie’s large scale print installation was activated by a vocal performance conjuring abyssal voices of deep, cosmic time, performed and devised with Eleanor Westbrook whose voice produces incredible hauntingly beautiful sound.
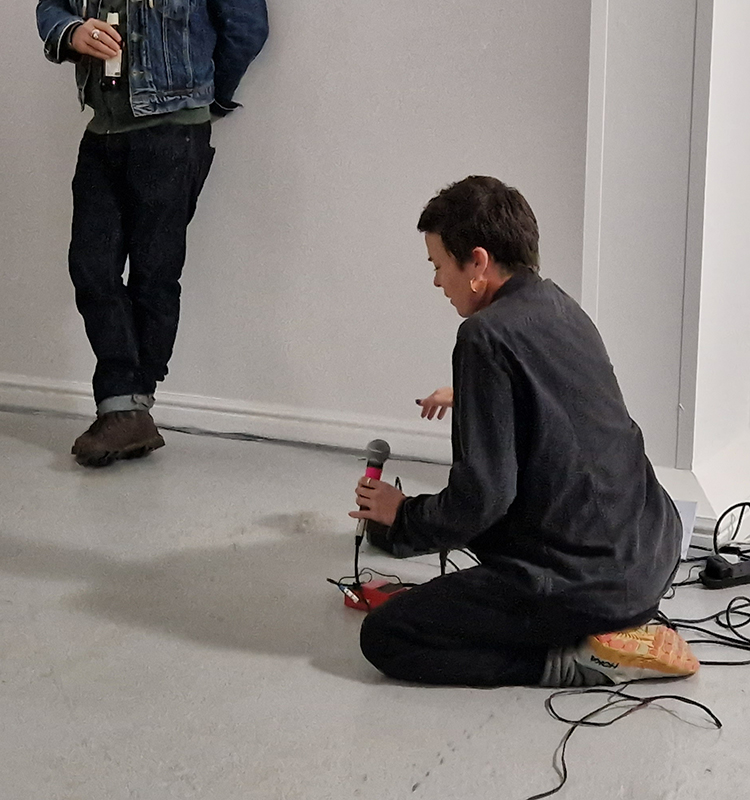
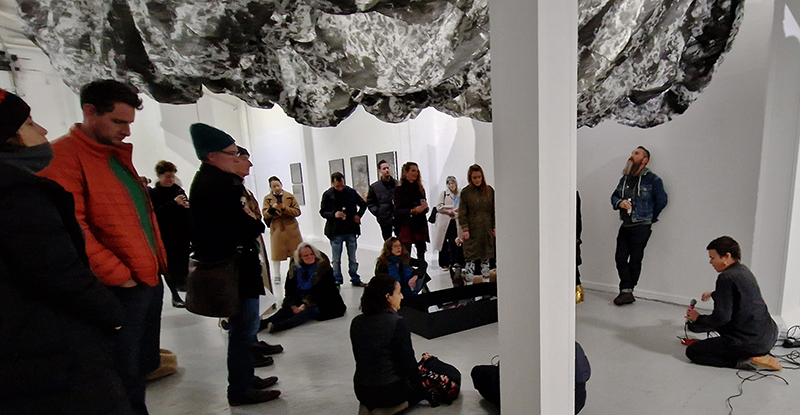
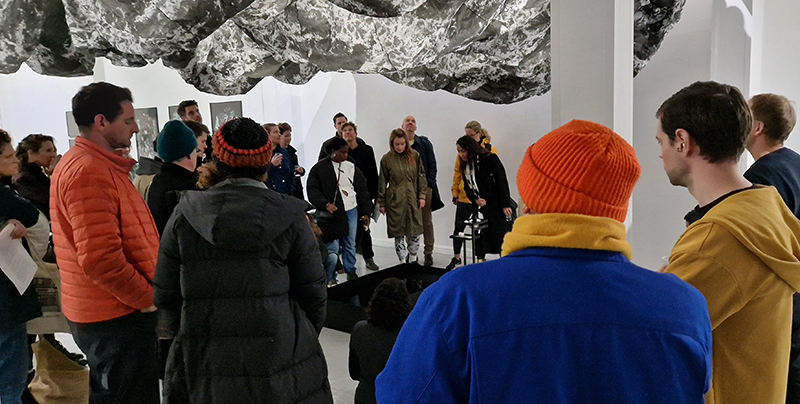
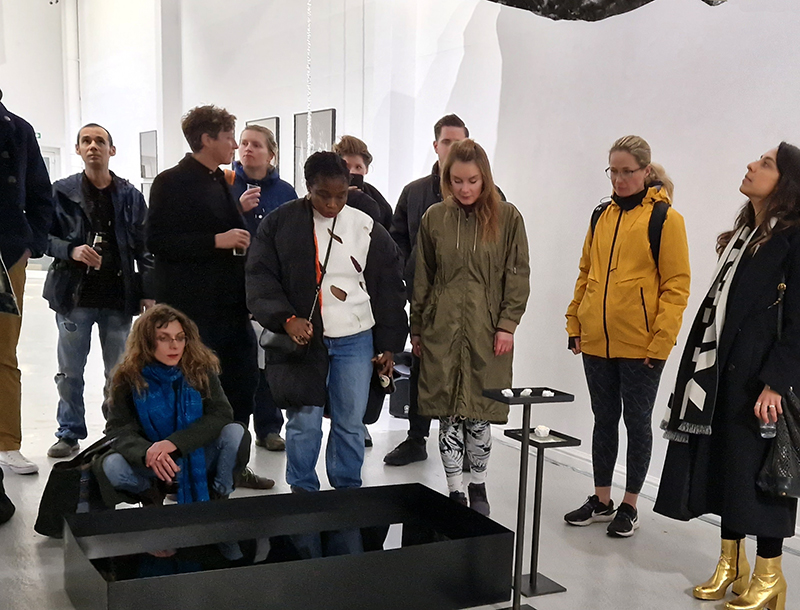









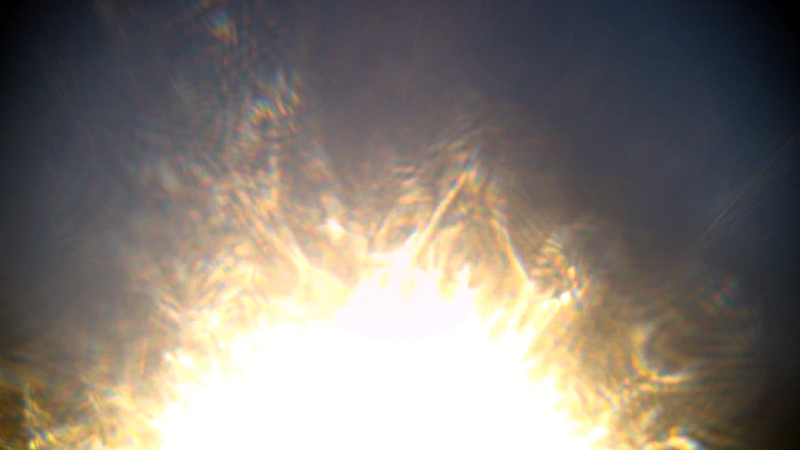
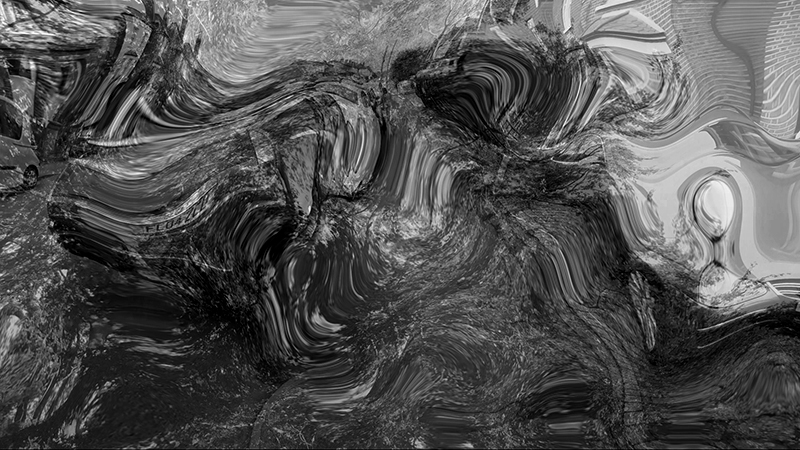
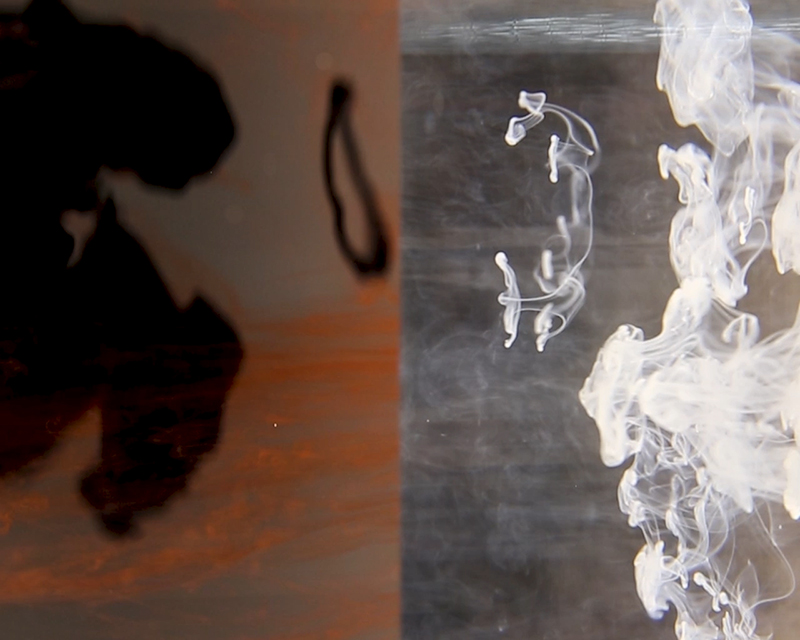
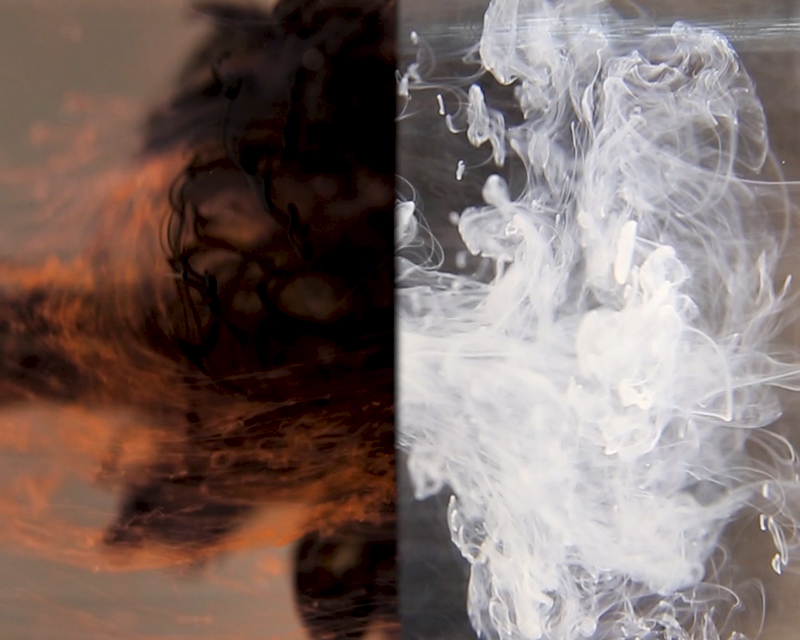
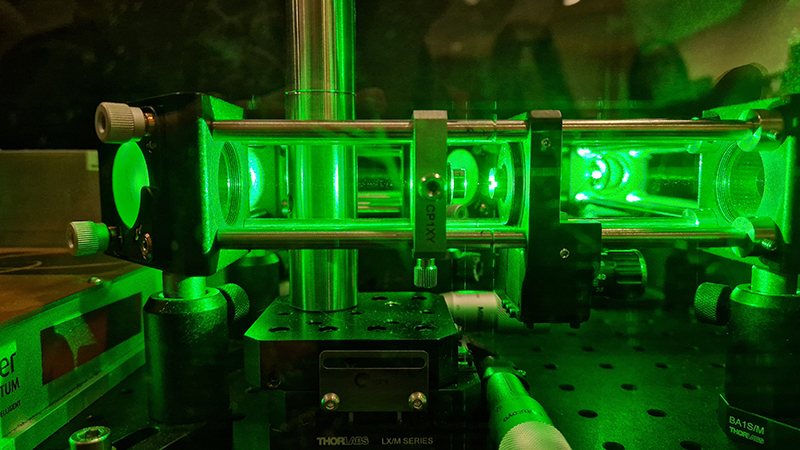
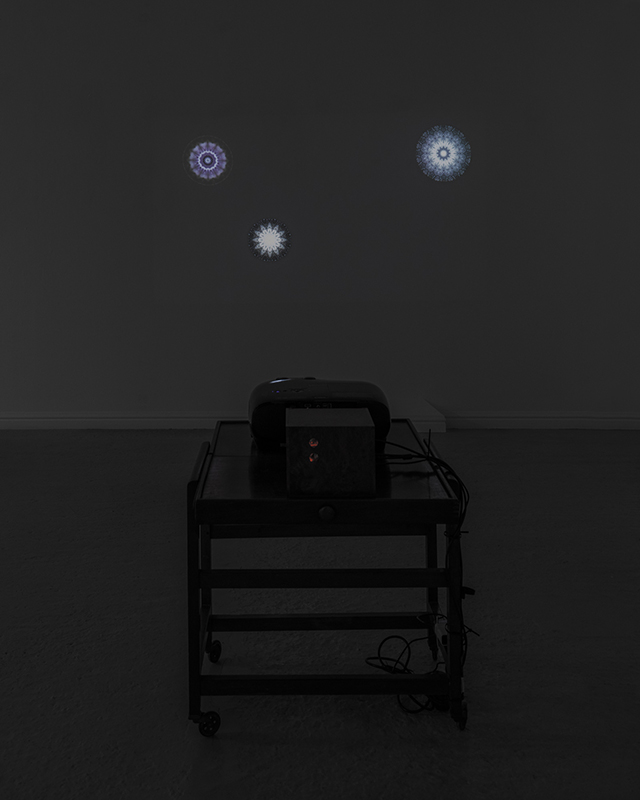
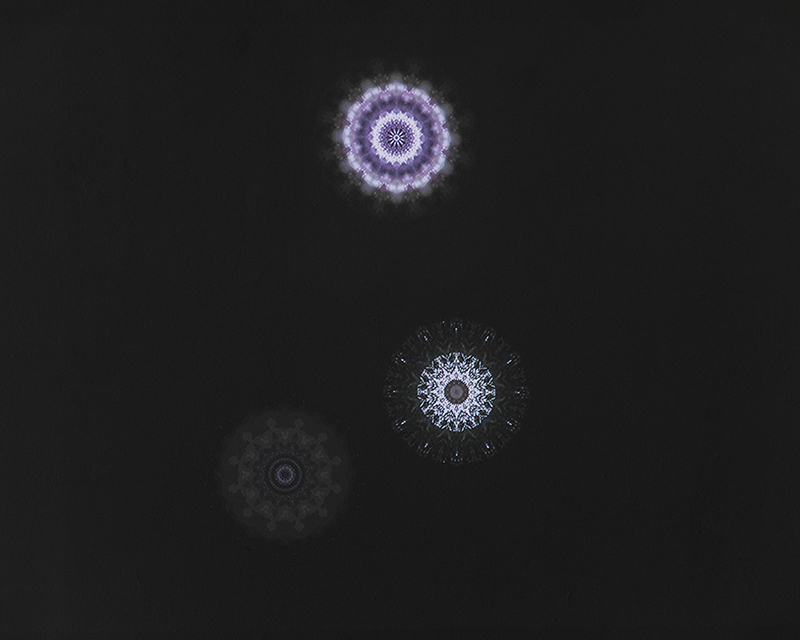
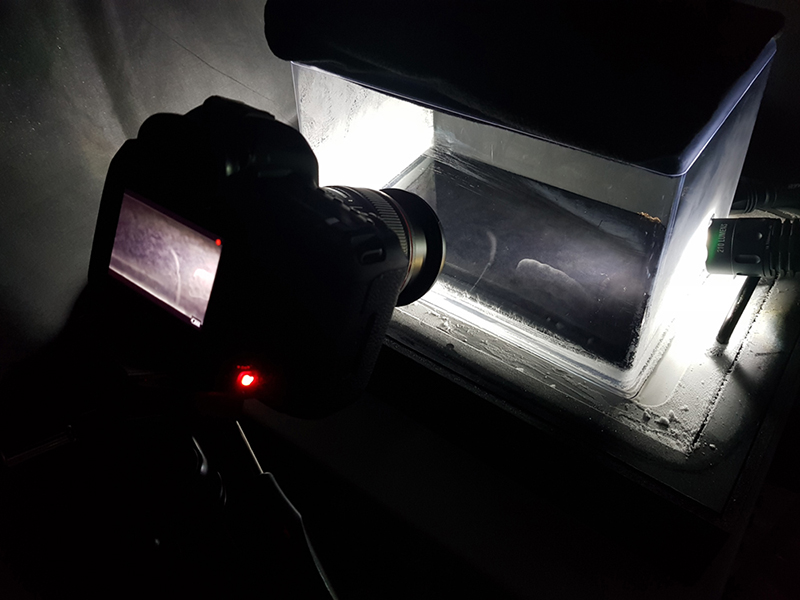
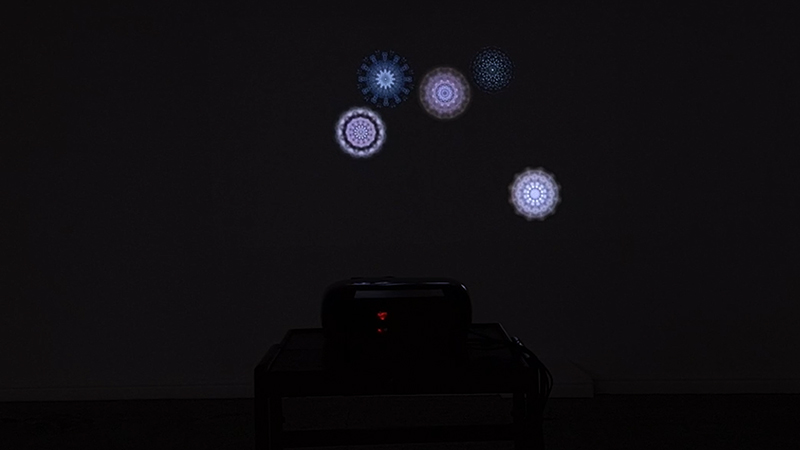
I was particularly excited to share The Breath of Stars, digital video work activated in real time by the passage of cosmic rays through a scintillator detector. After two years in development it was so exciting to watch the random starbursts appear in real time as witness to the unseen activity of cosmic rays passing through the gallery.
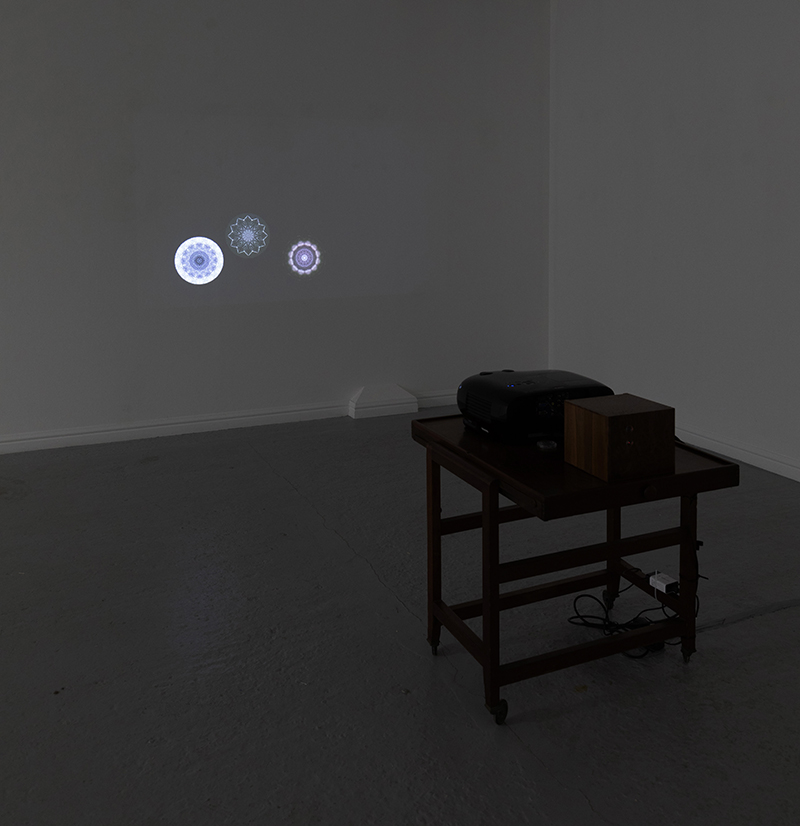

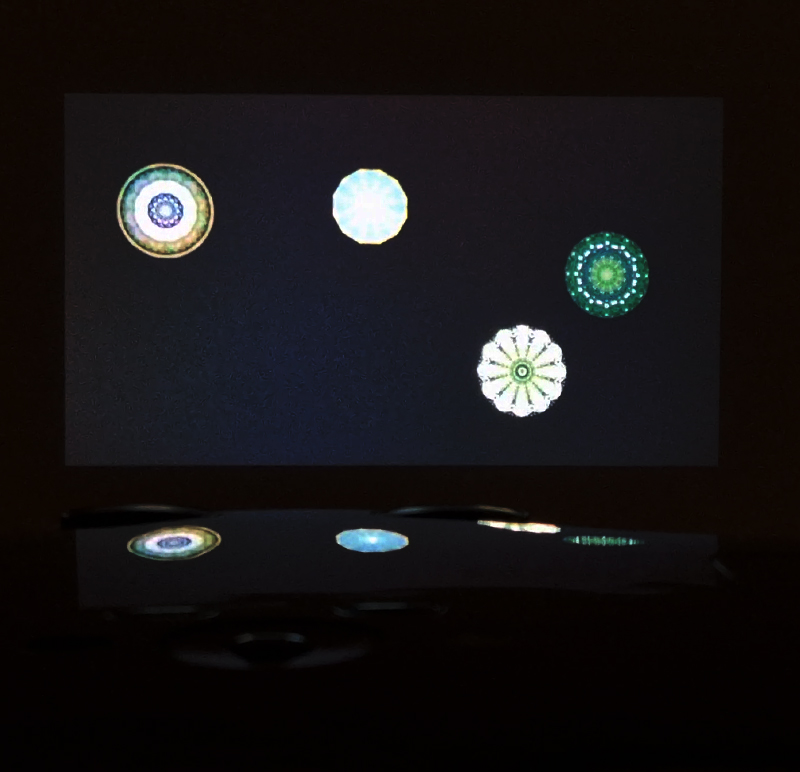
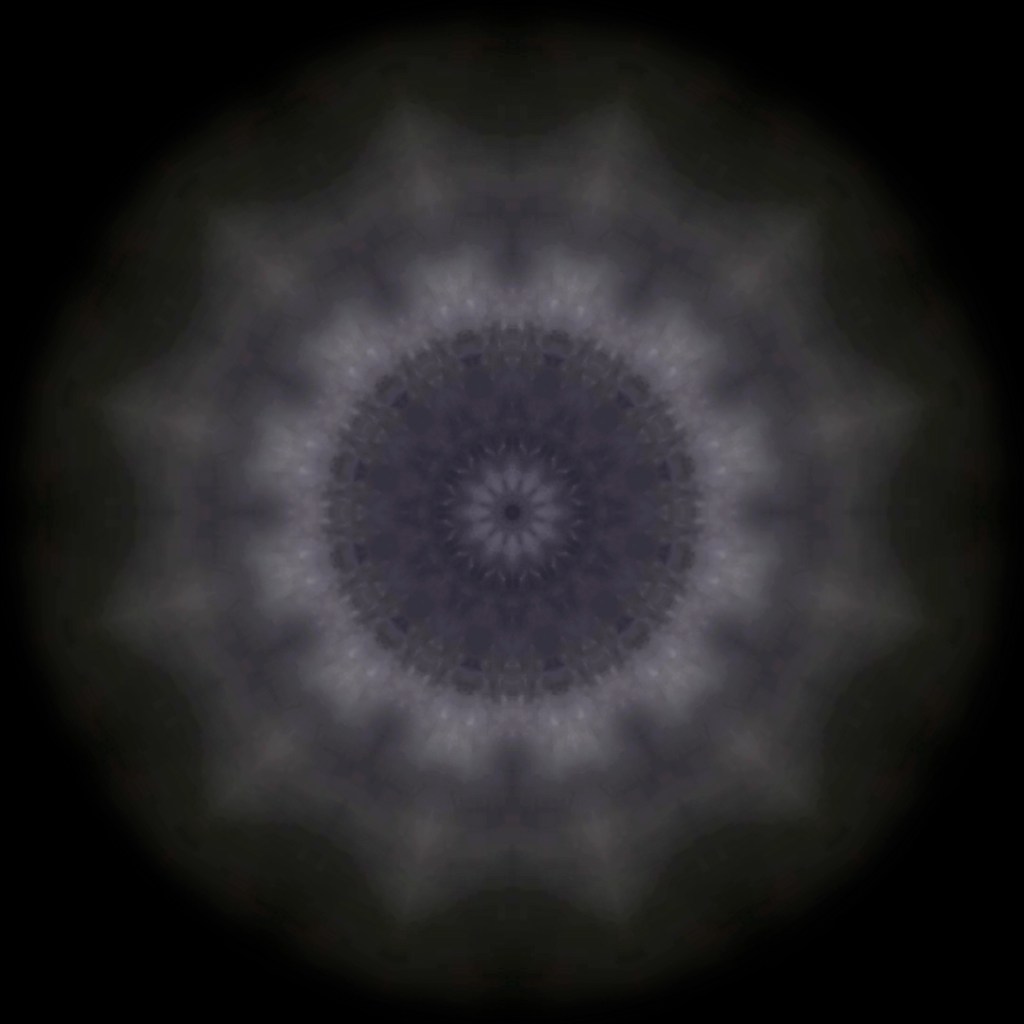
The kaleidoscopic video images that appear for every particle recorded by the detector, are created from footage of cosmic ray trails filmed in a cloud chamber.
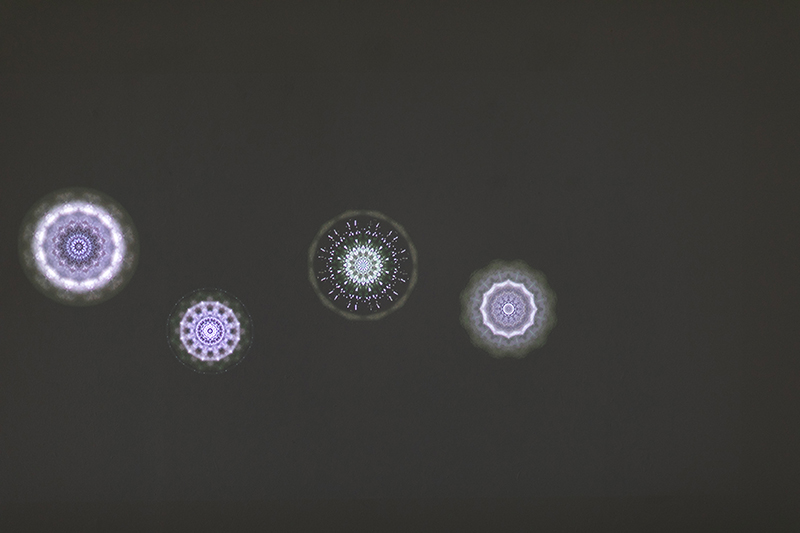


The interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric electrical fields influences the unpredictability of the magnetosphere and this random activity can be witnessed by the sudden flurries and silent gaps of the live video imagery.

These subatomic visitors from outer space power across the universe with unimaginable energy, coming from the heart of exploding stars or the depths of black holes; some may come from phenomena yet to be discovered or even from other dimensions. Travelling at close to the speed of light cosmic rays spiral along magnetic field lines, strike the edge of the Earth’s atmosphere, break apart and shower down upon us. Some particles collide and silently interact with atoms and technology on Earth. Most cosmic rays heading for Earth are deflected by the planet’s magnetic field and without this protection life on Earth could not survive this bombardment of radioactive matter. The interaction of cosmic rays and the solar wind with atmospheric electrical fields combines to influence the unpredictability of Earth’s magnetosphere, impacting the functioning of GPS satellite technology and computer processors on which humans have come to rely in daily life.

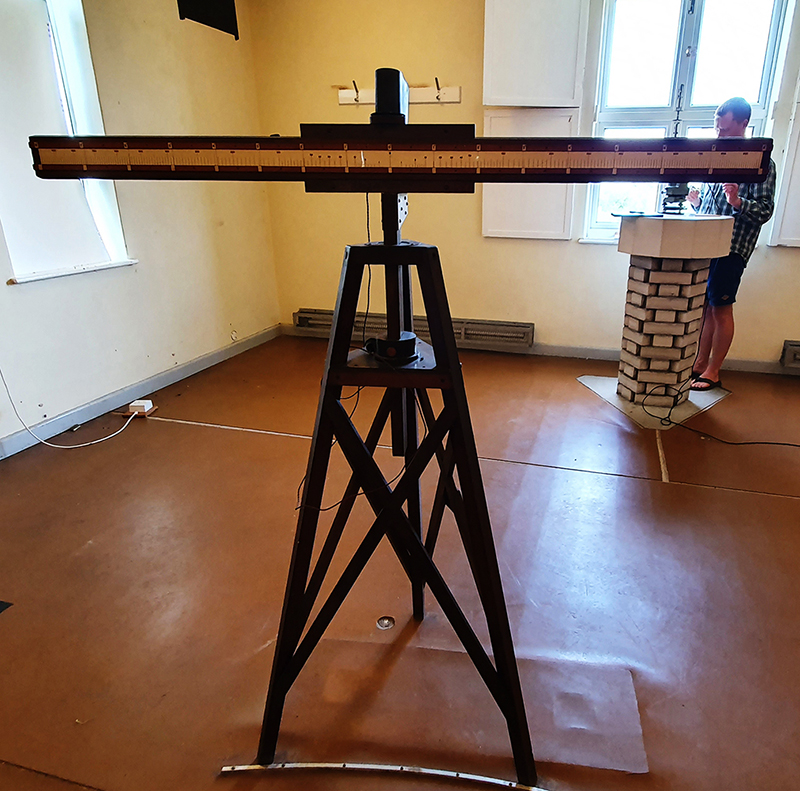
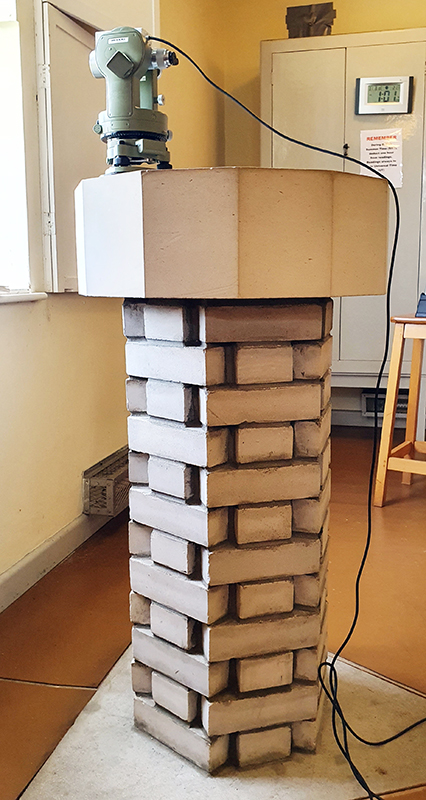
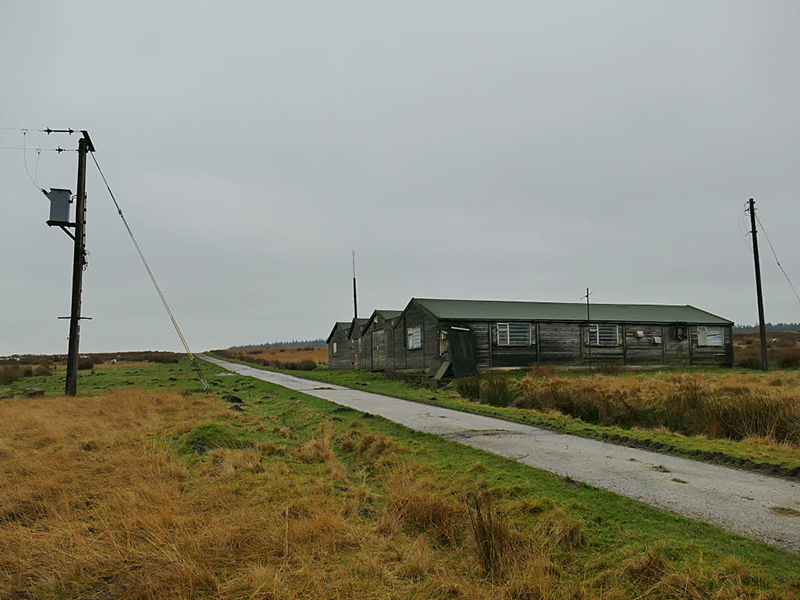
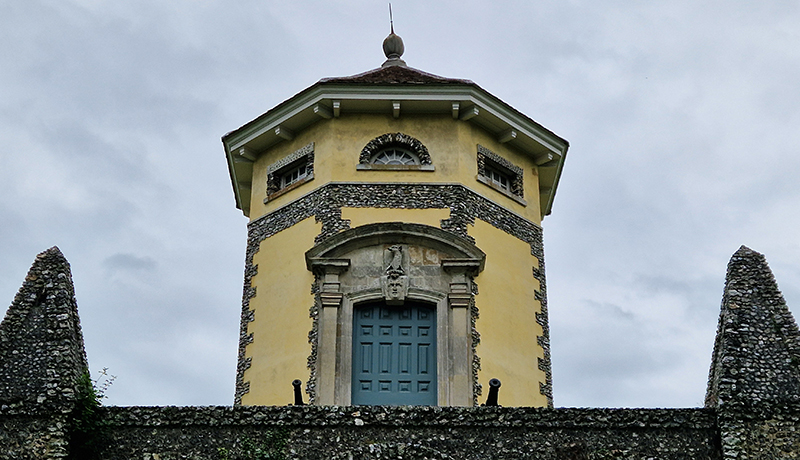
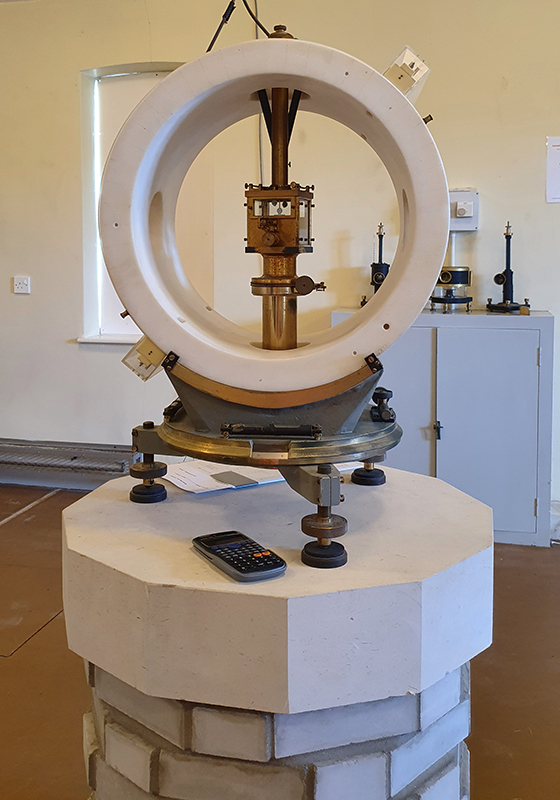
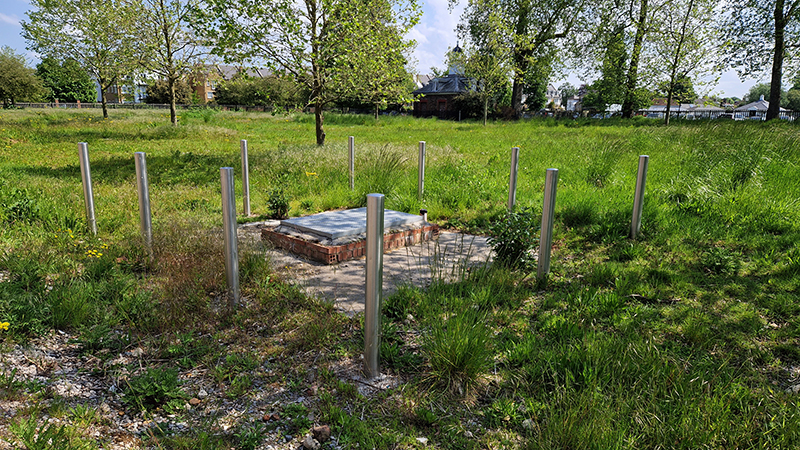
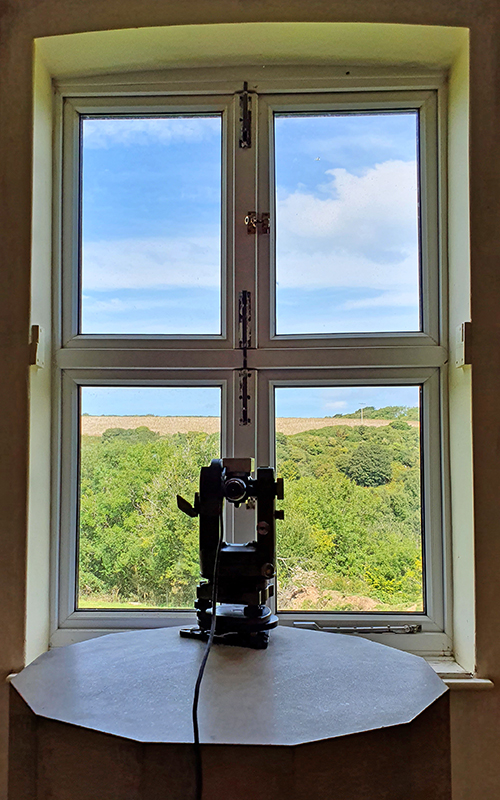
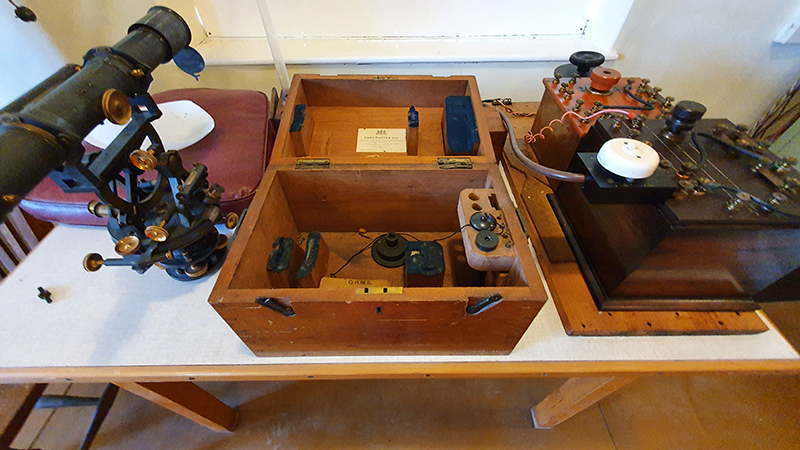
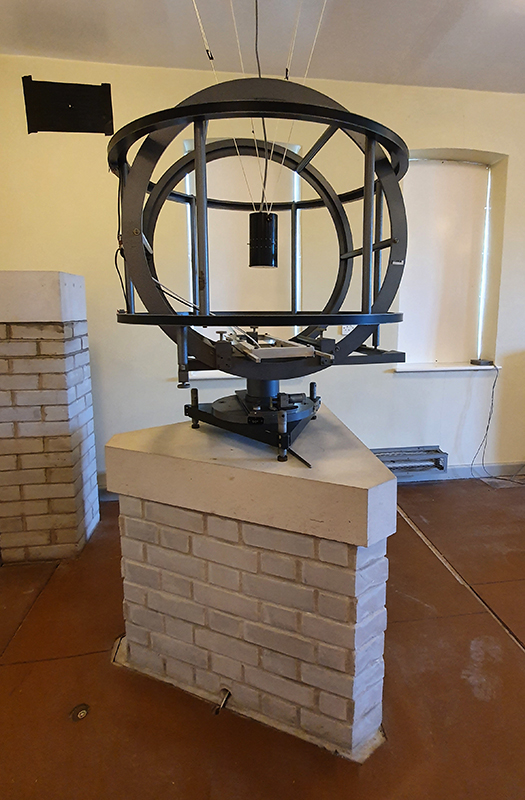
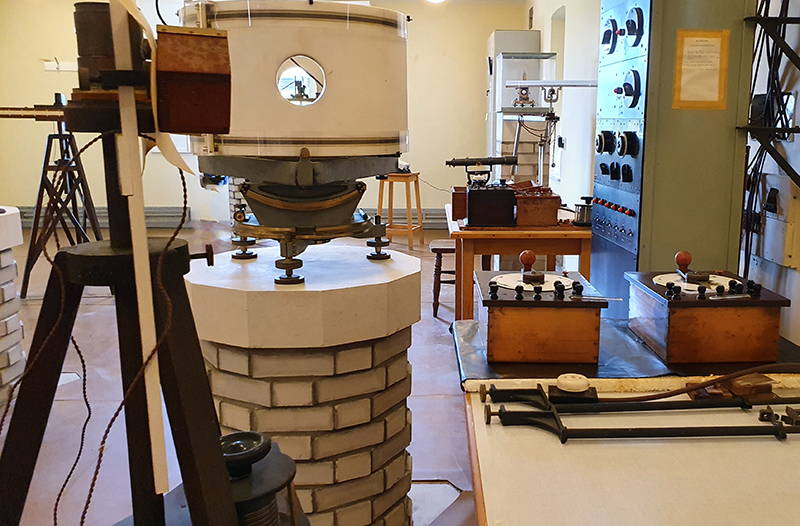
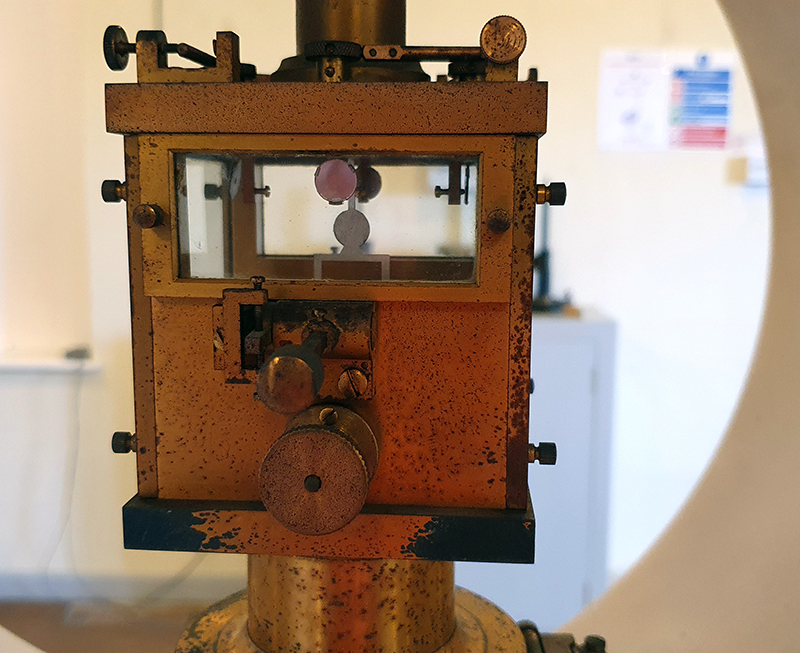
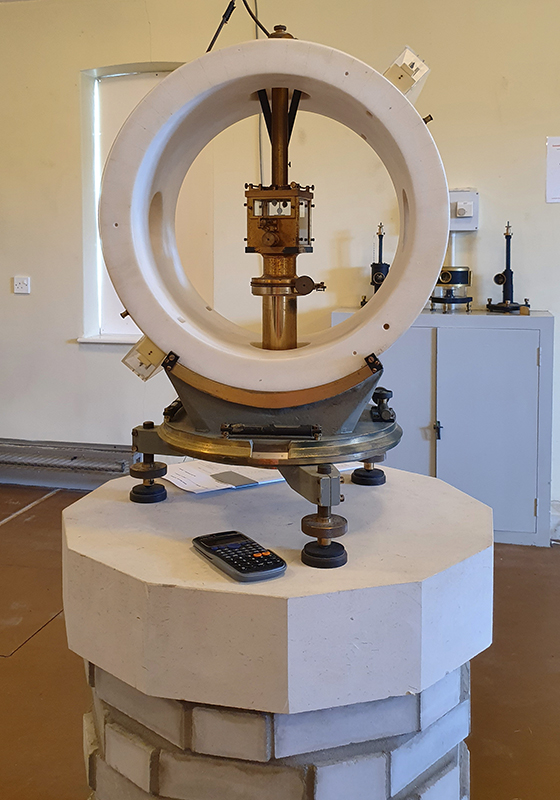
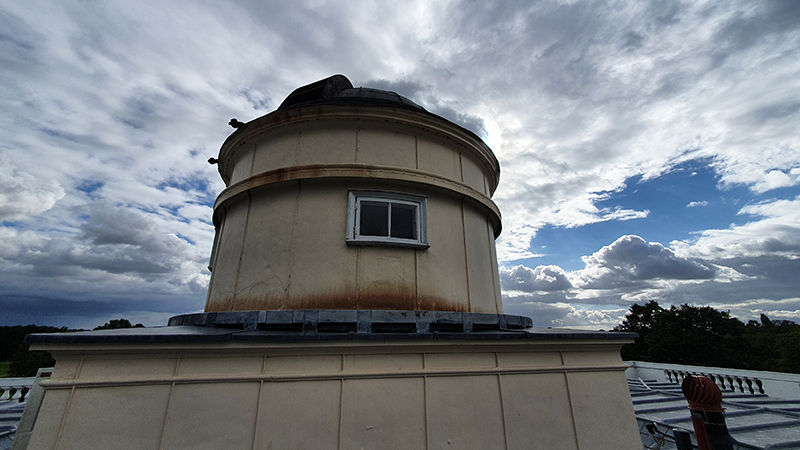
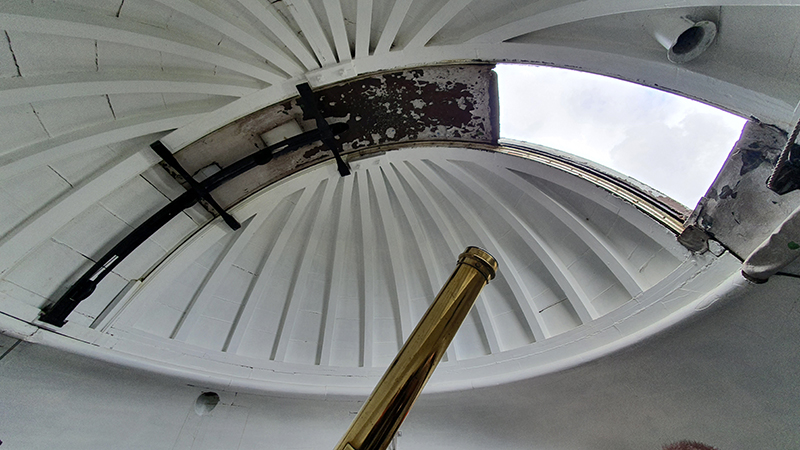
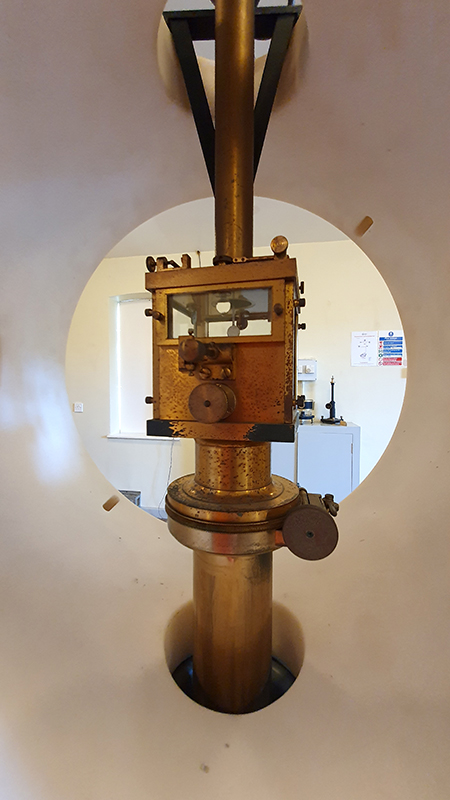
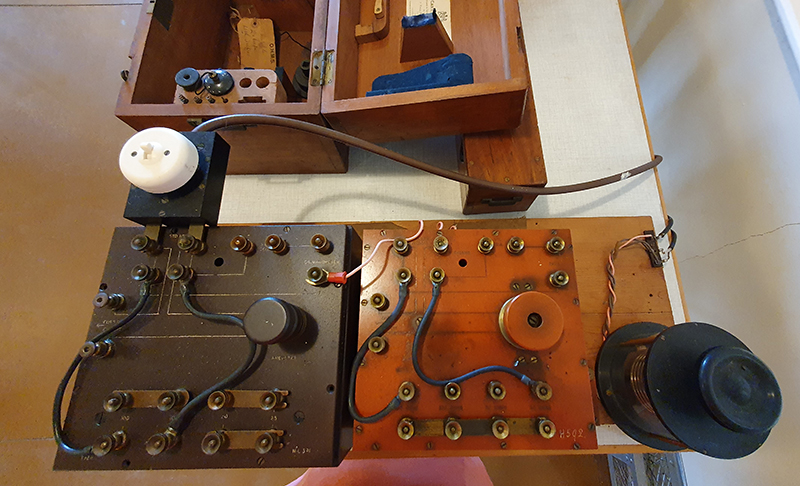
My research trip to Hartland Magnetic Observatory in North Devon was a catalyst for this body of work centring around a north facing observation hut aligned with an obelisk as a fixed azimuth mark. I am very grateful to The British Geological Survey for allowing me access to the site and particularly to Tom Martyn who shared his knowledge and gave a fascinating tour of the observatory.
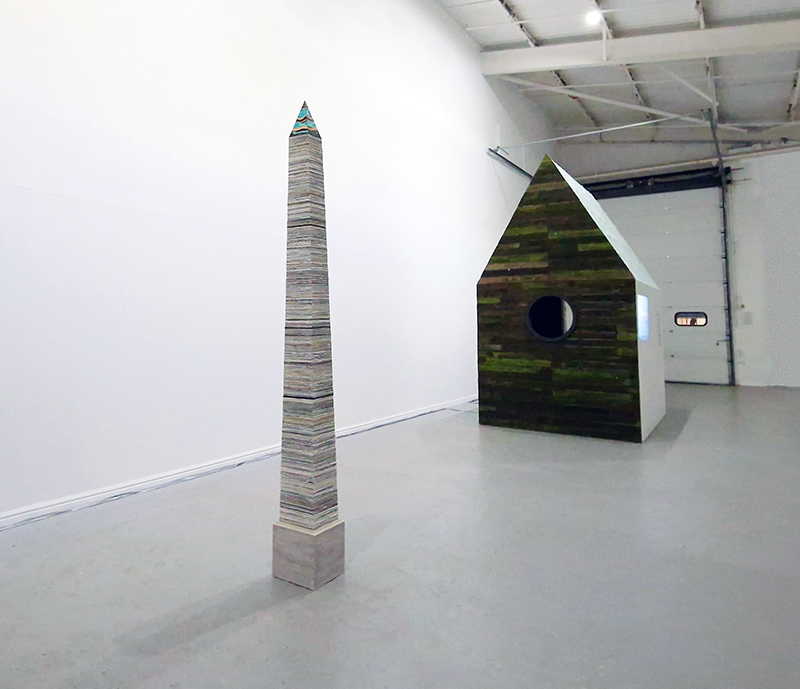

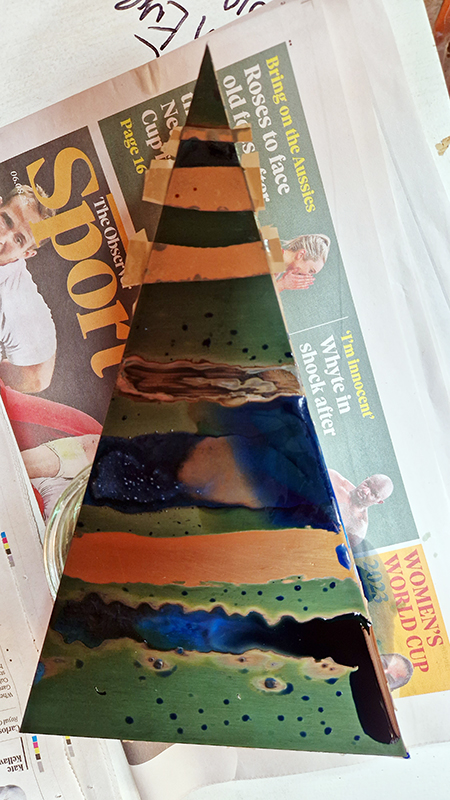
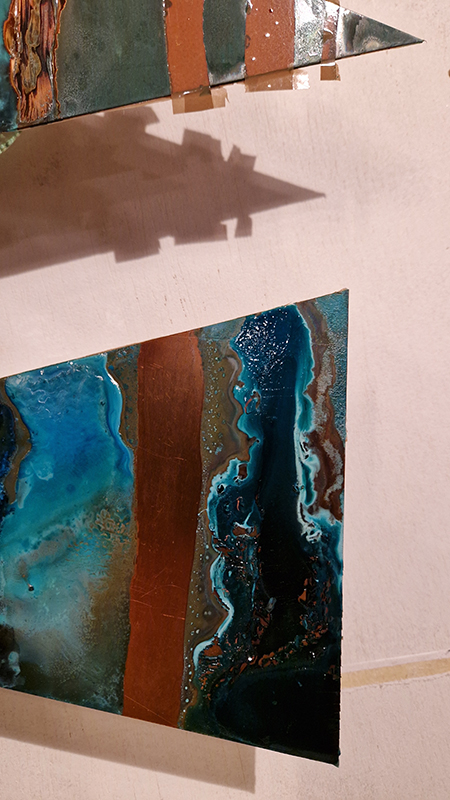
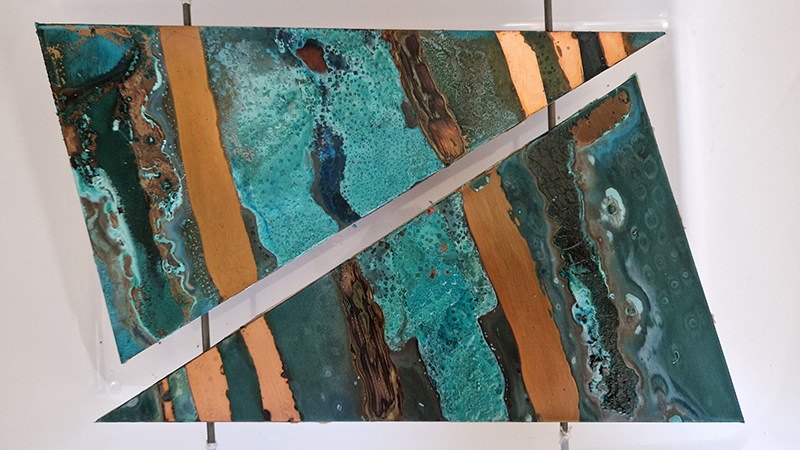
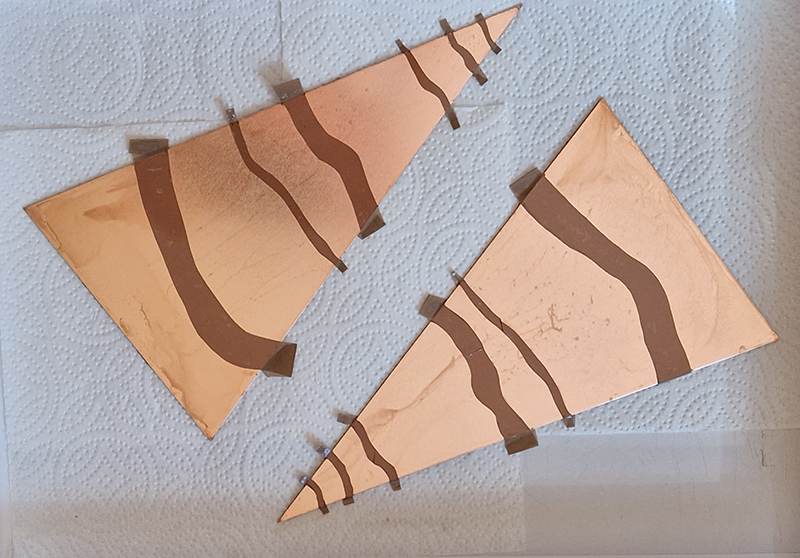
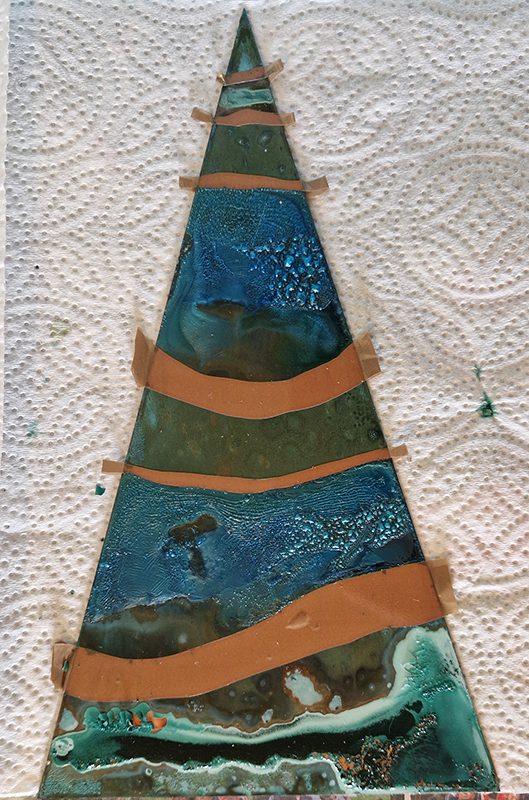
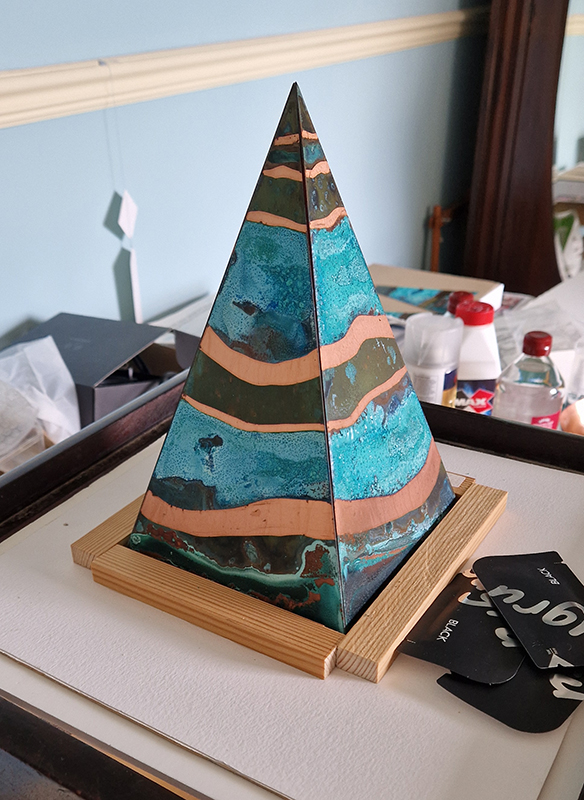
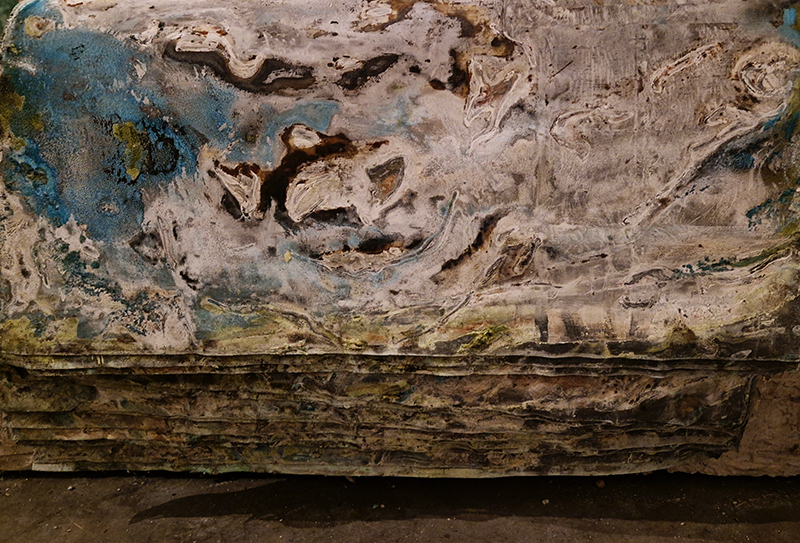
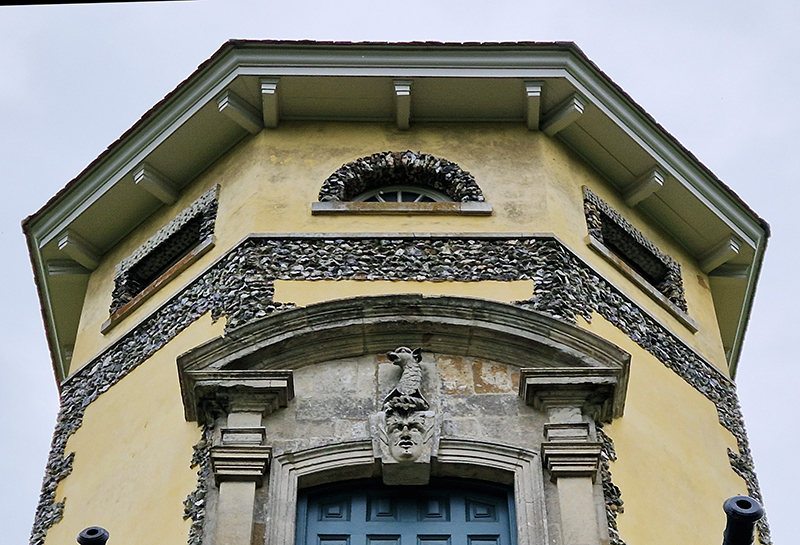
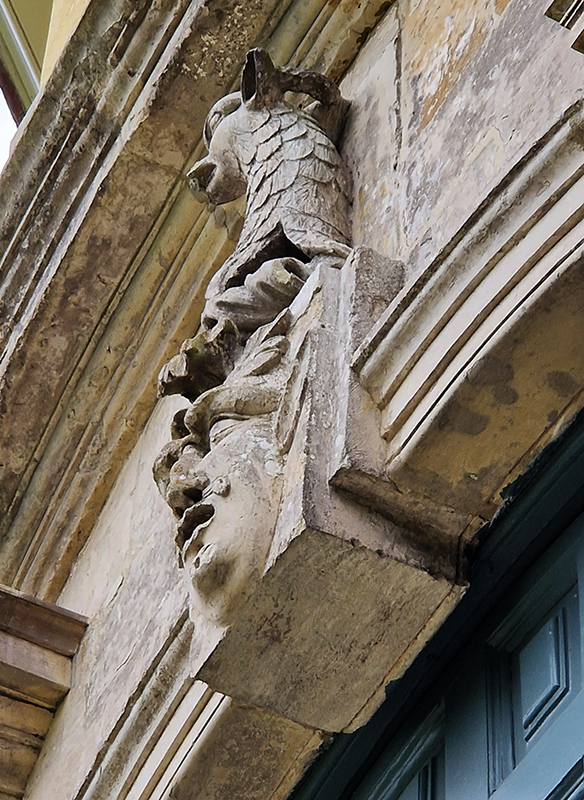
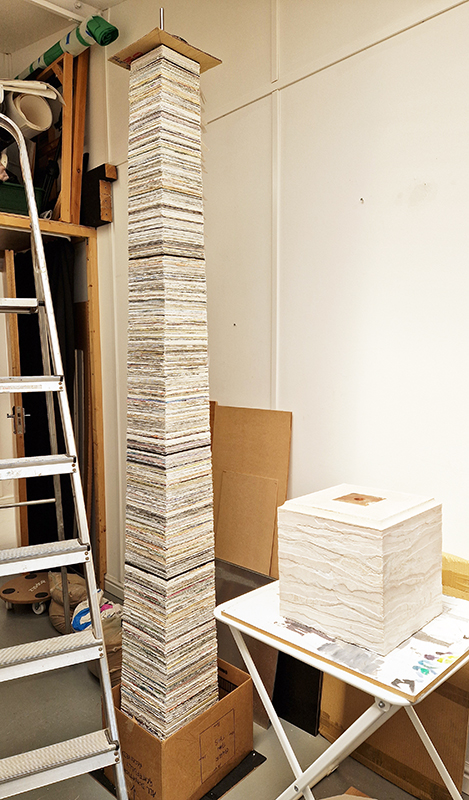
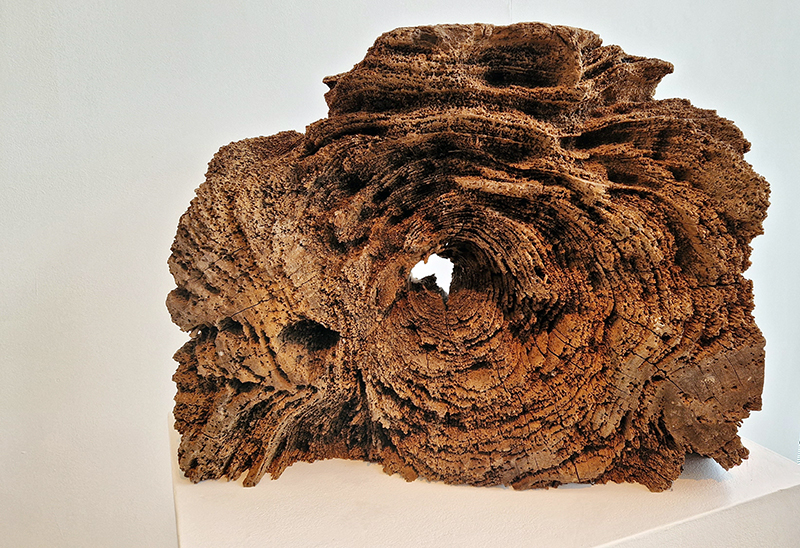
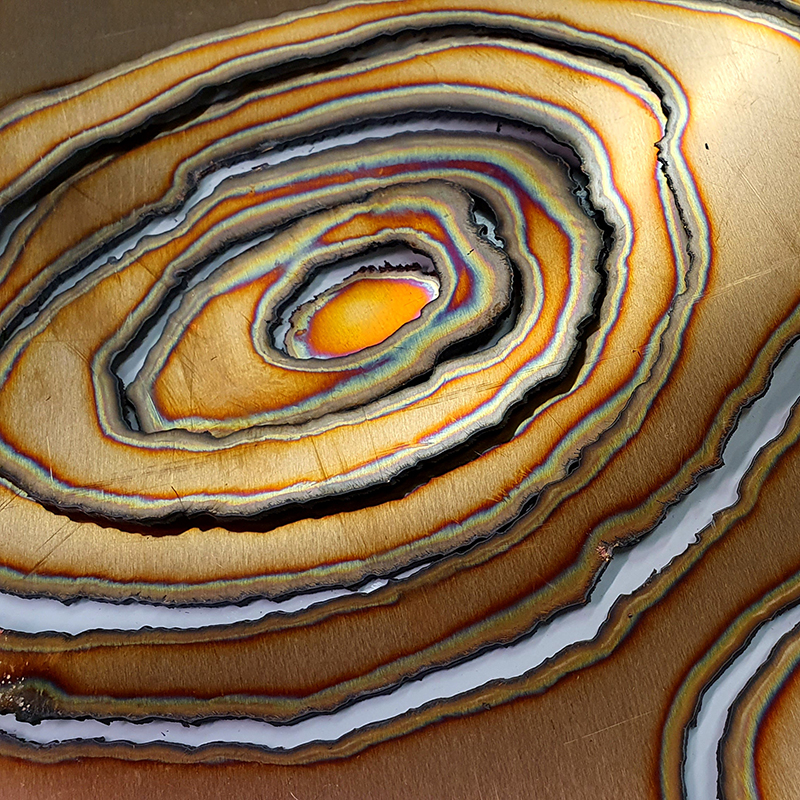
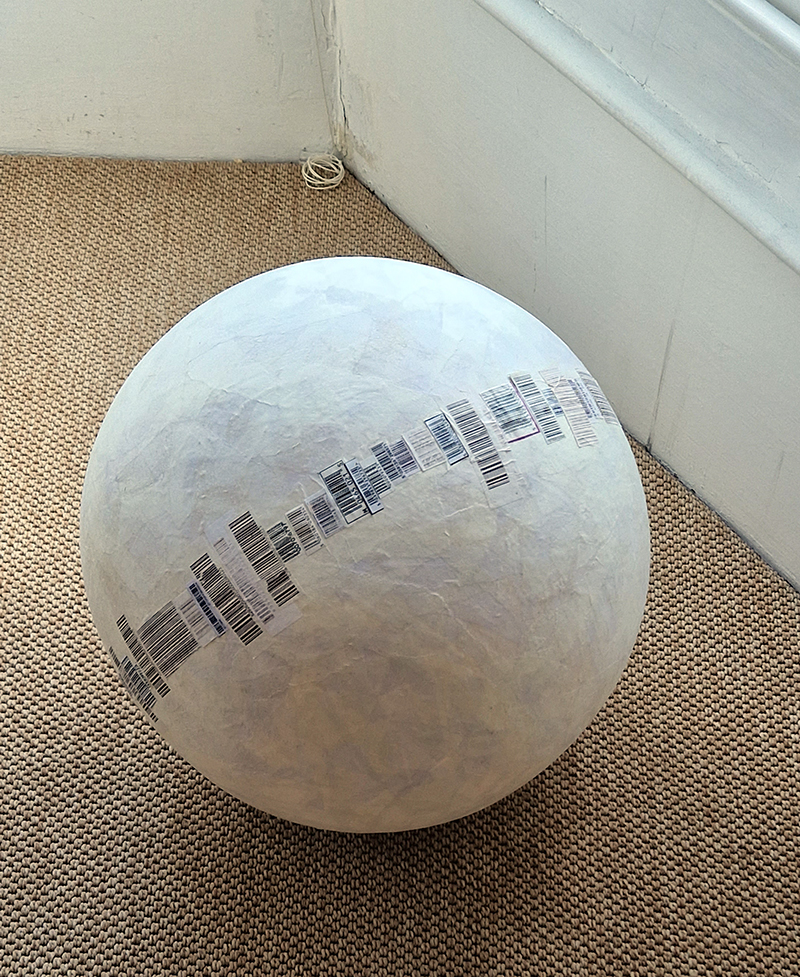
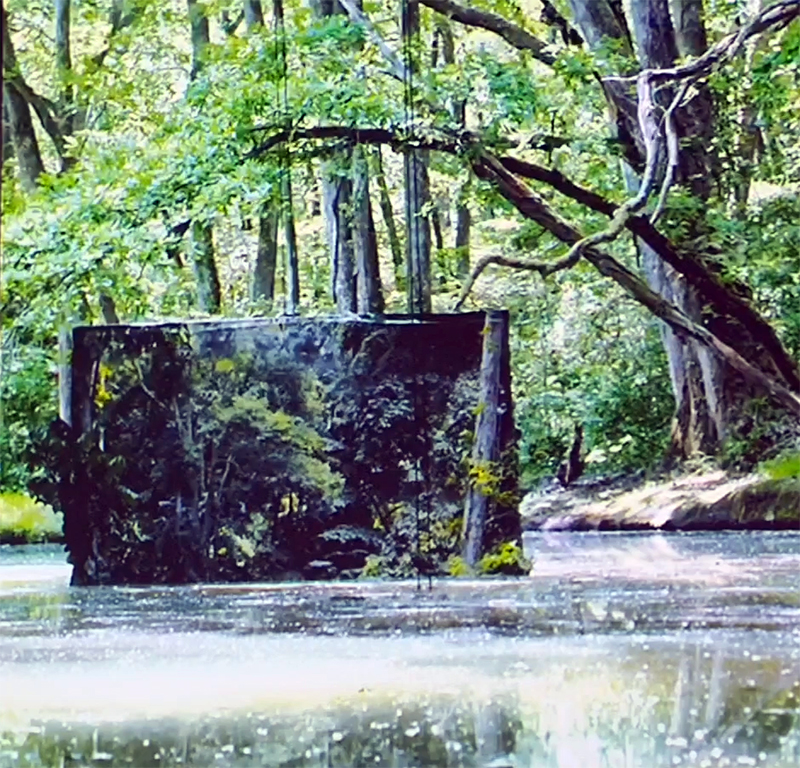
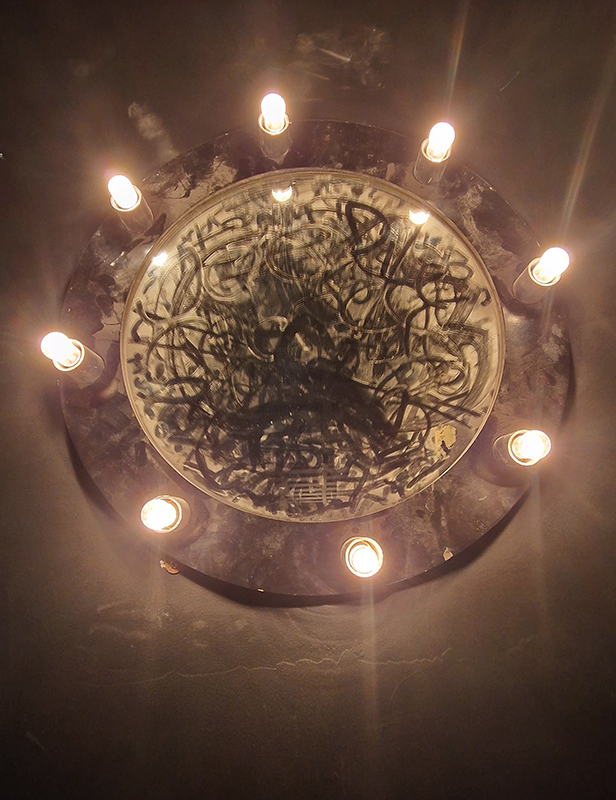
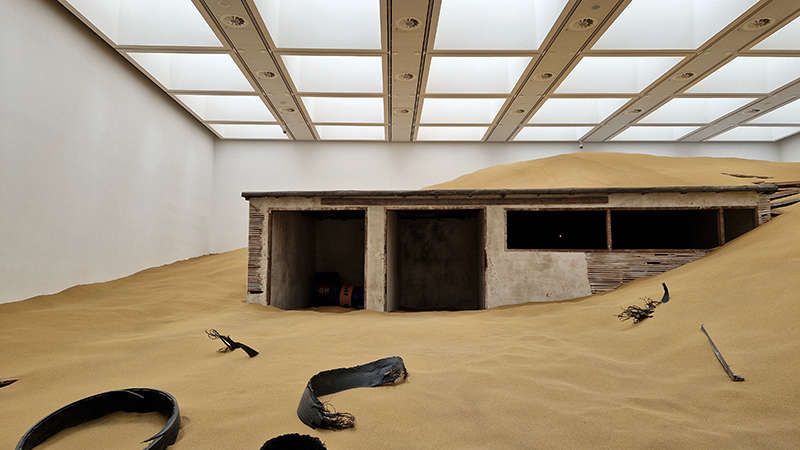
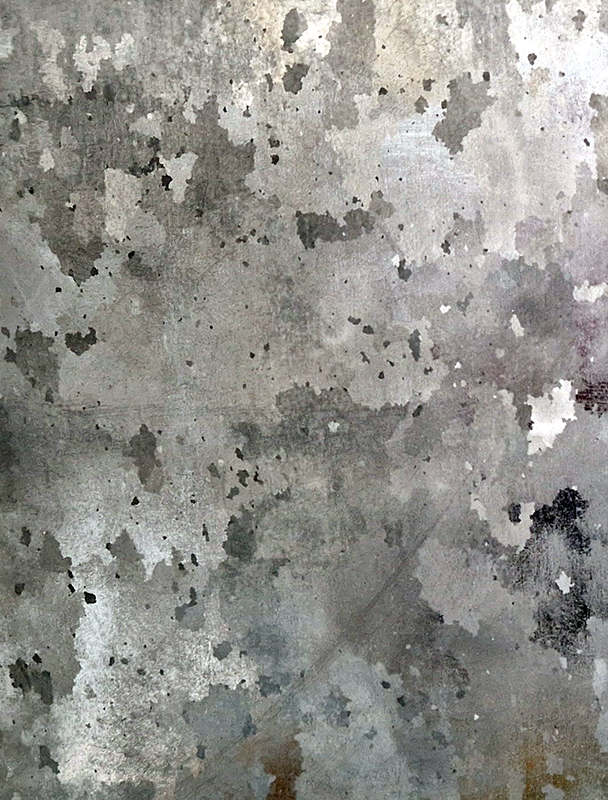
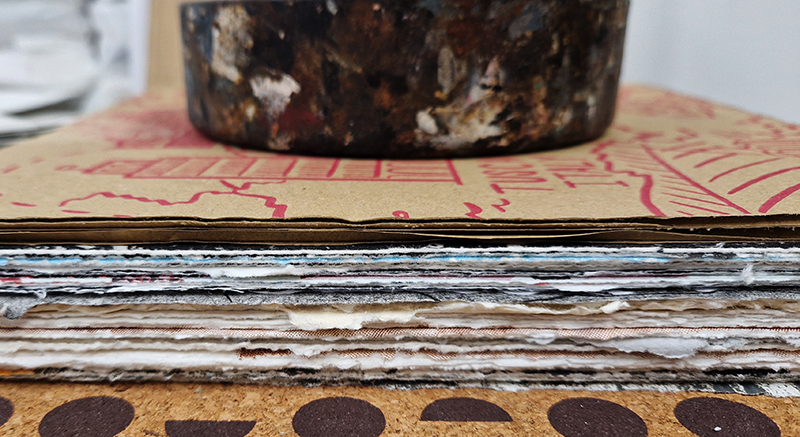
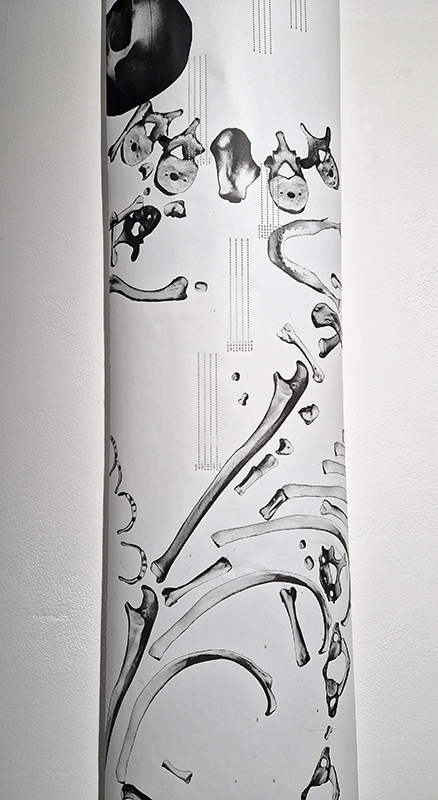
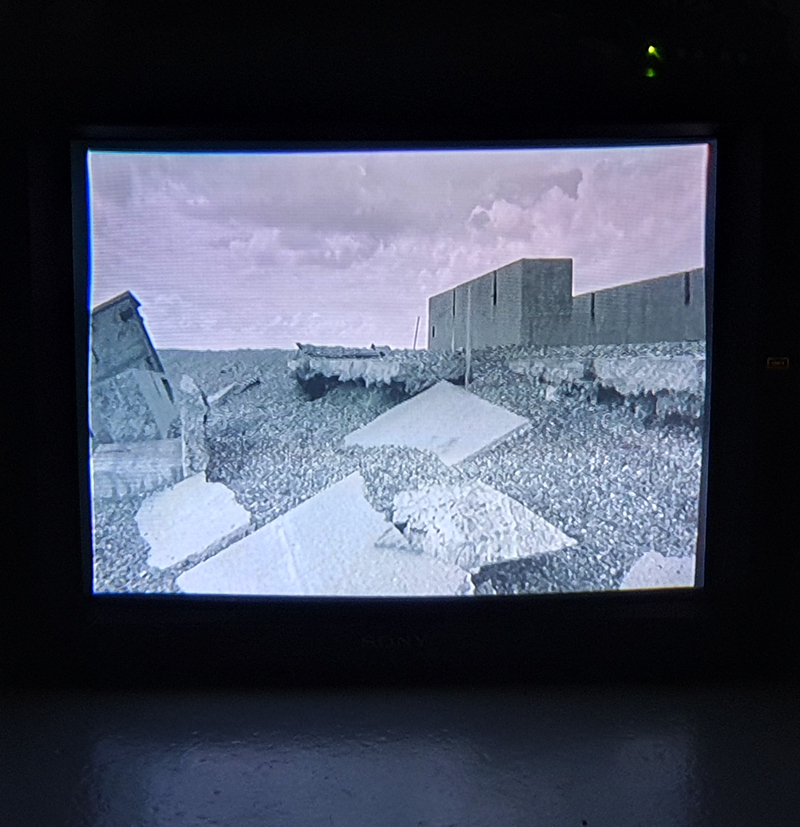
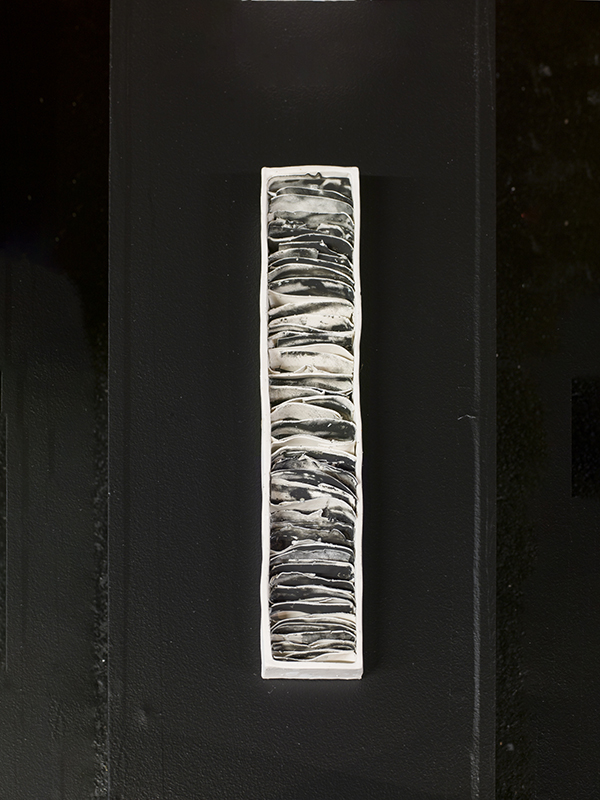
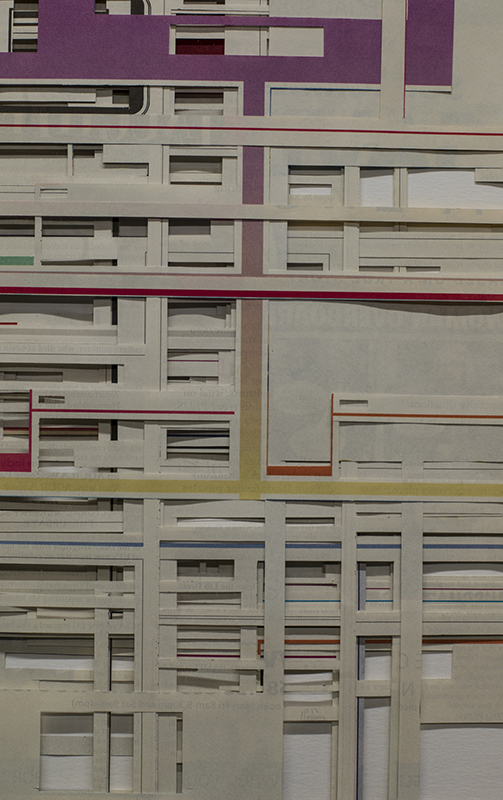
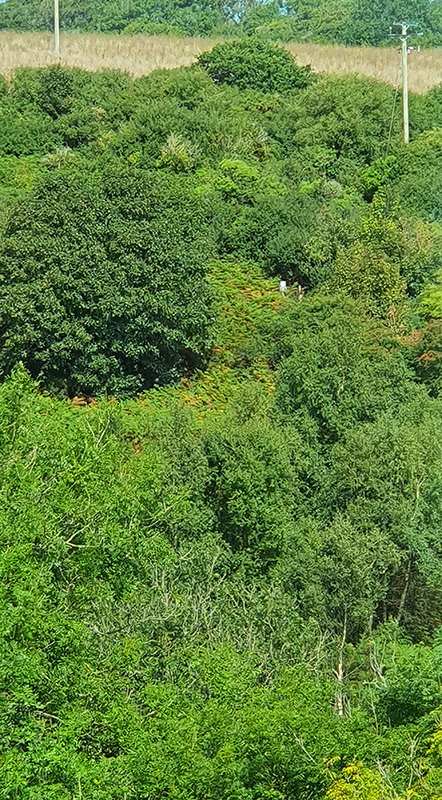
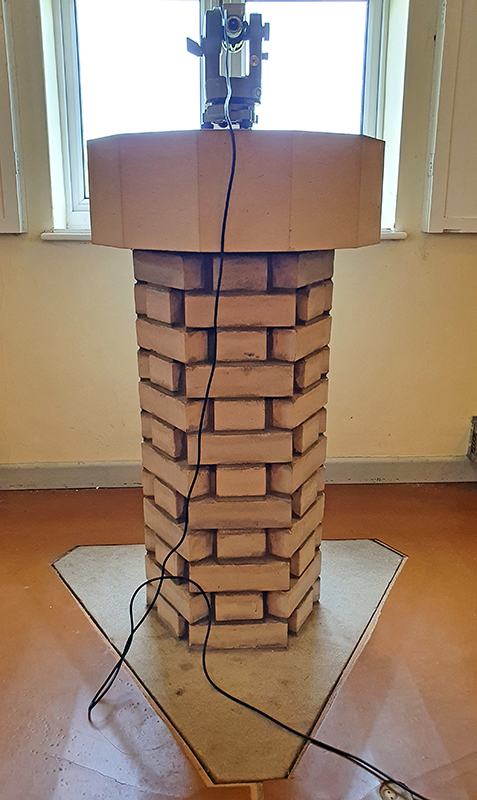
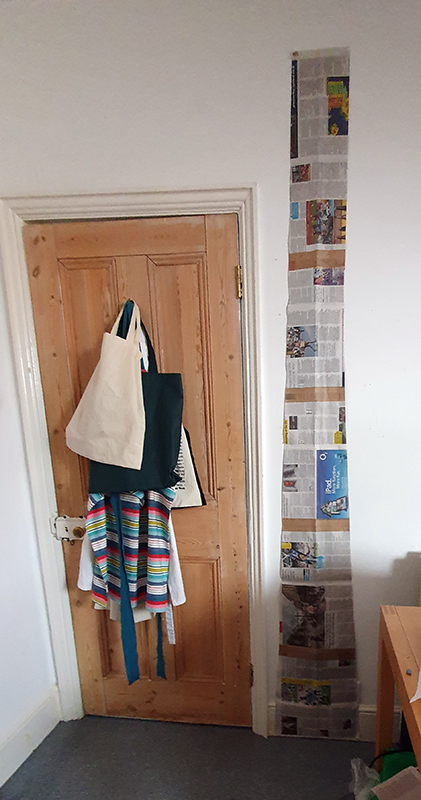
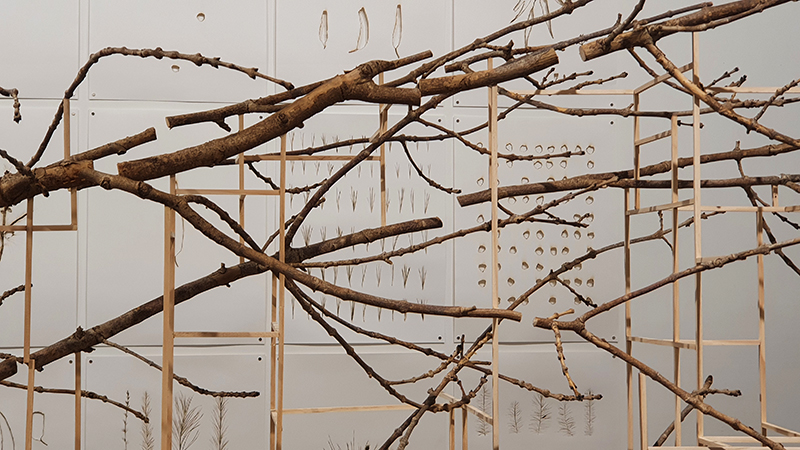
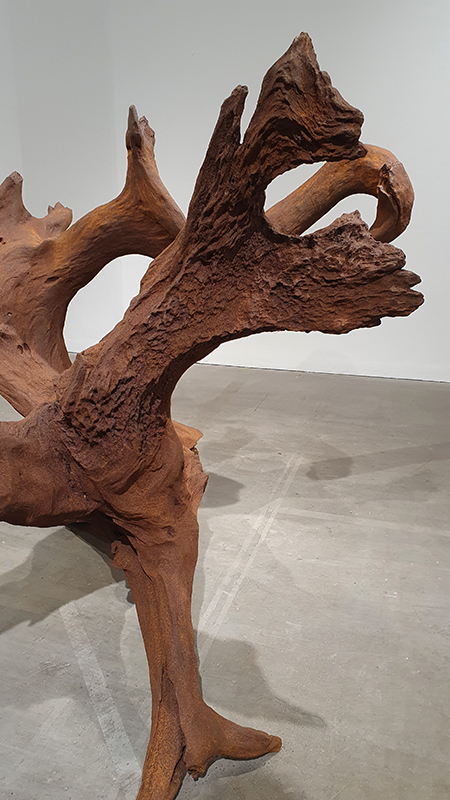
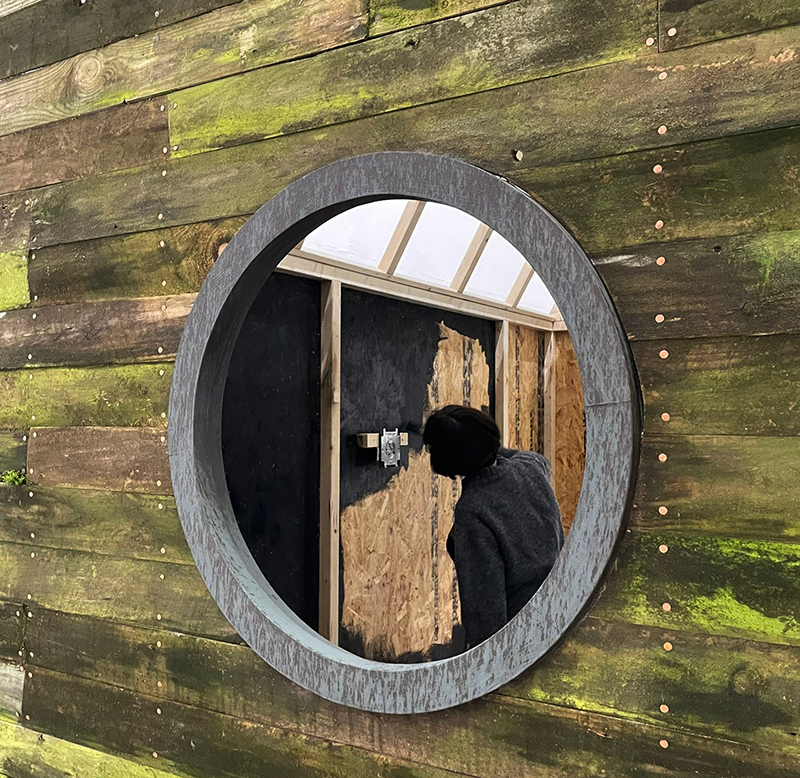
The Azimuth Obelisk (of sedimentary knowledge) is a reimagining of an obelisk erected at Hartland Magnetic Observatory in the late 1950’s near the site’s northern boundary. Viewed through the window in the north wall of The Observing Building (also known as the Absolute Hut) it acts as a permanent azimuth mark from which the drift of the magnetic north pole is monitored. Currently almost hidden by undergrowth, the observatory’s concrete azimuth mark has been replaced by a digital GPS position. Much as the Earth’s geological and magnetic history is secreted into the strata of sedimentary rock, this sculpture also expresses the passage of time through the layering of recycled paper prints and drawings whose history becomes embedded within the stacked layers.
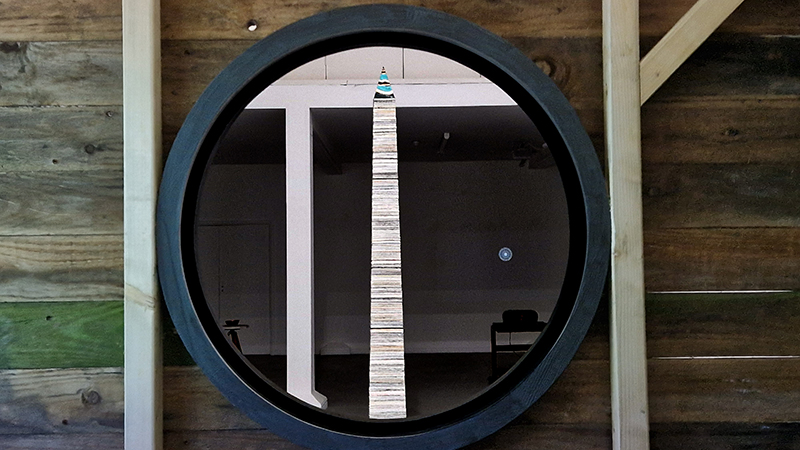
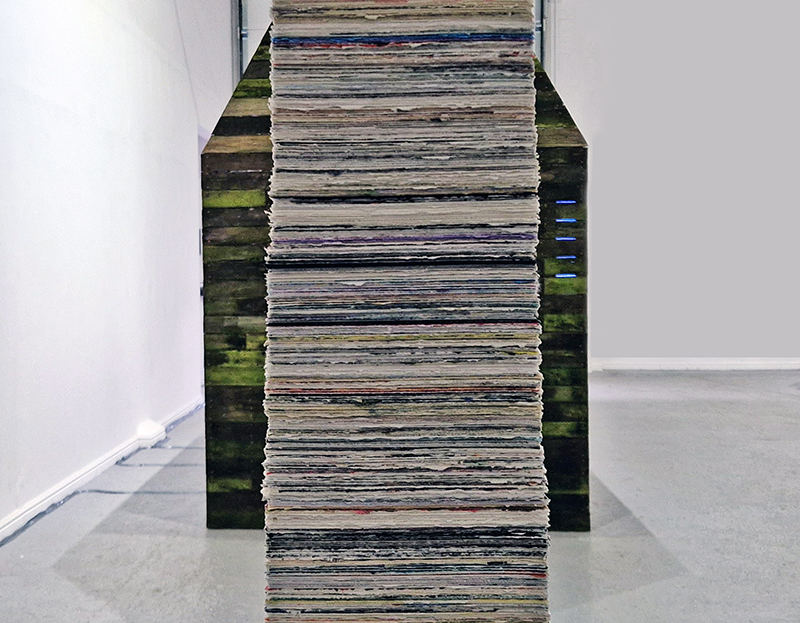



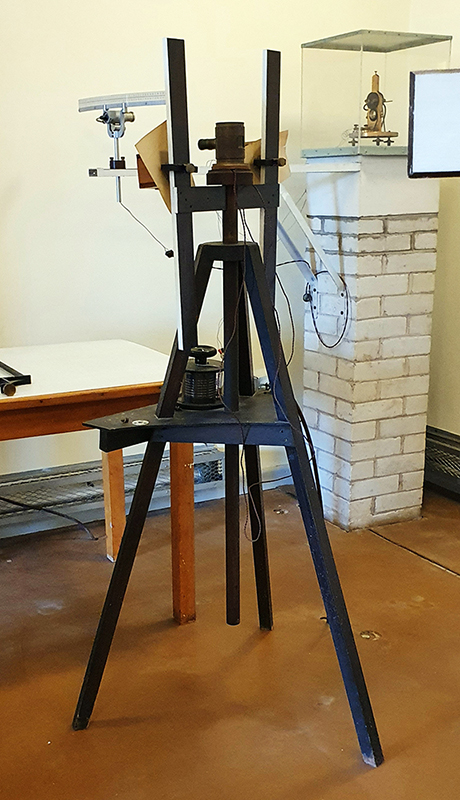
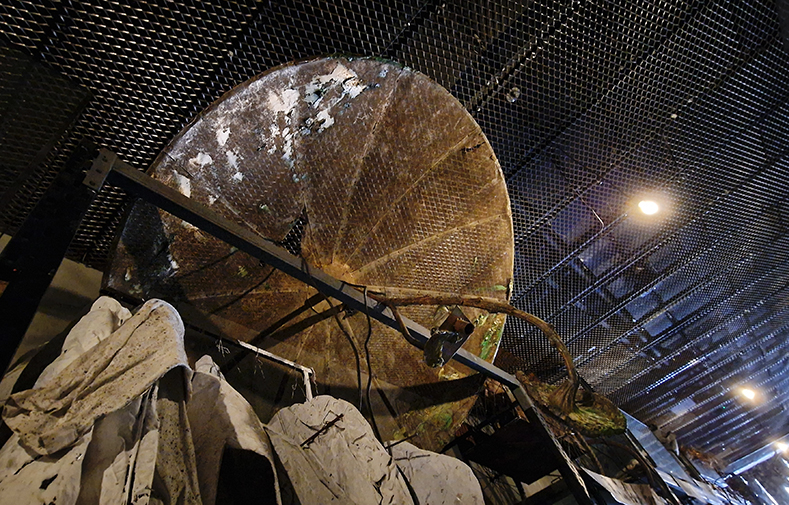
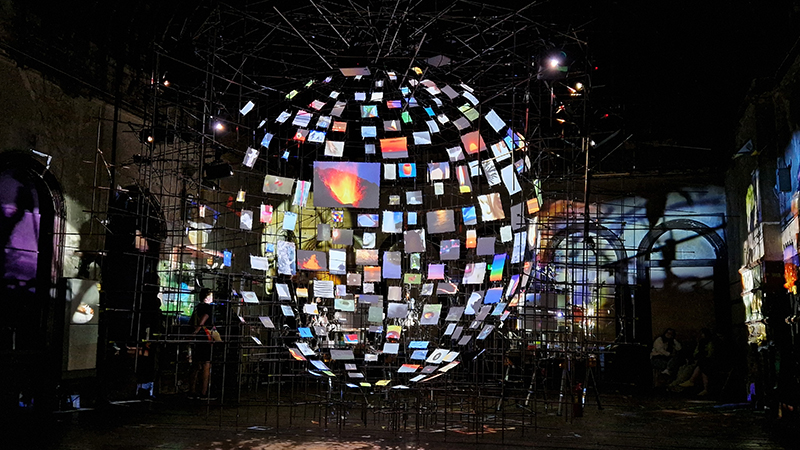
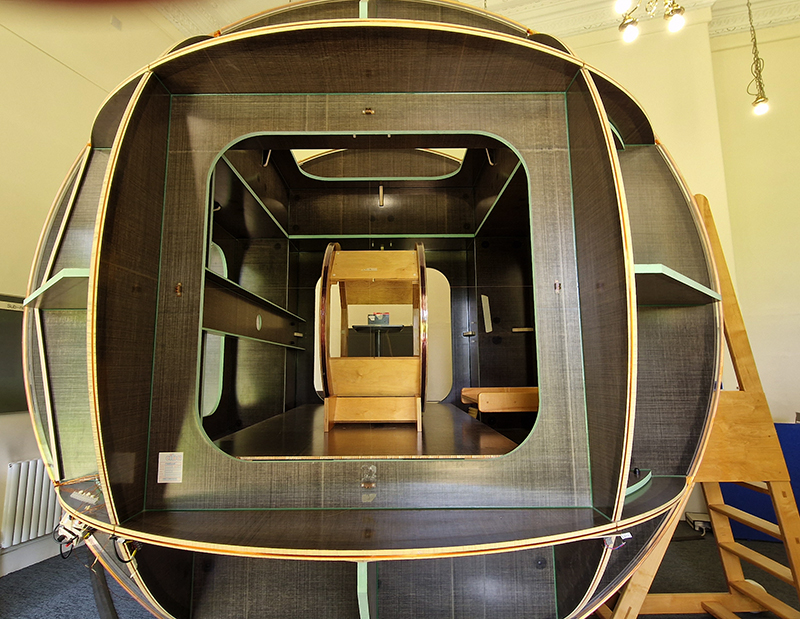
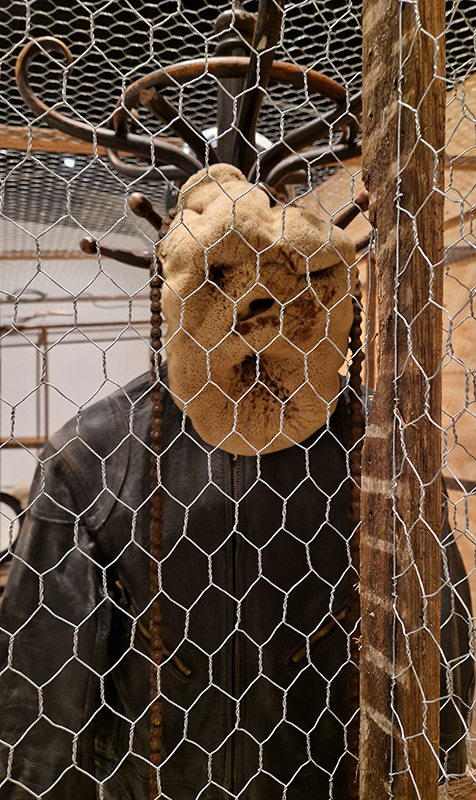
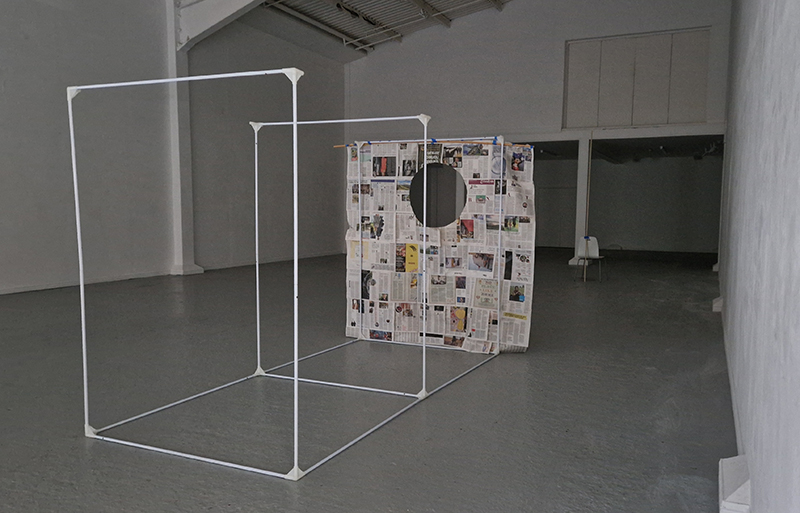
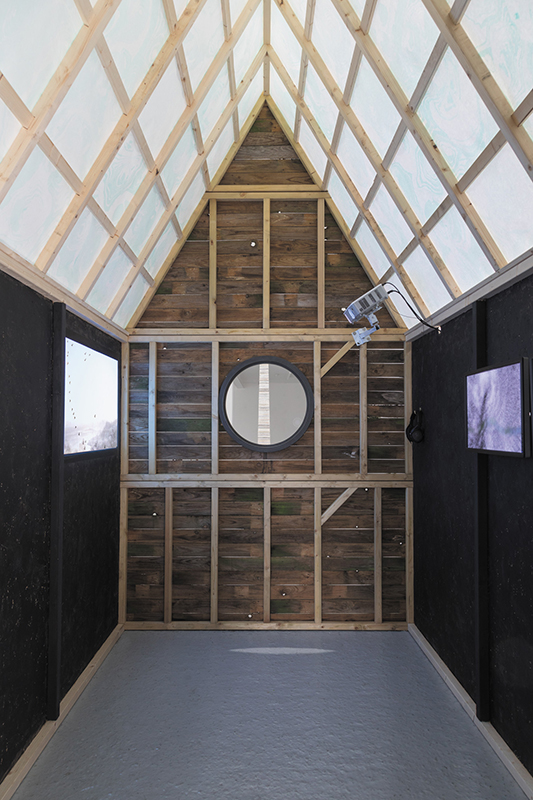
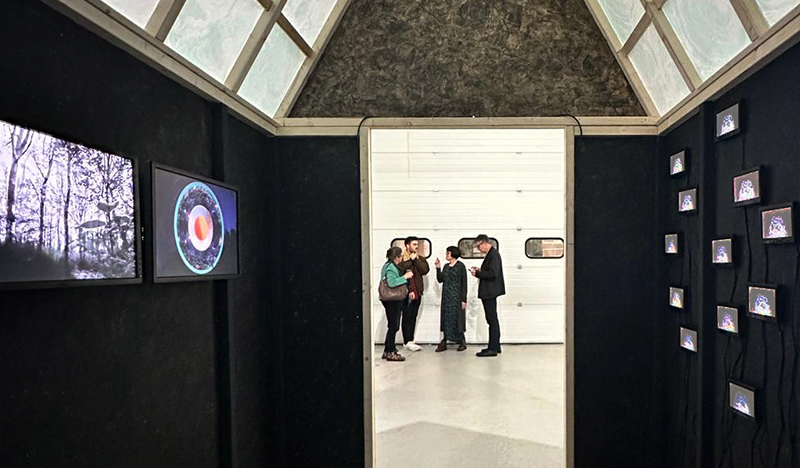
The Absolute Hut (of action potential) operates as a sensory hub with video screens suggesting portals into a web of neural pathways where a range of actions and processes are running concurrently reflecting on the dynamics between the Earth’s geologic structure and navigation using the magnetic field.


The title refers to the way neurons send information electrochemically around the body. The signals they send are called action potentials which is a temporary shift from negative to positive within the cell caused by certain ions entering the cell. Action potentials can be triggered by an interaction with the magnetic field causing a reaction in the body.
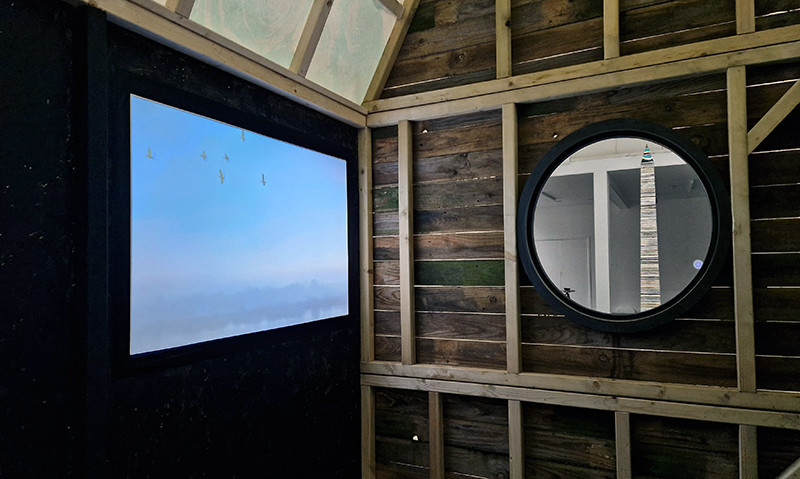
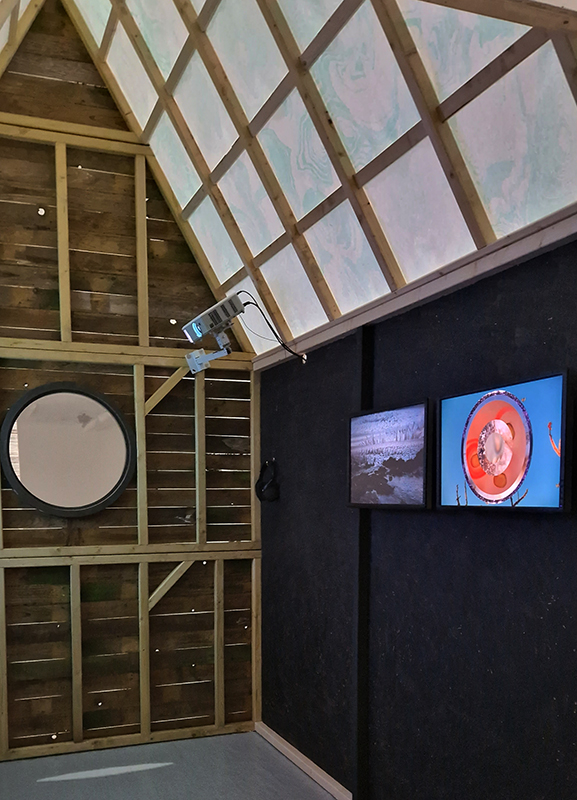



The installation is conceived from a combination of features, impressions and functions of the observing building and instruments at Hartland Magnetic Observatory in North Devon and the observation huts built in the 18th century at The Kings Observatory in Kew for meteorological and magnetic observations.

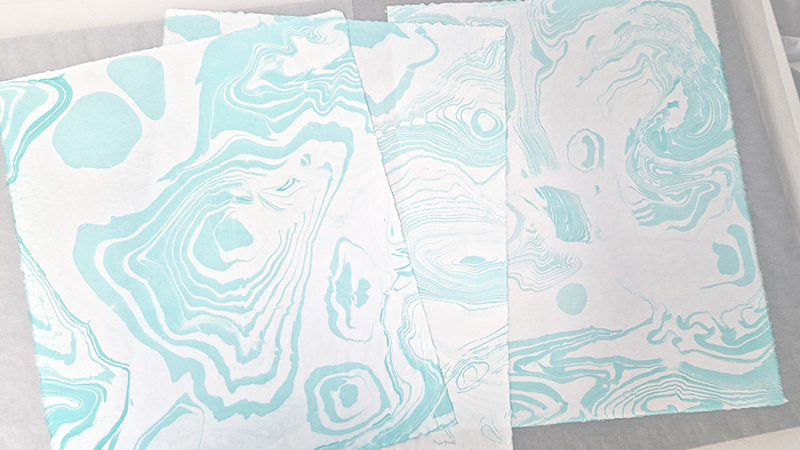
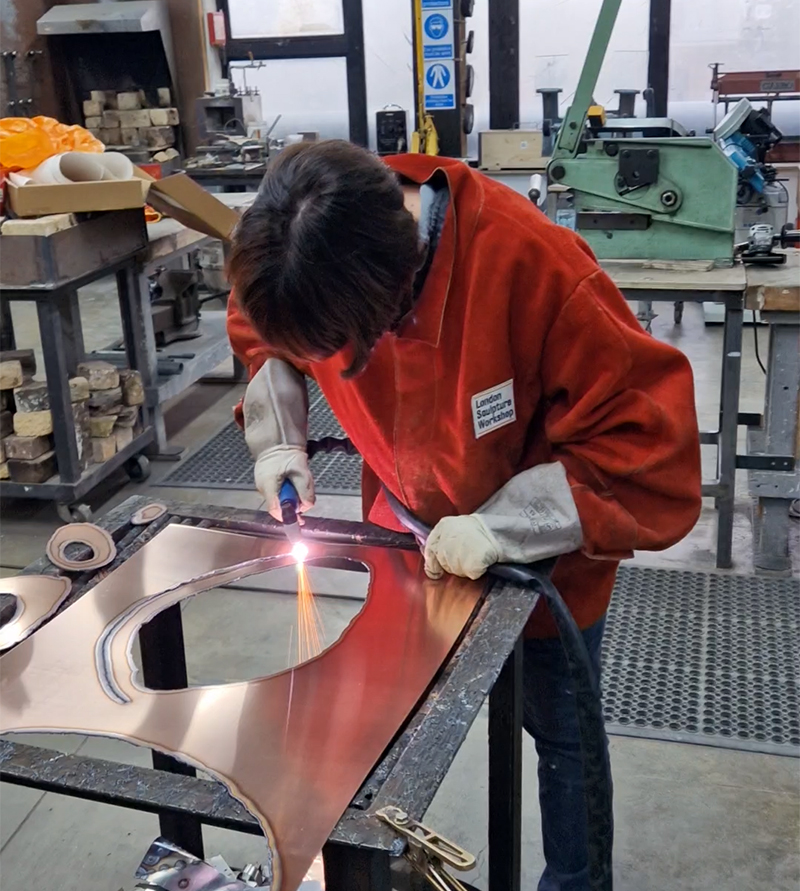
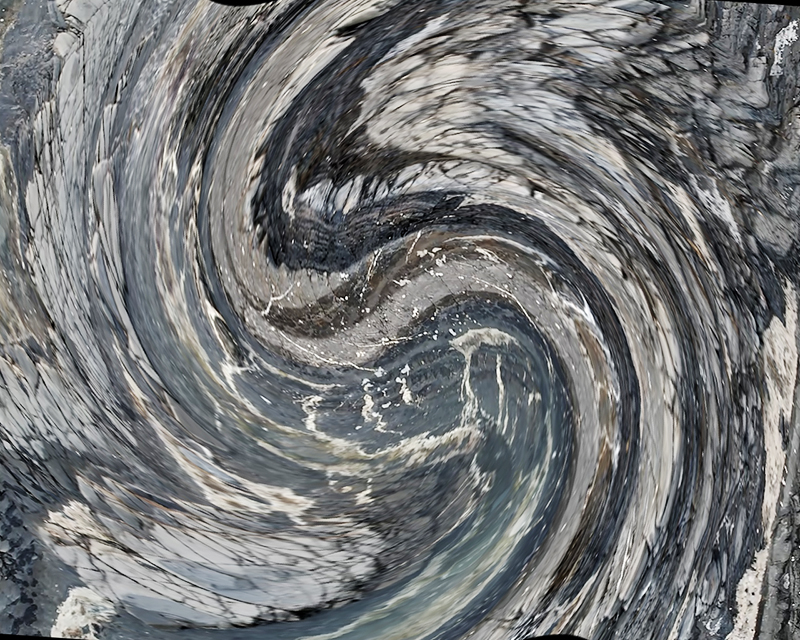
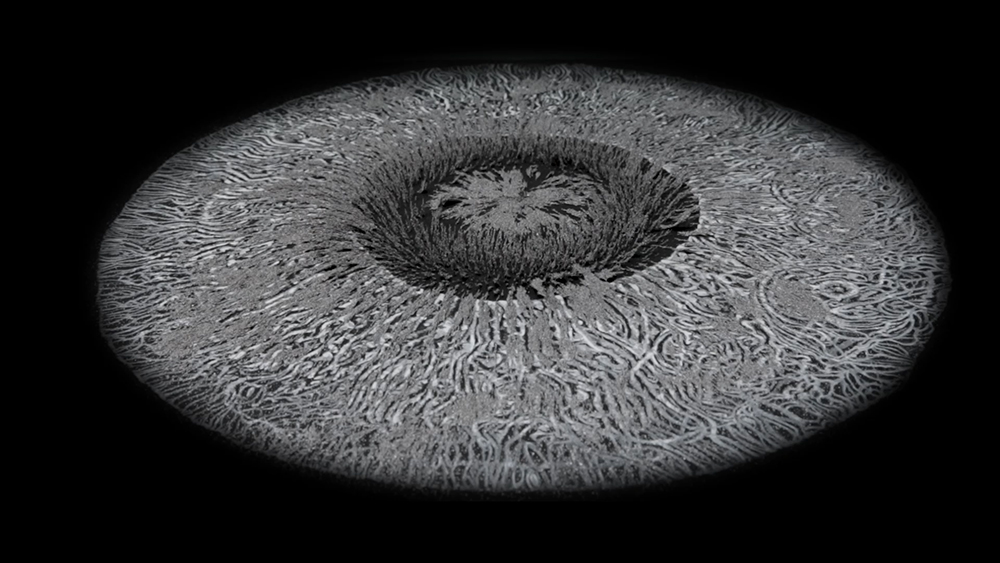
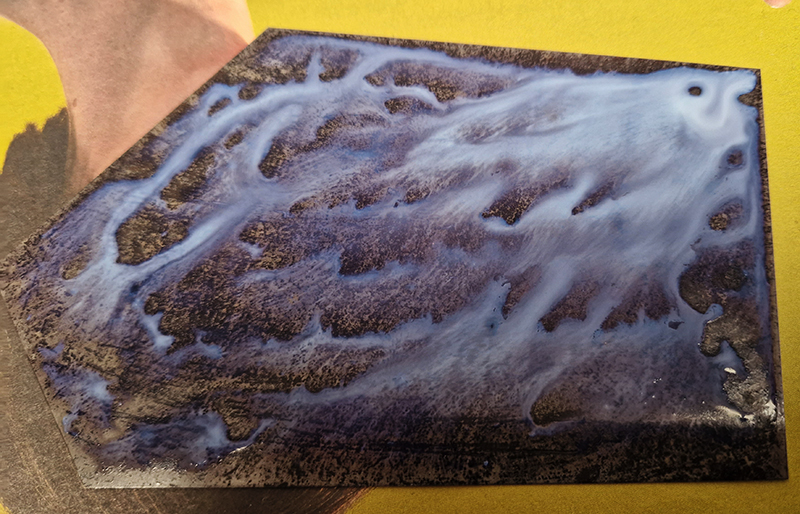
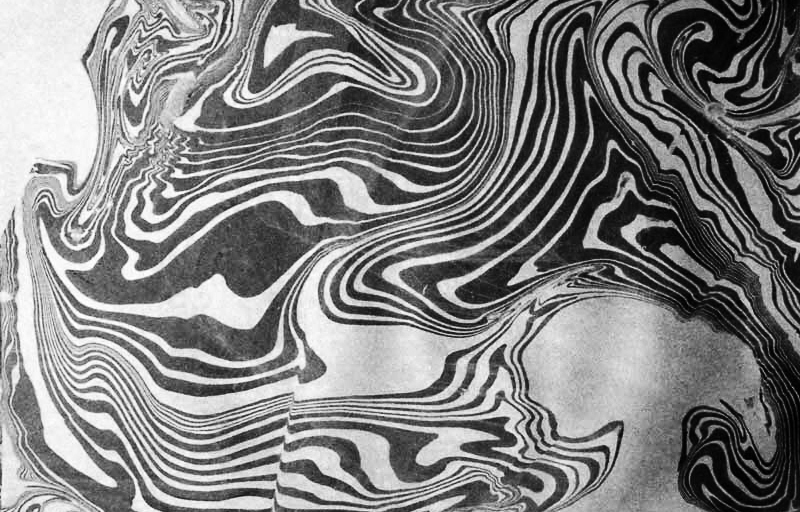
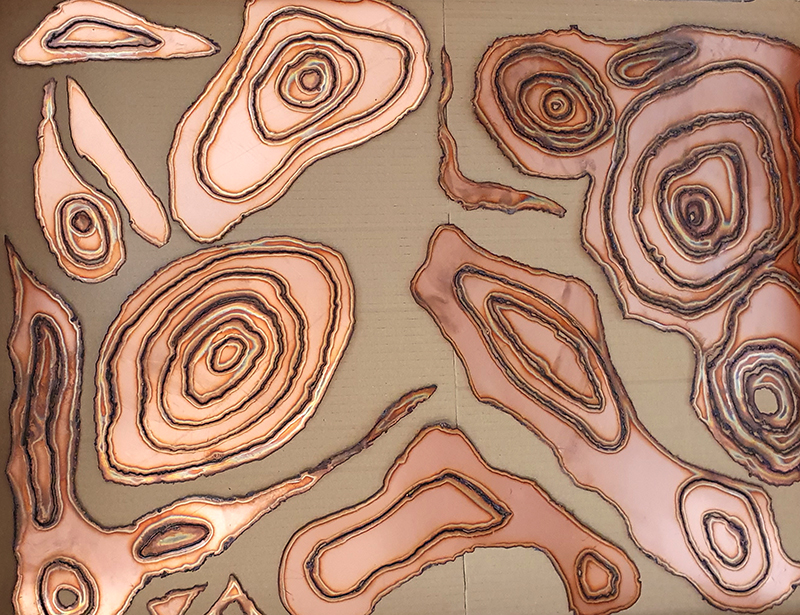
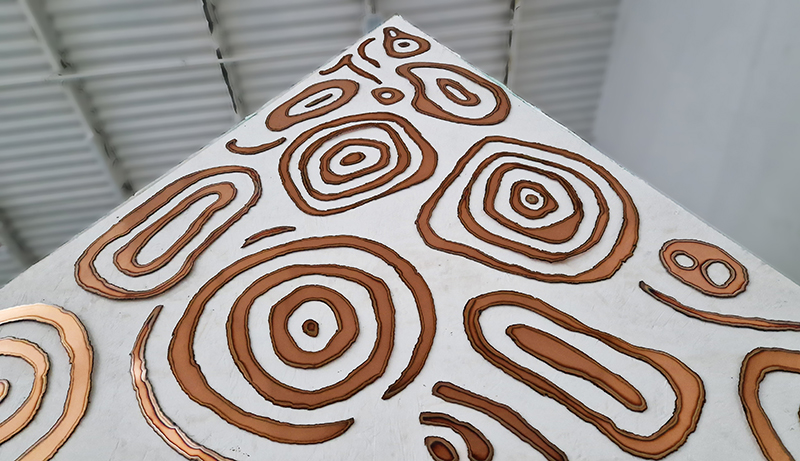
Topological contours of suminagashi marbling and plasma cut copper reflect the fluid motion of the Earth’s molten iron core and the pulsating alpha waves of the human brain when subjected to magnetic fields.


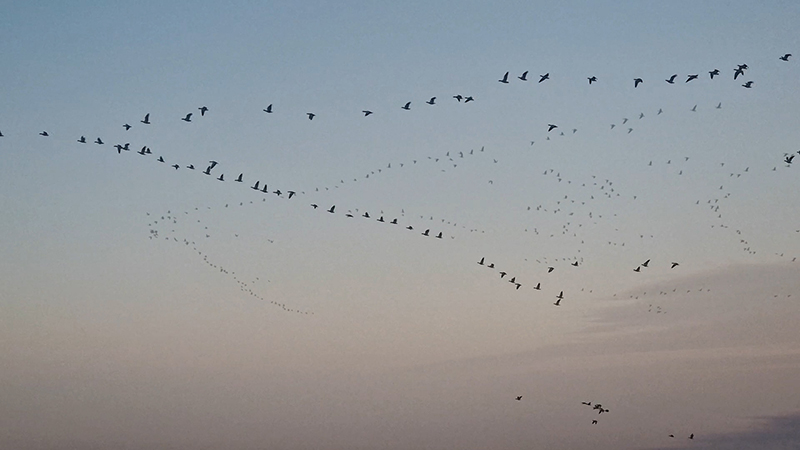
‘the internal skies have their own birds’ Italo Calvino Cosmicomics
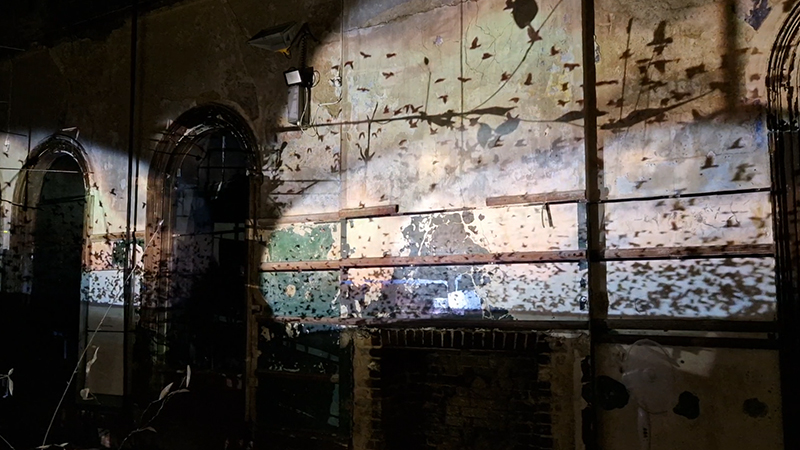
The fascinating and perilous journeys made by migrating birds has been a natural wonder for centuries with the first records of this phenomena made more than 3,000 years ago. The innate knowledge of migratory birds is mentioned in Job and Jeremiah and the ancient Greek writers Homer, Hesiod and Aristotle noted their passage.
Job 39:26 Doth the hawk fly by thy wisdom and stretch her wings towards the south?
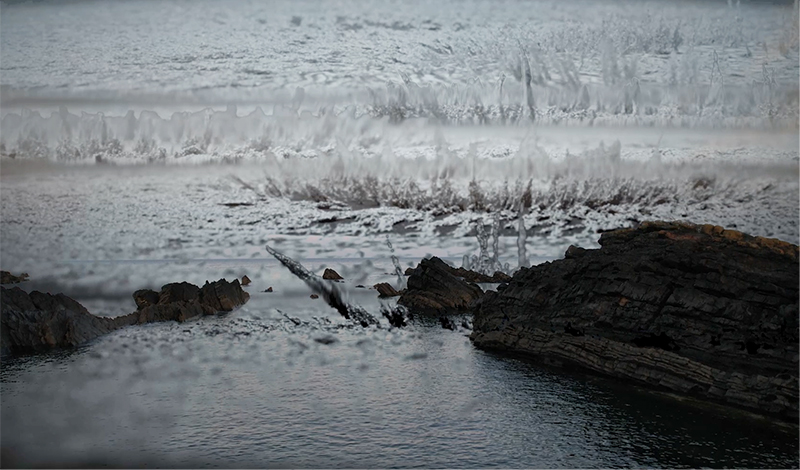
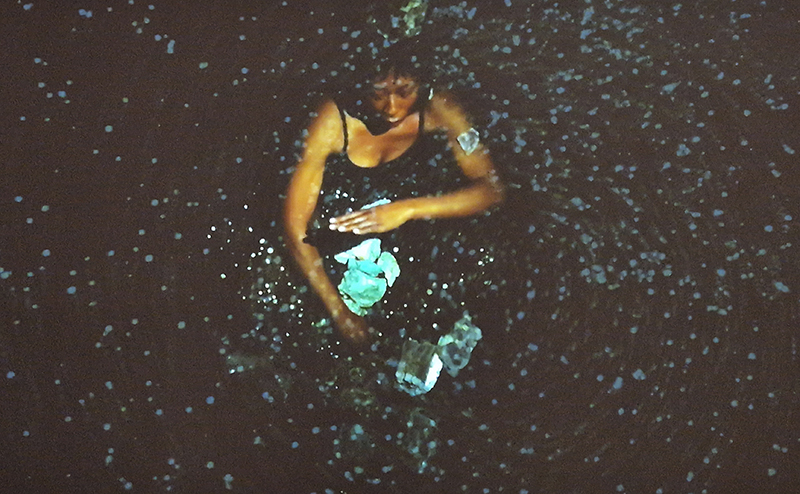
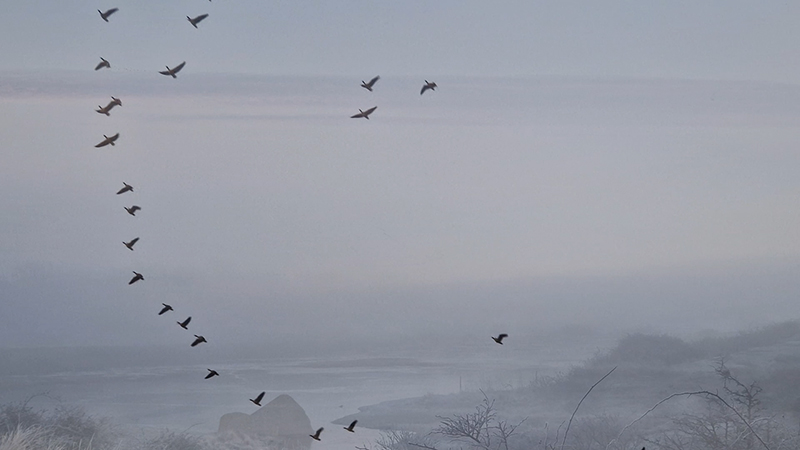
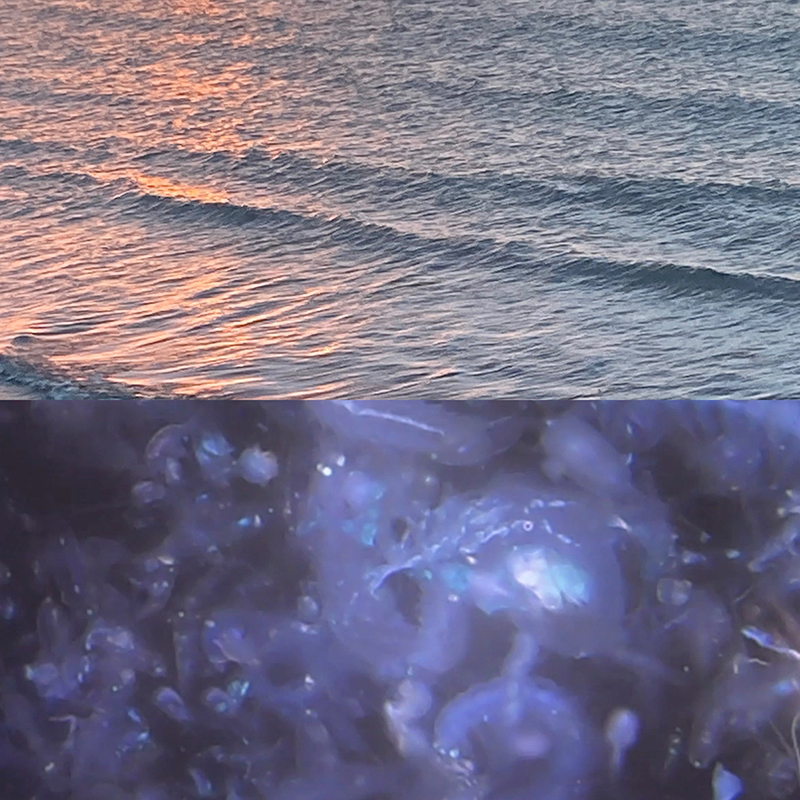
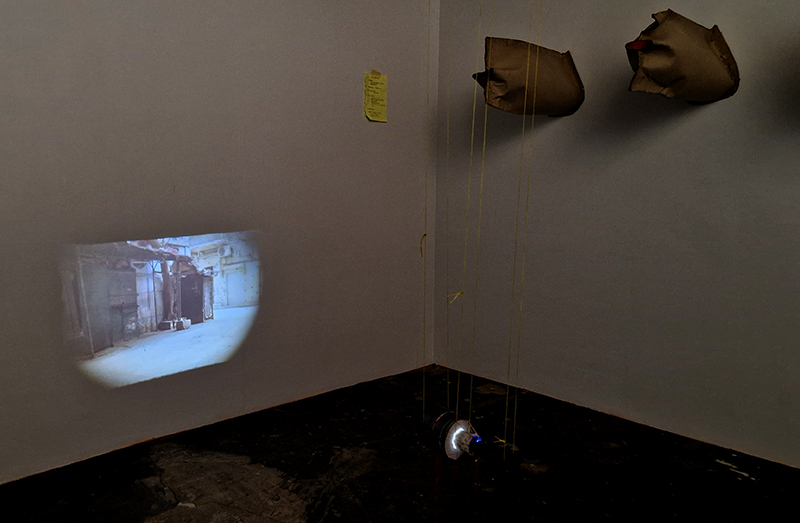
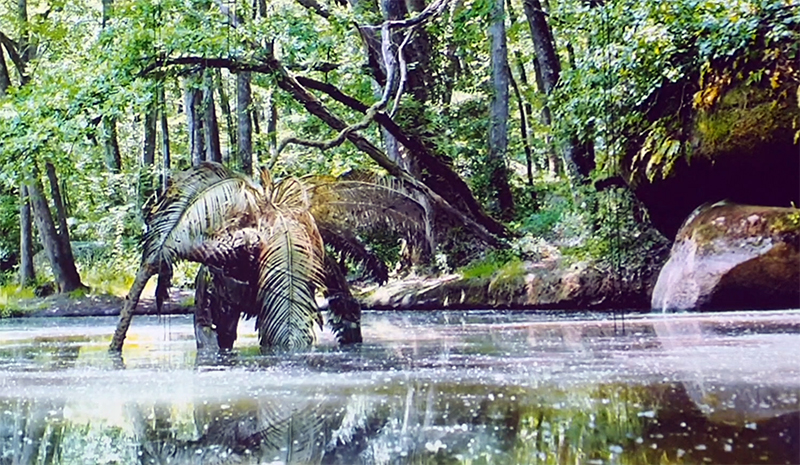
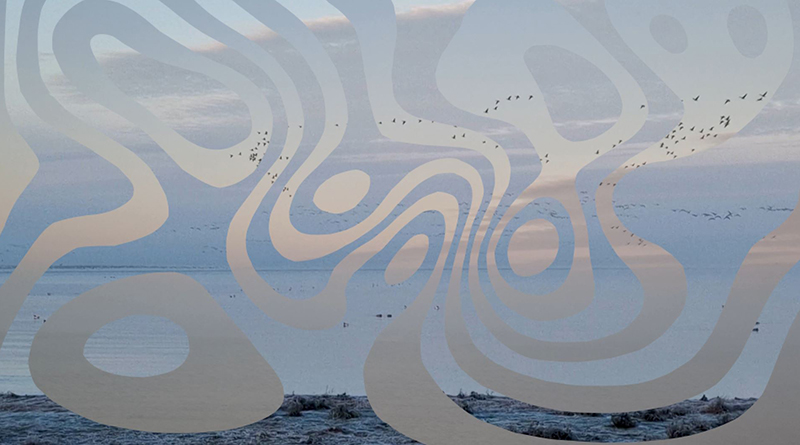
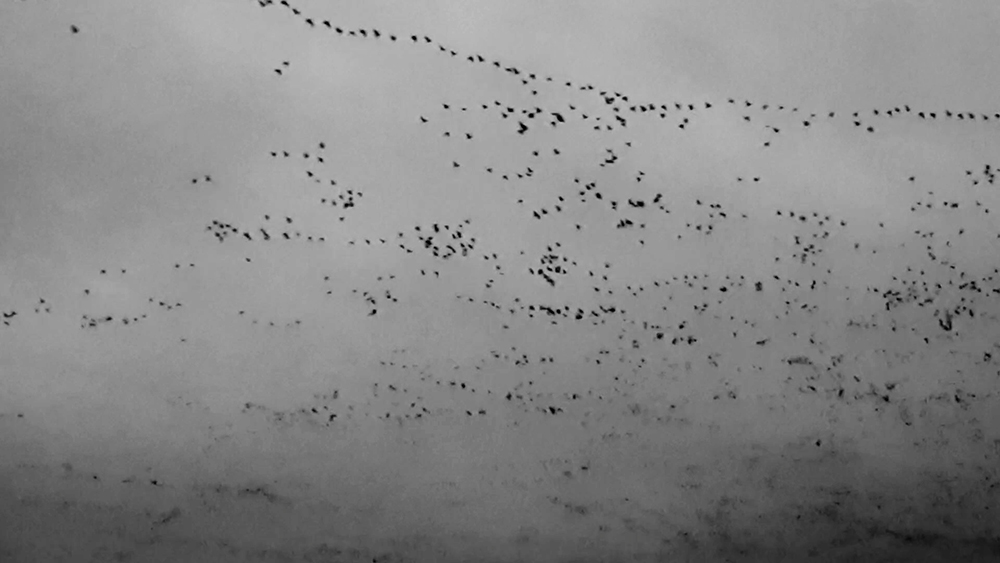
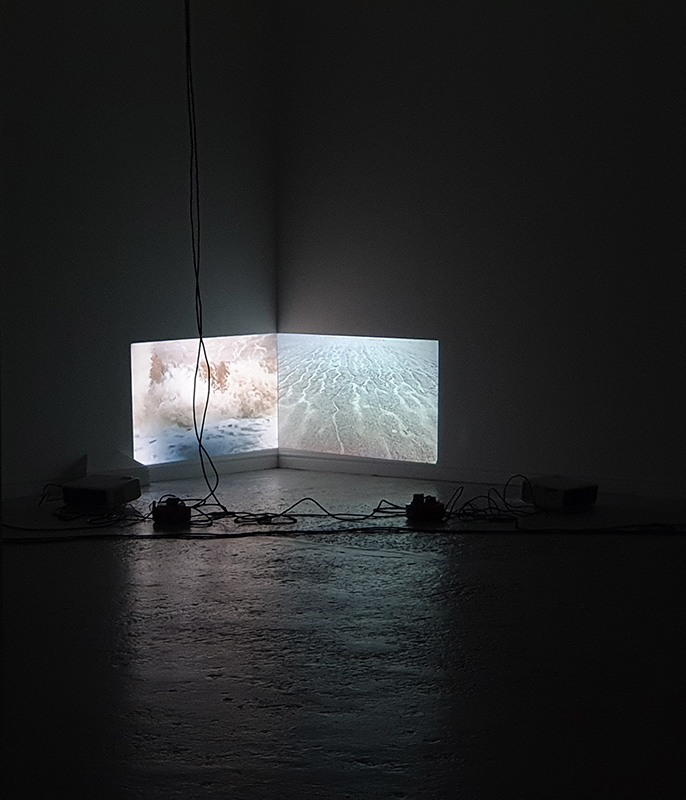
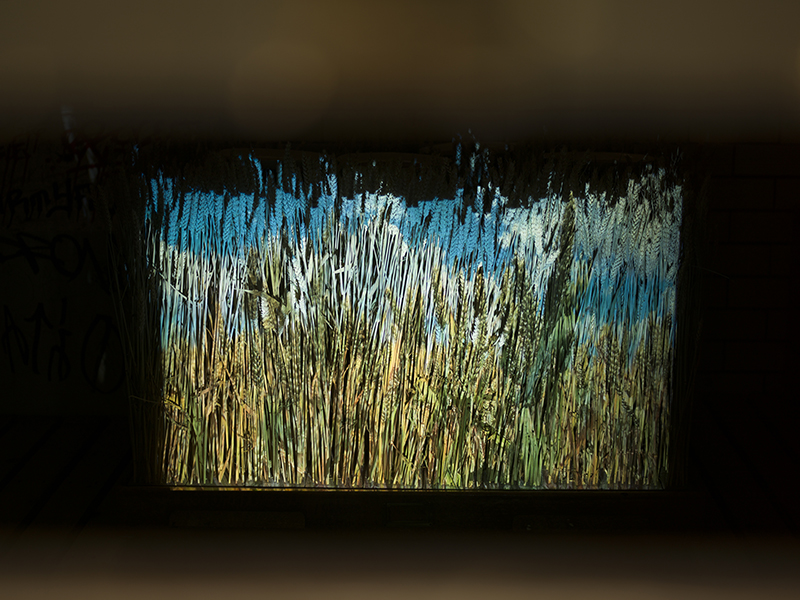
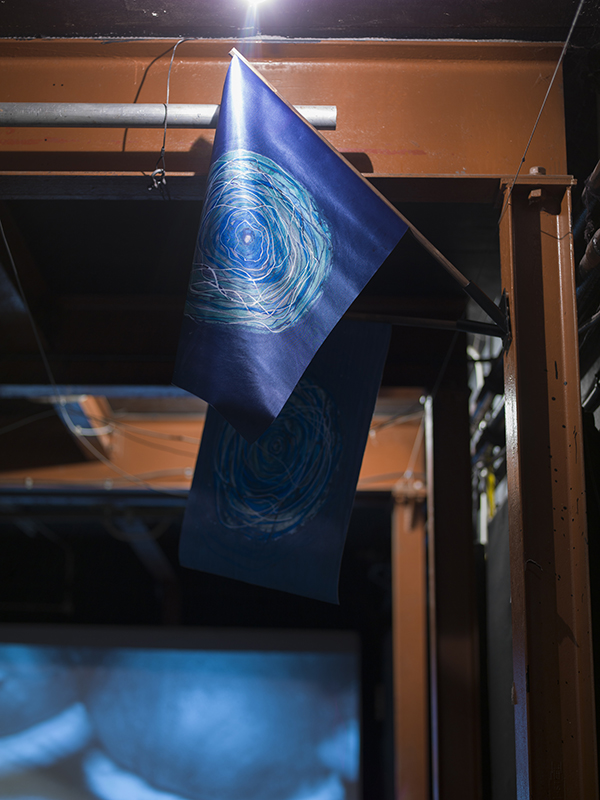
Wintering light two way video projection of migratory pink footed geese filmed at RSPB Snettisham on the North Norfolk coast.

Research has proven that birds and many other animals can use the earth’s magnetic field for navigation. There are two ways this happens. In birds there is a protein in the retina of the eye – (cryptochrome molecules) which trigger action potentials enabling them to visualise the magnetic field. In other animals and magnetotactic bacteria tiny crystals of magnetite respond to the field. This may also be true of humans as we do have these crystals in our brain cells.
Birds use three different compasses to navigate across the globe; the sun, the stars and the magnetic field.
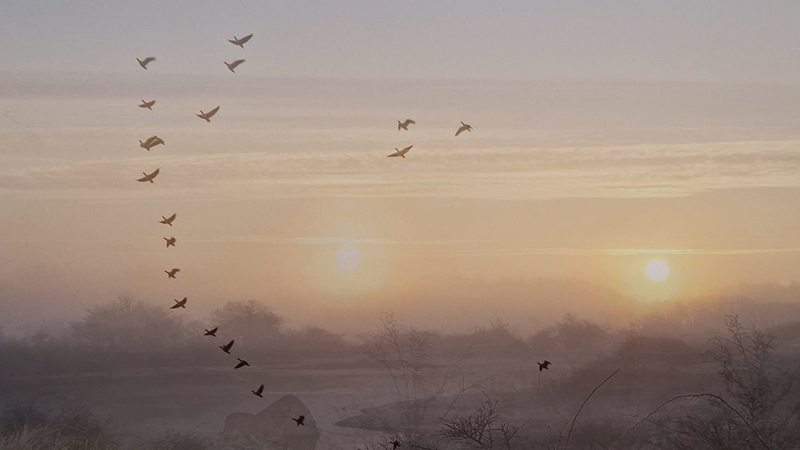

Birds are also able to detect rapid movement such as individual flashes or flickering of a fluorescent light which humans see as a continuous light. Hawks which pursue other birds through dense forests at high speeds, follow the movement of their prey while avoiding branches and other obstacles. To humans travelling at this speed, the fleeing prey, branches and obstacles would just be a blur.
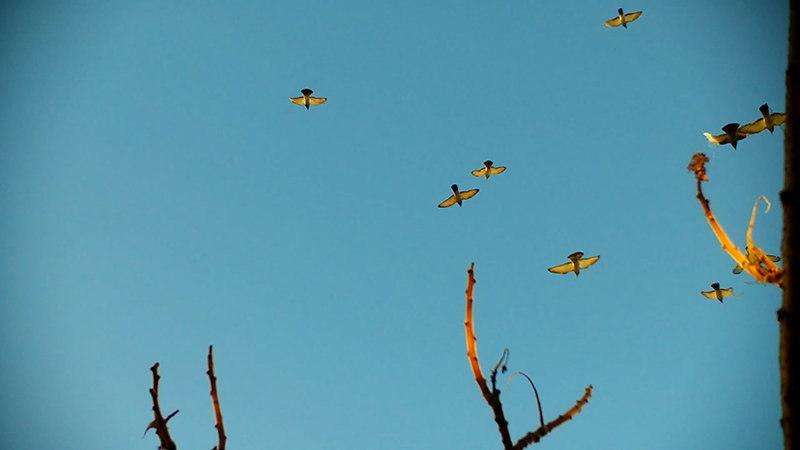
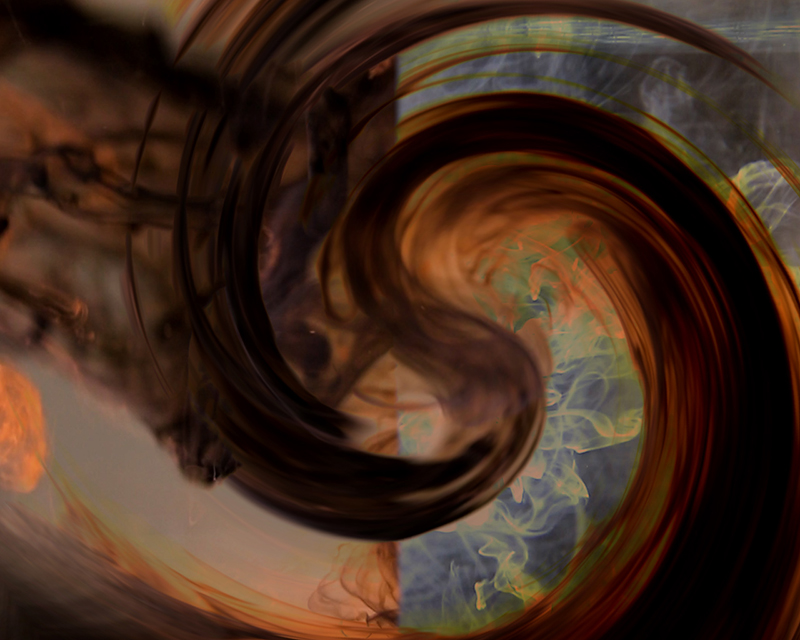
Degrees of Variation considers what it might be like to have the sensory powers of a bird where a protein in the eye is excited by polarised light making it possible to see the magnetic field and follow a visual navigatory cue in an accelerated world. The video imagines flight over water and through woods while being guided by the force of a magnetic field.
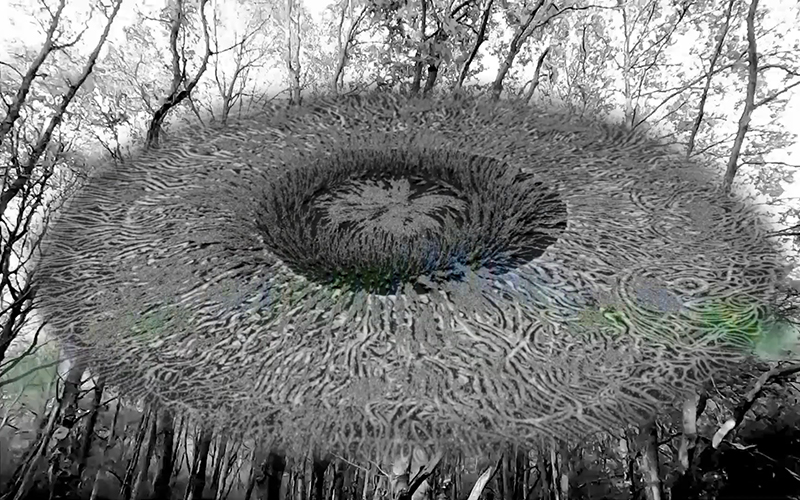




Calvino’s story The Stone Sky is wonderfully descriptive of the volatile geological structure of the Earth. This fluidity is what makes life on Earth possible. Only planets with fluid cores have magnetic fields. The geological interior generates a field that reaches into outer space offering a protective shield.
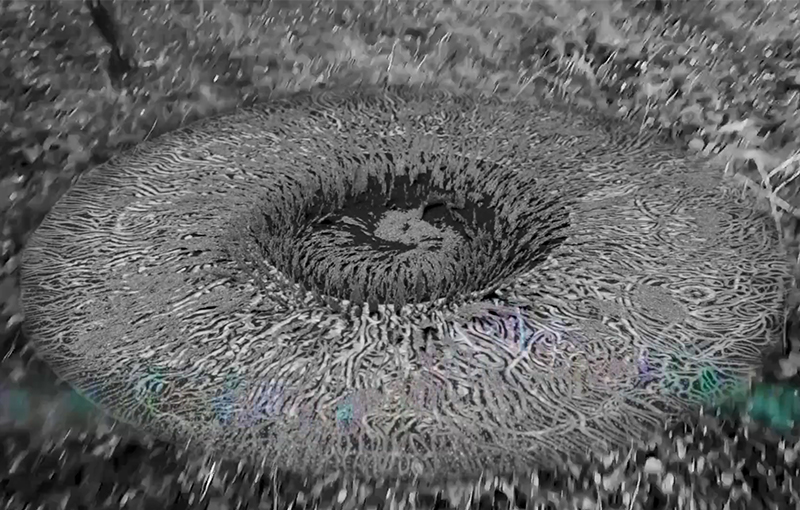
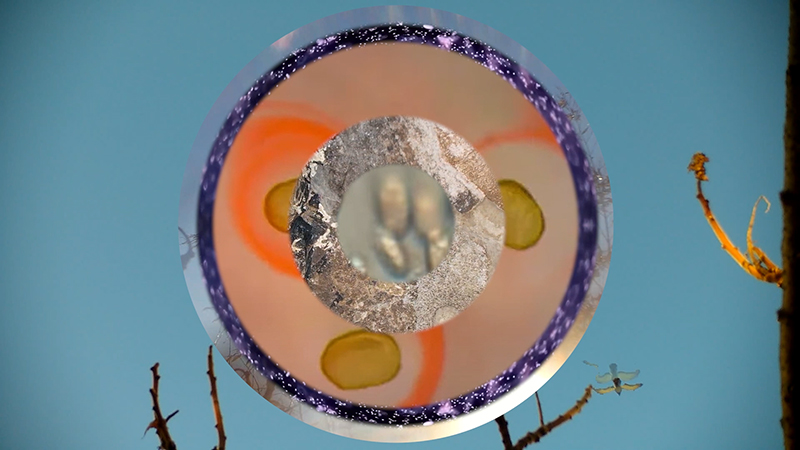
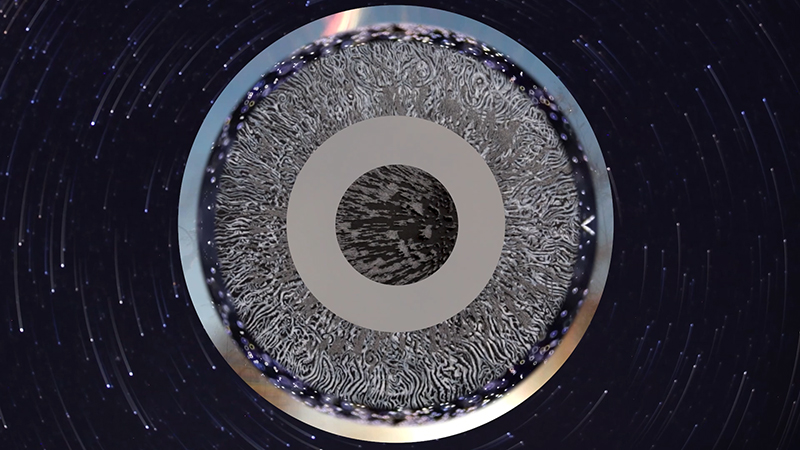
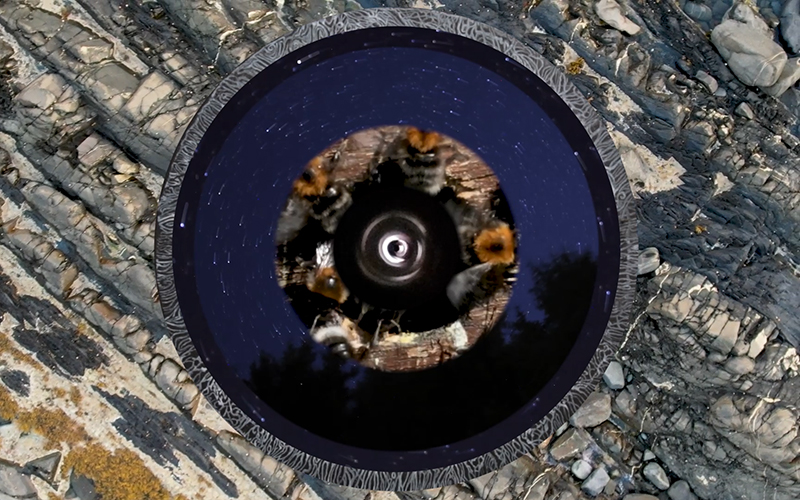
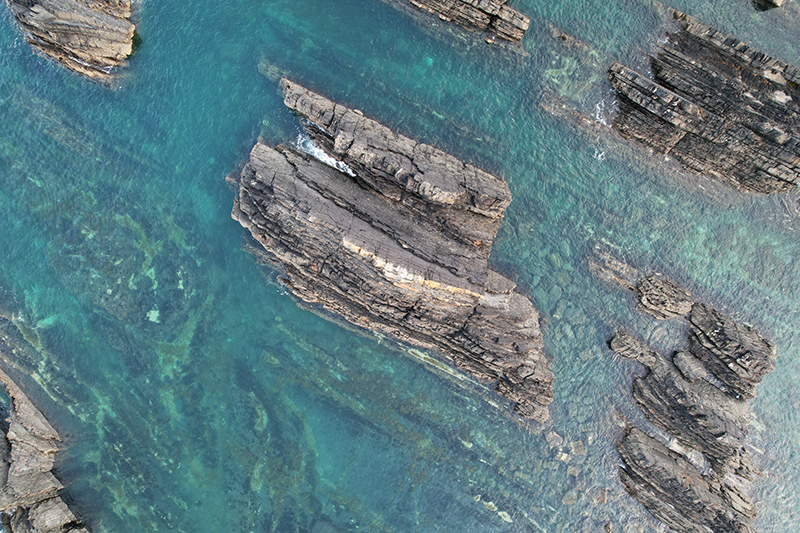
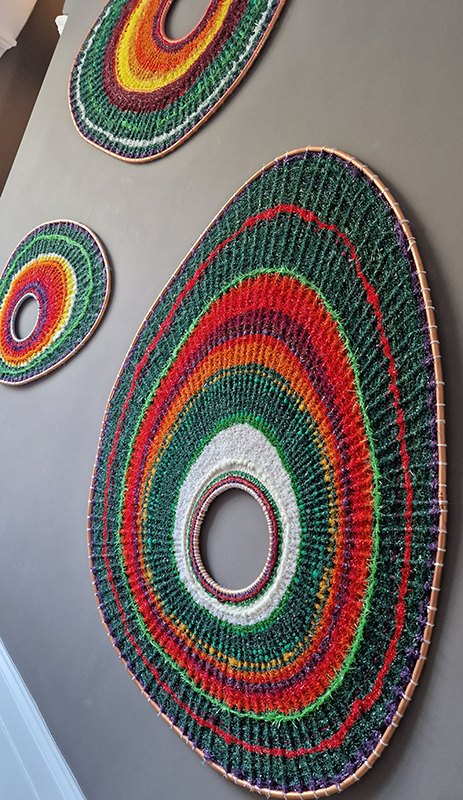
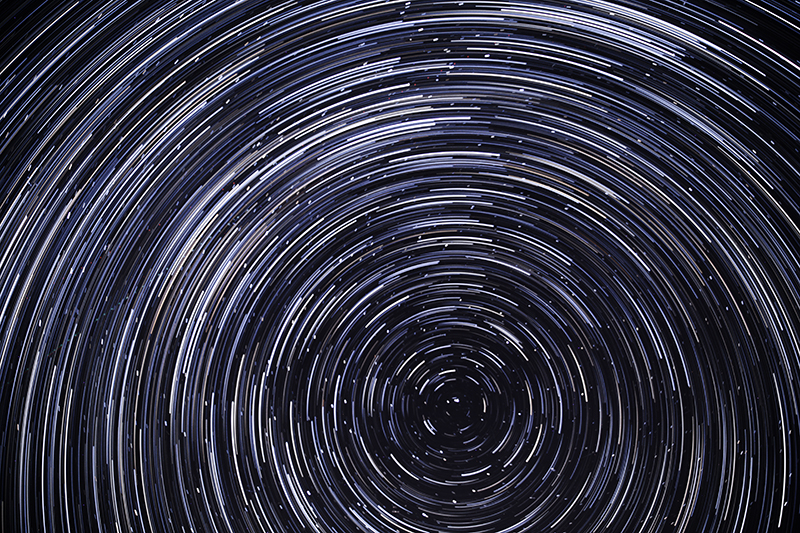
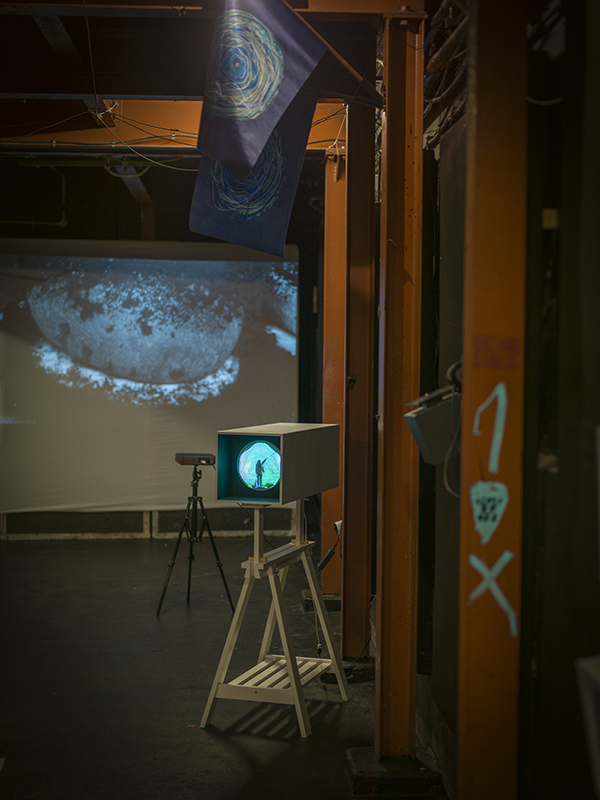
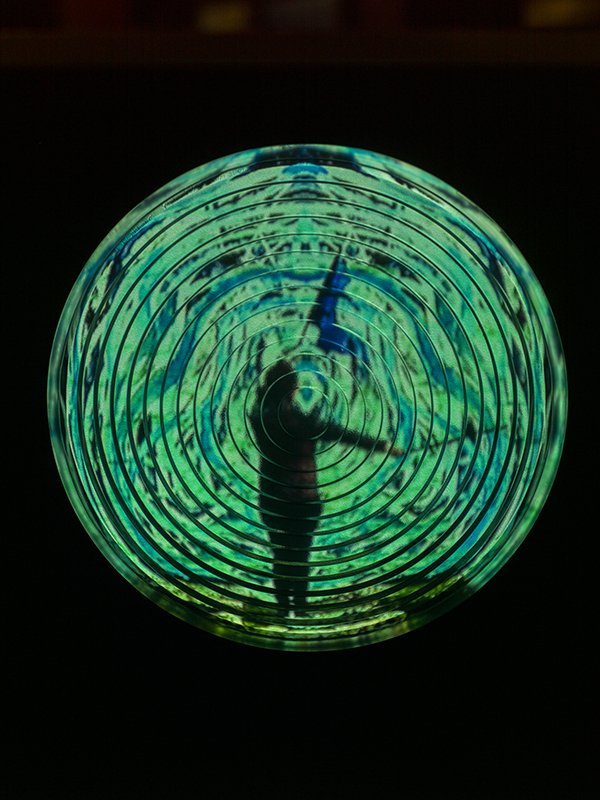
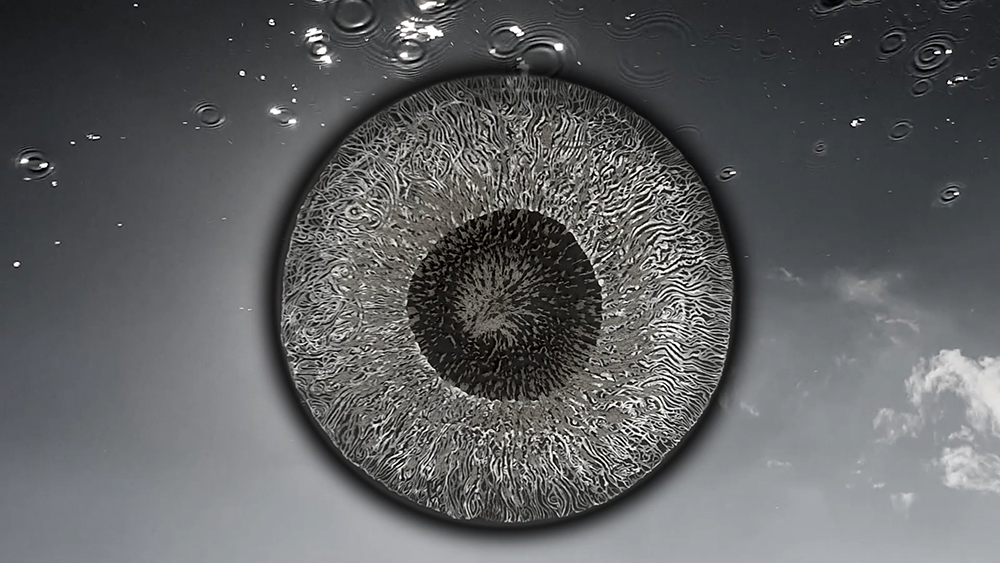
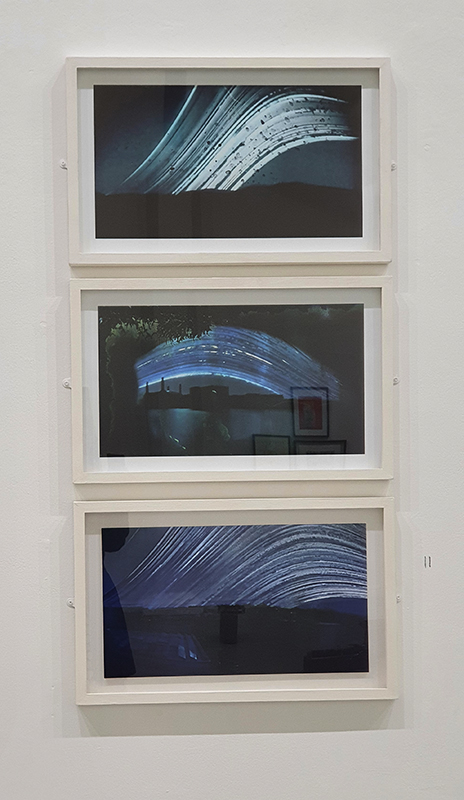
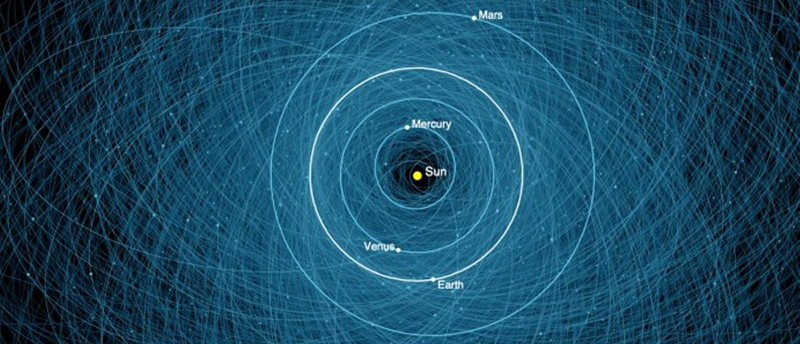
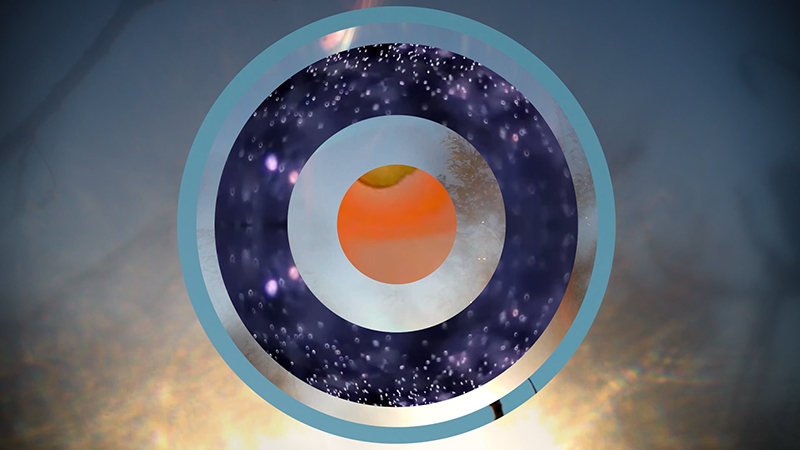
internal skies : external spheres video sequences within concentric circles mimic the geological structure of the Earth to explore the relationship between Earth’s magnetic field and various methods of navigation including via magnetoreception and celestial observation. Sequences include star trails around Polaris (the current north star), birds and bees that use the magnetic field for navigation, magnetotactic bacteria, magnetised iron filings, aerial views of the coastline around Hartland and early morning polarised light which excites the cryptochrome protein in a birds eye.


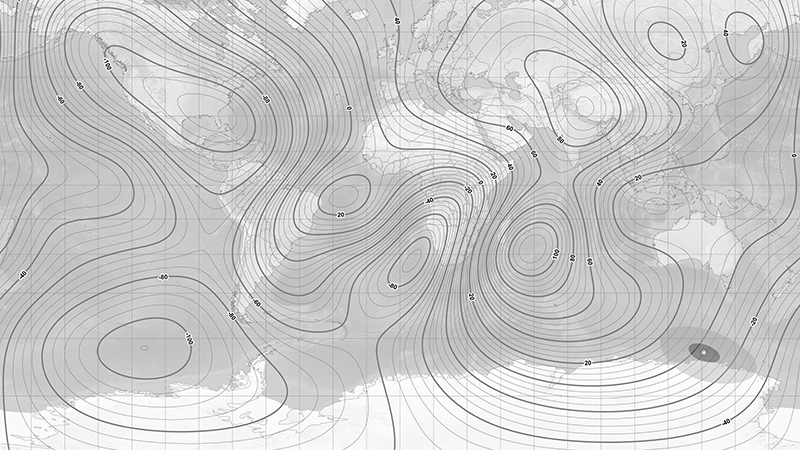
The Earth’s geomagnetic field is created by a combination of three separate fields and timescales. The main field is generated in the earth’s molten iron core. Observing the field gives clues to the planet’s deep interior which is inaccessible to direct observations. Changes are measured in the annual drifting of magnetic poles. Secondly electrical currents caused by solar weather and cosmic rays bouncing off the Earth’s main field charge the surrounding ionosphere causing fluctuations in the field. This field changes by the micro second as we orbit the sun. The Earth’s magnetic field also acts as a shield against most potentially harmful charged particles from outer space. Finally the residual magnetisation of the geology of the rocky mantle and crust, measured in deep geological time also offers clues to the geological history of Earth.

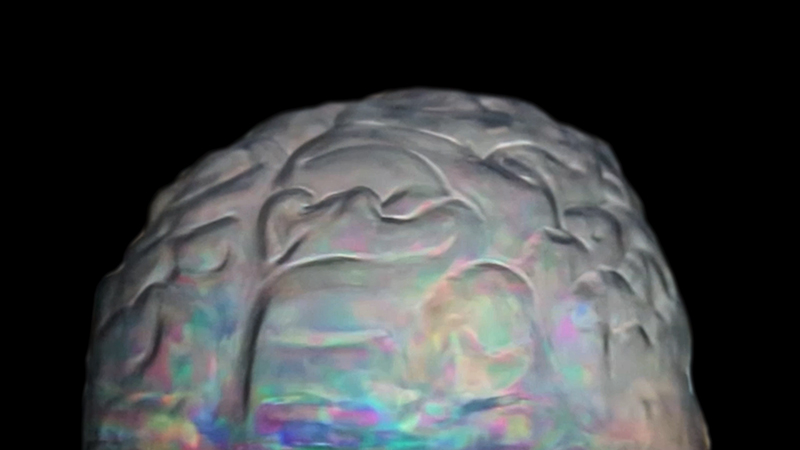
The understanding of the world surrounding us forms in the darkness of our skulls.
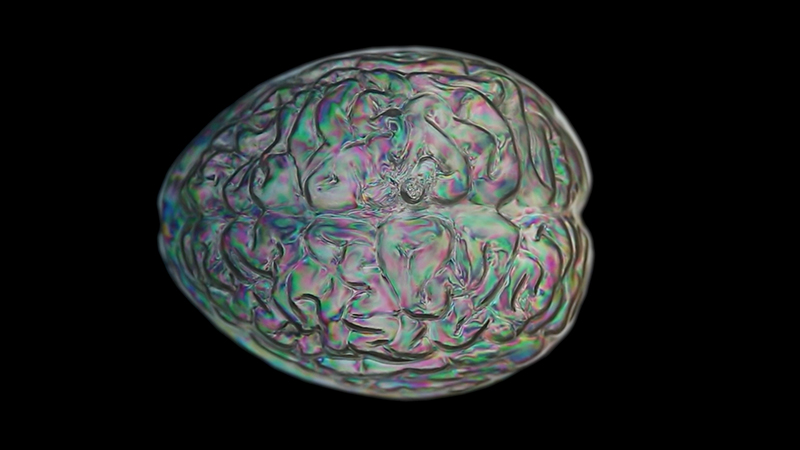

interference – a panel of 12 small video screens inside The Absolute Hut (of action potential), showing images of the human brain filmed by using polarizing filters to create pulsating birefringence colours, relate to the narrative pinned to the outside of the hut.
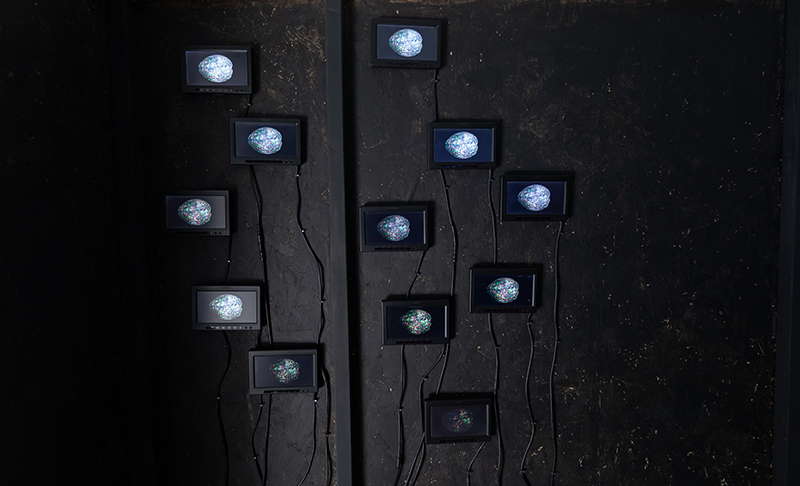

The narrative is a mix of fact and fiction based on a real experiment carried out at Caltech where scientists found Alpha waves in the human brain do respond to Earth’s magnetic field and other research suggesting that it could be possible for the magnetic field in one animal’s brain to transmit information to another animal’s brain by triggering action potentials creating the same thoughts and emotions.

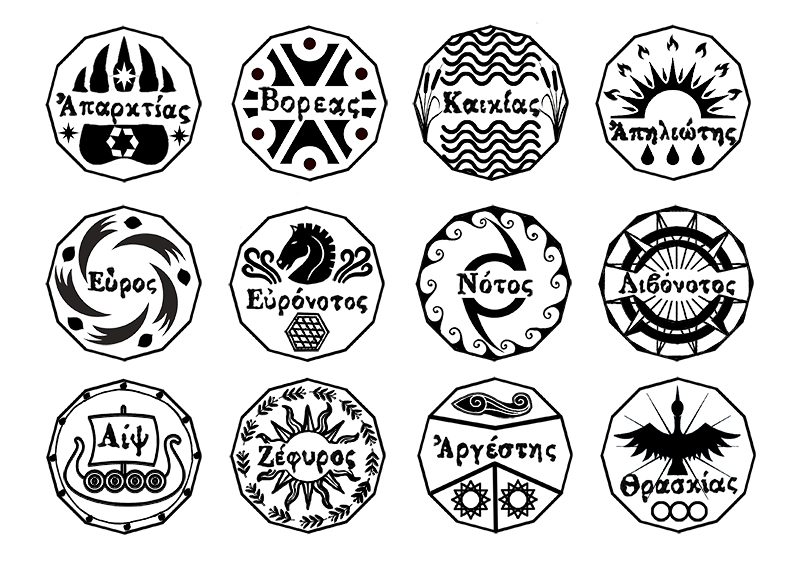
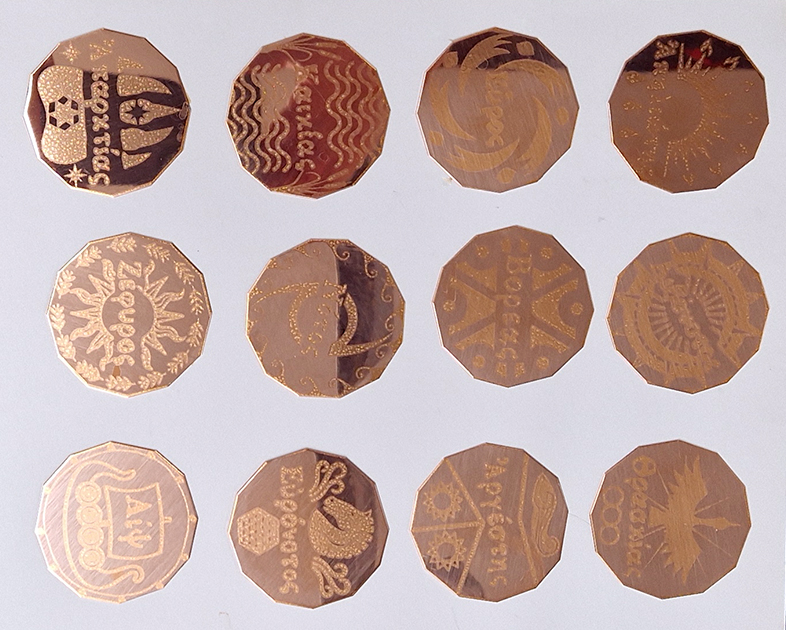
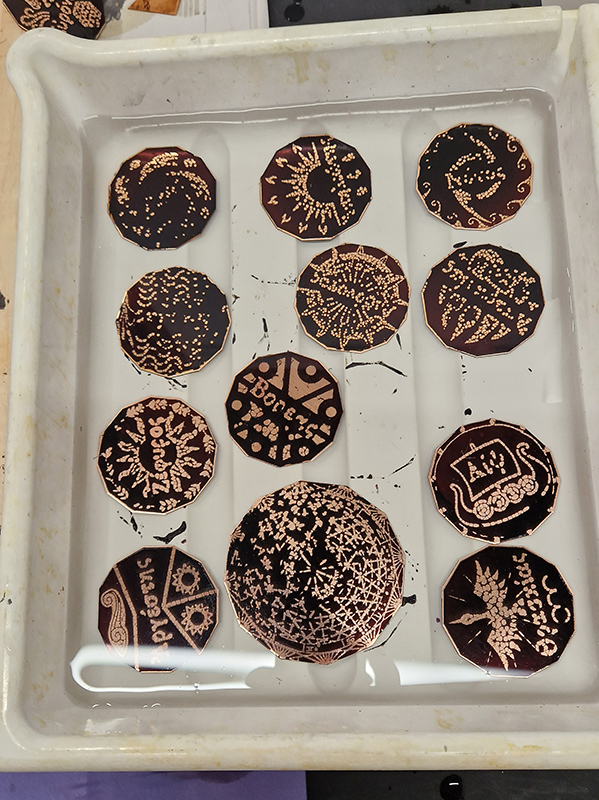
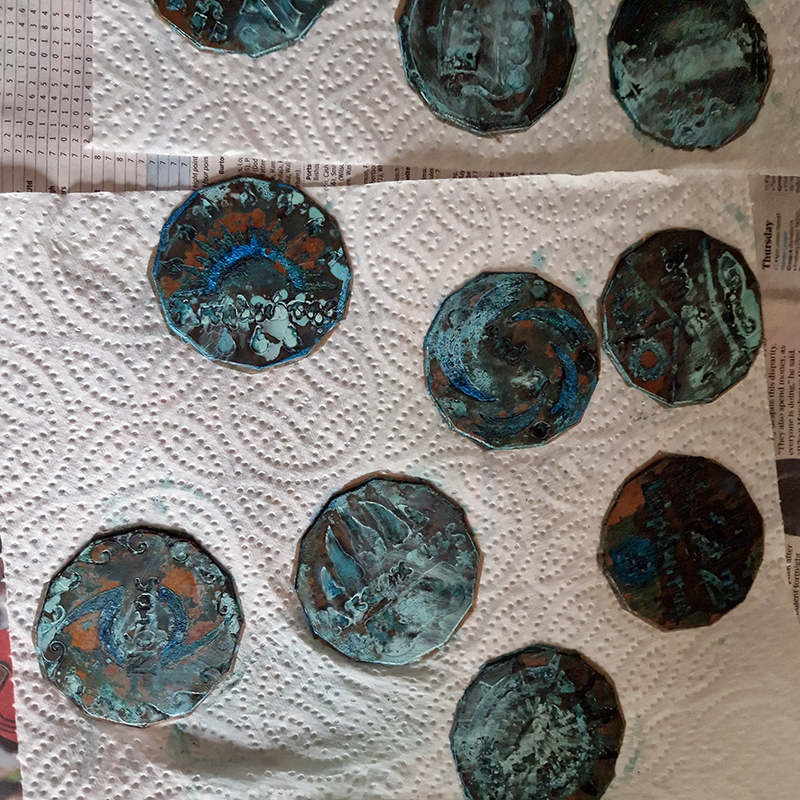
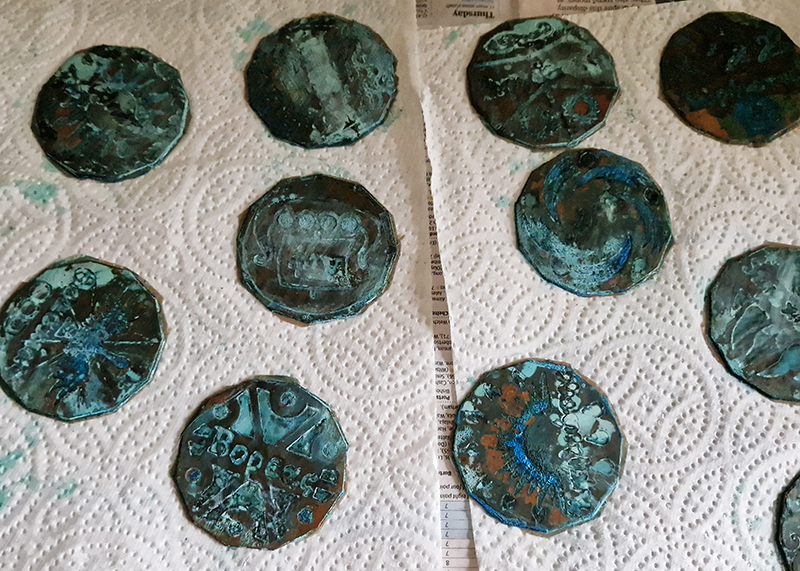
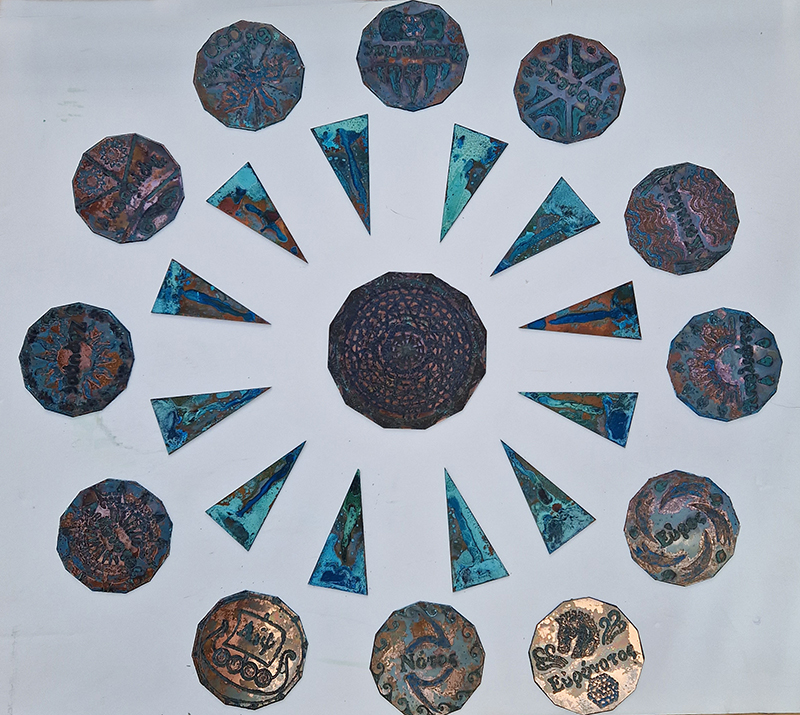
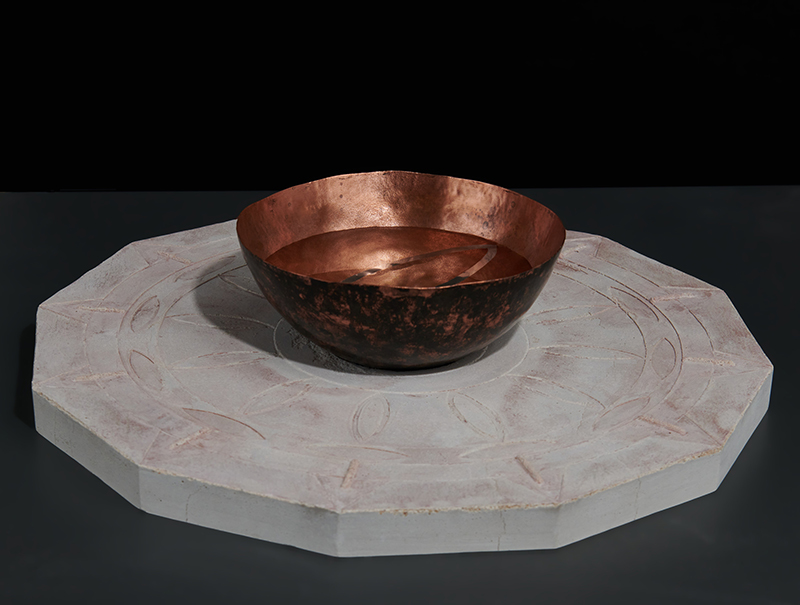
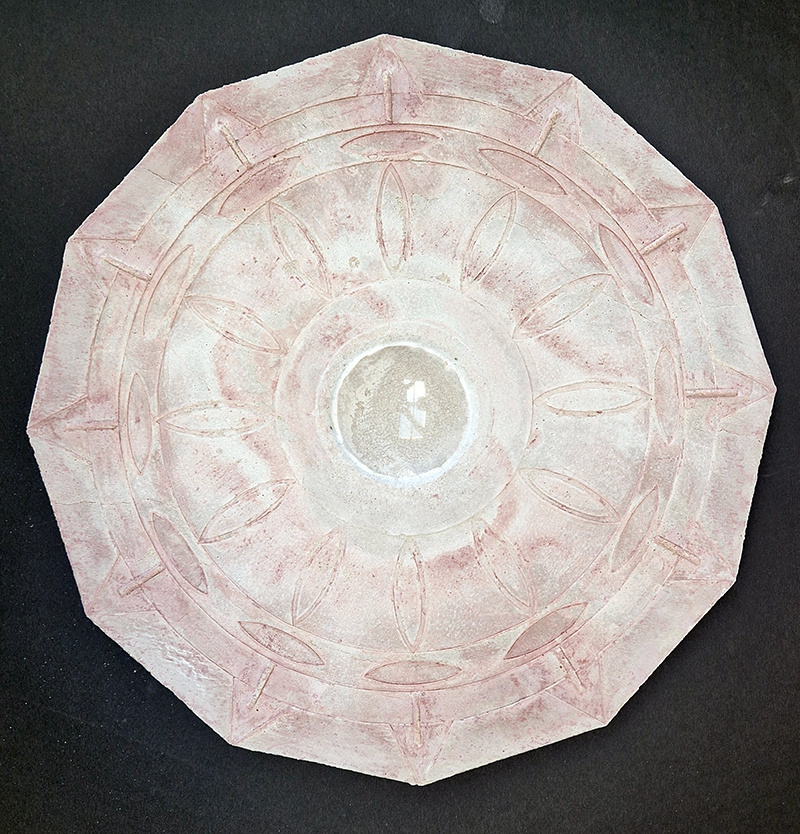
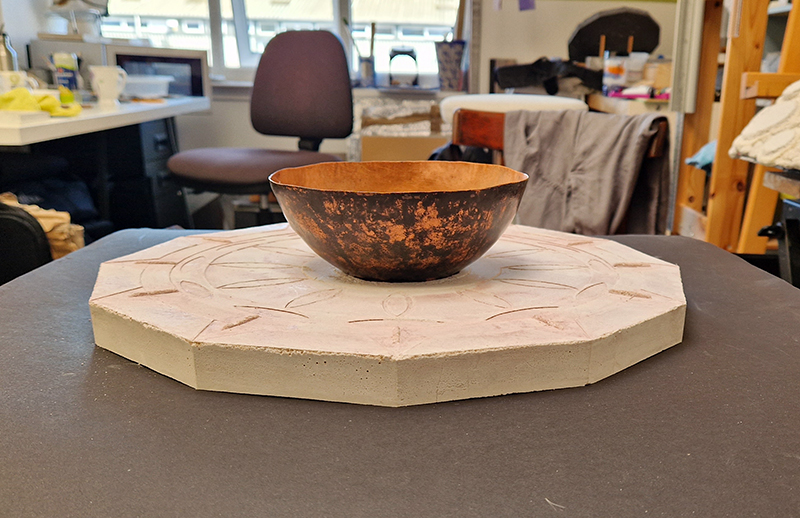
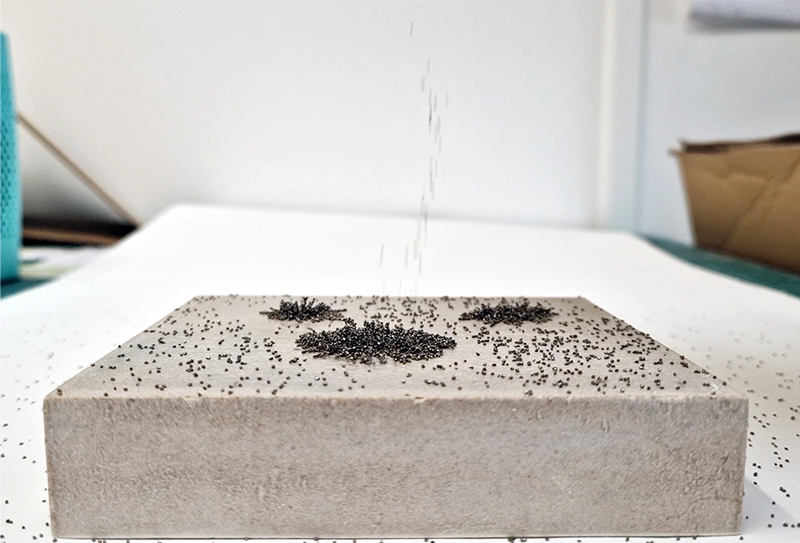
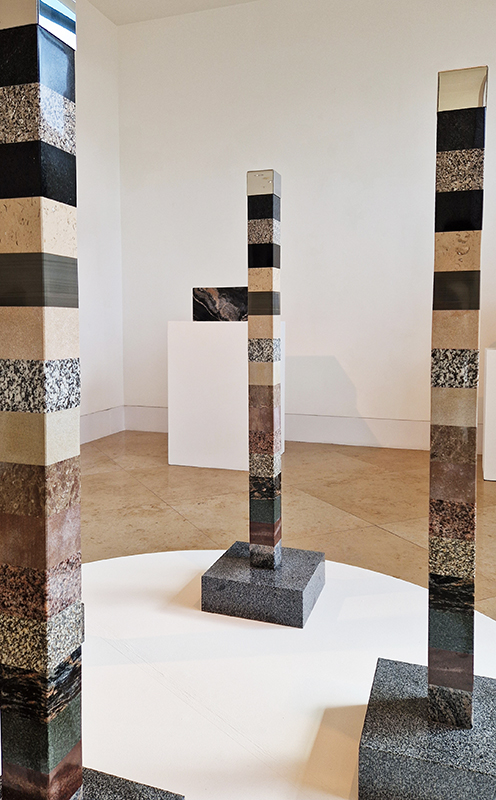
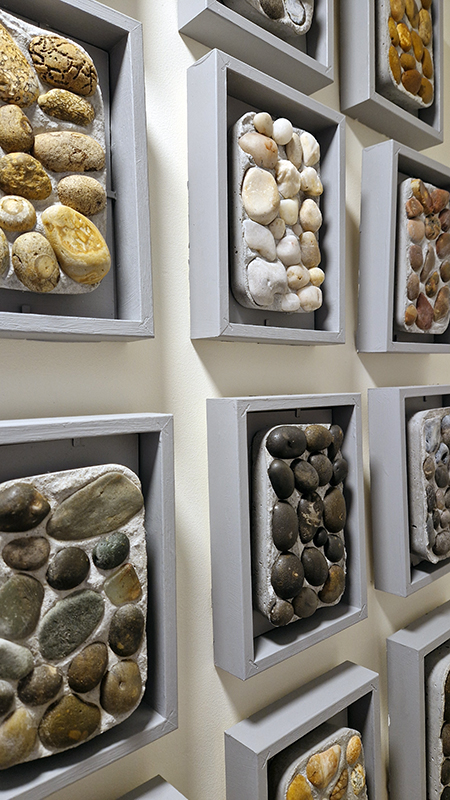
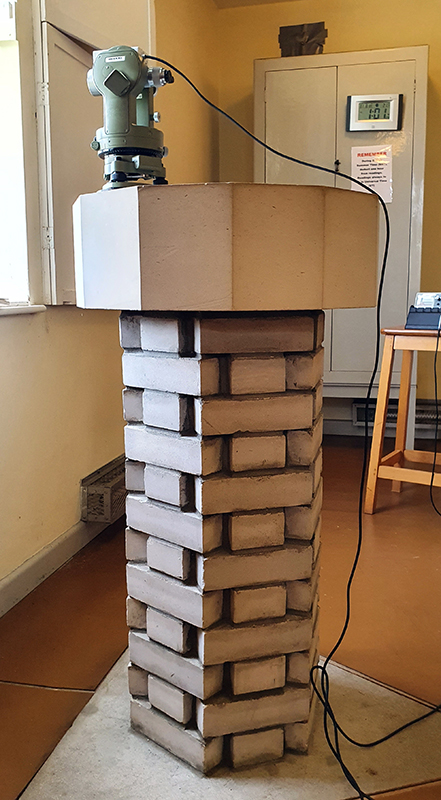
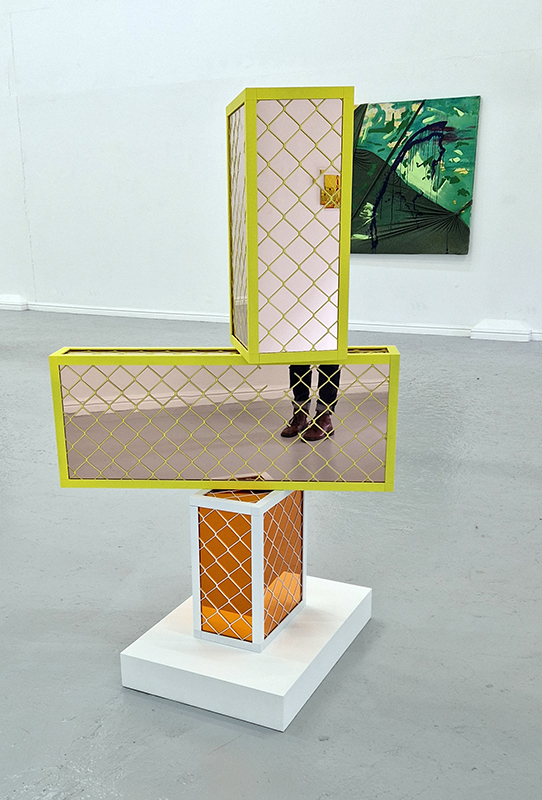
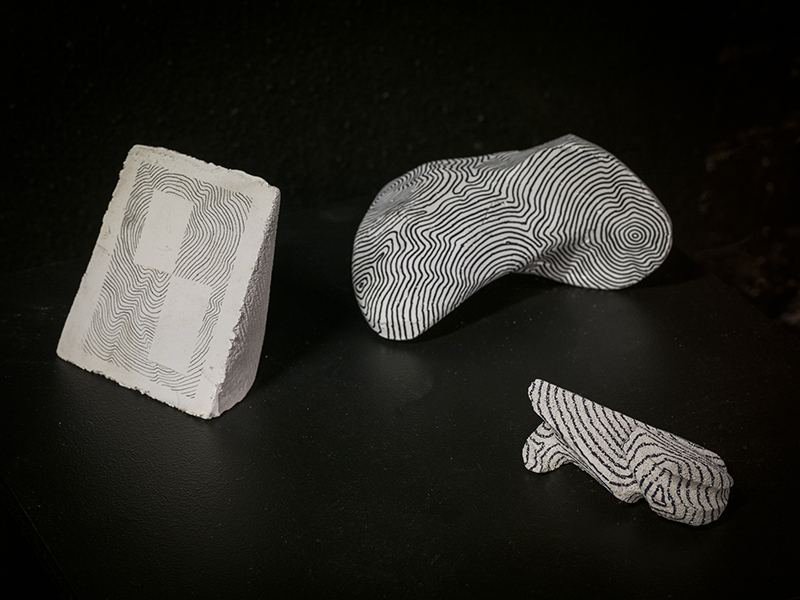
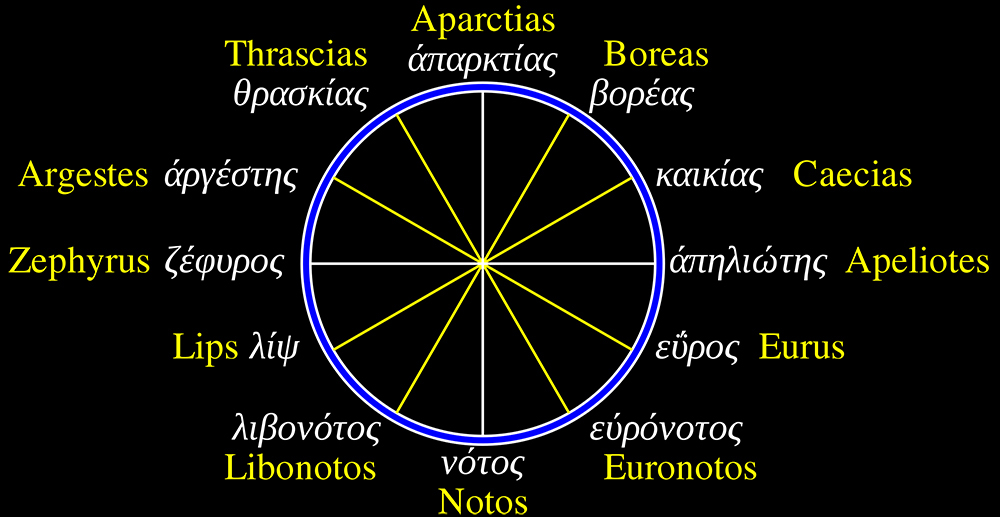
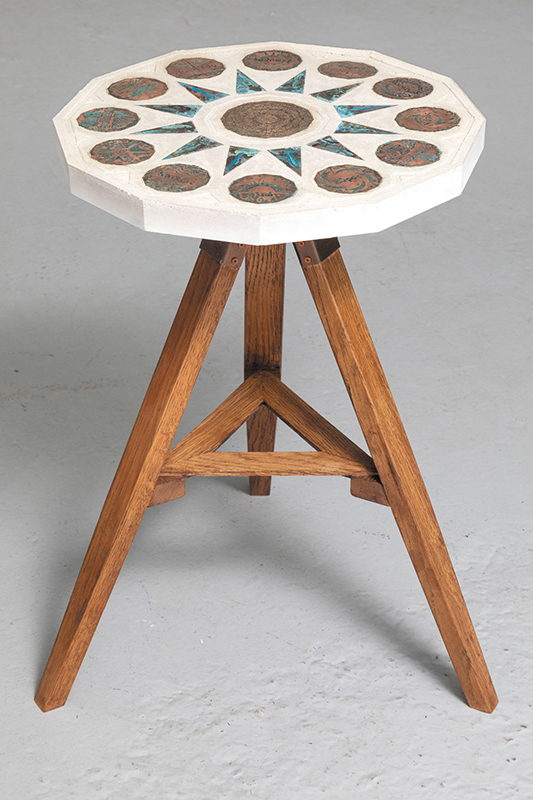
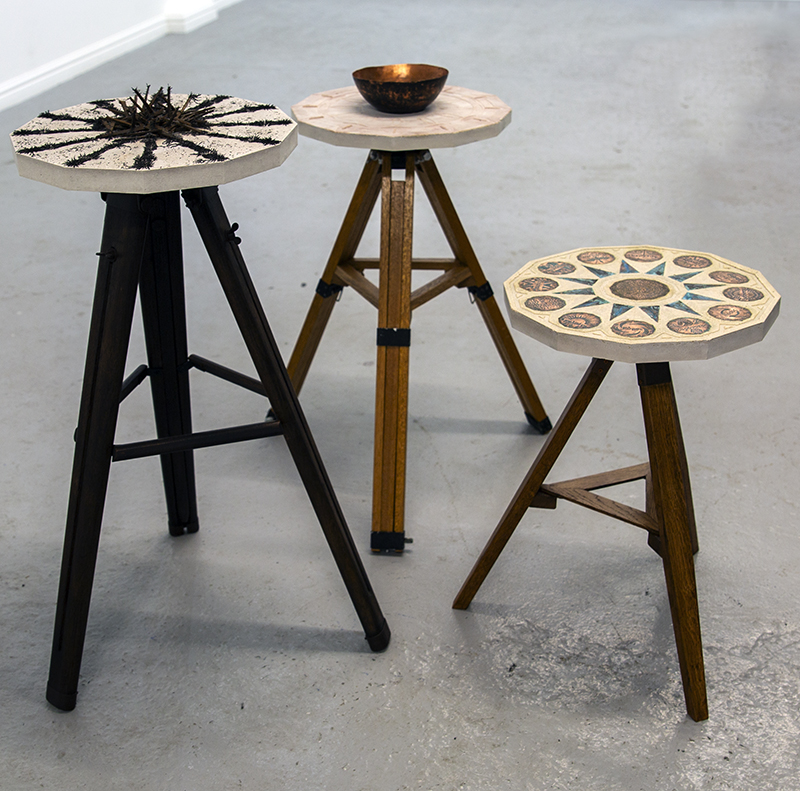
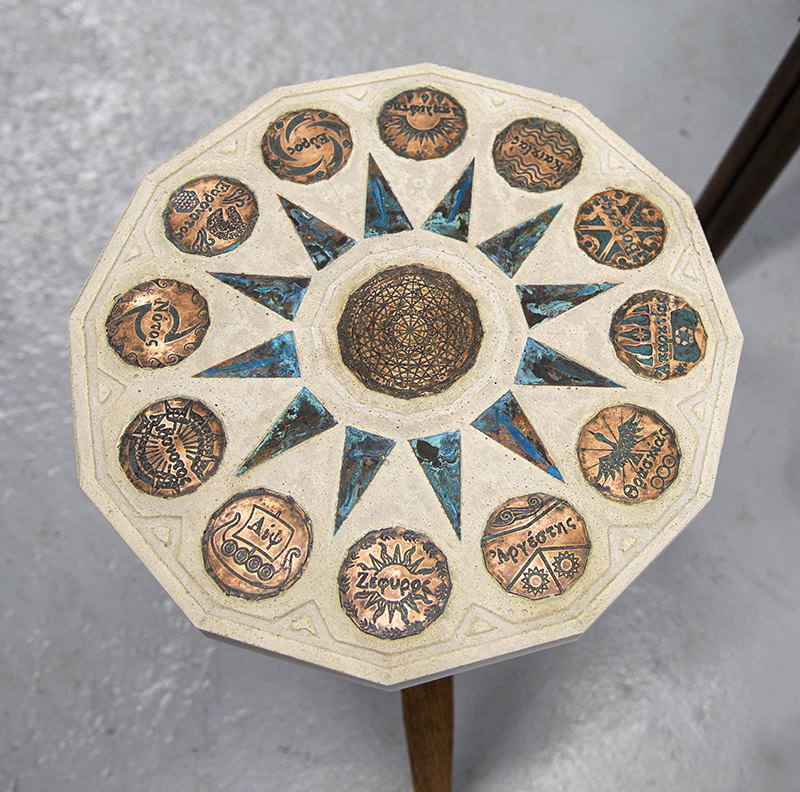
Instruments of the Anemoi are a set of dodecagon tablets cast in Snowcrete, a non-magnetic cement, as used in a magnetic observatory. Suggestive of the pedestals that support various instruments used in monitoring the Earths’ magnetic field they also respond to an ancient anemoscope “table of the winds” carved in marble around eighteen hundred years ago and inscribed with the Greek and Latin names of classical winds on each of its twelve sides. Envisaged here as speculative objects, instruments and schematics wrought by the wind gods, the first emissaries of navigation and orientation.

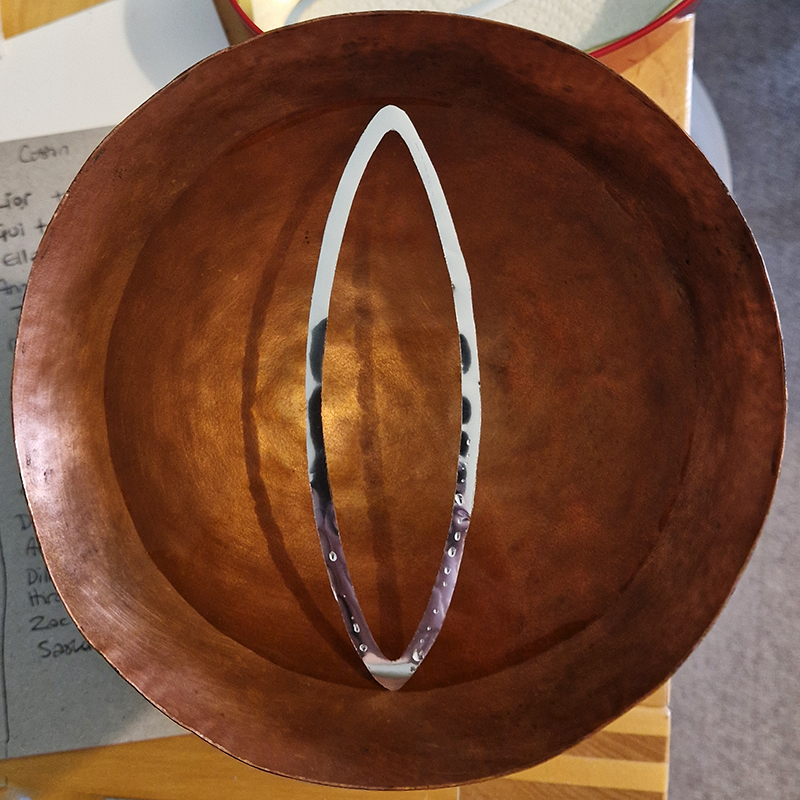
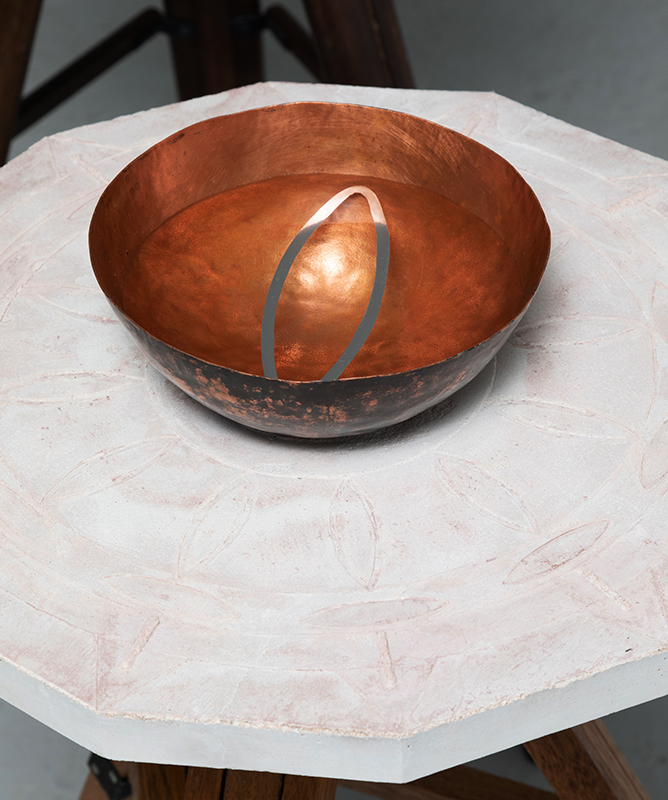
One tablet holds a copper bowl with a ‘silver fish’ floating in water. The shape of the ‘silver fish’ is based on the oval shaped compass needle (illustrated in Breve Compendio de la Sphera de la arte Navegar by Martin Cortes 1551) and refers back to wafer thin fish shaped iron leaves used by 11th century Chinese geomancers.

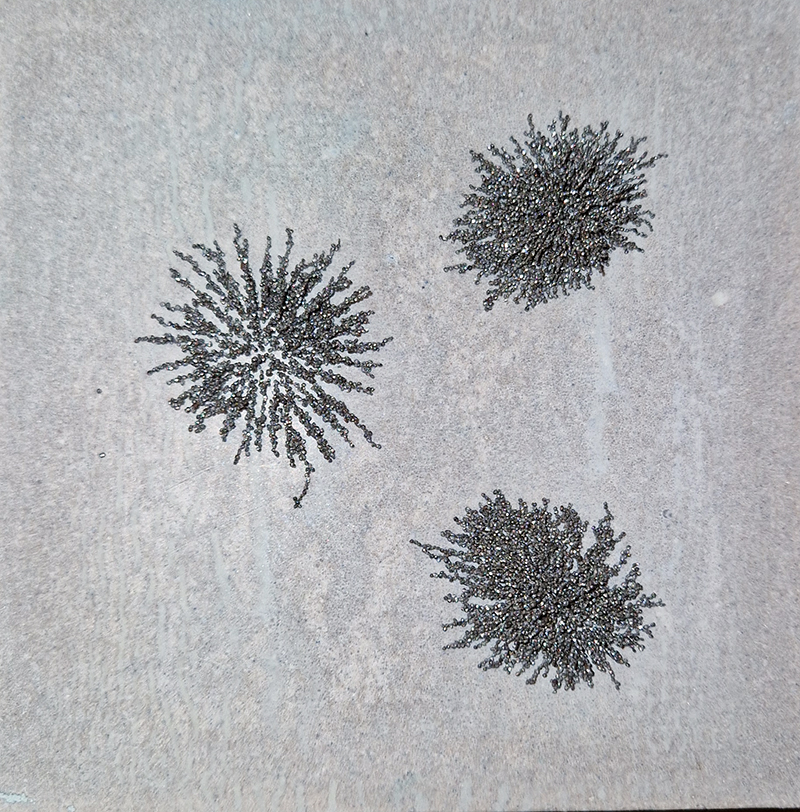
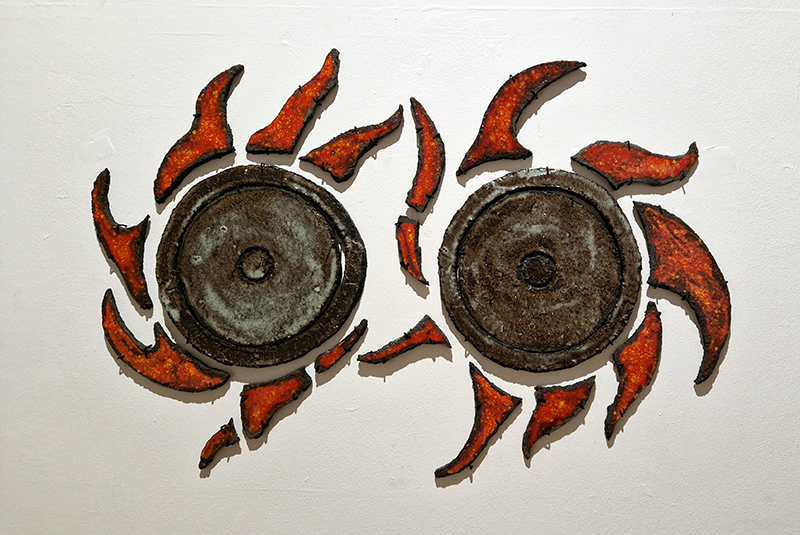
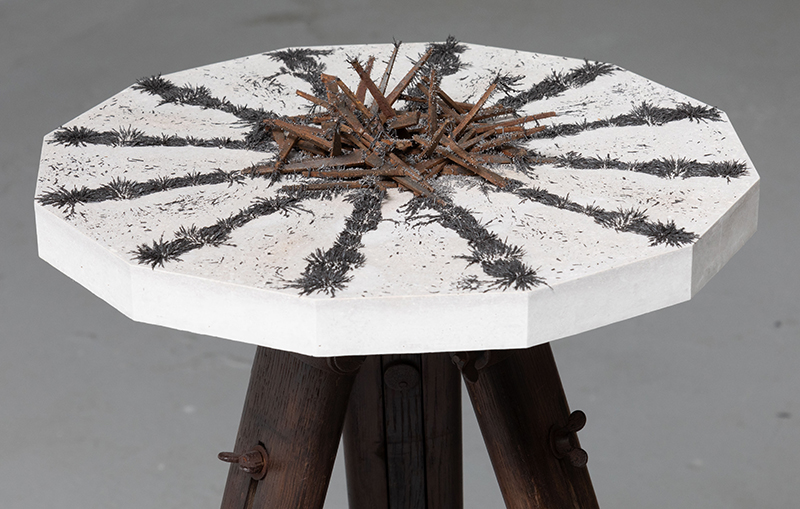
Nails and iron filings on the second tablet reveal an embedded magnetic field recalling a legend that the discovery of the lodestone was made by a Greek shepherd who noticed the nails in his boots were attracted to the rock (magnetite) beneath his feet.

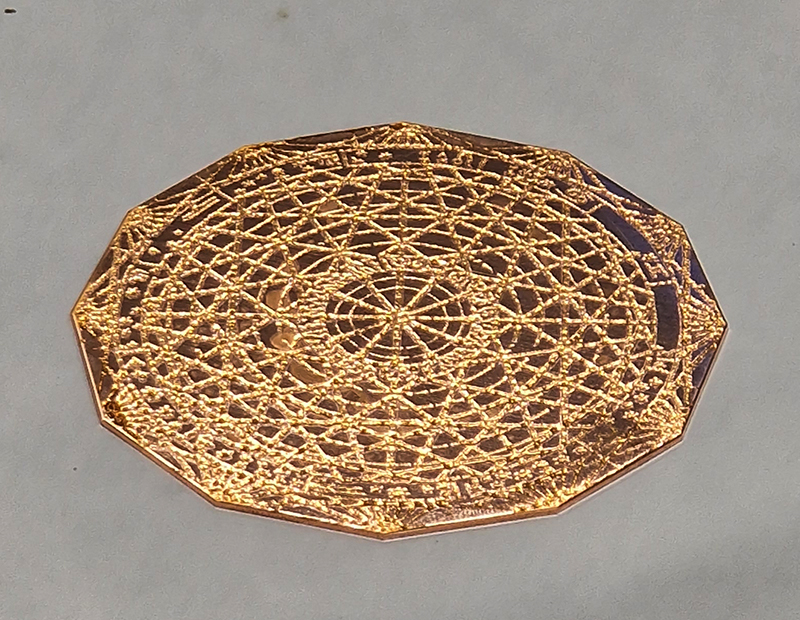
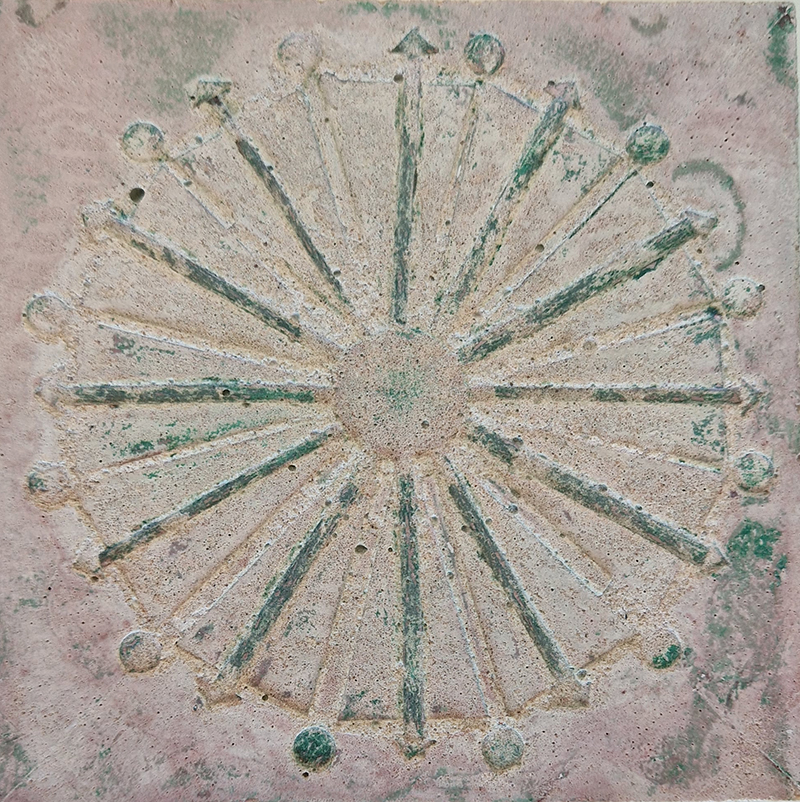
The third tablet is embedded with copper etched with images and names based on associations and attributes of the twelve Greek wind gods set in a traditional compass rose.

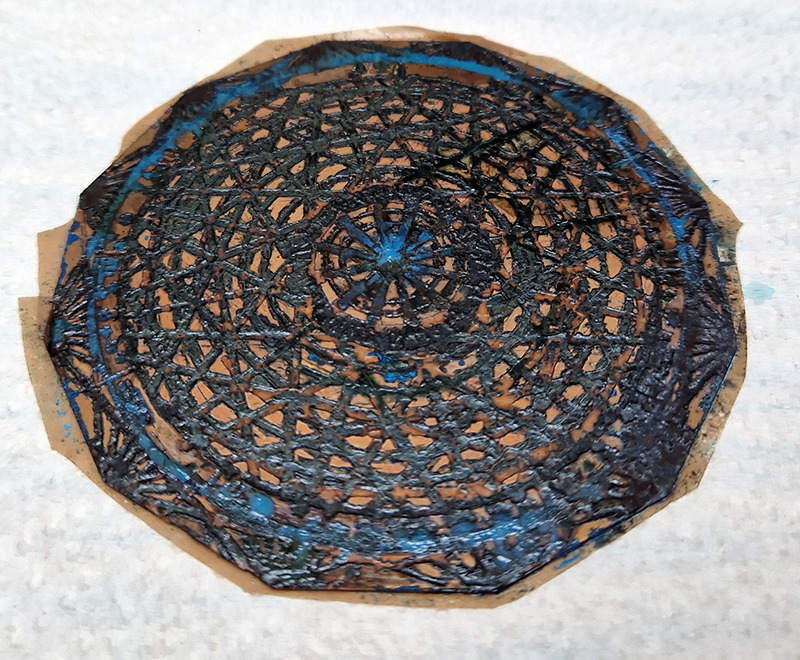
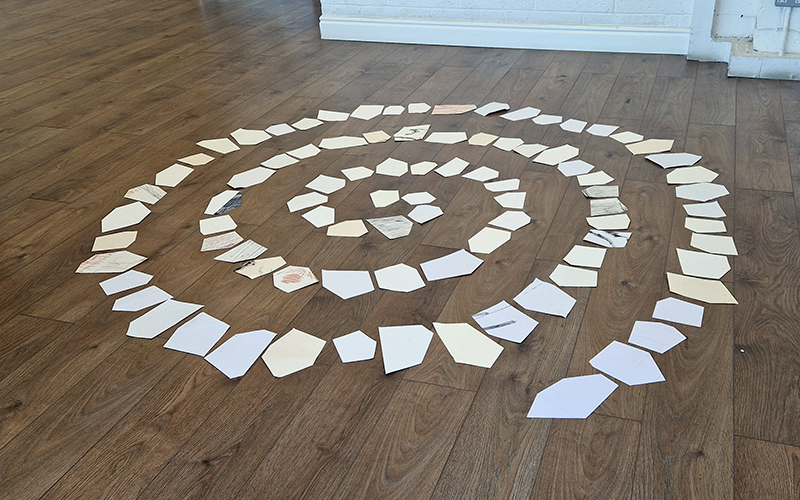
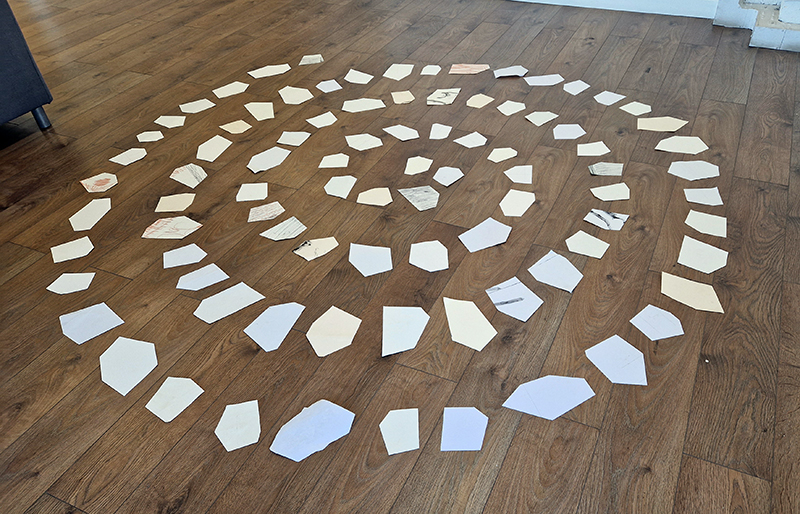
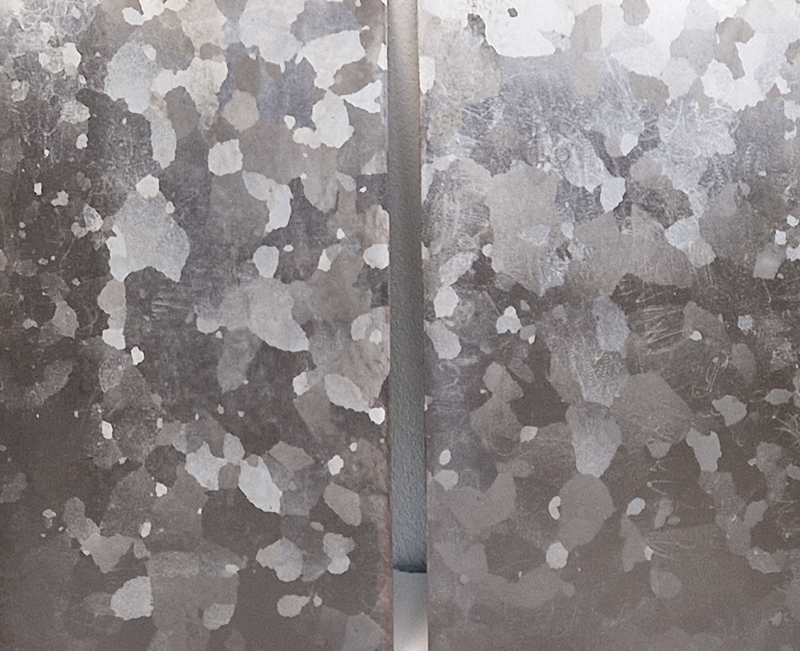
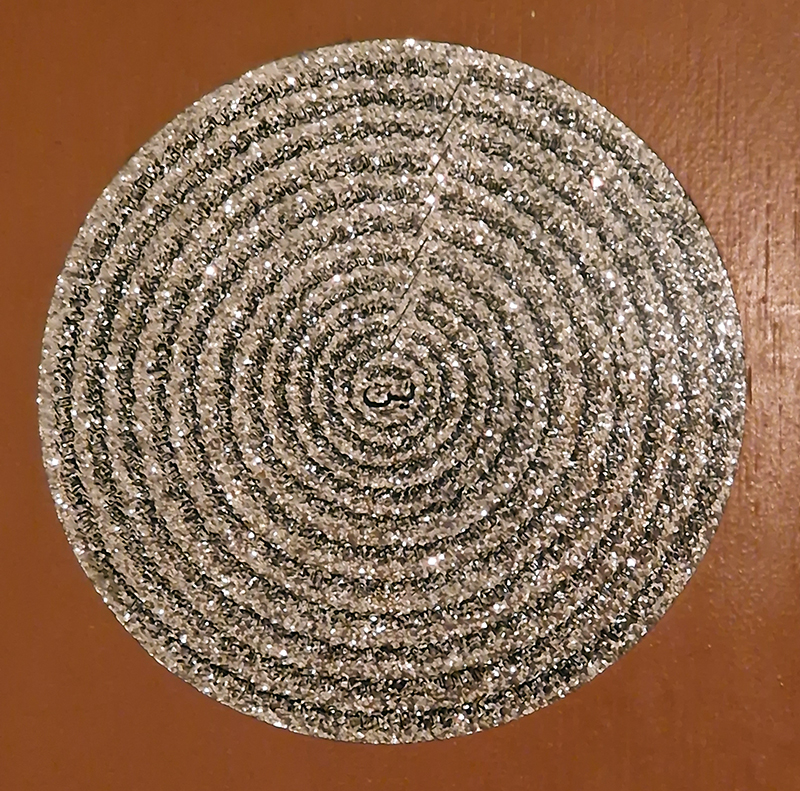
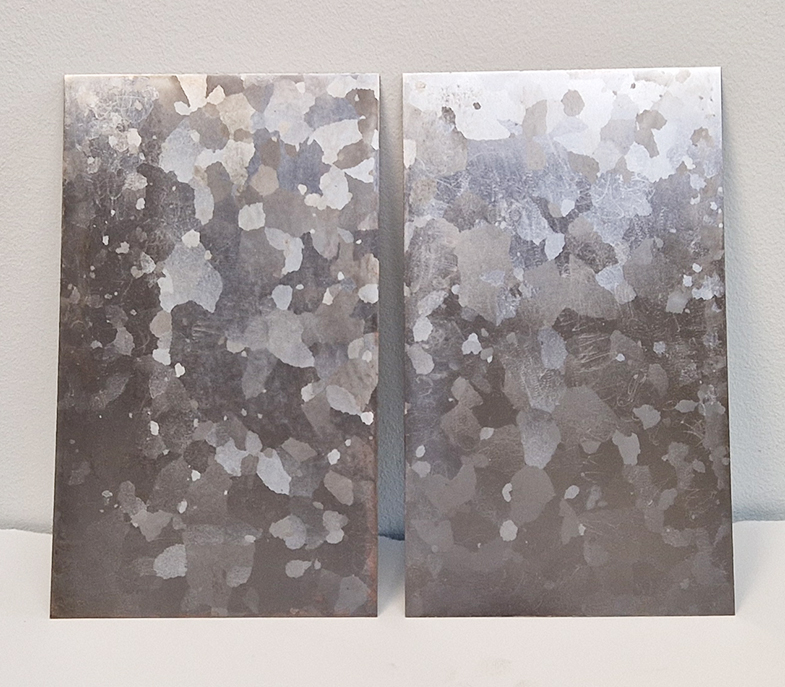
Domain of the Devil Valley Master uses industrial directional magnetic steel, sanded and etched to reveal the Goss texture of rolled iron silicon alloy crystals. The jigsaw pattern of magnetic domains give this material exceptional magnetic properties. The simple evocation of a spiral described in geologically informed polygons draws upon many references, from the shape of our own Milky Way Galaxy sculpted by vast cosmological magnetic fields and the spiralling molten dynamo generating Earth’s magnetic field, to the inner pathway of spiritual growth and the route to the symbolic omphalos (navel) at the centre of the world where the sky entrance and the underworld meet. The title of this work originates from an ancient Chinese manual on the skills of persuasion, The Book of the Devil Valley Master, containing the first known mention of a compass, known at the time as a south-pointer.

The exhibition closed with an afternoon event launching our publication which includes the essay Dark Nights and Signs of Unseen Things by Anjana Janardhan. There was also a live cloud chamber demonstration of mesmerising cosmic ray trails, artist tours and informal readings.




Publication available – DM via blog comments box for more details or visit Julie’s shop