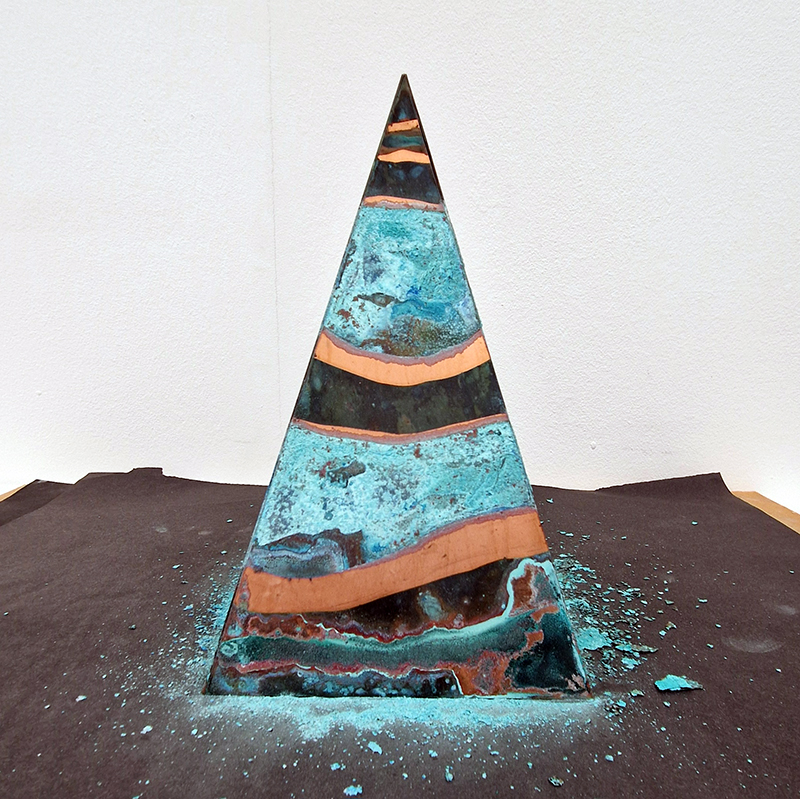
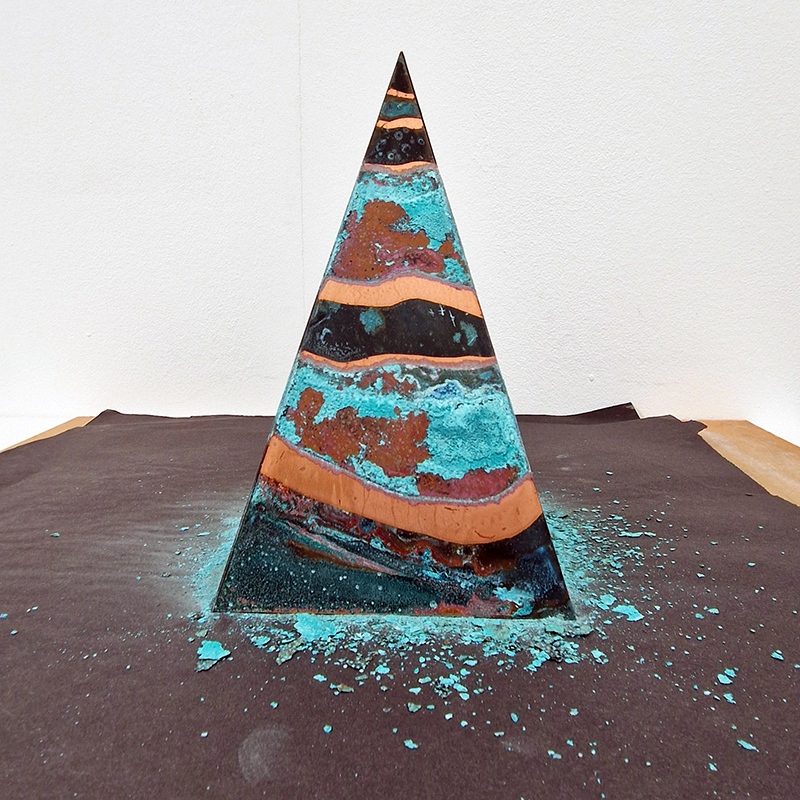
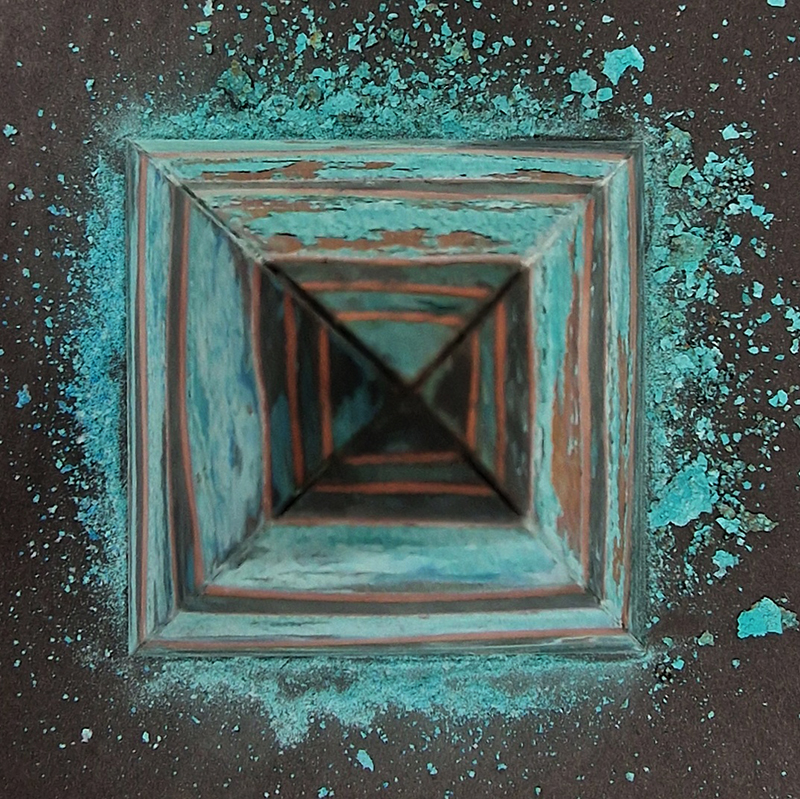
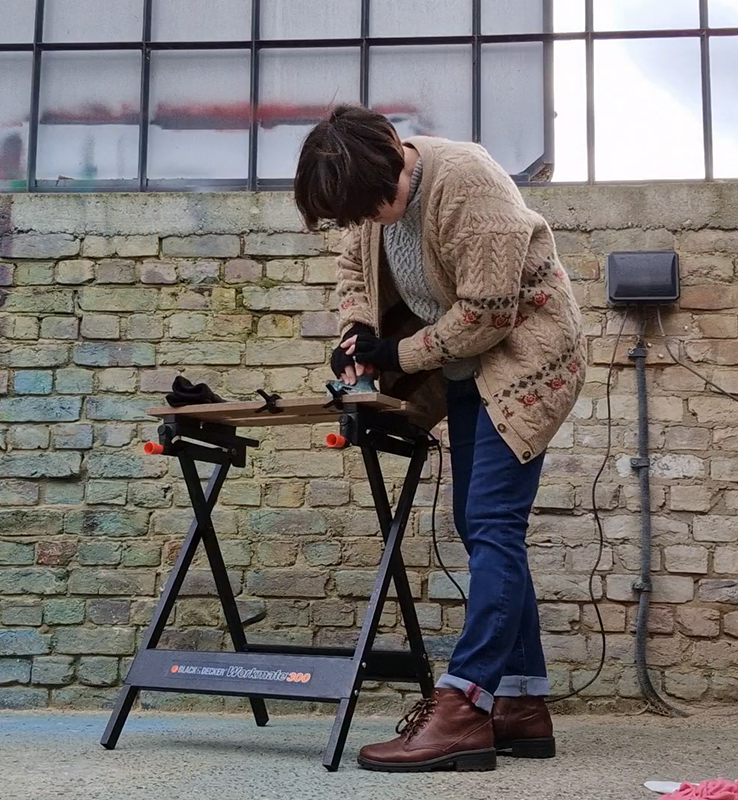
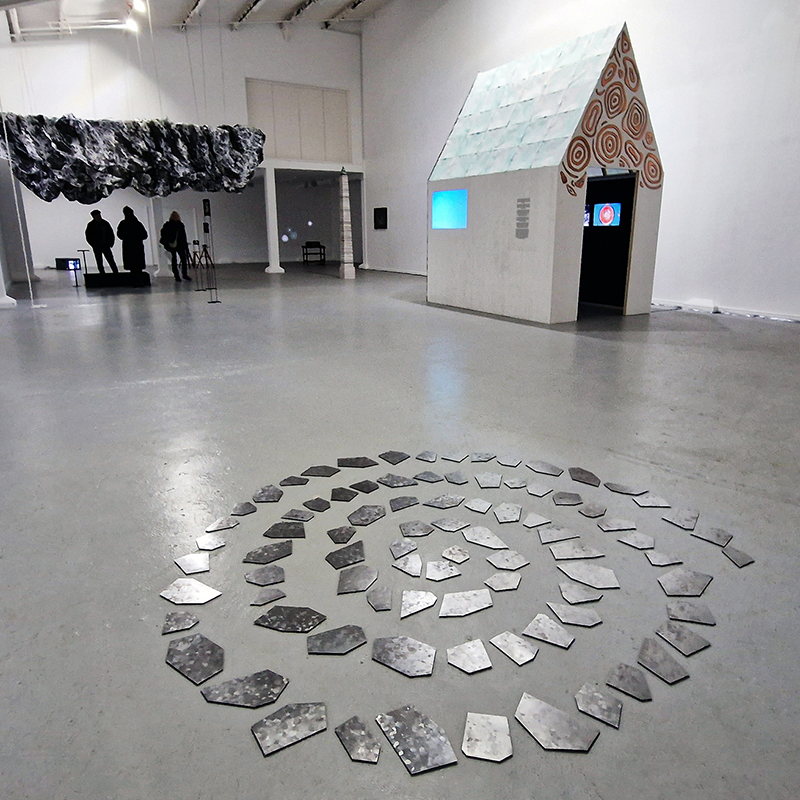
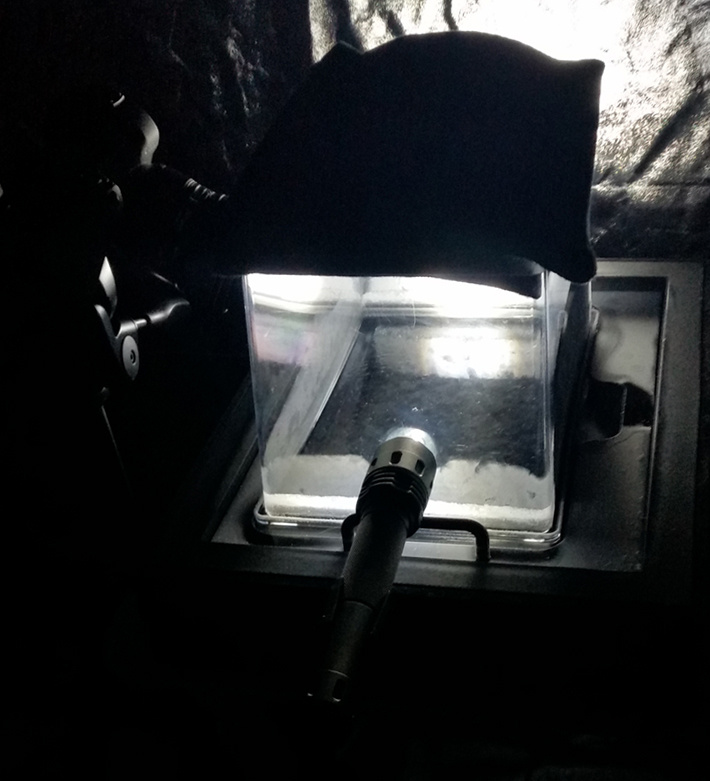
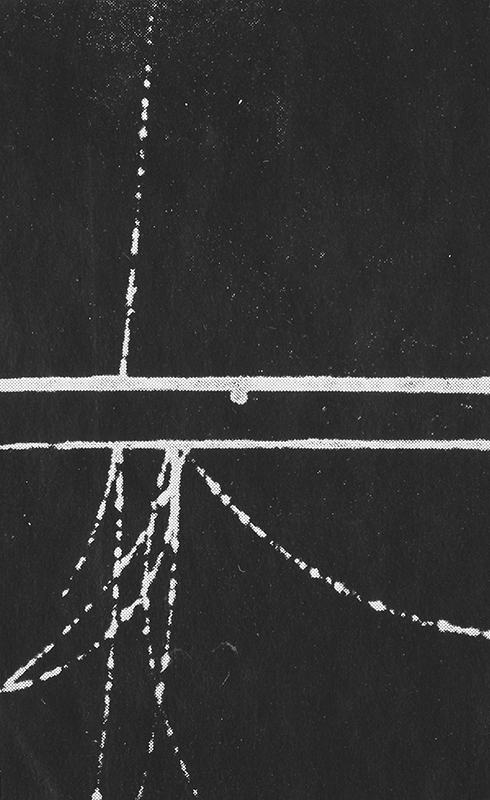
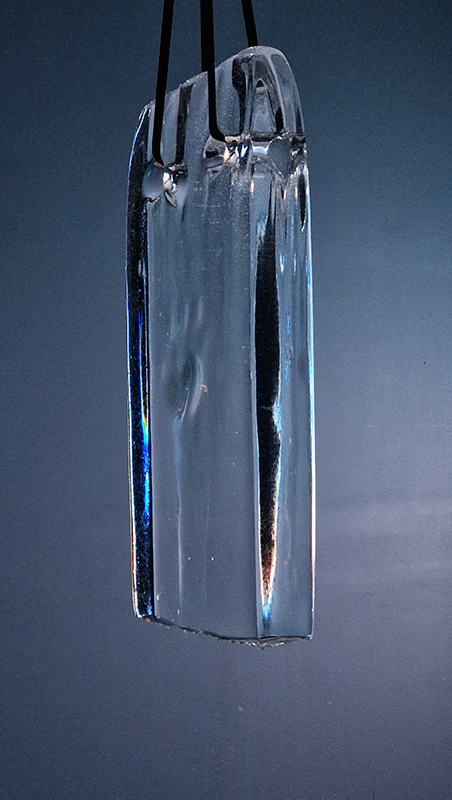
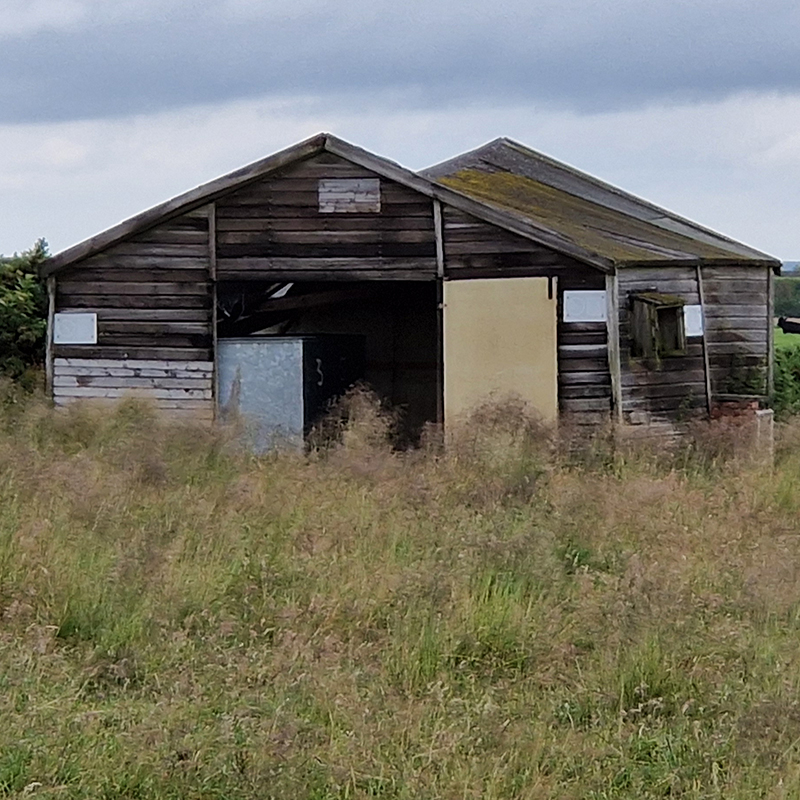
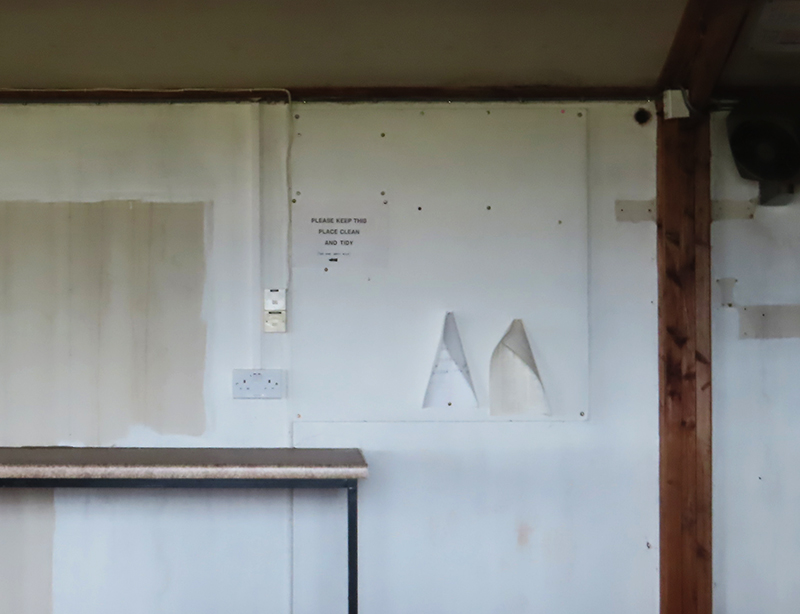
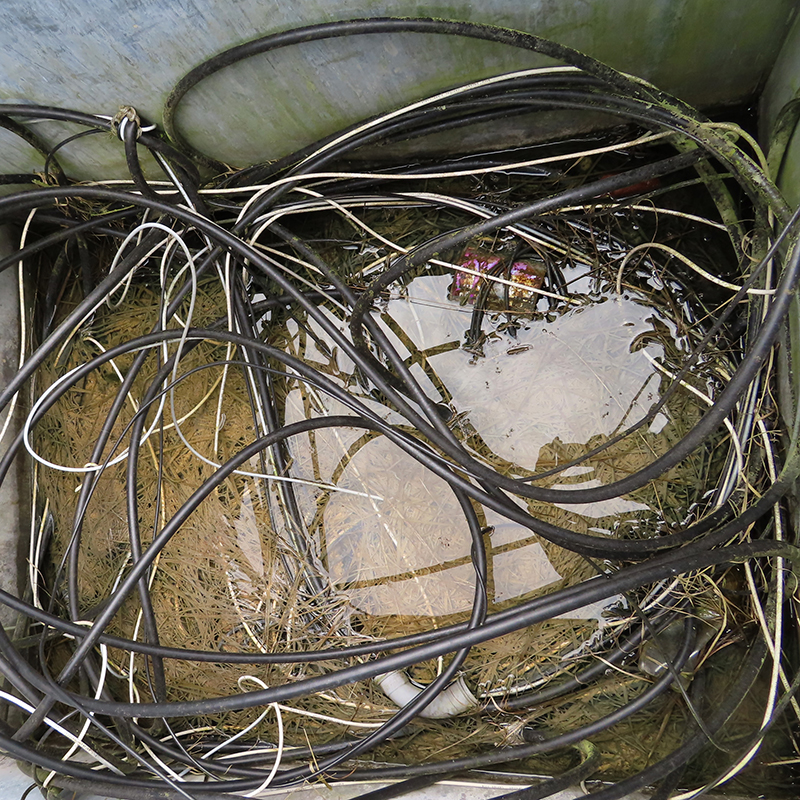
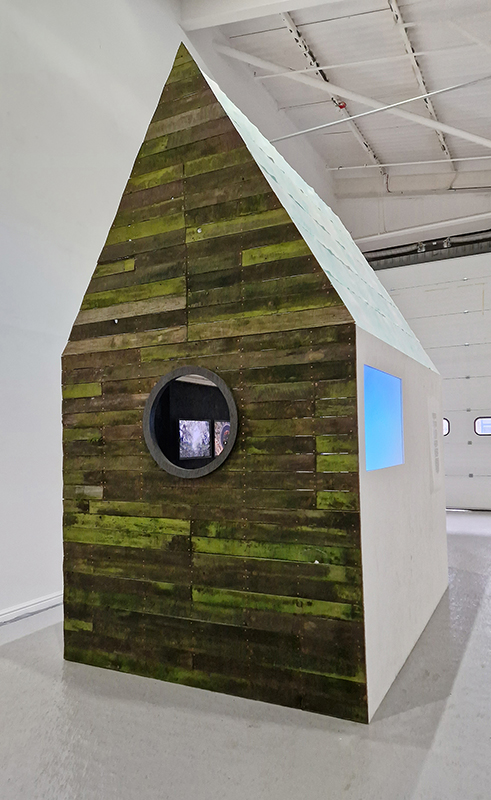
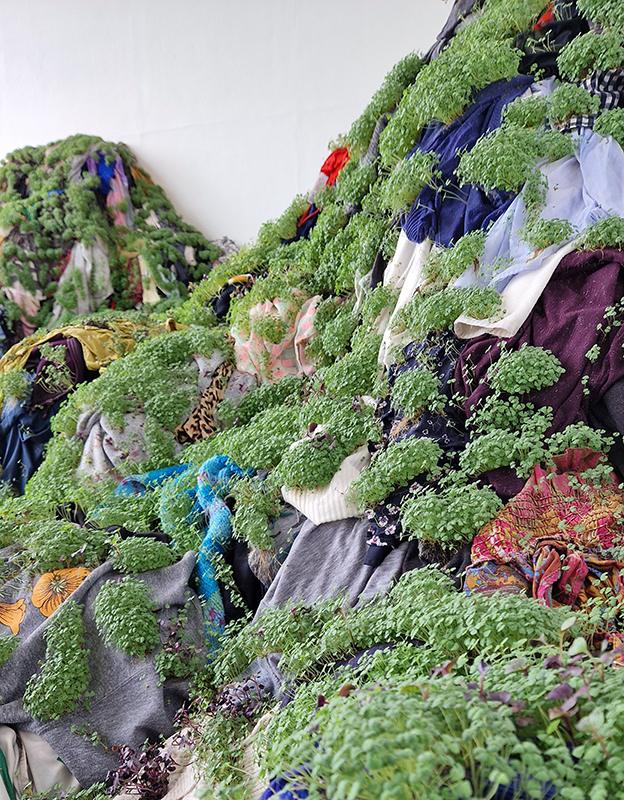
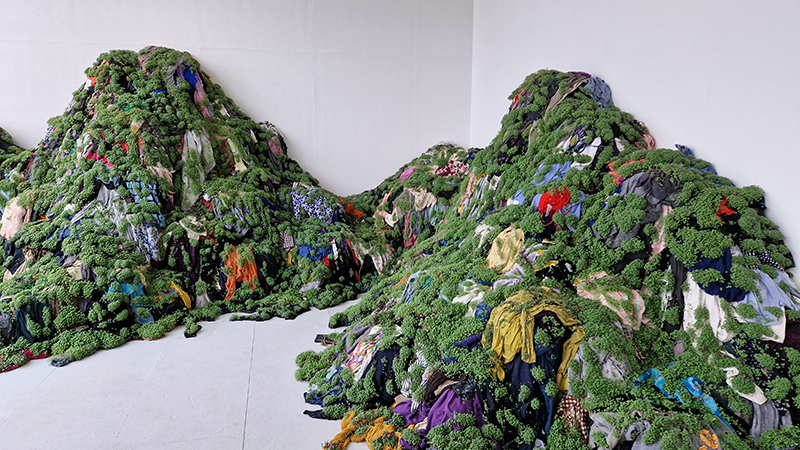
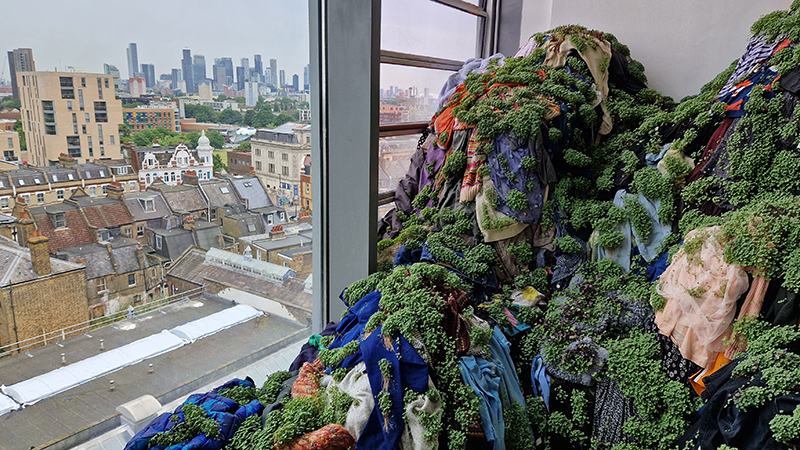
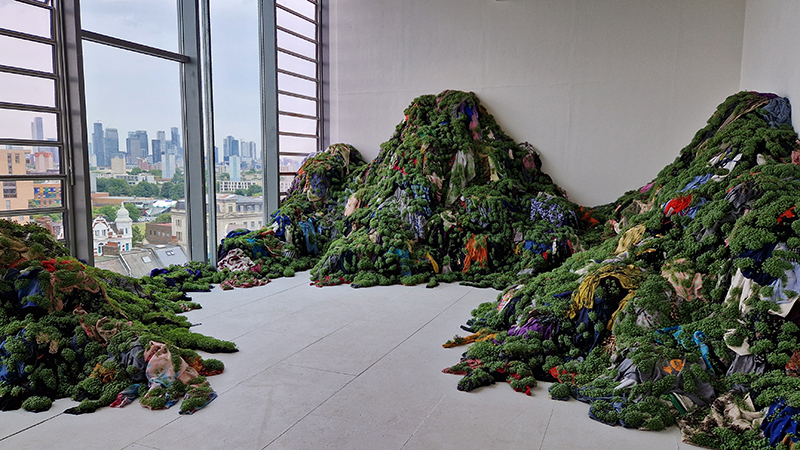
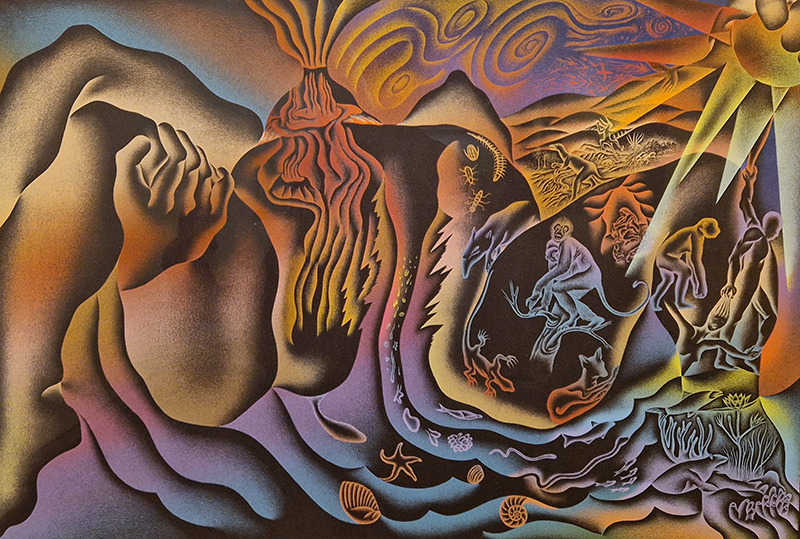
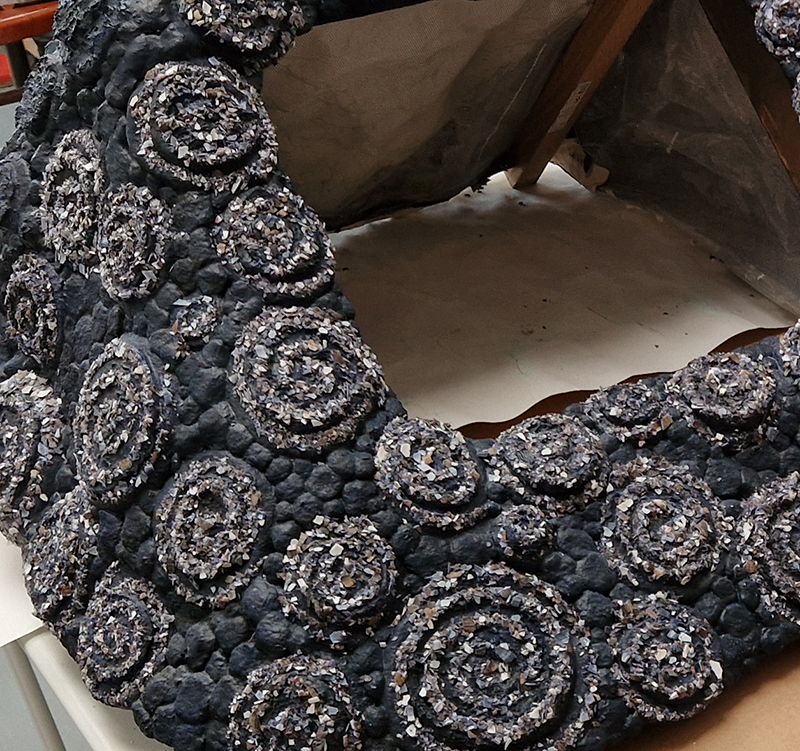
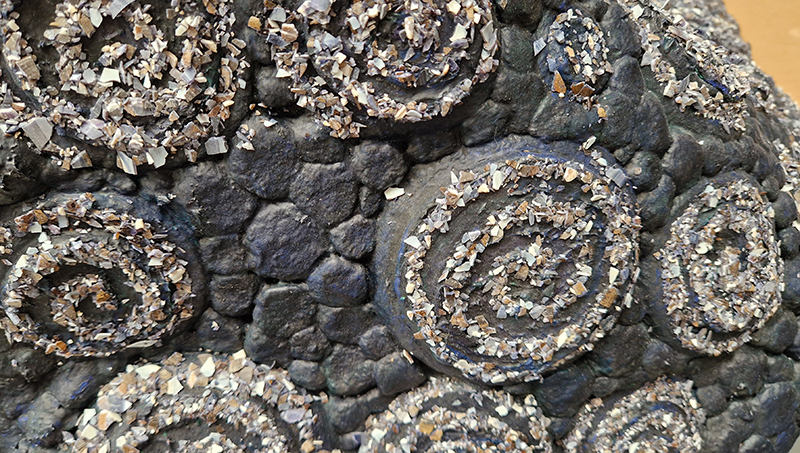
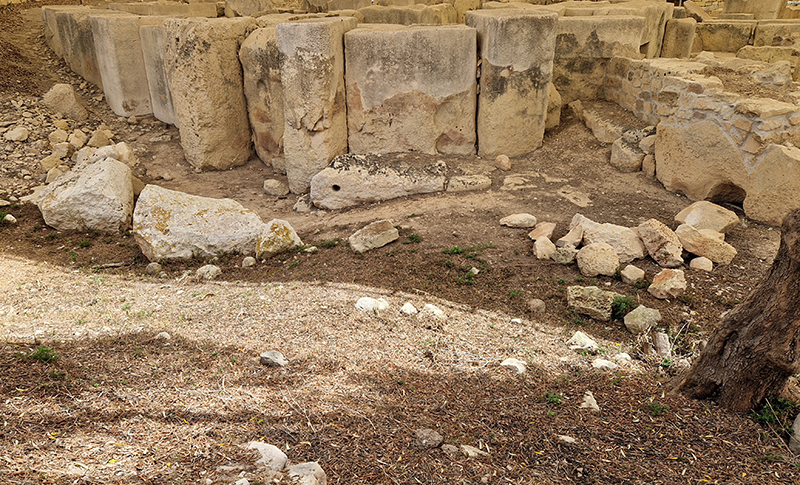
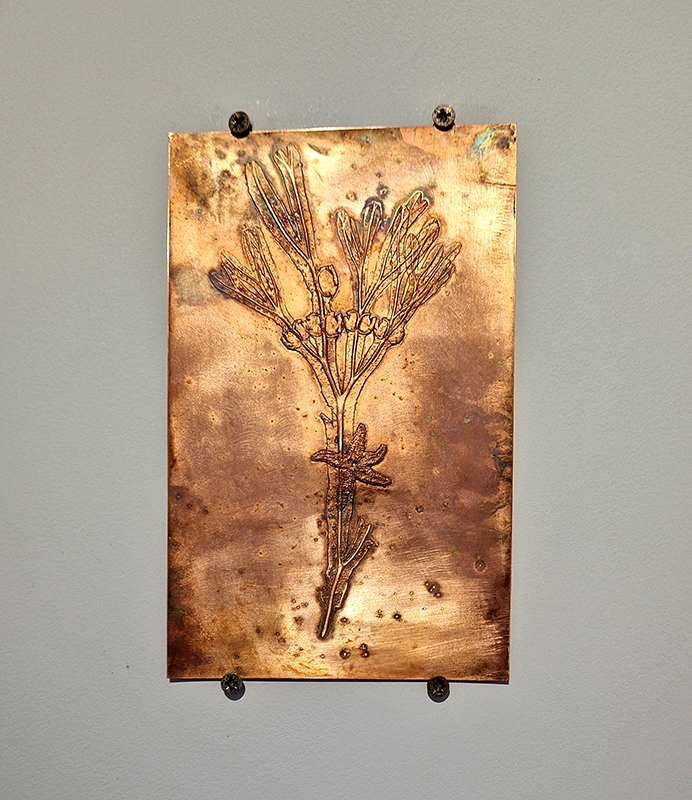
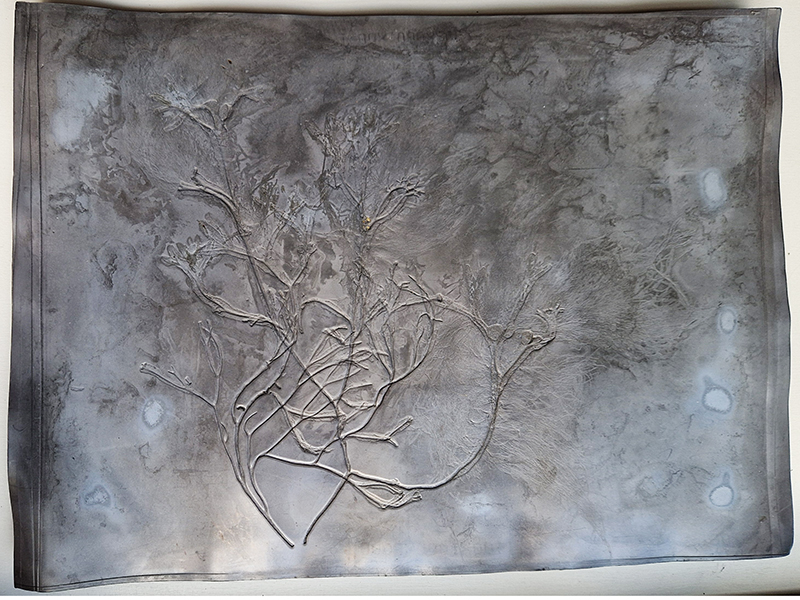
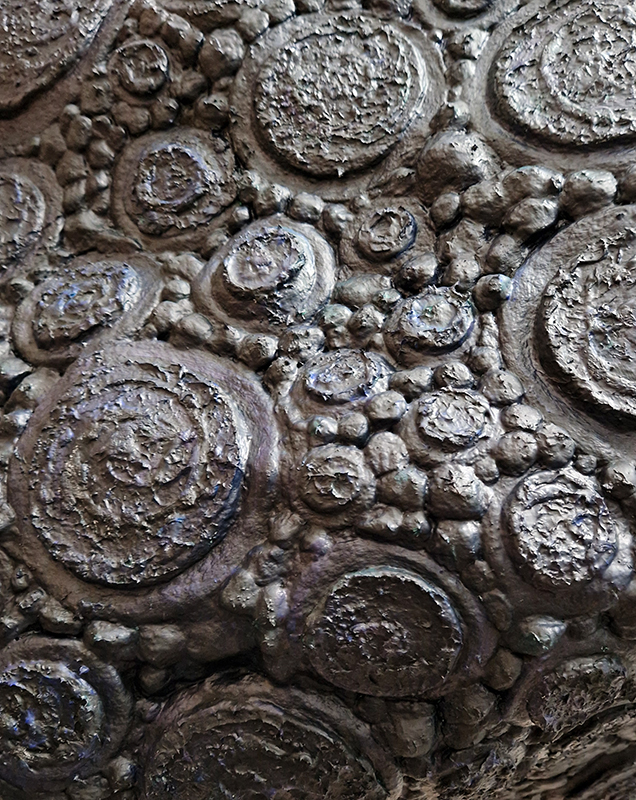
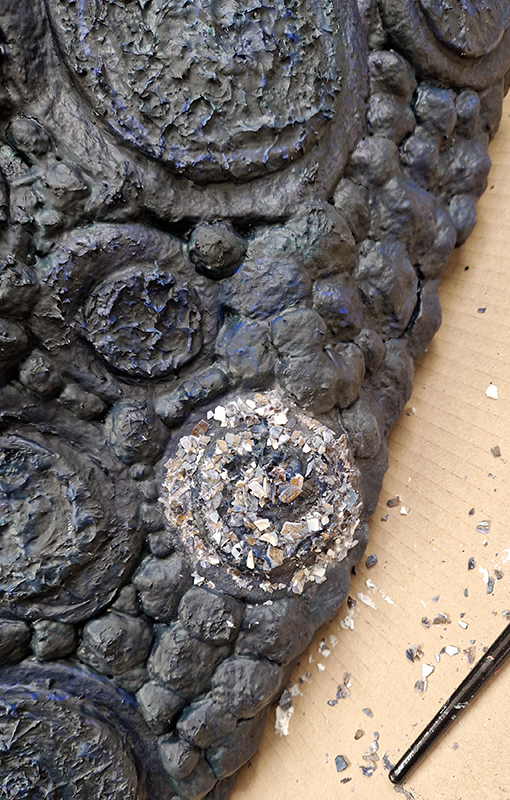
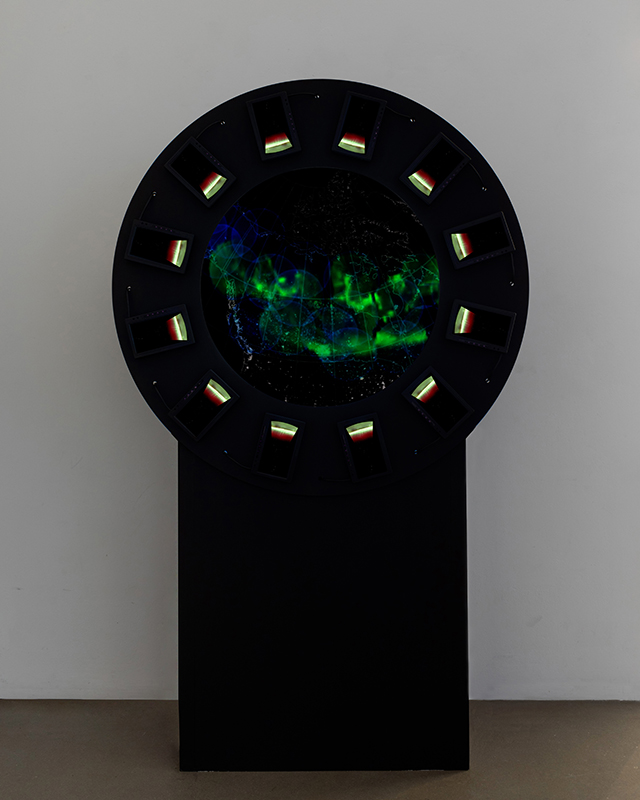
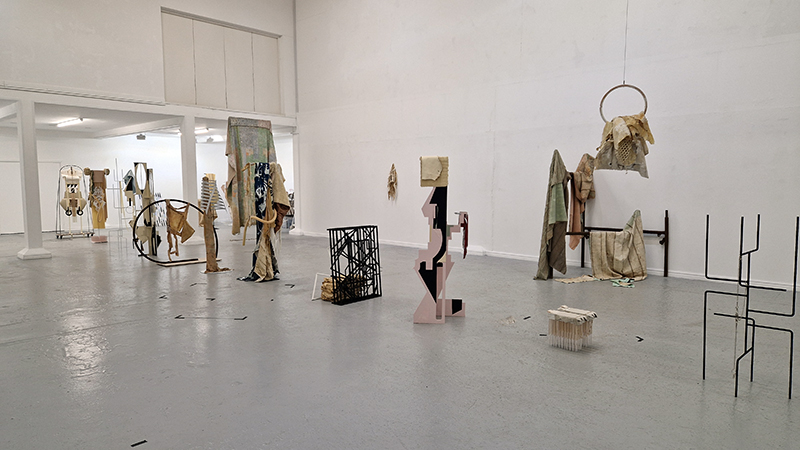
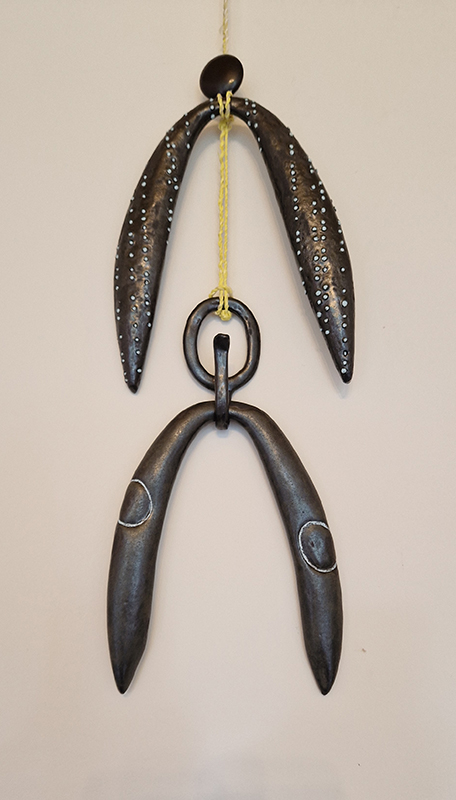
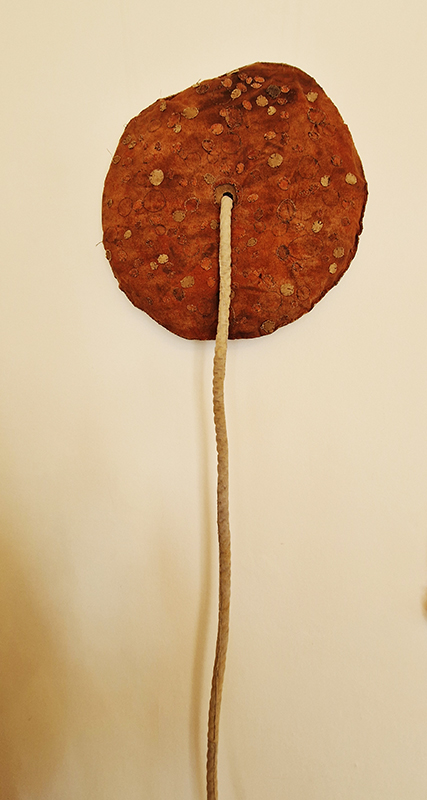
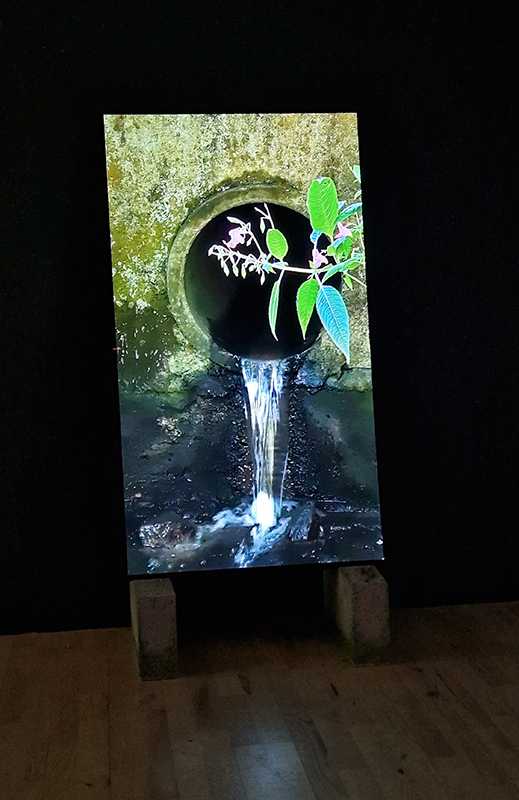
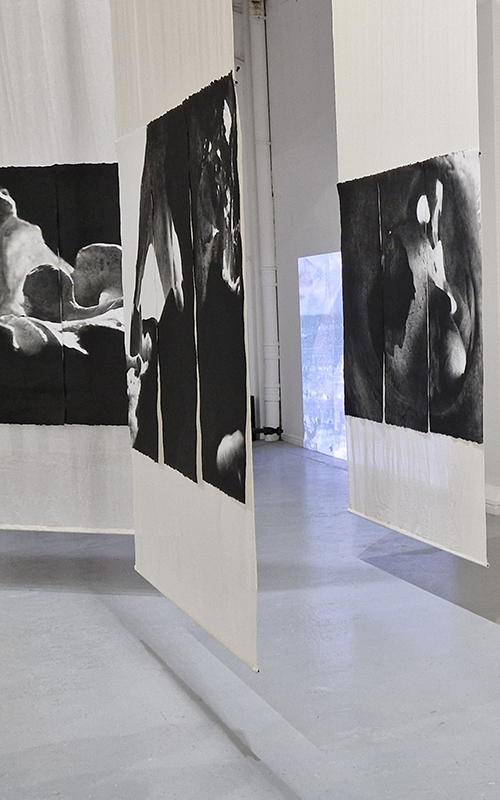
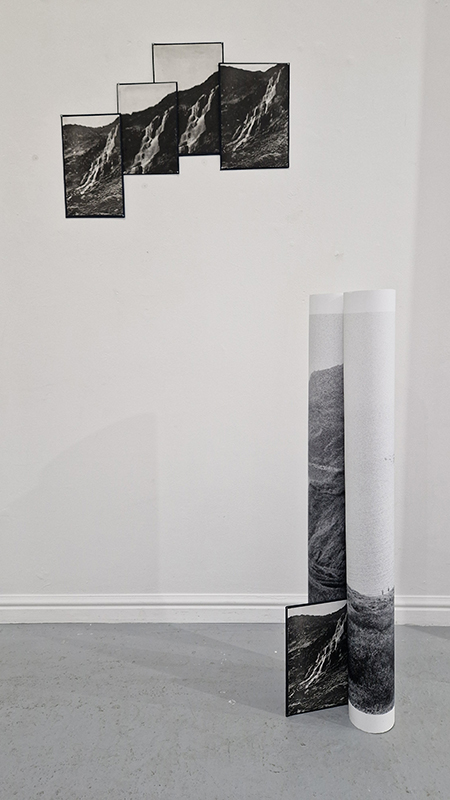
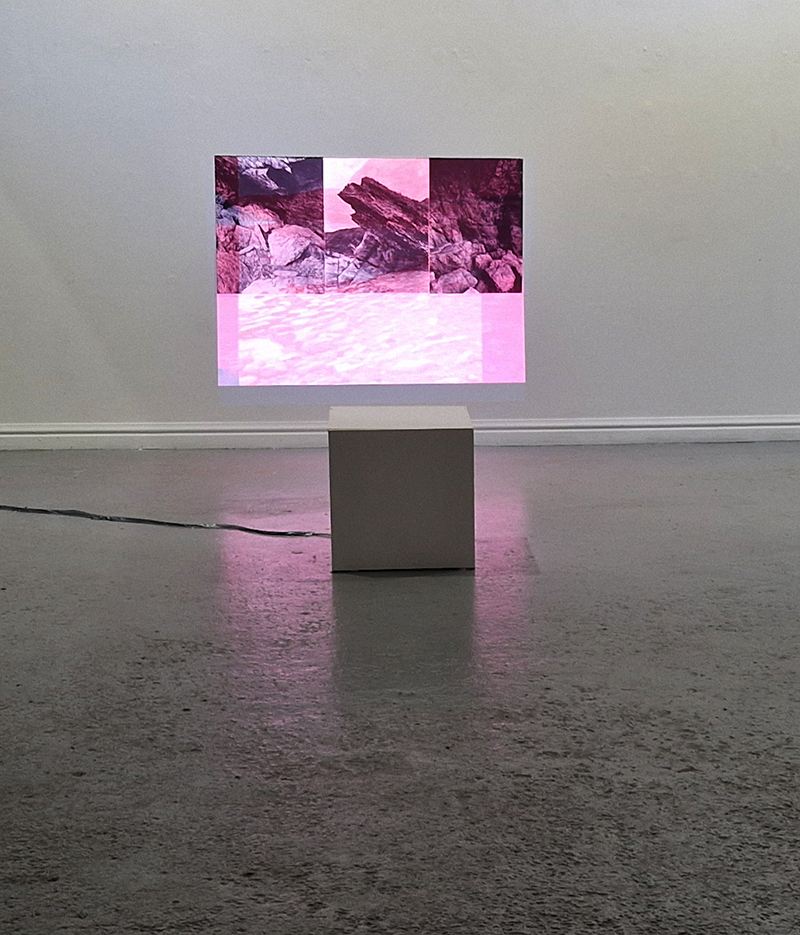
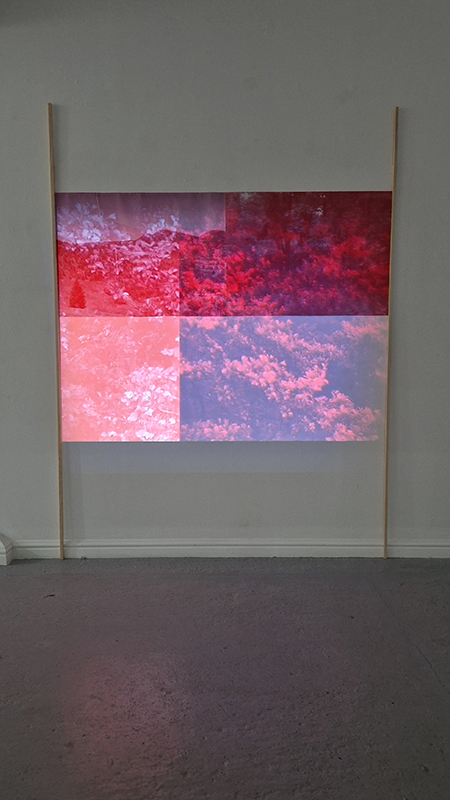
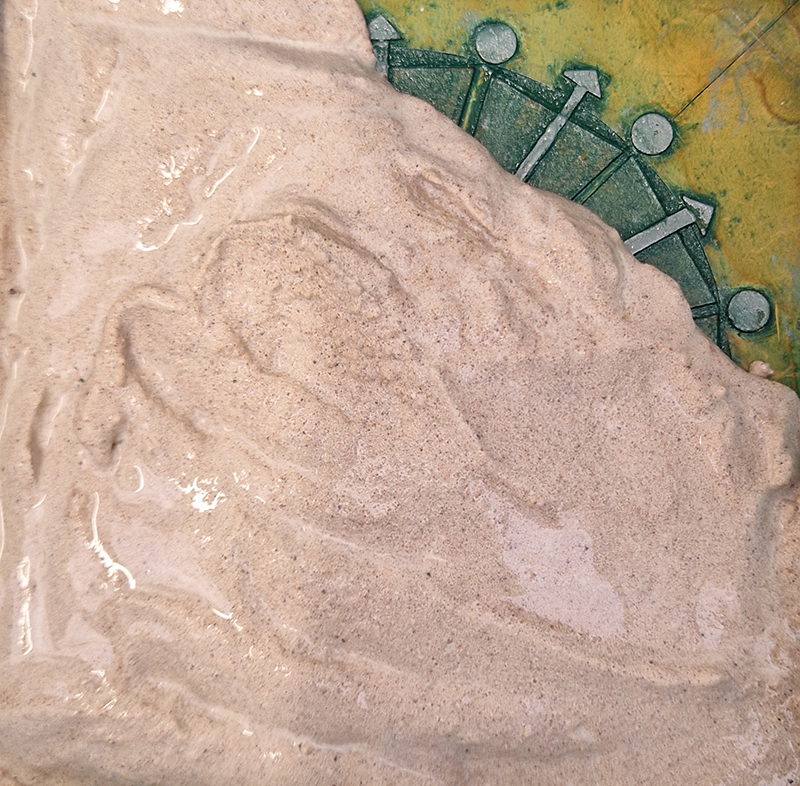
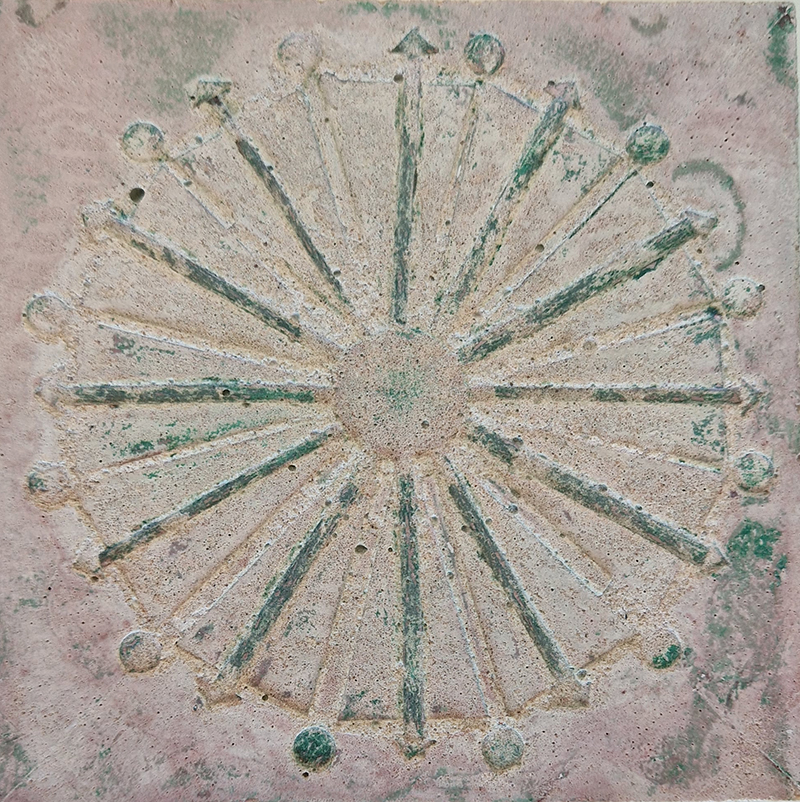
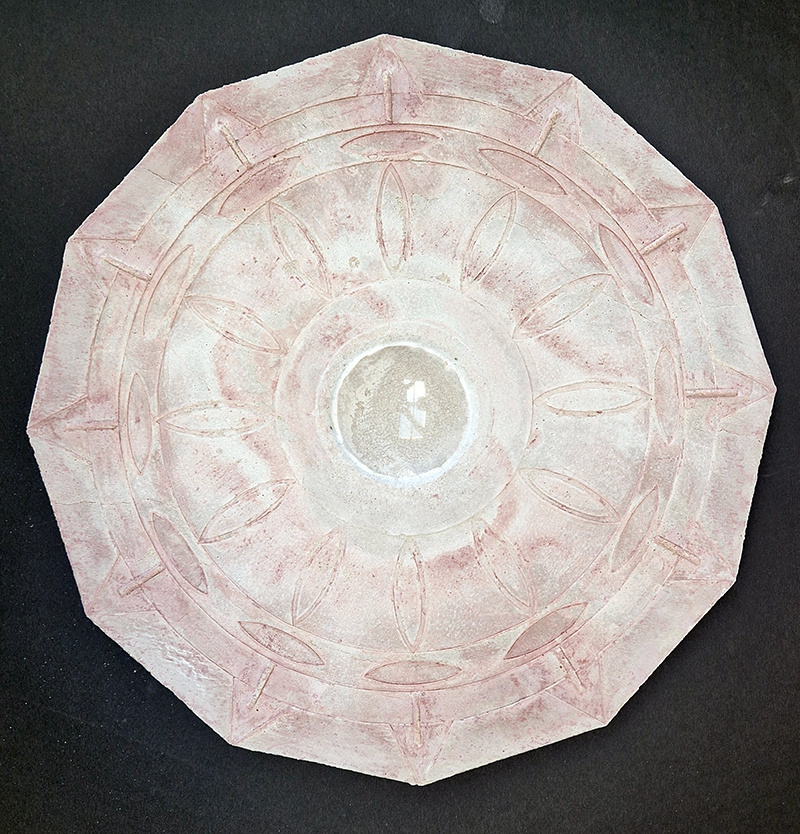
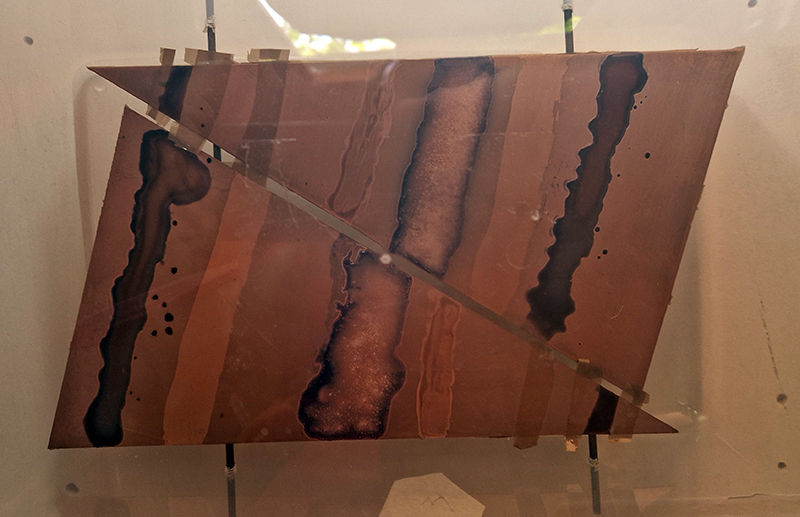
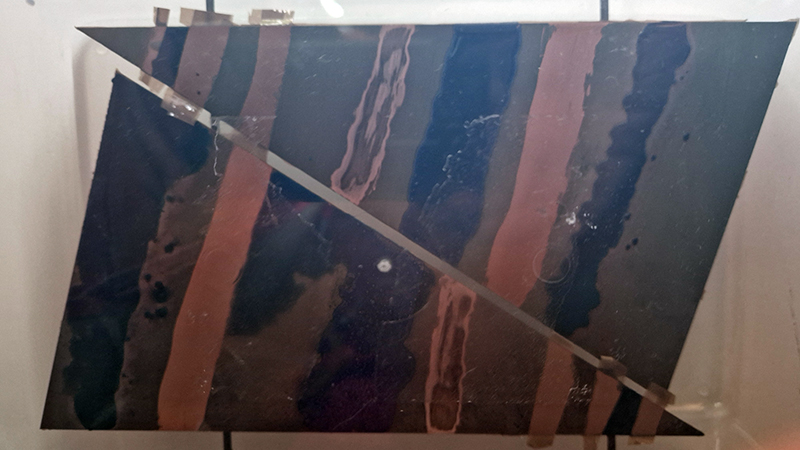
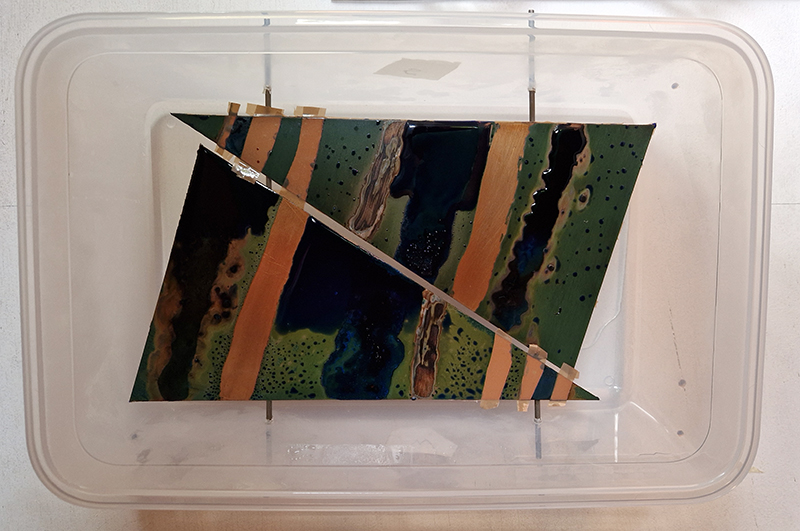
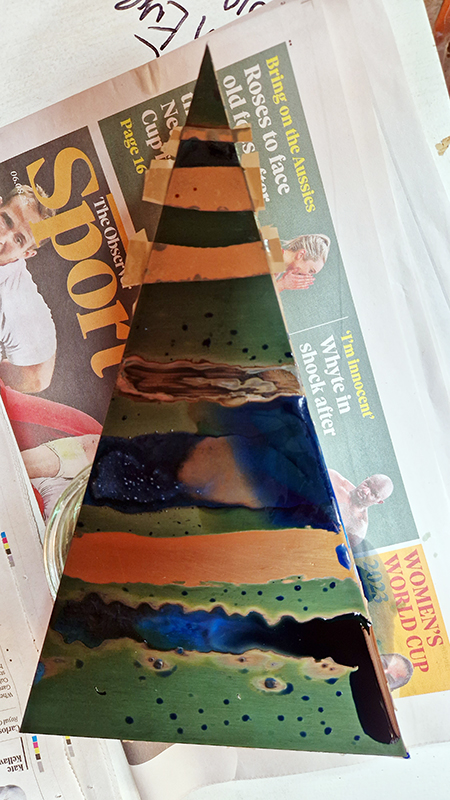
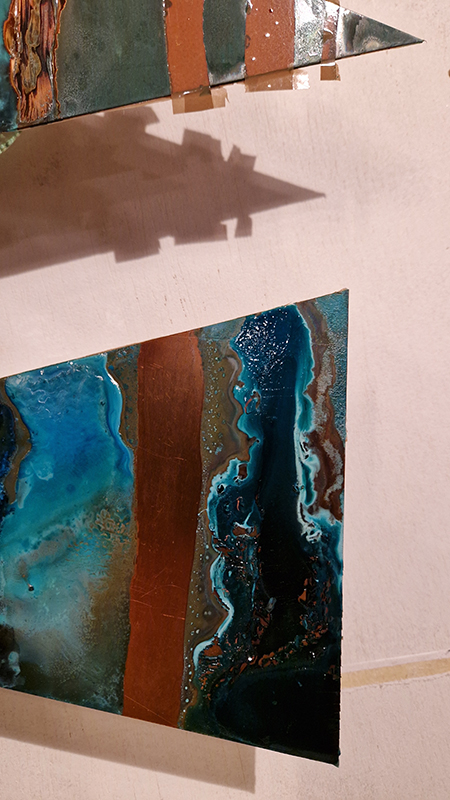
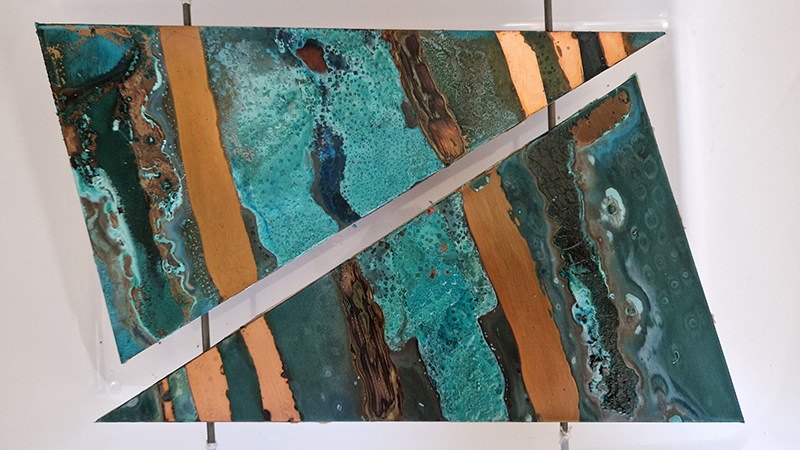
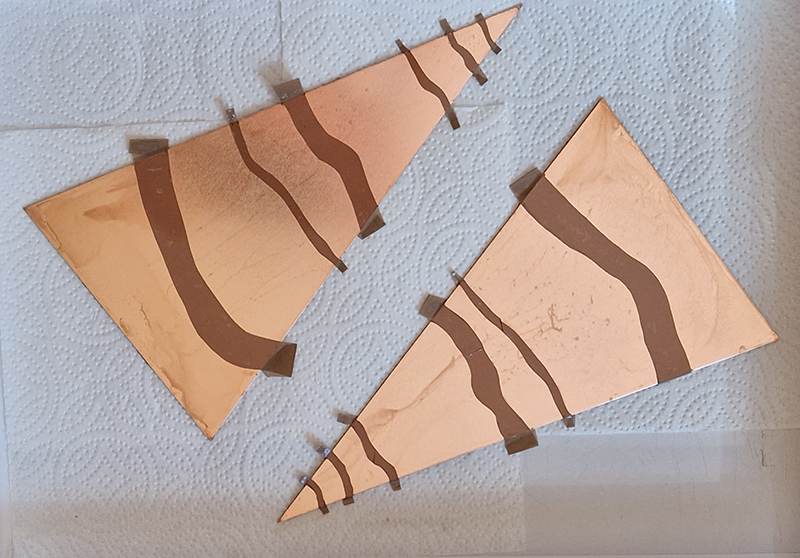
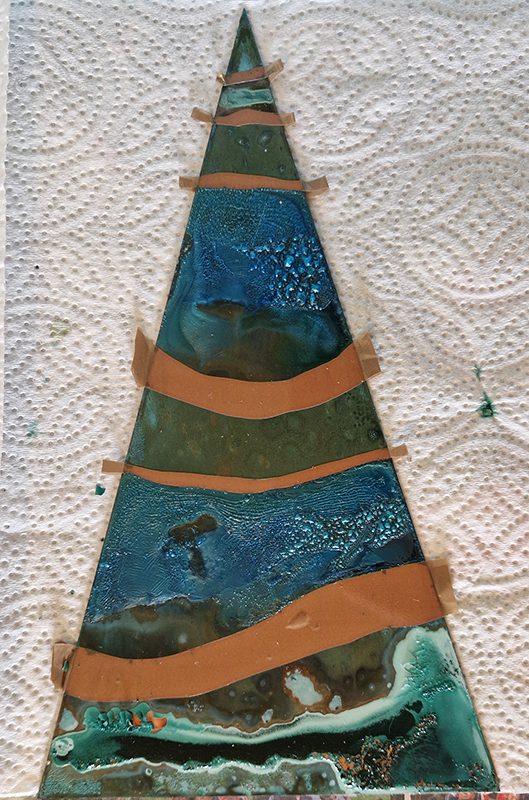
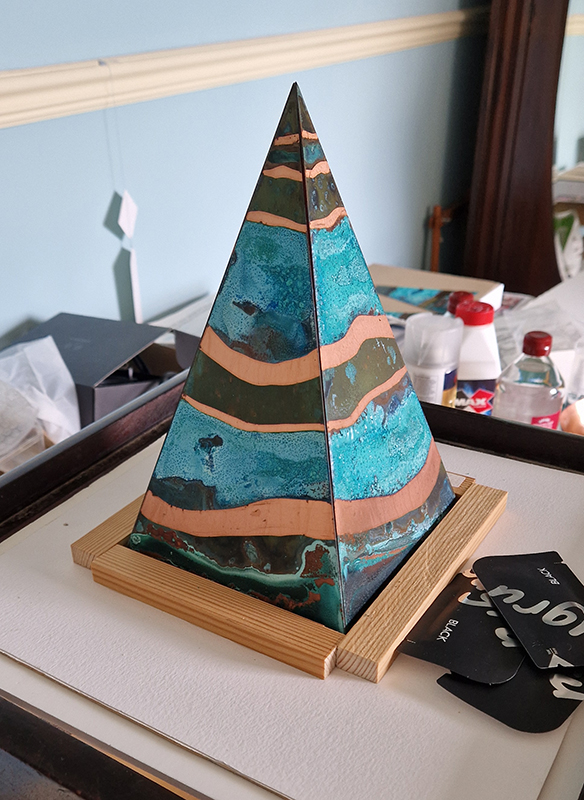
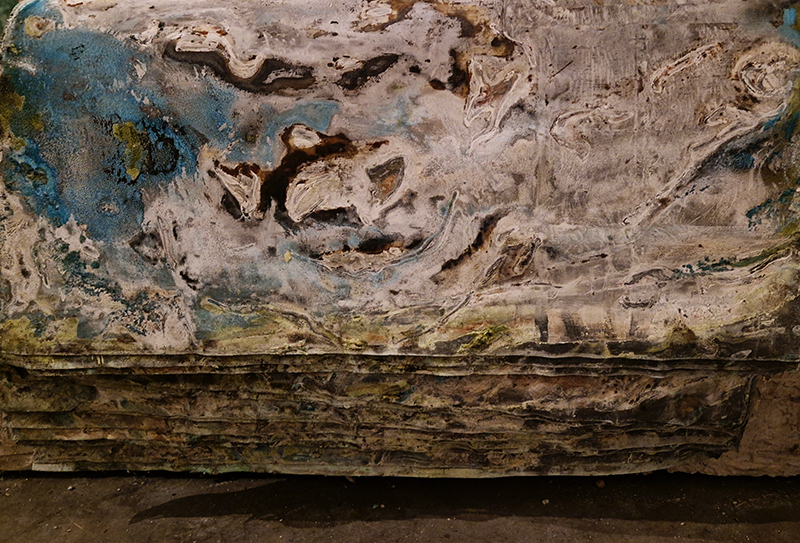
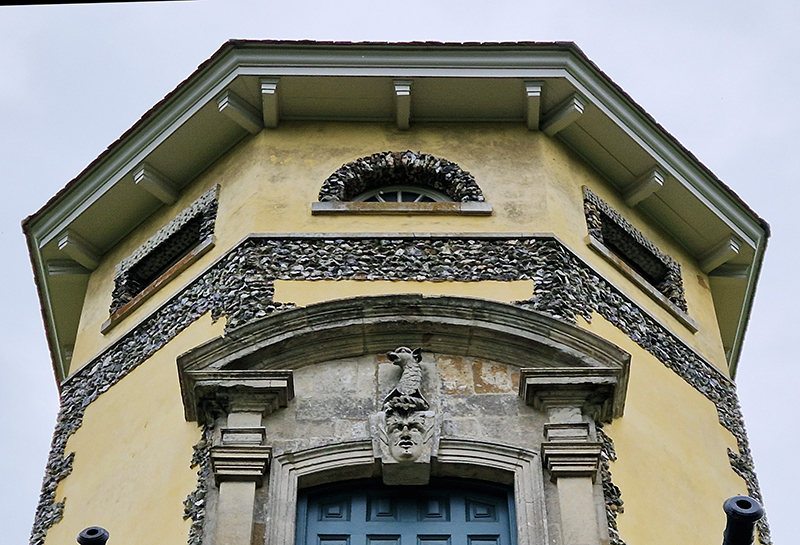
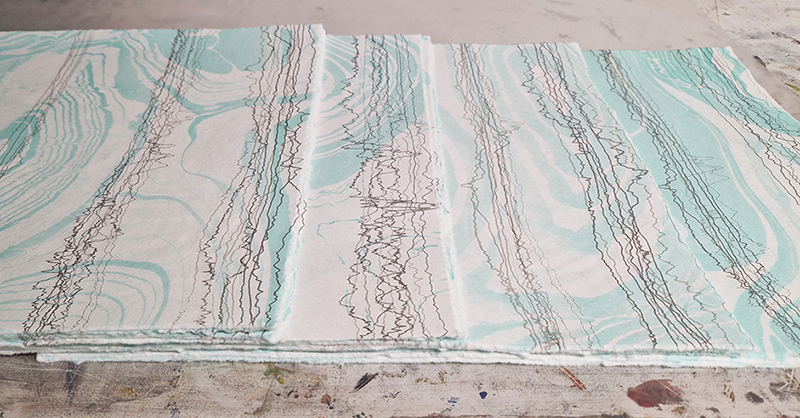
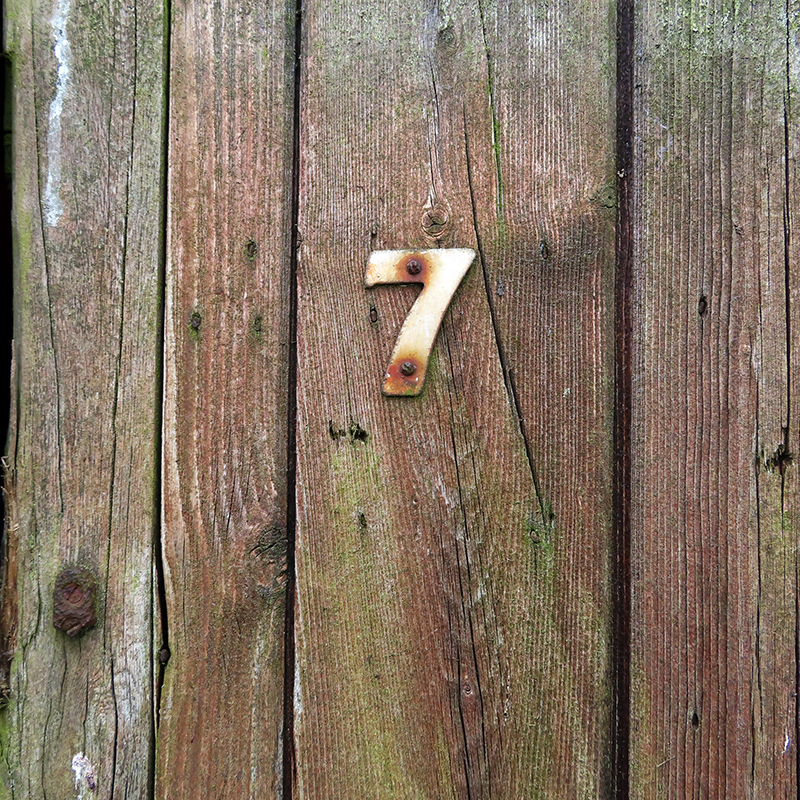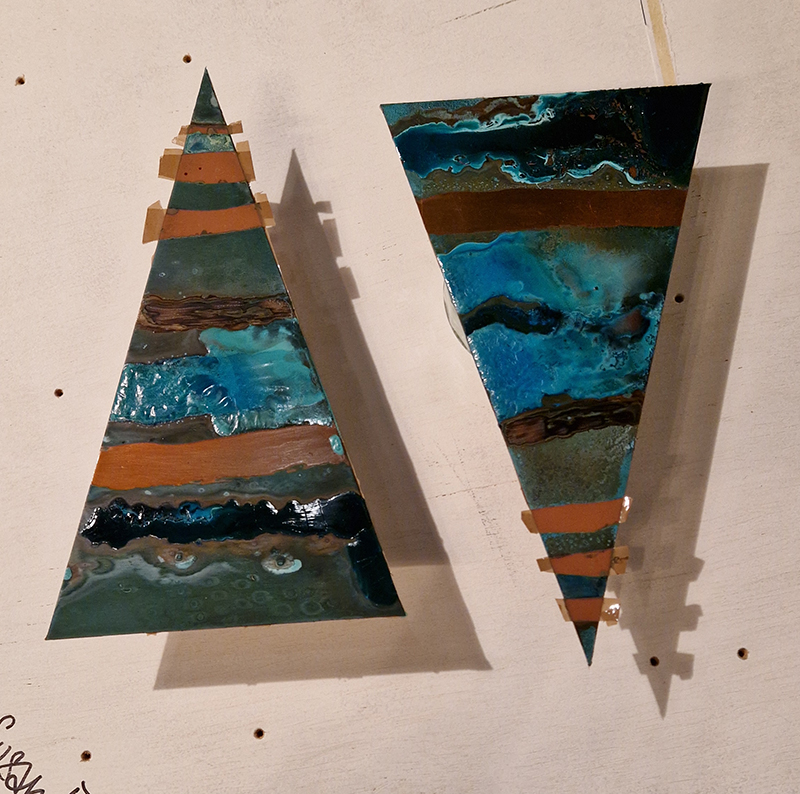Spending time in the print studio layering up magnetometer lines describing fluctuations in the Earth’s magnetic field. Using sheets of Japanese paper with Suminagashi ink swirls to evoke both ocean and magnetic currents. The lines are printed in metallic inks, relating to the idea of a lode, which in geology is a deposit of metalliferous ore that is embedded in a fracture in a rock formation or a vein of ore that is deposited between layers of rock.
The bands of magnetometer lines are used to signify the last three magnetic pole reversals. The most recent at 42,000 years ago (a short 500 year blip), then 780,000 years ago (continued for 22,000 years) and 1,000,000 years ago (continued for 40,000 years). This history of these reversals is stored in the ocean floor as magma flows up between cracks in the Earth’s crust, spreads and solidifies, capturing the direction of the poles in the orientation of the minerals.





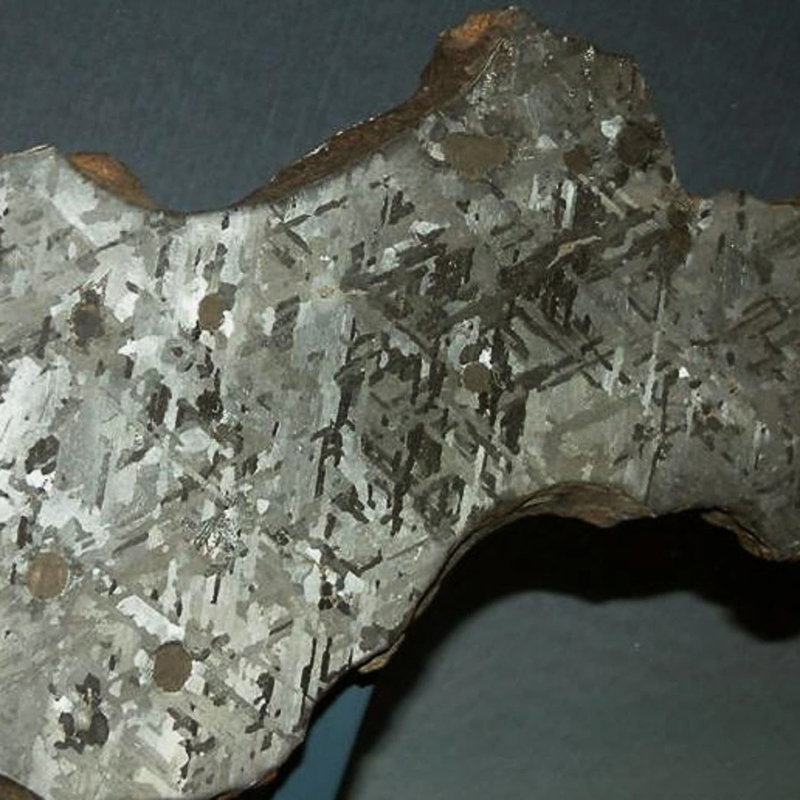
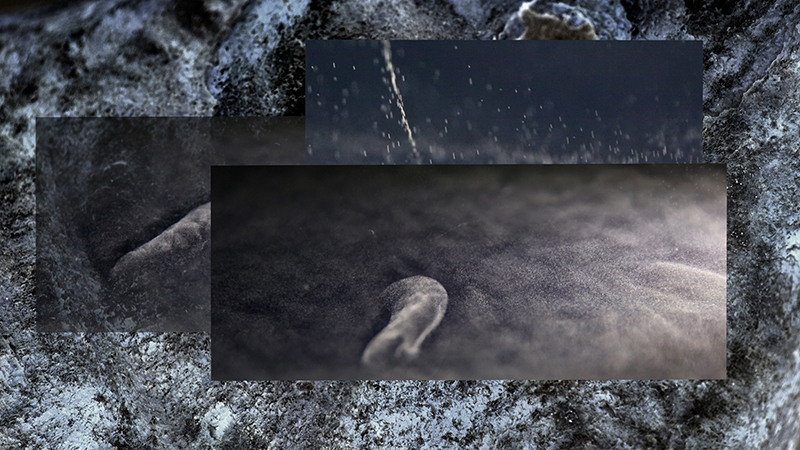
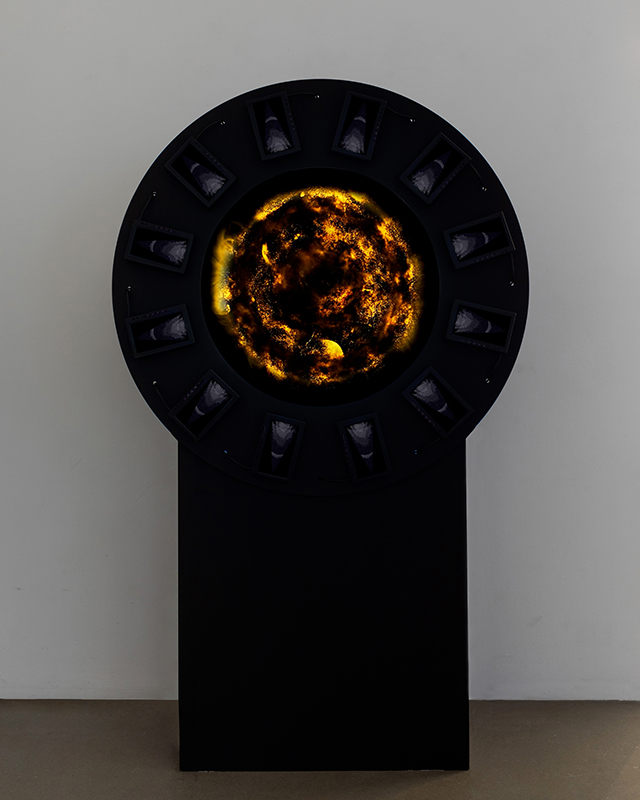
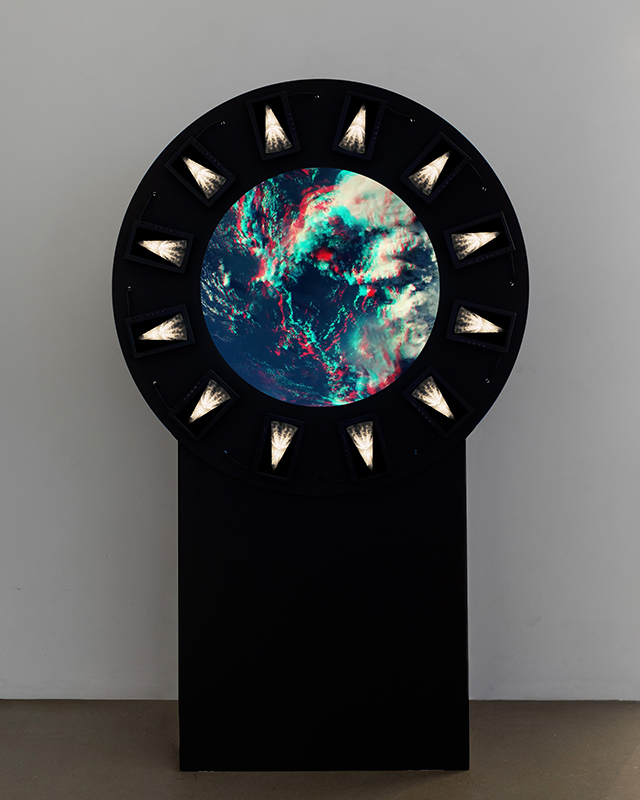
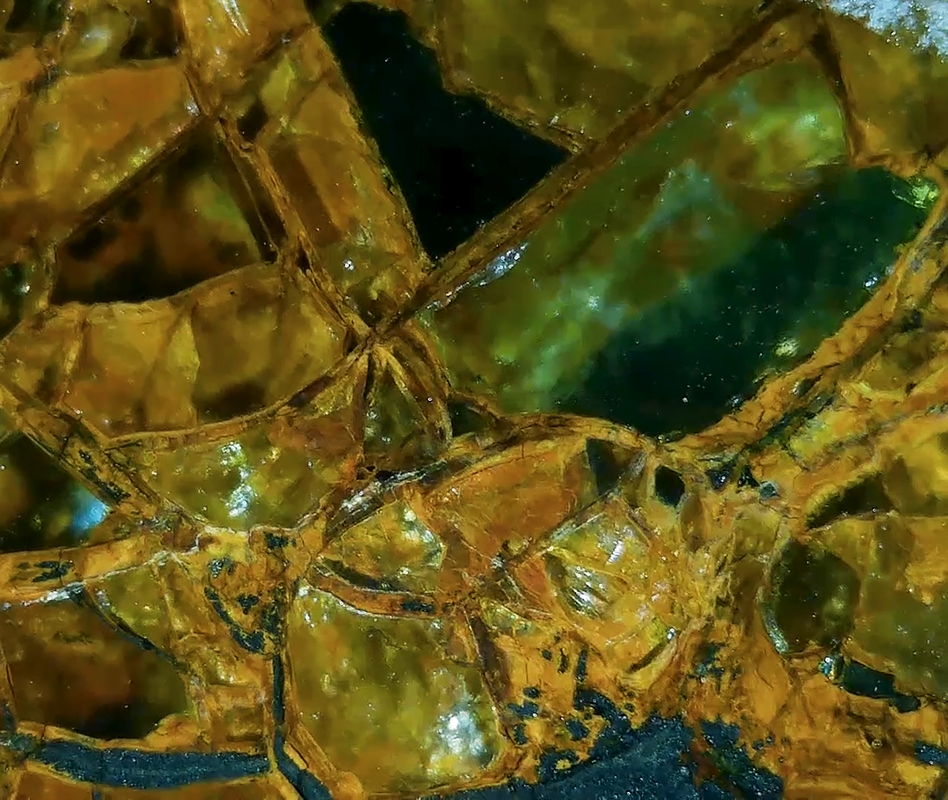
Work in progress on Mineral Visions, a video sculpture with a particular focus on magnetite/magnetism and human relations. Editing video of Jepara seen under the microscope. This is a magnetic pallasite meteorite with an interior structure of densely packed olivine and iron-nickel, discovered in Indonesia in 2008. Pallasite meteorites formed in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. They’re made up of minerals and remnant materials from the first few million years of the solar system, forming at a time when planets were only just coming together.

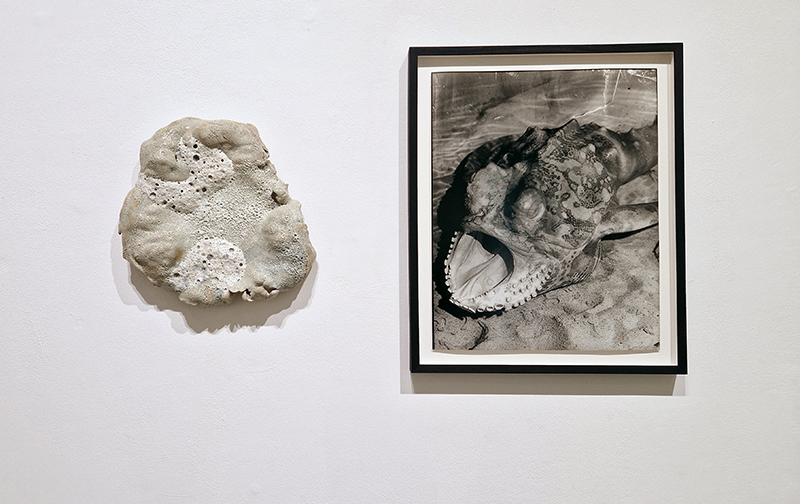
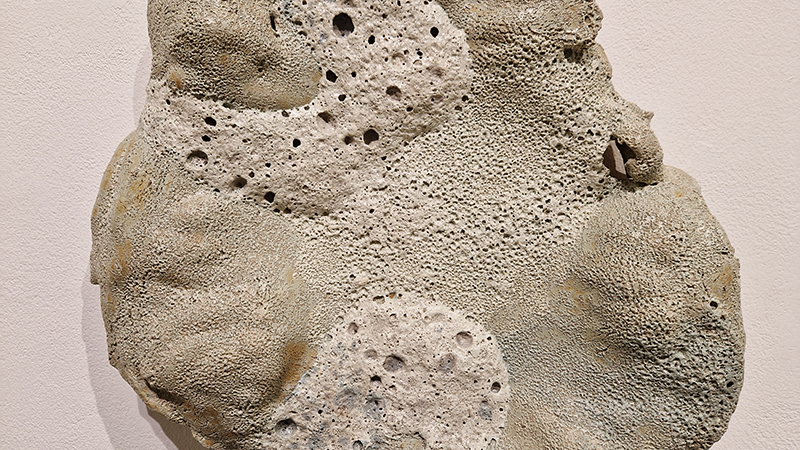
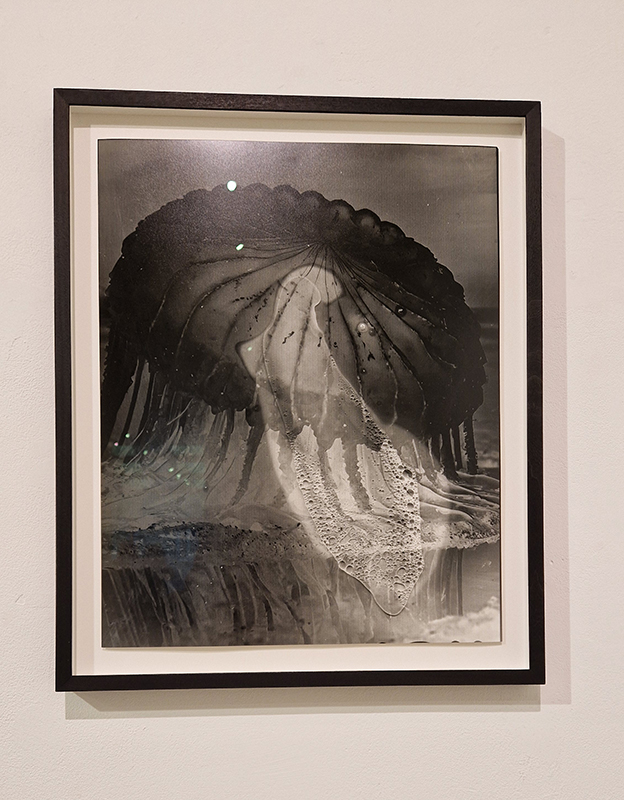
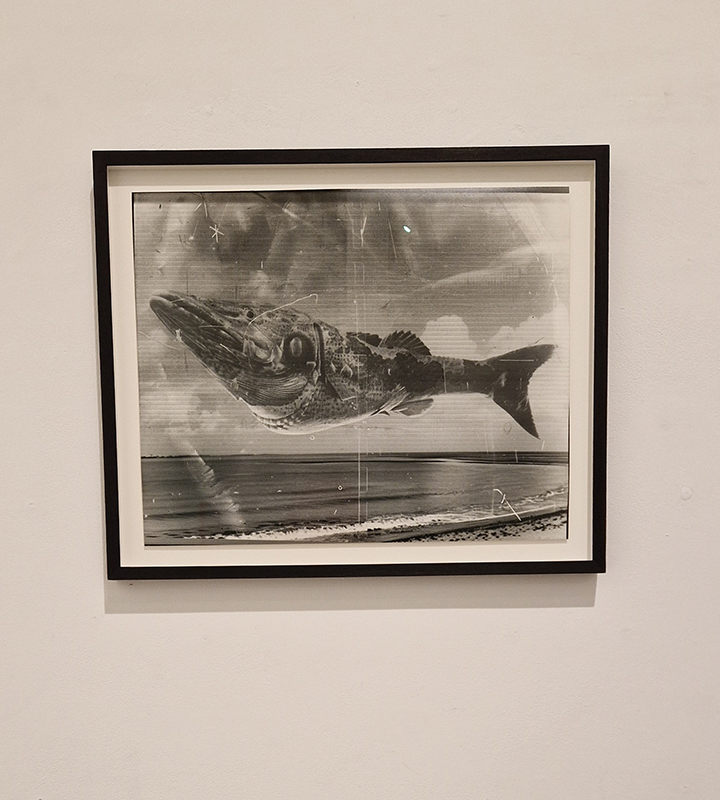
A very special research trip with fellow artists exhibiting in the upcoming show at Hypha HQ, The Geological Unconscious, to visit la Galerie de Géologie et de Minéralogie, Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris. Hosted by the curator of minerology we were privileged to see a selection of stones in the museum vault. The museum holds Roger Caillois’ stone collection as featured in his book The Writing of Stones. The photographs of this extraordinary collection do not compare to seeing them up close, from every angle. Must larger than anticipated, they are extracted from their snug foam packaging for yet another scrutiny of the human gaze. Caillois wrote at length about each stone, allowing his imagination to conjure metaphor and analogy from the syntax of the ancient crystal and sediment. He was fascinated by his own fascination with the stones which he saw as a desire to connect with the more than human and lose oneself in the enormity of the universe.

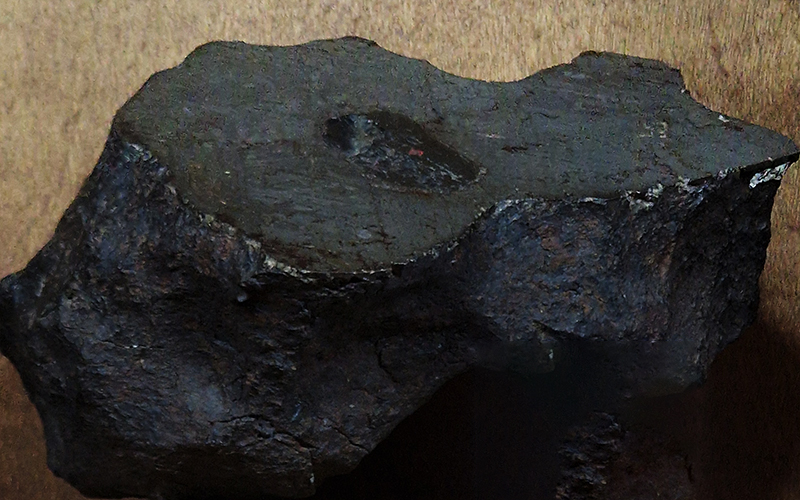
We also got to see some meteorites in the collection including a large one containing diamonds that had belonged to Caillois. The Canyon Diablo meteorite originated in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter and crash landed into the Arizona desert approximately 49,000 years ago, with the force of more than 100 atomic bombs. The crater it left is nearly a mile across and 600 feet deep. Fragments were flung over an area of over 11 sqm from the point of impact where the main mass vaporized on contact. In the force of collision small diamonds formed from graphite and are found inside the highly recrystallized meteorite fragments at the rim of the crater.

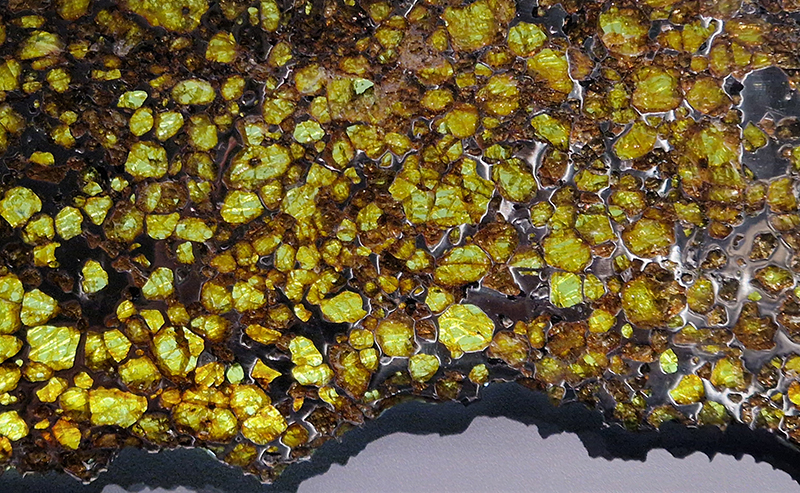
I was also interested to a slice from one of the world’s largest specimens of pallasite, the Imilac pallasite discovered in 1822 which exploded over the Atacama Desert in northern Chile, possibly in the fourteenth century.

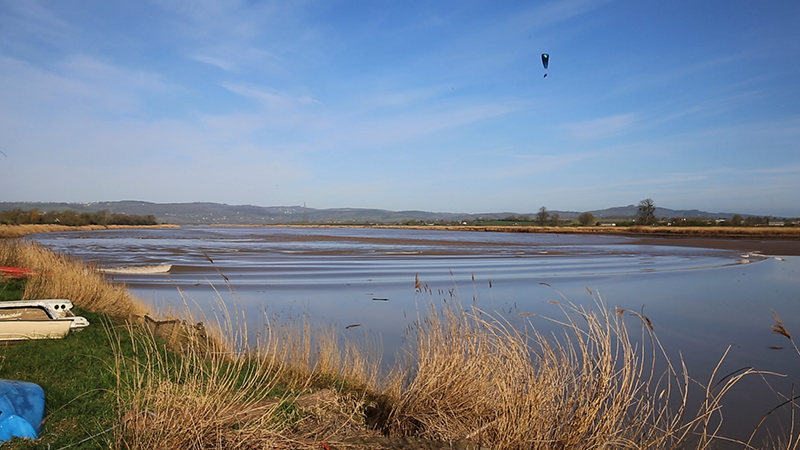
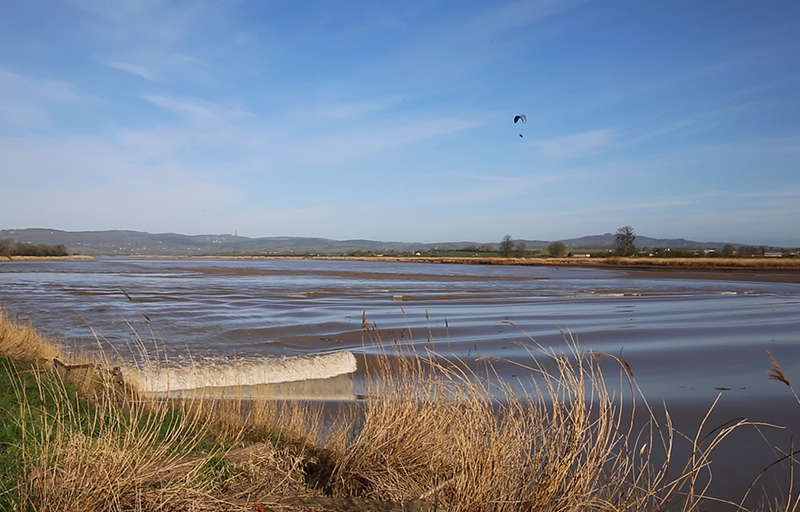
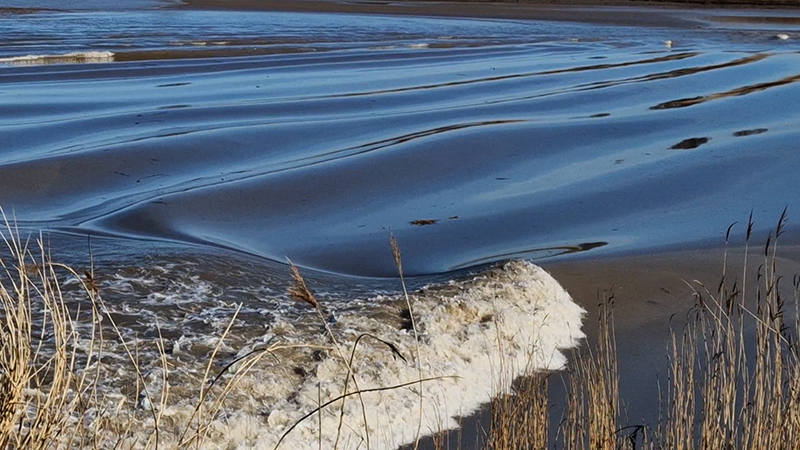
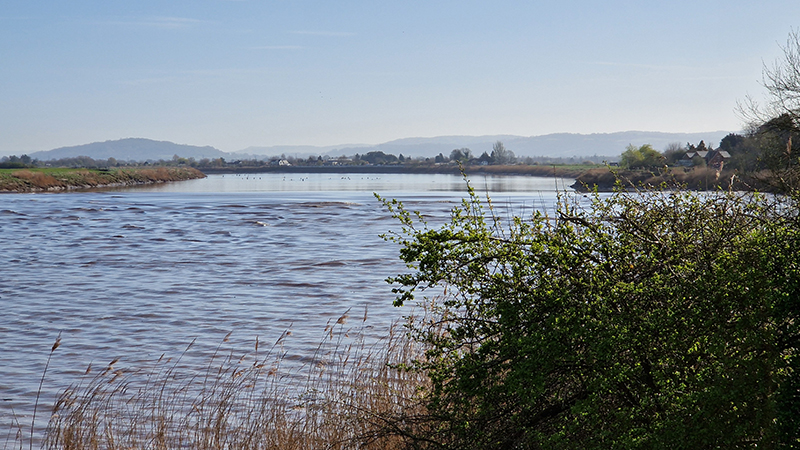
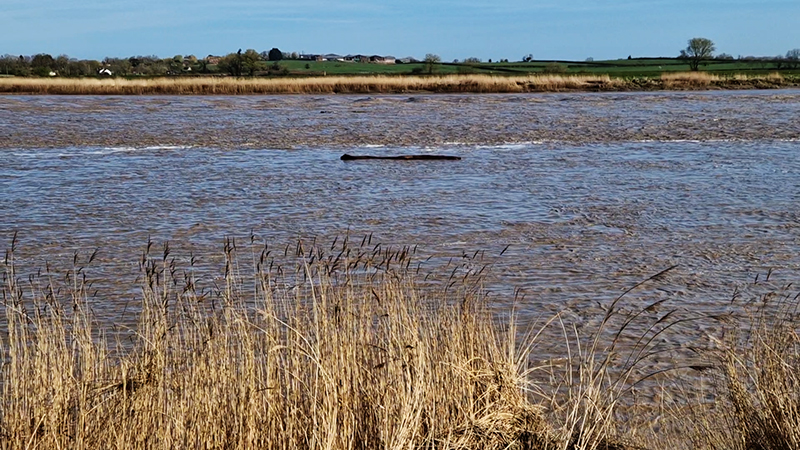
This spring Severn bore had been forecast to be a 4* event but arrived earlier than expected as more of a ripple. Not enough rain from the Welsh hills and no uplifting wind meant it was a more gentle, leisurely wave. It was still exciting to witness the change in the river from the slow glassy seaward flow to choppy, muddy turbulence carrying logs and assorted debris inland as the tidal wave rose into the channel. Such a beautiful morning to be on the river bank.









Gallery Visits
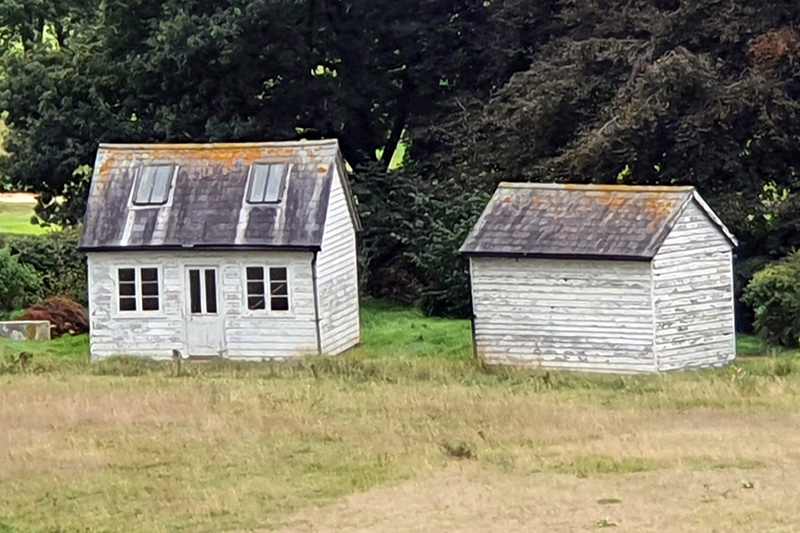
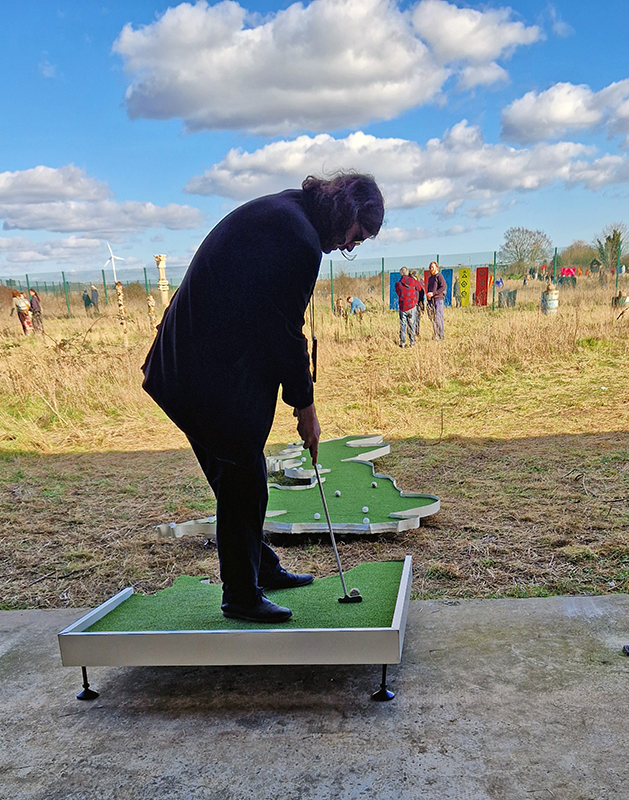
Glorious sunshine spot lit exuberant work at the Winter Sculpture Park hosted by Gallery No32 at a former Thamesmead golf course along the banks of the River Thames.
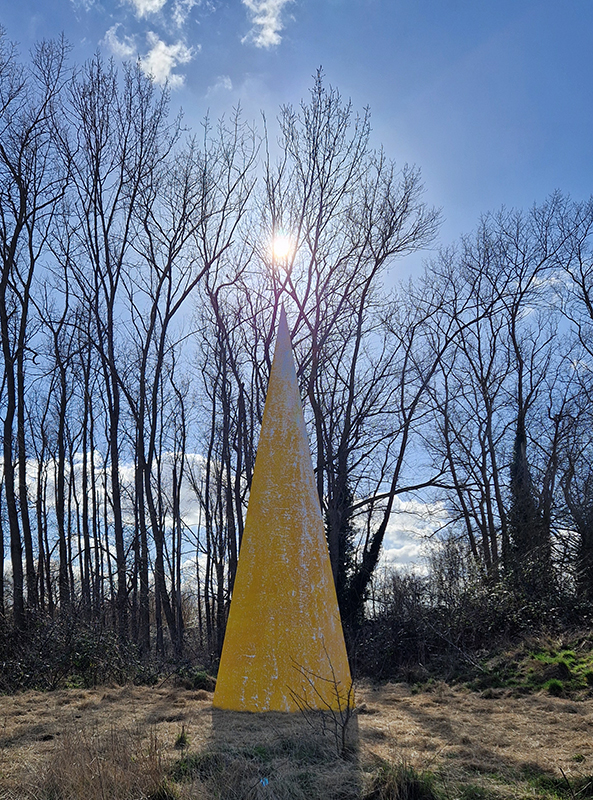
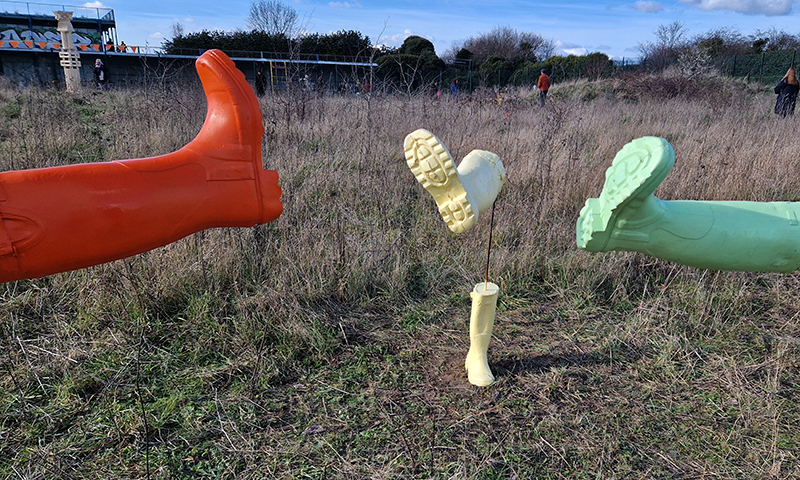
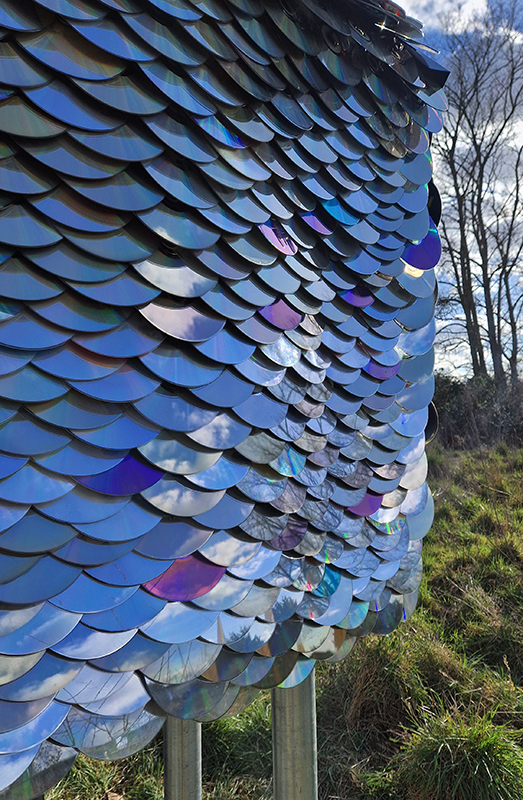







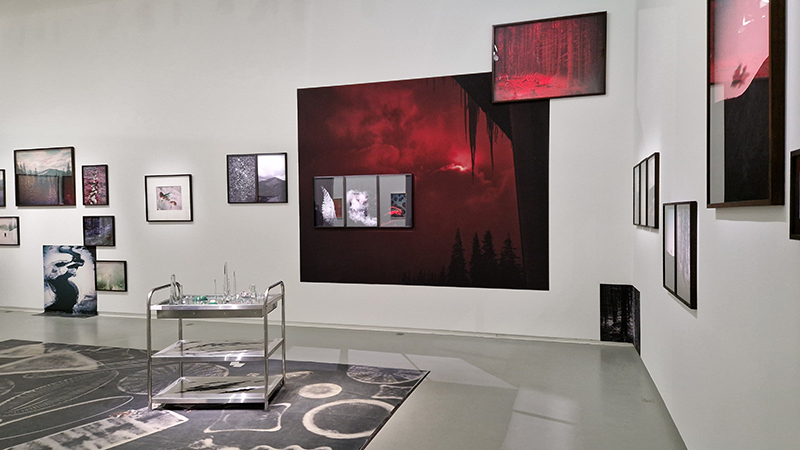
Clinging On, an exhibition of wall based sculptures curated by Poppy Whatmore at Glassyard Studios SW9. Instability is growing across the world, as we cling to liberal norms, ideas and values; these works connect a feeling of uncertainty to the physical, defying a gravitational pull or some internal force. These are physical, material or conceptual investigations of precariousness and the accompanying need to hold on. A packed PV means I have few images but I did capture the excellent Ocean Chasms/Crystal Chasms by Julie F. Hill and Caught Moon by Jane Millar.
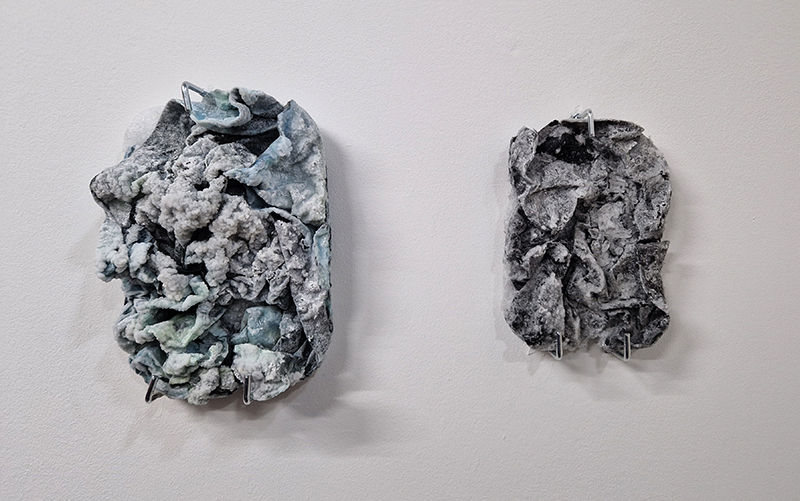


Moving Landscapes at Jeu de Paume, Paris. This exhibition brings together photography, literature and science to address environmental questions but also those of identity or migratory flows; the landscape thus becomes a living and constantly changing territory. Artists include Mounir Ayache, Julian Charrière, Edgar Cleijne, Ellen Gallagher, Yo-Yo Gonthier, Laila Hida, Eliza Levy, Julien Lombardi, Andrea Olga Mantovani,Mónica De Miranda, Richard Pak, Mathieu Pernot, Prune Phi, Léonard Pongoa and Thomas Struth.
















Events
More Life By Lauren Mooney and James Yeatman at Royal Court Theatre. Asking the question ‘what is life?’ but also what is the quality of life you would accept if you discovered you were a computer file. What constitutes real human experience? A brain sliced, scanned and rebuilt in the future to be transplanted into a new synthetic body holds memories of a past life and feels emotion but has limited access to new physical sensory experience – no need to eat or sleep. Does the urge to live, live on? Is it possible the first person to live forever has already been born?


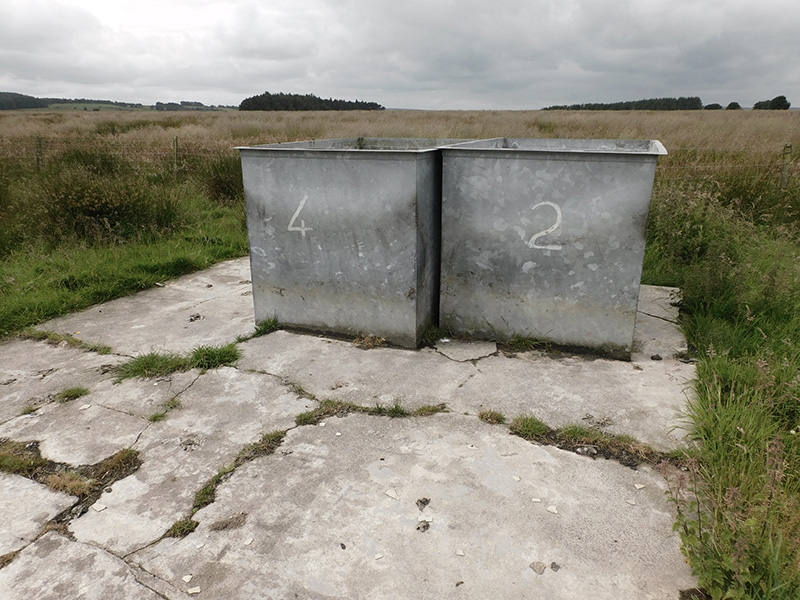
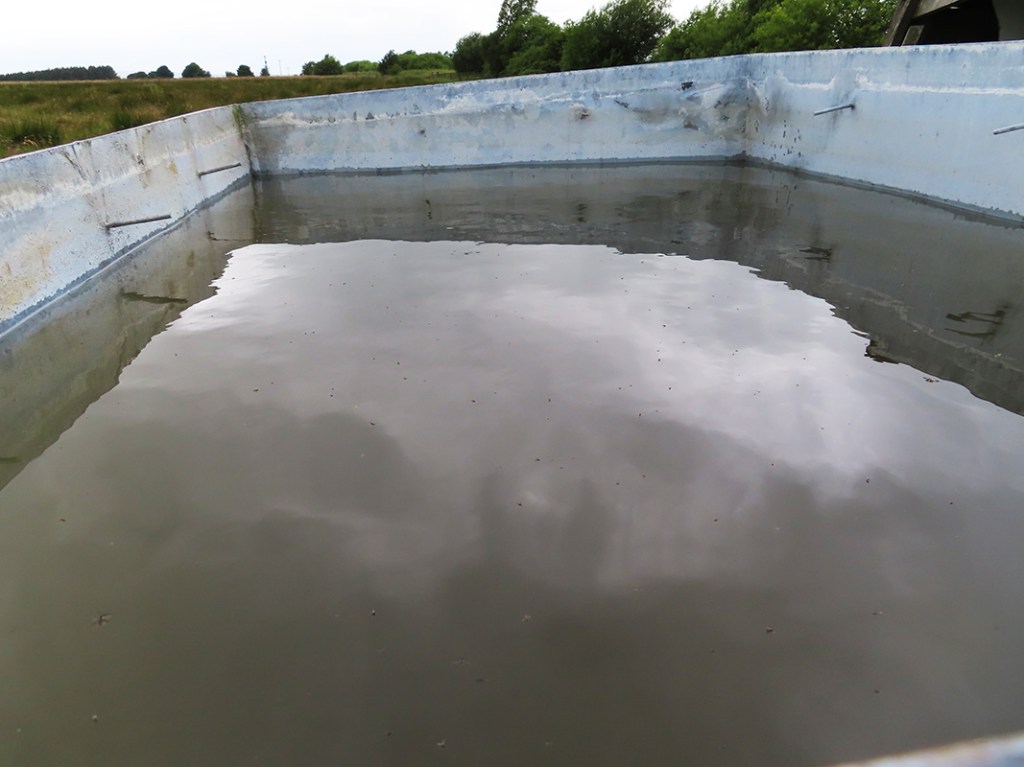
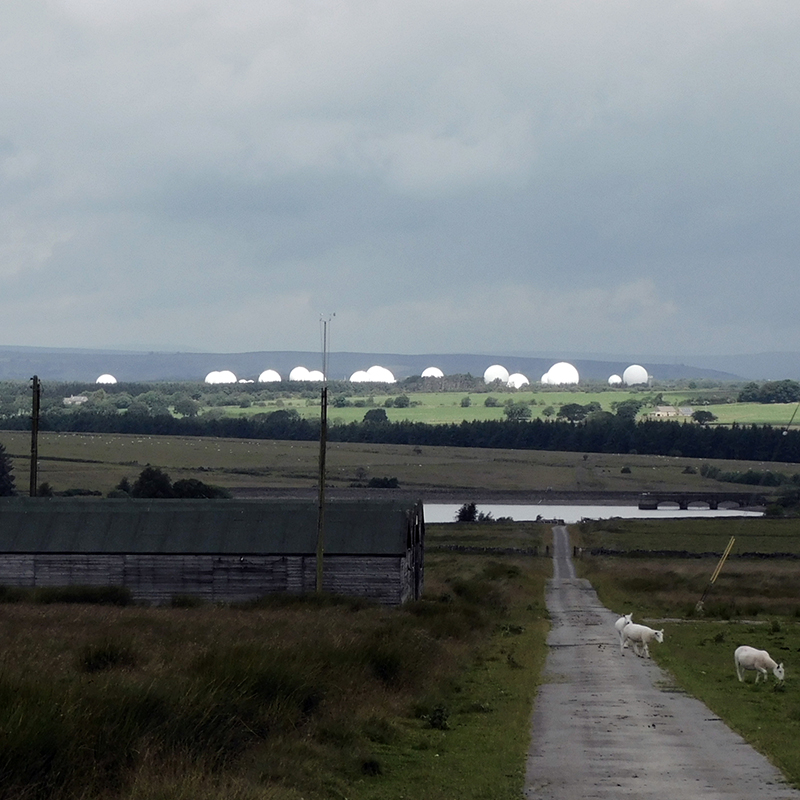
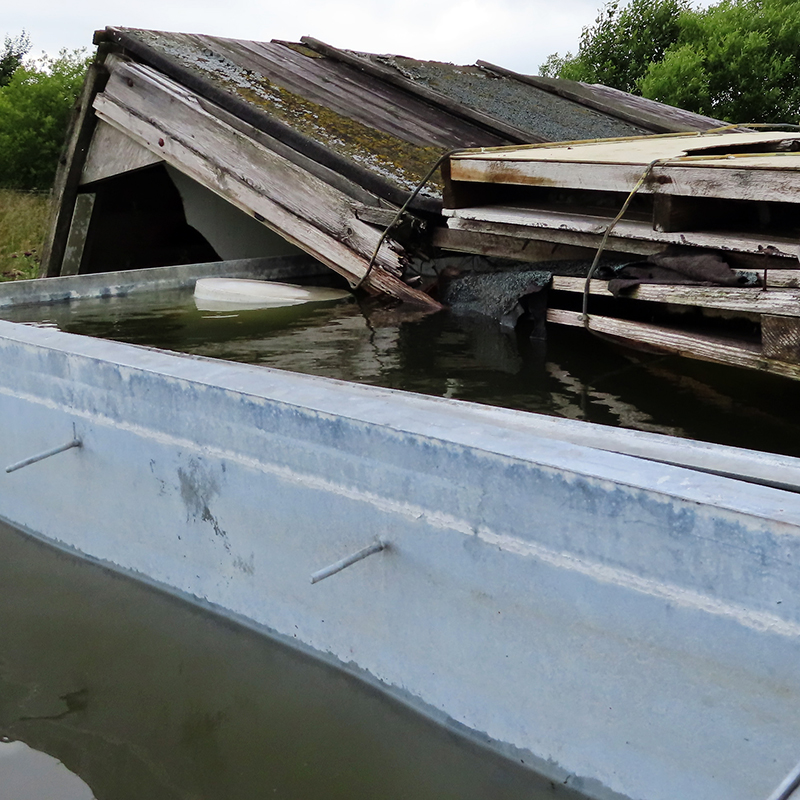
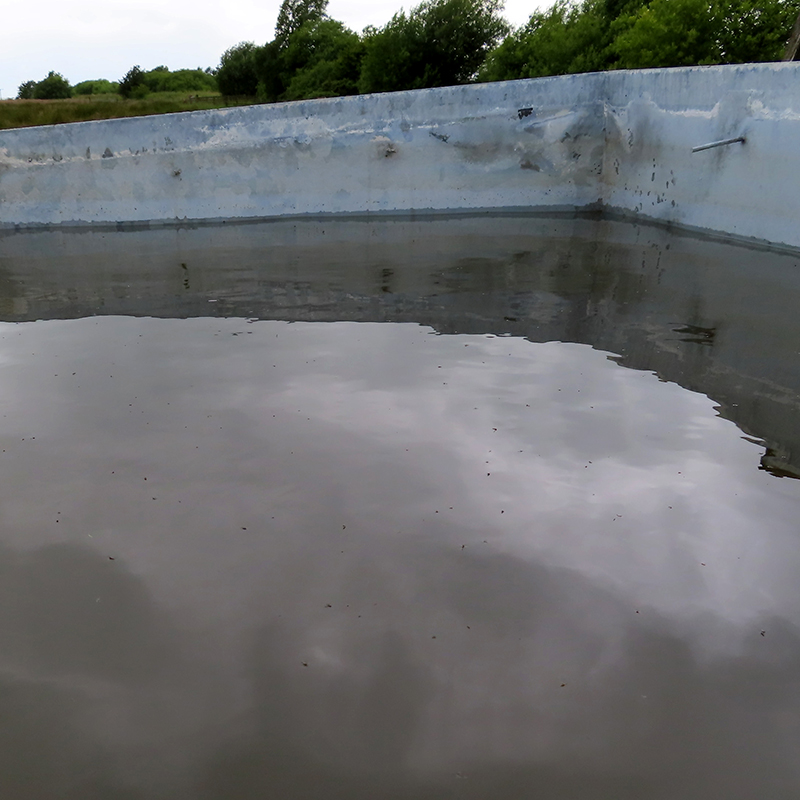
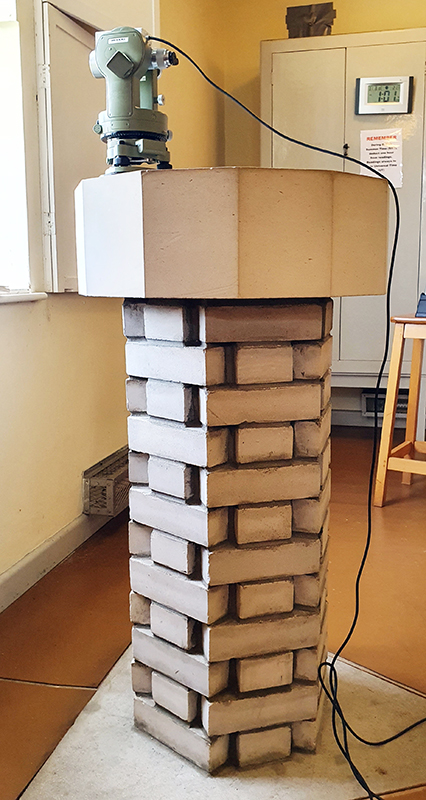
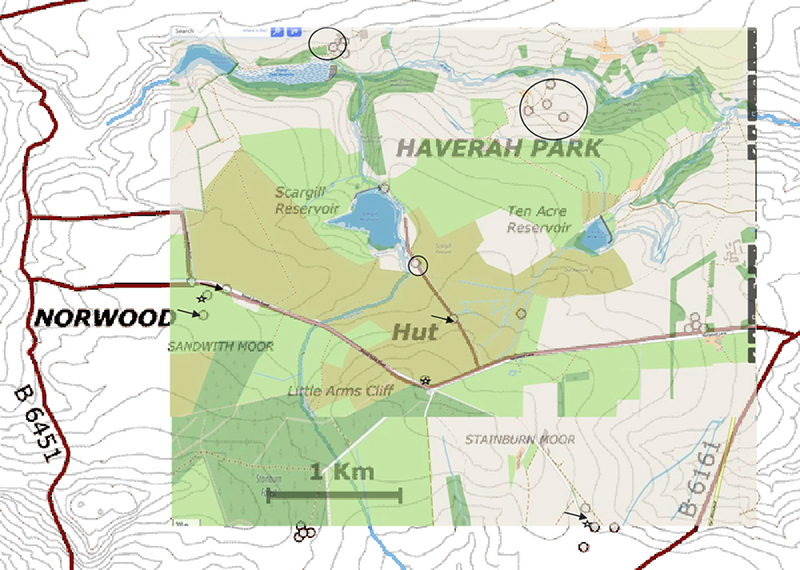
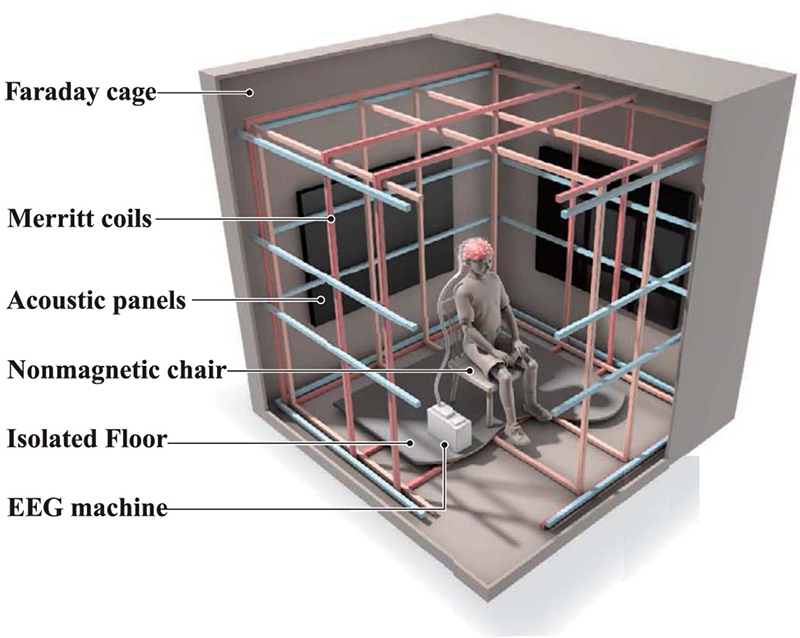
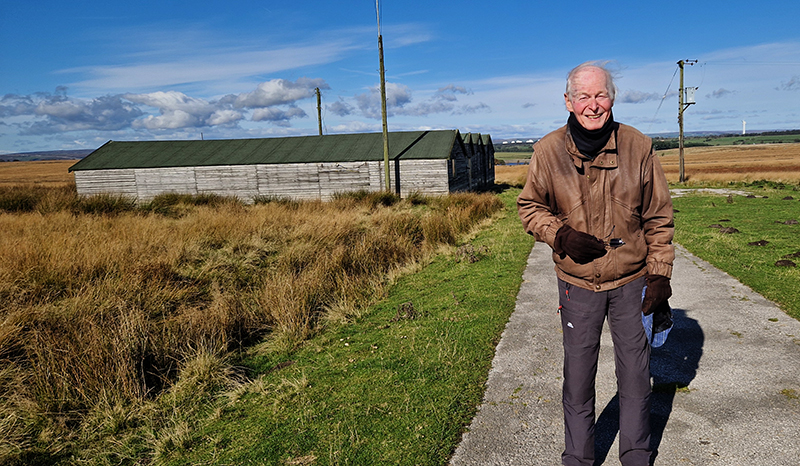
Great to see Alan Watson again, after visiting Haverah Park with him last year, to hear more about Searching for the Origin of the Highest Energy Particles in Nature. This water being sampled in the image below had been in the tank for nearly 30 years yet was still clear and drinkable.


He began his lecture at The Royal Astronomical Society with a short history on the discovery of cosmic rays, taking us right back to 1785 and Charles-Augustin de Coulomb who discovered that bodies with like electrical charges repel and if they have different signs, the force between them makes them attract. In his experiments testing electrical charge with two metal balls suspended on silk threads to easily repel or attract he was surprised to find that even if his experiment was very well insulated the charge still leaked away. It took over a century before it was realised that the air was being ionised which spurred physicists to discover the source of this ionization. In 1912 Victor Hess made his famous balloon flight to over 5km with a rudimentary Geiger counter and no oxygen to discover that ionization increased with altitude and must have an extra-terrestrial source. Over another century on and cosmic rays still present a mystery as to their origin and how they gain their enormous energies.
Alan is interested in the ultra high energy subatomic particles from extragalactic sources with energies about a million times as high as the energy reached by human-made particle accelerators. To put these energy scales in context – a laser pointer has an energy of about 3 electron volts, which is also typical of the photons that come from the sun. The molecules in the air are rushing around at 300m per second with an energy of 1/40 eV. A low energy cosmic ray, the sort that passes through your body a million times in a night, has an energy of 1 giga-electron volts, a proton created at CERN ( the European Organization for Nuclear Research) has around 7 tera-electron volts. If there was a race between a CERN proton and a high energy cosmic ray (over 1018 eV ) starting at the centre of the galaxy, by the time the cosmic ray had reached Earth the CERN proton would not even have reached the moon.
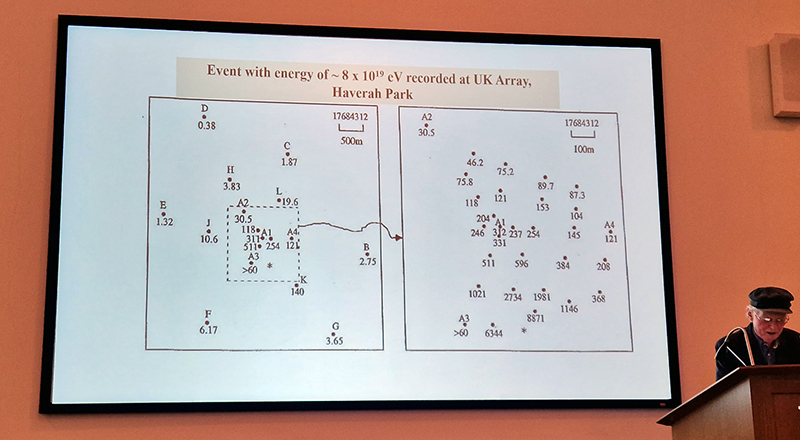
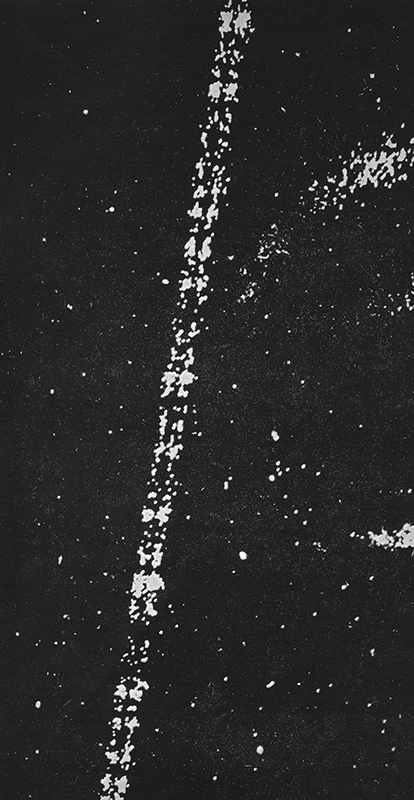
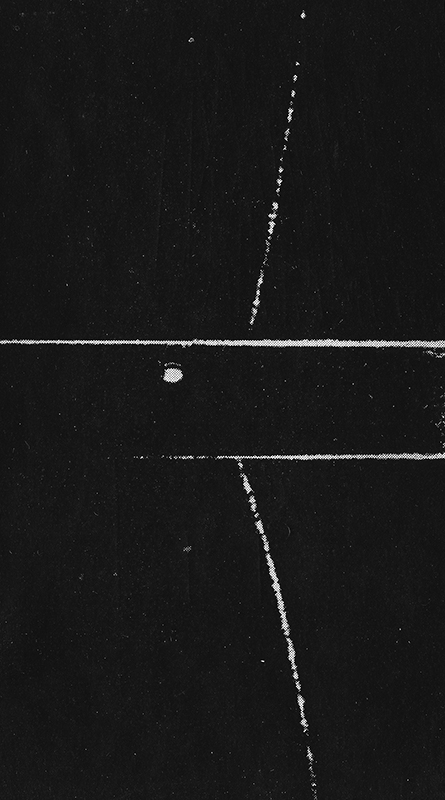
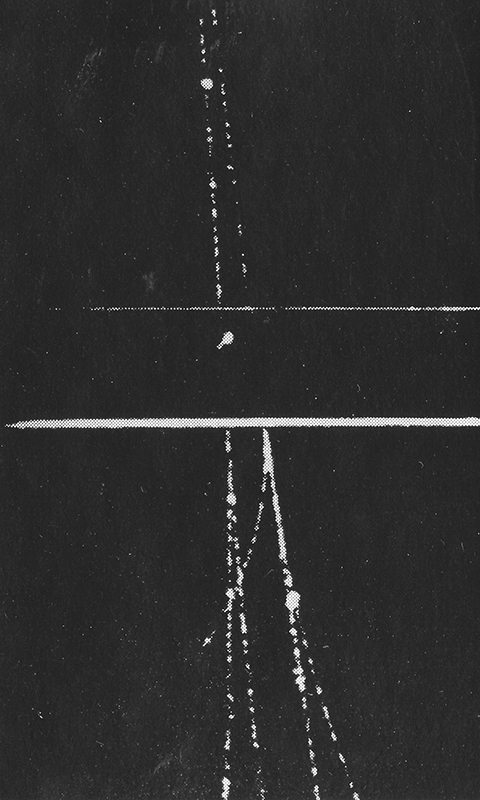
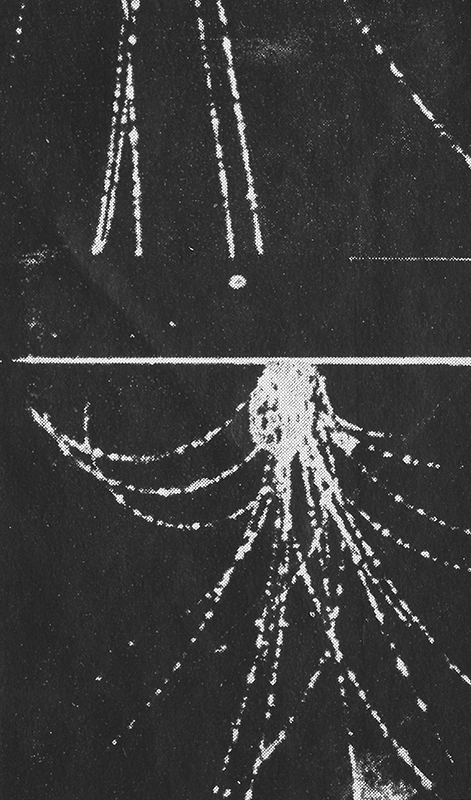
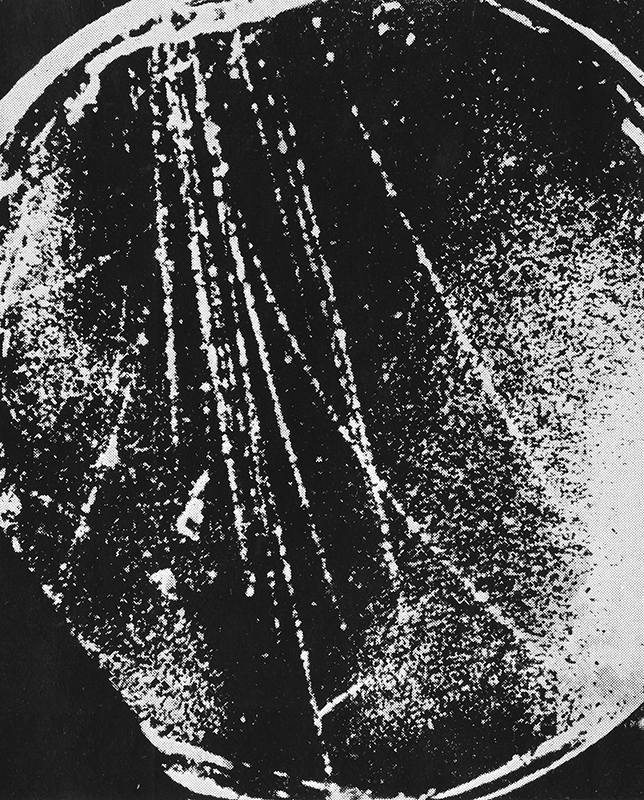
The ultra high energy rays are very rare. To detect these particles physicists rely on observing extensive air shower arrays to amplify the arrival of the particle. By recording the secondary particles that are produced when a cosmic ray hits the upper atmosphere the energy of the particle can be calculated. The showers arrive is a disc like formation with footprints of around 1sqkm so it is necessary to have detectors spread over a large area. The detectors measure the arrival time of the secondary particles and this can help determine the direction of the particle to within 1 degree. The trajectory of the cosmic ray is affected by galactic and intergalactic magnetic fields making it very difficult to find the origin of the particle.
The shadow of the moon can be seen in data recordings of cosmic ray arrivals.
There are a few different methods of detecting cosmic rays. This can be done using scintillator plastic which gives off a flash of light when a particle passes through the medium. Using Cherenkov radiation is another method – this takes advantage of a naturally occurring electromagnetic shock wave giving off energy as light when a particle passes through a medium faster than light can travel through the same medium. The speed of light through water is only 3/4 as fast as when it passes through air, a cosmic ray with much more energy will travel through water at almost the speed of light. This phenomenon can even be seen with the naked eye if the location is dark enough. Astronauts experience flashes of light in the eyes from particles directly hitting the retina but also from particles passing through the vitreous fluid and causing Cherenkov radiation.
Another method is to detect the excitation of nitrogen, the same process that produces the aurora. This light is in the ultra violet spectrum.
By the end of the 1980’s when Haverah Park closed the discovery of the origin of high energy cosmic rays was still a long way off. What had been established was that at the very high energies, only one particle would fall within one km per century. To make further progress a much larger area of detection would be needed. The Pierre Auger Observatory in Argentina at 3000 sq km is about twice the size of Surrey with many hundreds of water tanks. These tanks hold 10 tonnes of water but are the same depth as those at Haverah Park at 1.3m which turned out to be the optimal depth for the water tanks. Charged particles generated during the development of extensive air showers excite atmospheric nitrogen molecules, and these molecules then emit fluorescence light. The Cherenkov detectors at Pierre Auger are supplemented by fluorescence detectors installed at four elevated observation sites with 24 large telescopes specialized for measuring the nitrogen fluorescence in the atmosphere above the array.

The most exciting discovery came in 2017 when a convincing anisotropy in the arrival direction of cosmic rays of a certain energy was determined with some evidence that Centaurus A might be a source of these cosmic rays. There was also evidence of particles clustering close to the super galactic plane, an enormous, flattened structure extending nearly a billion light years across.
The galactic year is the duration of time required for the Sun to orbit once around the centre of the Milky Way Galaxy equivalent to approximately 225 million Earth years.
Art After Dark cosmic takeover around Piccadilly and Leicester Square from Nelly Ben Hayoun-Stépanian. I saw the iridescent asteroid-sized moon rocks and inflatable UV reactive sculptures inspired by Schrödinger’s famous quantum physics paradox in bright sunshine
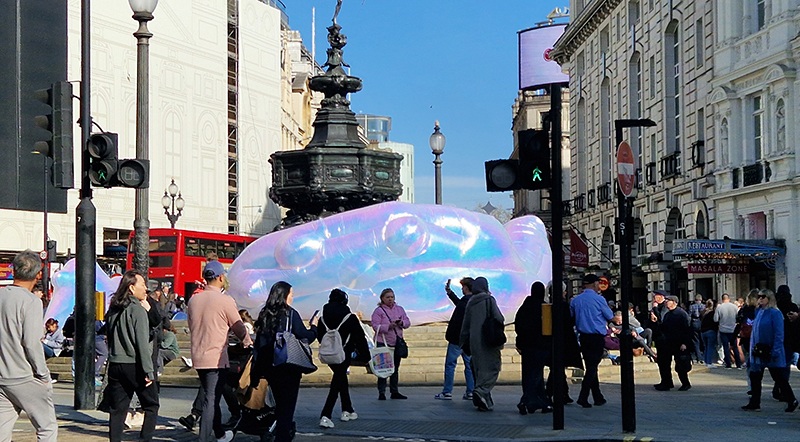
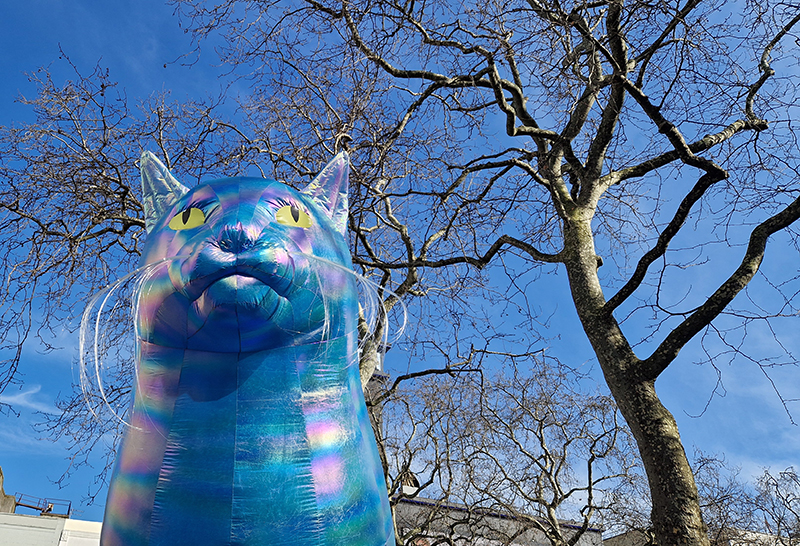





Book launch at Matt’s Gallery – Aqueous Humours Fluid Ground, edited by Kirsten Cooke published by Matt’s Gallery and the Poorhouse Reading Rooms. A night of experimental nonfiction, fiction, diagram, scent and moving image. An evening that activates a watery mapping, which denatures cartography through practices of immersion, aquatics, time travel and the posthuman lenses of geological, animal and machine vision. With contributions from Linda Stupart, Harun Morrison, Ezra-Lloyd Jackson, Melanie Jackson, Joseph Noonan-Ganley, Charlie Franklin, Michelle Williams Gamaker, Lucy A. Sames, Maggie Roberts, Carl Gent. I was only able to stay for the first half of the evening but this gave a wonderful flavour of the book which I look forward to dipping into.


Listening
Journey to the Centre of the Earth – an Infinite Monkey Cage podcast with guests seismologist Ana Ferreira, geologist Chris Jackson and comedian Phil Wang. The immense pressures and searing temperatures that present engineering difficulties of ‘going into the Earth’s crust’ to explore what lies beneath are discussed along with the relationship between the tectonic plates and a stable atmosphere and new evidence of hidden subterranean shifting globular continents.
Reading
The Periodic Table by Primo Levi. My initial reaction to this book was surprise that it was so engaging, but a few elements in, I was surprised to find the chapters shifted from autobiography to fiction with dubious and misogynistic content. I have persevered as the chapter on Carbon, which was recommended to me, is the last chapter in the book and I thought I should start at the beginning not the end. This final chapter is written with a different emphasis, with the explanation that carbon cannot be treated like other elements as it is not specific to one story but is everything to everyone. ‘Every two hundred years, every atom of carbon that is not congealed in materials by now stable (such as, precisely, limestone, or coal, or diamond, or certain plastics) enters and renters the cycle of life, through the narrow door of photosynthesis.’ The story of one atom of carbon is relayed but it is noted that the author ‘could tell innumerable other stories and they would all be true…. the number of atoms is so great that one could always be found whose story coincides with any capriciously invented story’.