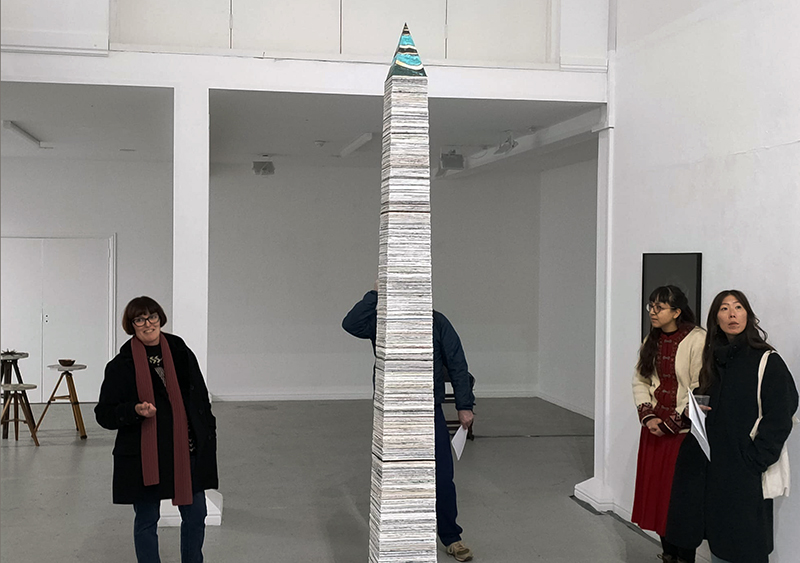
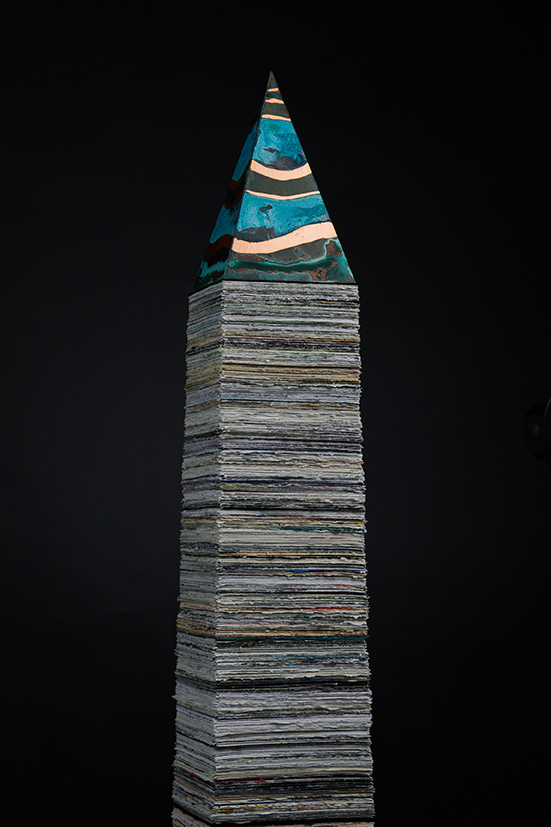
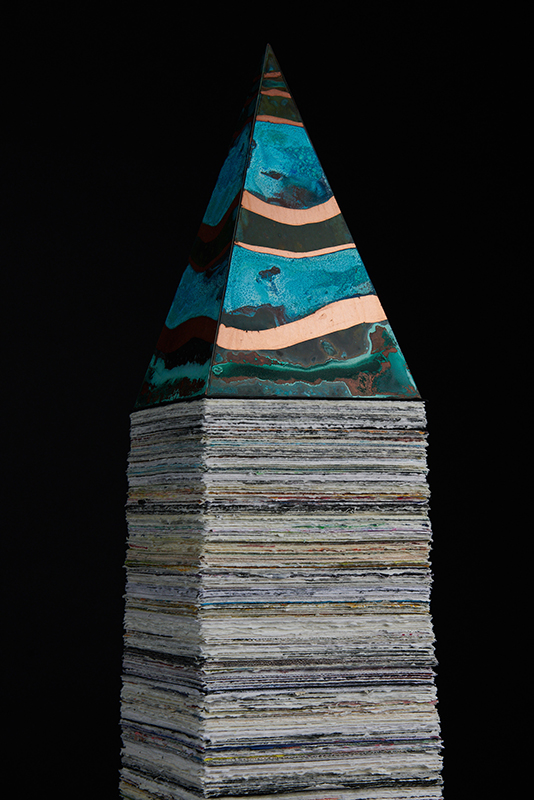
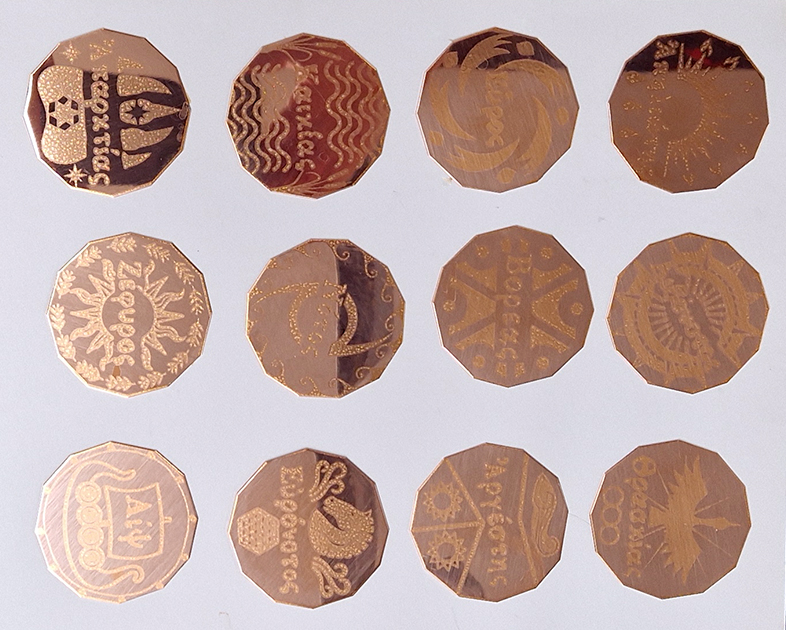
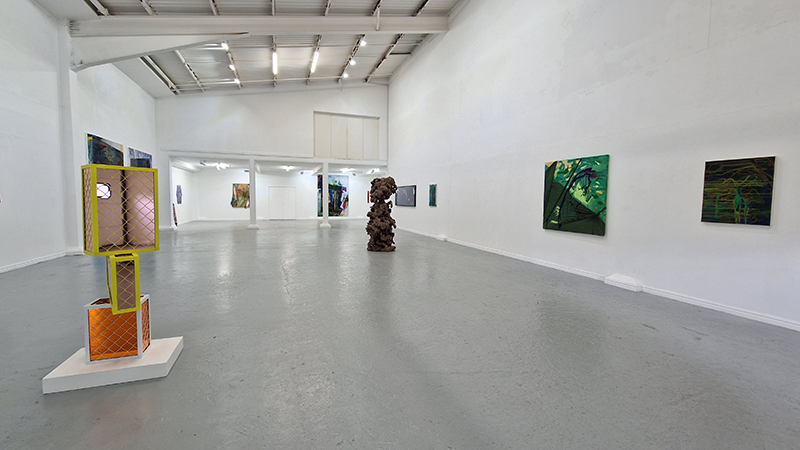
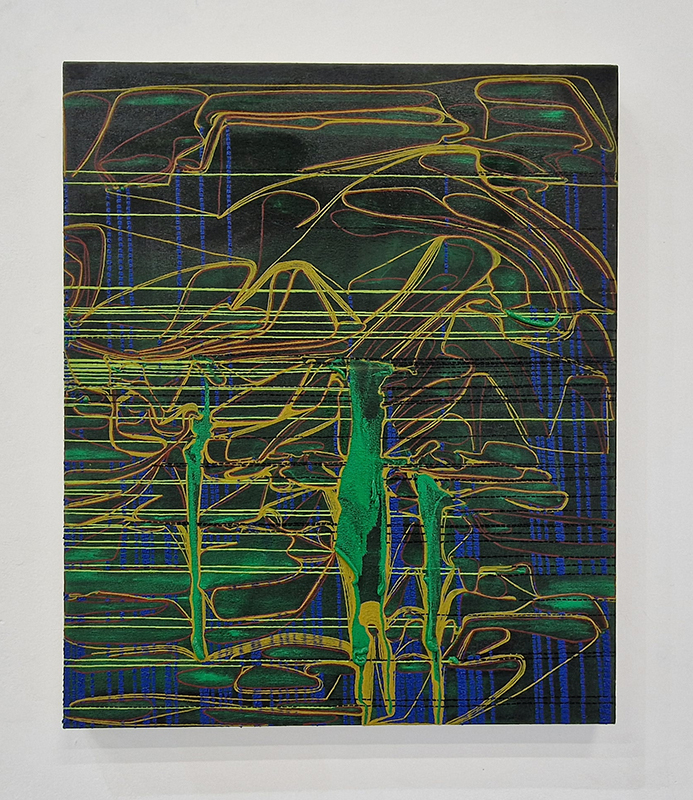
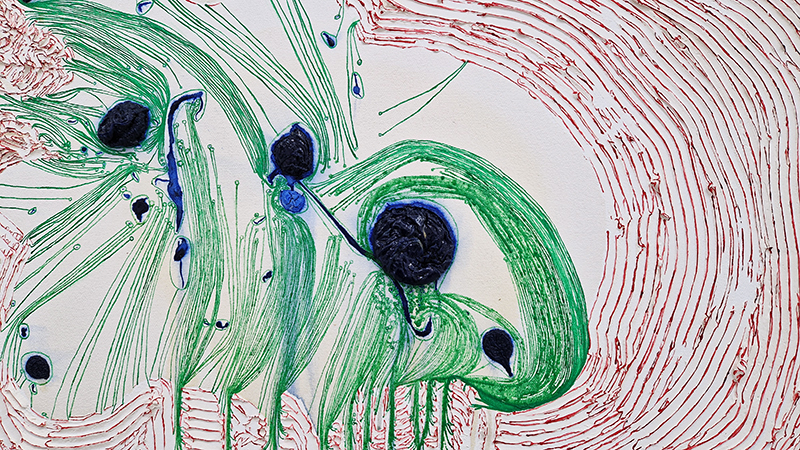
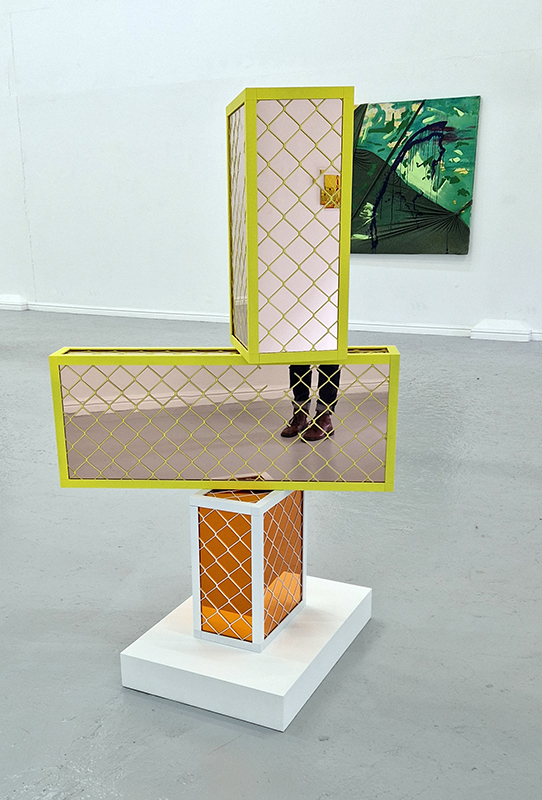
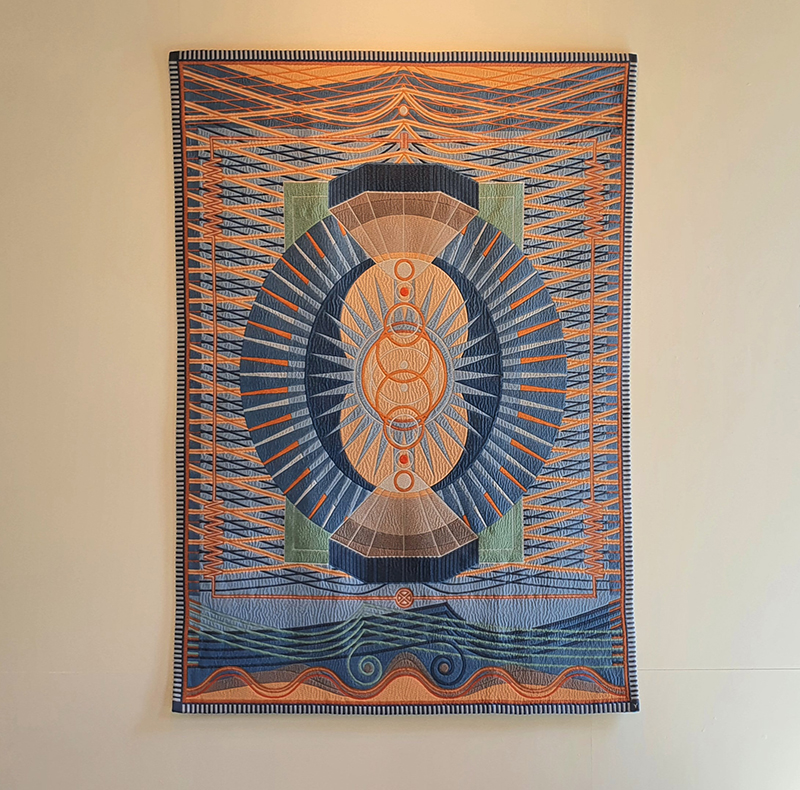
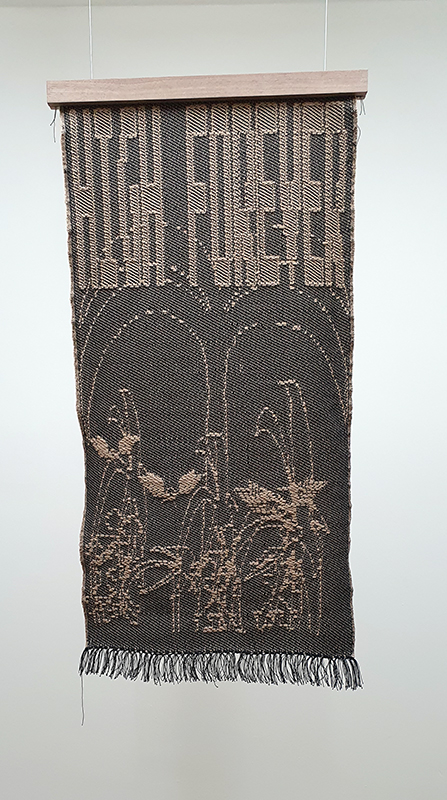
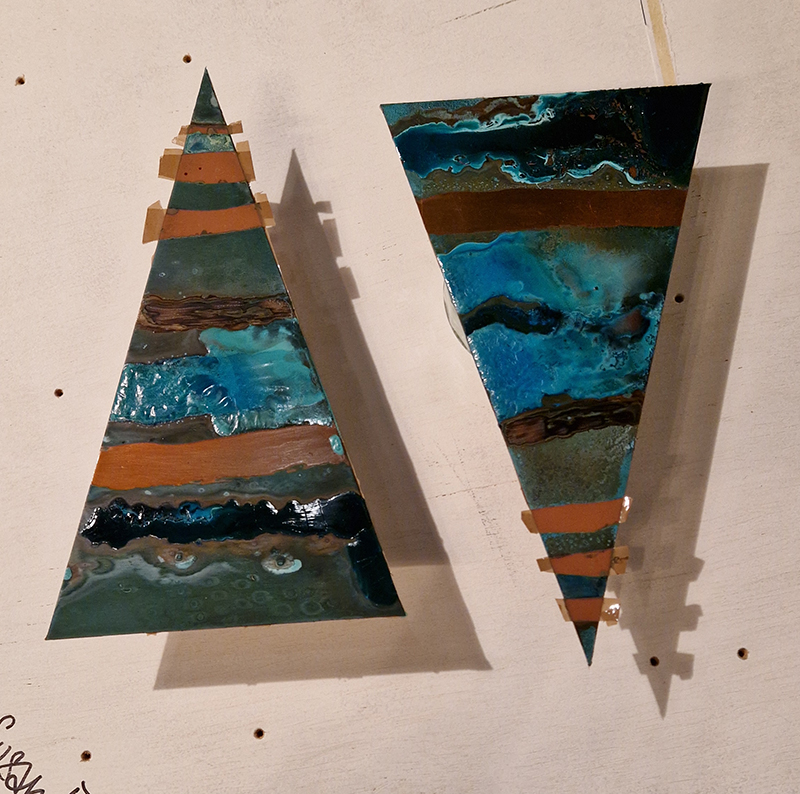‘What truth could be more unexpected ….than the one in which the mineral envisions while also being envisioned.’ Jason Groves, The Geological Unconscious
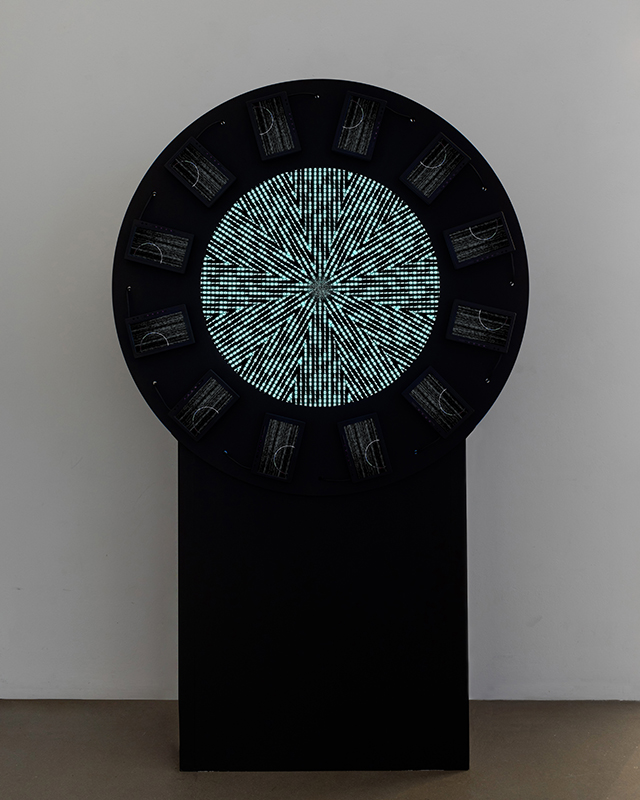
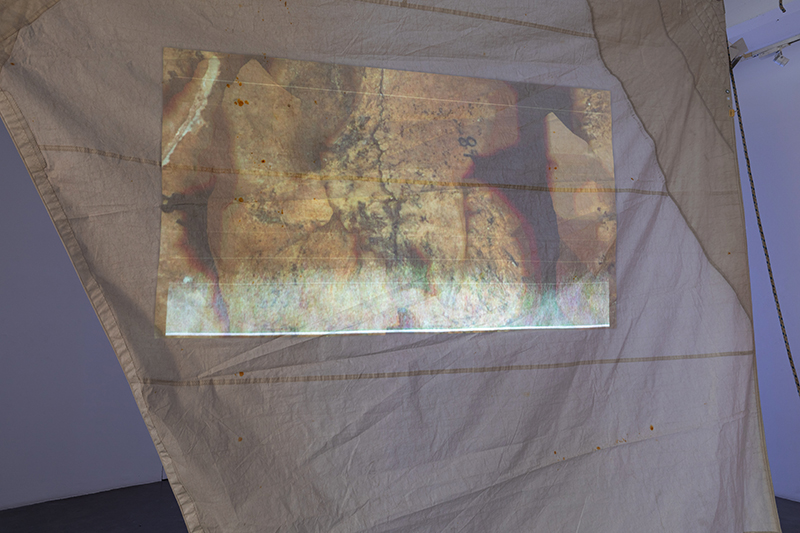
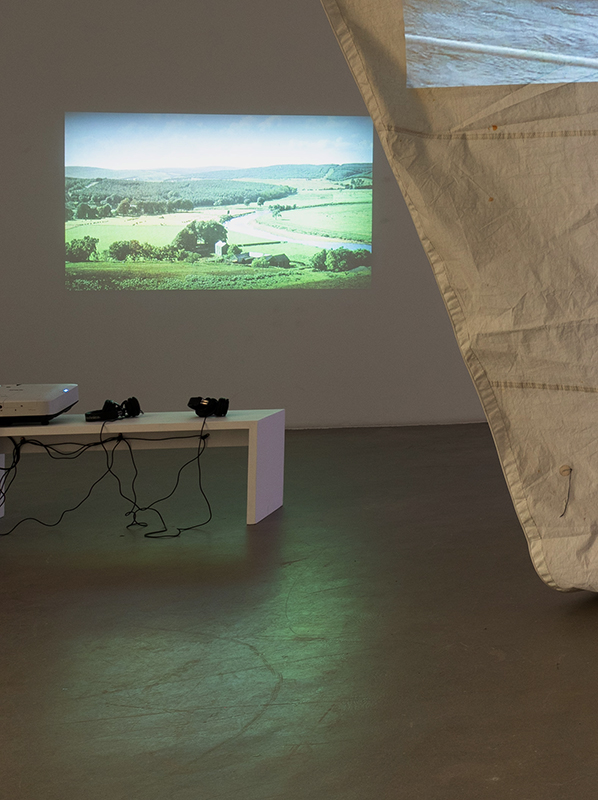
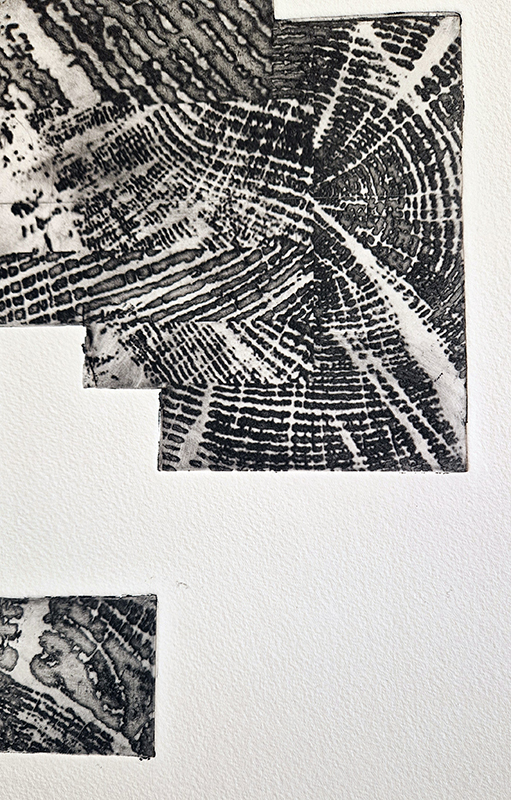
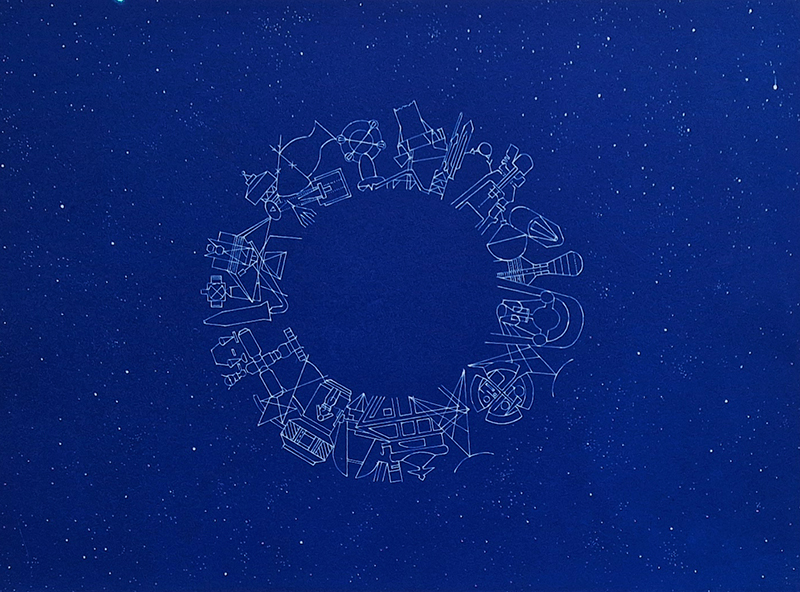
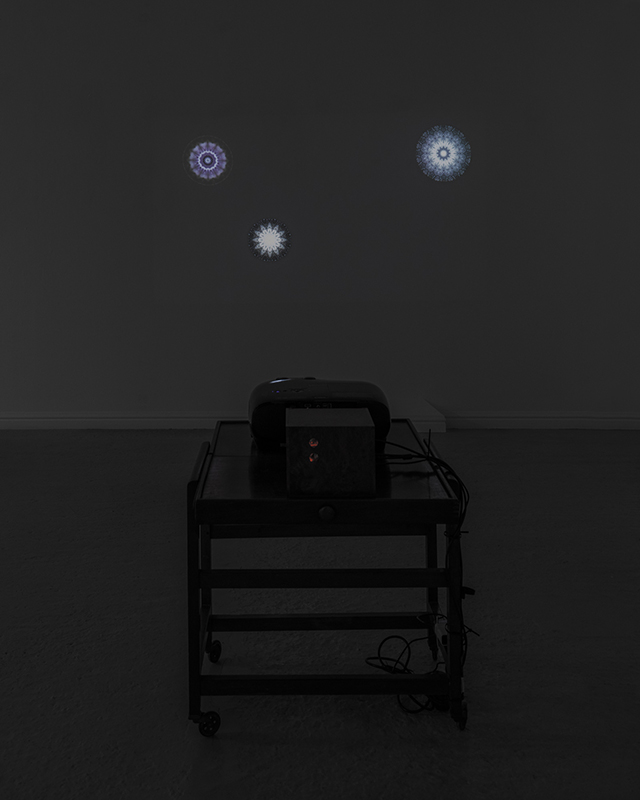
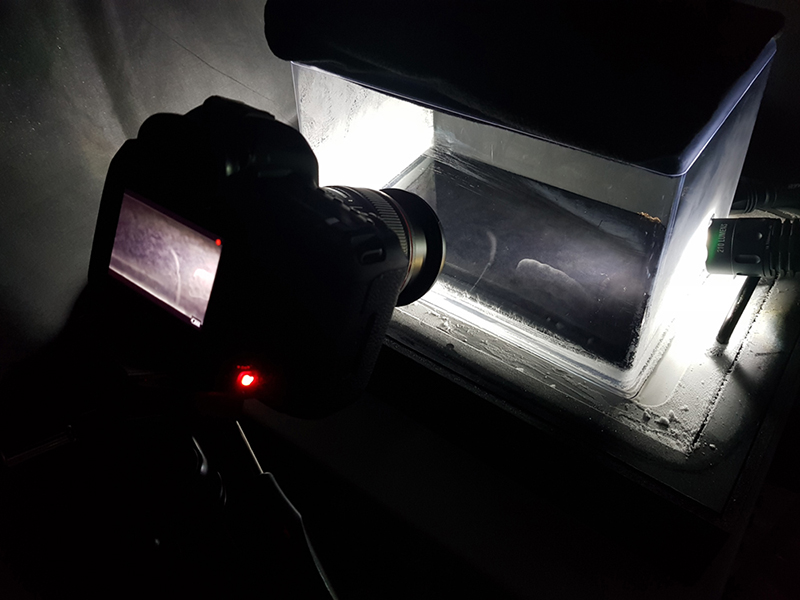
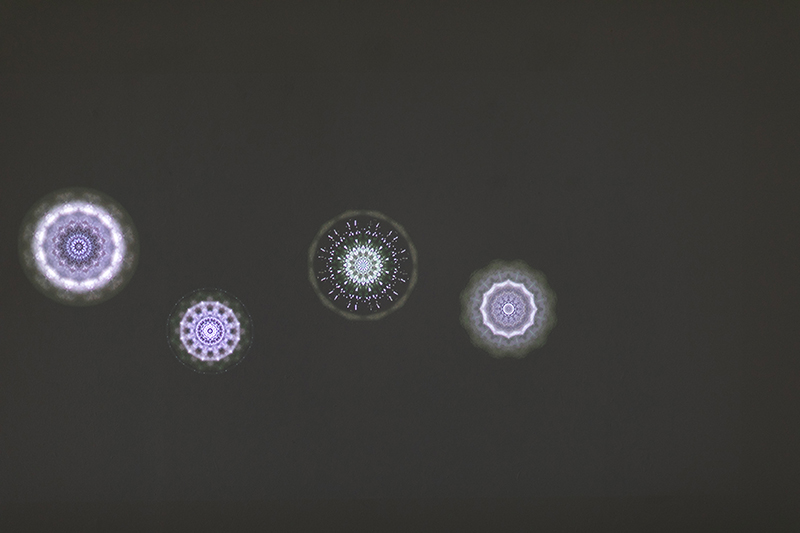
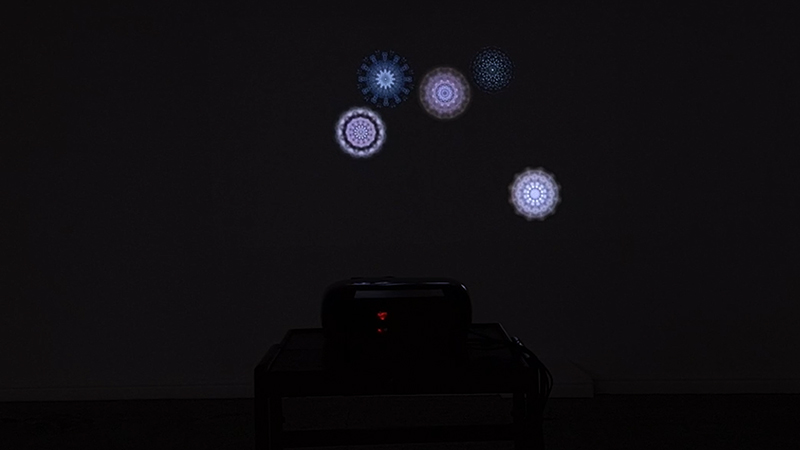
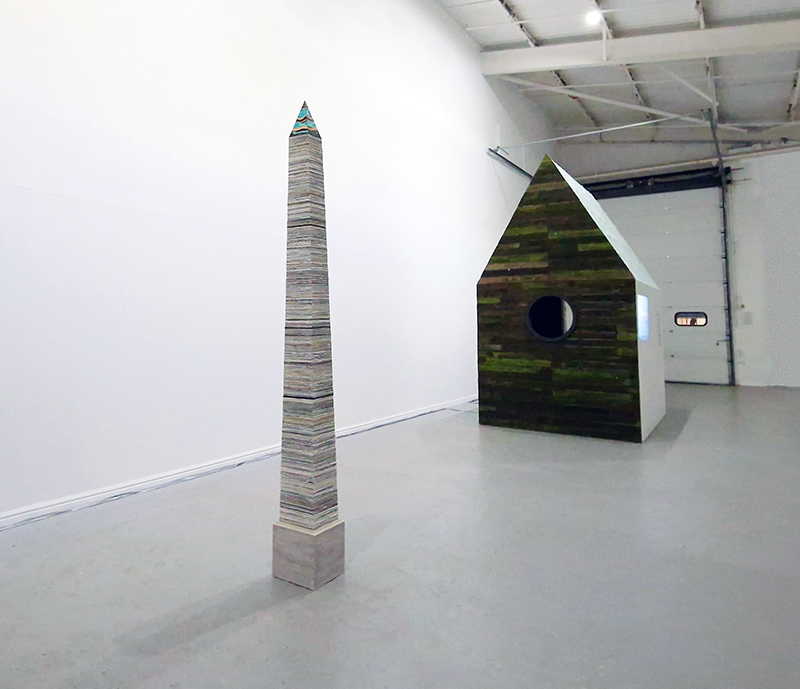
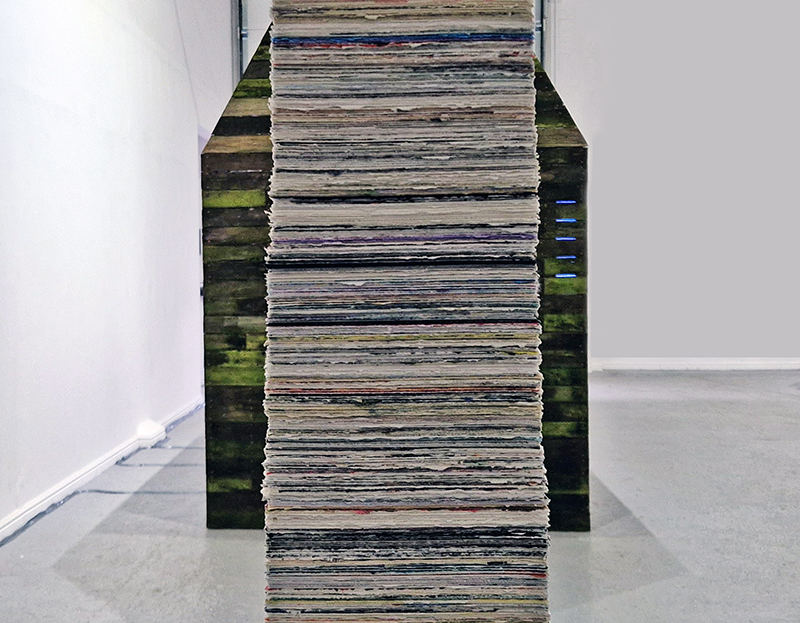
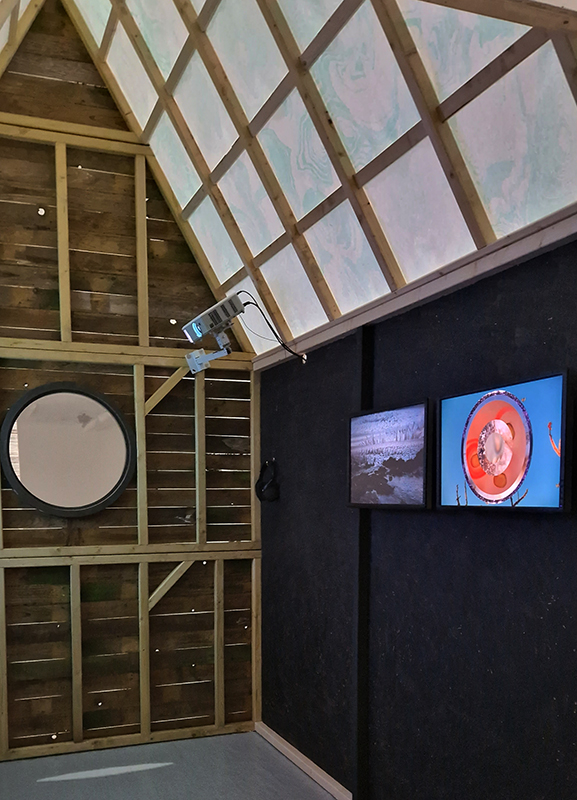
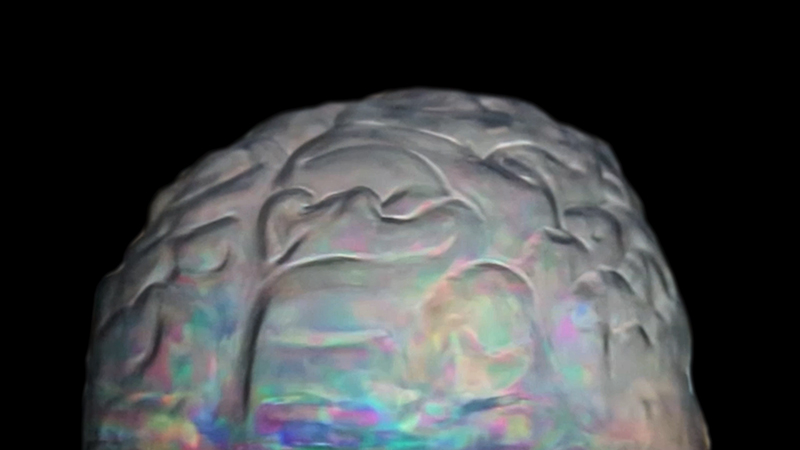
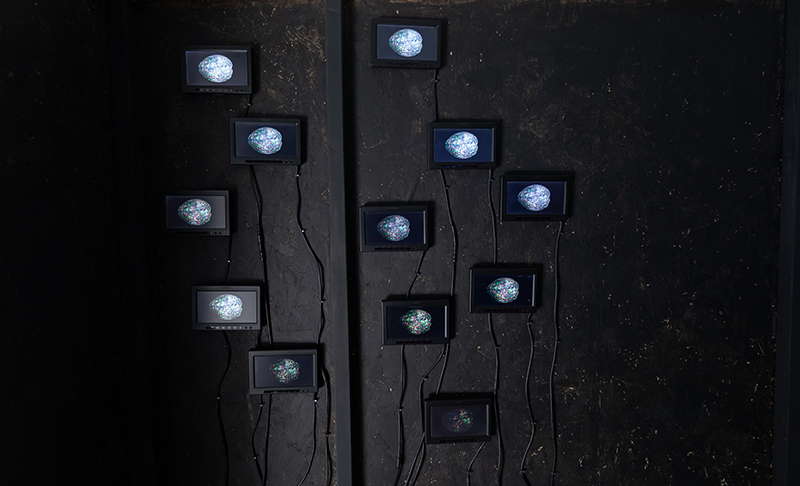
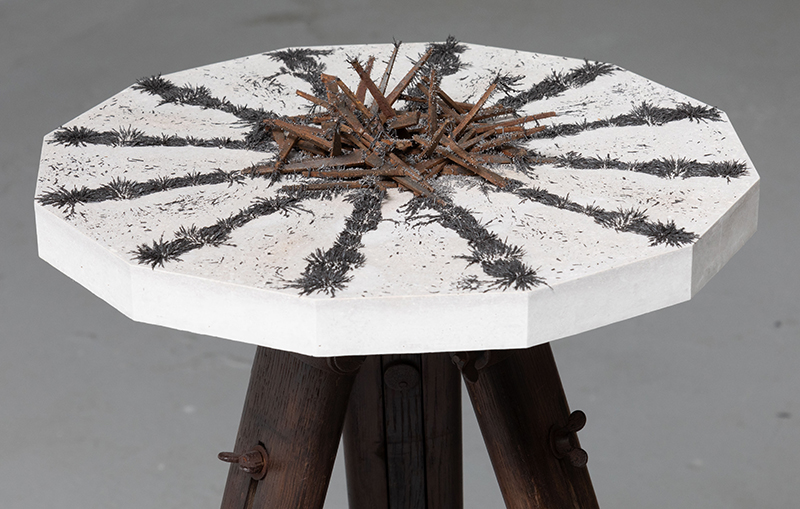
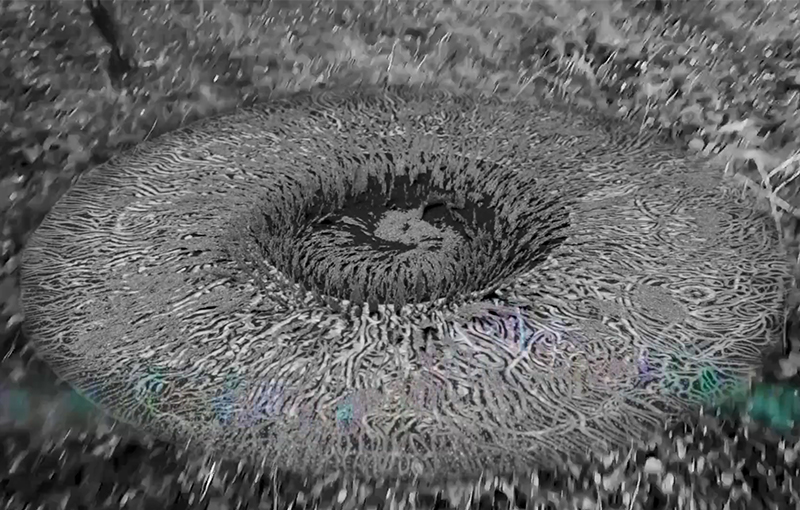
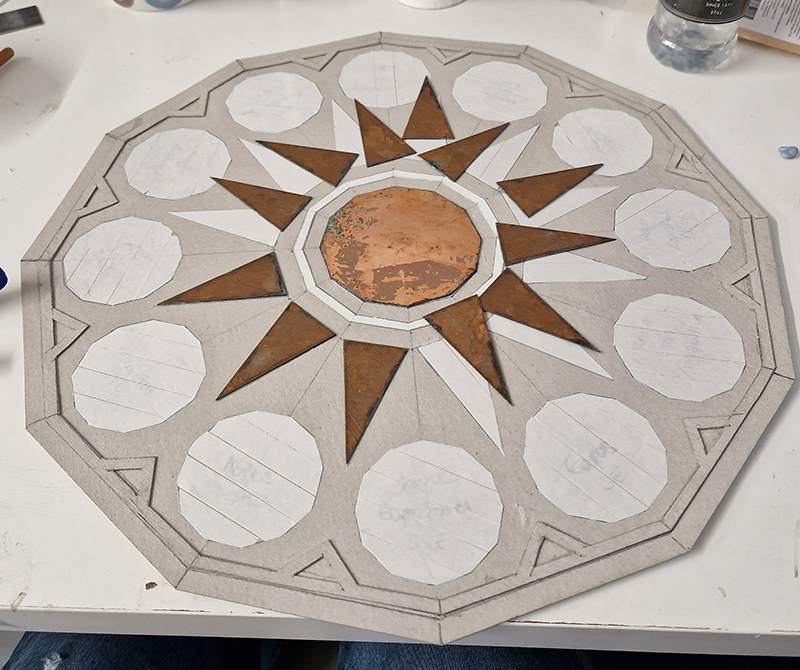
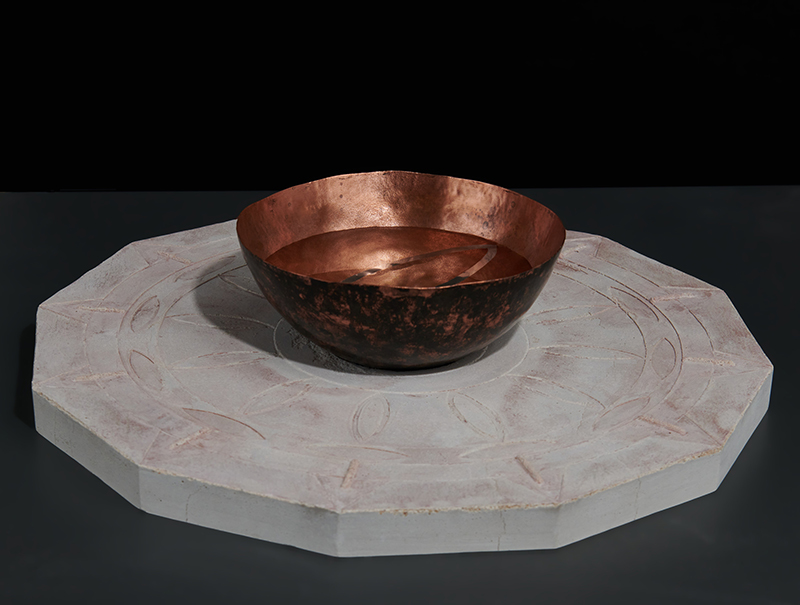
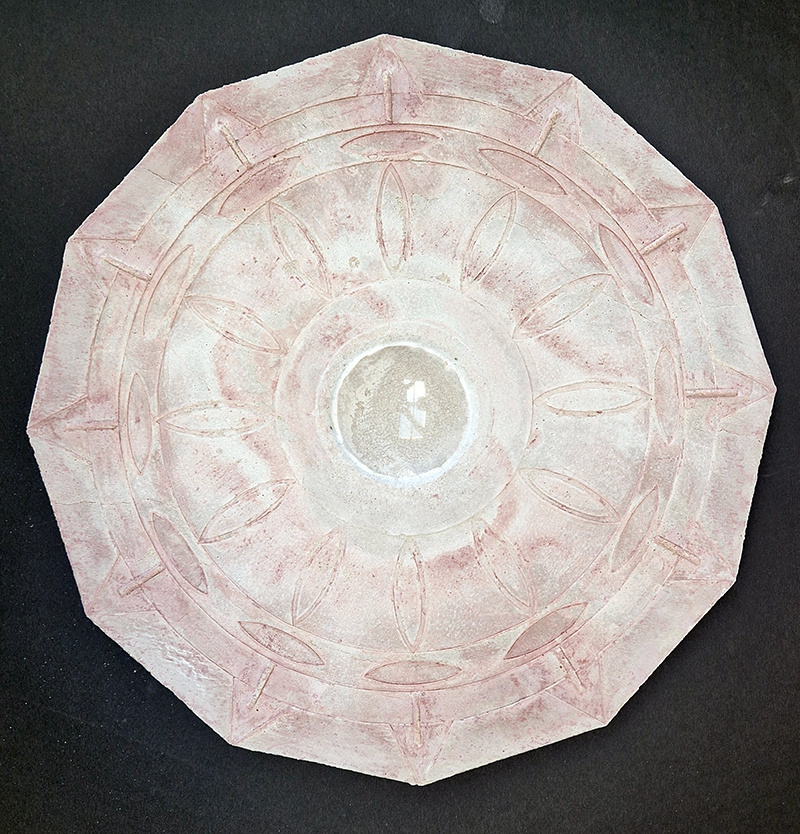
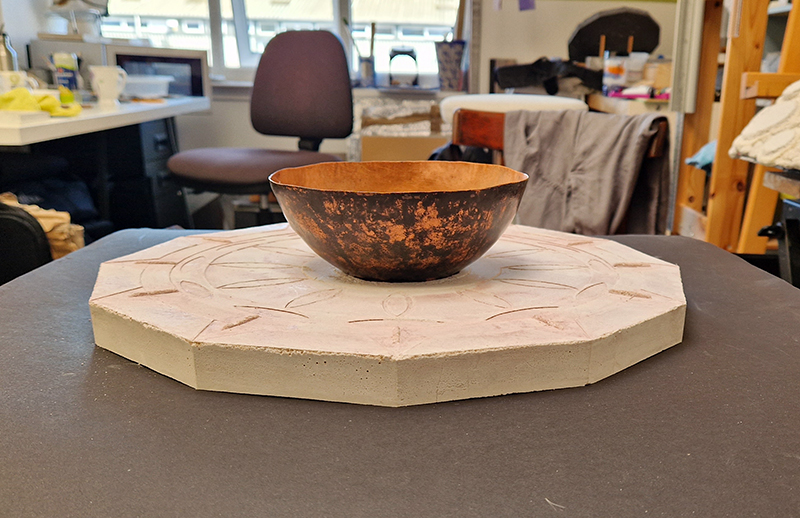
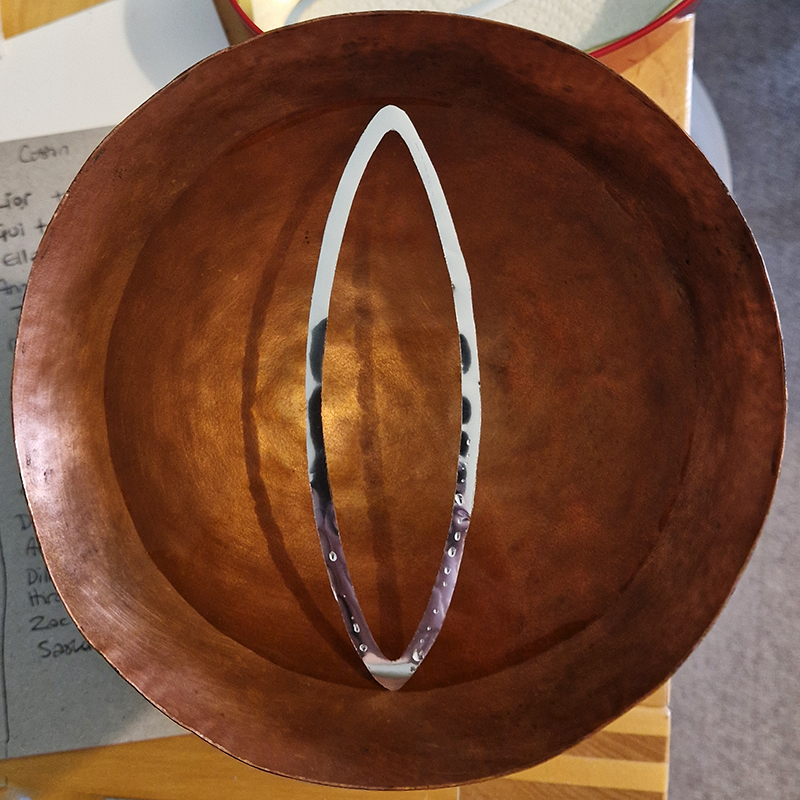
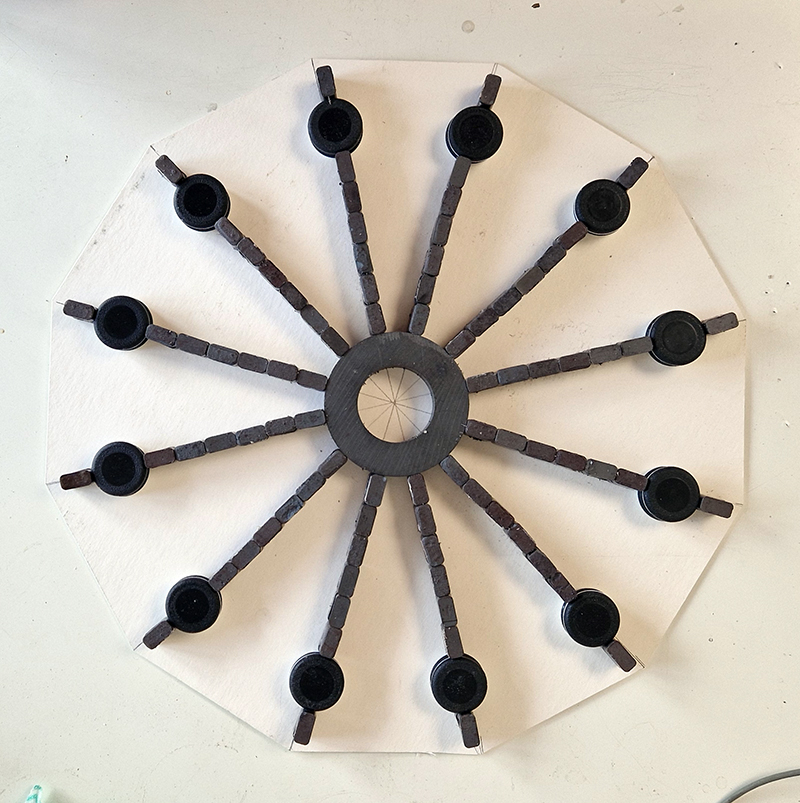
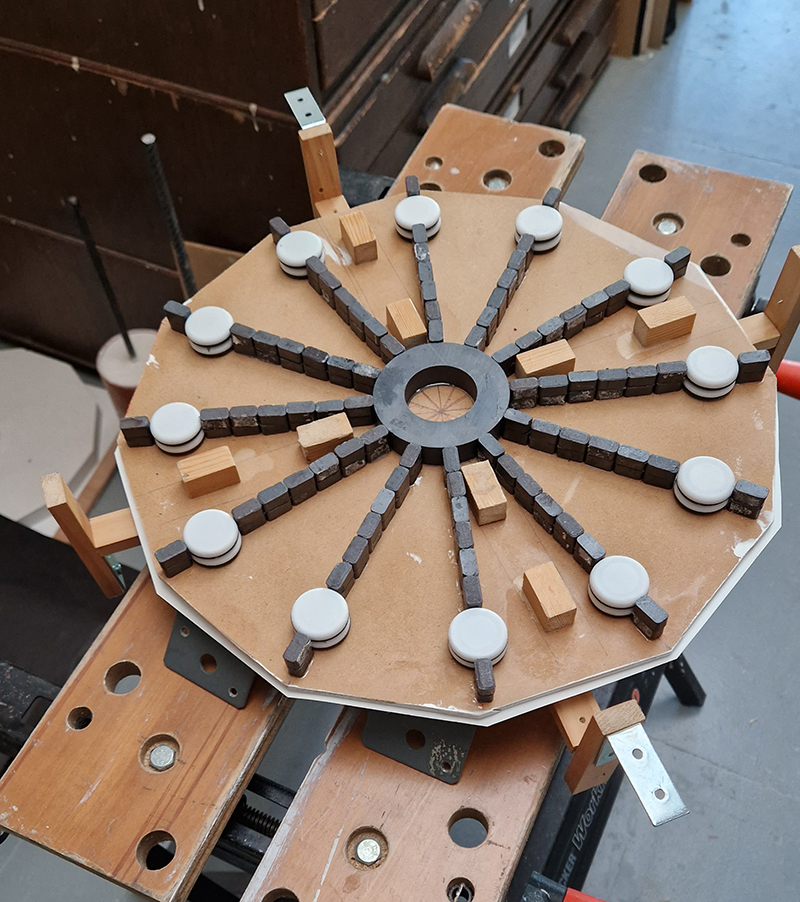
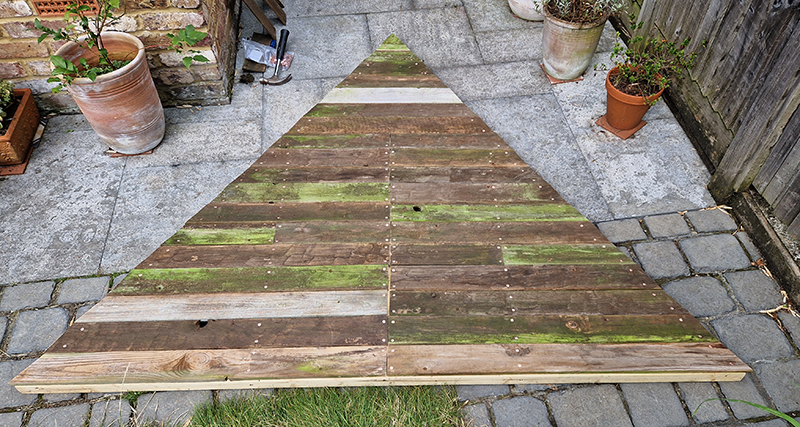
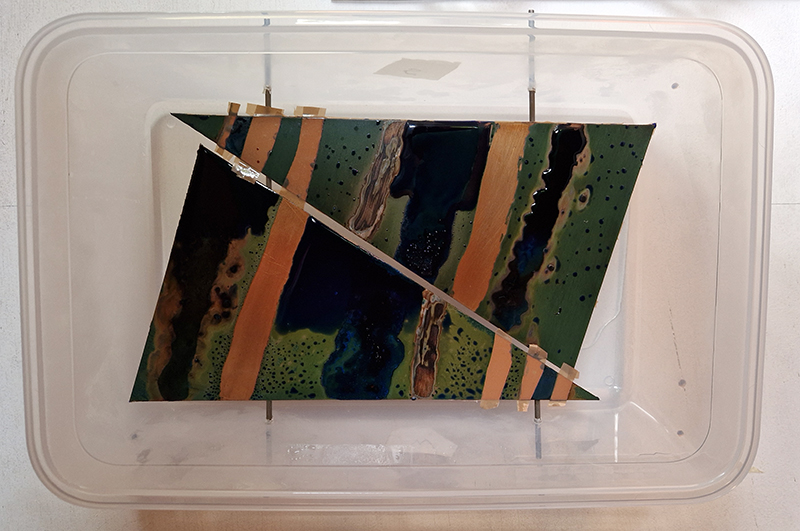
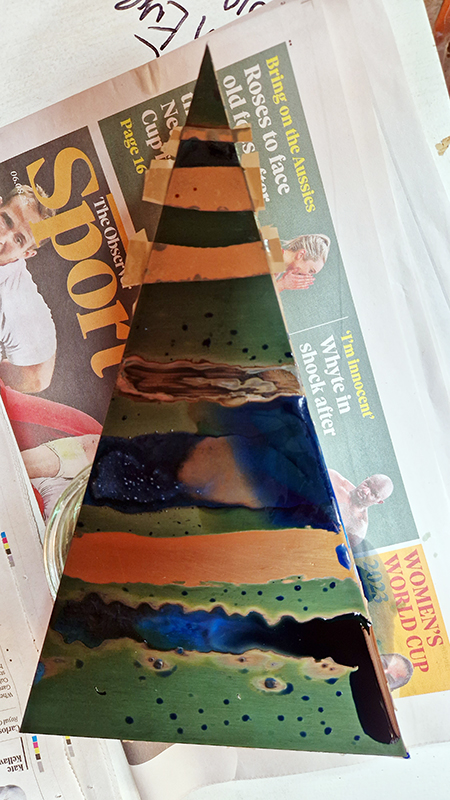
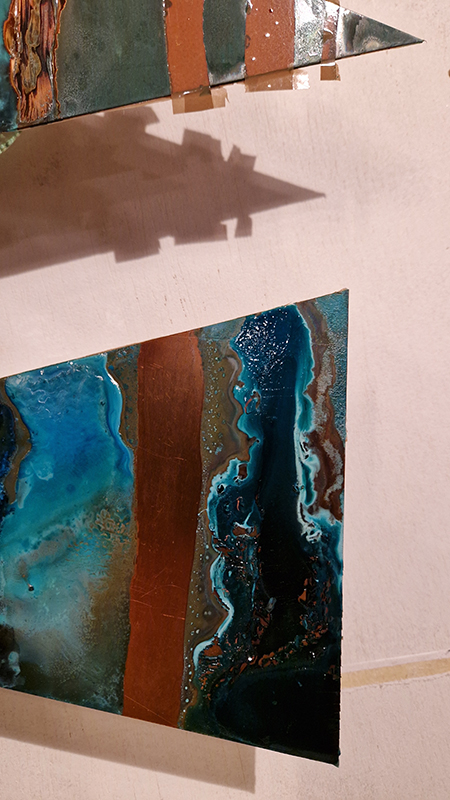
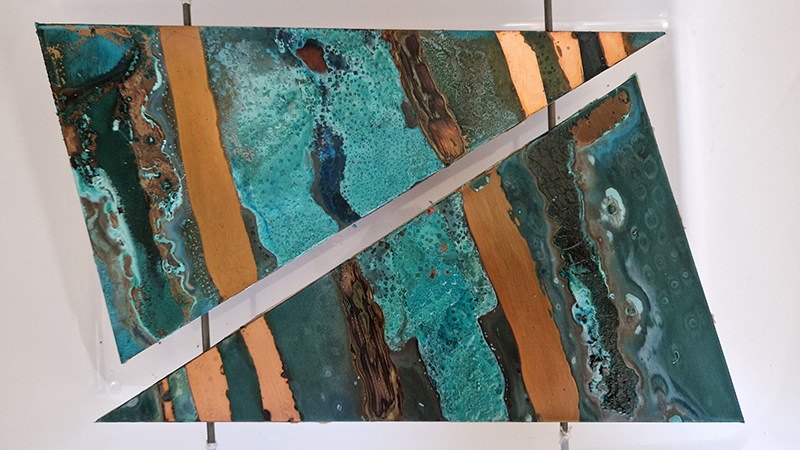
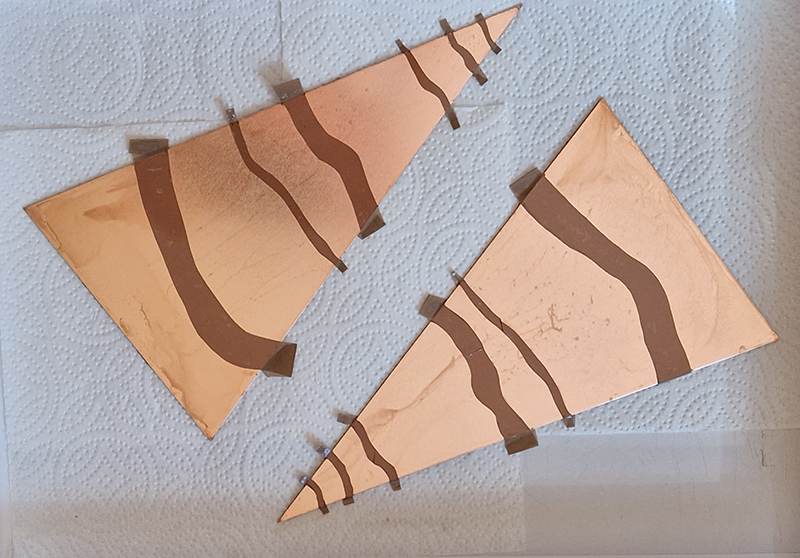
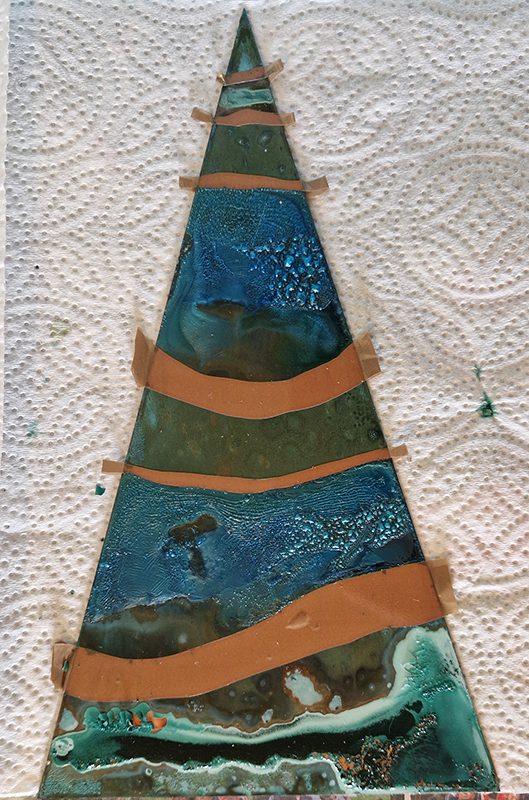
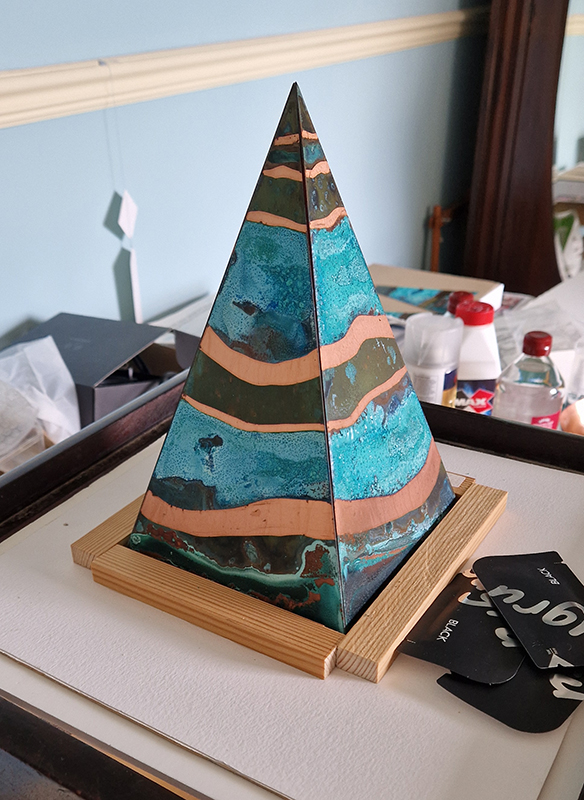
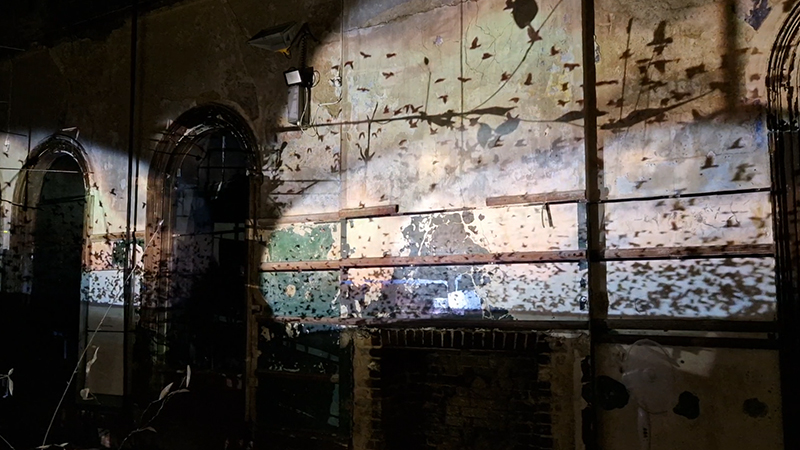
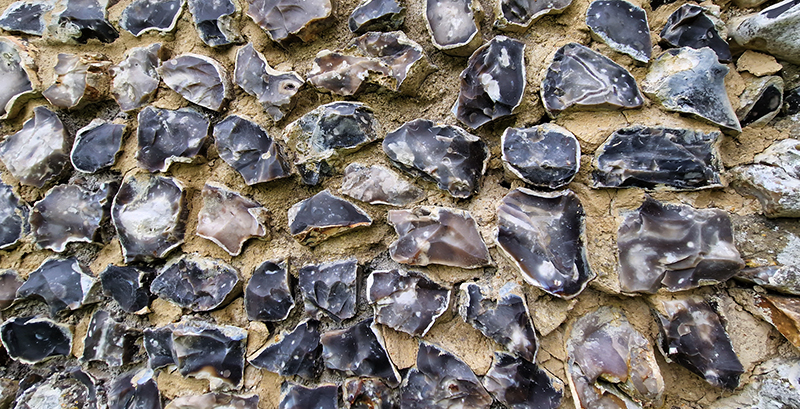
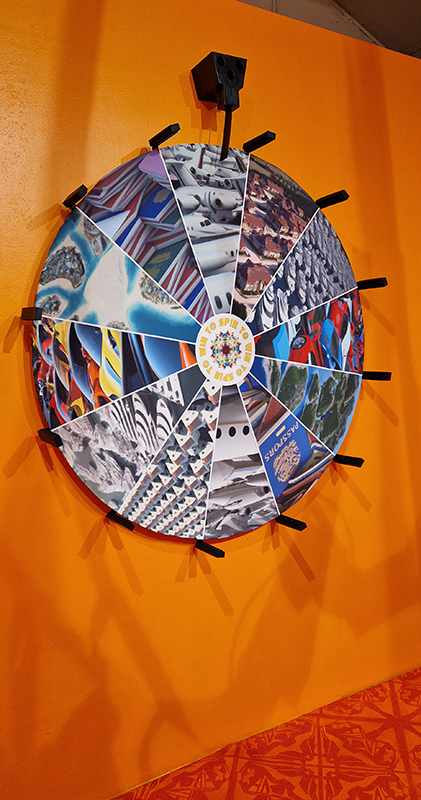
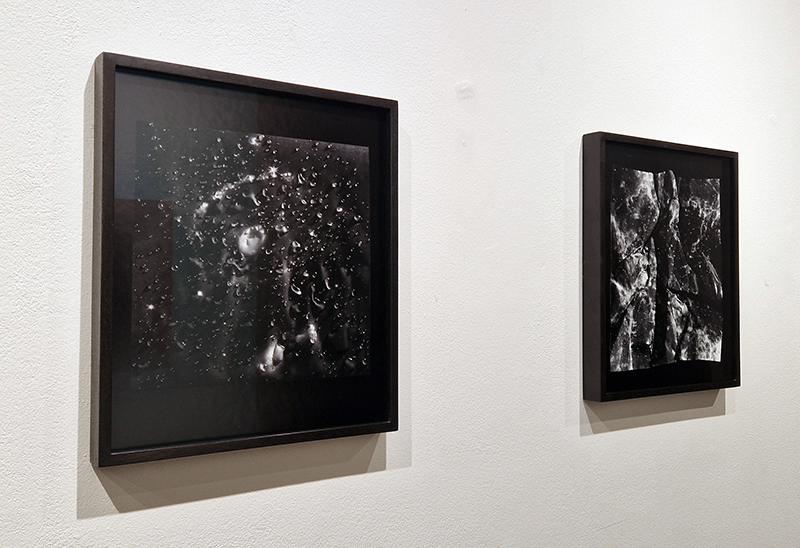
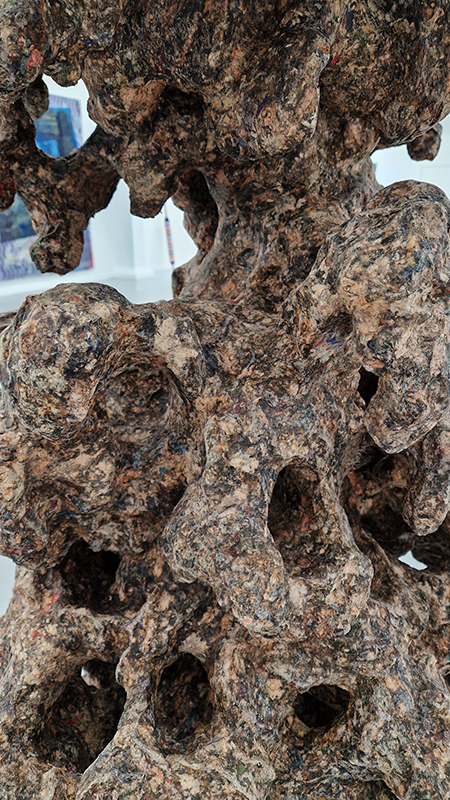
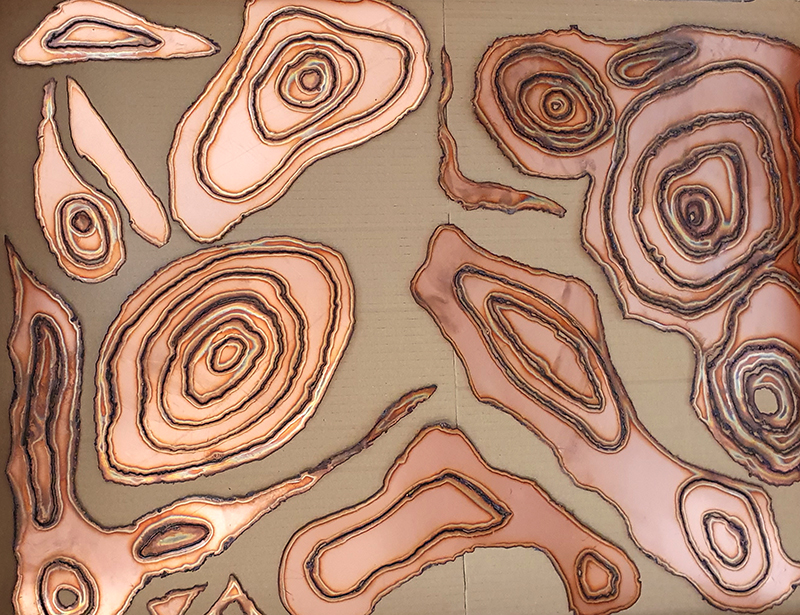
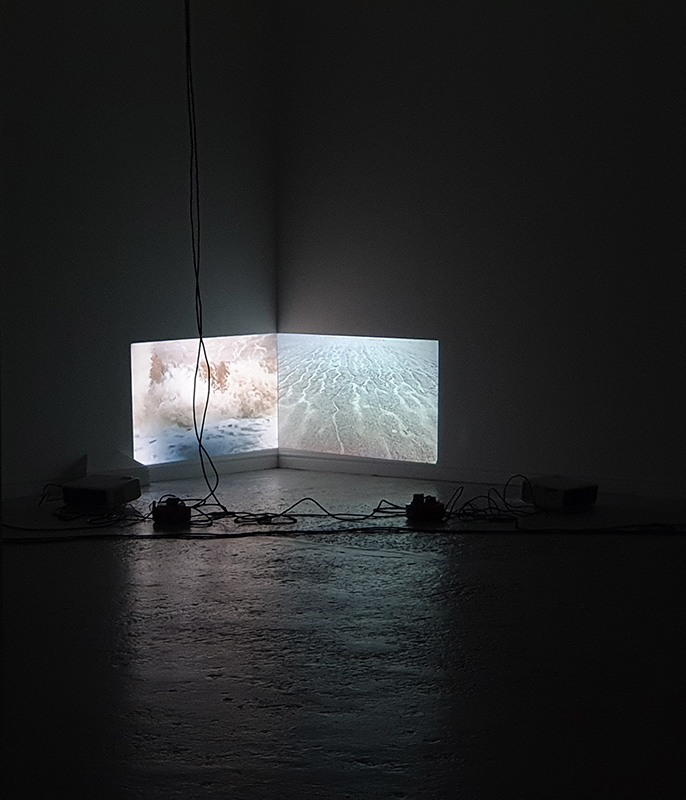
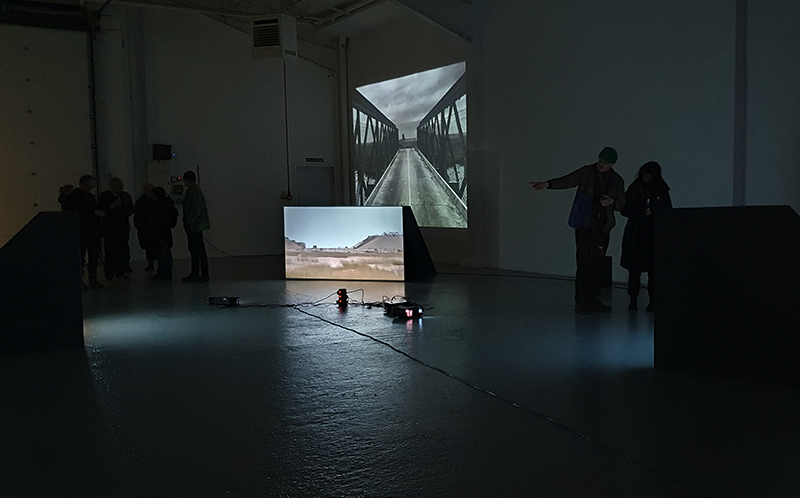
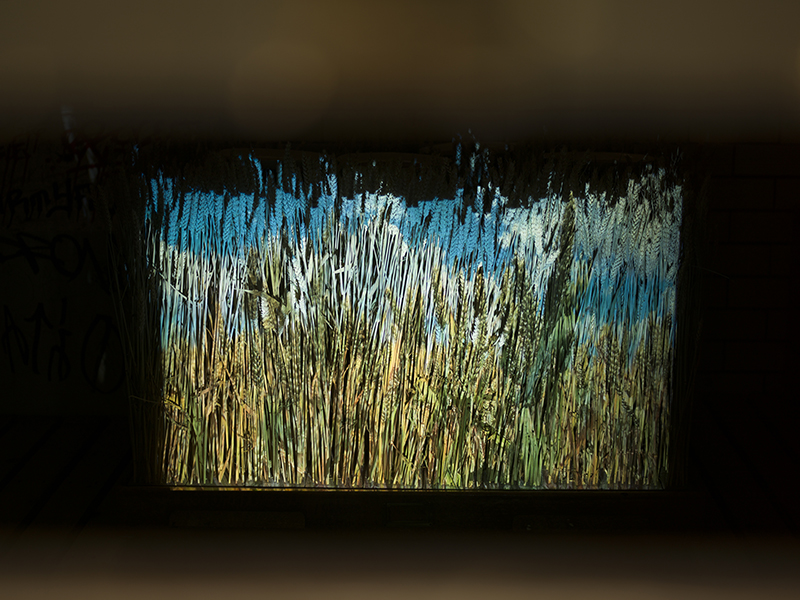
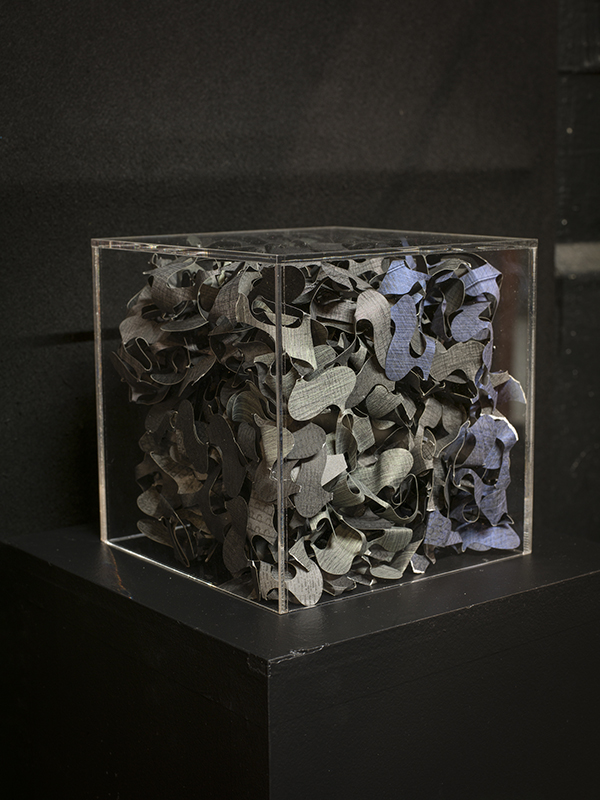
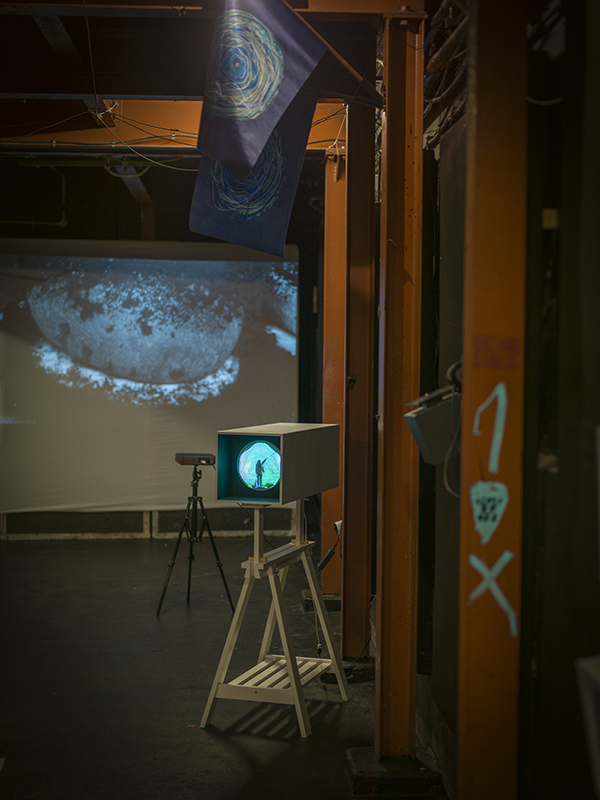
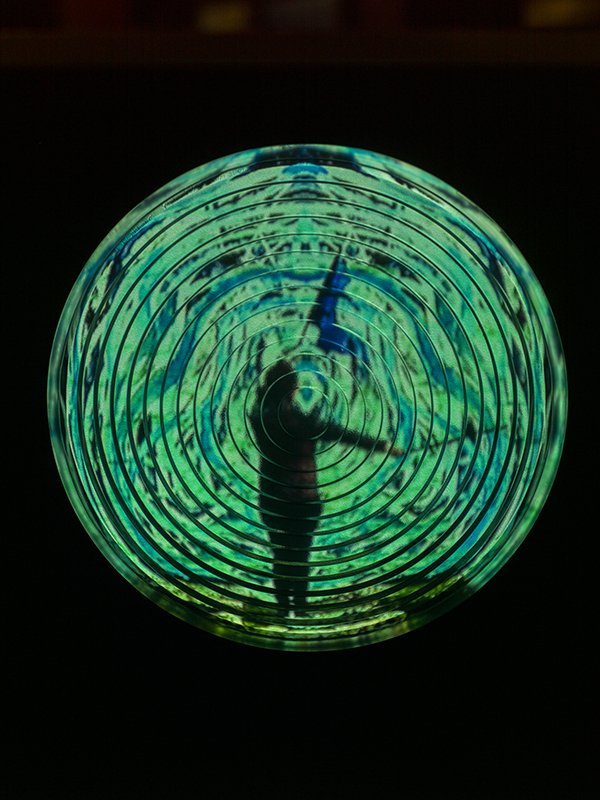
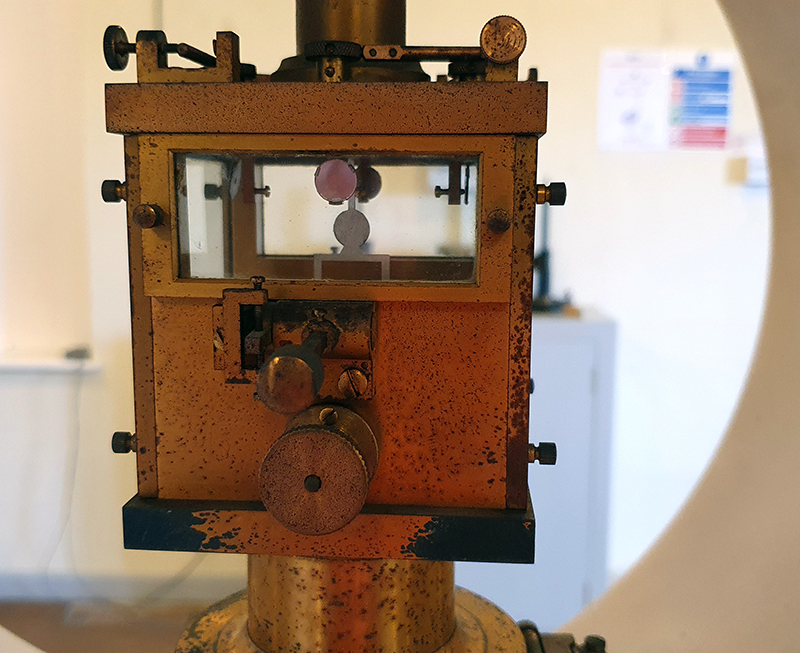
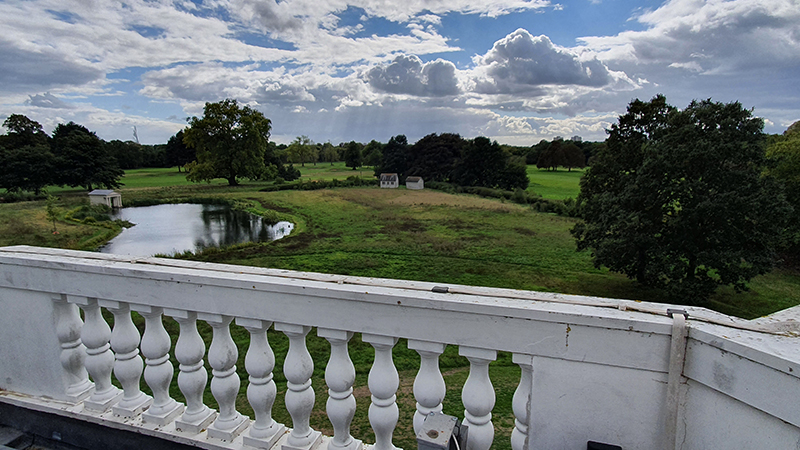
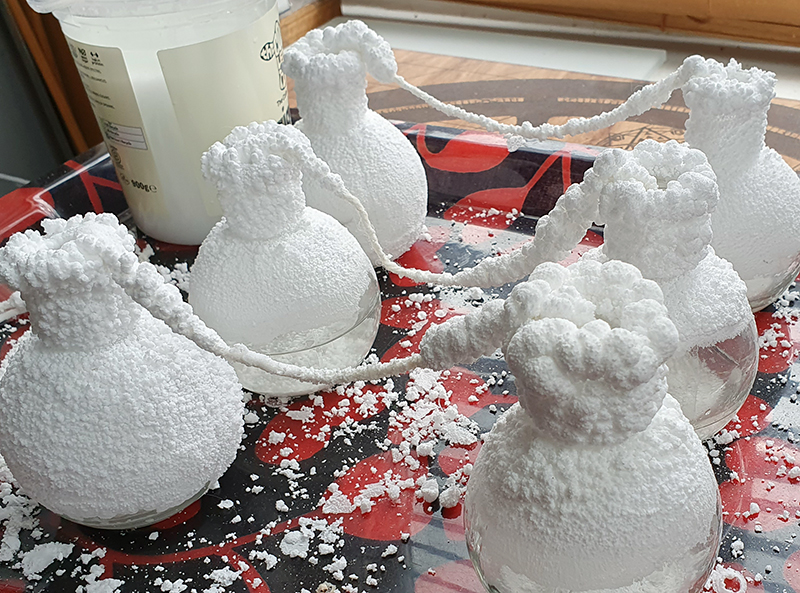
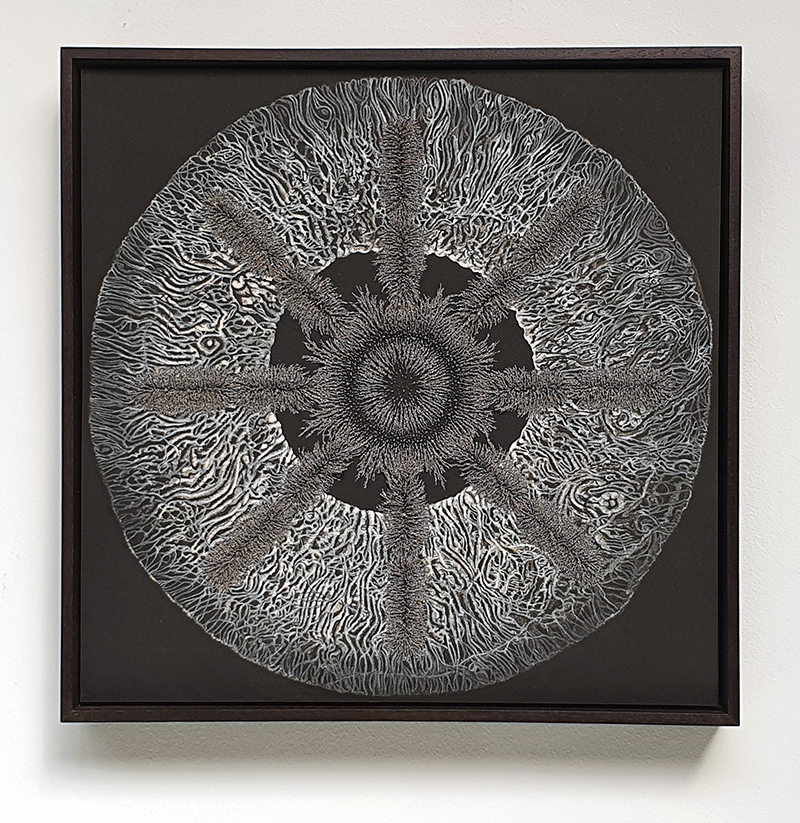
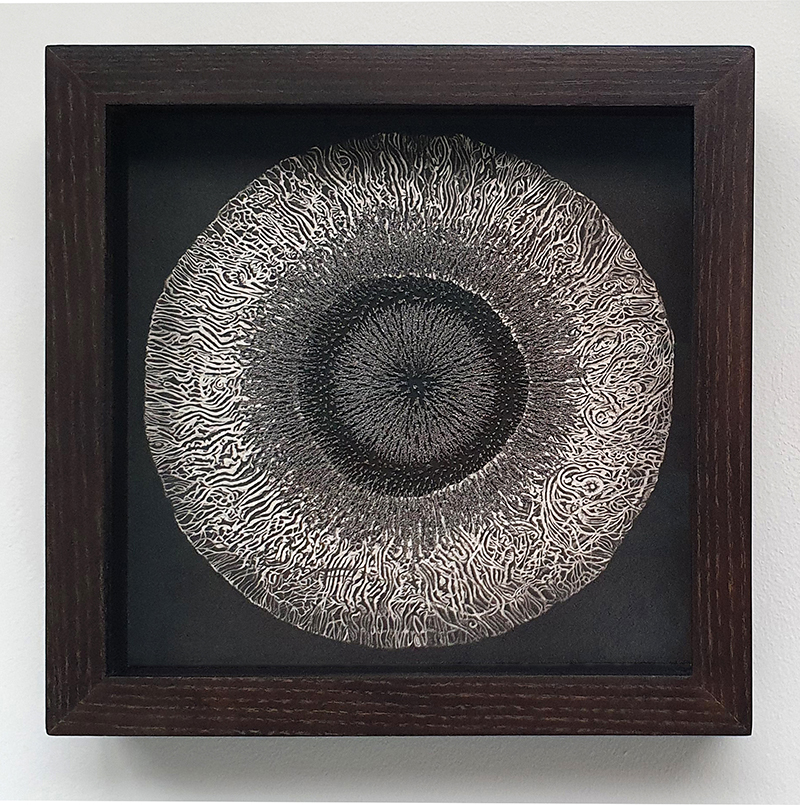
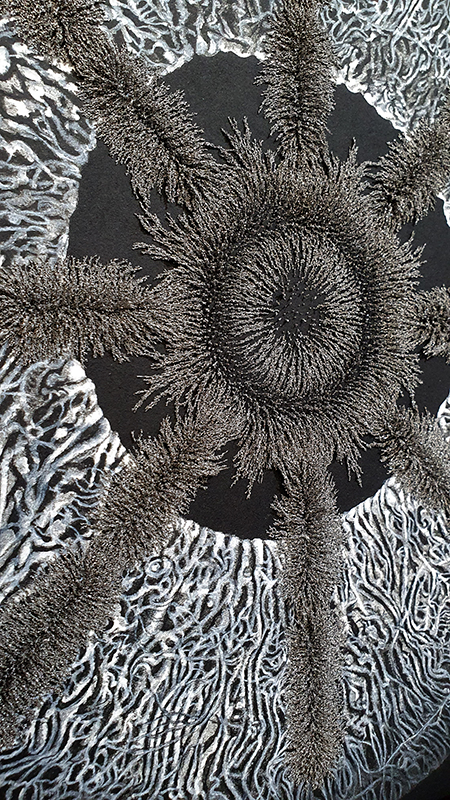
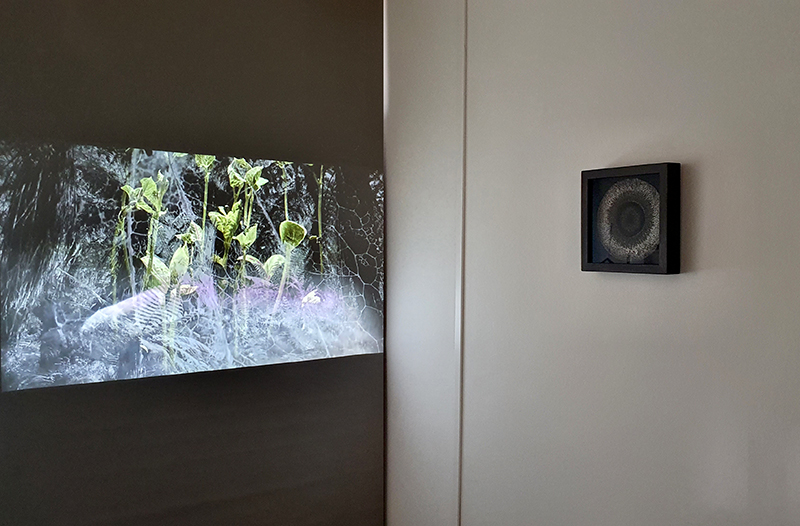
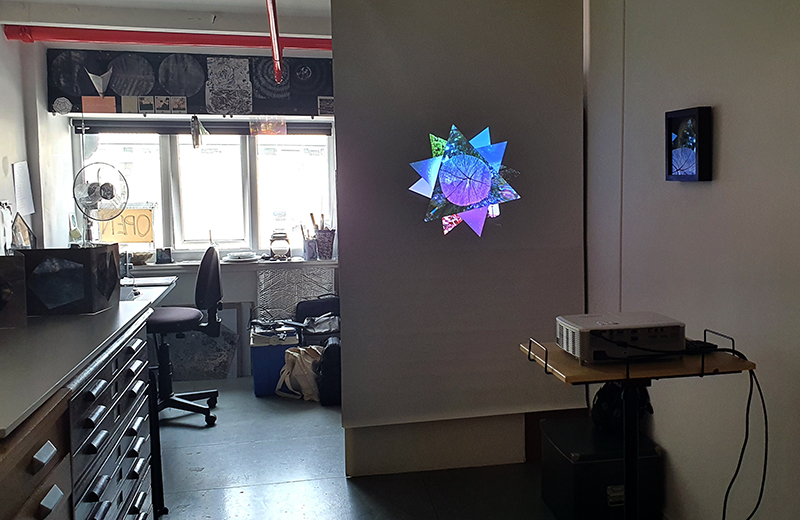
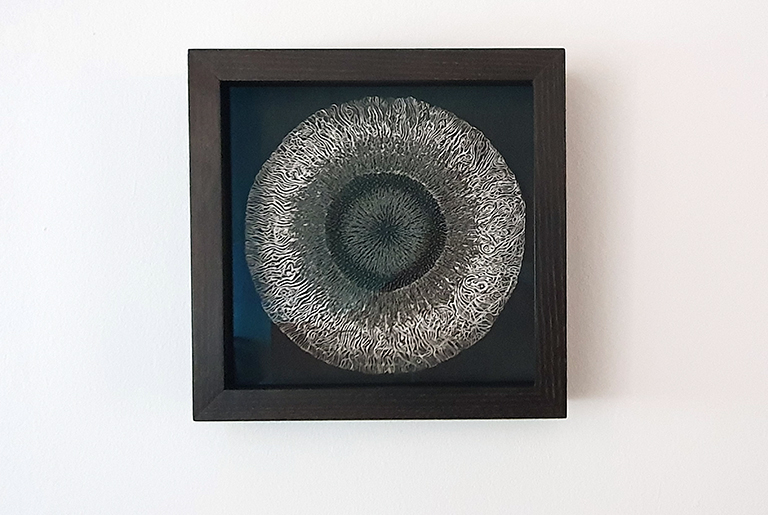
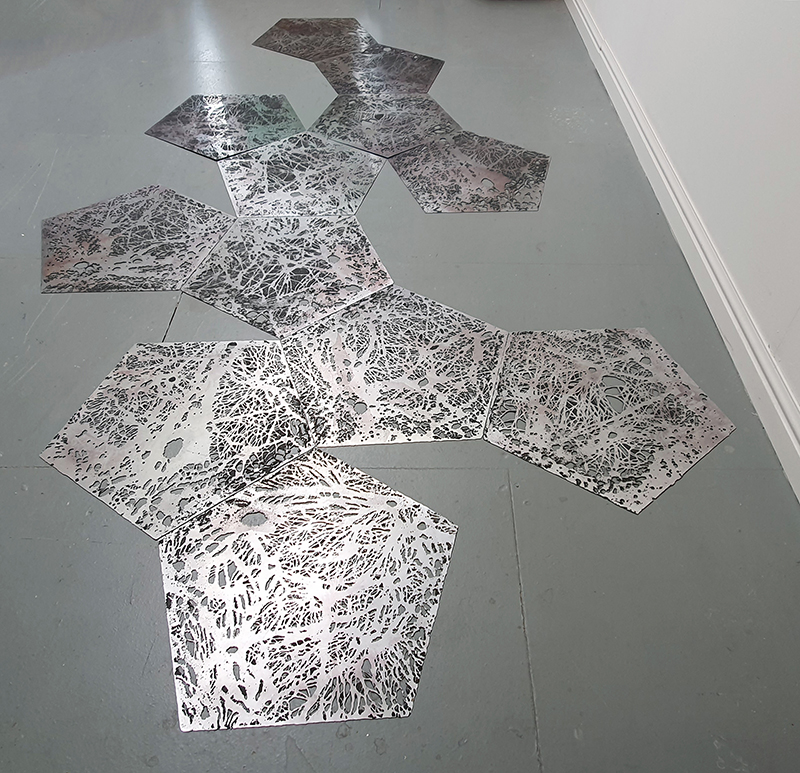
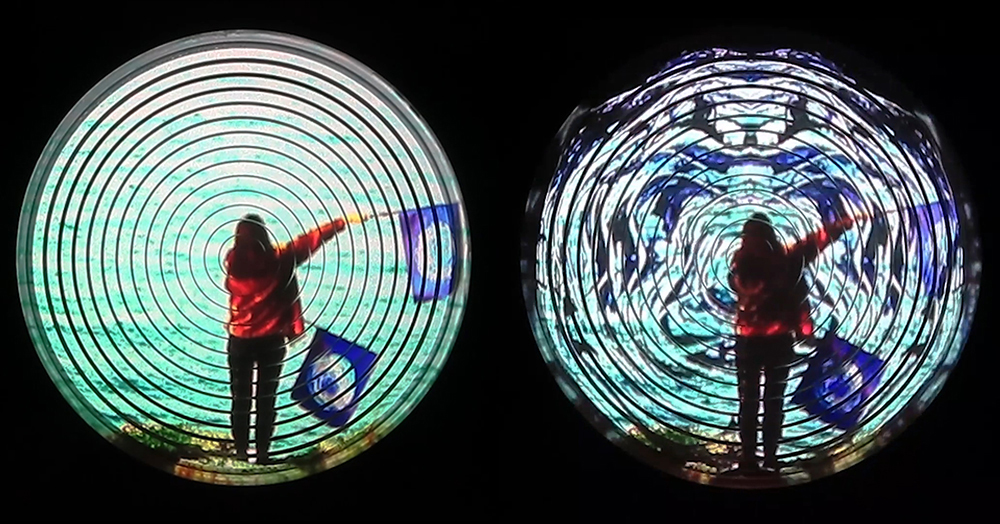
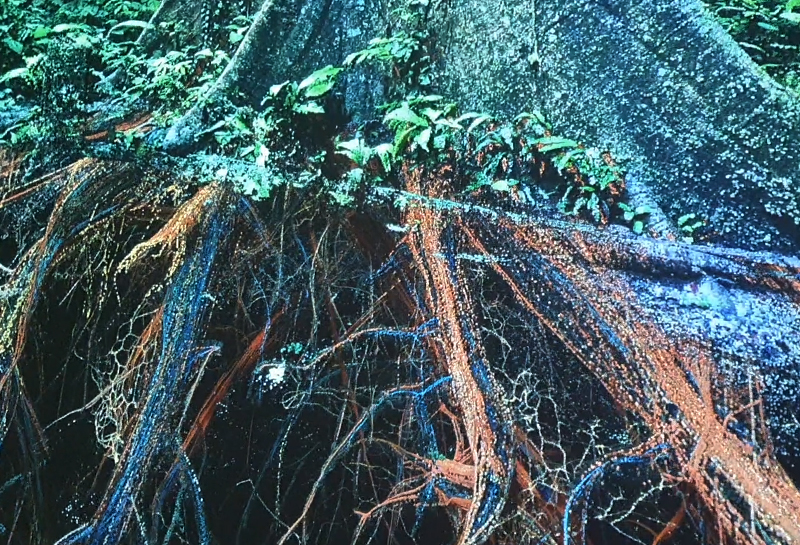
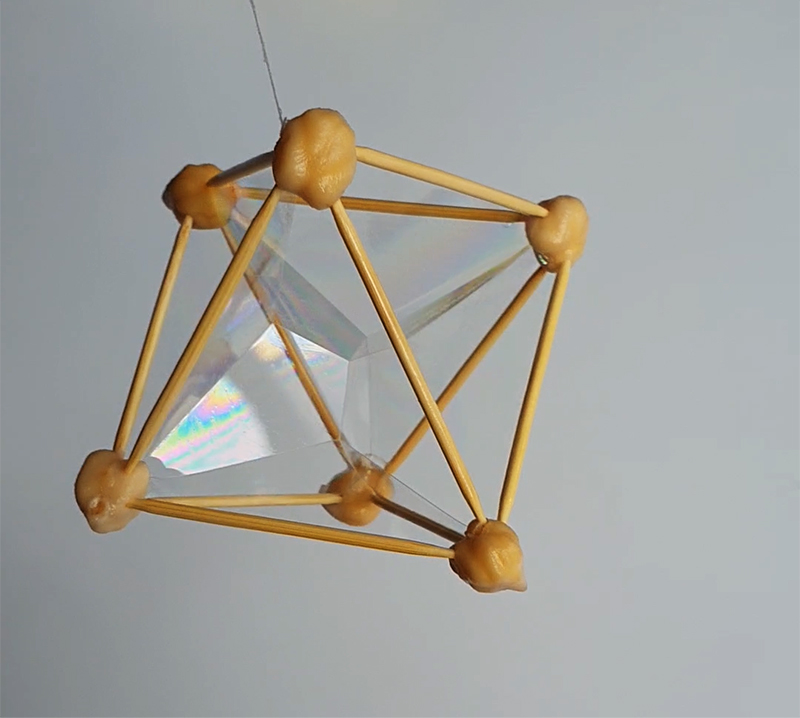
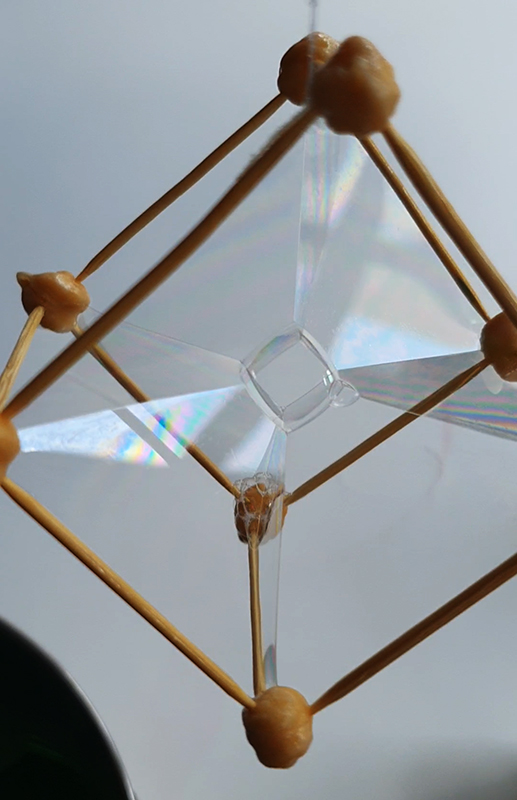
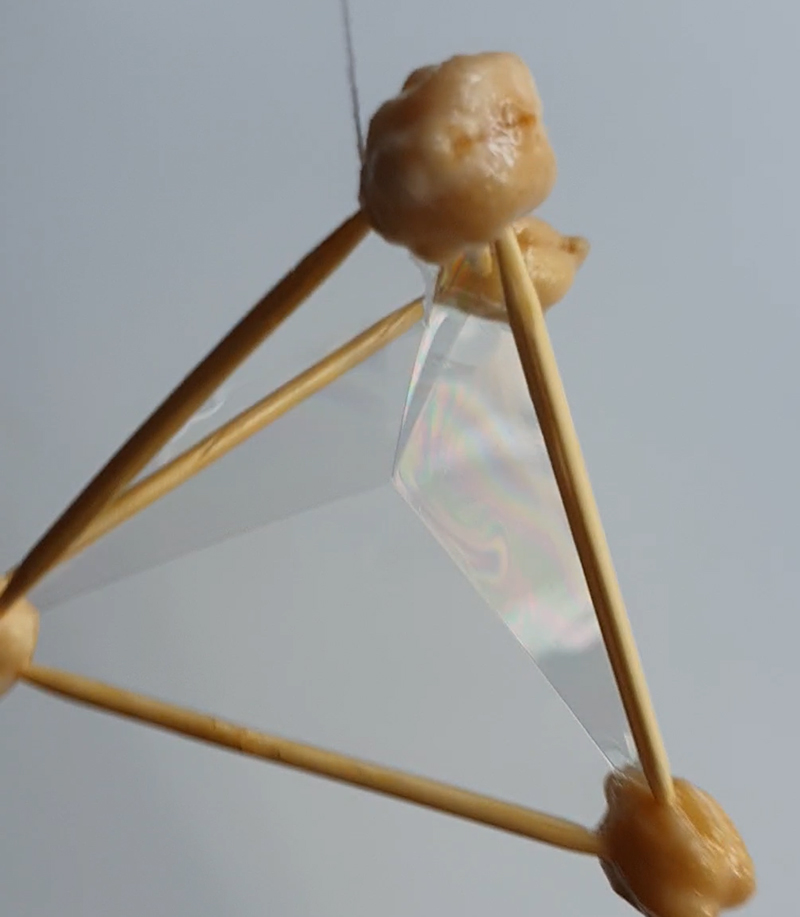
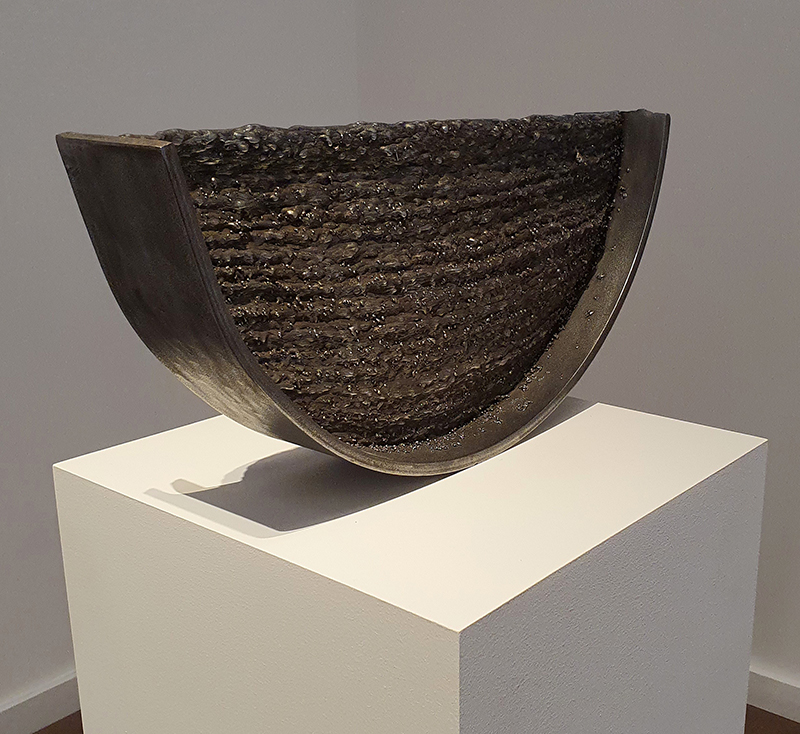
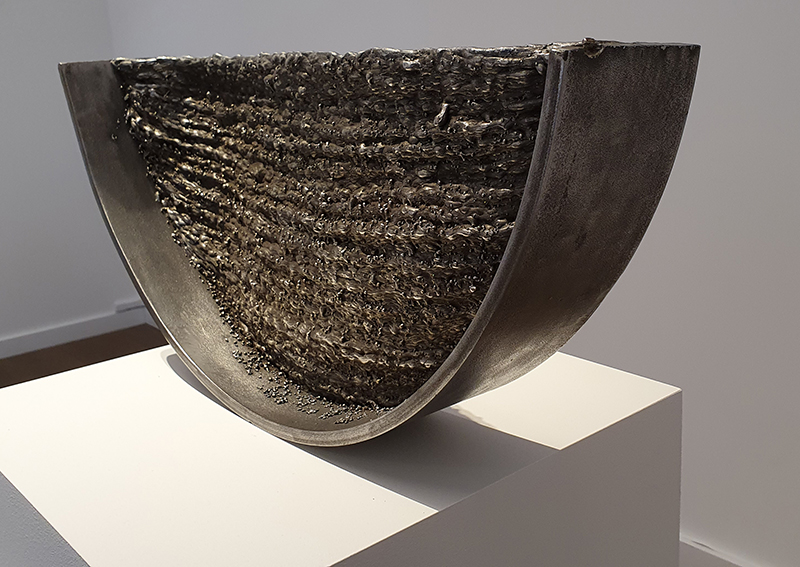
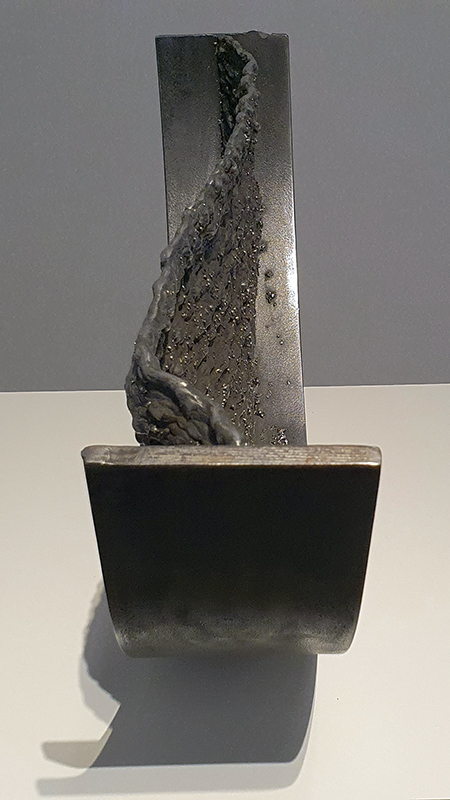
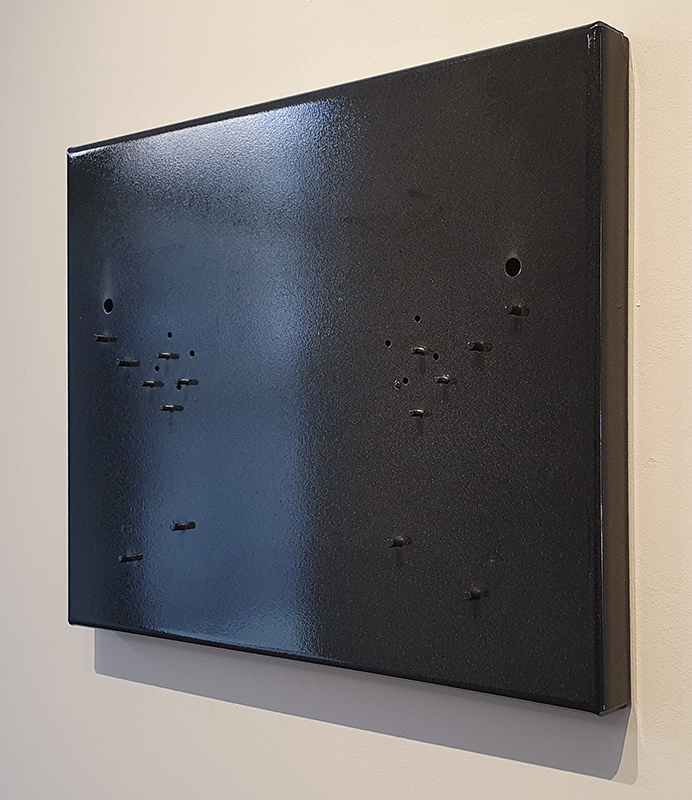
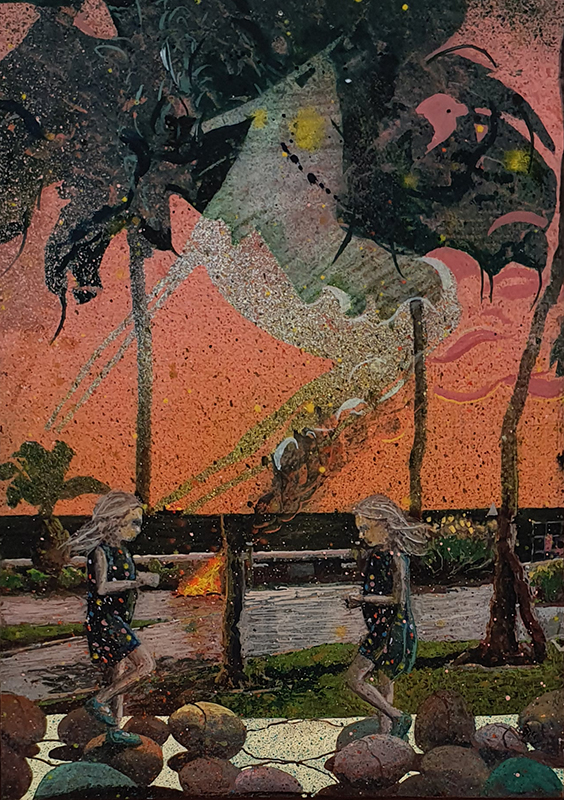
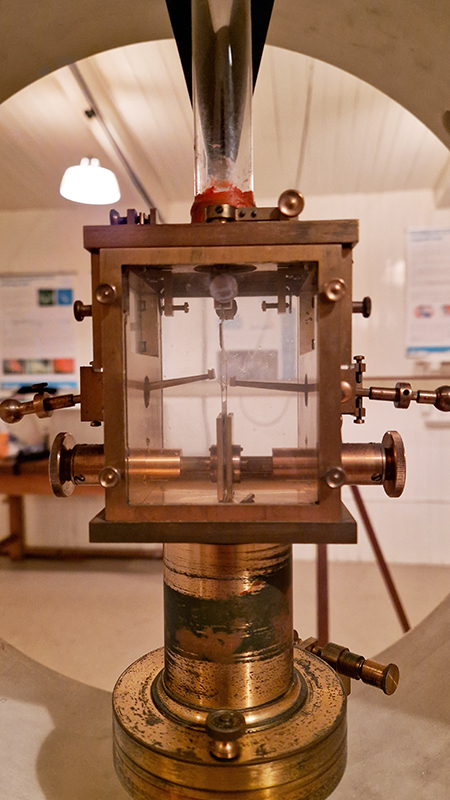
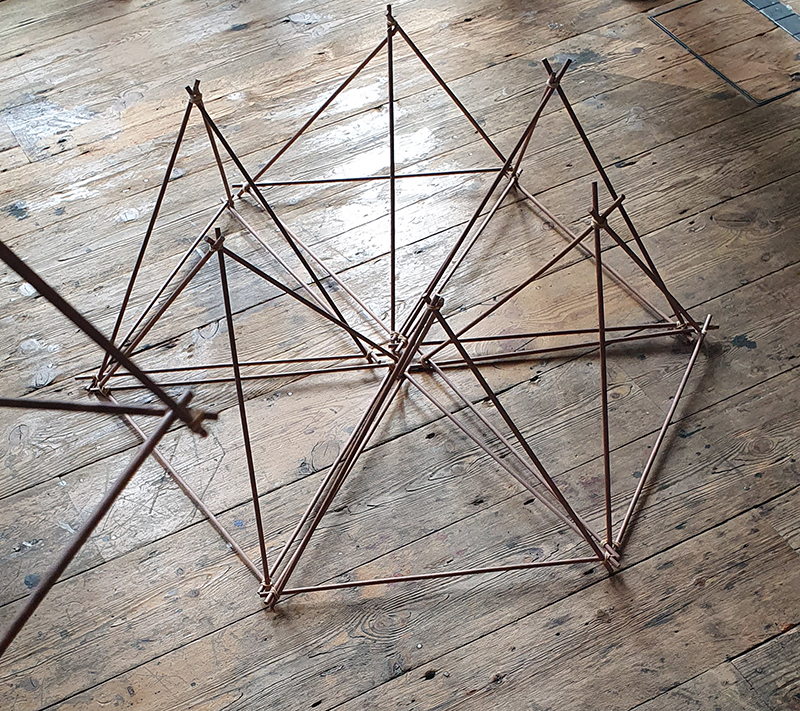
Speculating on a view of the world projected from the perspective of the rock. In the studio drilling more holes for optical lenses set out in a pattern based on the crystal structure of the naturally magnetic mineral magnetite which was determined in 1915 as one of the first crystal structures to be obtained using X-ray diffraction. Found in igneous rocks, sedimentary deposits and sand across the globe in many locations, magnetite is also found in the cells of organisms from bacteria to humans. Magnetite contains both ferrous (divalent) and ferric (trivalent) iron along with oxygen.
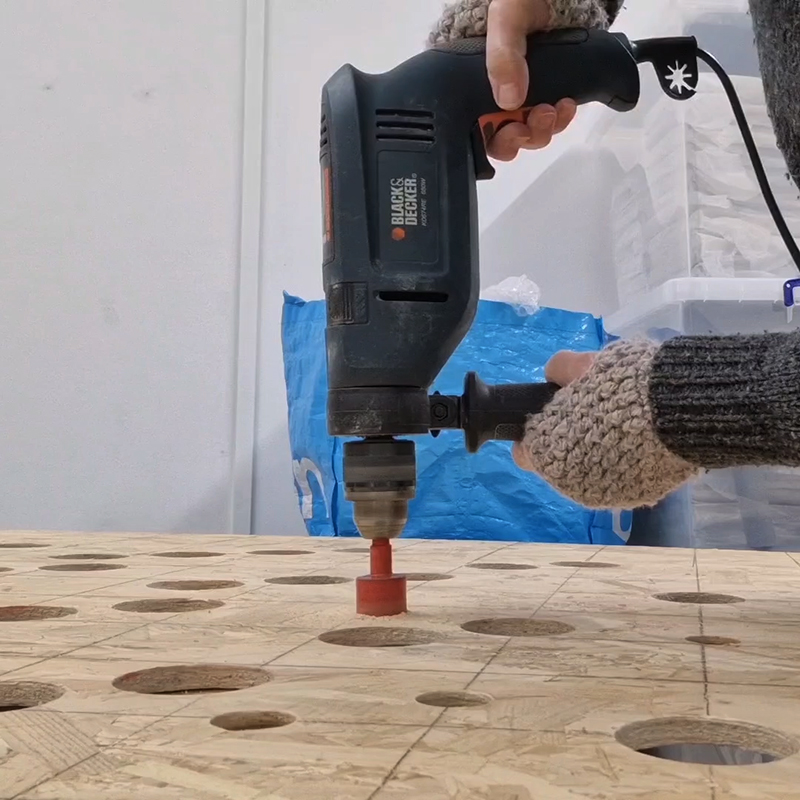


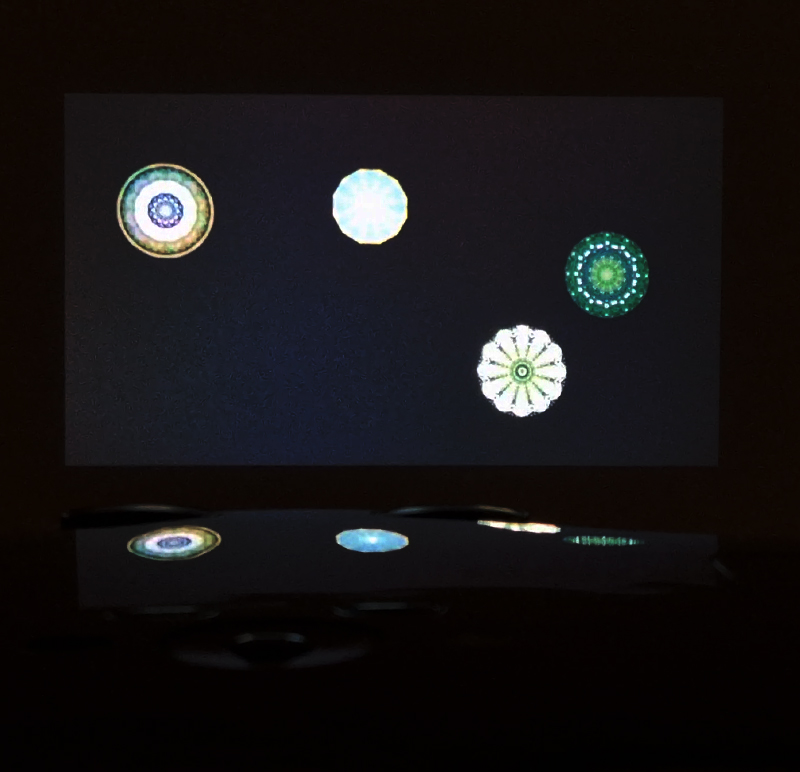
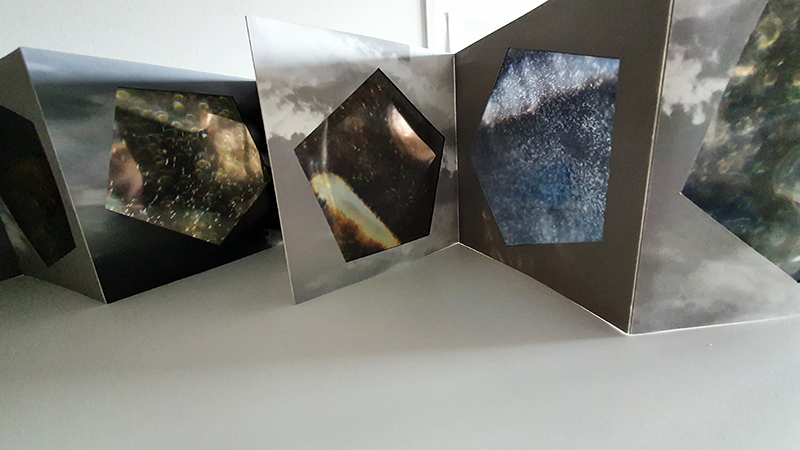
Testing projecting through the optical lenses I’m excited to see how the different lenses cause images to overlap and distort.
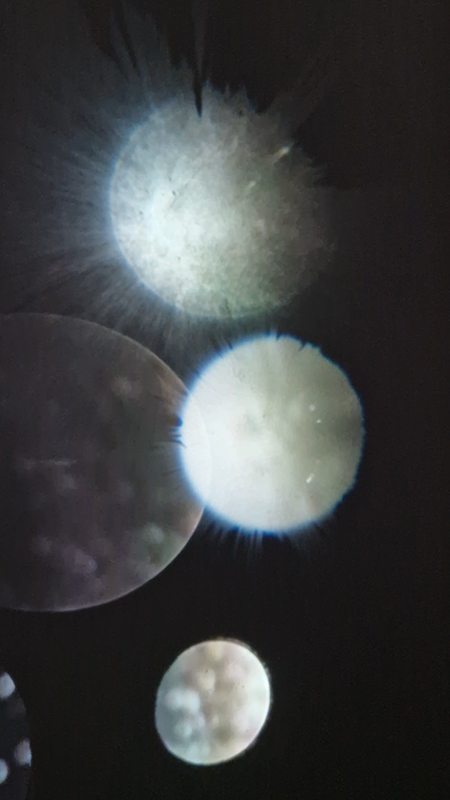





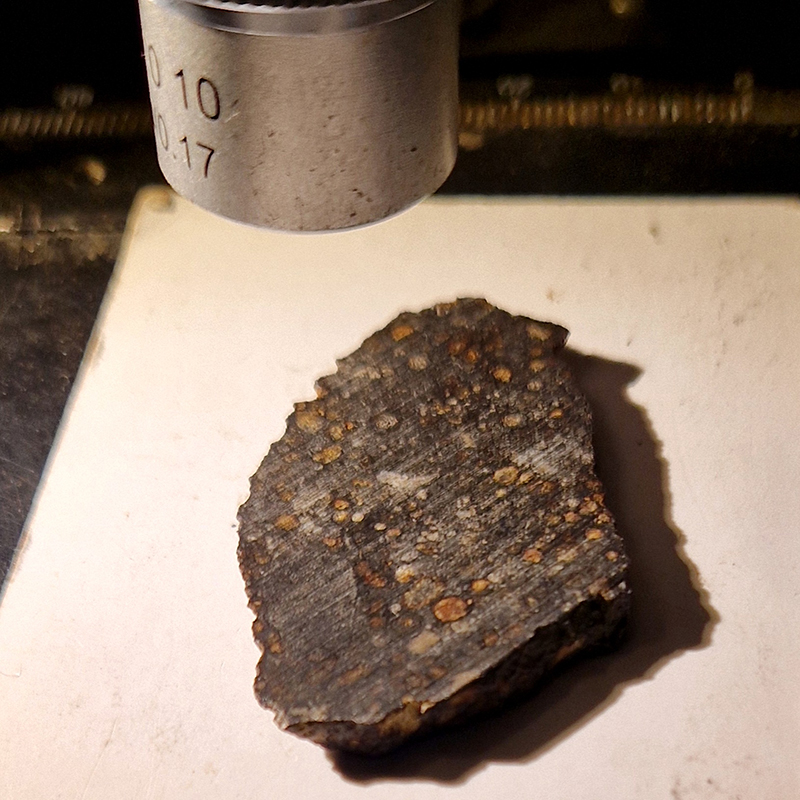
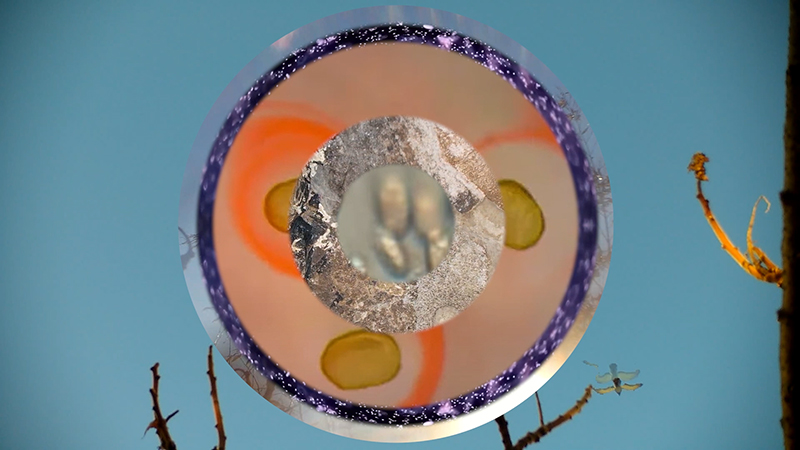
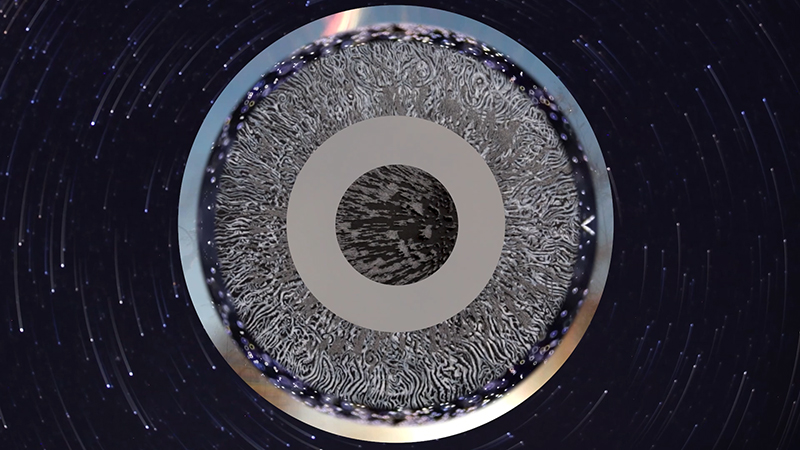
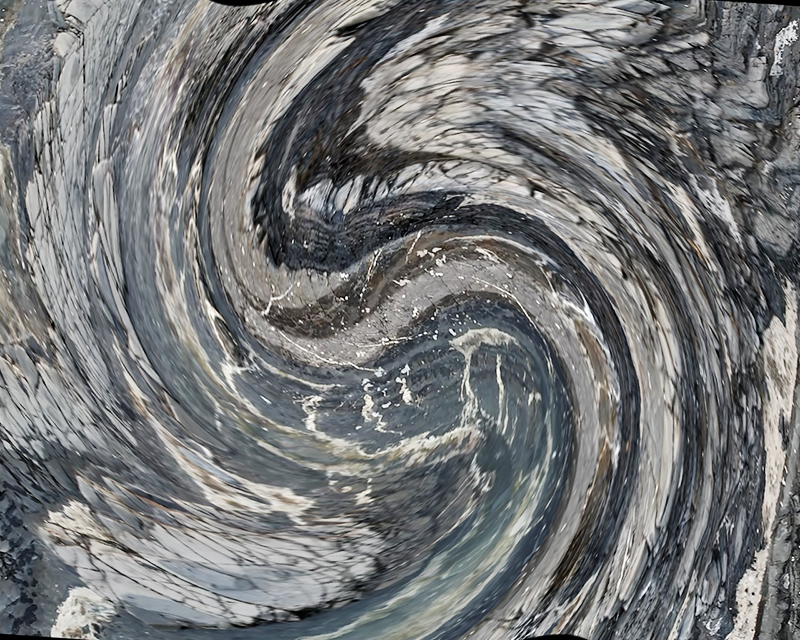
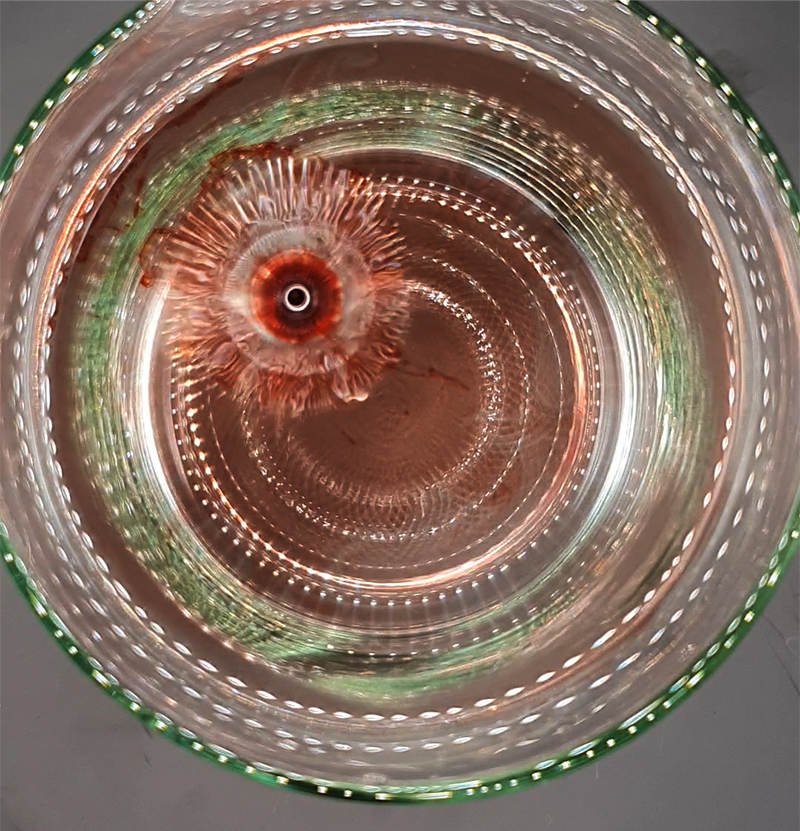
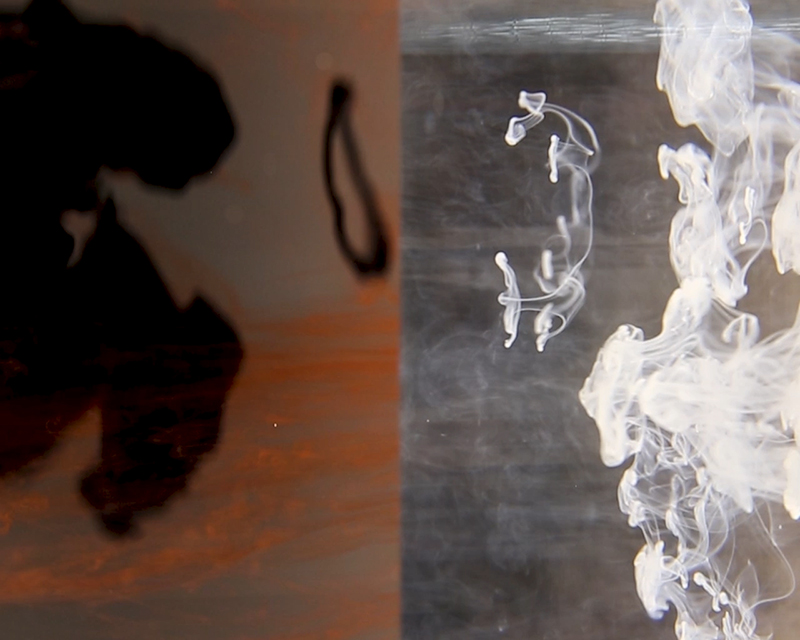
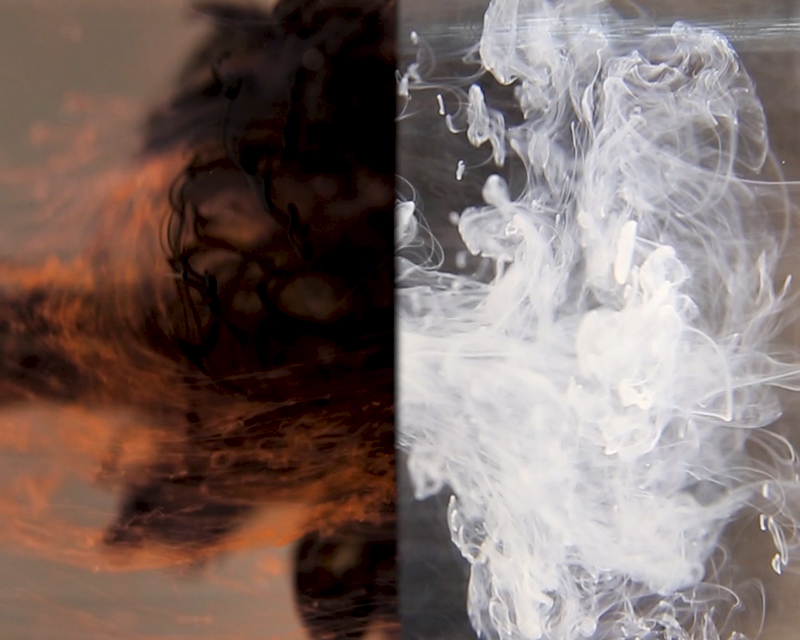
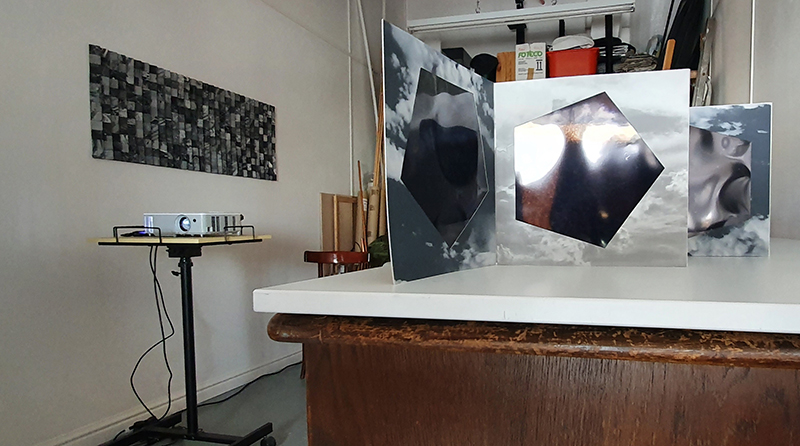
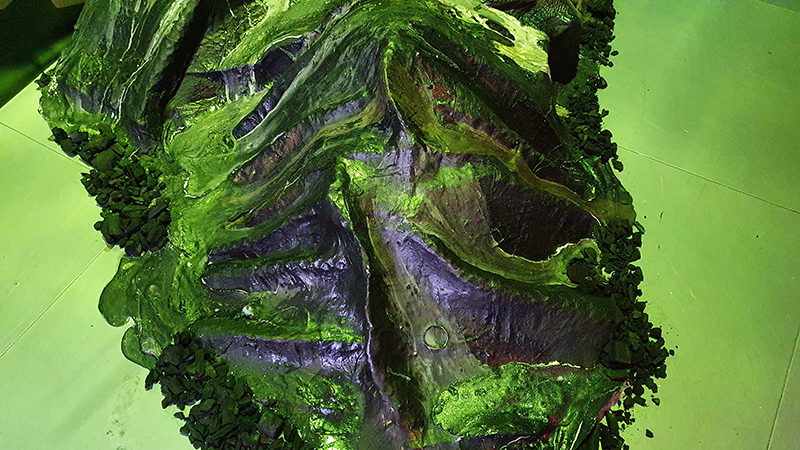
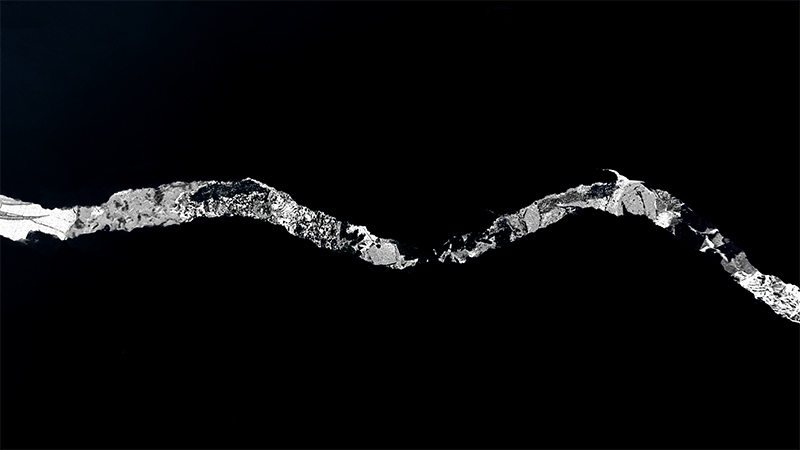
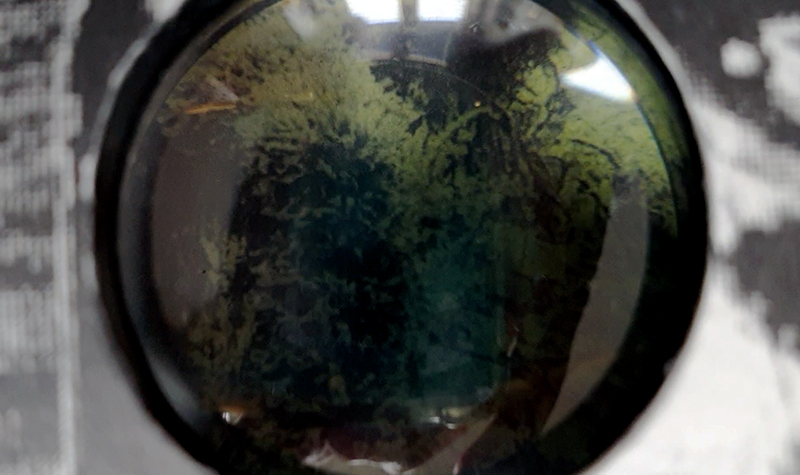
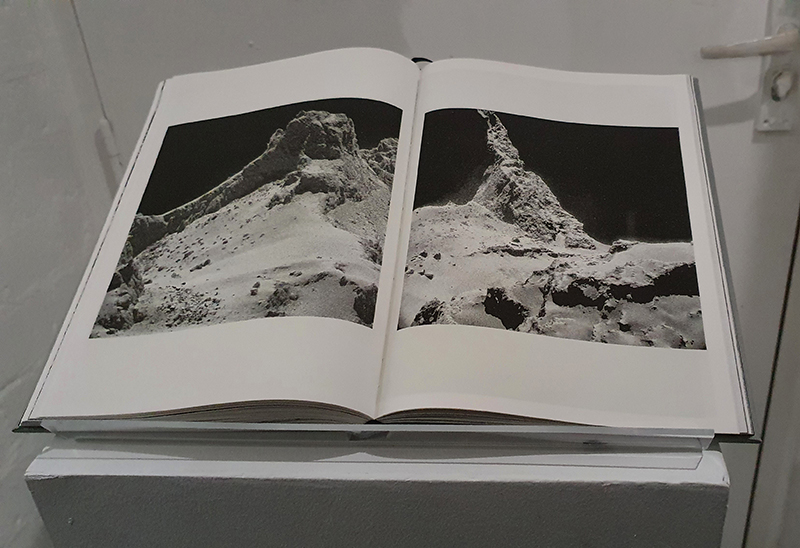
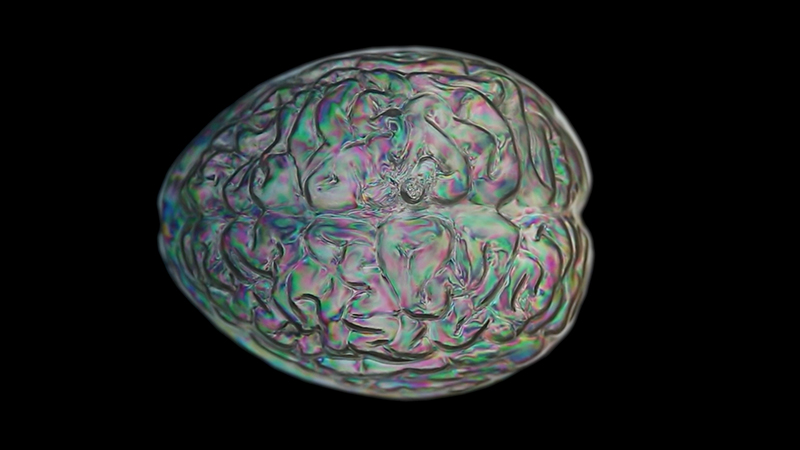
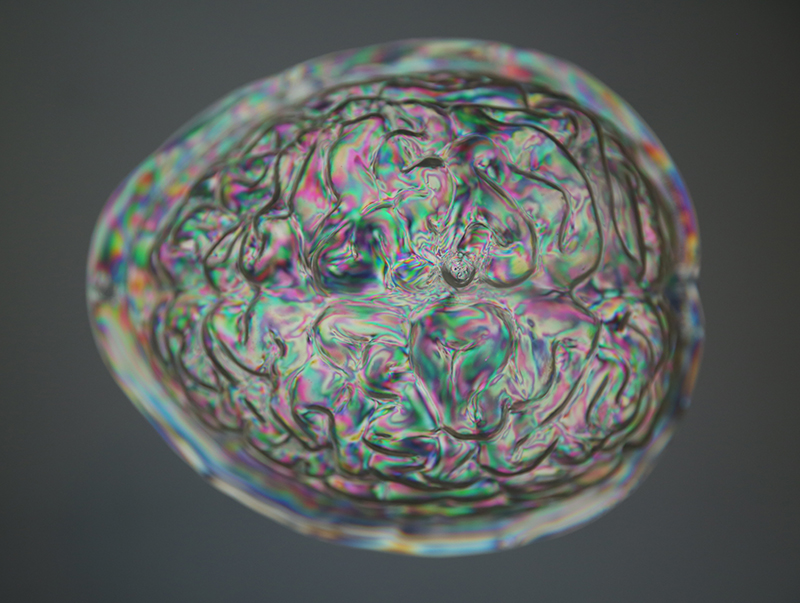
I received a Digital Microscope for my birthday and a selection of rocks and meteorites to look at. So far I have only used the lens with the least magnification capabilities yet this is revealing wonderful detail in the rocks which are further enhanced by using a polarising filter. I have chosen to look at rocks which originate near areas of tectonic activity or that may have magnetite in them.
Images on left have no filter, those on the right have a polarising filter.
This thin slice of Deep Ocean Pebble was collected in 1979 three miles deep in the Pacific Ocean Clarion Clipperton Fracture Zone. This zone is regularly considered for deep-sea mining due to the abundant presence of manganese nodules. In 2016, investigation of the seafloor in the zone was found to contain an abundance and diversity of life – more than half of the species collected were new to science.


This slice of Lewisian Gneiss is 3 billion years old. These ancient rocks from the Isle of Lewis were caught up in a mountain building cycle roughly 490–390 million years ago and were pushed above younger rocks formed during the late stages of this tectonic event.
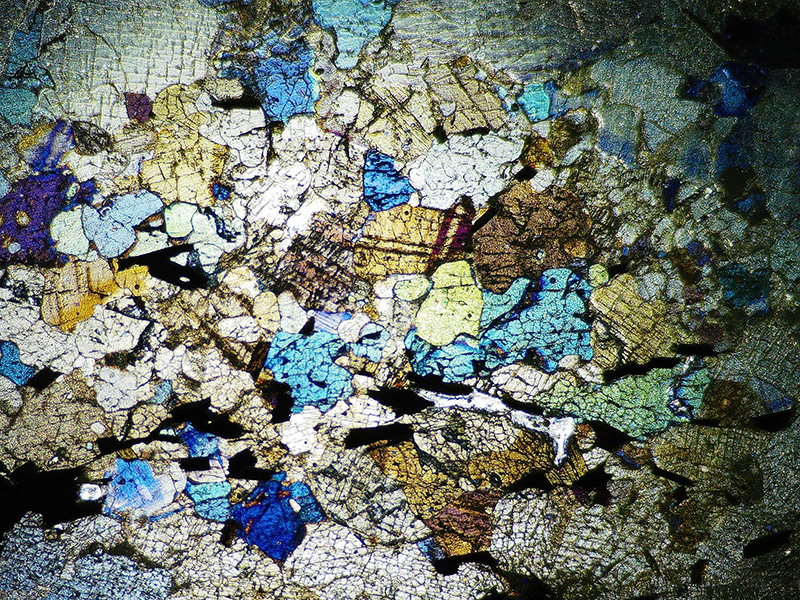


This slice of Olivine Basalt comes from Þingvallavatn, a rift valley lake in southwestern Iceland. The area is covered by lava. The cracks and faults around the lake is where the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates meet. This may be the only place where one can stand with two feet on two different tectonic plates. The sample is a mid oceanic ridge basalt (MORB) fine grained but consisting of small olivine, clinopyroxene fragments in ground mass dominated by plagioclase laths, an opaque magnetite.


This slice of Vesicular Basalt Lava – a type of lava that solidifies into a rock with trapped gas bubbles leaving small holes as the lava cools, comes from the Mid Atlantic Ridge near the Azores Islands.
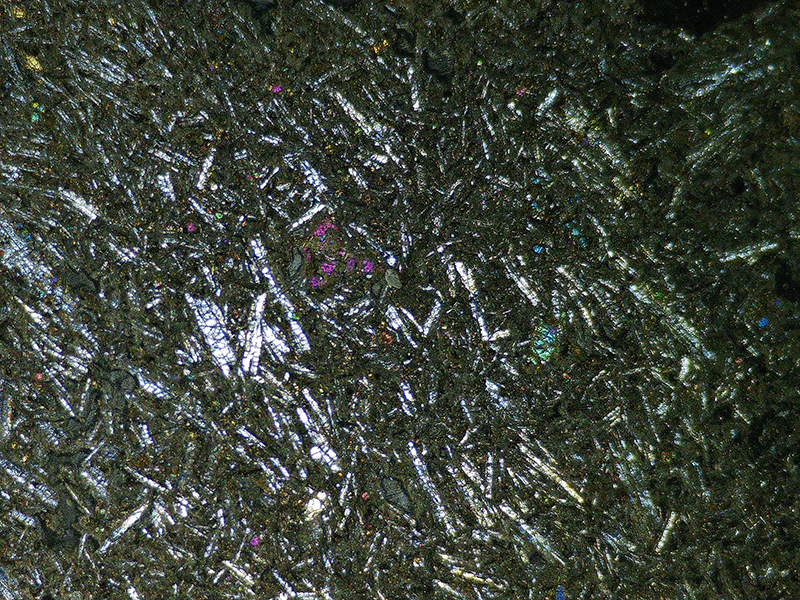
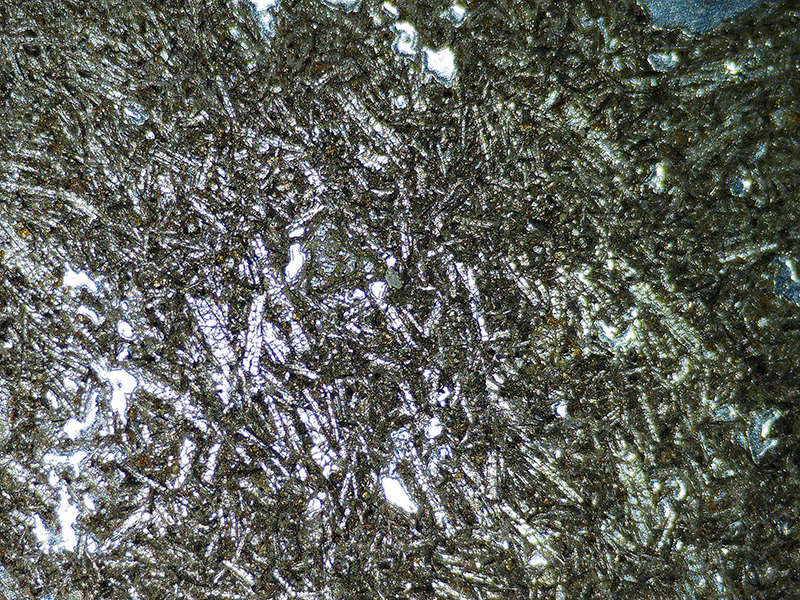

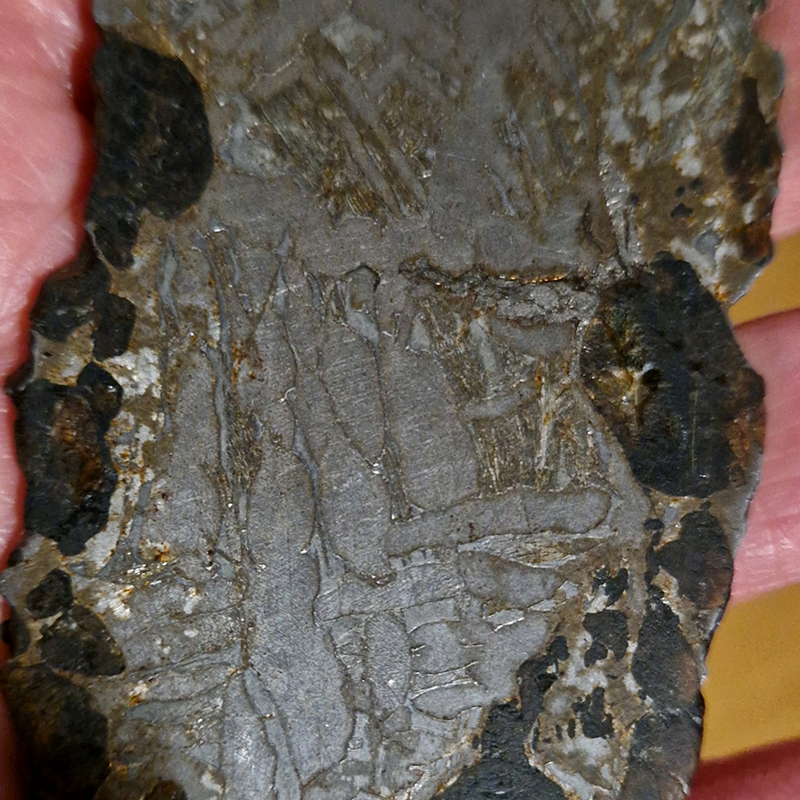
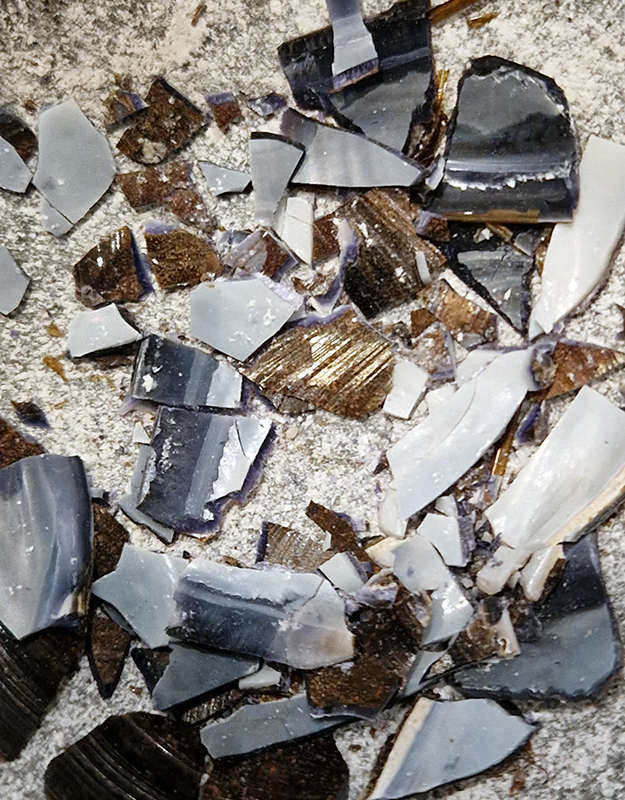
I also have a piece of Jepara taken from a pallasite, a class of stony–iron meteorite, discovered in Indonesia in 2008 during building excavations. The outside is heavily weathered but when cut and polished the inside reveals a translucent structure of densely packed olivine and magnetite. The sample has been coated with acrylic which has surface scratches so I think some of the detail has been compromised but it is still beautiful. No filters used here.


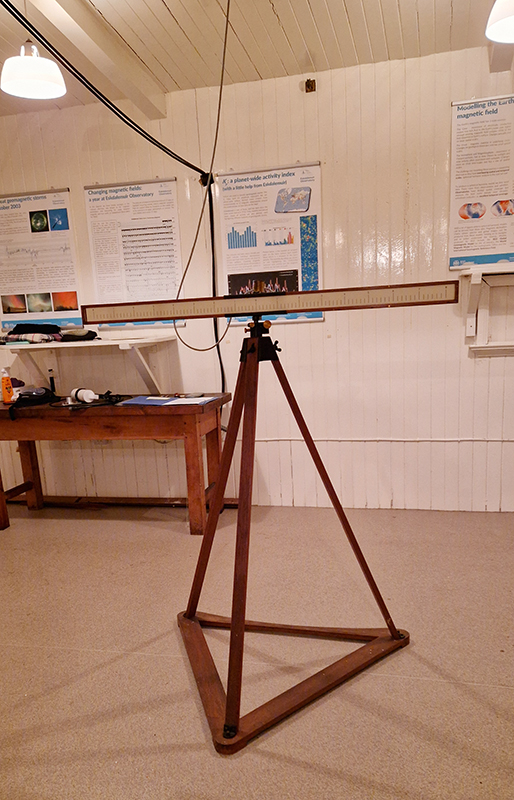
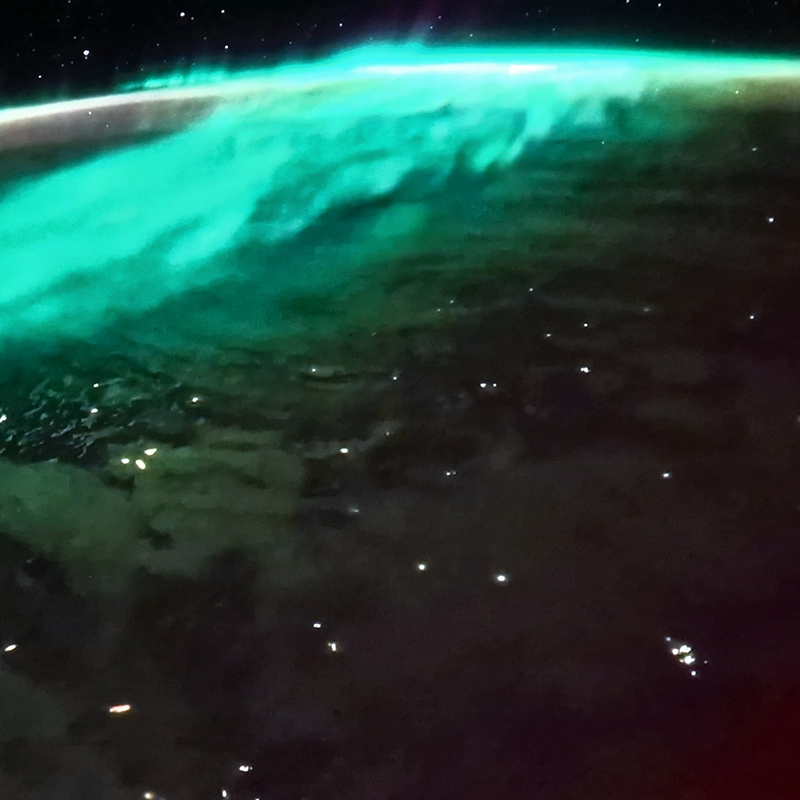
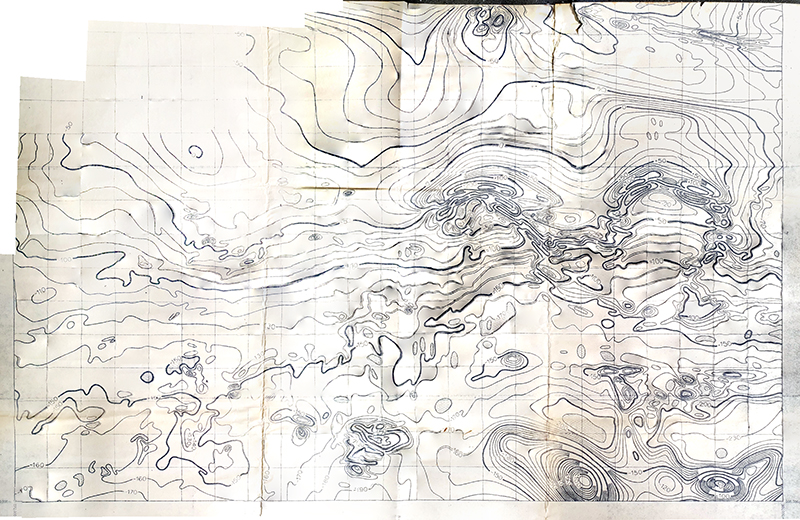
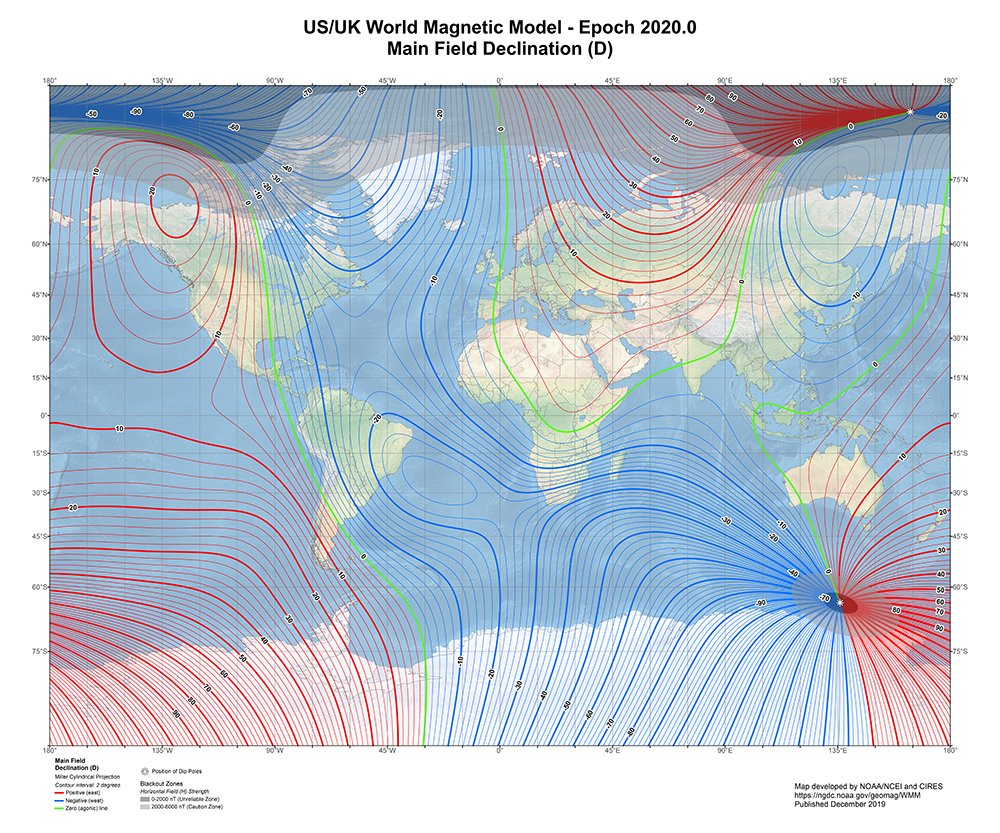
I am making use of public access to historical magnetograms recording of Earth’s magnetic declination to feed into new work inspired by palaeomagnetism. Magnetic studies of the ocean in the 1950’s had determined that the ocean floor was covered by bands of magnetic stripes that varied between normal polarity and reversed polarity. The Earth’s magnetic field has reversed polarity many times over the past hundreds of millions of years. These magnetic stripes were found to be symmetrical on the ocean floor about the mid-oceanic ridge. In 1963 British scientists, Fred Vine and D. H. Matthews proposed that the magnetic striping was caused by paleomagnetism, the storing of Earth’s ancient magnetic field in the sedimentary rocks that were forming as lava spewed up and spread across the ocean floor setting the history of pole reversals in stone.





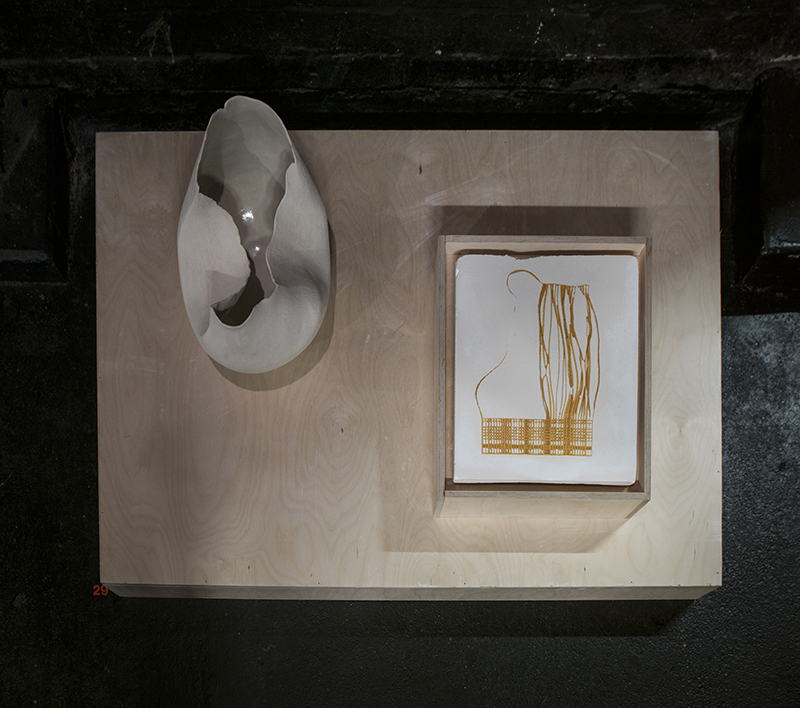
I have embarked on some crystal growing experiments using a seed crystal in a saturated solution of mono-ammonium phosphate and aluminium potassium sulphate. I am hoping these might become objects to view through a lovely old wooden magnifying box I have. The last time I experimented with crystals was when I was amazed by the speed and glut of salt crystals overwhelming the test area. Before that made a time lapse video over 5 days of crystal growth for the installation Time Crystals in Reading Stones at St. Augustine’s Tower 2019. I will be learning more about this as workshops are developed for The Geological Unconscious public engagement programme which will run alongside the exhibition at Hypha HQ Euston this coming spring. Both Julie F Hill and Sophie Mei Birkin work with crystal structures and growth in their own practices and will be leading on the workshops we will run in partnership with a local primary school.
A crystal is like a class of children arranged for drill, but standing at ease, so that while the class as a whole has regularity both in time and space, each individual child is a little fidgety. Dame Kathleen Lonsdale, 1948






Had some studio fun testing the possibilities of magnetic putty for future video ideas. Mesmerising the way it very slowly swallows the magnet.









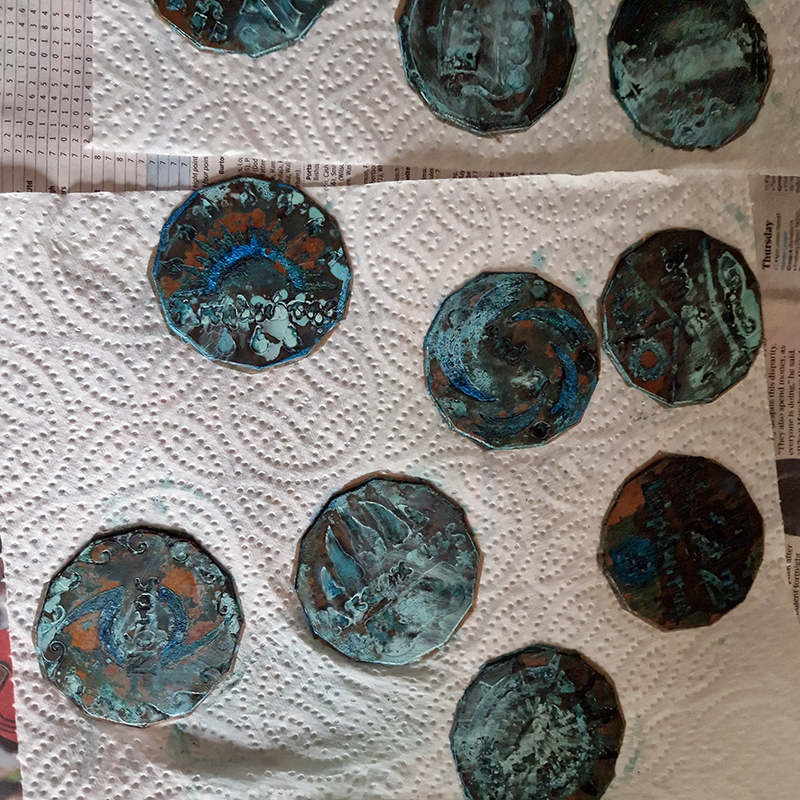
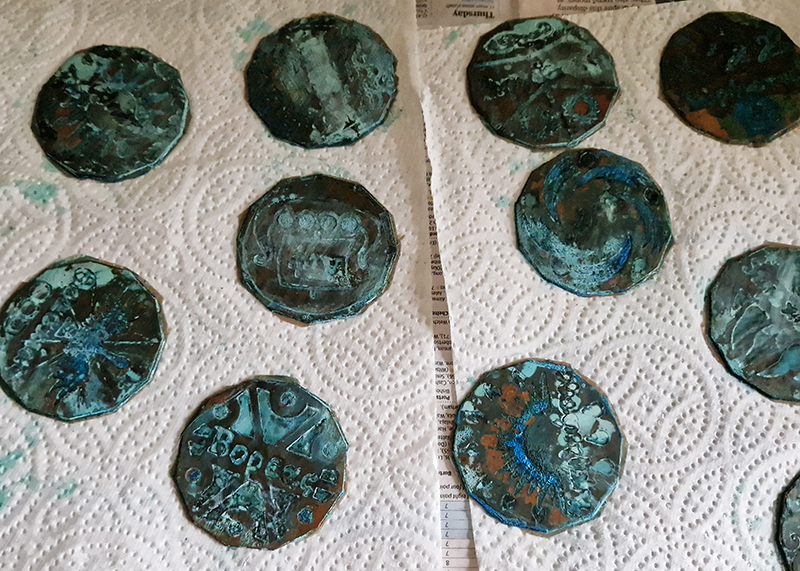
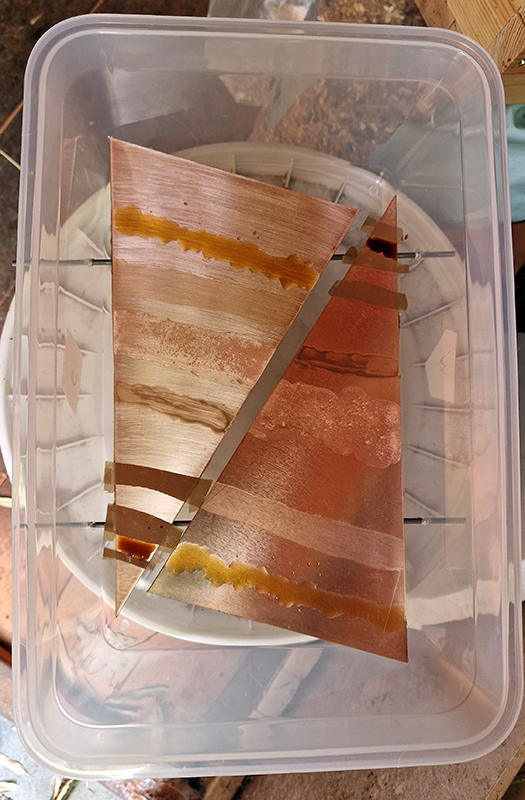
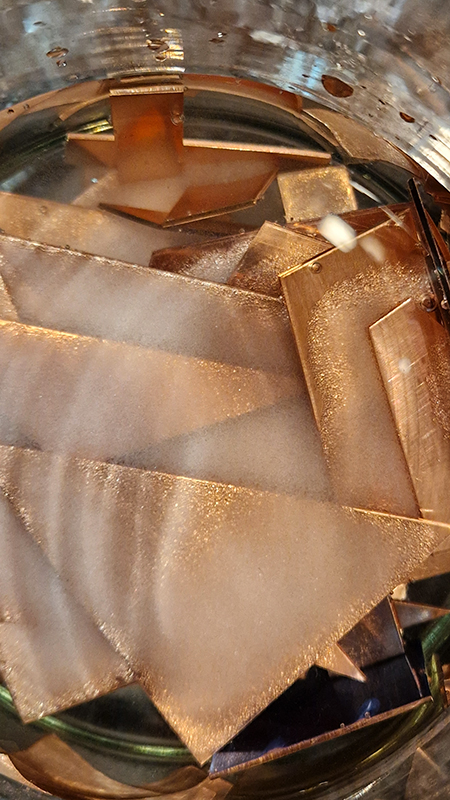
I began the magical process of making copper ink. Soaking pieces of copper in vinegar and salt, stirring daily and watching the liquid turn a milky turquoise blue. Looking forward to using this to patinate copper but also to paint with on paper.



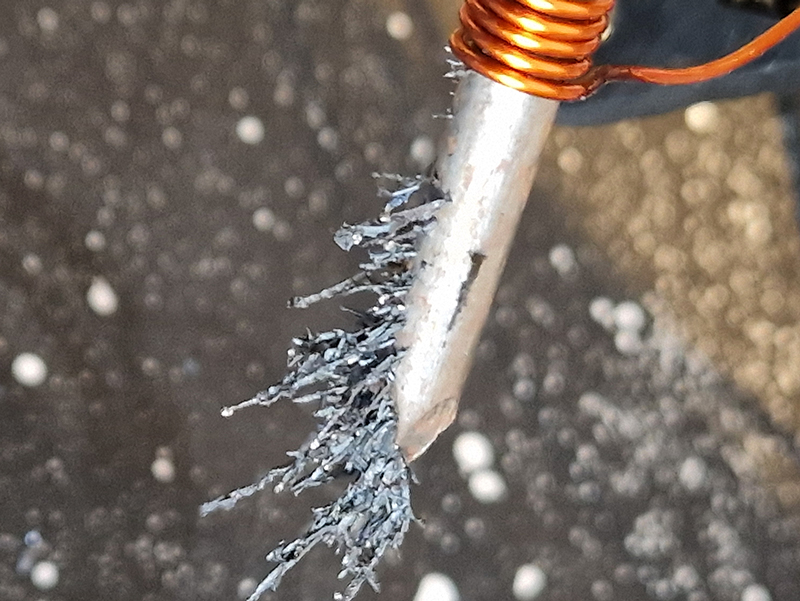
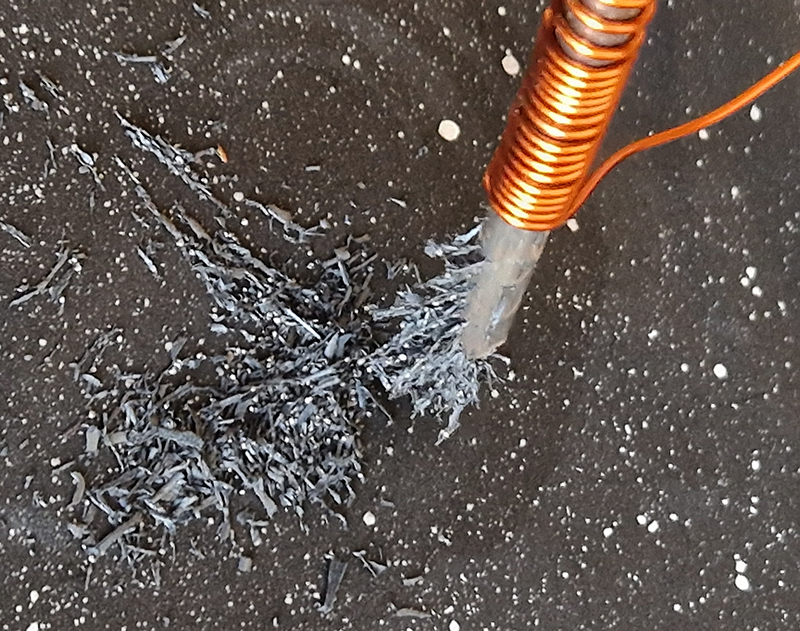
Experimenting winding a copper wire around an iron nail and connecting the wire to a battery cell. A magnetic field is generated around the nail which stays for a little while after the nail is removed from the coil. I used a 9v battery and large nail– it wasn’t a very strong magnet – a welding stick was better and seemed to retain the magnetic field for longer but in both cases the battery got very hot. I had hoped to maybe develop this idea to magnetise a sculpture threaded with iron. Needs more investigation.





I have been exploring the updated Digital Materials Library at the Institute of Making which led me to the Mindsets website which has some cool magnetic materials for sale. Future experiments upcoming.
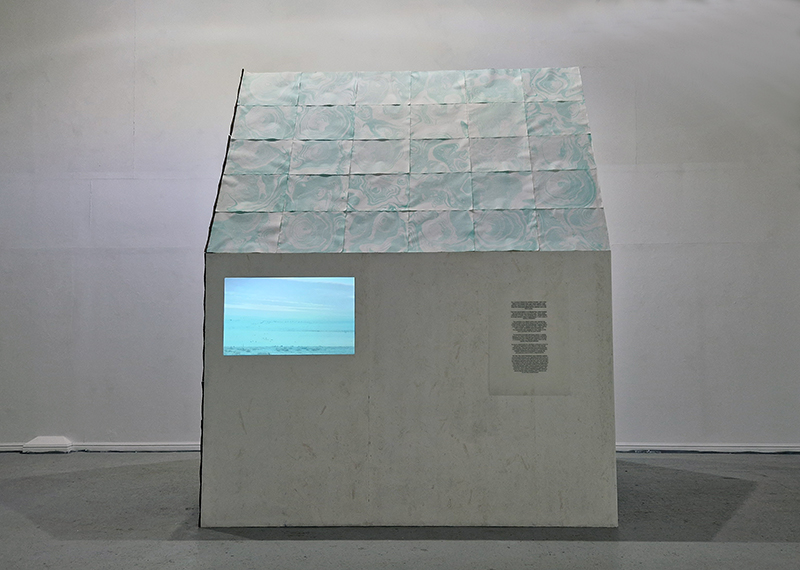
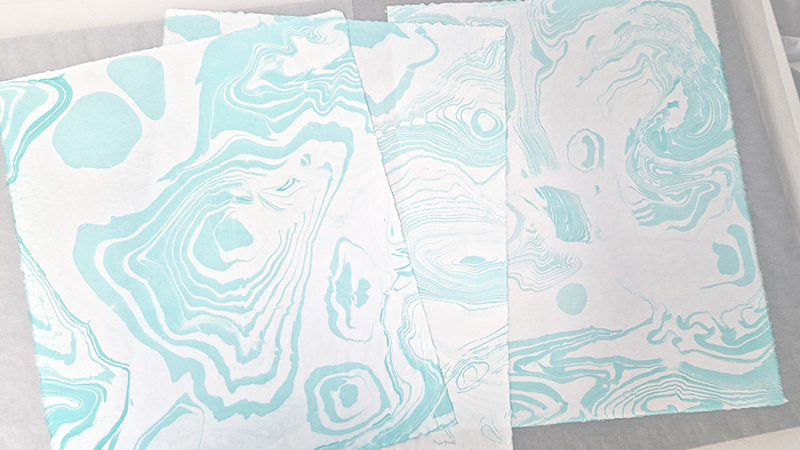
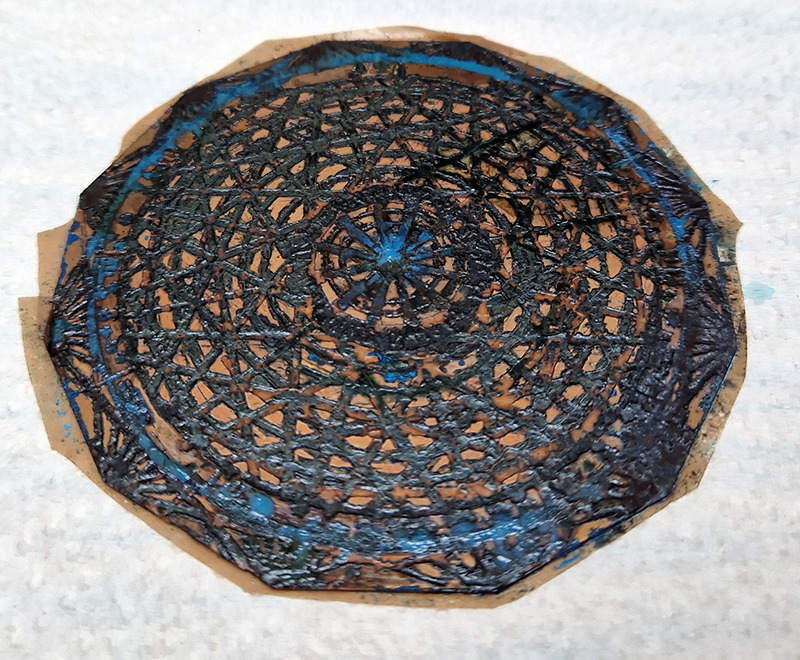
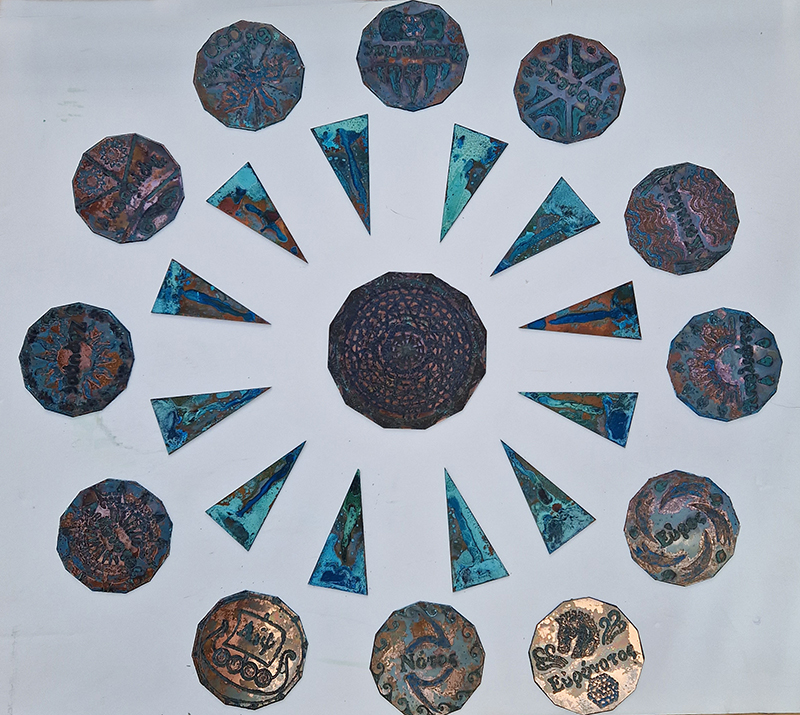
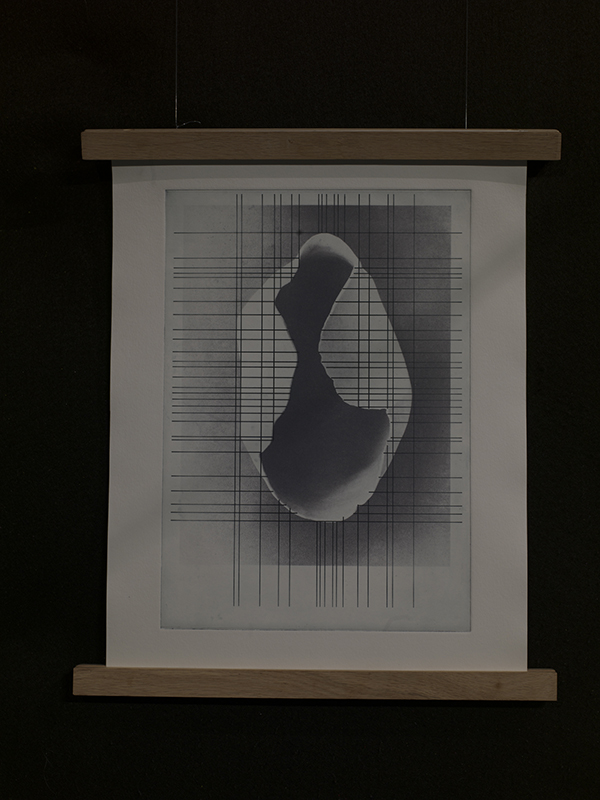
Exploring paper weaving patterns with a view to reinventing past works while thinking about ideas of cosmic planes in The Rosicrucian Cosmo-Conception, a 1909 text by Max Heindel. This text, setting out a theory of seven Worlds and seven Cosmic Planes, supposes an intermingling of spirit with matter where the intersection of the material and metaphysical world are not one above another in space, but inter-penetrate each with the other.

Astonishing that the preserved remains of the ancient kauri trees of New Zealand, alive over 42,000 years ago, can reveal the time of the last significant magnetic pole excursion within their rings. During what is known as ‘The Laschamps Excursion’, the north and south magnetic poles swapped places for about 500-800 years before swapping back again. During a magnetic pole reversal the magnetic field weakens so many more cosmic particles reach the surface of Earth. This means much more Carbon-14 is produced in the atmosphere and absorbed by plants.

Changes in radiocarbon levels were recorded from four ancient kauri logs found buried in peat swamps which seals them in a chemically balanced environment. Through high precision carbon dating processes at the University of Waikato in New Zealand the scientists discovered the most dramatic time was the lead-up to the reversal, when the poles were migrating across the Earth and our magnetic field practically disappeared, leaving life here very vulnerable to cosmic radiation. It appears, this weakening 42,000 years ago, in combination with a period of low solar magnetic activity – captured in evidence from ice cores, caused damage to the ozone layer and disrupted atmospheric conditions impacting the global climate so that devastating environmental changes took place. The research team links this climate change to extinction events which occurred at the same time, Neanderthals vanishing from Europe, and a proliferation of cave paintings appearing in Europe and Asia as humans find shelter from the turbulent weather and increased electrical storms. They have dubbed this period of excursion ‘The Adams Event’ in honour of Douglas Adams who wrote in The Hitchhikers Guide to the Galaxy that ‘42’ was the answer to life, the universe, and everything


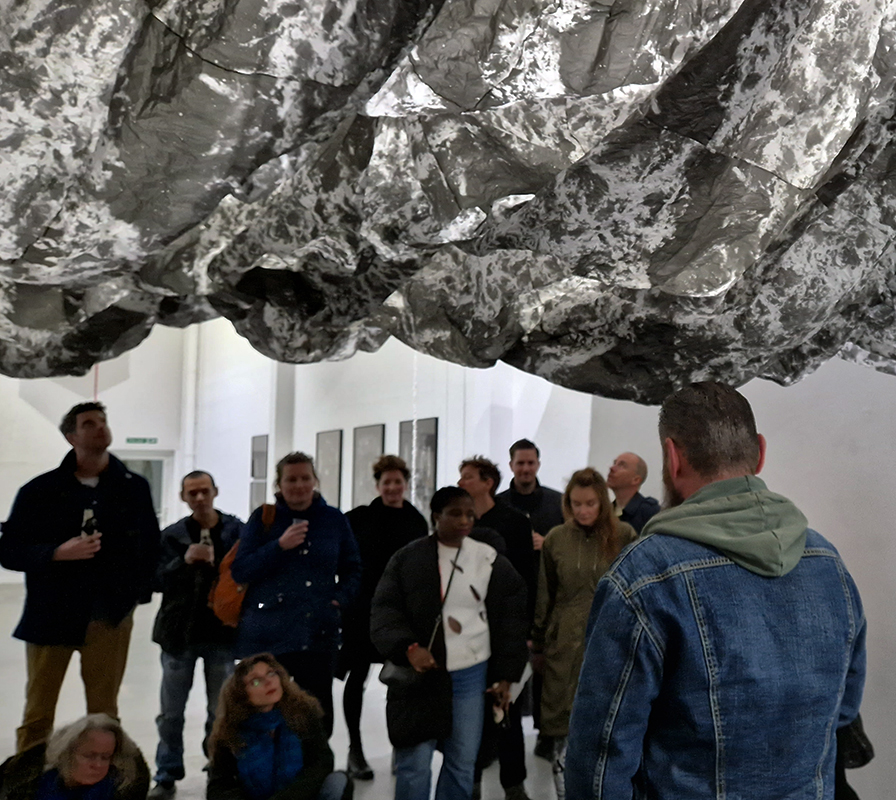
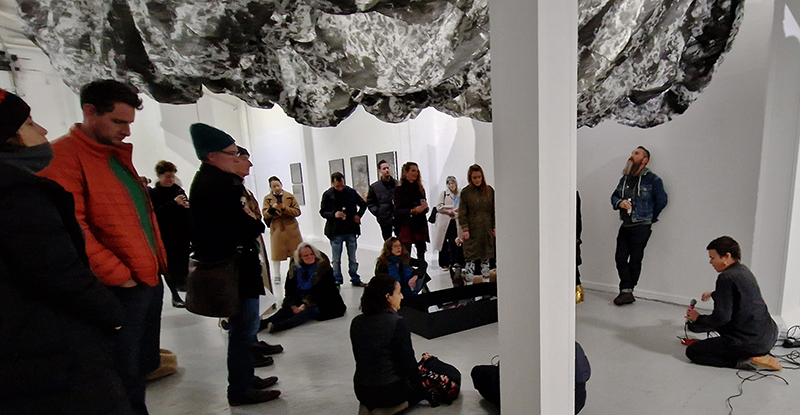
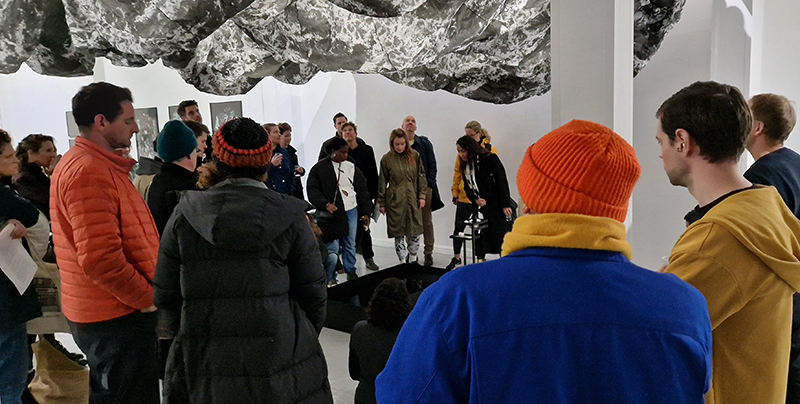
Studio Visits
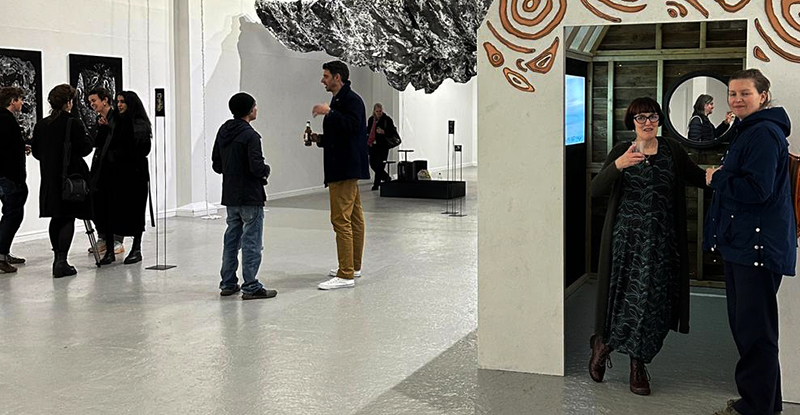
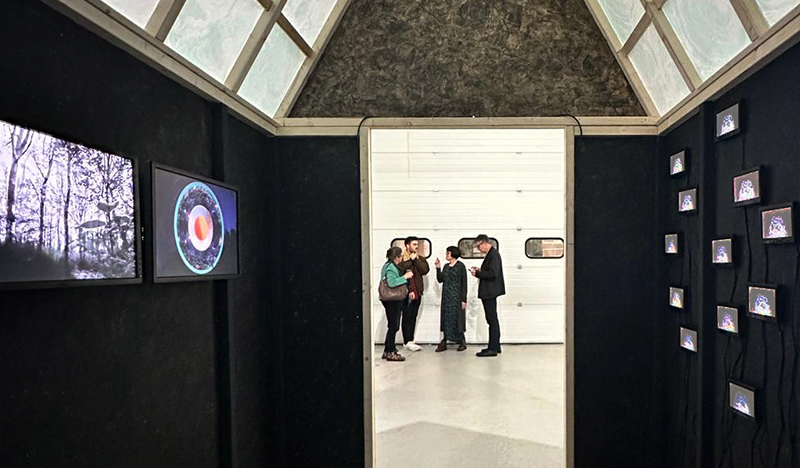
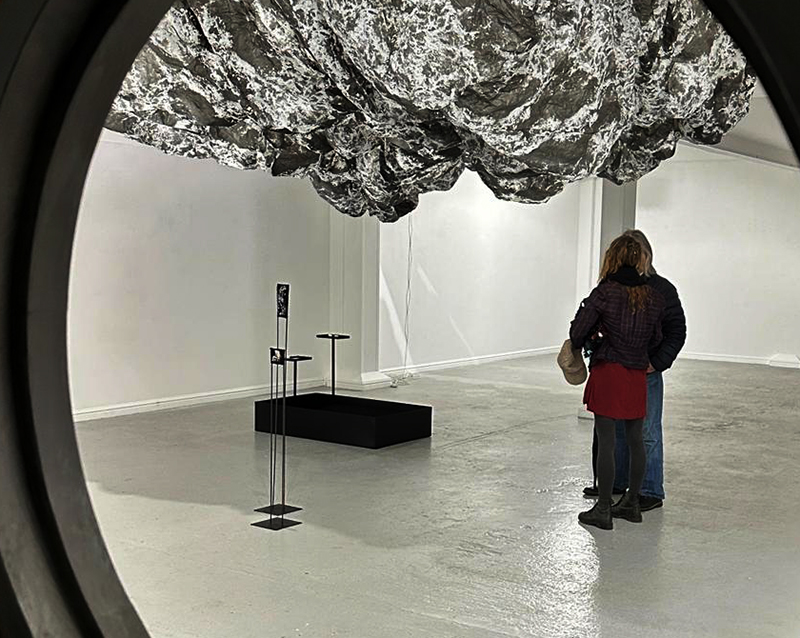
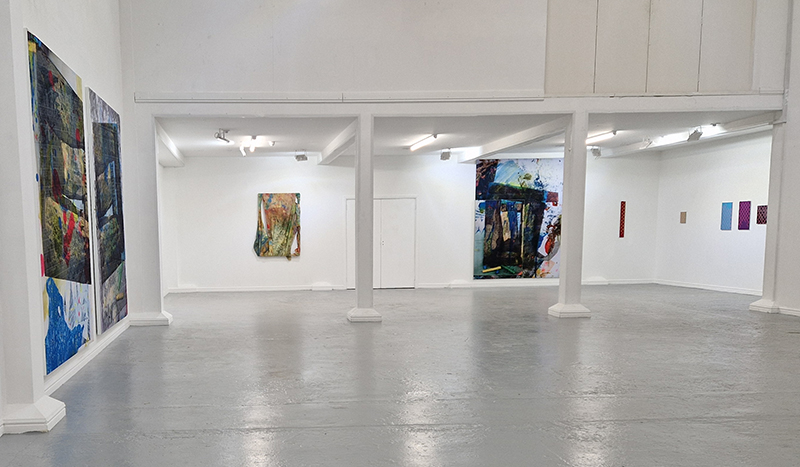
Julie F Hill and I have been visiting the other artists participating in the upcoming exhibition The Geological Unconscious at Hypha HQ Euston. We are so happy to be working with Charlie Franklin who considers control, physical experience and memory within the natural landscape, Deborah Tchoudjinoff who considers what the form is through the process of material and visual experimentations, Rona Lee who centres on the politics and aesthetics of Geo-materiality along with the human /more than-human entanglements of contemporary life and Sophie Mei Birkin who investigates the generative potential in the transformation of matter through a variety of material processes such as growing salt crystals and exploring amorphous and decomposing substances.
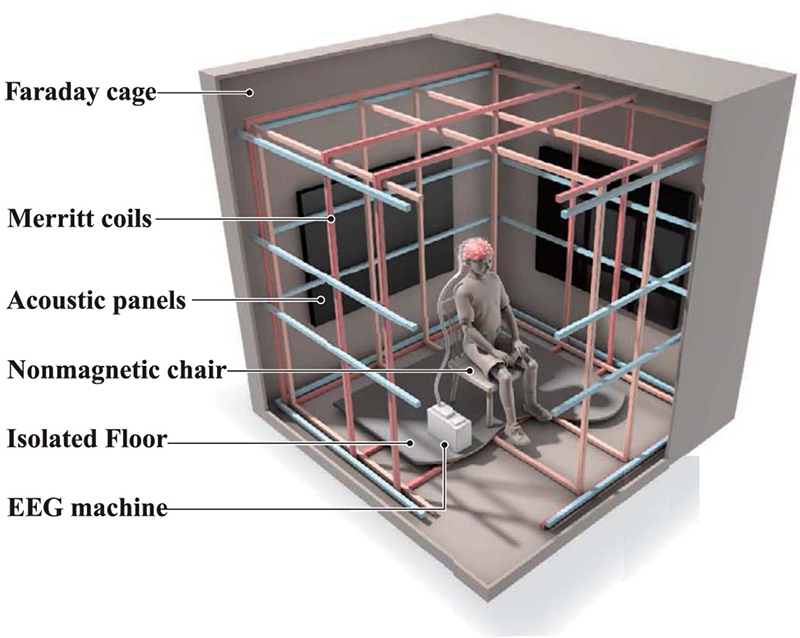
I have also been lucky to have Charly Blackburn and Victoria Rance visit my studio to chat about our respective work and shared interests. Charly is beginning a period of research into rare earth materials and extractive processes and we share a fascination with things magnetic. Victoria came to chat about our shared interest in the sun but is also interested in magnetic fields and the potential they offer for brain to brain communication.
Gallery Visits
Haegue Yang Leap Year at Hayward Gallery. With colourful works festooned by garlands of bells and strewn with fairy lights this was a perfect show for the festive period. Folklore, surrealism and ritual, collage and costumes combine with the modern domestic/utilitarian in hybrid works that have a playful carnival air.
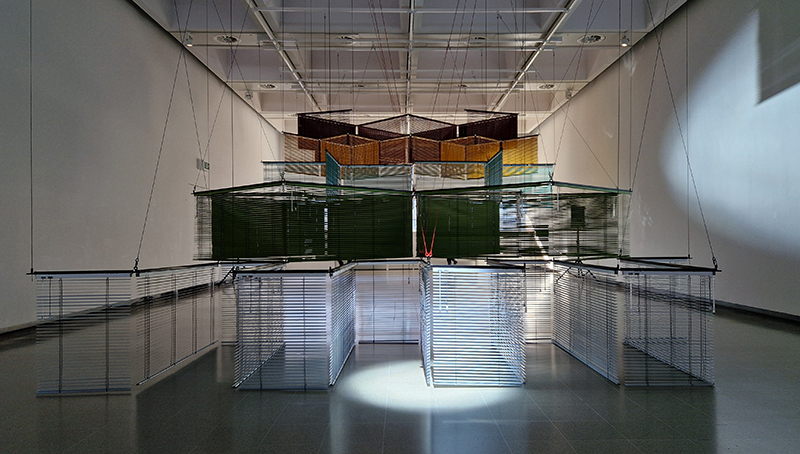
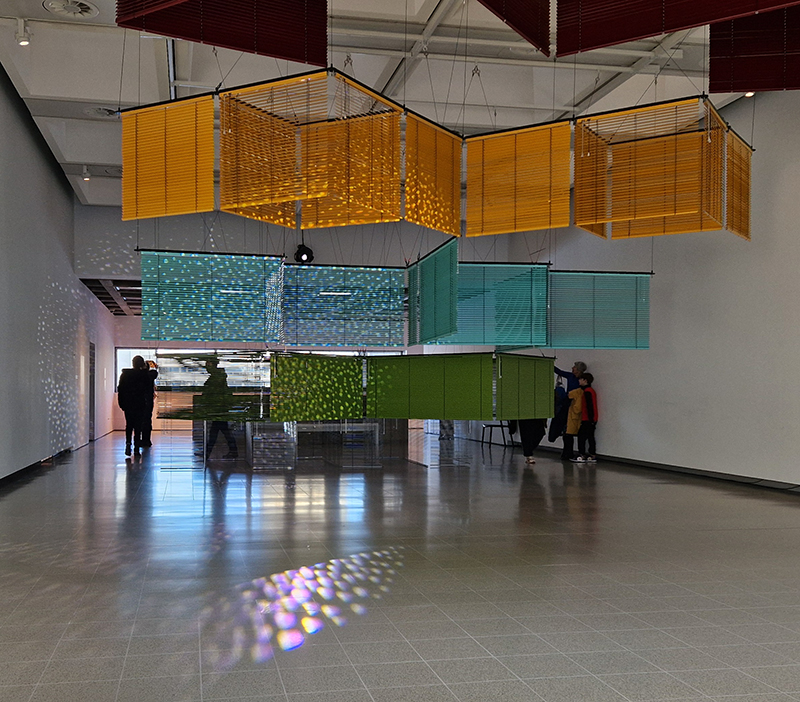
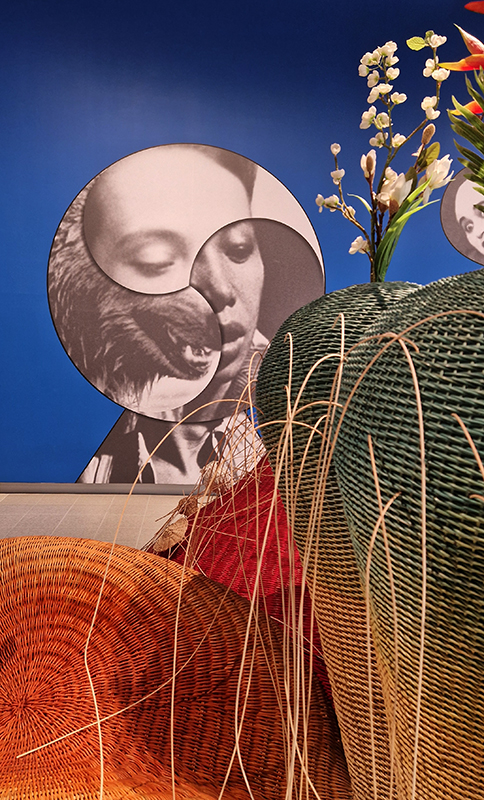
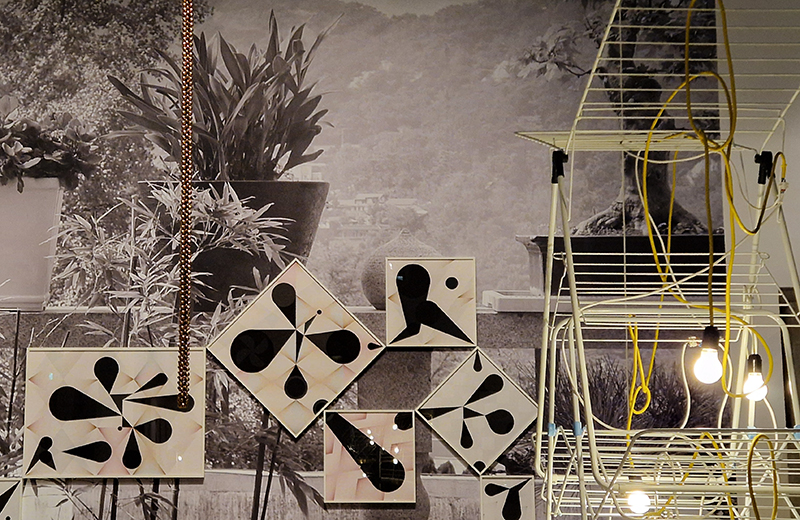























Thoughtful works beautifully presented Each Place Its Own Mind at Edel Assanti with Mirtha Dermisache | Noémie Goudal | Sky Hopinka | Anna Hulačová | Marguerite Humeau | Bronwyn Katz | Kat Lyons | Yukultji Napangati | Emmanuel Van der Auwera. An ongoing collective reimagining of our relationship with the living world, rooted in revelations from indigenous knowledge, ecological research, literature, science, and artistic experimentation. Each Place Its Own Mind borrows its title from ecologist David Abram’s 1996 book The Spell of the Sensuous, which traces the ways the human mind came to renounce its “sensory bearings” in the natural world, visualising a myriad of “lost” faculties that link the “inner, psychological world and the perceptual terrain that surrounds us.”














IN ATTENDANCE – Paying attention in a fragile world competing for attention in the stunning Fitzrovia Chapel includes work by Etel Adnan, Emmanuel Awuni, Phyllida Barlow, Berlinde De Bruyckere, Gabriella Boyd, Miriam Cahn, Eve Sussman, Rachel Kneenbone, Anj Smith, Paula Rego and Cathy Wilkes. Ultimately the gangly body of a foal on the alter arrests the attention here.




Damian Taylor Things Past at Thames-side Studios Gallery. These paintings hover on the edge of discovery where content and surface are ambiguous but reward study with tantalizing recognizable glimpses.

Events
A little out of my depth at the A&G Highlights Meeting at The Geological Society where some talks were quite specialised, involving graphs and terminology beyond my understanding. I do enjoy hearing clever people talk though, even if I can’t grasp exactly what they are explaining. A fascinating presentation by writer Nilanjan Choudhury on ‘The Square Root of a Sonnet’, his play which explores the fraught personal relationship between the brilliant Indian-American astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar and his mentor, Sir Arthur Eddington of Cambridge University who publicly humiliated him at a Royal Astronomical Society meeting 90 years ago to the day. Guardian Article here

Dr Jessica Irving (Bristol University) gave The Harold Jeffreys Lecture on ‘Hearing planetary hearts: seismology of the cores of Earth and Mars’. An engaging speaker, she led us through the milestones of the last 130 years of theories on what is at the centre of the Earth and the discoveries made using seismology.



Dr Chris Lovell (University of Portsmouth) spoke on his research into ‘Accelerated modelling of the entire observable Universe’. I recognised the dark matter simulations and was fascinated by the different views of a galaxy depending on the band of the light spectrum used to observe it.


I joined a sobering Royal Astronomical Society webinar We Need to Talk About Space Junk presented by Professor Mike Lockwood. Our use of space is increasingly limited and threatened by space junk. The concern is that we are heading towards a runaway effect called the Kessler syndrome, in which the debris from one collision causes many others, to the point where space becomes unusable.






I went to see the fast paced RSC production of Kyoto at Soho Place. Welcome to the Kyoto Conference Centre, 11 December 1997. The nations of the world are in deadlock and 11 hours have passed since the UN’s landmark climate conference should have ended. Time is running out and agreement feels a world away. The greatest obstacle: American oil lobbyist and master strategist, Don Pearlman… Set nearly 20 years ago its depressing how little progress was made and we are currently sliding backwards. Would never have guessed it at the time but now am nostalgic for the politics and positivity of the 90’s.
Time to email your MP to join The All-Party Parliamentary Group for Dark Skies. The group’s primary focus is to preserve the night sky within the UK and promote the adoption of dark sky friendly lighting and planning policies. Surprisingly the committee is made up mostly of tories – come on the rest of you!
Go to this link where it is quick and easy to message your MP to act on this important issue.

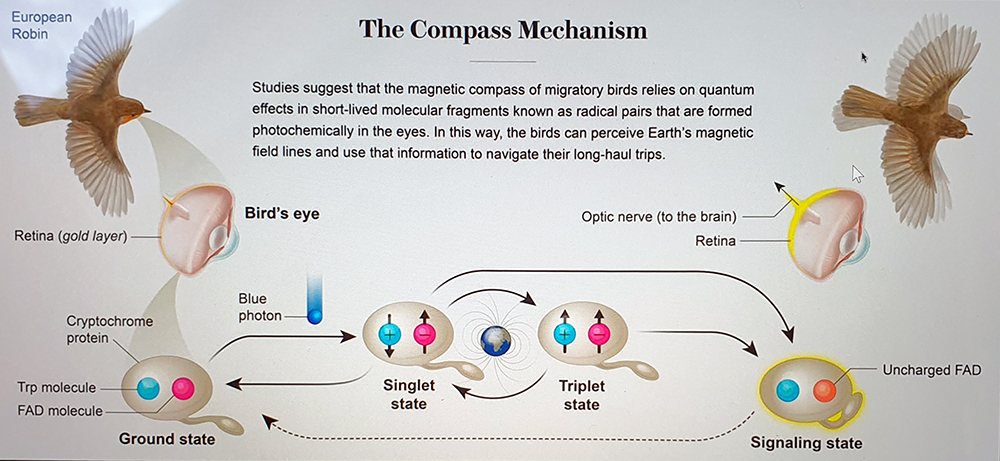
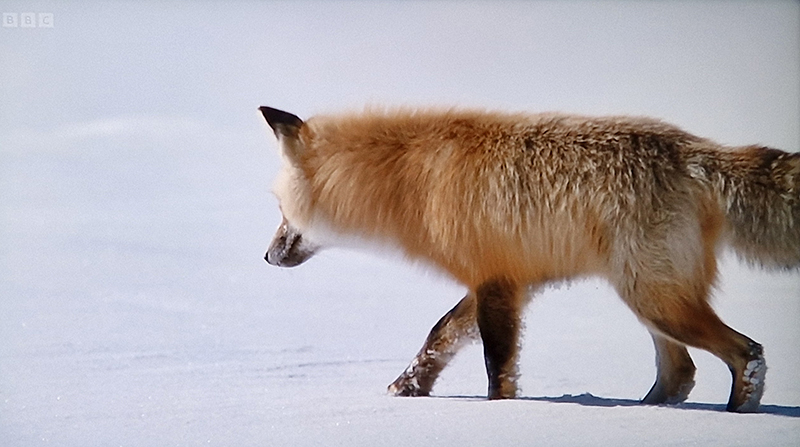
Watching Chris Packham’s The Wonder of Animals – Foxes A red fox catches its prey using more than pinpoint hearing and an accurate pounce: it also involves alignment to the slope of Earth’s magnetic fields. I contacted Peter Hore FRS, Professor of Chemistry and Magnetoreception expert at Oxford University who was so helpful to me before in explaining how birds ‘see’ the magnetic field to see if he had come across any new research on this. He has pointed me in the direction of other research conducted by the group looking at fox behaviour so this is something I will pursue further.


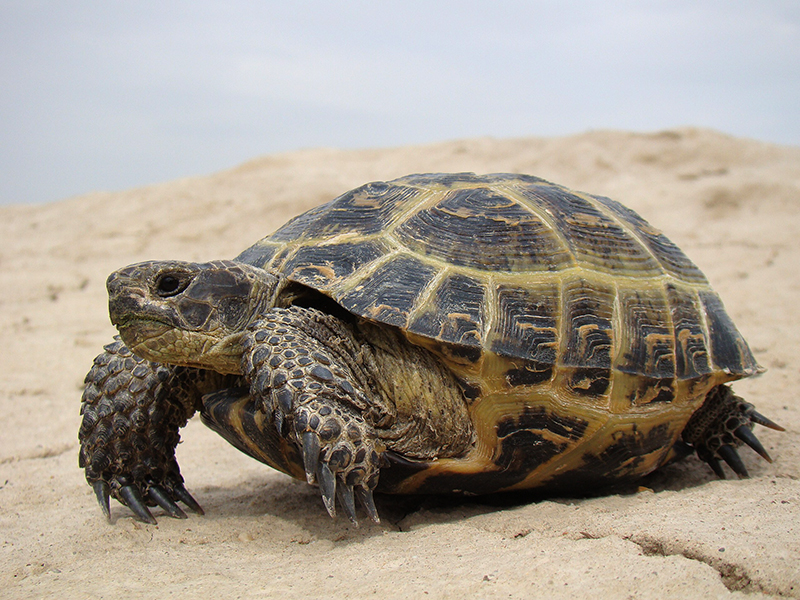
Listening to What? Seriously?? with special guest Helen Sharman, the first British astronaut, about how humans learned to survive in space. Quite a few animals were sent to space before humans including two Russian Steppe tortoises (Testudo horsfieldi), who did a circuit of he moon and returned to Earth – alive but starved. The tortoises were chosen as they have a unique ability in the animal world to resist radiation and their blood may be useful in the treatment of radiation sickness. In recent research a string of amino acids have been extracted from the blood of these tortoises and if you inject those amino acids into other animals they become radiation resistant too.


Listening to The Year in Science 2024 podcast – One of the UK’s first military communication satellites’ Skynet 1a launched in 1969 was abandoned a few years later above Africa. Orbital dynamics should have dragged it out somewhere above India but it has been found wandering above the Americas in a busy area of live satellites and no-one knows why. Space consultants think it must have been commanded to move in the 1970’s but can find no record of this and although research has been undertaken it is still a mystery how this satellite moved. BBC article
There is no mention of a cosmic ray interaction forcing the command, but that would be my theory!