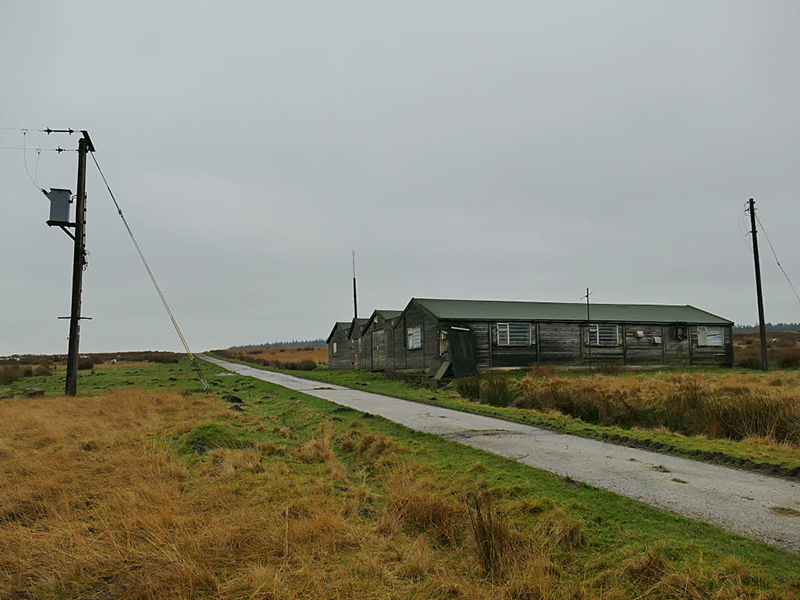
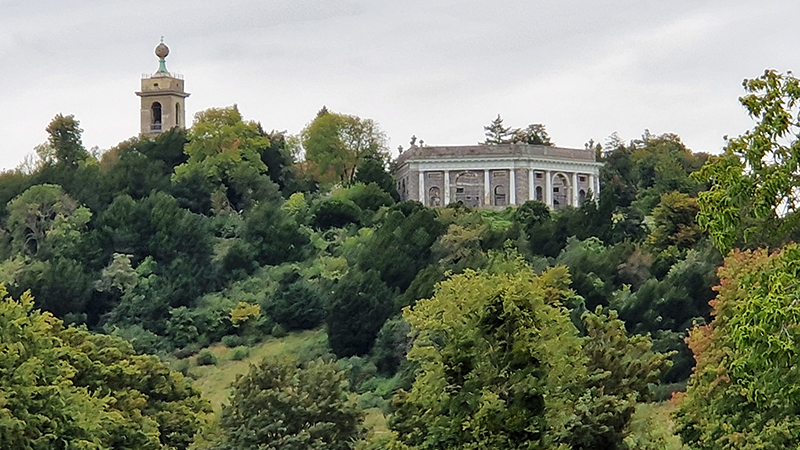
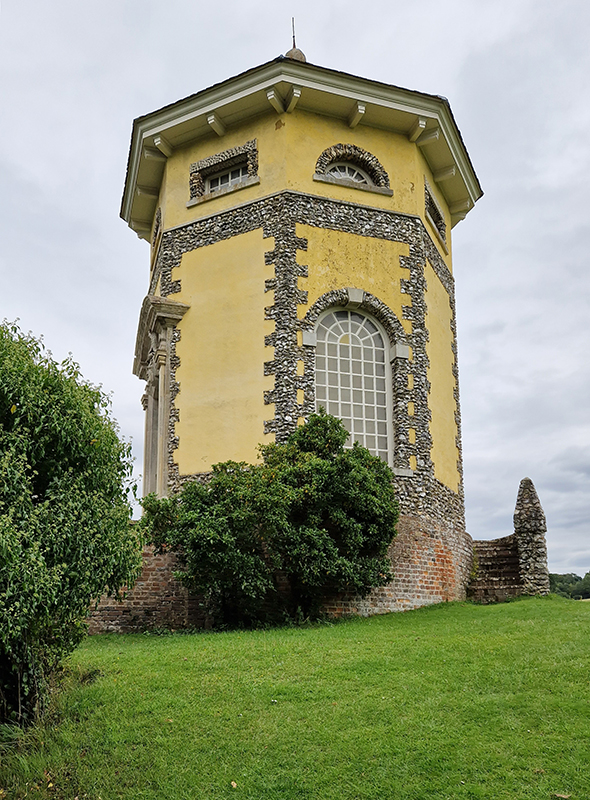
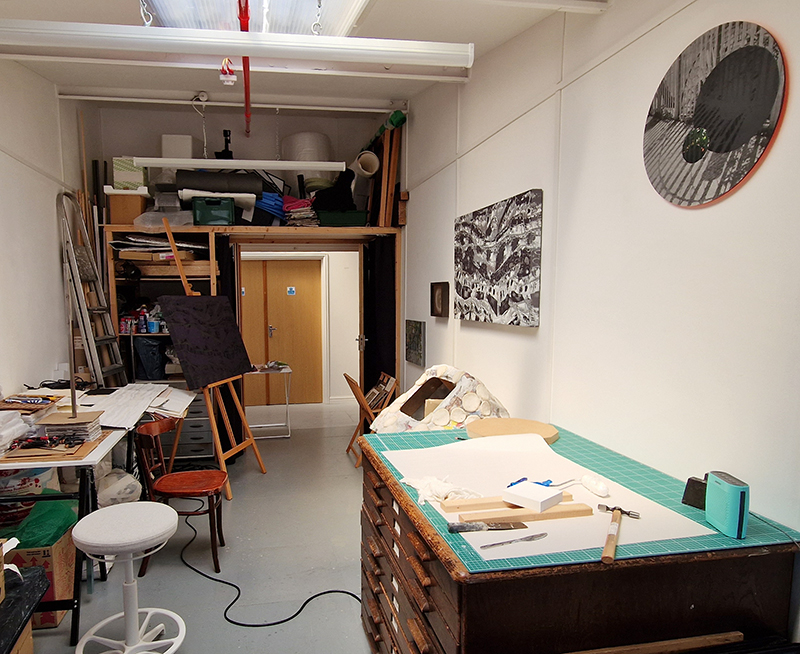
I am extremely grateful to a-n Artists Newsletter for the professional practice and creative development bursary that allowed me to visit Kielder Observatory in Northumberland and Eskdalemuir Observatory, Dumfriesshire to research how space weather impacts Earth’s magnetic field. I am also grateful to Claire Brown, site manager at Eskdalemuir Magnetic Observatory, for her time showing me around the site and explaining the many measurement processes that happen here. Despite the first survey of the site at Eskdalemuir, by the National Physical Laboratory in 1903, reporting back that “the weather was wet and stormy, and somewhat unfavourable to “field work” an observatory was established in this remote location, and recordings monitoring Earth’s magnetic field have been made from this site for 120 years.
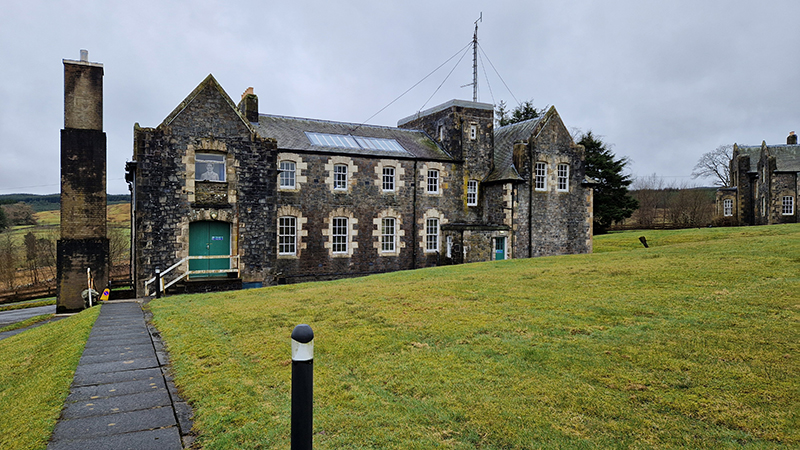

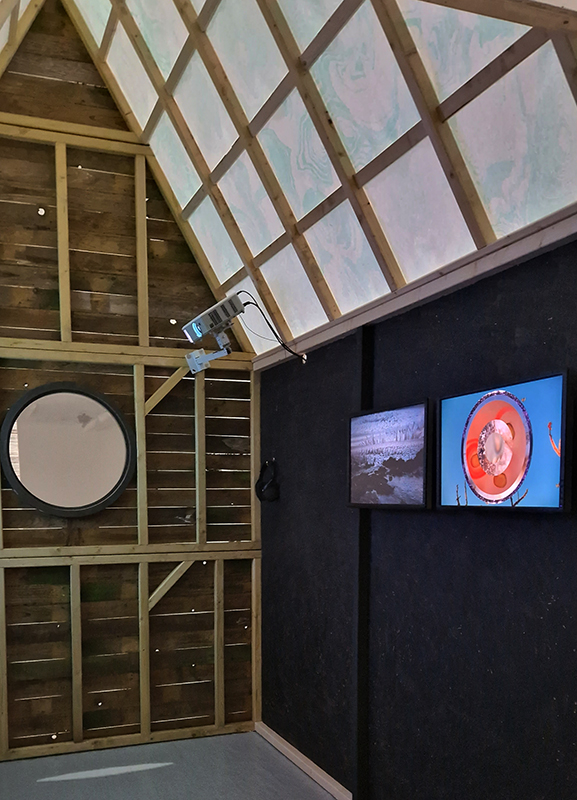
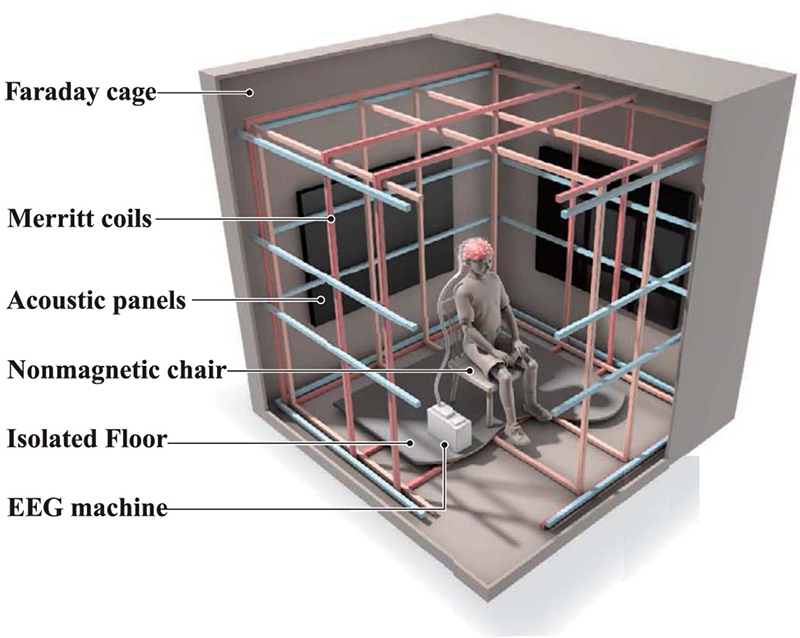
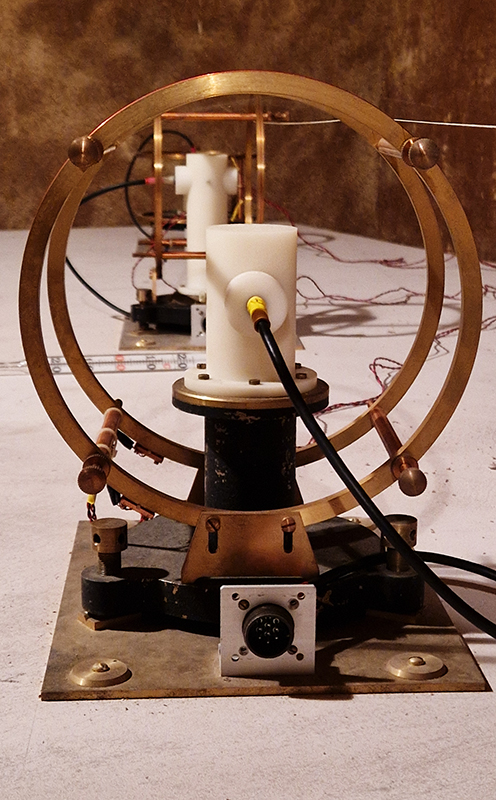
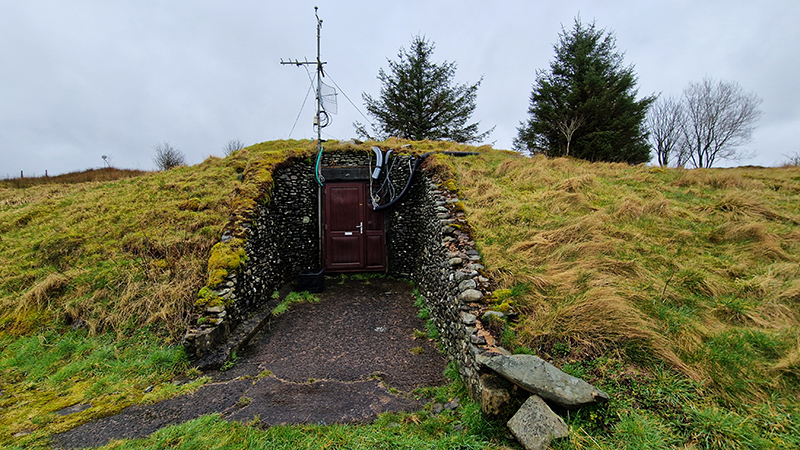
I was able to visit the East Absolute Hut, the Underground Chamber, and the Seismic Vault along with the main building and museum rooms. The interaction of space weather with magnetic currents in the surface of the Earth is monitored here, and there is a camera on the roof to record visual aurora on a loop which is then sent to the British Geological Survey research teams in Edinburgh for analysis. Meteorological observations are also made here, along with solar radiation, atmospheric pollution, and seismological activity. The monitoring of radiation pollution was inaugurated here after the Chernobyl incident in 1986 when explosions at the nuclear plant scattered radioactive elements over a wide area across Europe.
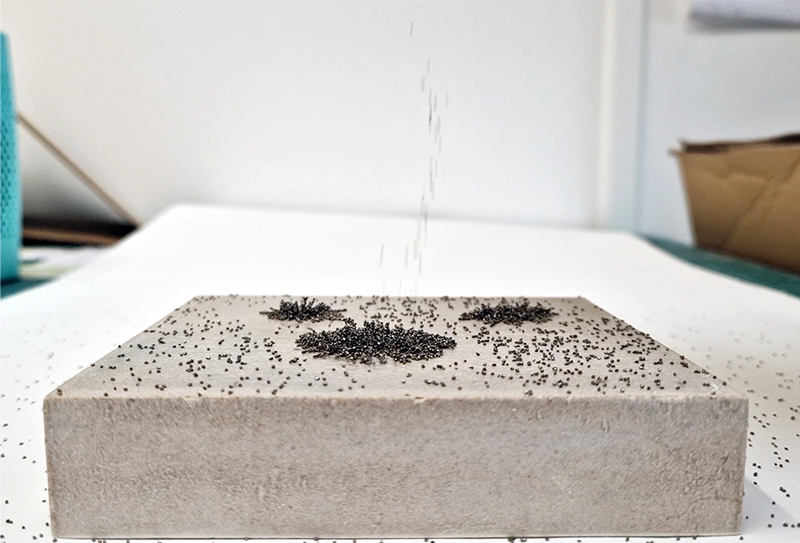
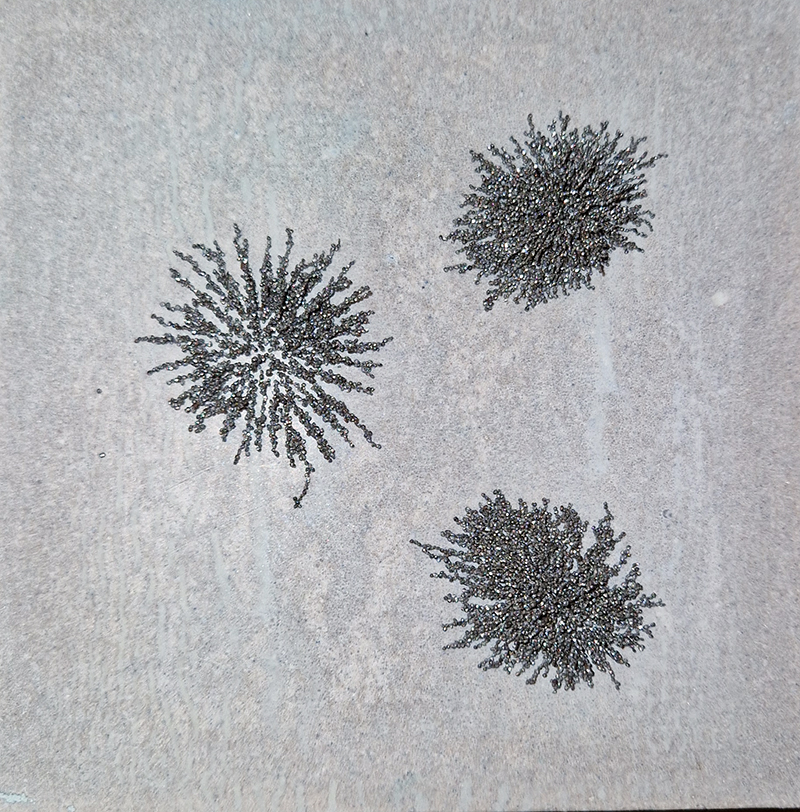
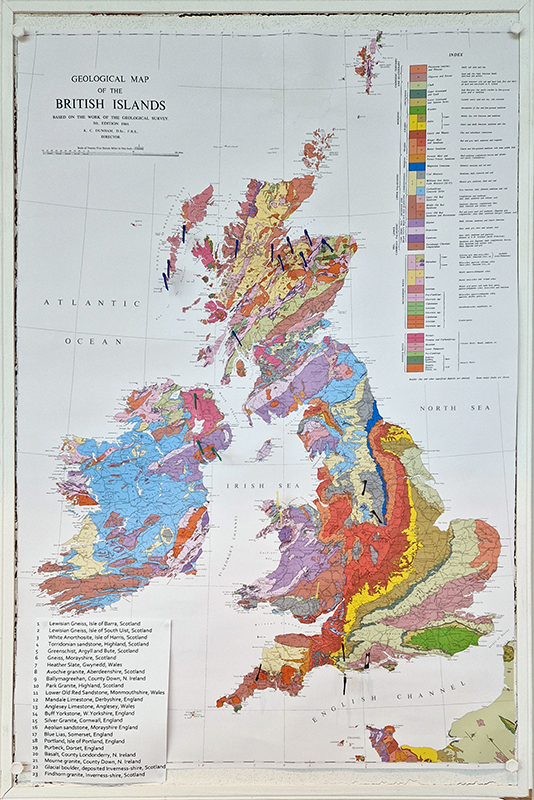
95% of Earth’s magnetic field comes from the swirling outer core of the Earth and changes are due to convection pattern turbulence. As compasses have been used for over 400 years, and records kept of magnetic declination, there is a long history of measurements to refer to. The magnetic north pole had been drifting westwards at about 55km a year up until 2020 but has recently slowed to 45km. Consistency of observations is very important for magnetic field modelling, which is why many of the instruments at Eskdalemuir are located underground to maintain an even temperature.
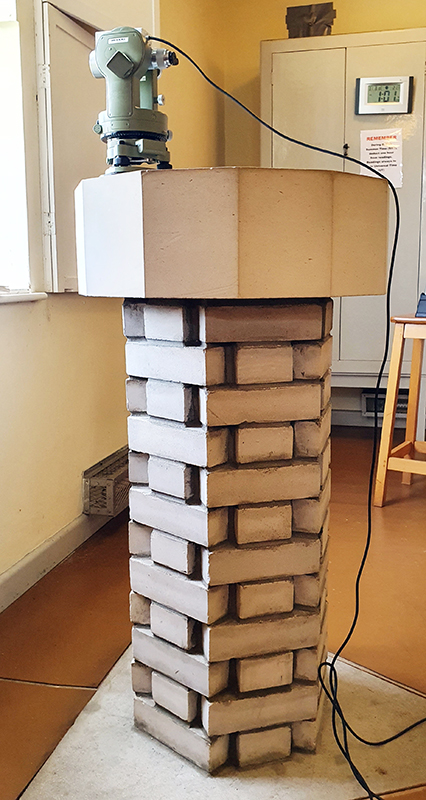
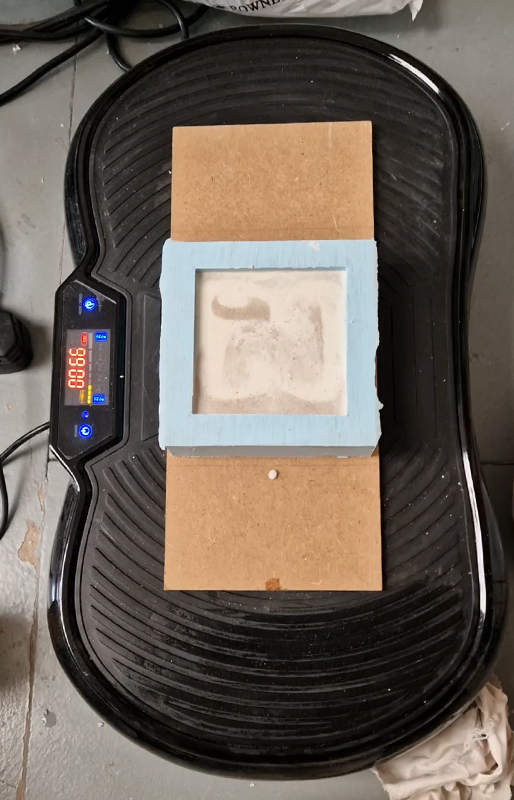
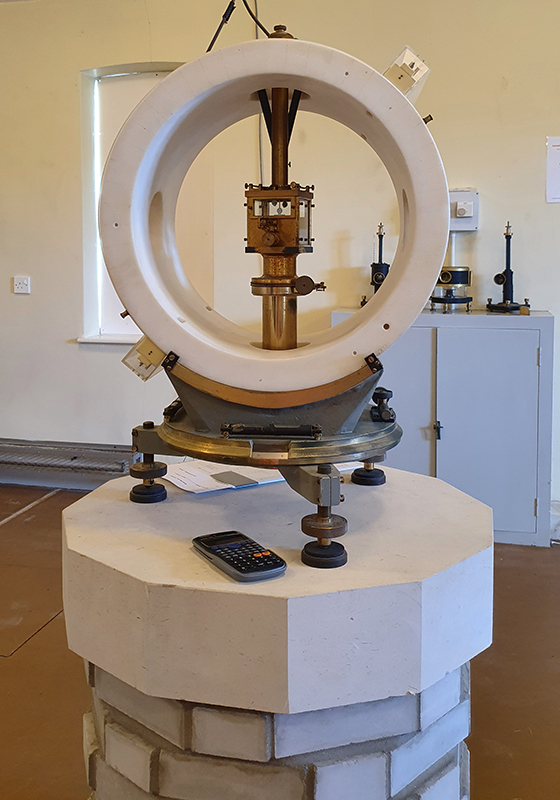
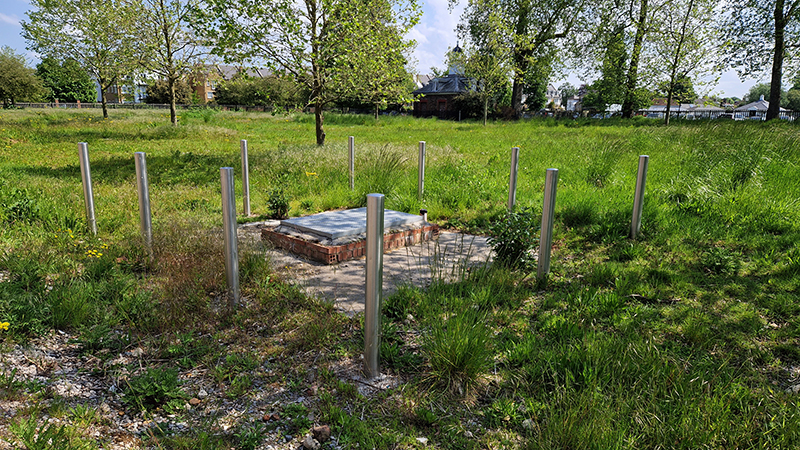
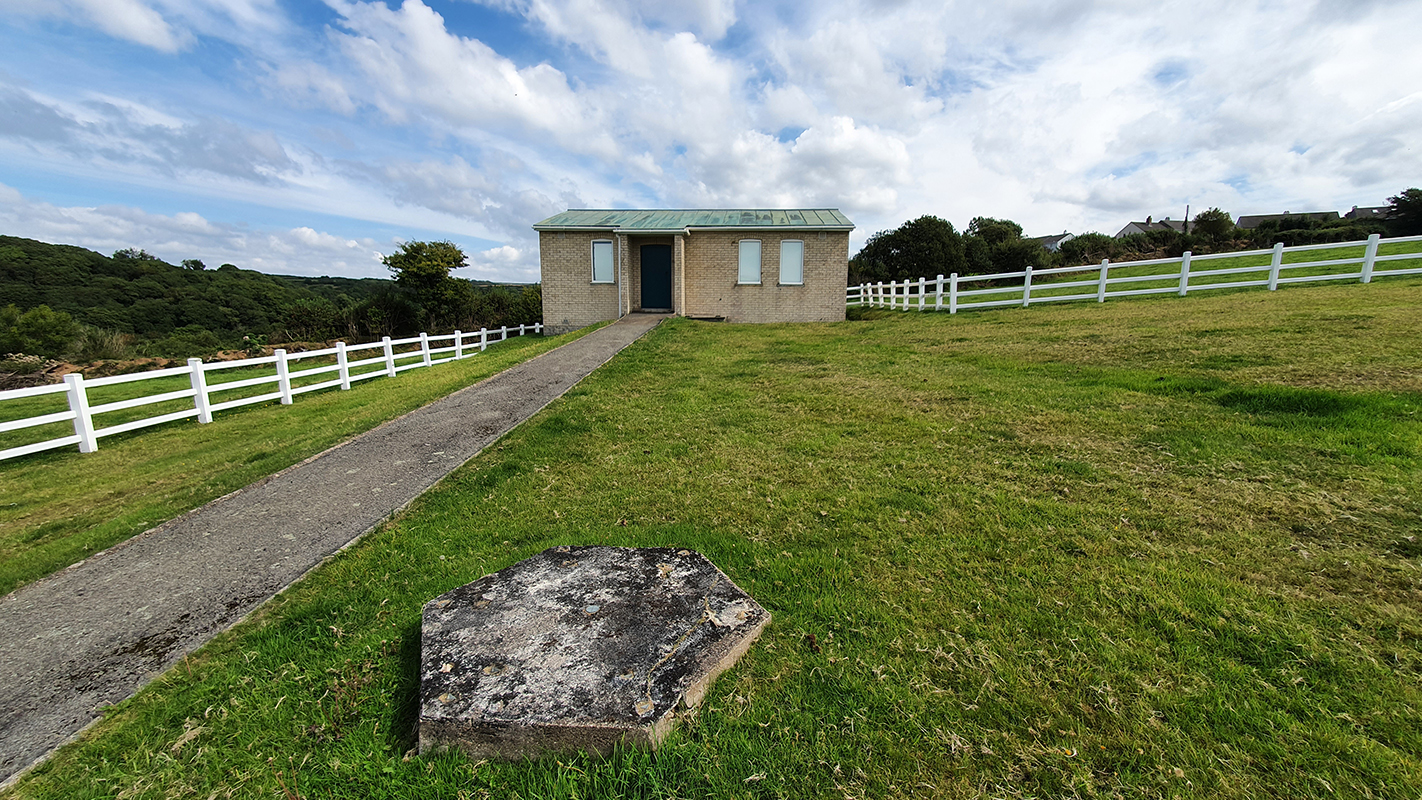
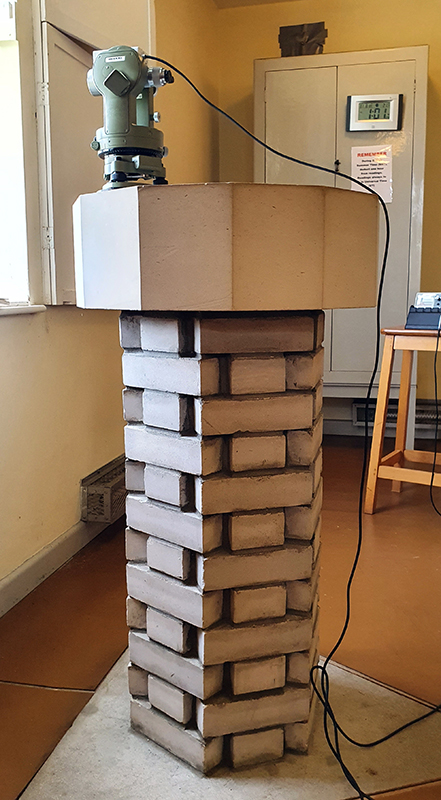
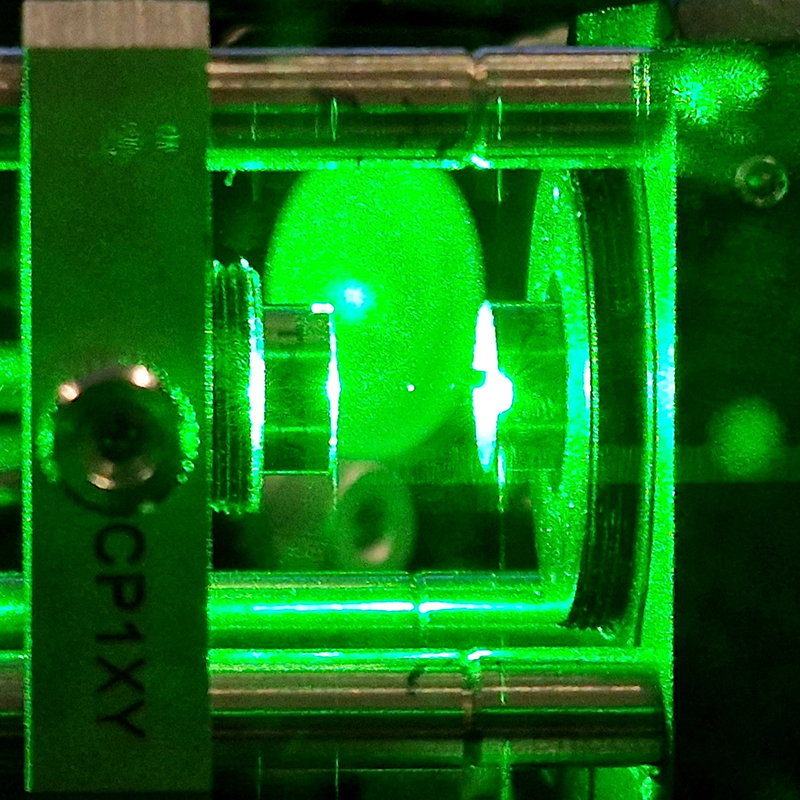
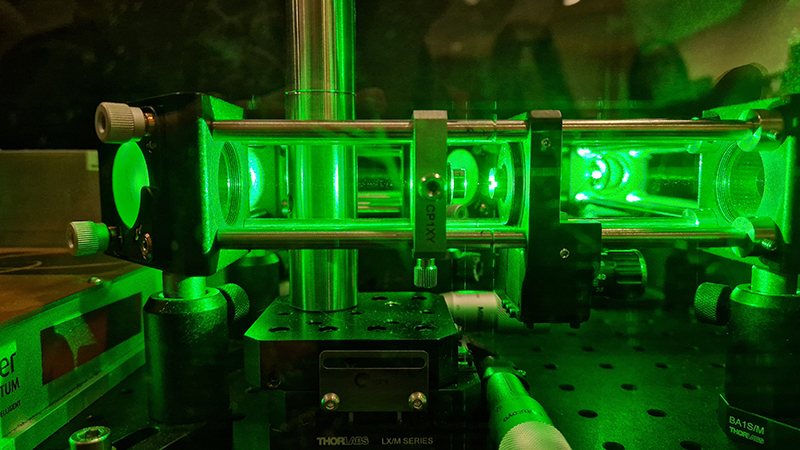
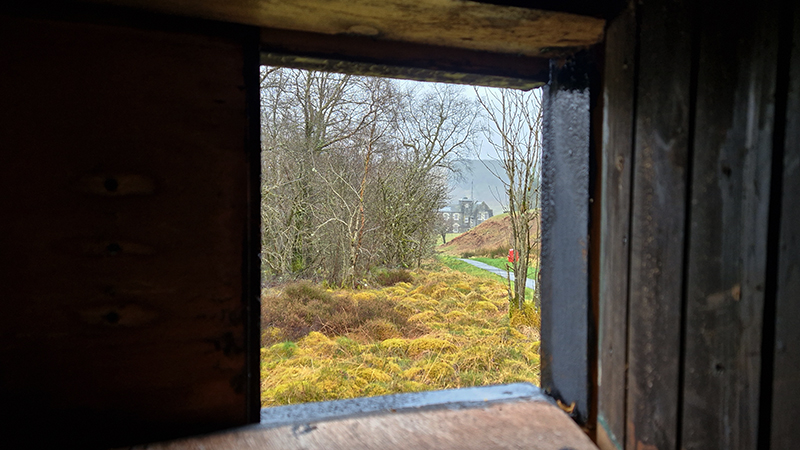
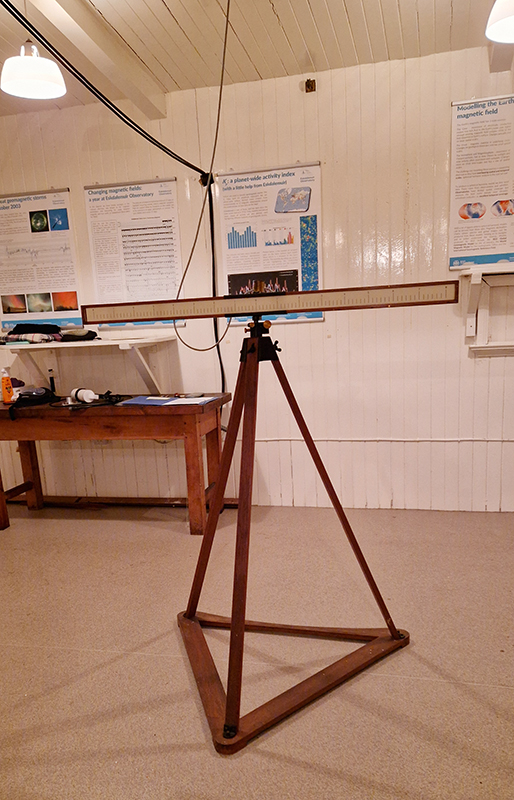
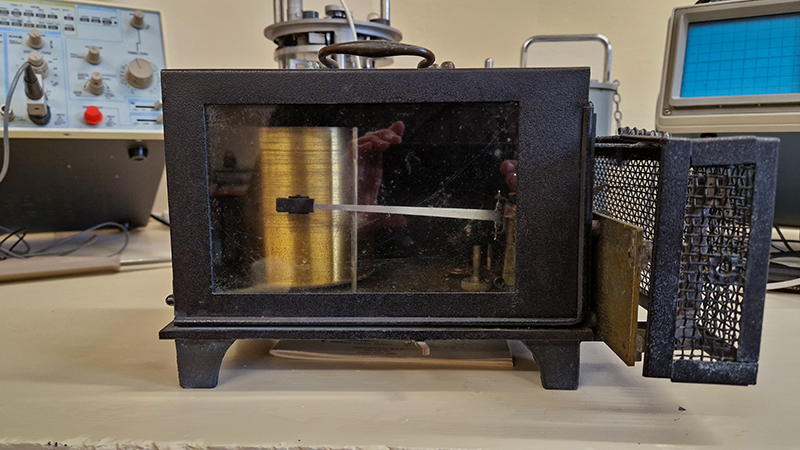
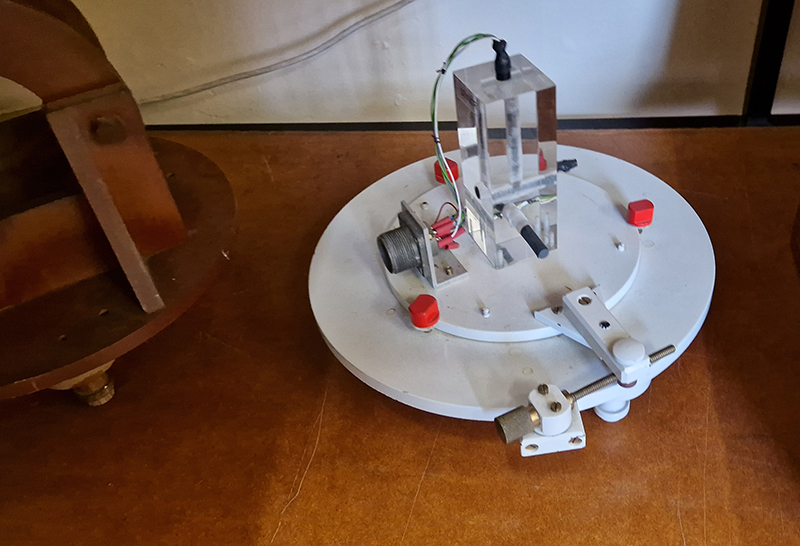
Manual observations of the direction of the magnetic field are taken once a week from the East Absolute Hut. A small sliding window in the wooden hut is pulled back to reveal a distant fixed azimuth mark, not always easily visible during inclement weather. The mark, viewed through the fluxgate theodolite, must be lined up with the north south meridian line until the reading on the digital recorder is at zero. At the same time the digital clock must read zero. These numbers fluctuate rapidly but once both machines read zero a measurement of the position of the magnetic north pole can be recorded. A separate recording is taken through a series of 12 angles on the theodolite to give an accurate position. The instrument is very sensitive and the operator wears the same clothes each time with no metal fixings etc to ensure consistency in the records. The measurements are then plotted on a graph which usually follows a smooth line describing the drift of the magnetic north pole. Sudden deviations alert the operator to errors in the recordings or dramatic movement in the field known as a geomagnetic jerk.




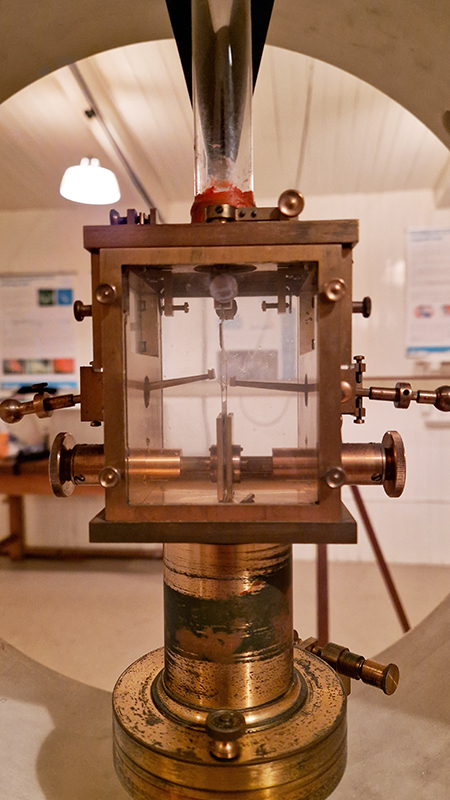


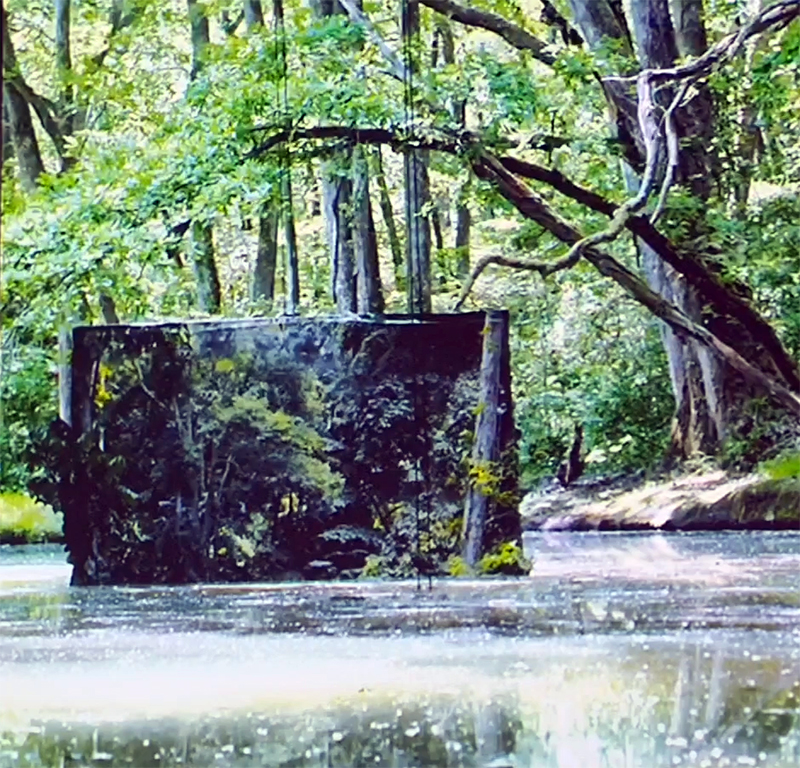
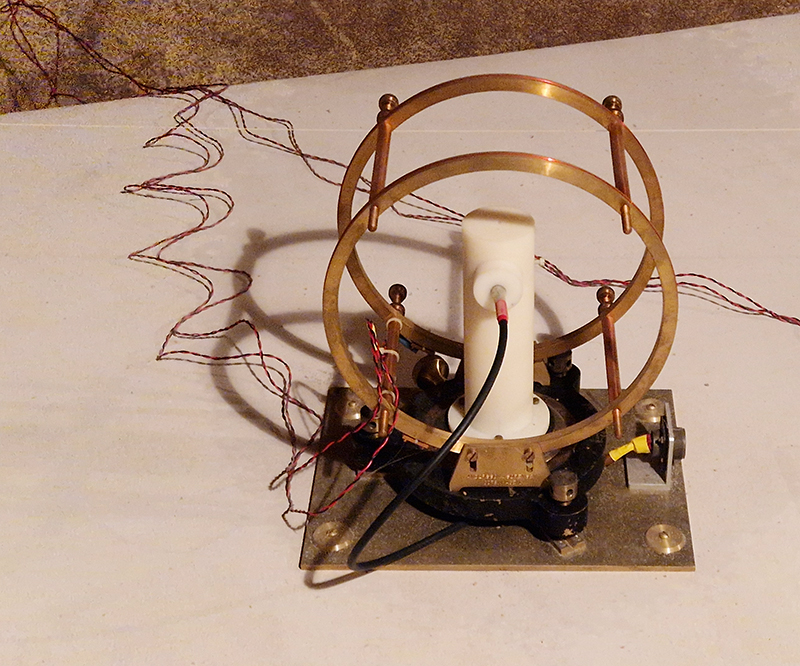
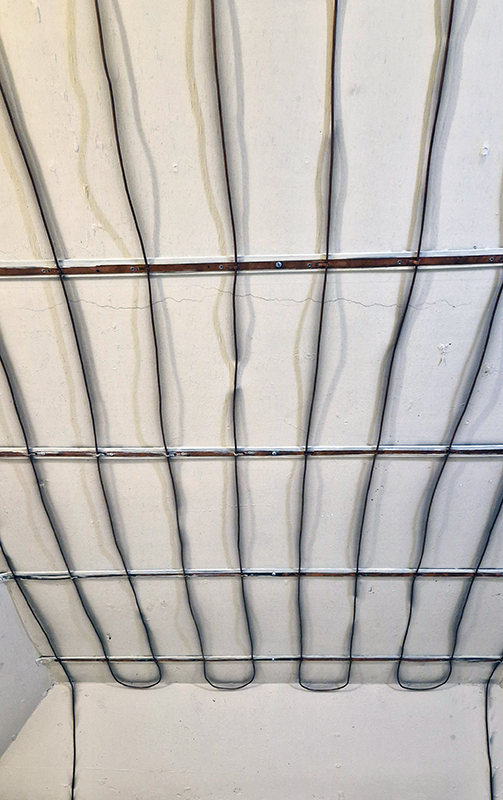
The instruments in the underground chamber measure the strength of the magnetic field in three directions.


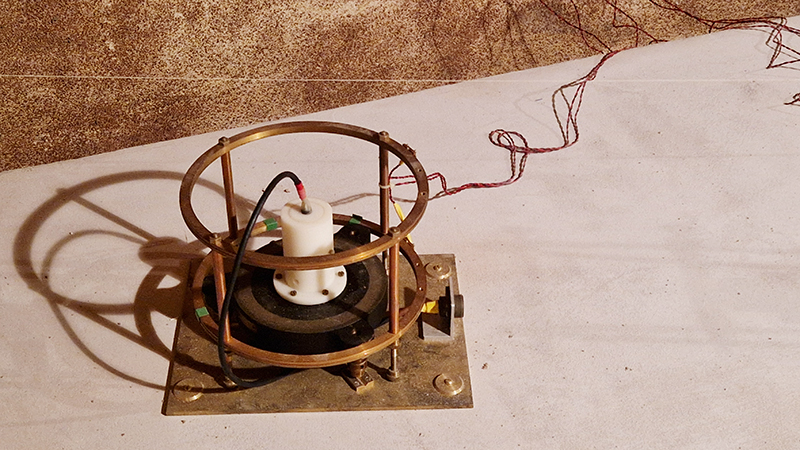

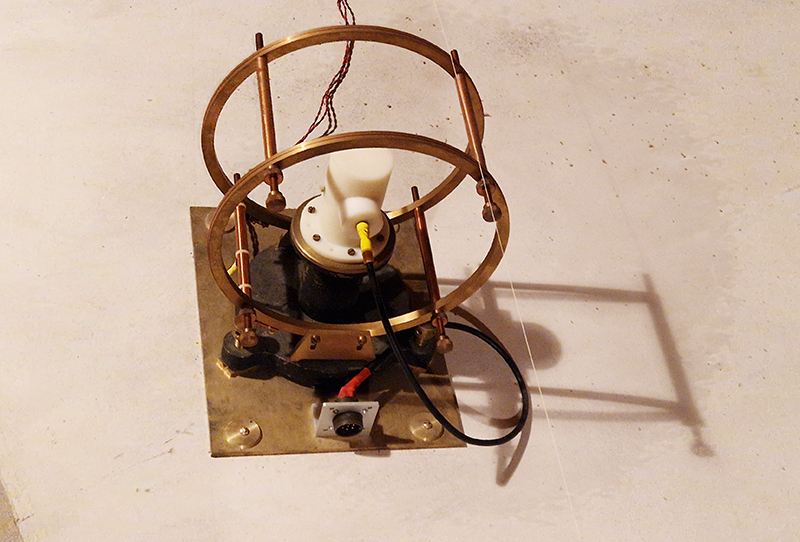



Surface readings are also taken automatically from instruments in small enclosures in the back field. During my visit these instruments were used to record data rather than those I came in close contact with.

In the vault, seismograph readings are made of vibrations in the bedrock. Seismic activity around the UK is fairly low level but sensitive structures can still be effected. These instruments pinpointed the magnitude 4.7 Longtown earthquake on Boxing Day 1979, and a swarm of tremors in the Dumfries area in 2001. The network also detected the air crash at Lockerbie in 1988, accurately recording the time of impact for crash investigators.
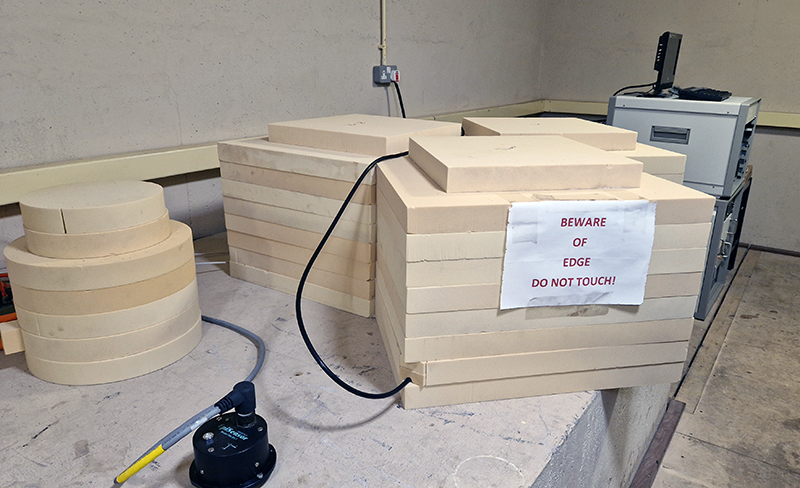





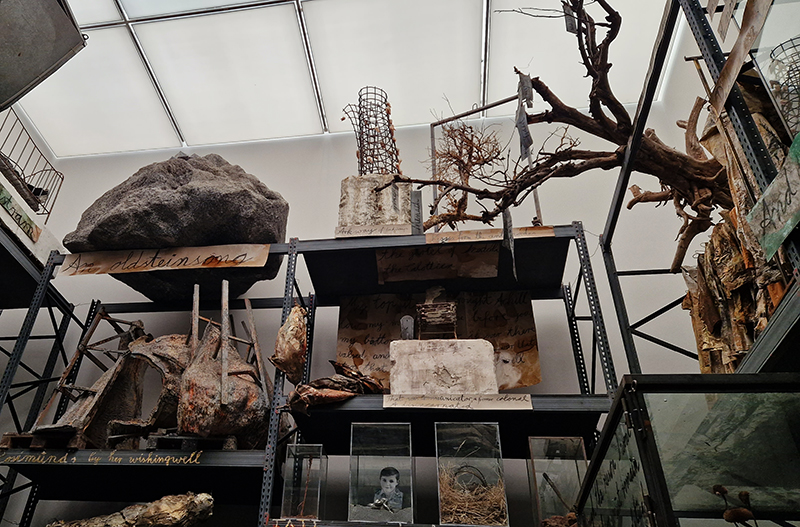
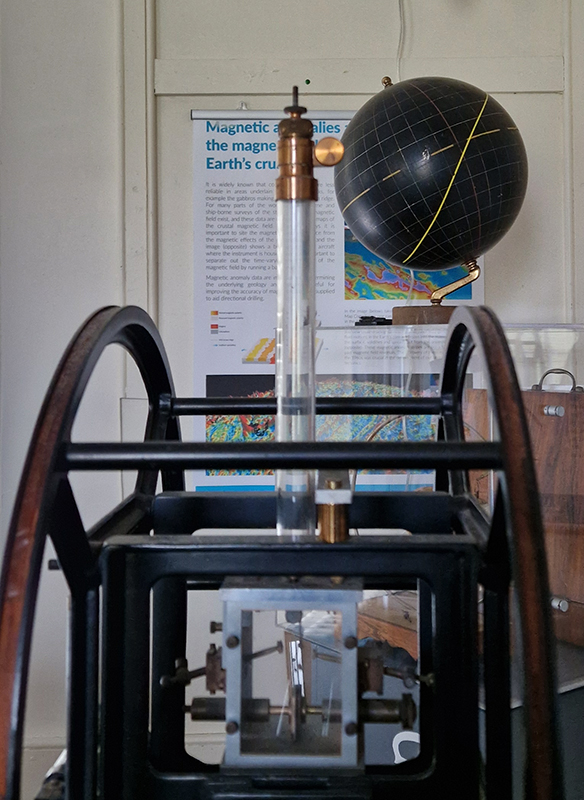
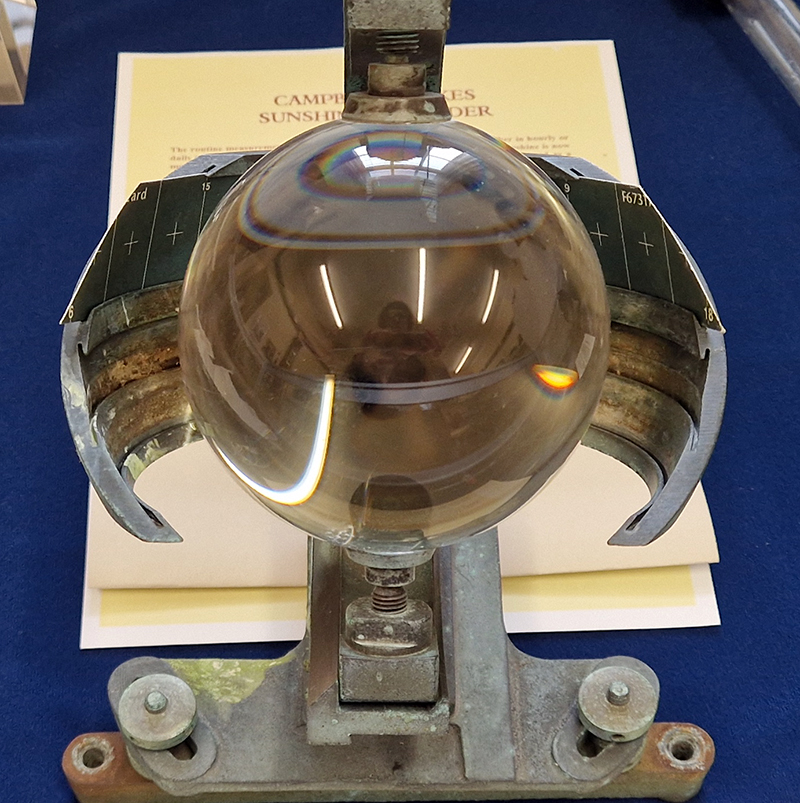
The museum holds a wonderful collection of mysterious instruments.








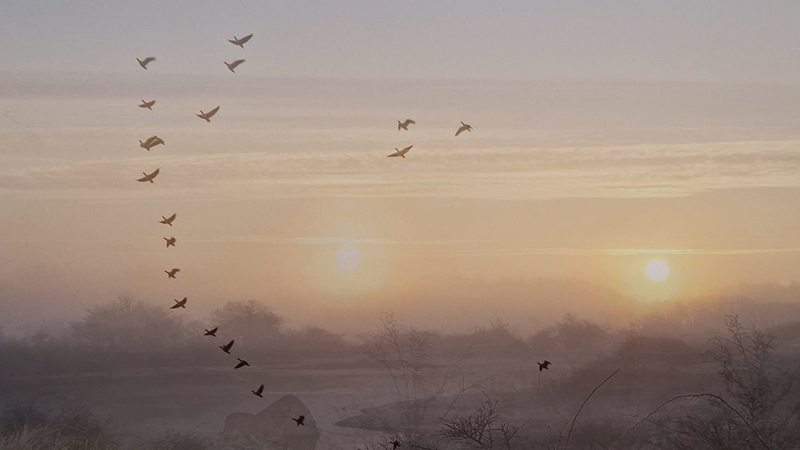
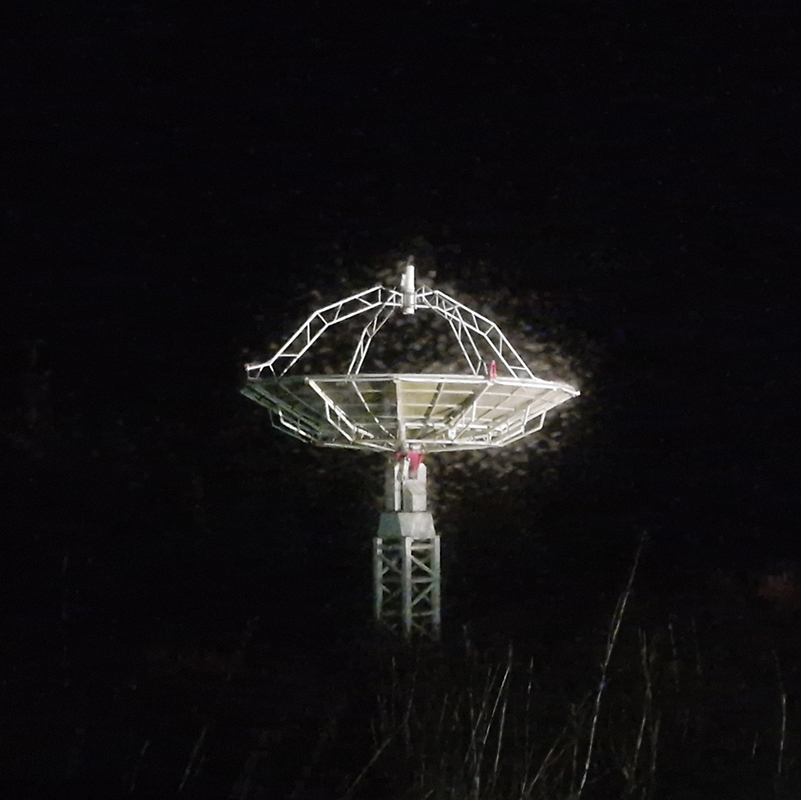
I attended Aurora Night at Kielder Observatory, established in 2008 under some of the darkest skies in Europe, to learn about how solar activity interacts with Earth’s atmosphere and creates the Aurora. The skies were very dark but also cloudy, and the sun was quiet, so no chance of seeing any aurora or even stargazing. However, we were given fascinating presentations on what causes the ethereal coloured lights seen at Earth’s poles and further towards the equator when solar activity is peaking.


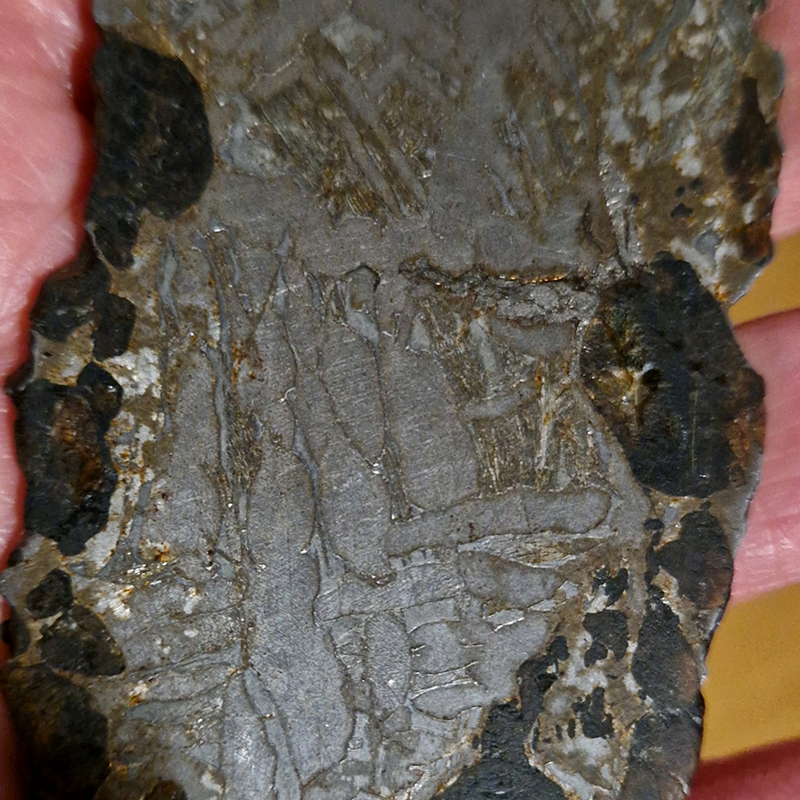
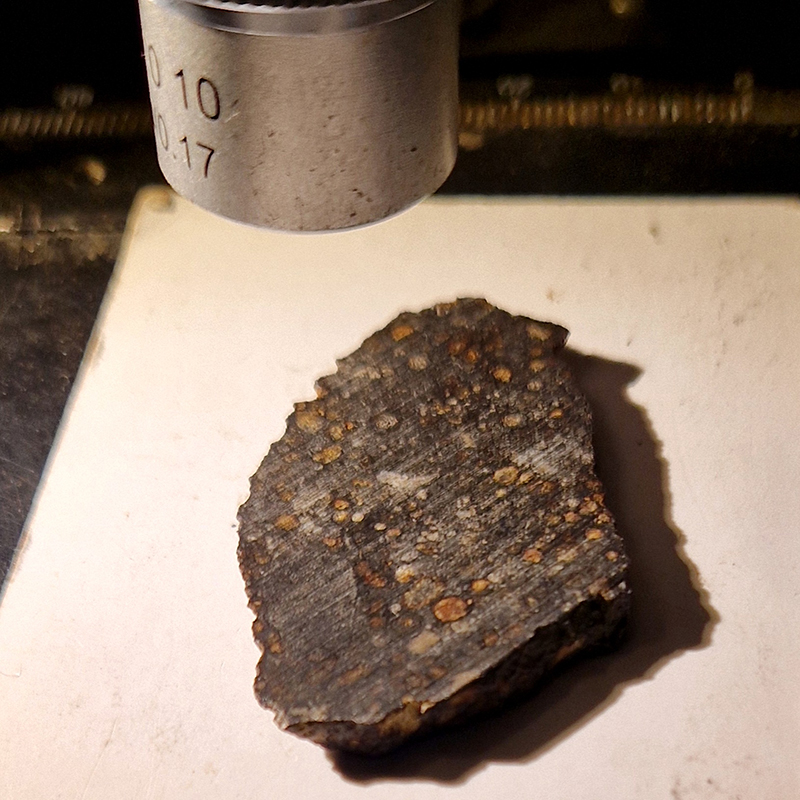
We were also given some cool meteorites to handle including a carbonaceous chondrite, one of the most primitive objects in our solar system.




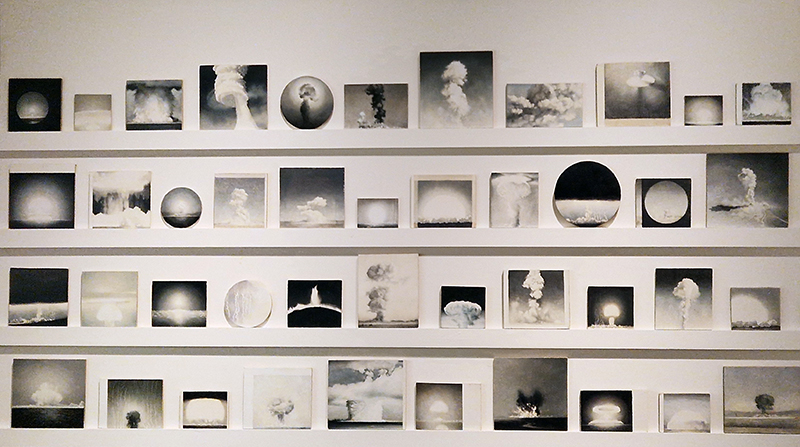
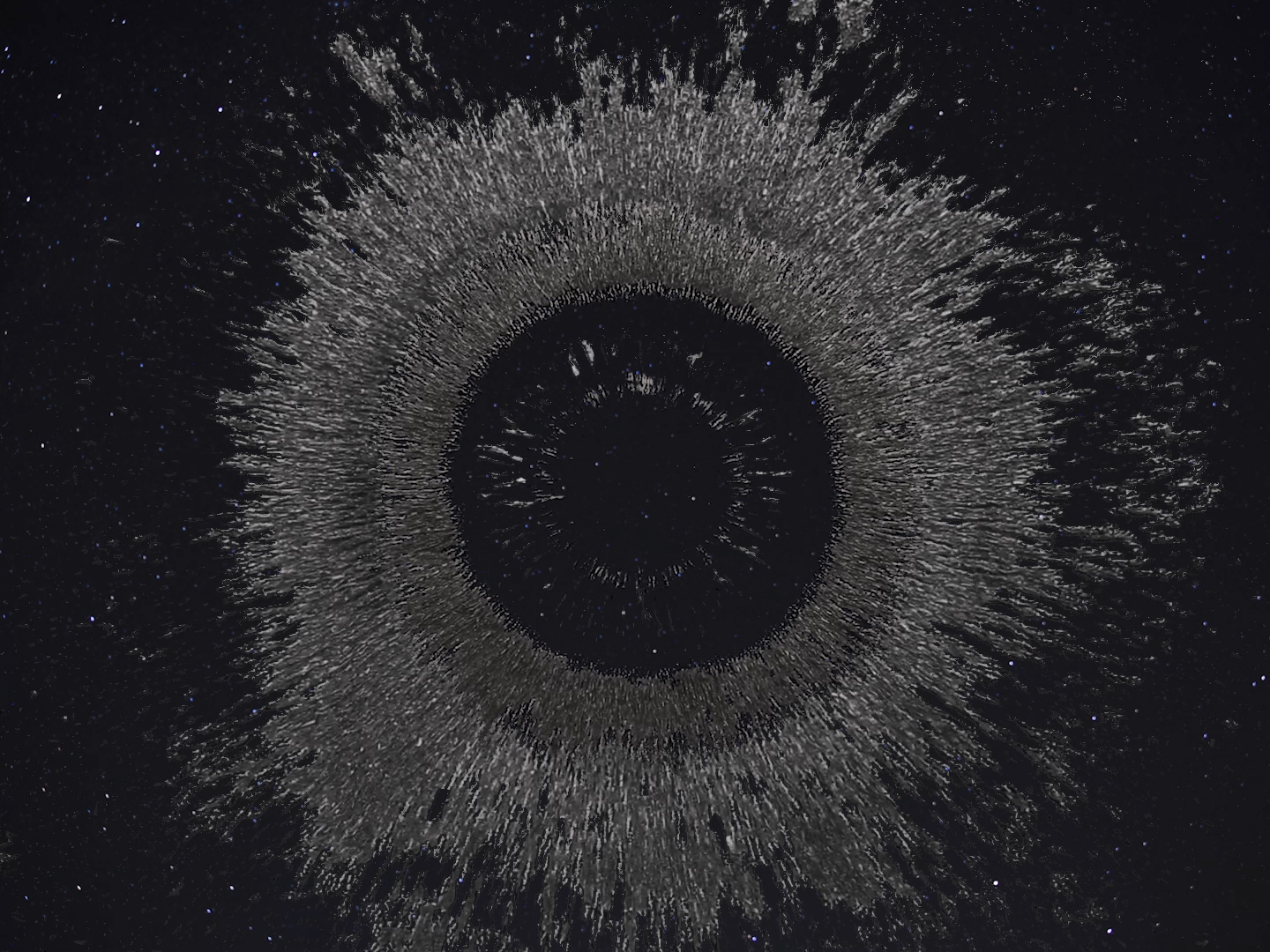
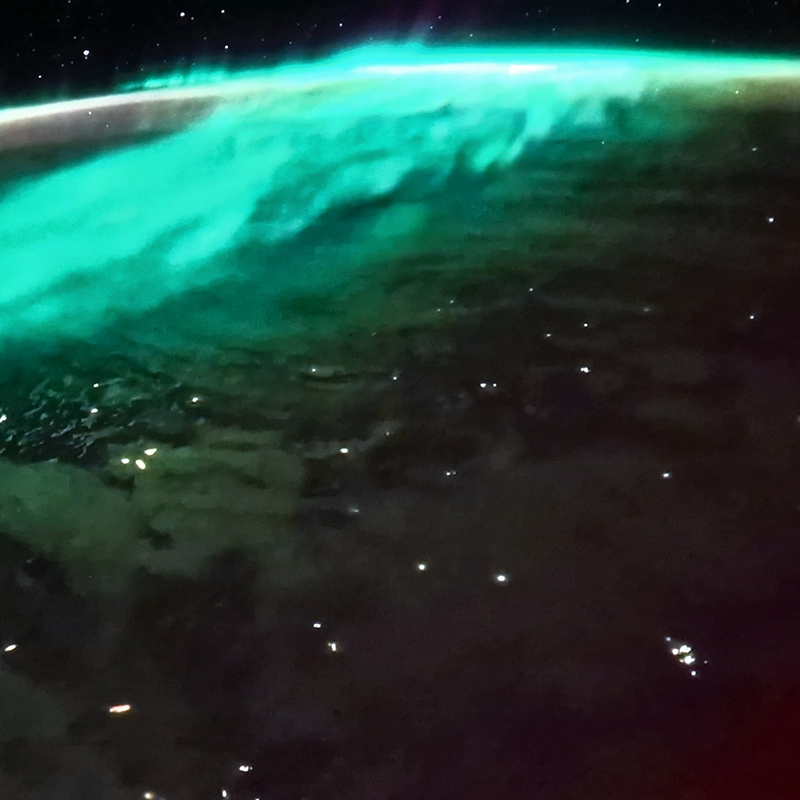
The sun rotates faster at the equator than at the poles and this causes disruption in its magnetic field. The solar flares that we see loop out from the surface of the Sun are caused by localised incidents of polarity, where plasma and particles loop around what could be thought of as areas acting like independent bar magnets. Millions of tons of plasma and chunks of magnetic field can be ejected during one coronal mass ejection and this matter hurtles out into space, if we are in the line of fire we will be bombarded with energetic particles and Earth’s magnetic field will be disrupted. The solar wind brings the particles from the Sun that envelop Earth and are drawn to the polar regions by the geomagnetic field. The aurora is caused by the interaction of these high energy particles (usually electrons) with neutral atoms in the earth’s upper atmosphere. The particle collisions that occur in the upper atmosphere cause photons of light to be emitted. The Earth’s geomagnetic field is not symmetrical and changes as the Earth rotates, it responds to the disturbance of particles coming from the Sun and as the field adjusts to this disturbance, magnetic energy is released, thereby accelerating charged particles to high energies. These charged particles are forced to stream along the geomagnetic field lines which is why the aurora lights can appear in vertical columns or other dancing shapes depending on where in the magnetosphere they entered the atmosphere. The colours of the lights are dependent on which atmospheric gas is being excited by the solar particles, oxygen emits either a greenish or a red light and nitrogen gives off a blue light.
Solar activity is monitored and space weather forecasts are posted online. To be in with a chance of seeing the Aurora in the UK, the KP level should be 5 or above as this index increases as the aurora’s southern edge moves southward. It can take up to three days for the particles ejected from the Sun in a CME to reach the Earth. The lights are fainter than sunlight so a dark night sky is needed to see them. It is also often the case that the greater photo sensitivity of a camera can capture lights that are barely visible to the human eye. The aurora is more likely to be visible during the spring and autumn equinox because of the angle of the Earth’s magnetic field in relation to the Sun, not because storms are more frequent.
2024 is predicted to have a high number of solar storms so there may be opportunities to see the Aurora but it also comes with the risk of severe space weather that could cause havoc with our reliance on satellites and related technologies.
The connection between solar activity and the impact on technology was made during the 1859 Carrington Event, the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history. Strong auroral displays were reported globally and even seen in London, while sparking and fires occurred in multiple telegraph stations.
Satellites are vulnerable to space weather which can cause ongoing degradation or single event upsets where a charged particle can trigger a command in the satellite. During space weather events the ionosphere can become enhanced making it harder to communicate with satellites. Errors can occur in precision navigation and timing situations. Aviation crews are at risk to higher doses of radiation during solar activity and the HF radio communication system can have interference. Induced geoelectric fields in the ground can cause currents to flow in power grids and railway lines damaging transformers.
During the 2003 ‘Hallowe’en’ solar storms, when the largest single solar flare ever recorded was followed by severe storms, over half of all Earth-orbiting spacecrafts were impacted, disrupting satellite TV and radio services, GPS systems, damaging a Japanese scientific satellite beyond repair, sending several deep-space missions into safe mode or complete shutdown, and destroying the Martian Radiation Environment Experiment. The solar storms also led to communication problems for flights passing over the North Pole and Antarctic science groups had a full communications blackout for several days.
In acknowledging these risks we can gain an awareness of our vulnerability to the forces of nature and a respect for the power of the sun, the protection offered by our home planet and the interconnectedness of the universe.
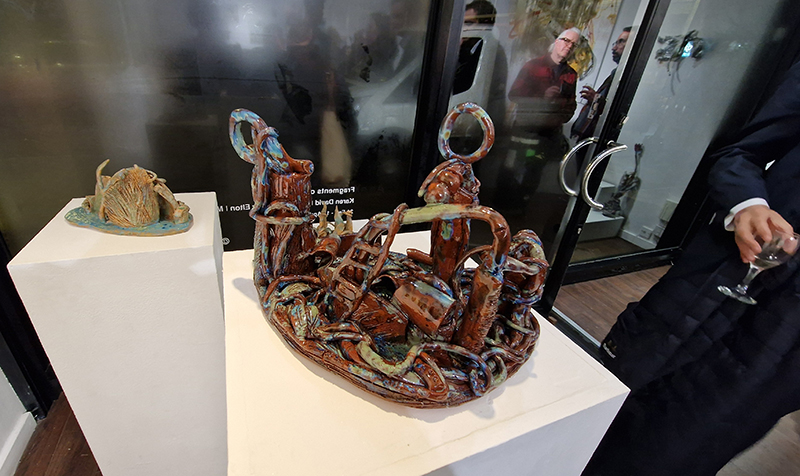
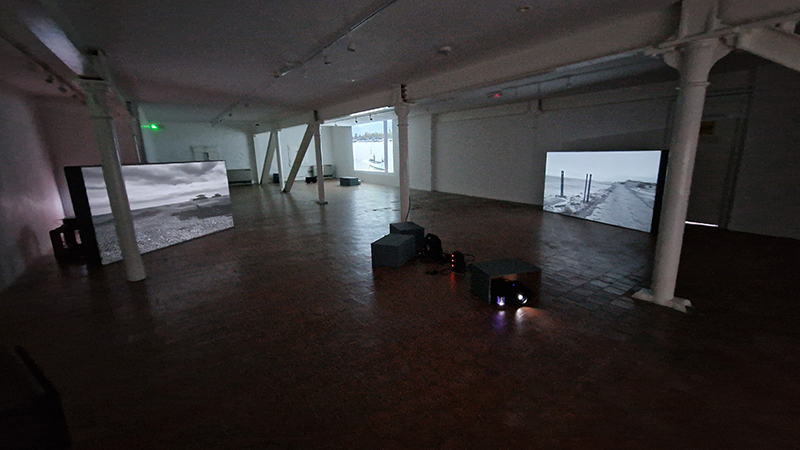
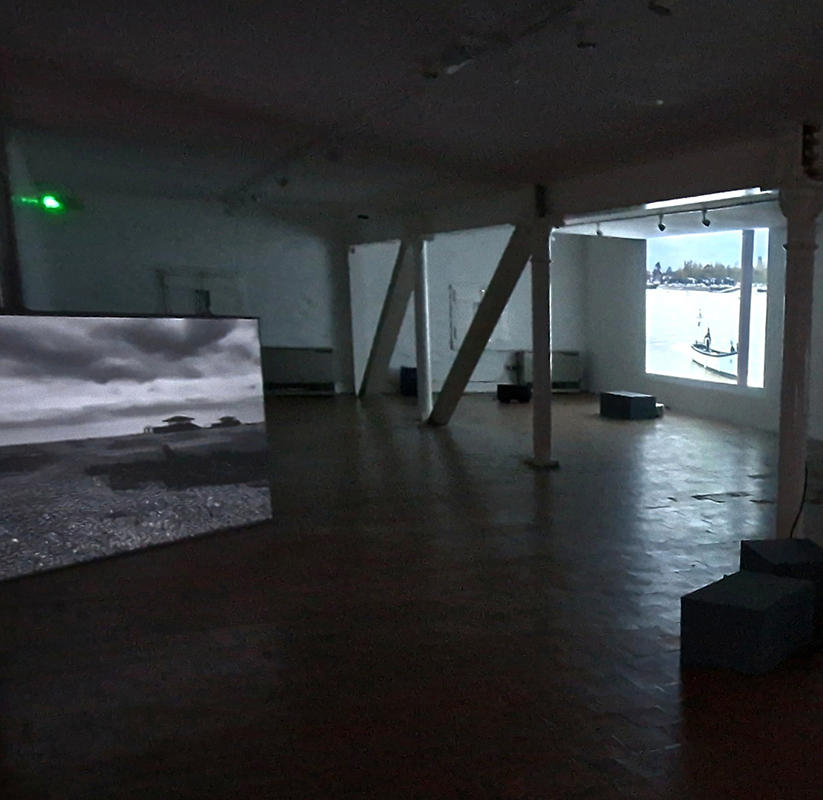
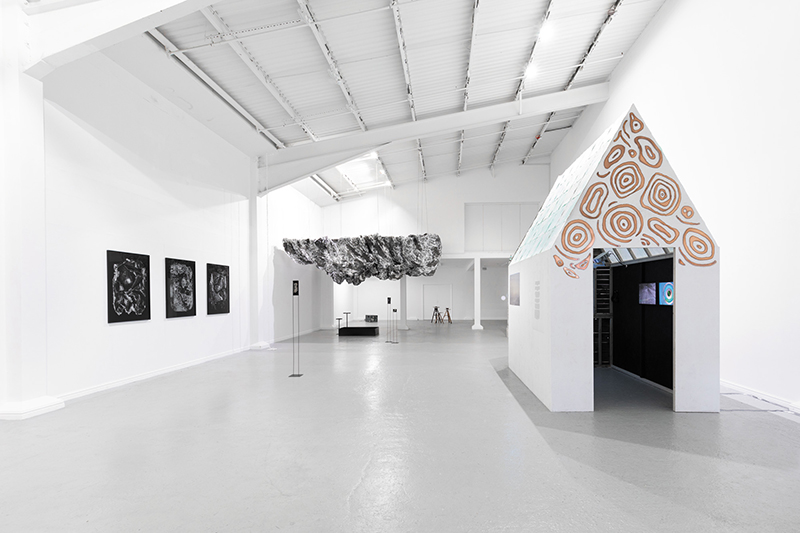
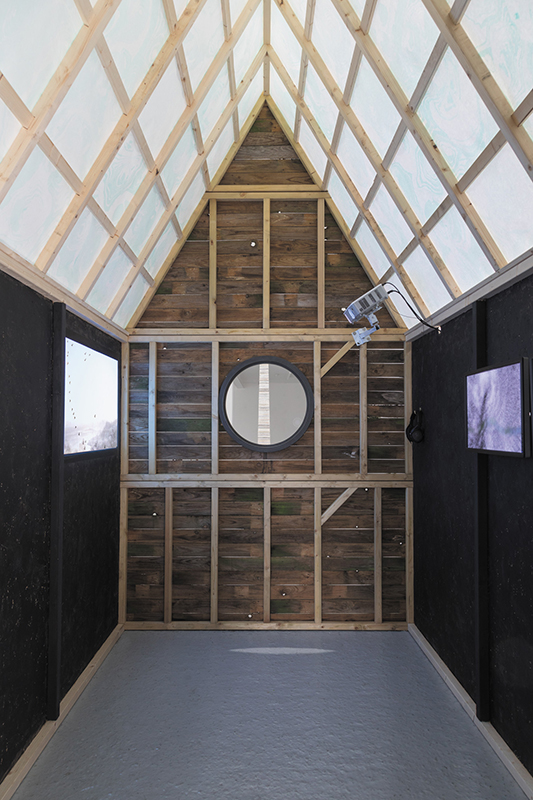
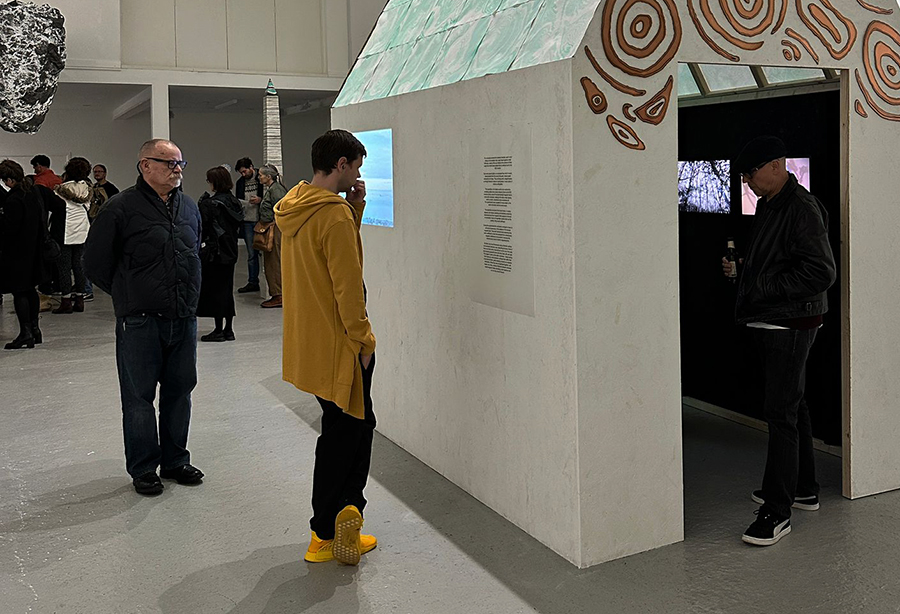
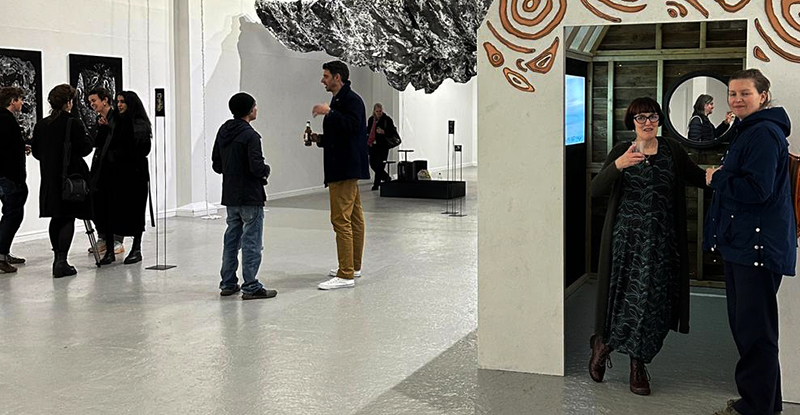
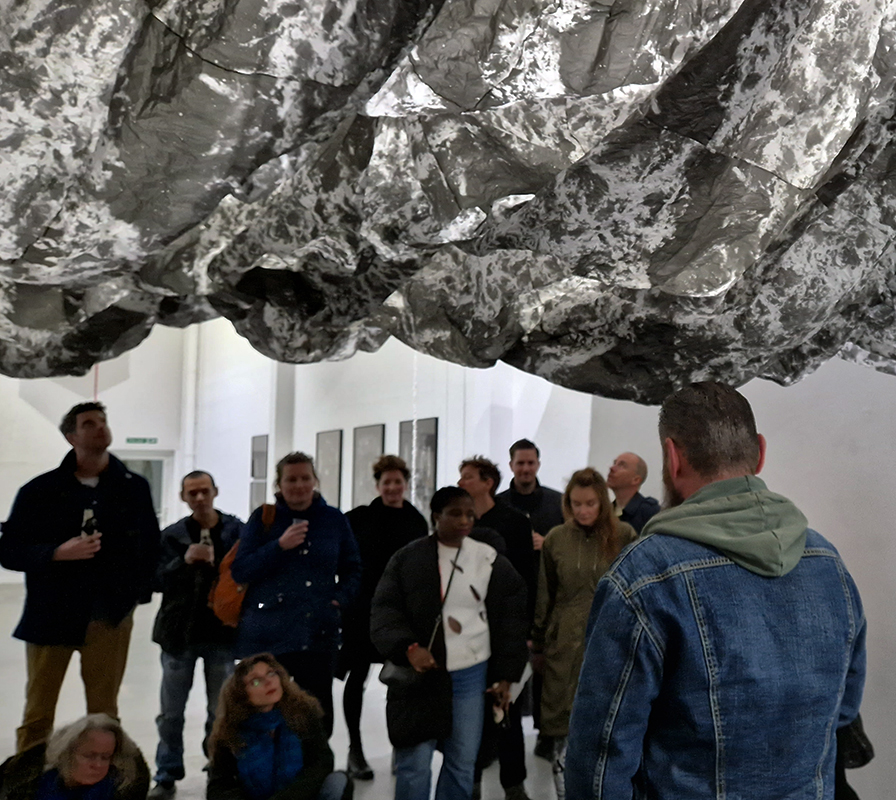
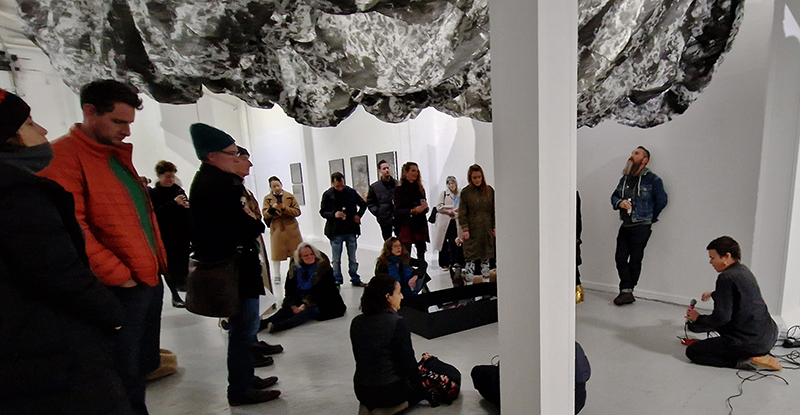
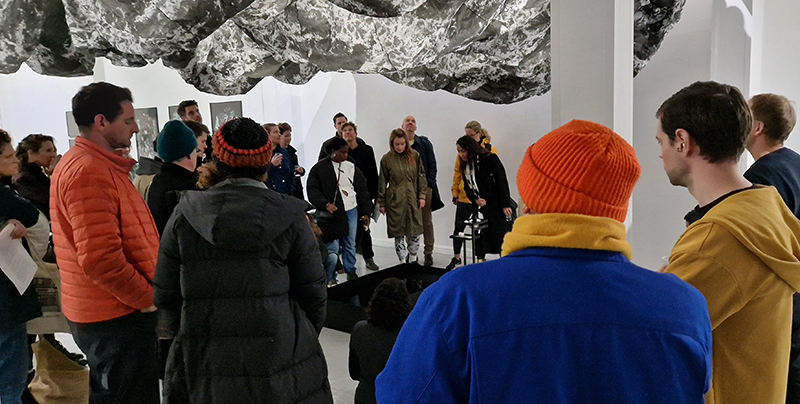
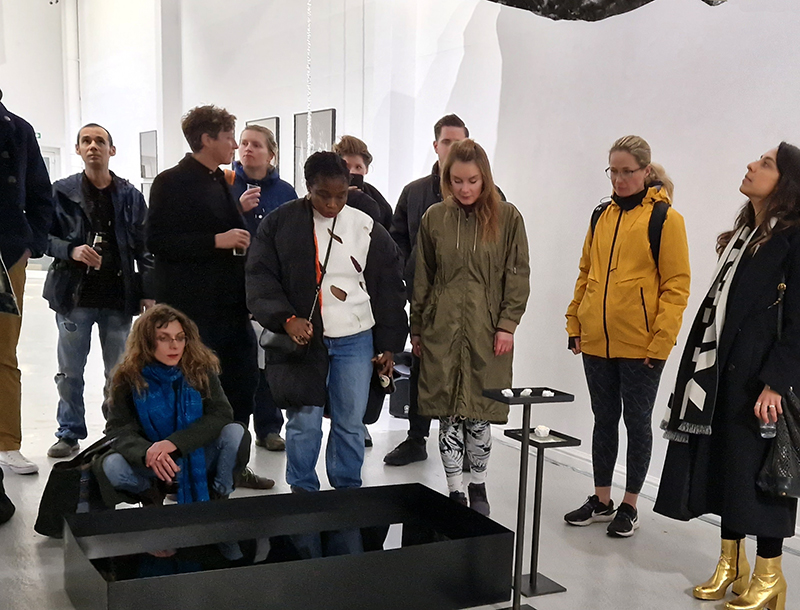
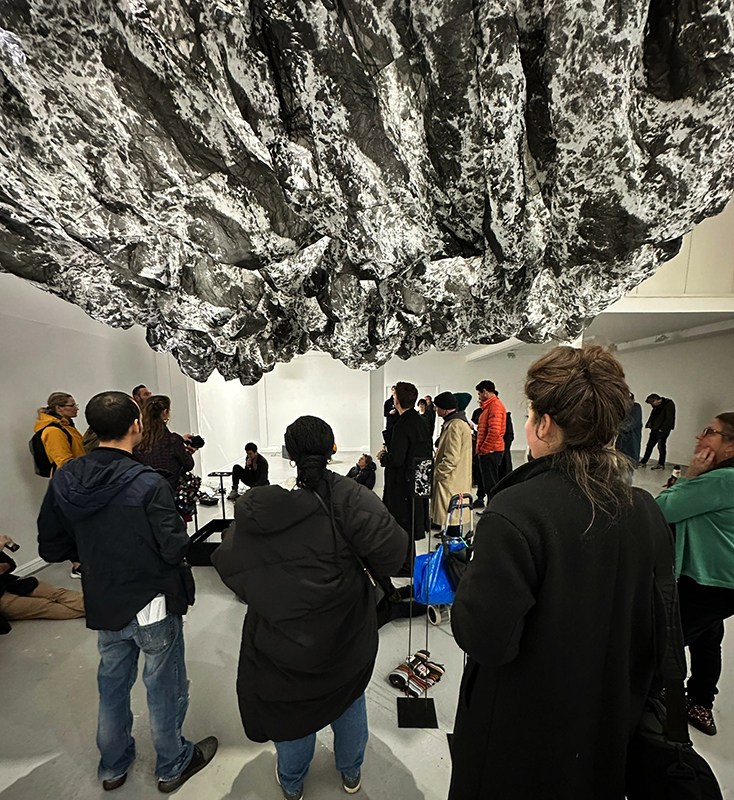
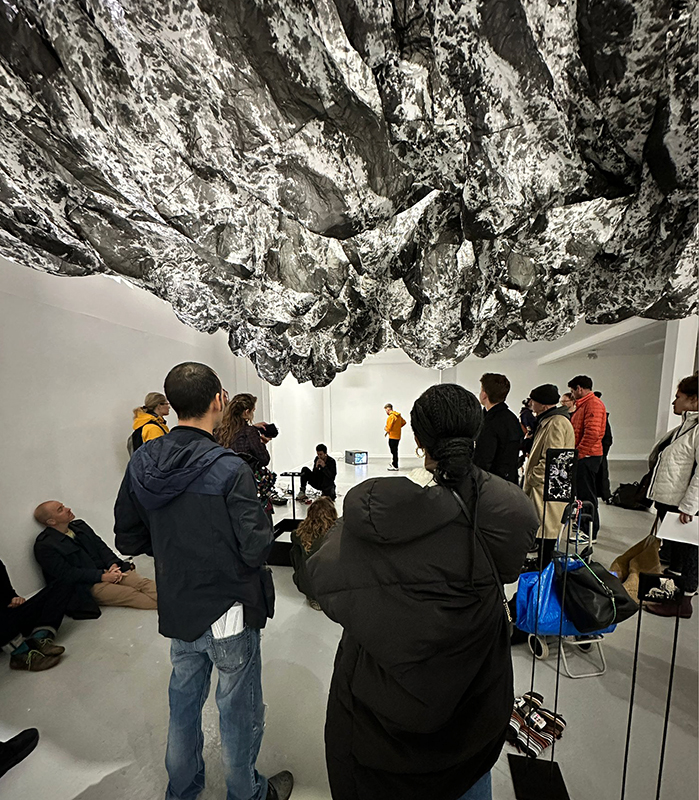
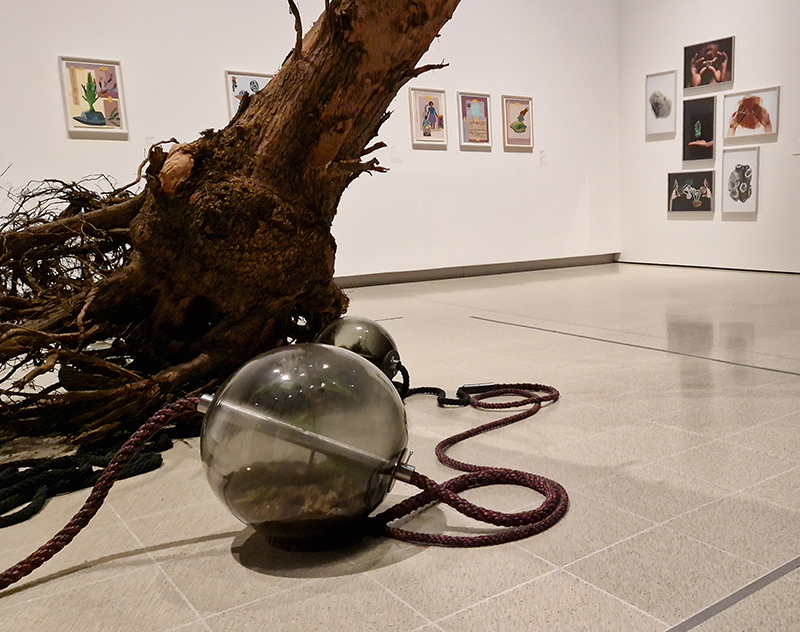
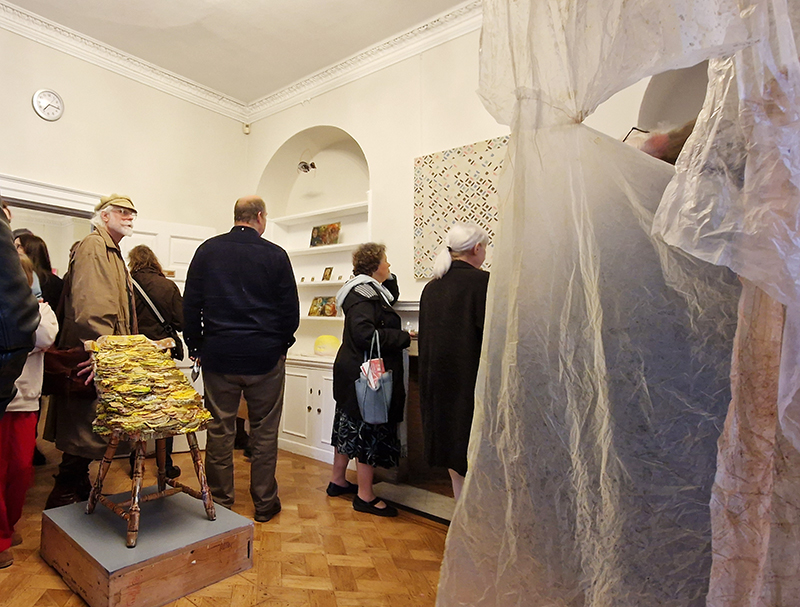
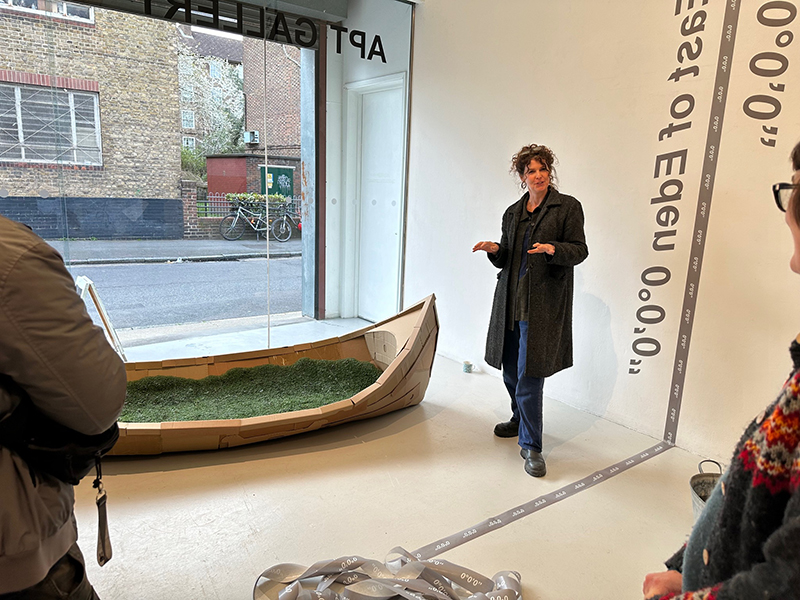
Life Boat at APT Gallery

Life Boat brings together artists with a shared interest in exploring precarity as a site of dynamic transition. Each takes an investigative approach to the environmental, social and historical themes evoked by the lifeboat, as a means of addressing ecological crisis, liminal landscapes, close and distant horizons, boundaries and displacement, lines of rescue, navigation and transformation.
Very happy to be exhibiting with Rachael Allain, Caroline AreskogJones, Beverley Duckworth, Liz Elton, Kathleen Herbert, Kaori Homma and Anne Krinsky.
We had a fantastic opening night.
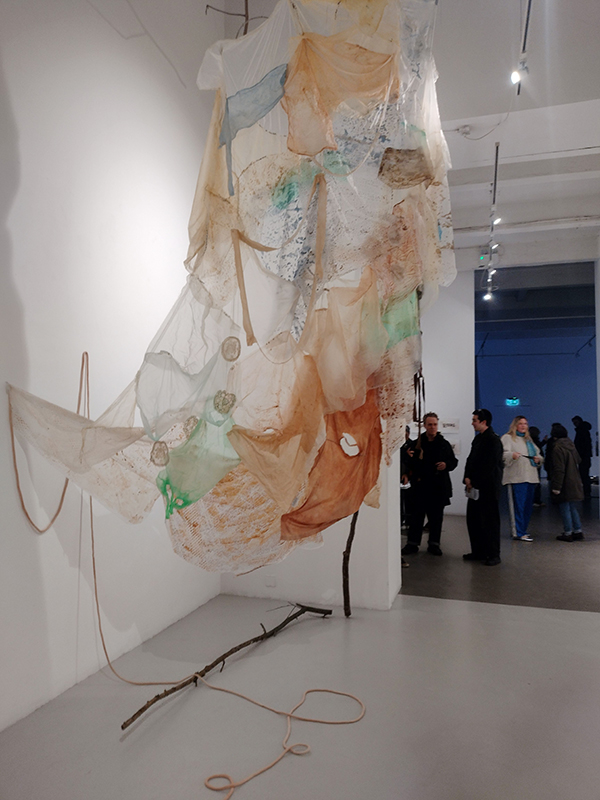
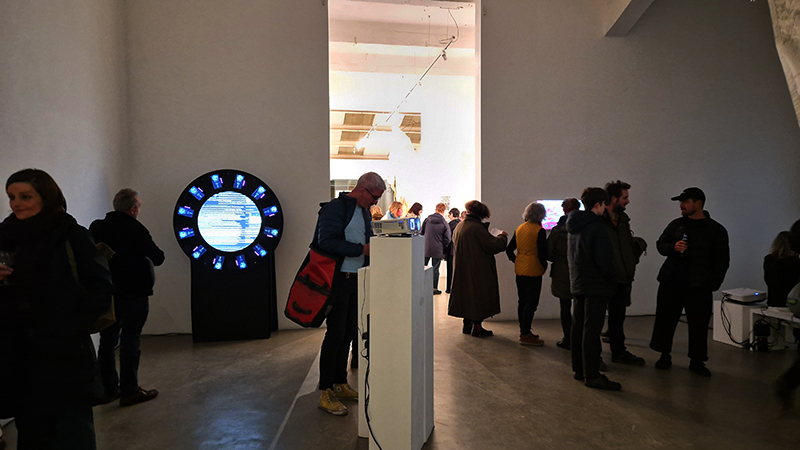
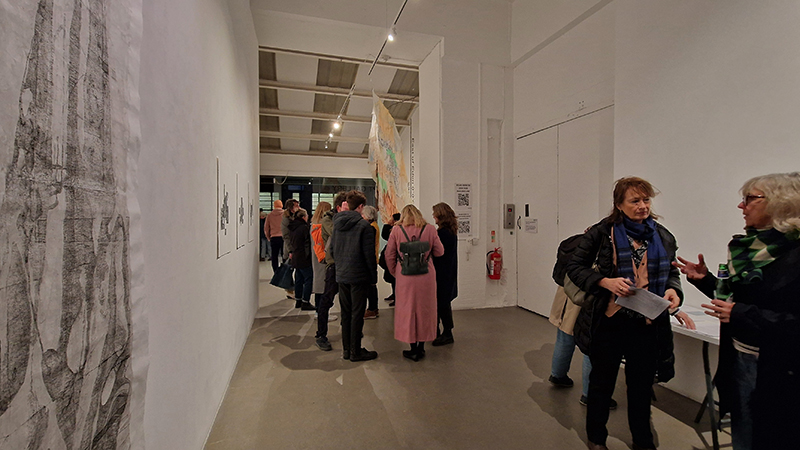
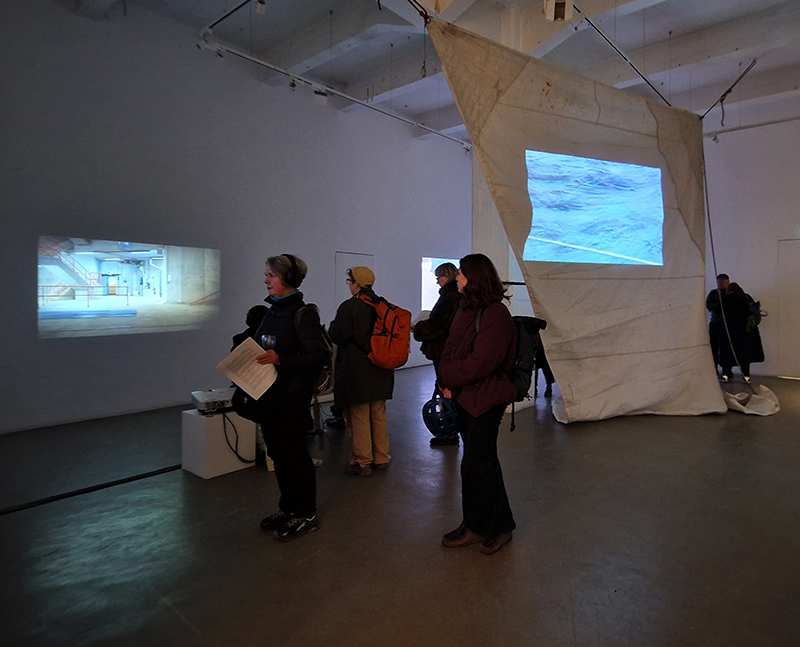
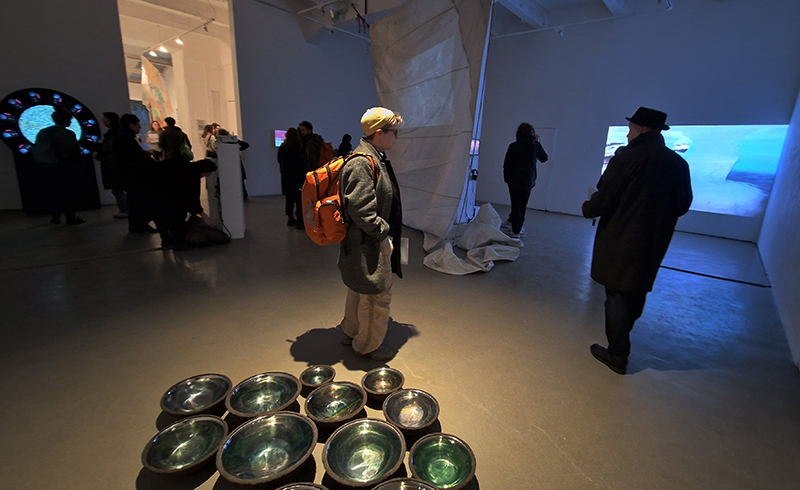
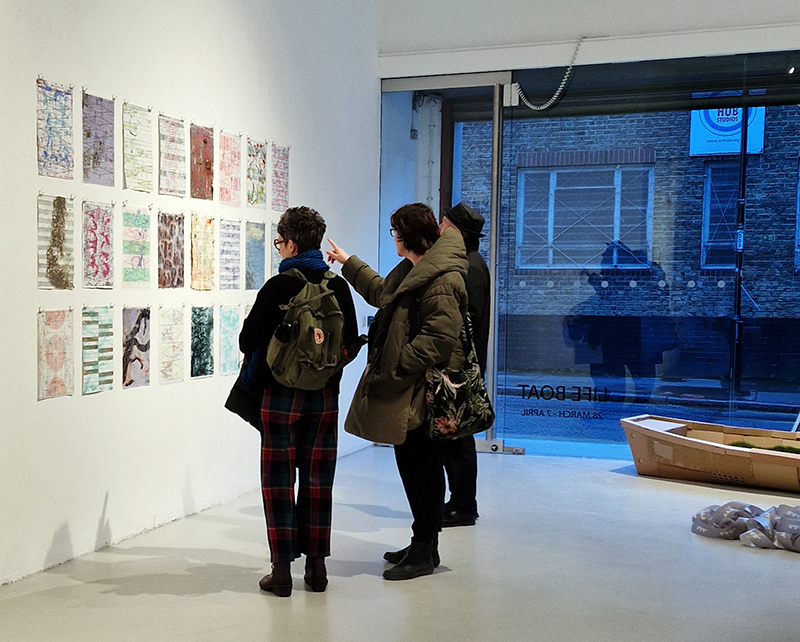











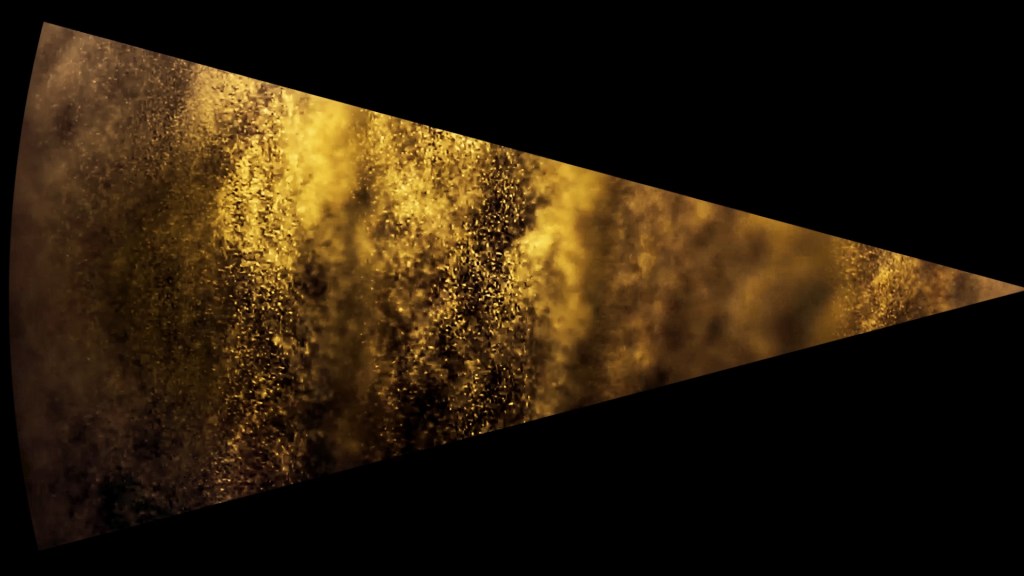
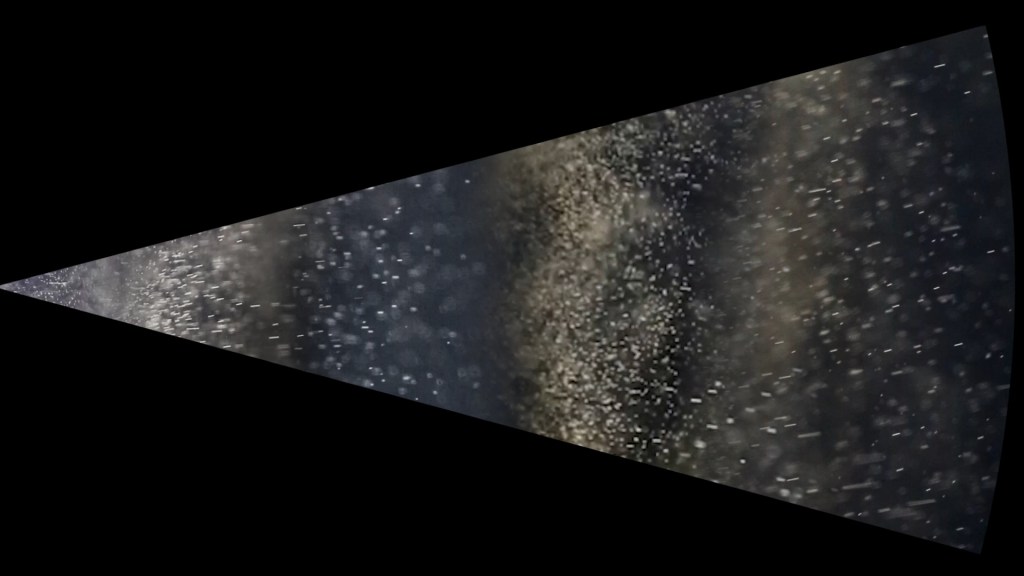
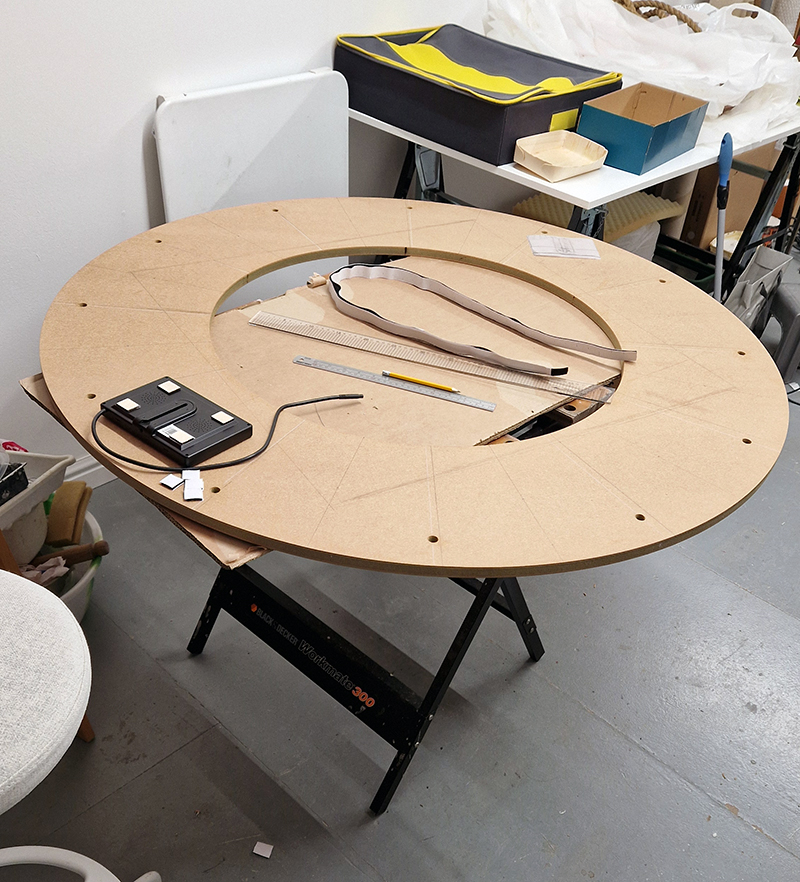
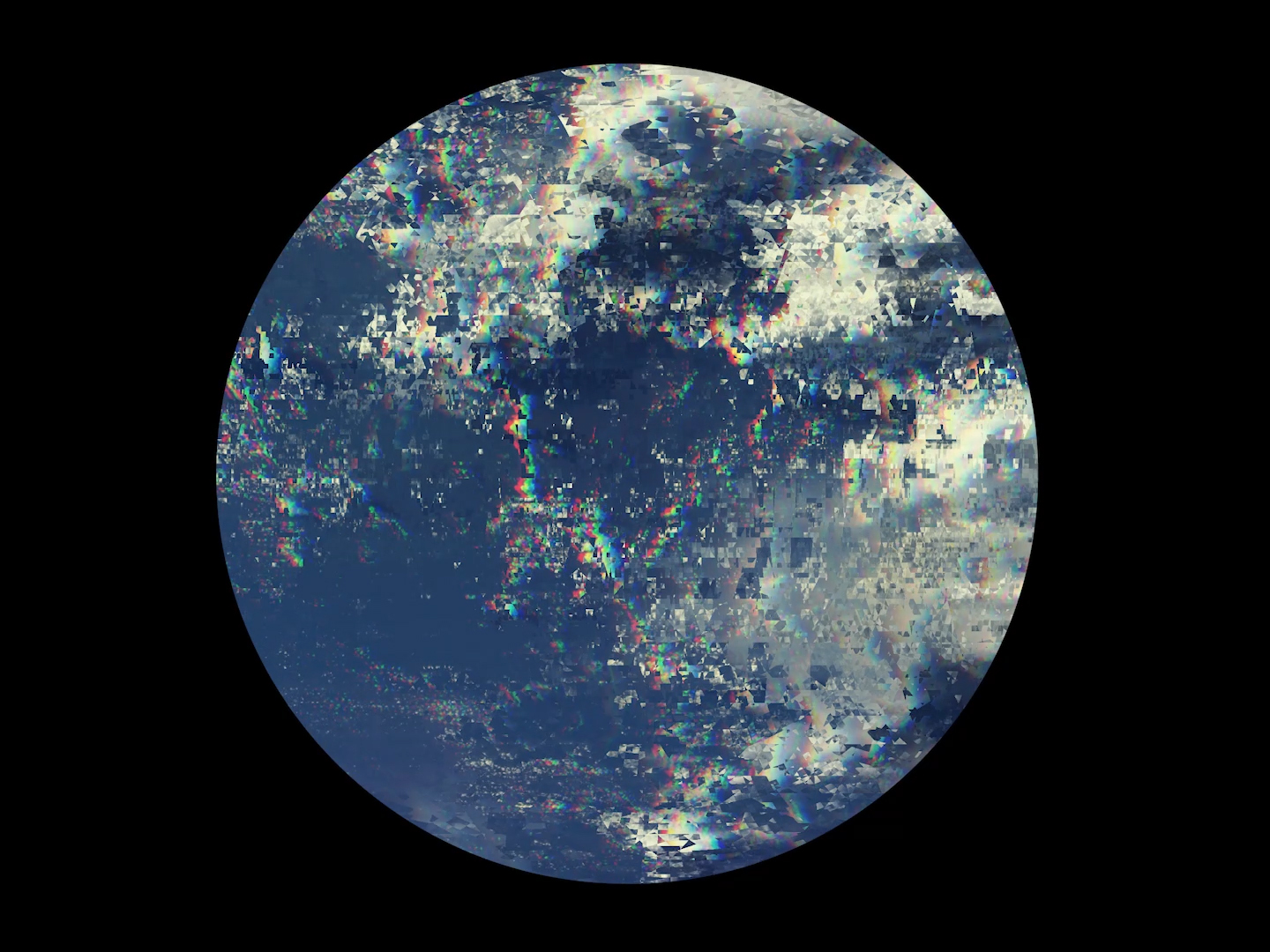
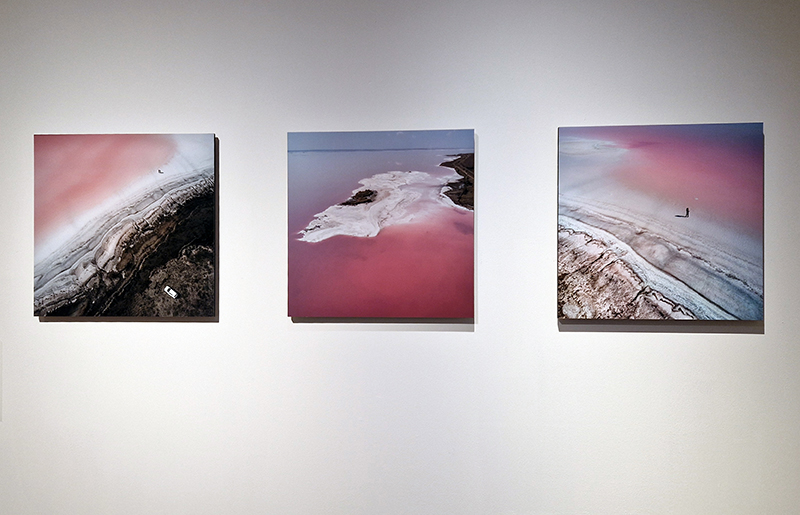
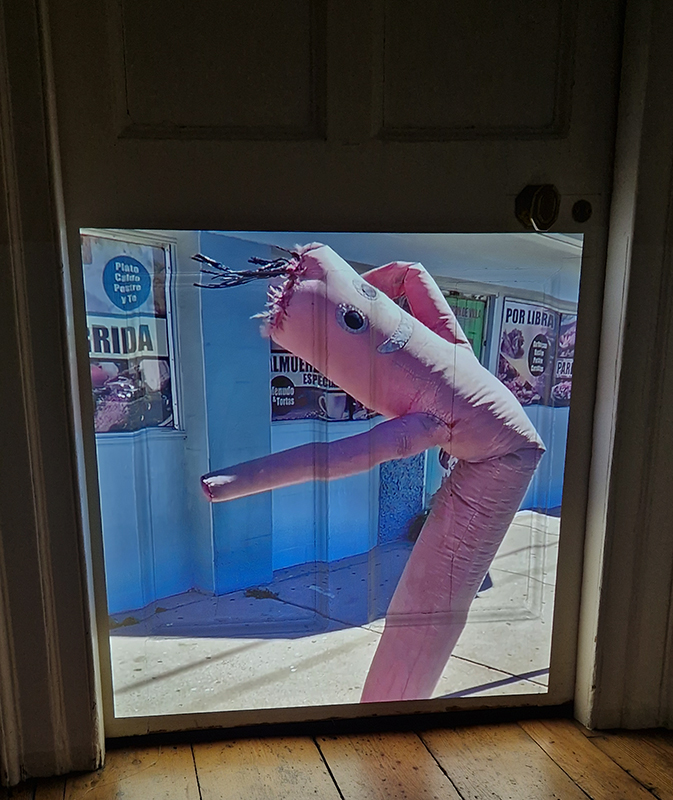
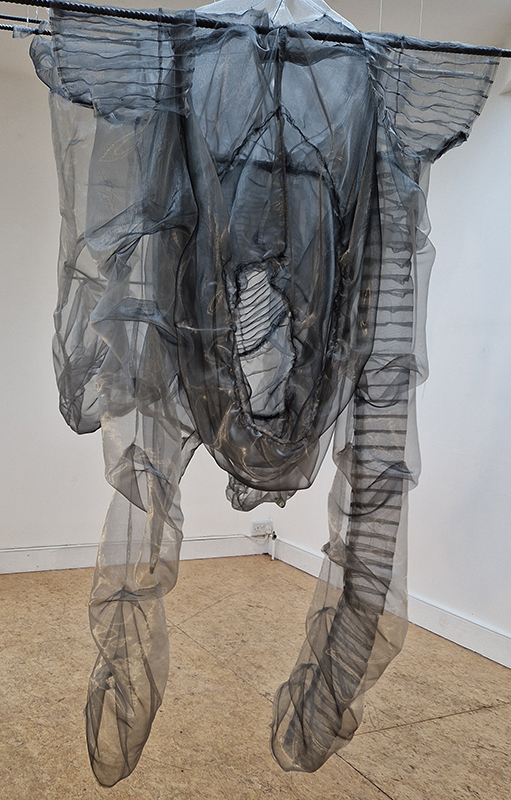
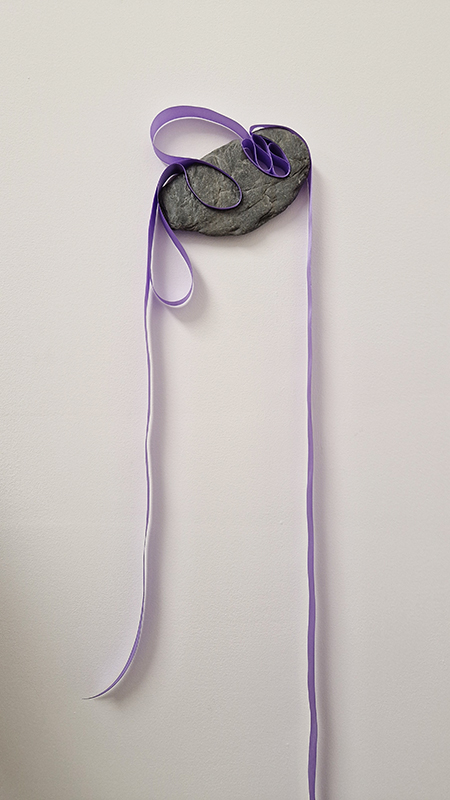
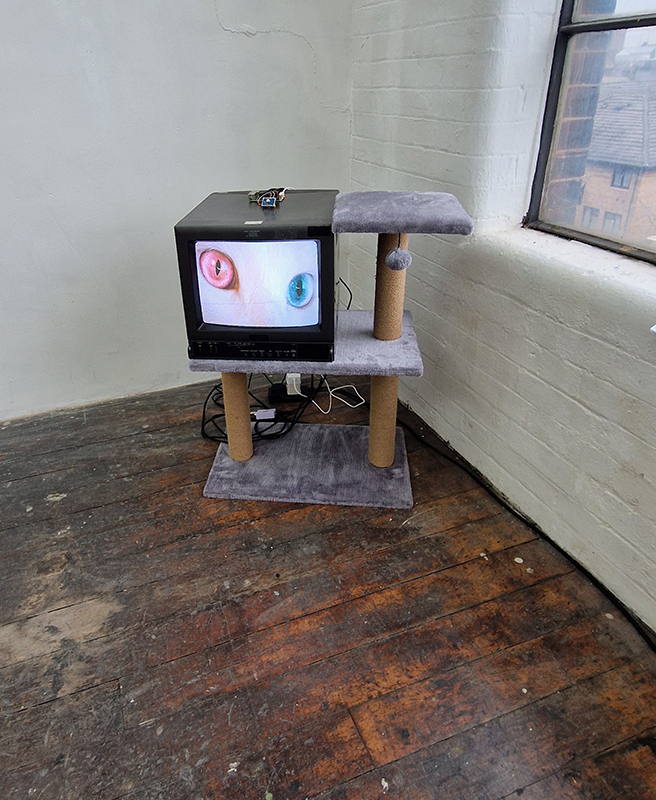
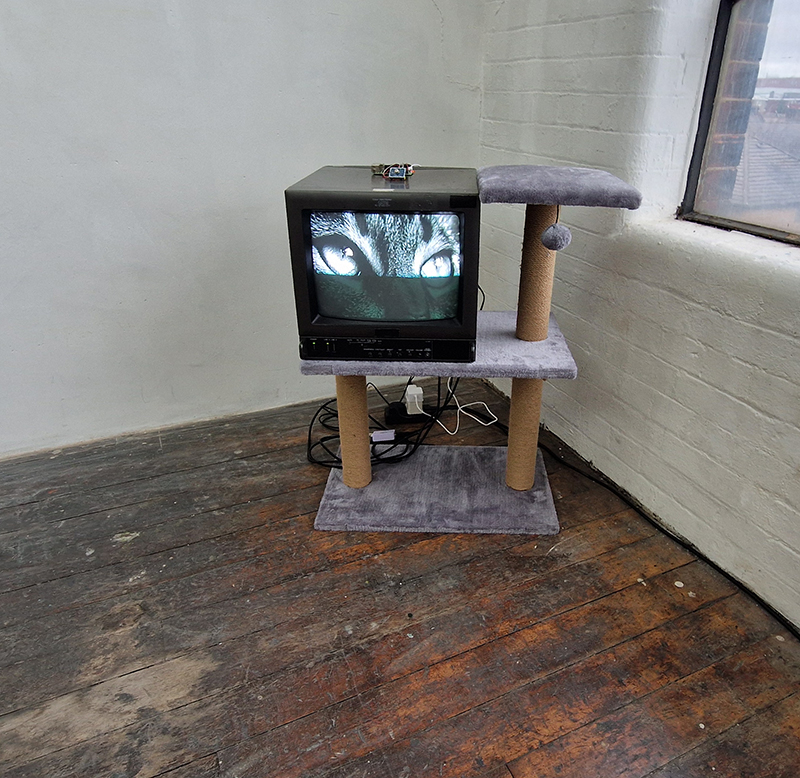
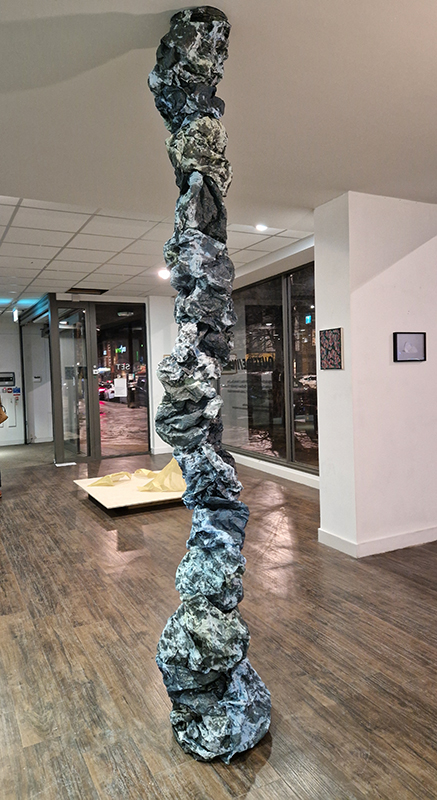
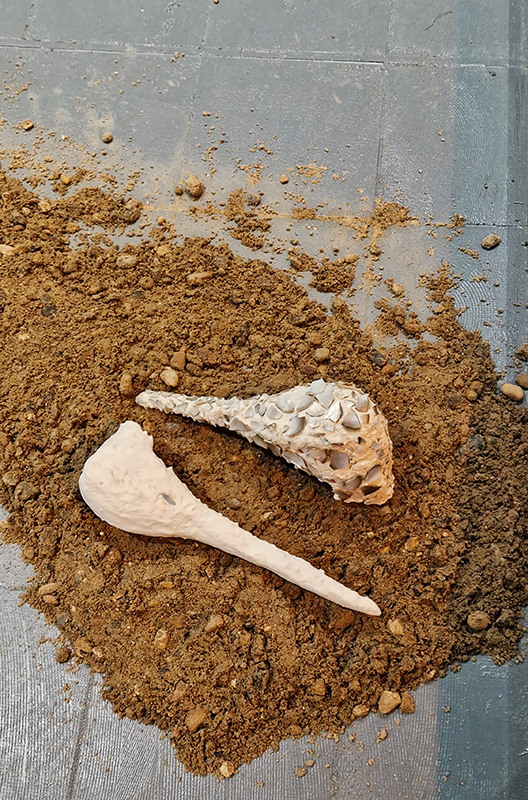
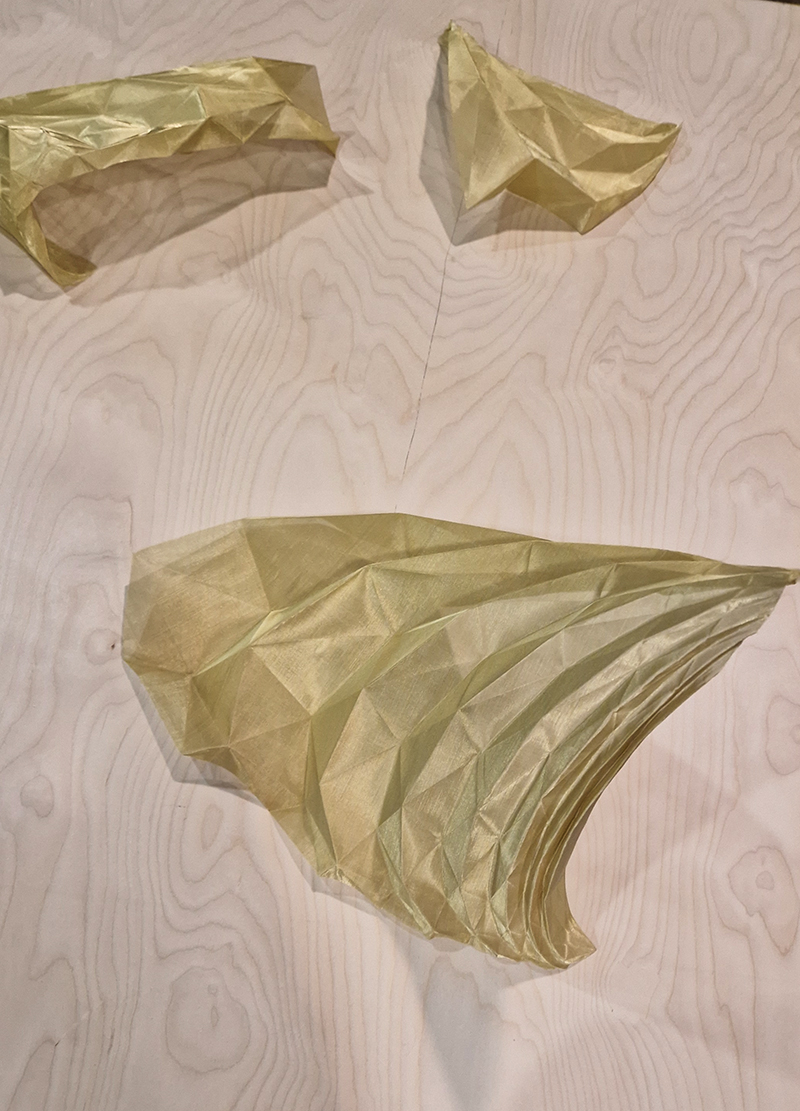
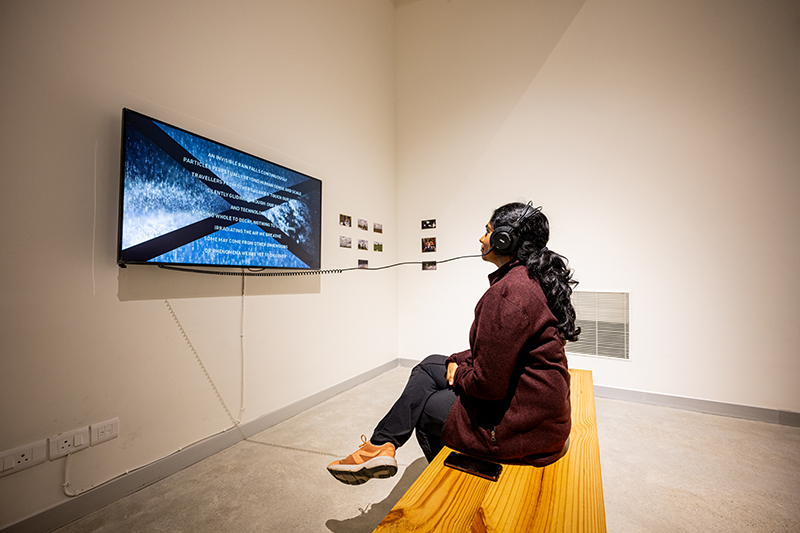
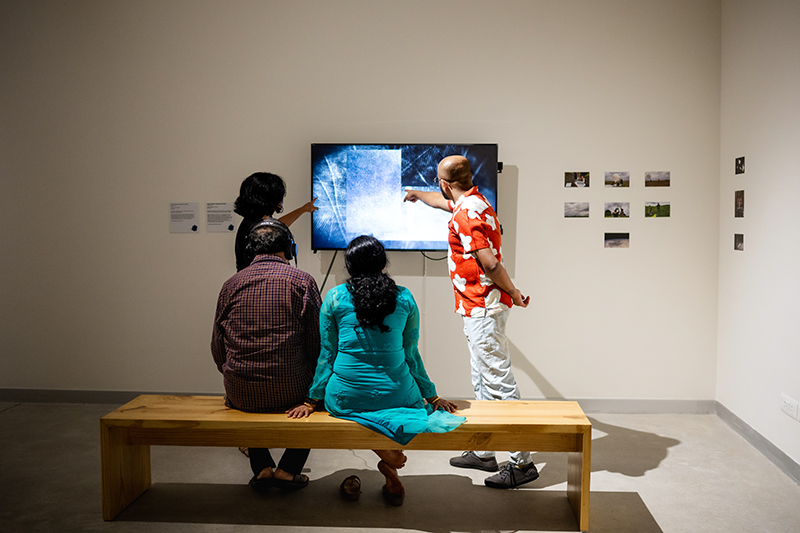
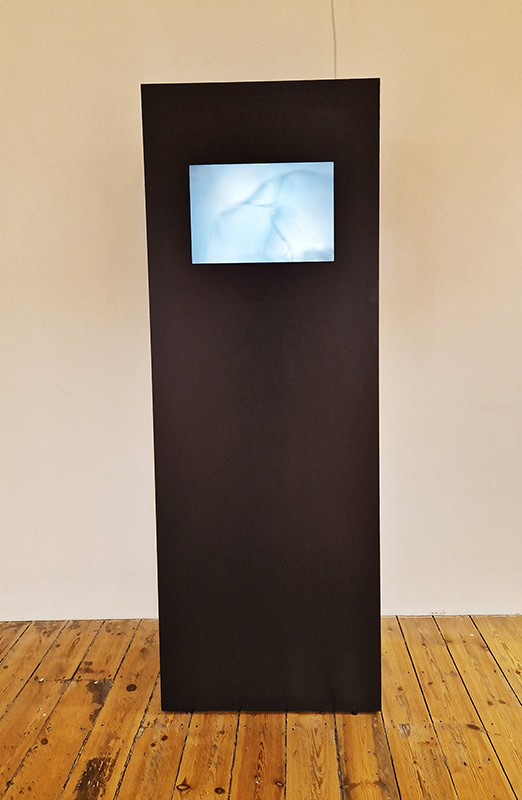
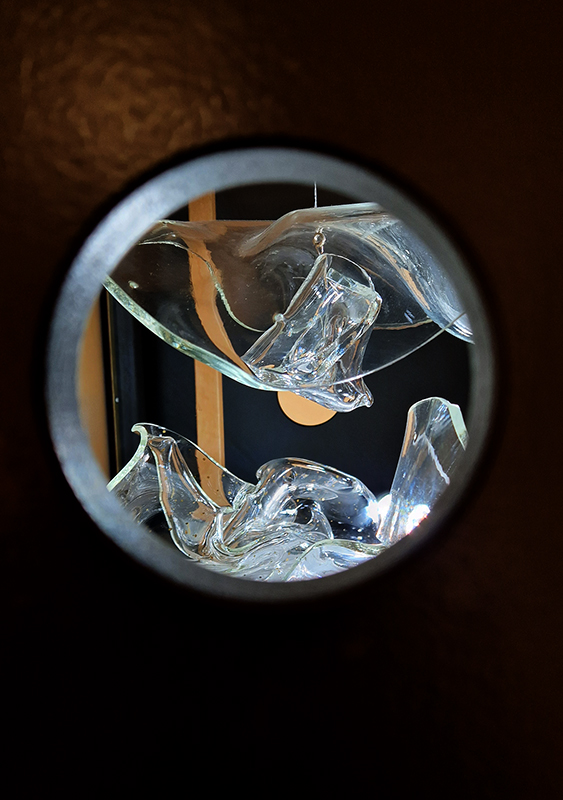
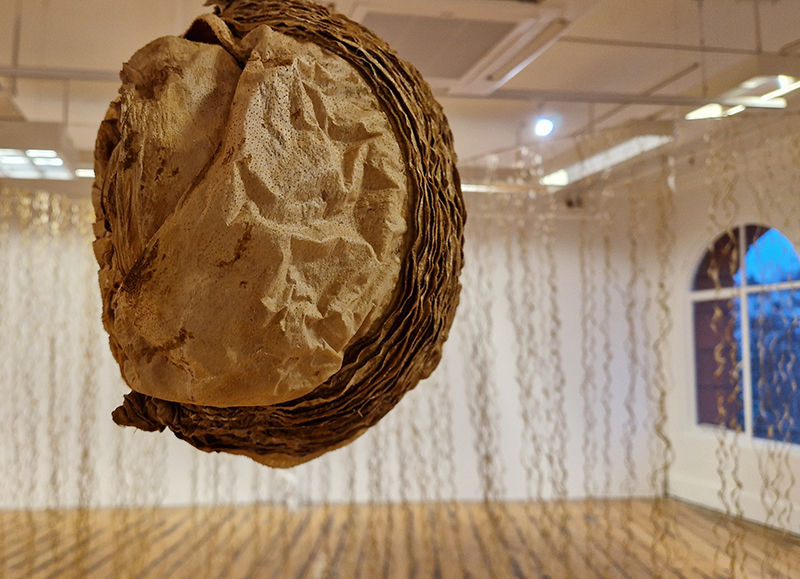
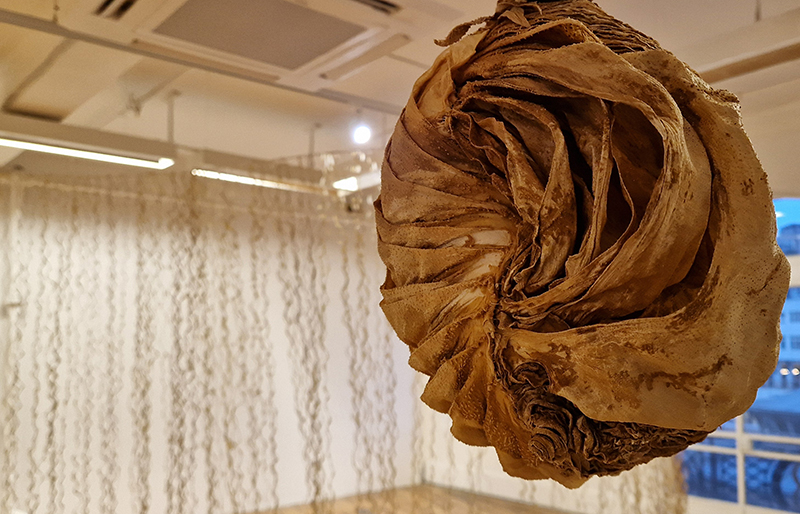
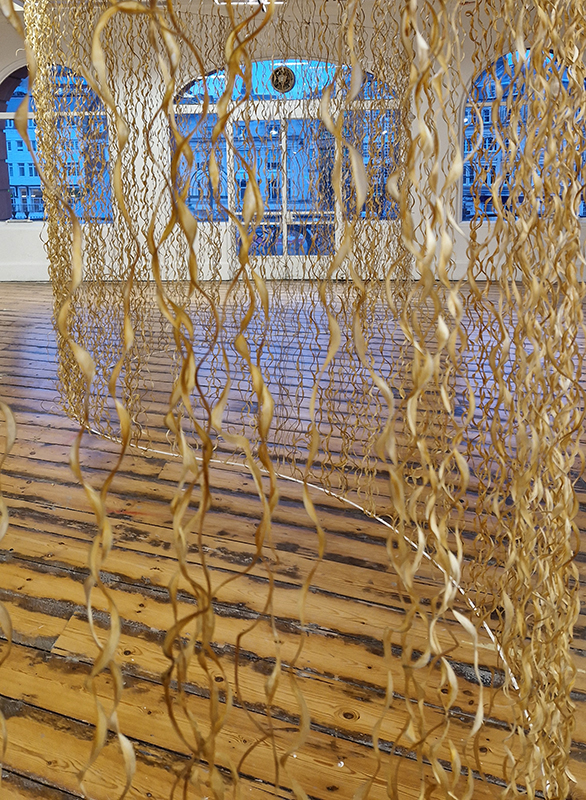
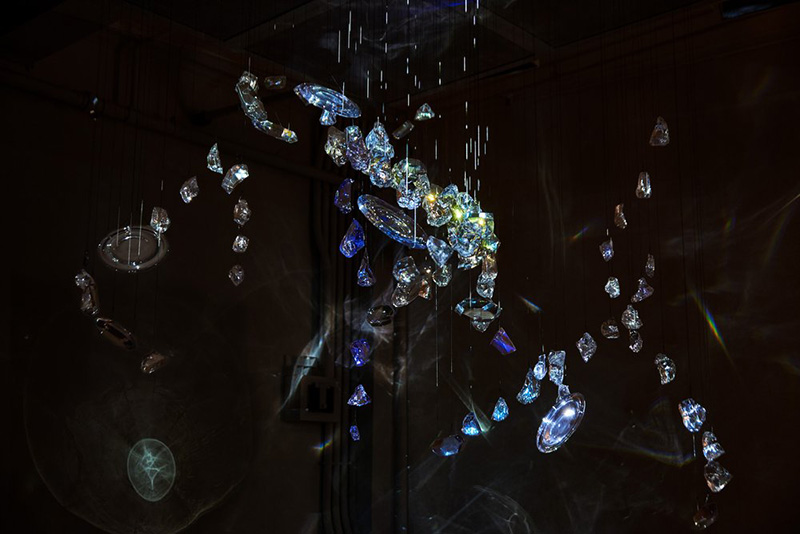
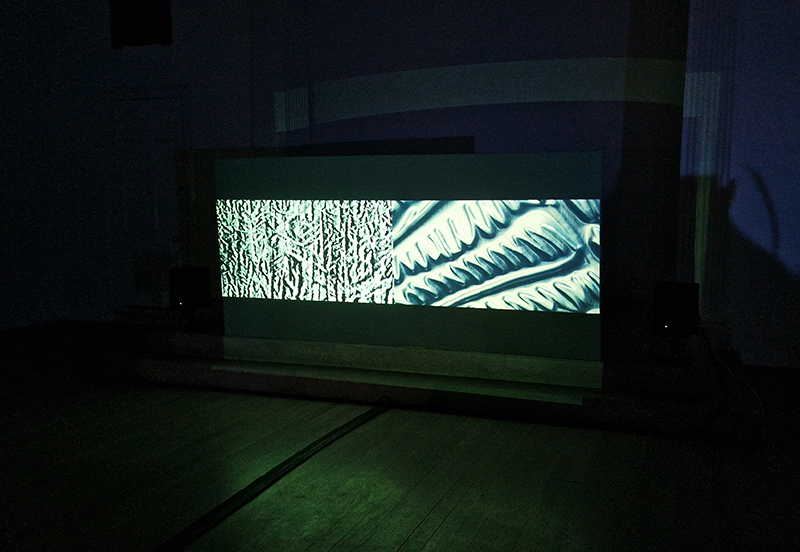
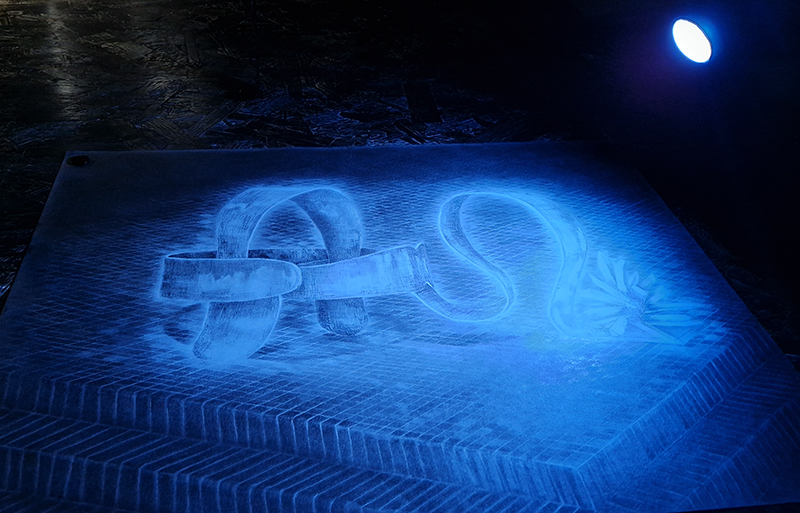
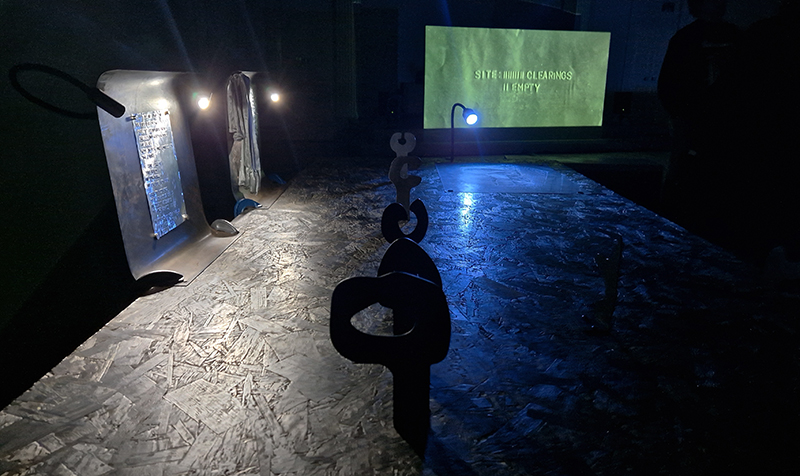
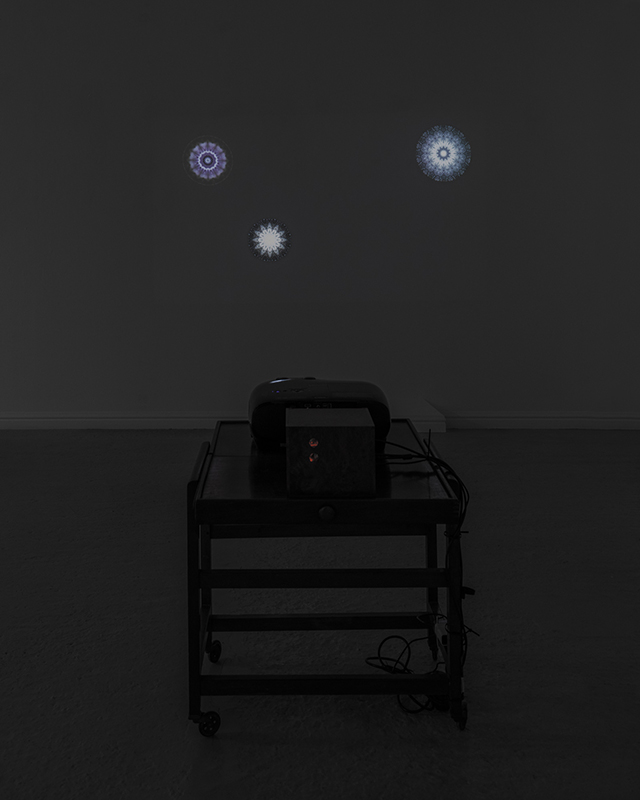
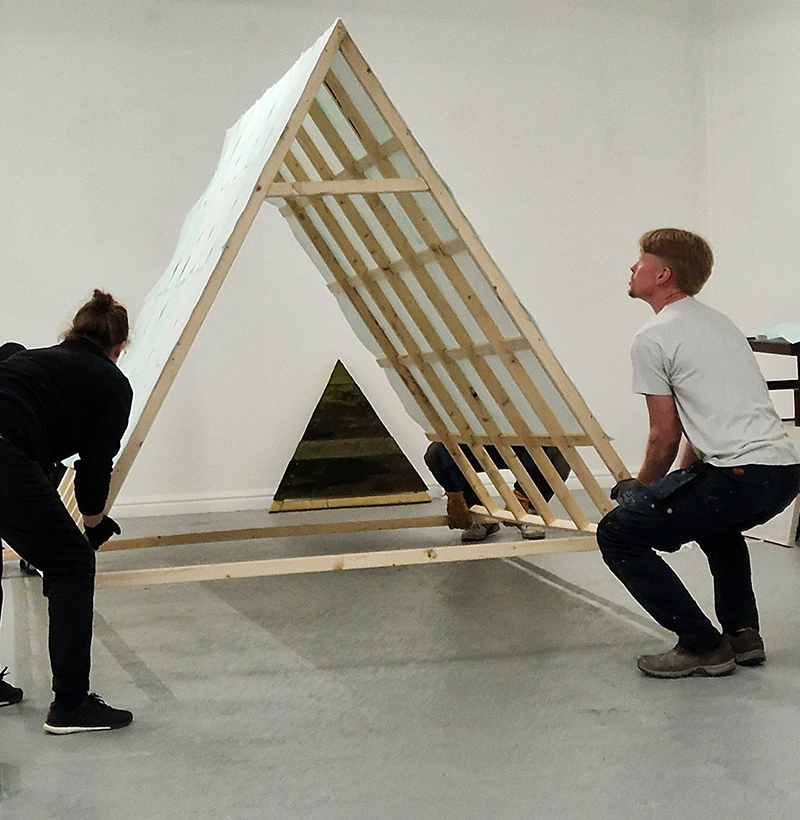
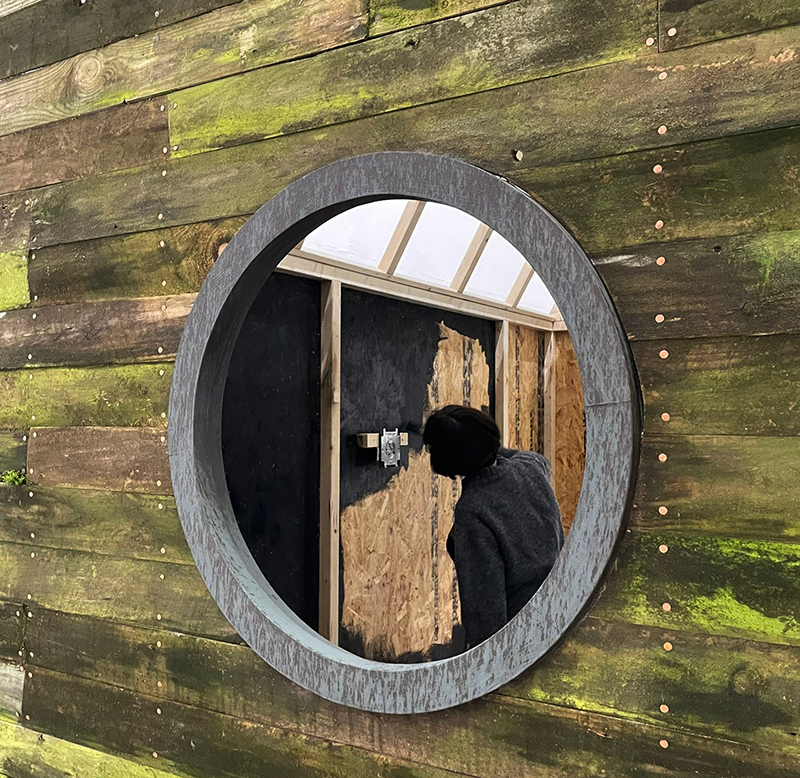
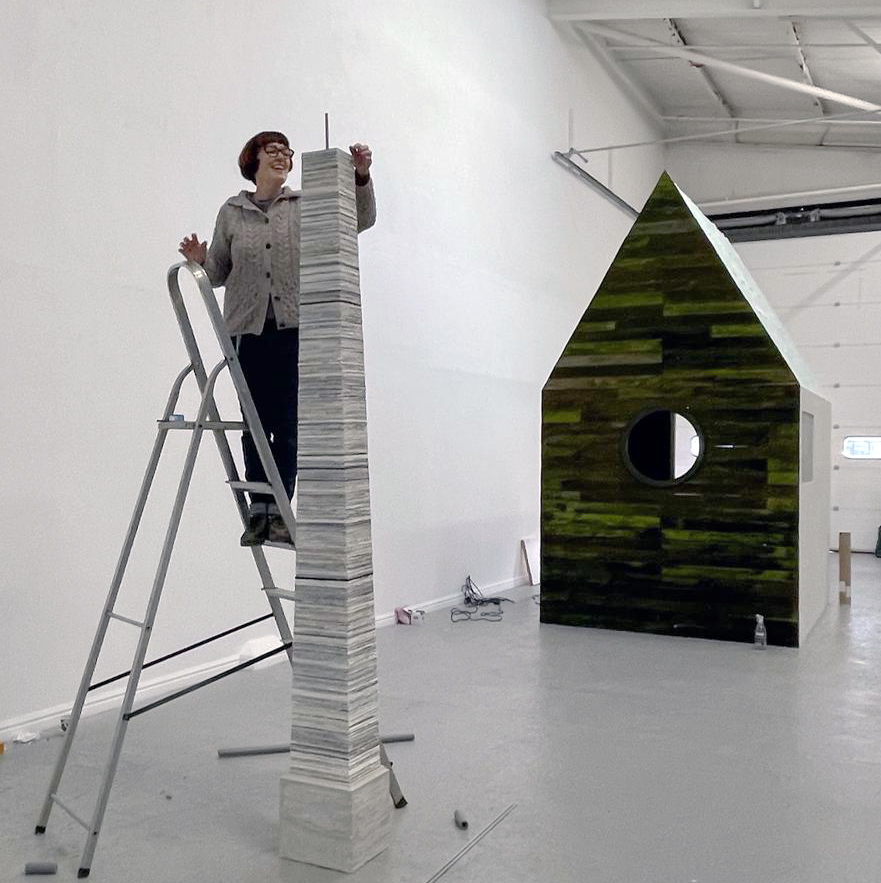
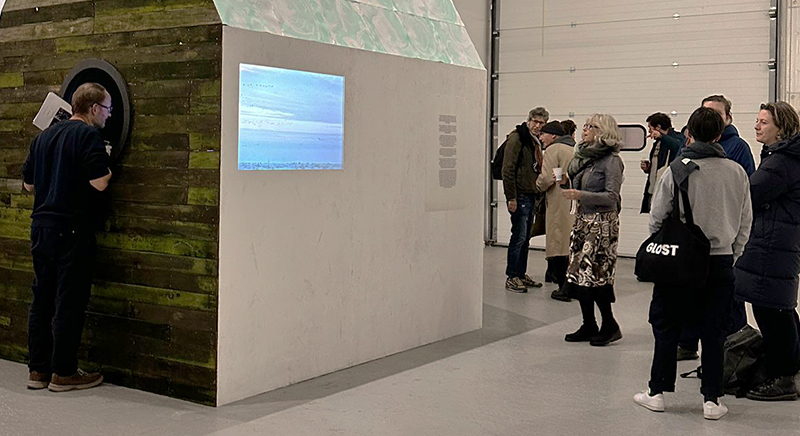
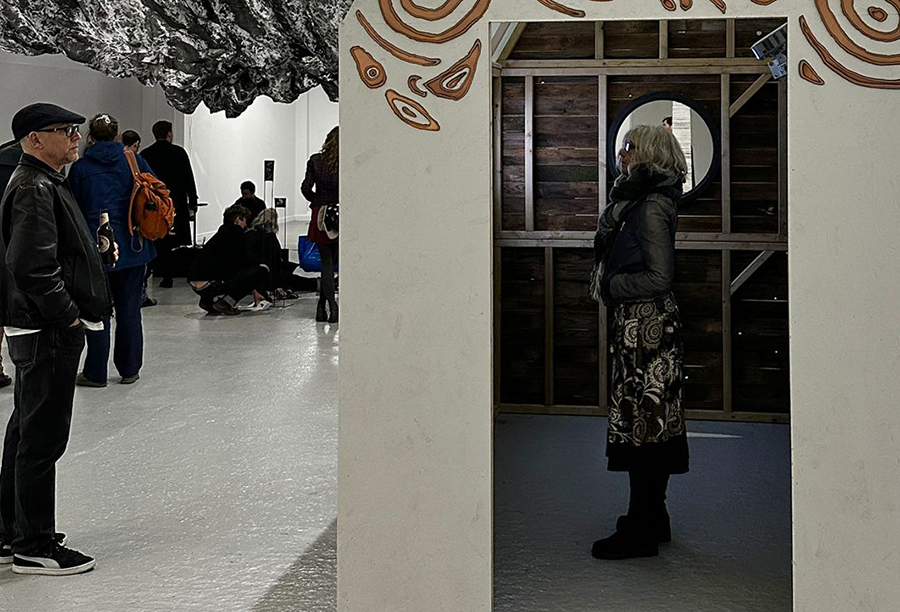
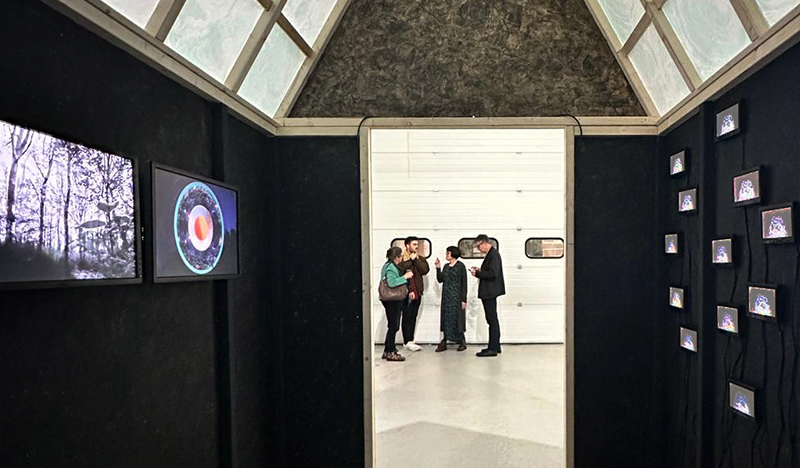
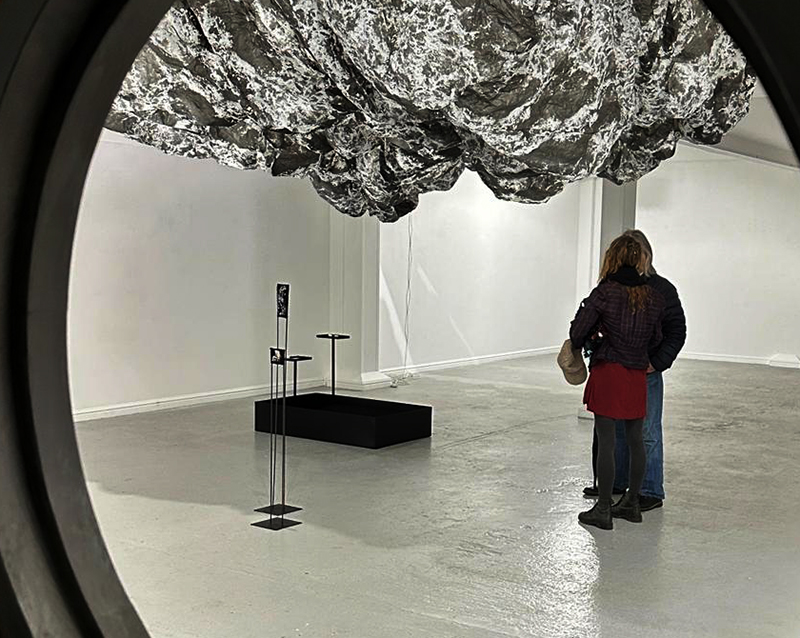
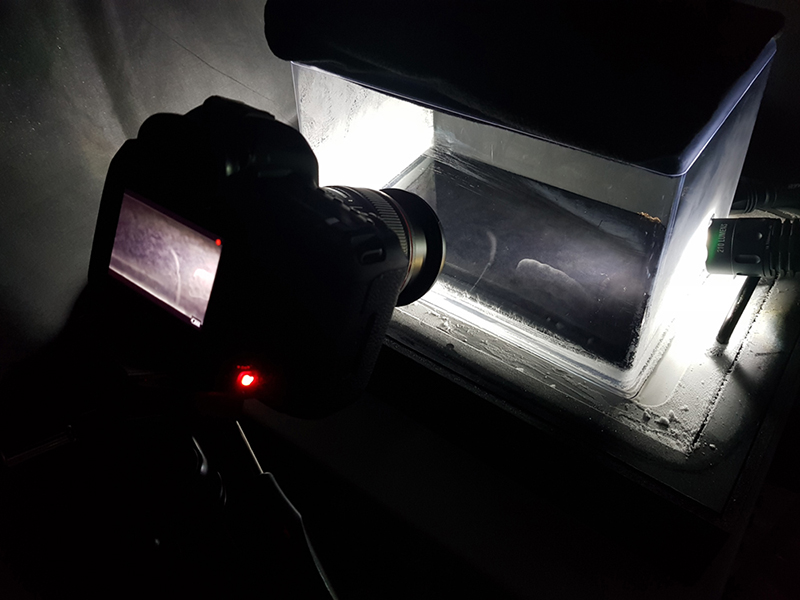
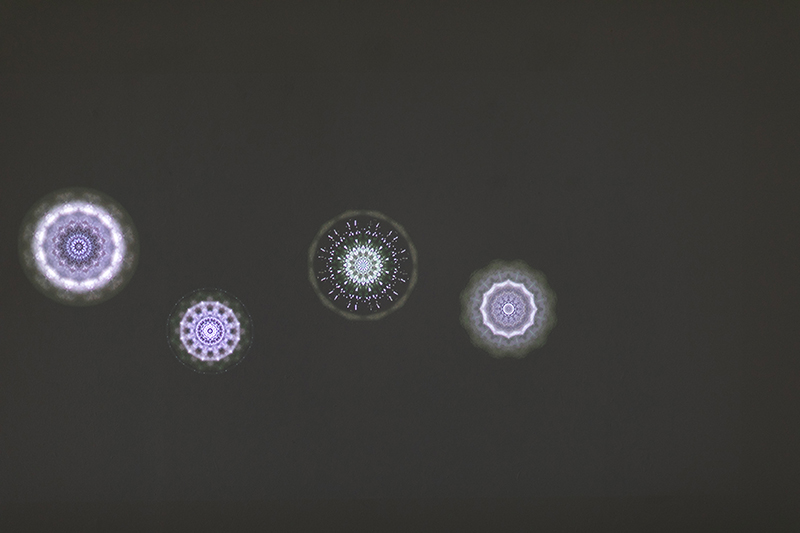
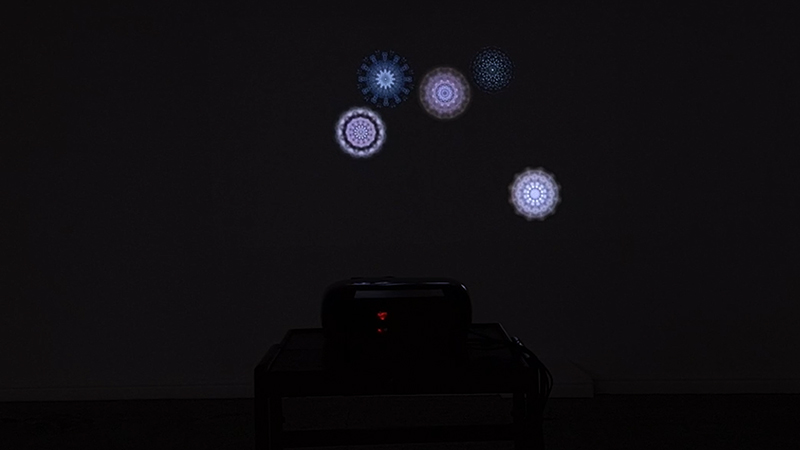
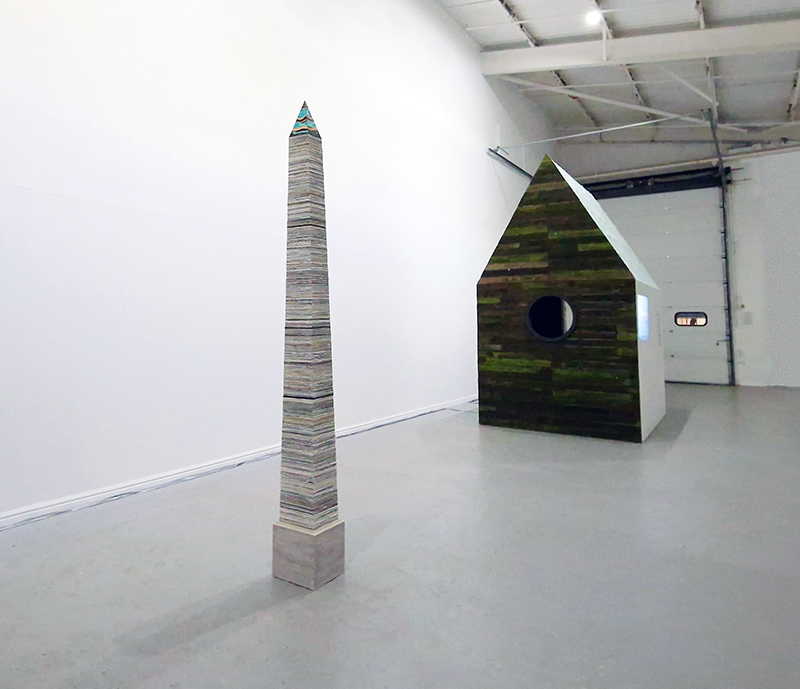
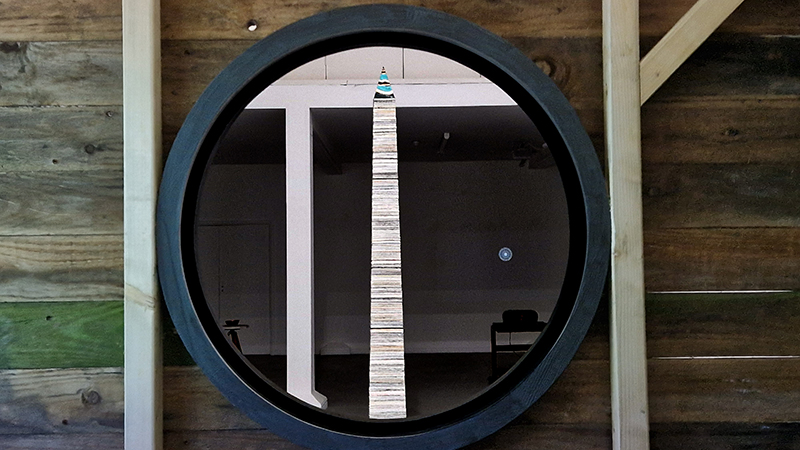
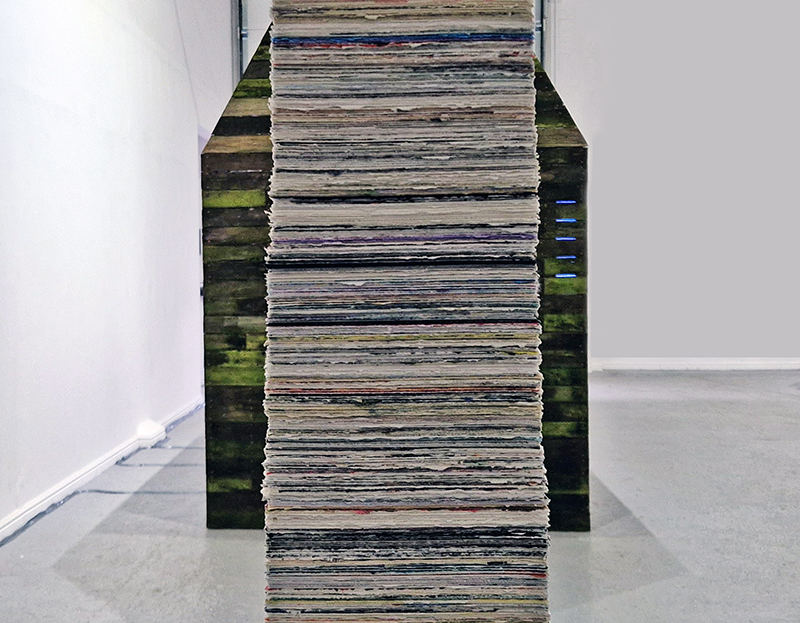
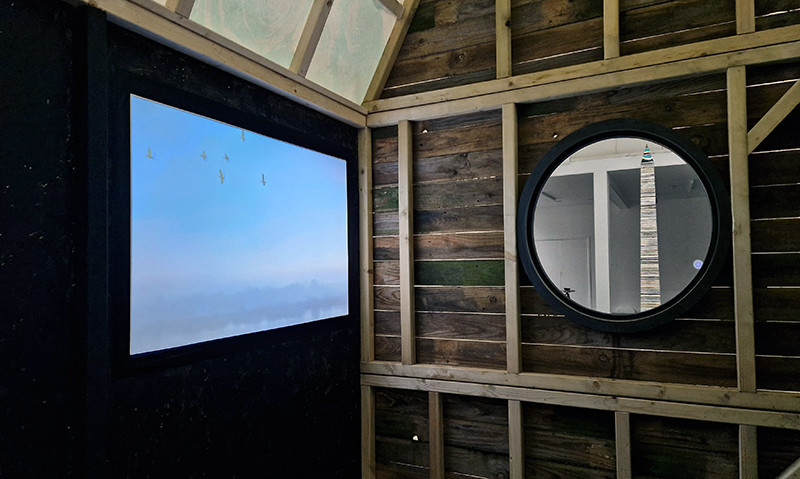
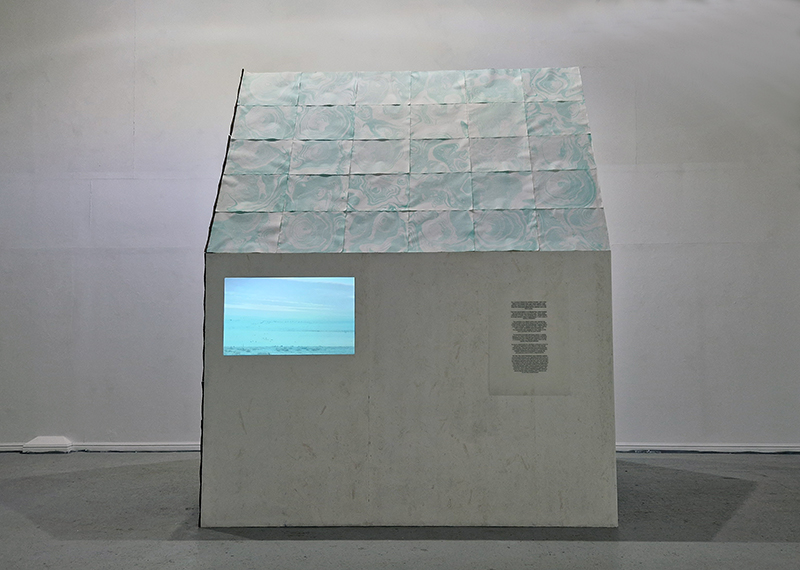
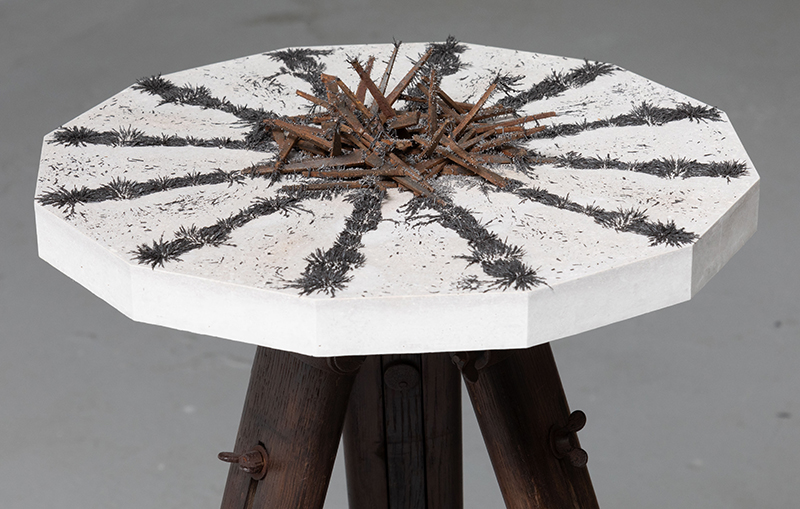
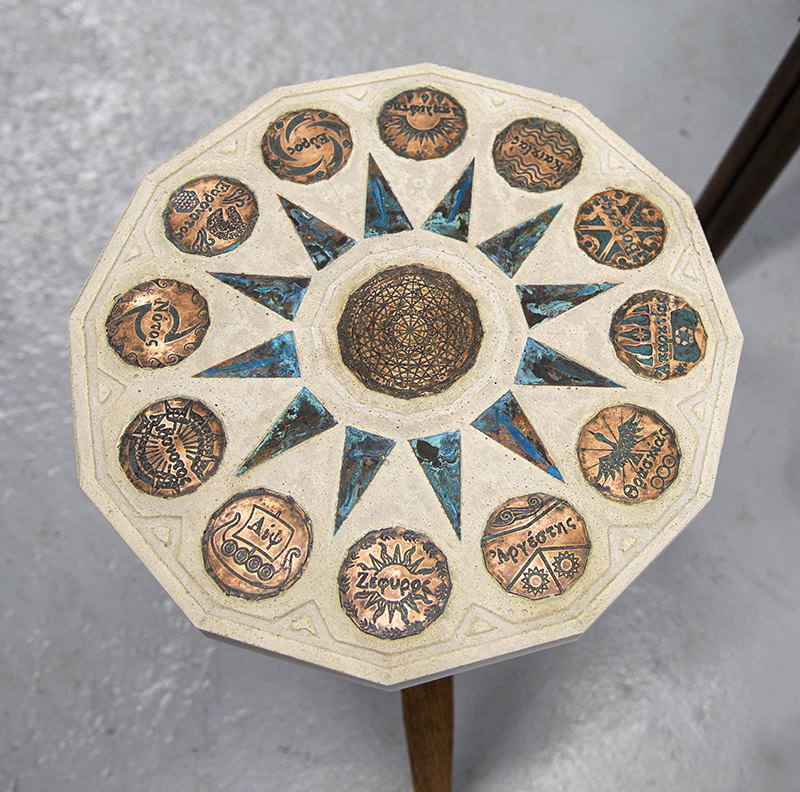
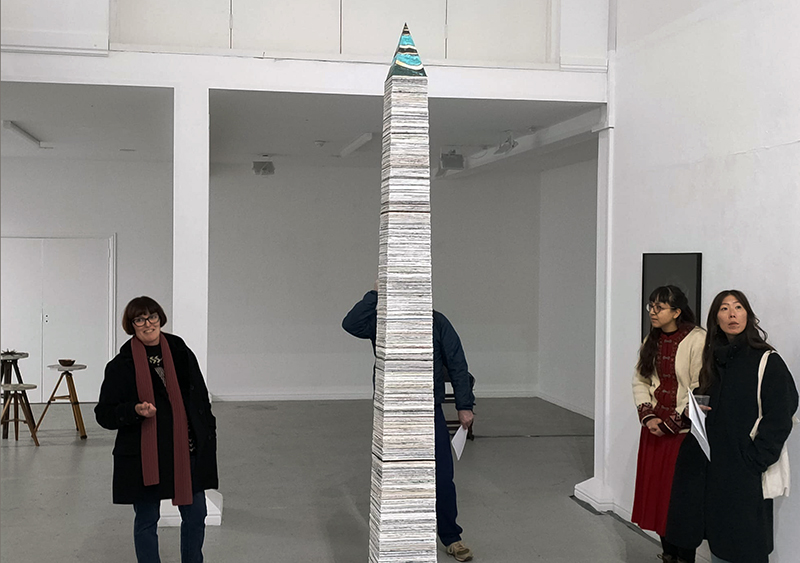
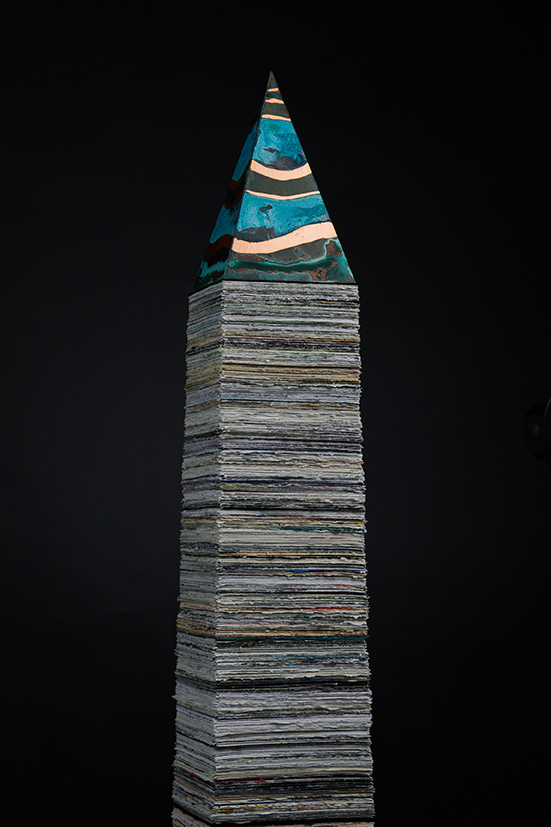
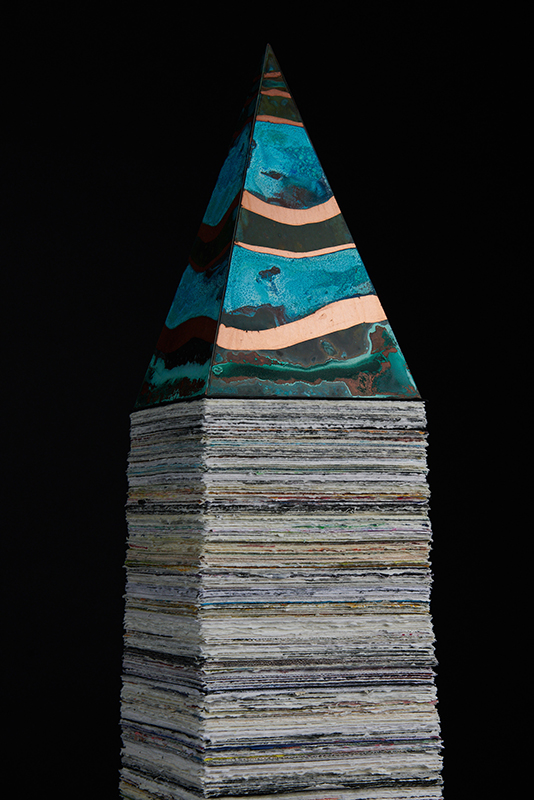
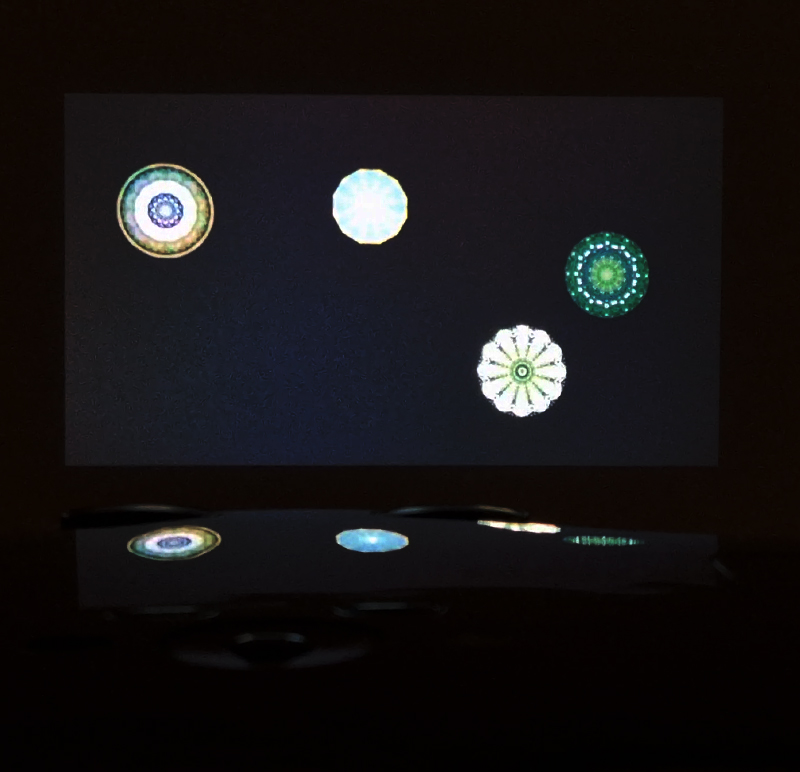
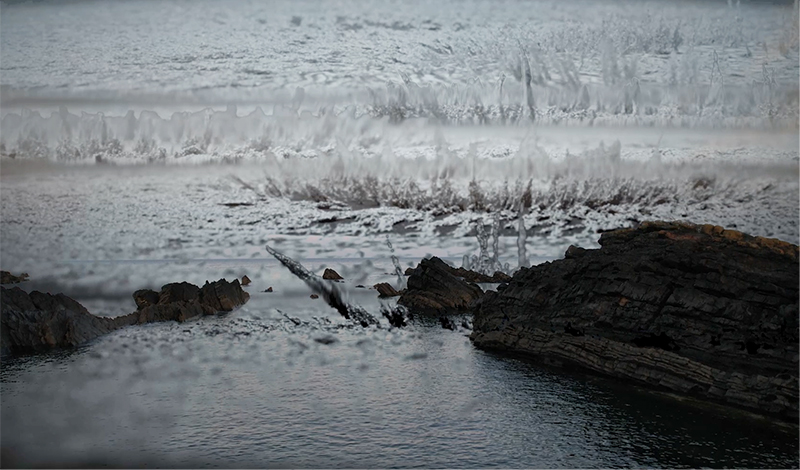
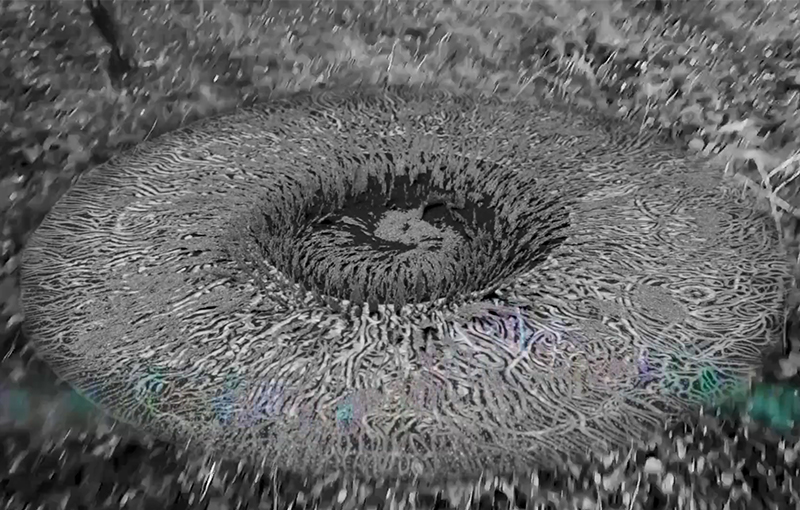
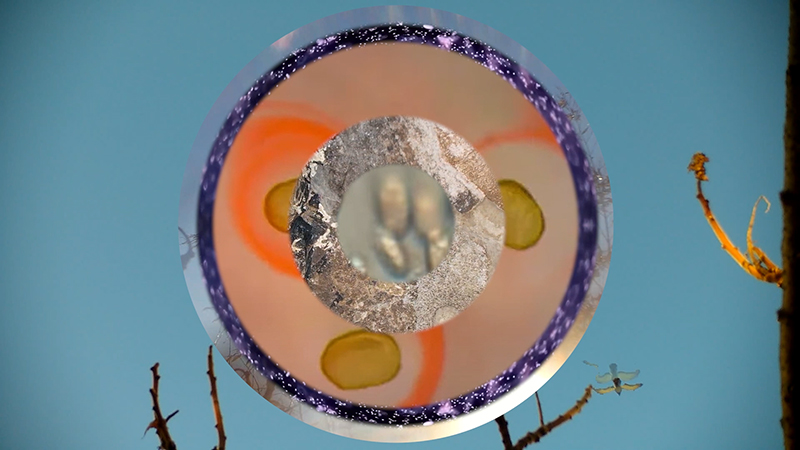
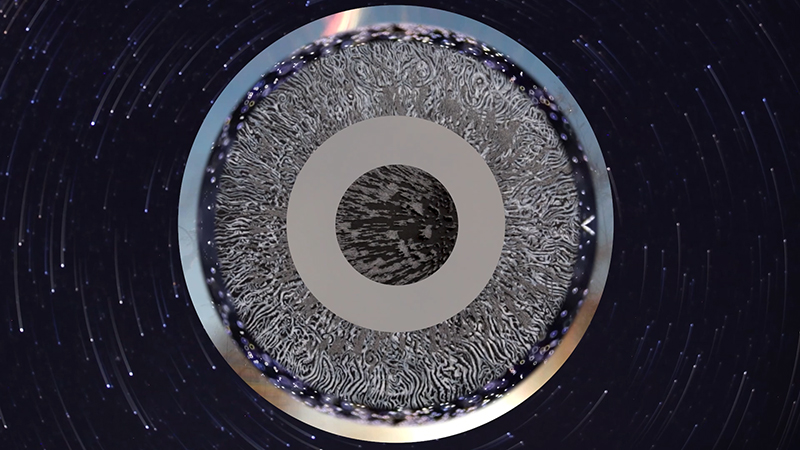
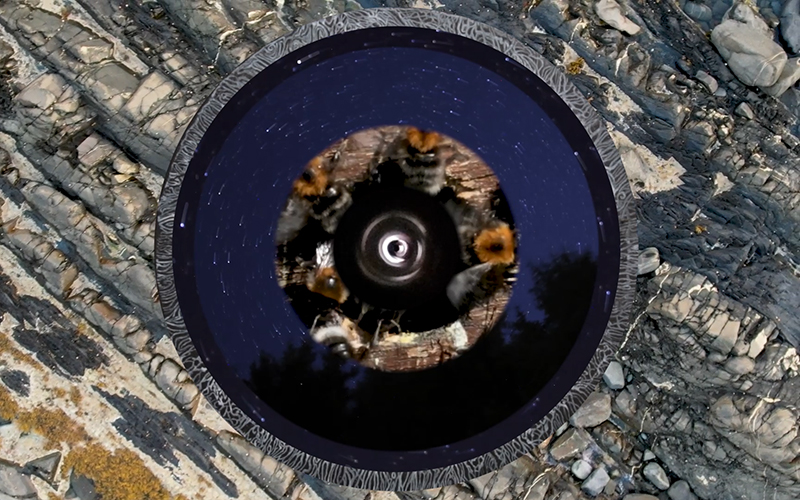
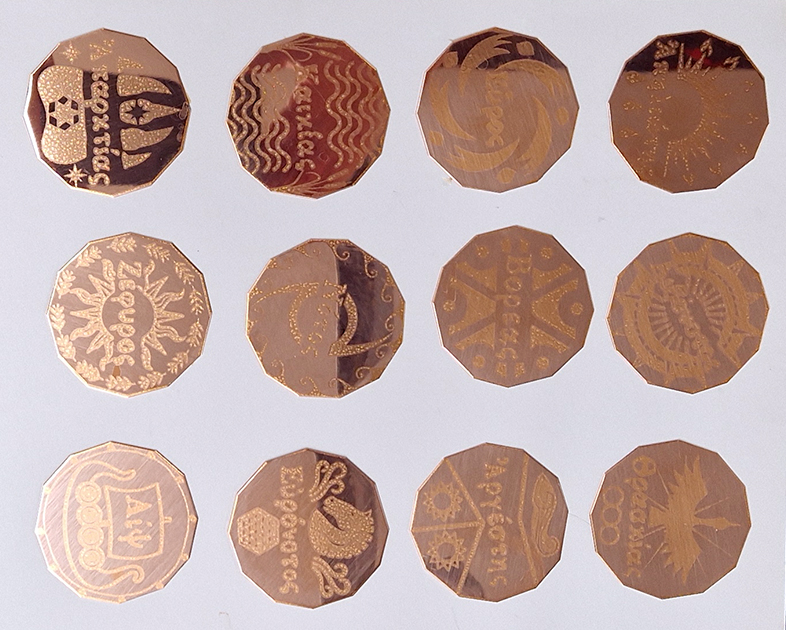
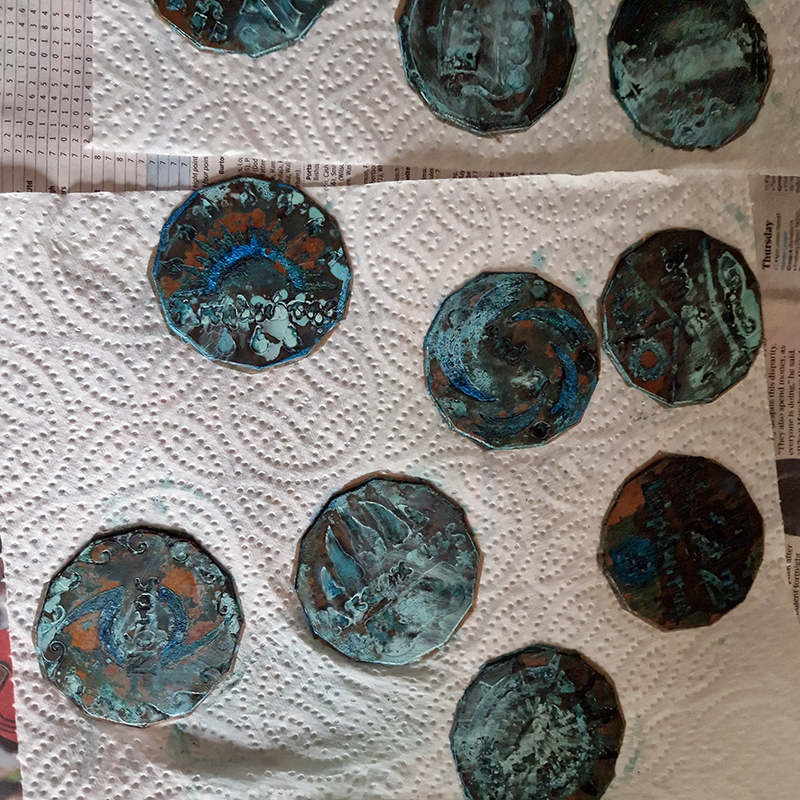
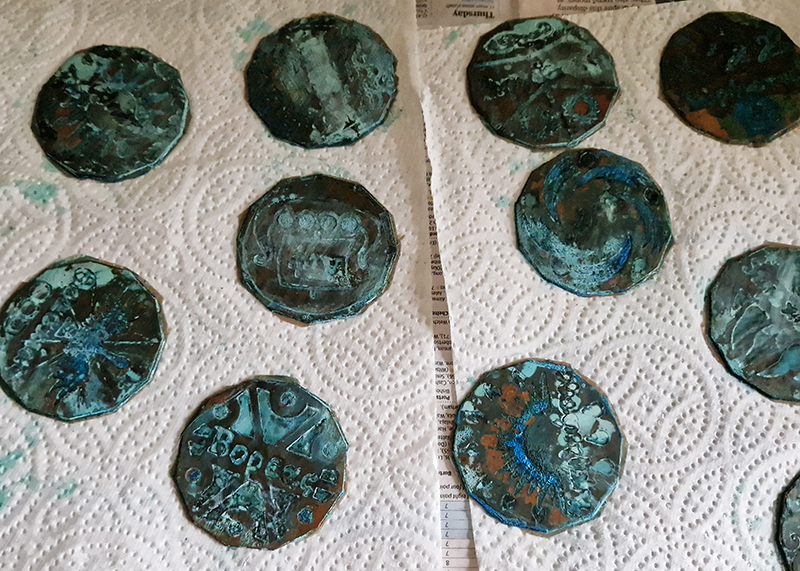
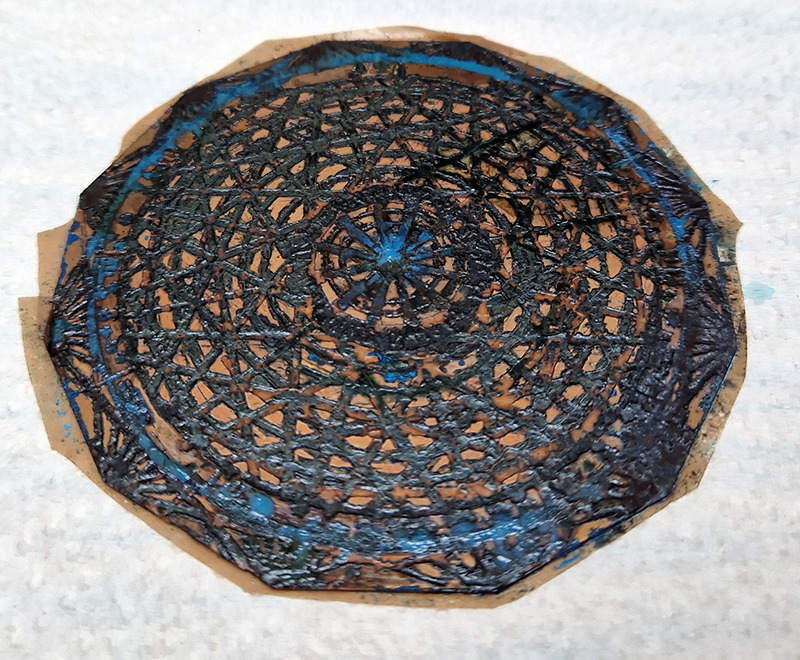
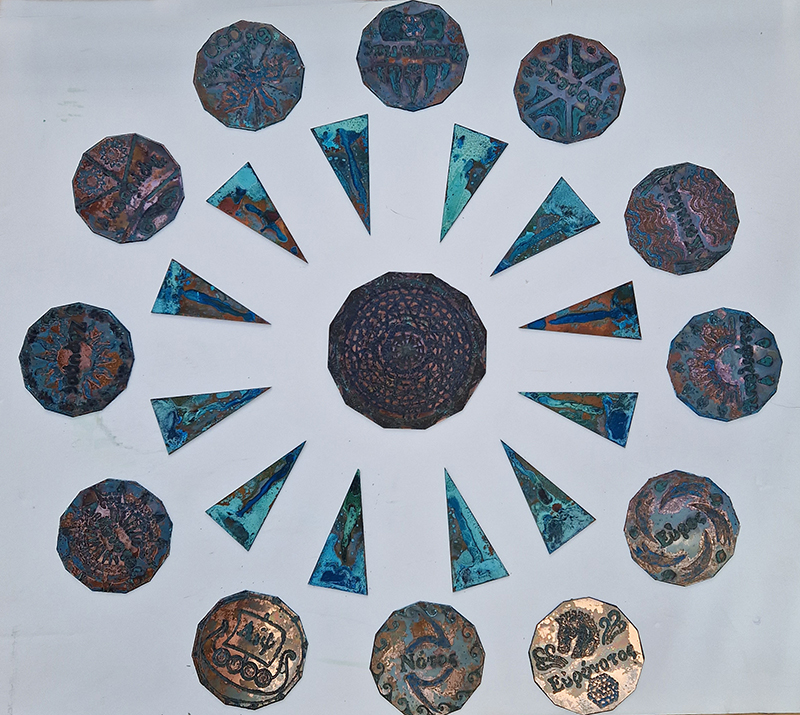
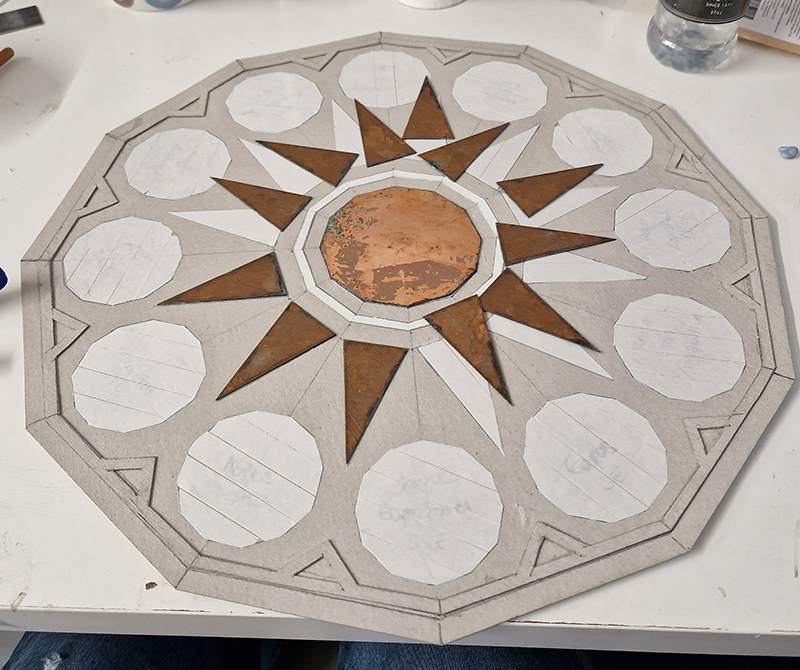
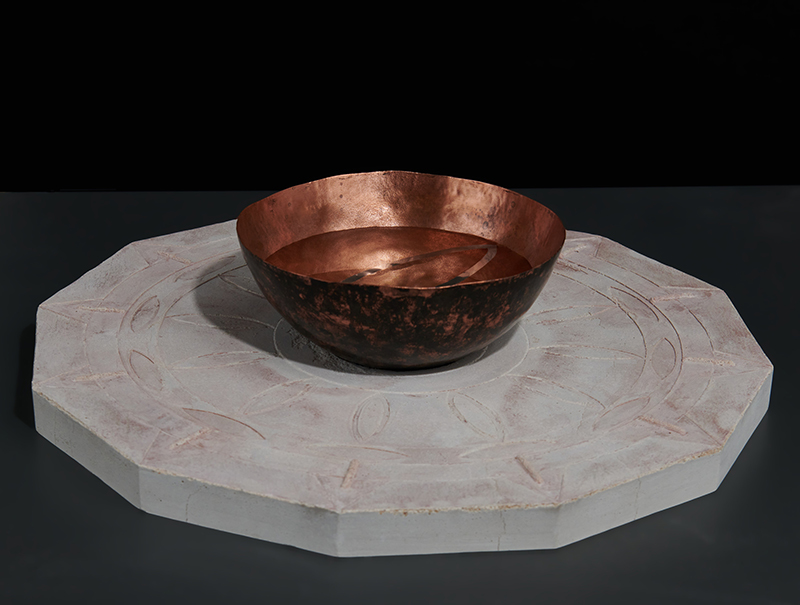
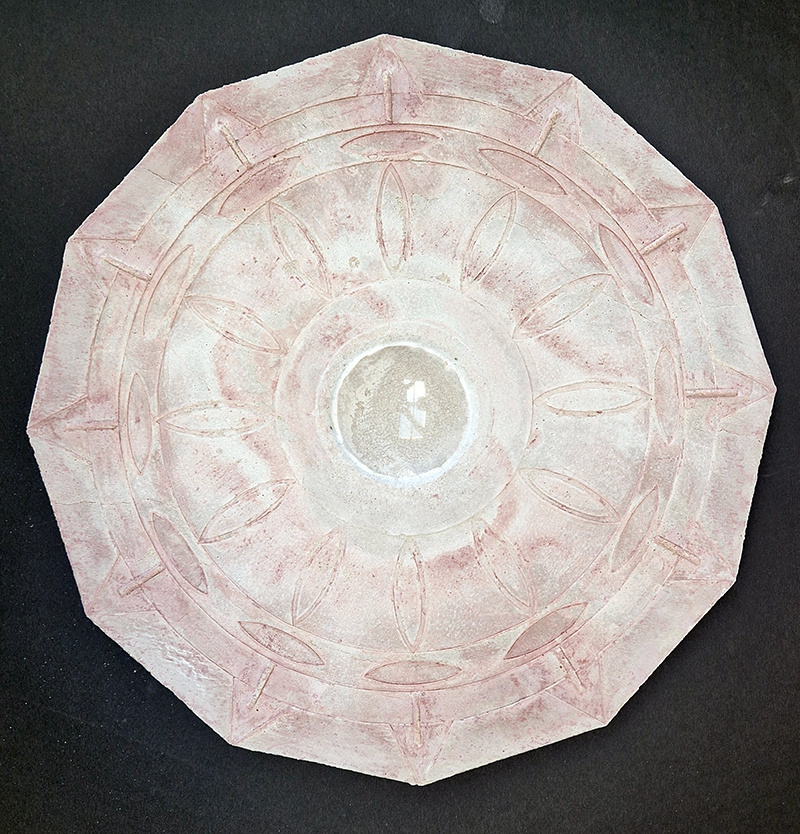
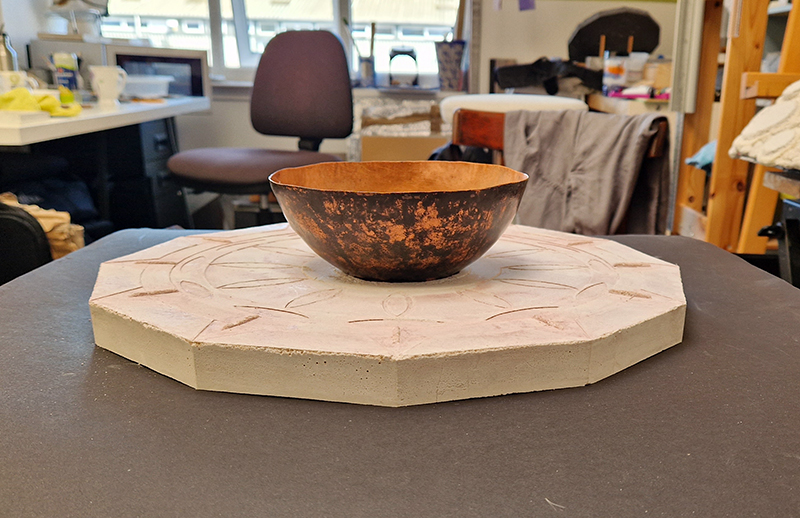
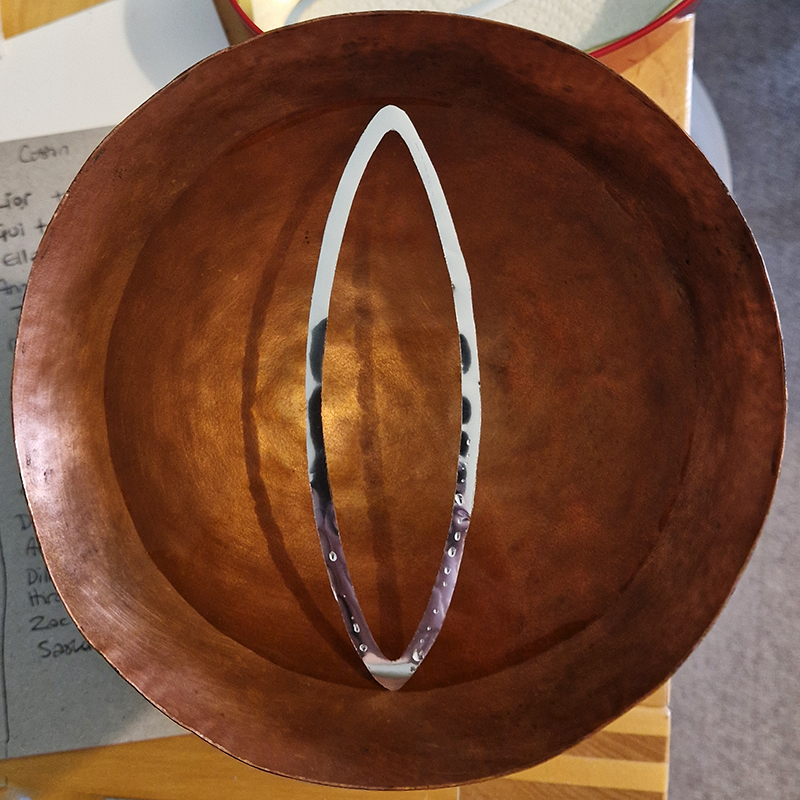
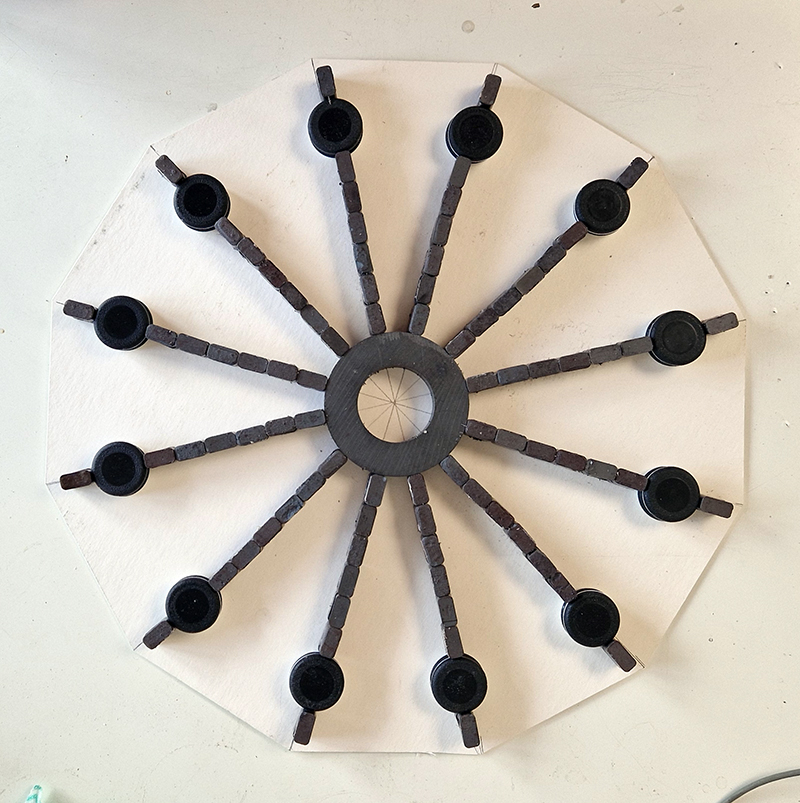
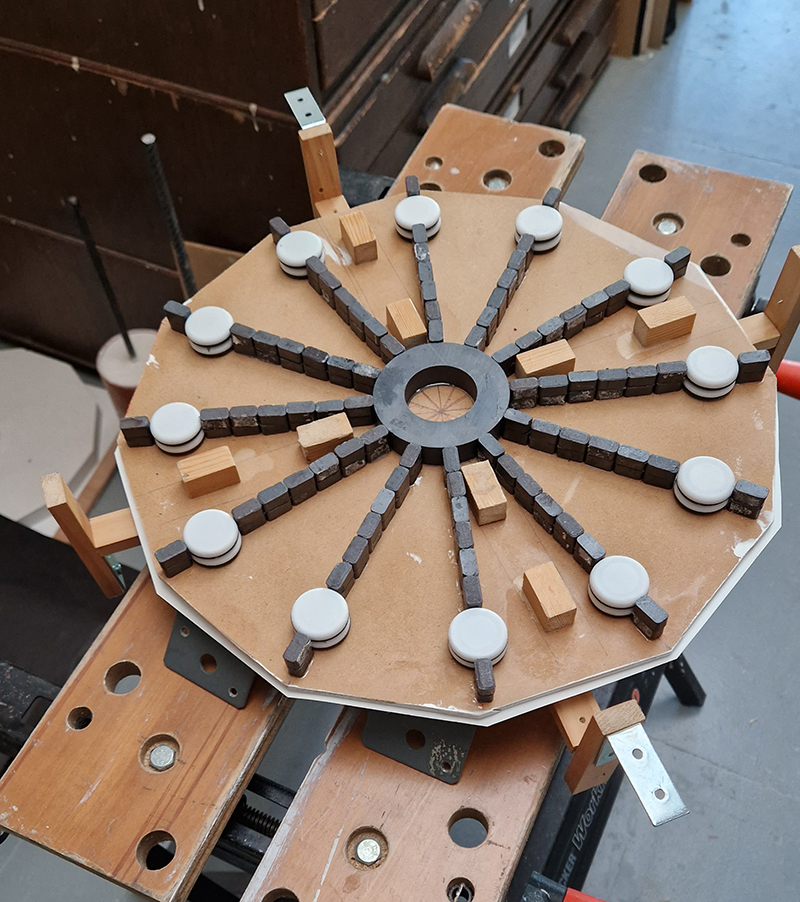
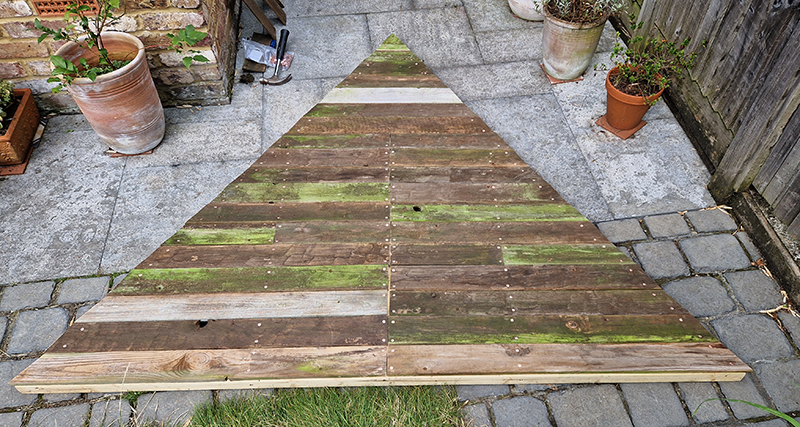
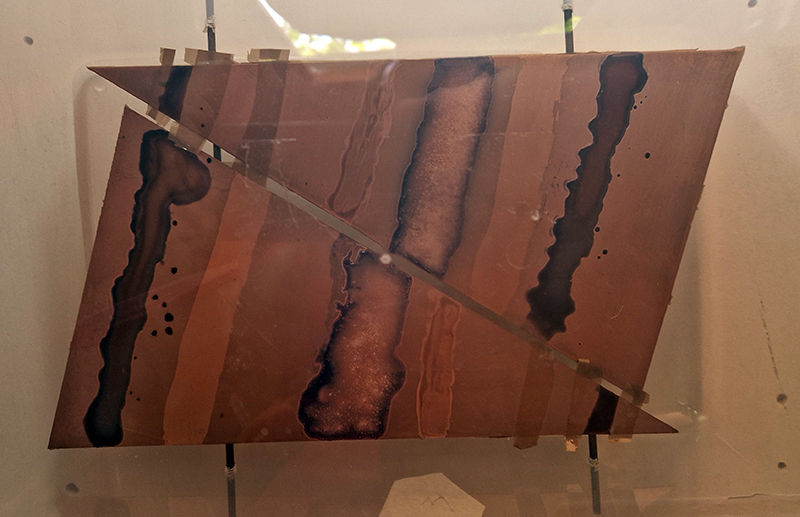
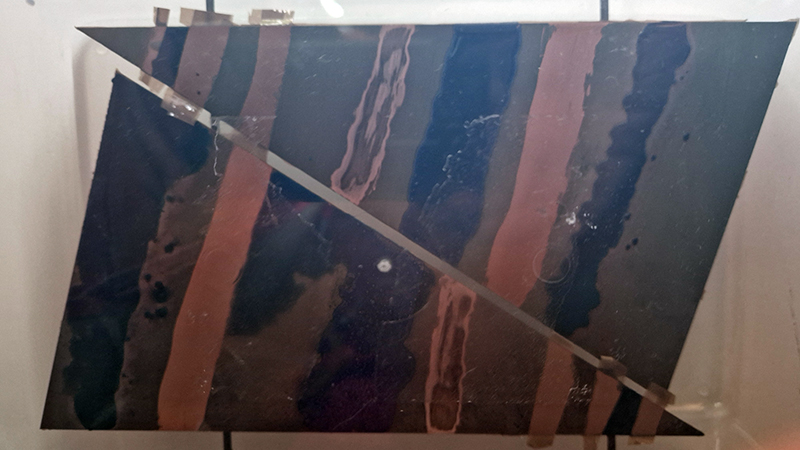
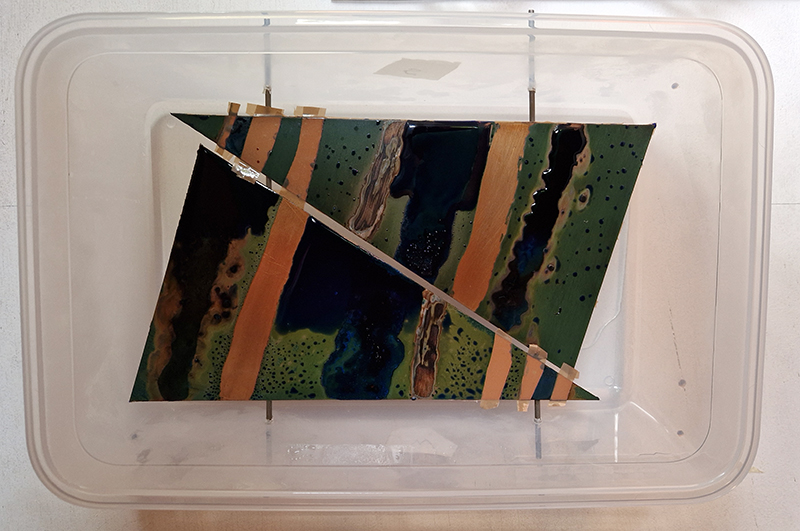
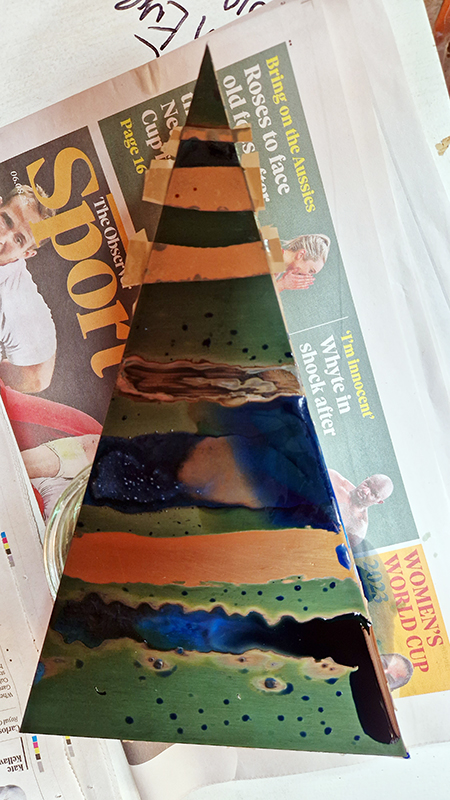
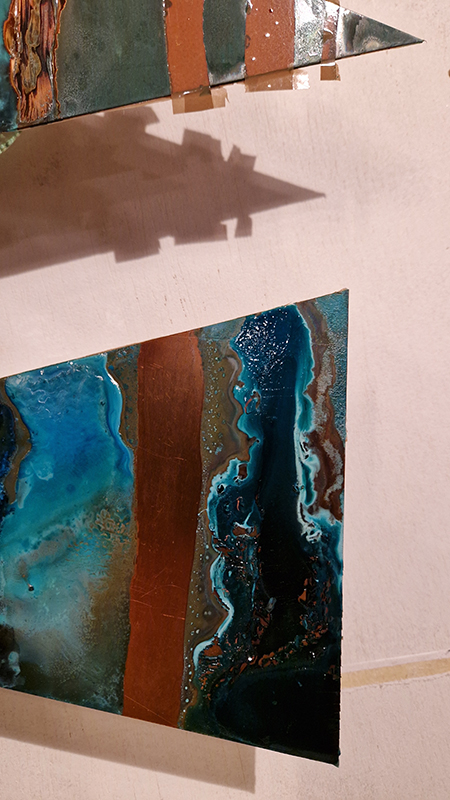
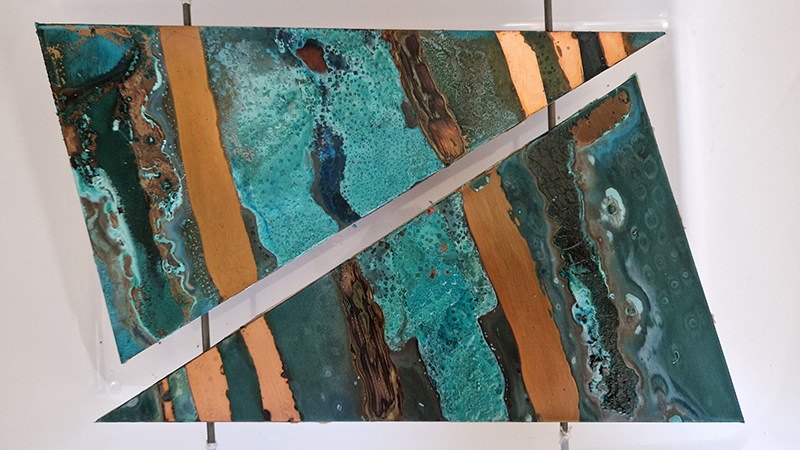
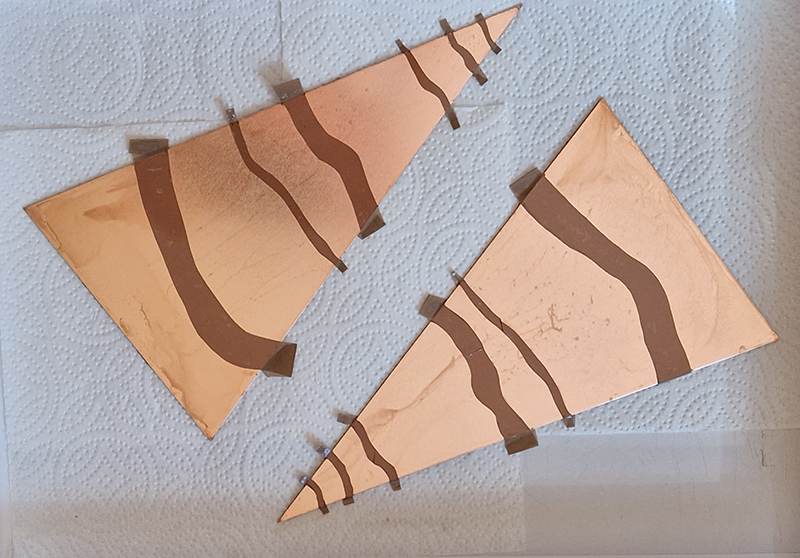
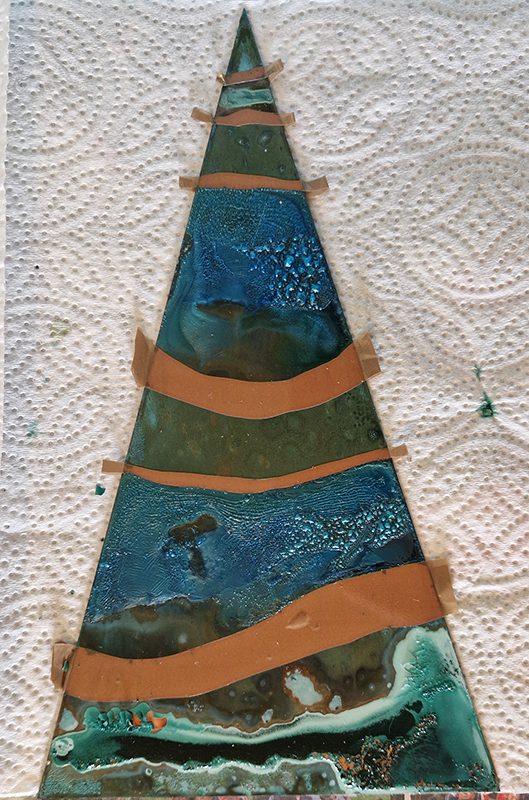
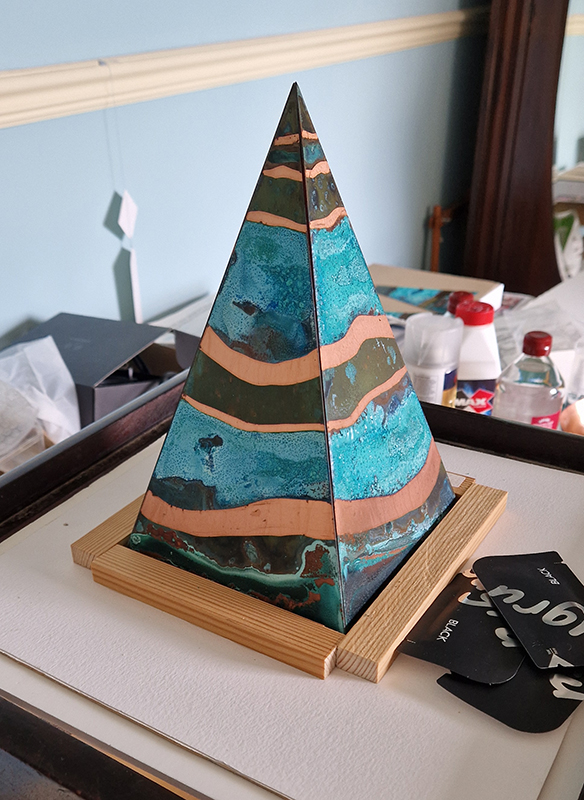
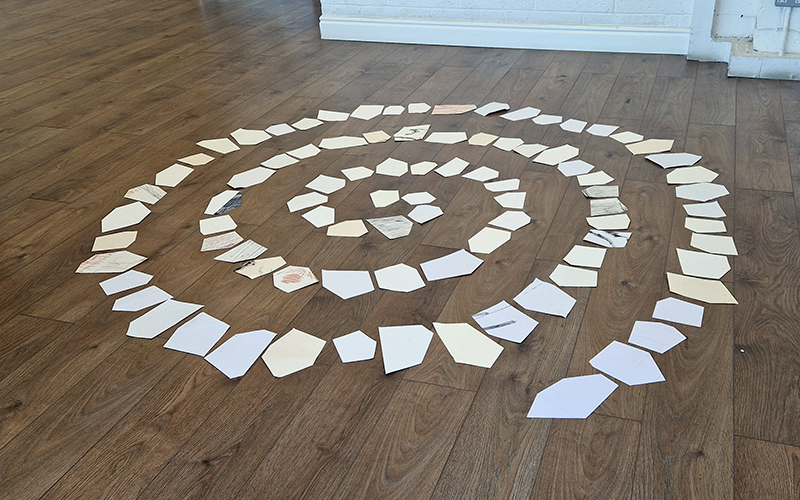
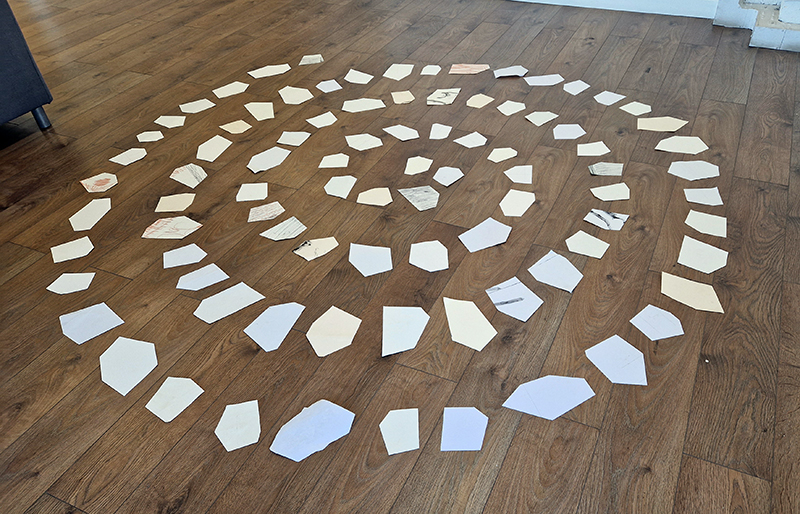
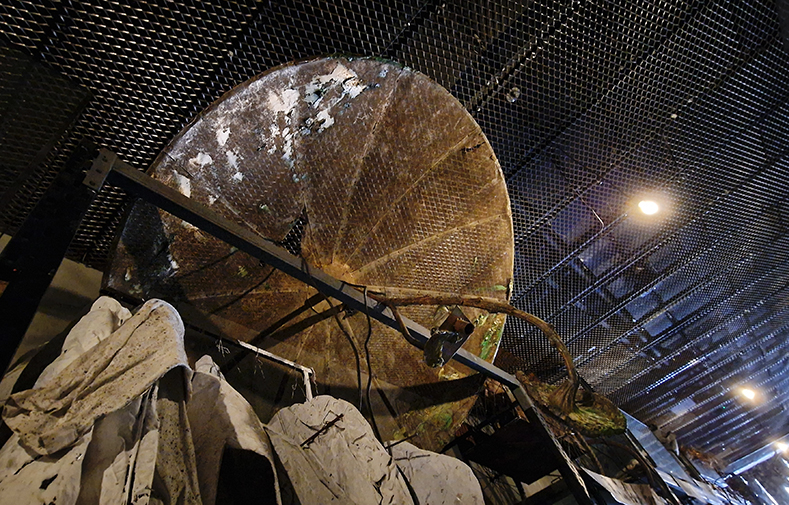
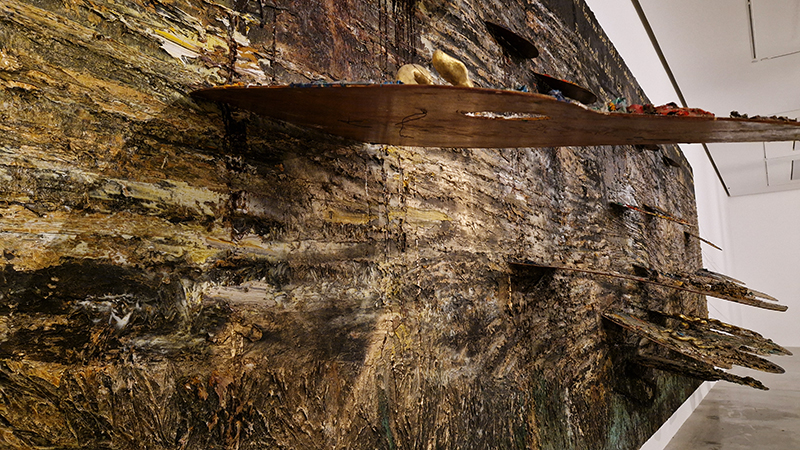
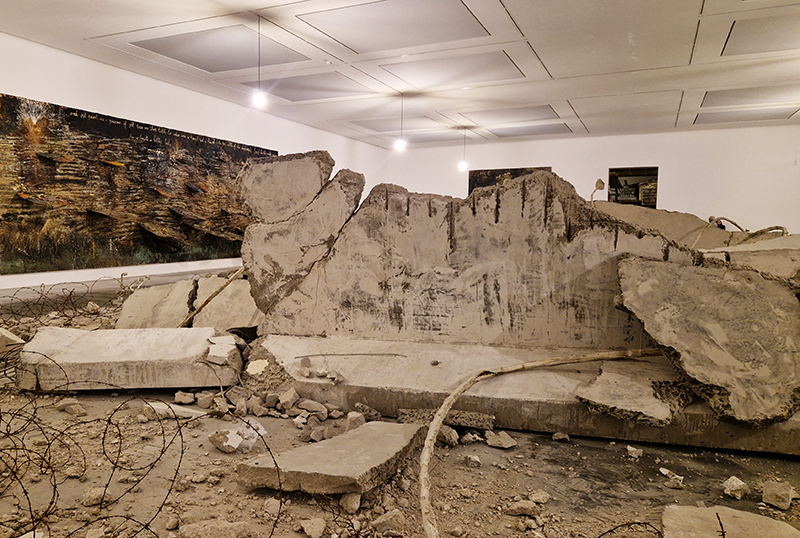
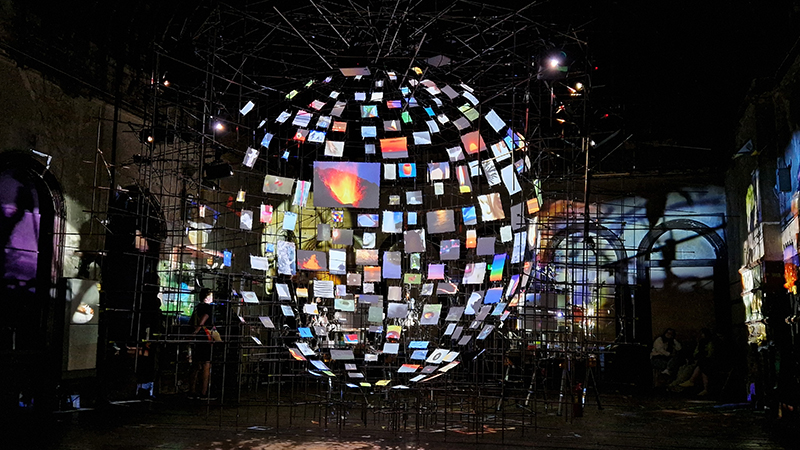
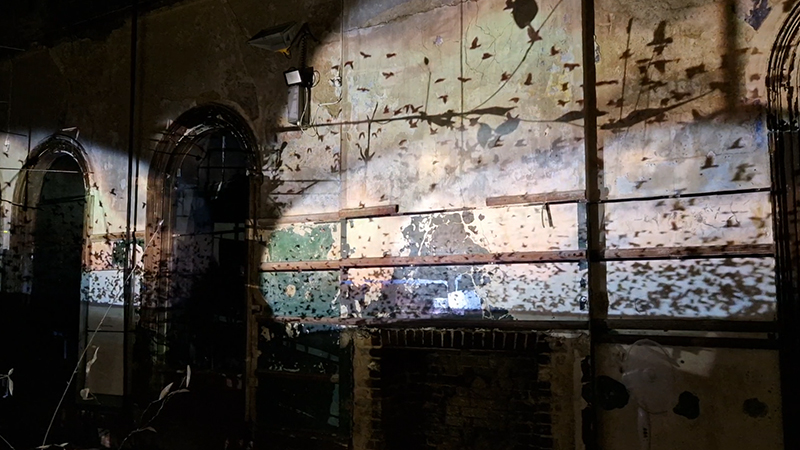
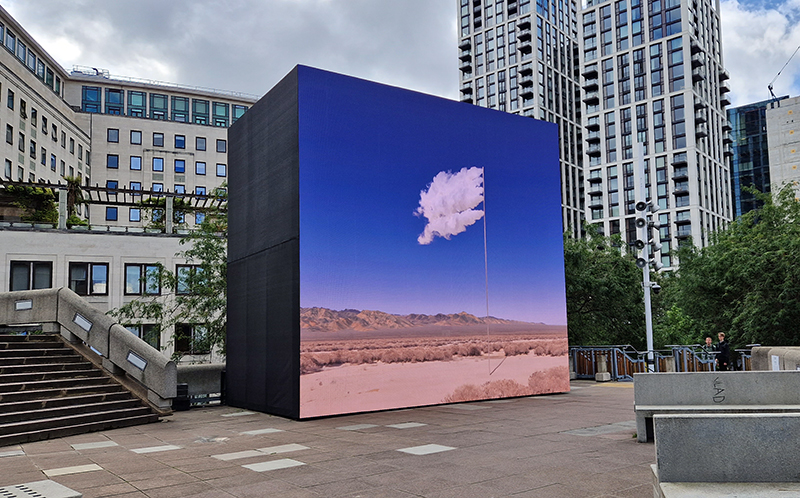
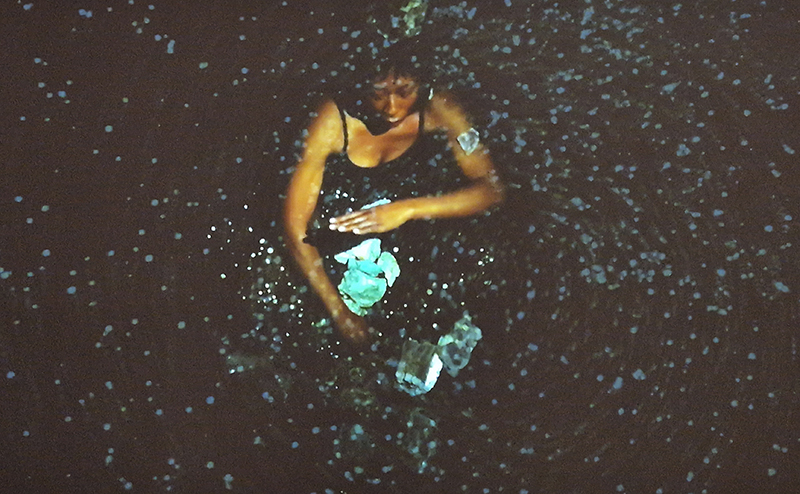
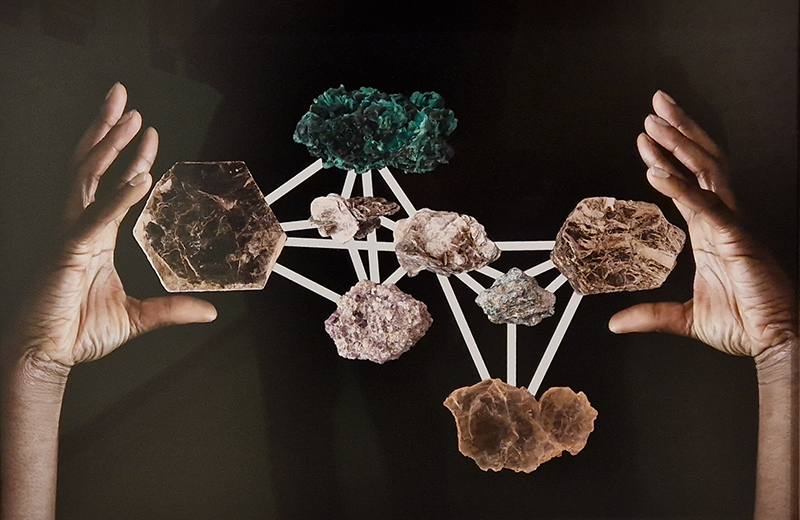
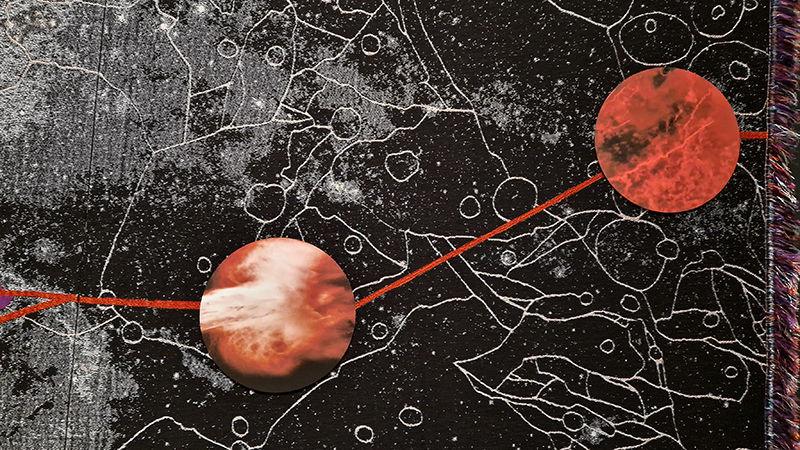
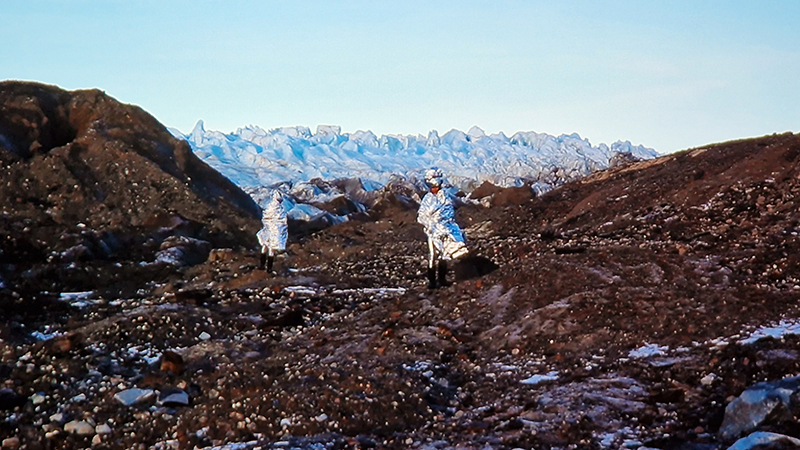
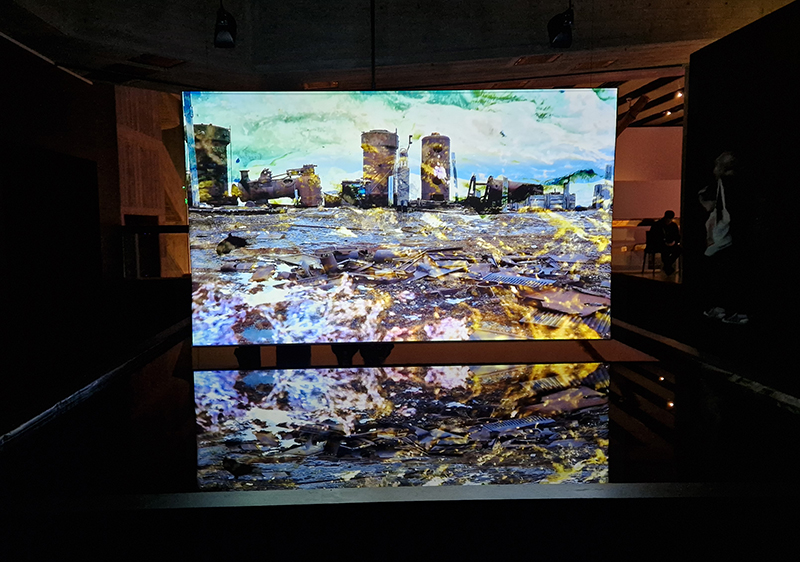
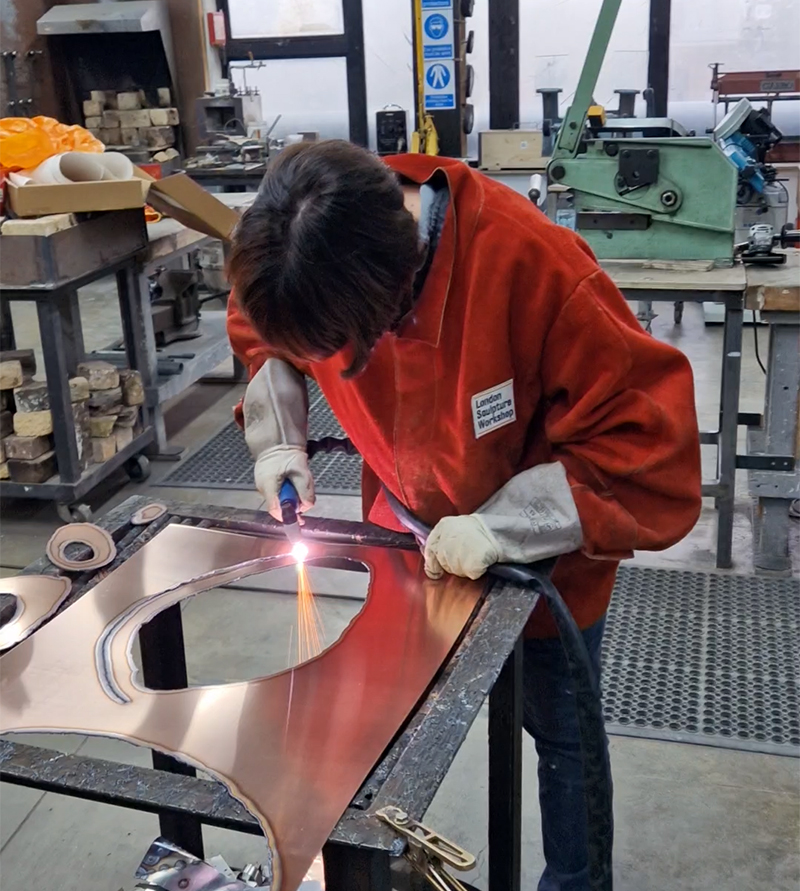
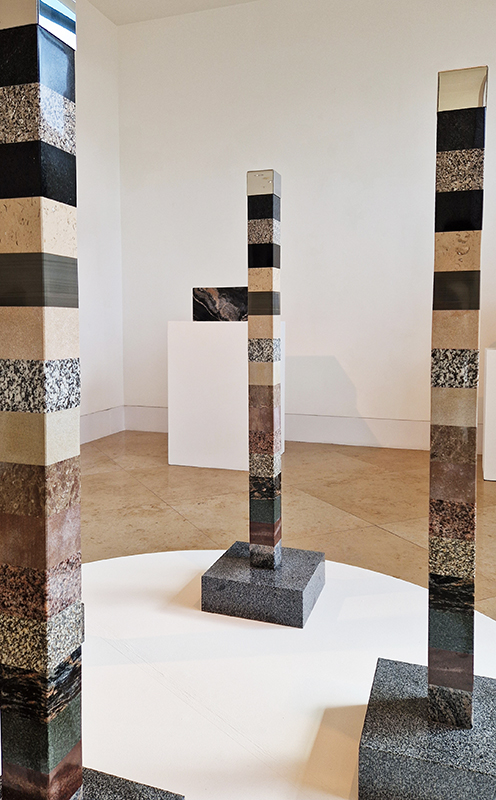
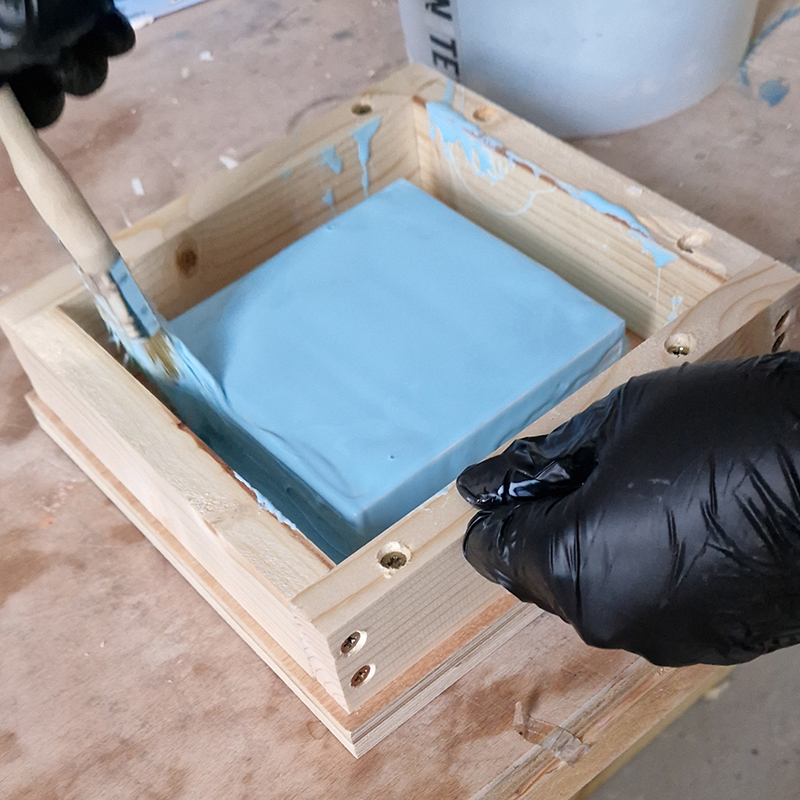
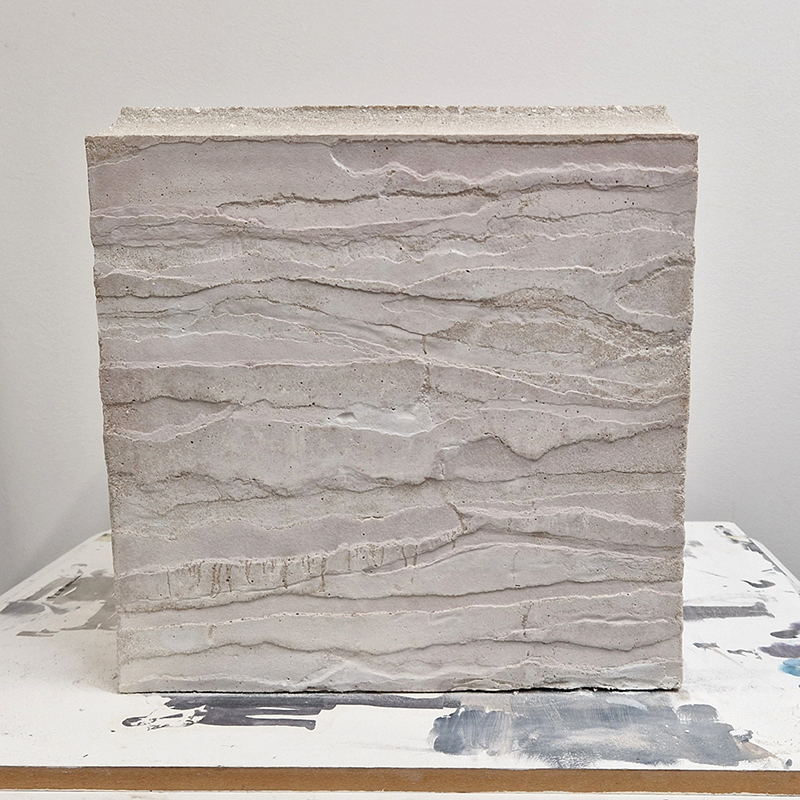
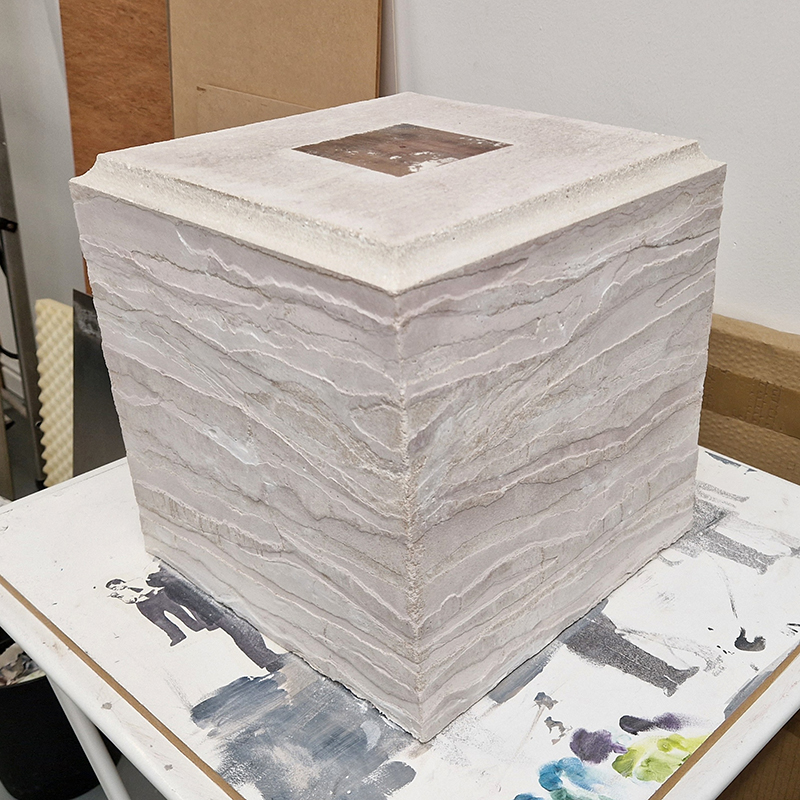
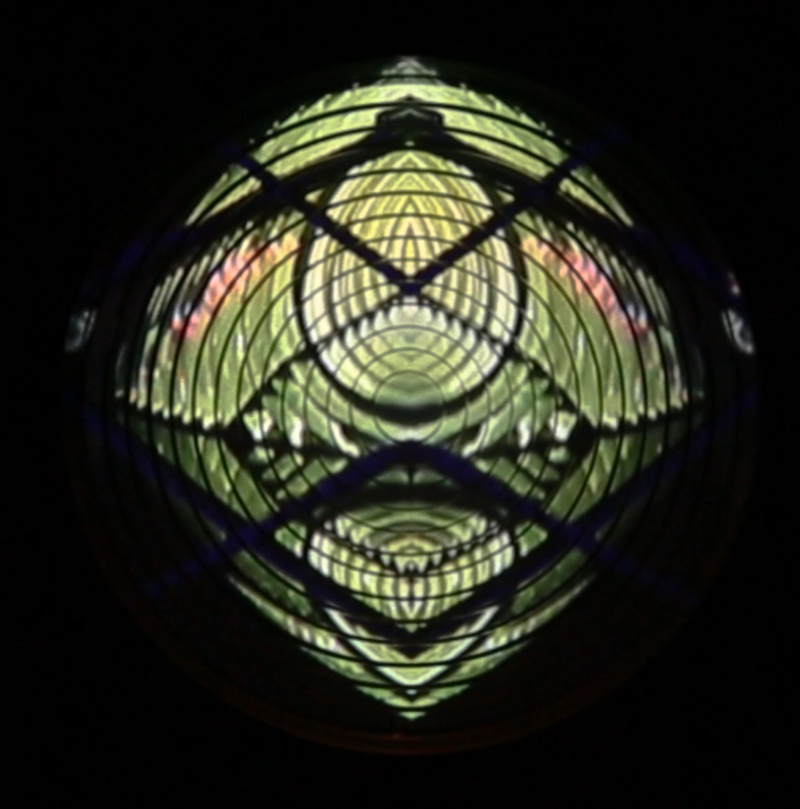
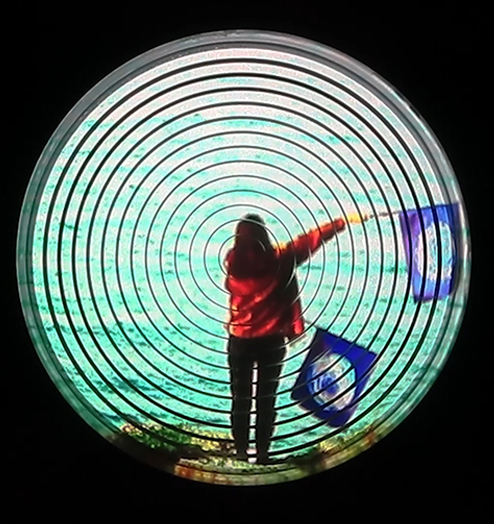
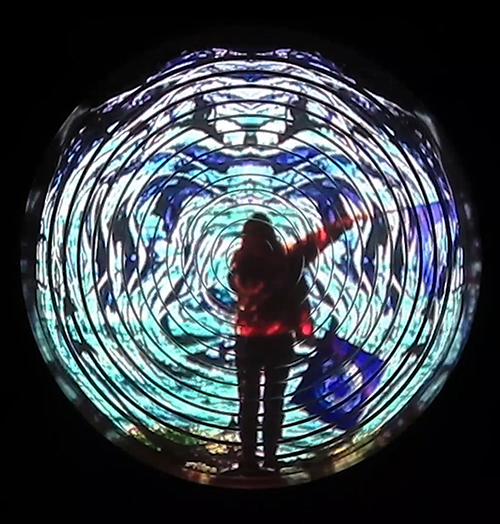
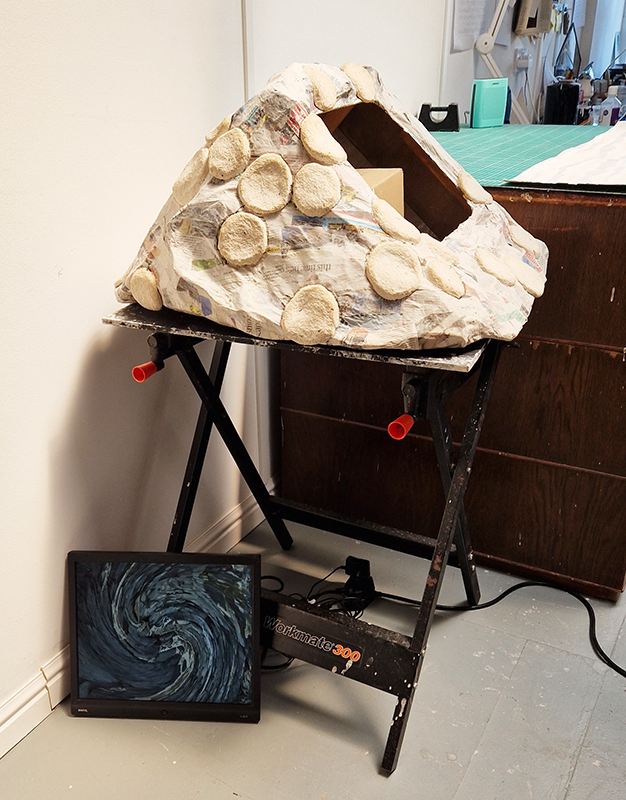
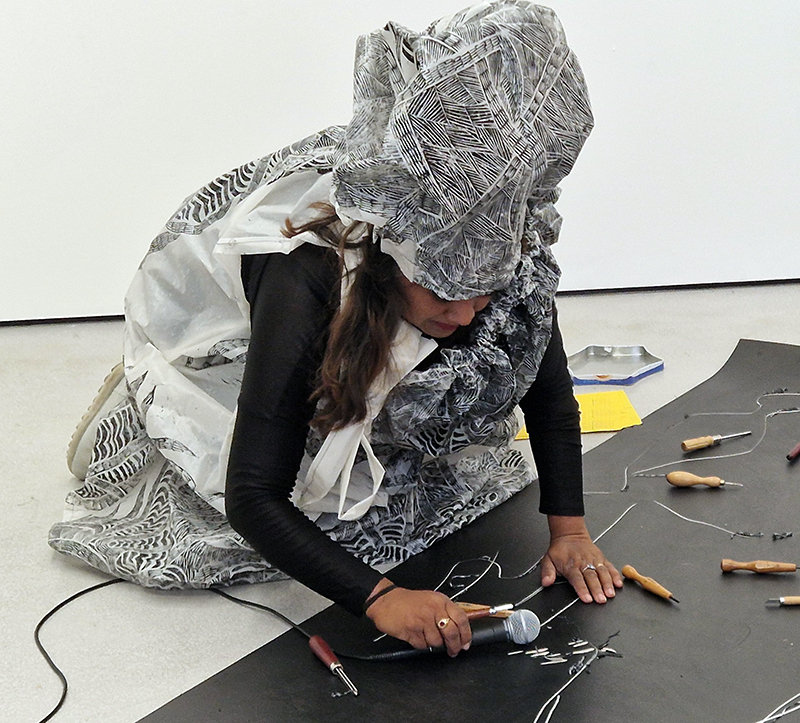
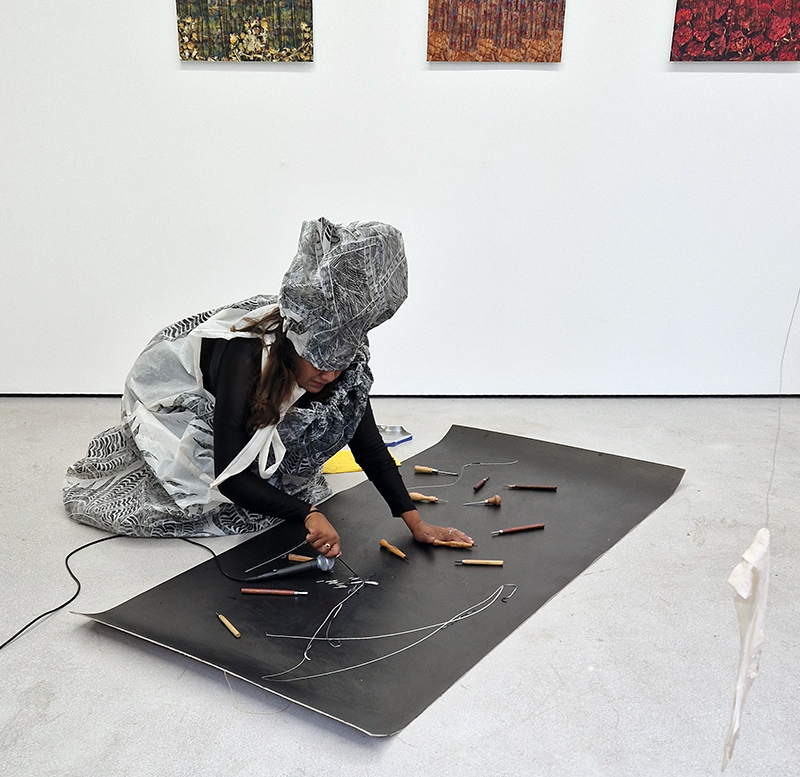
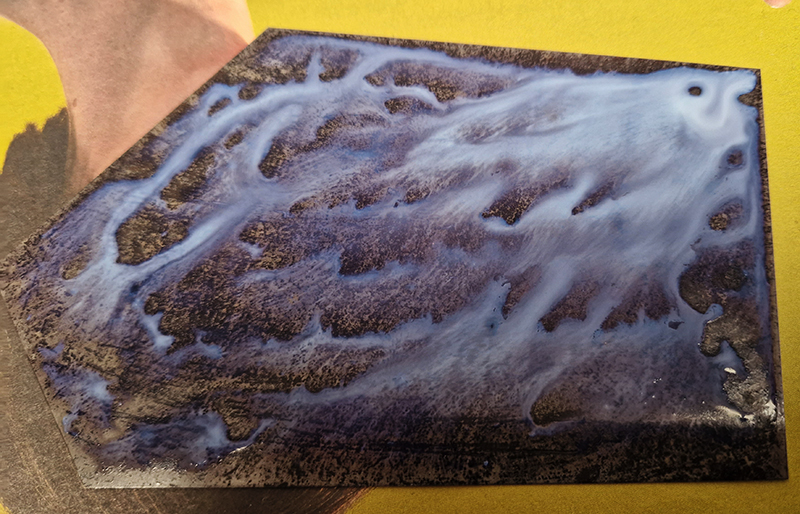
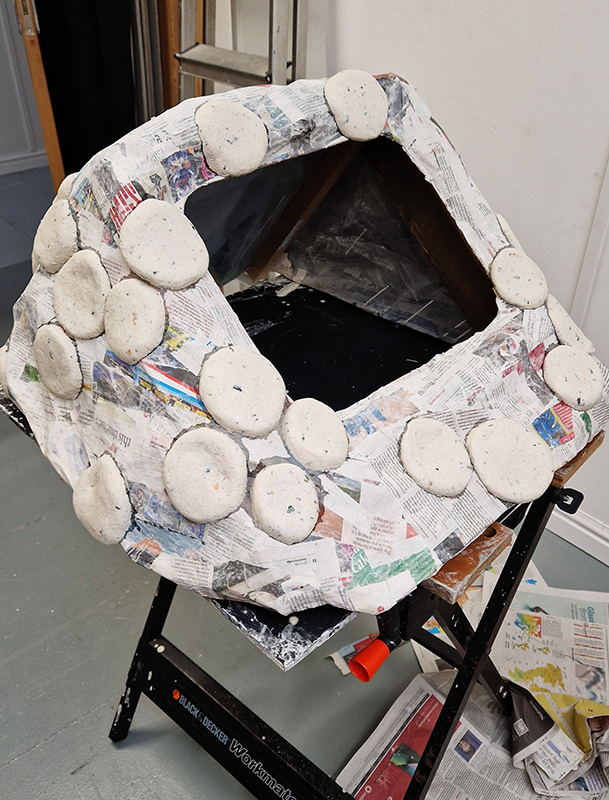
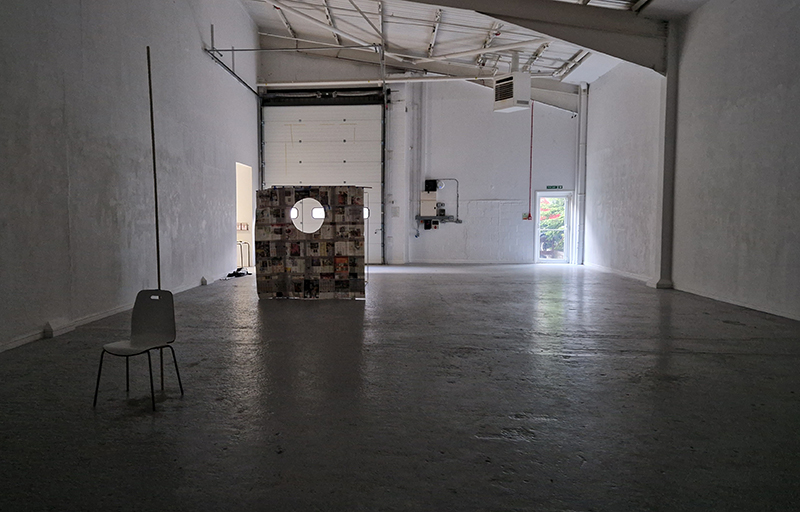
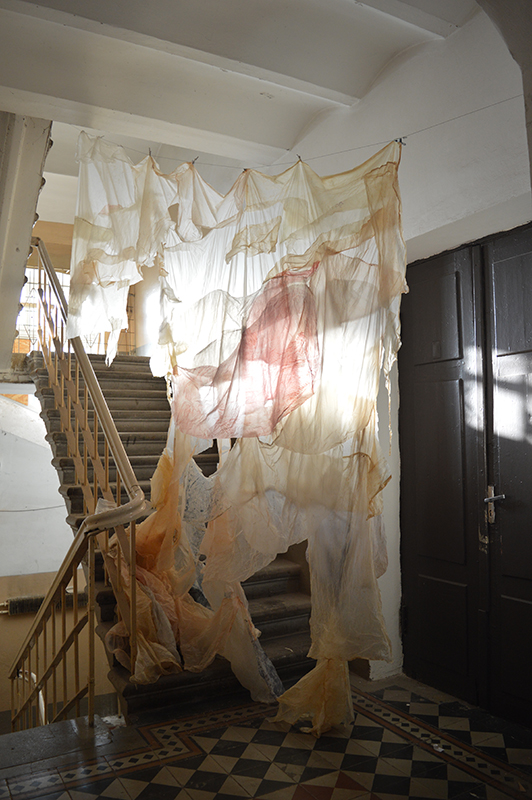
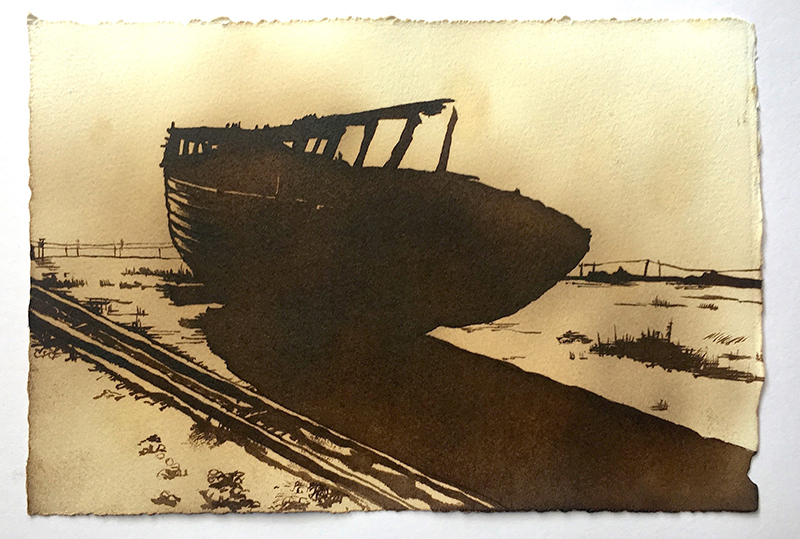
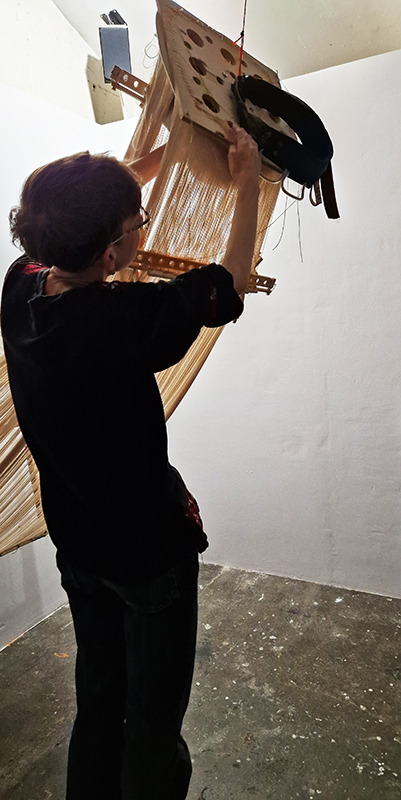
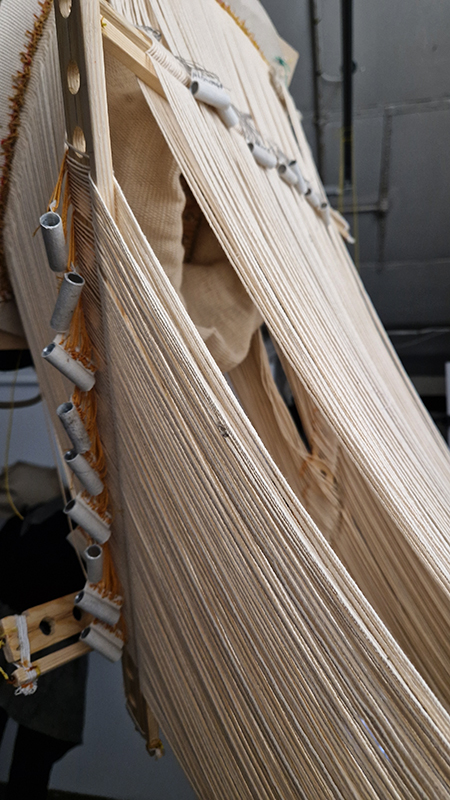
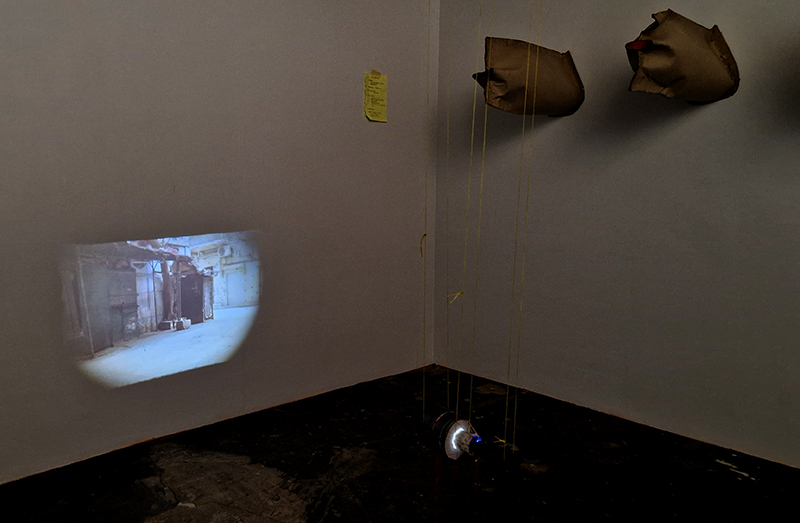
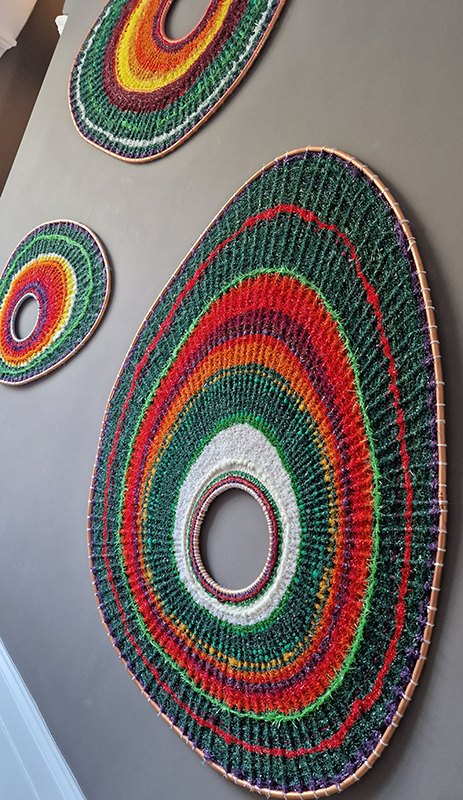
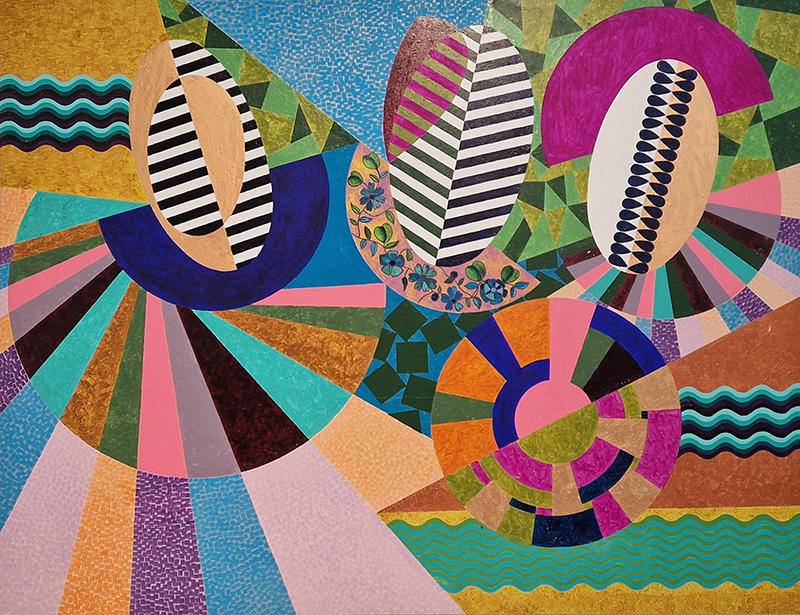
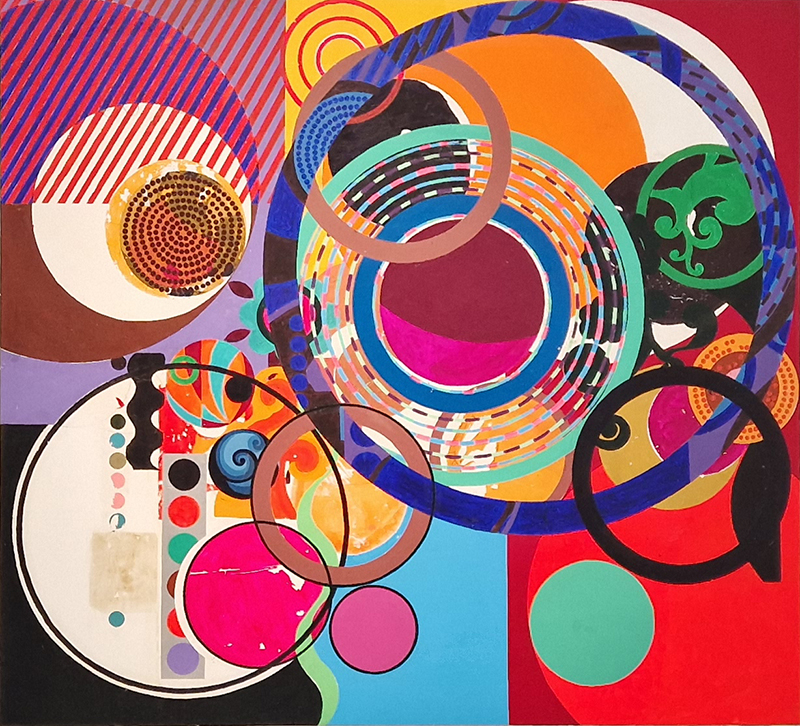
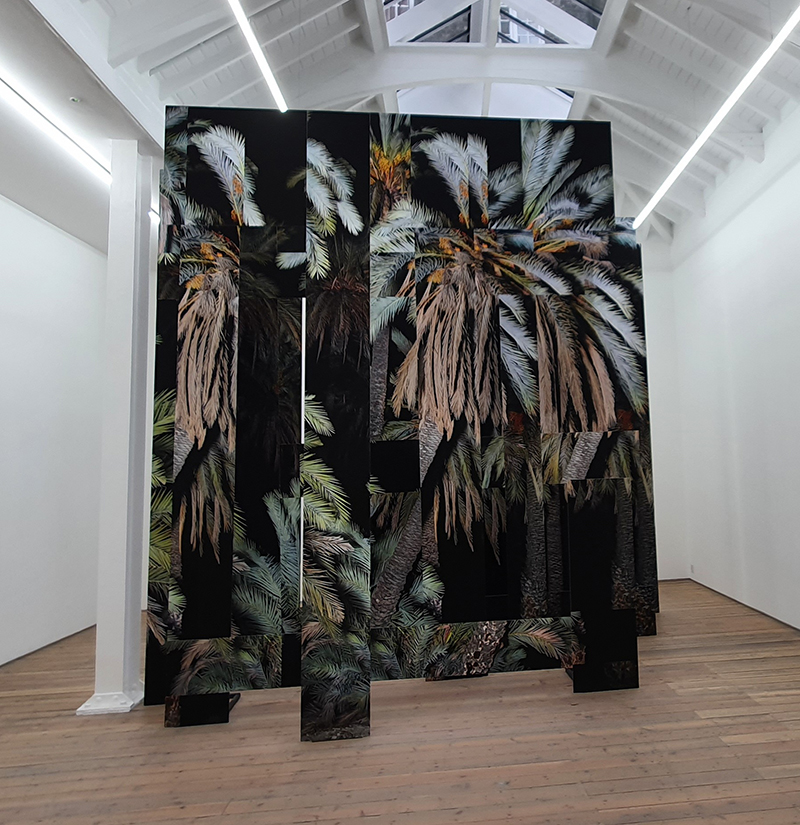
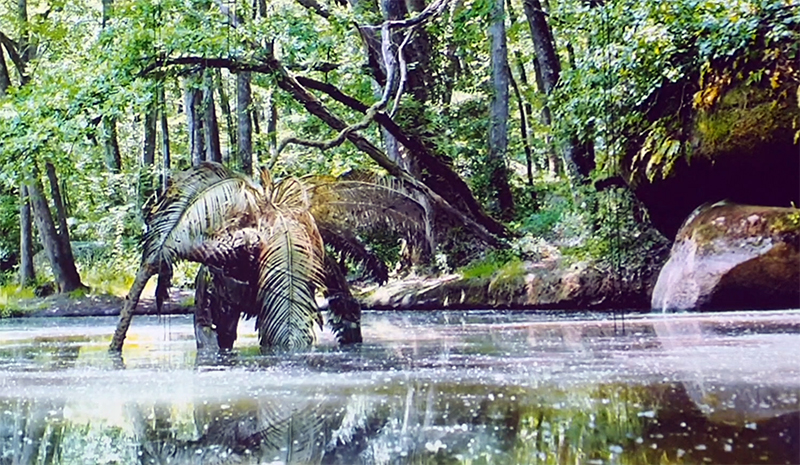
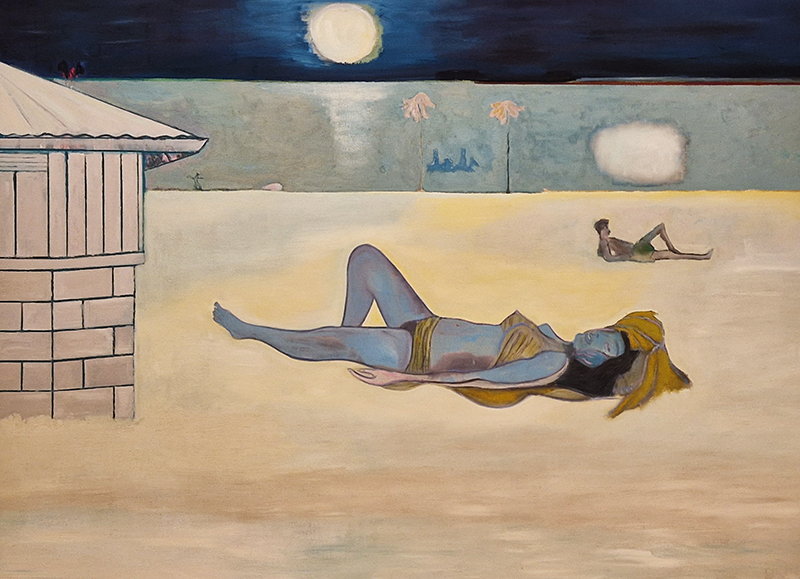
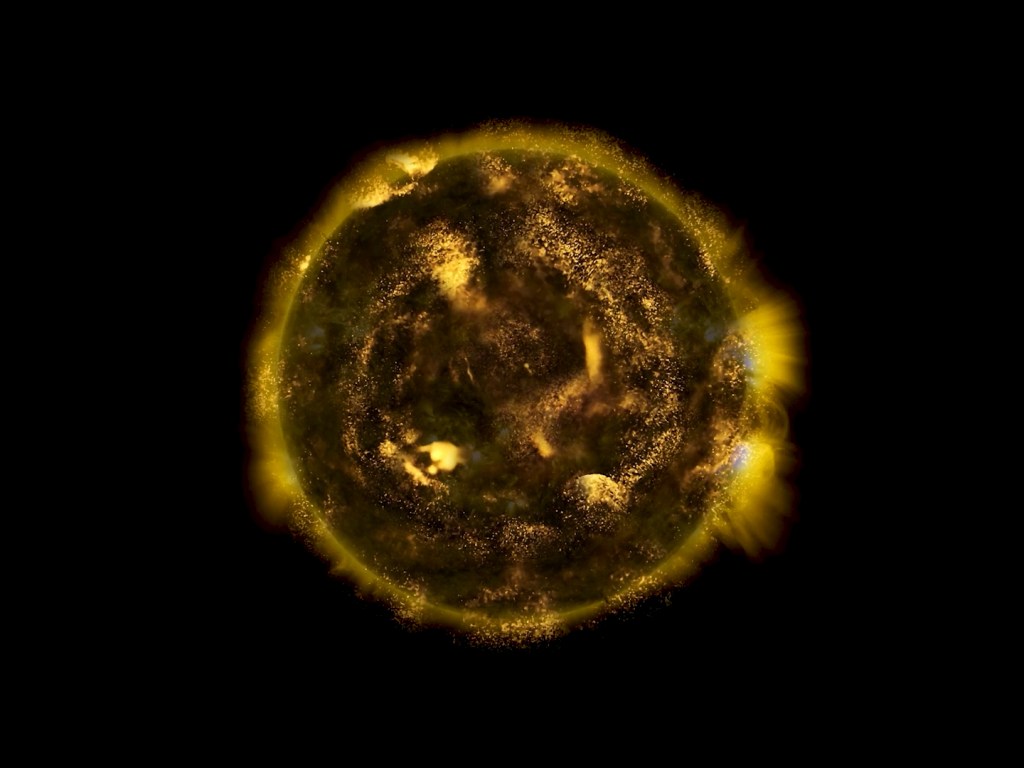
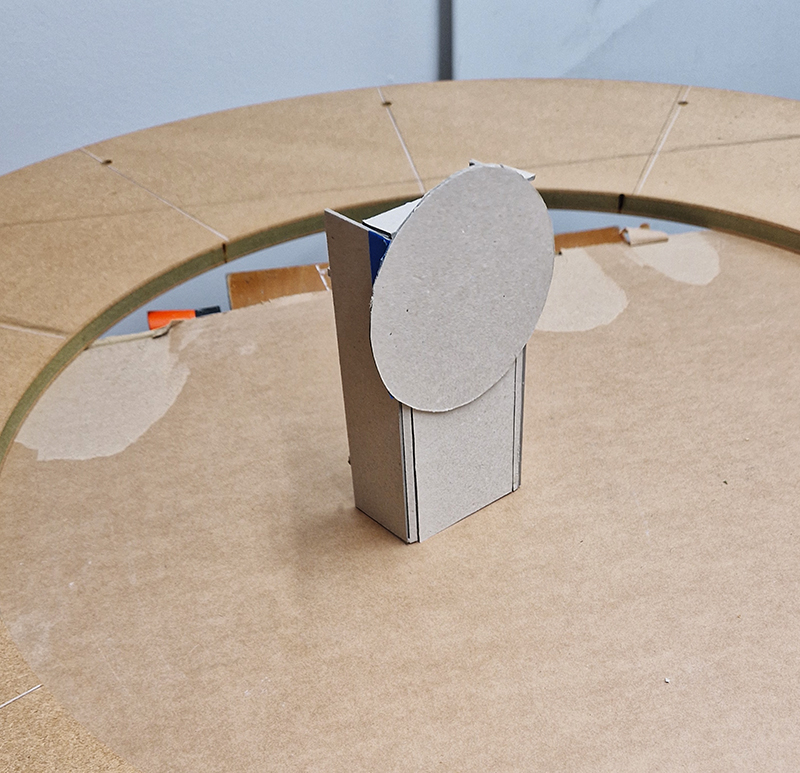
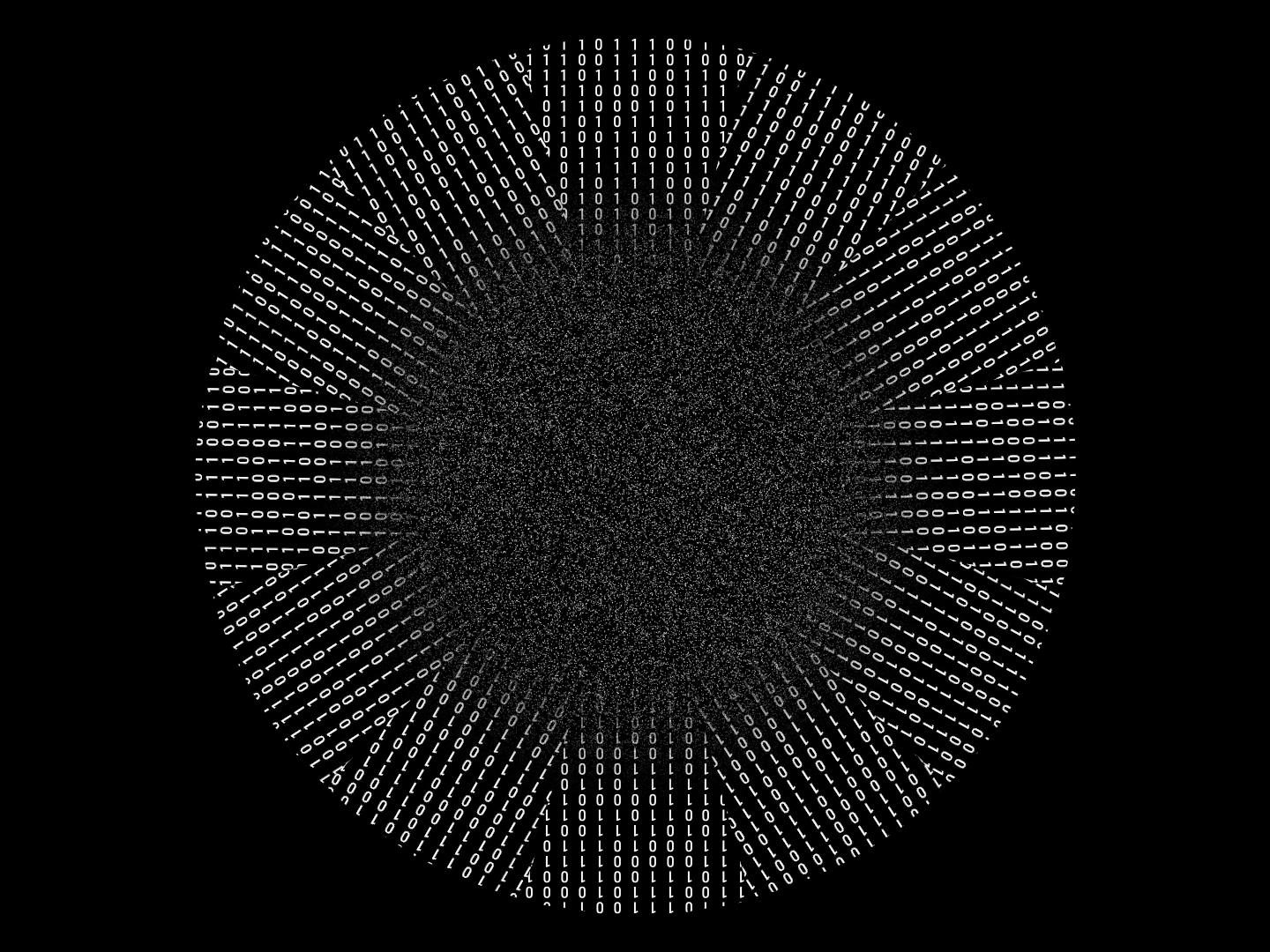
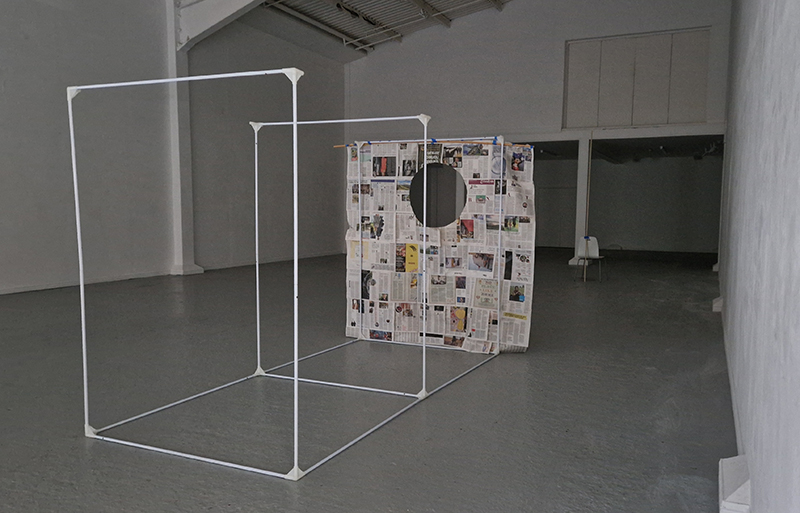
I was showing submīrārī (earthbound) and a new video installation Orbital – these works both consider transient landscapes, ecological landscapes on the cusp of disappearance and the digital landscape at risk from obliteration by an extreme solar storm.
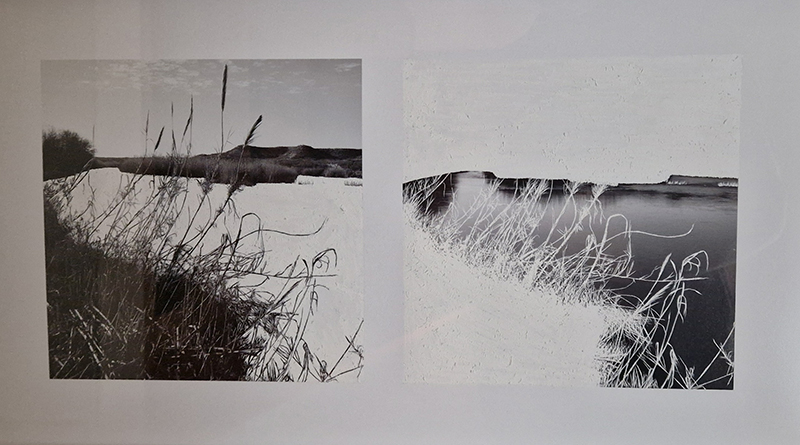
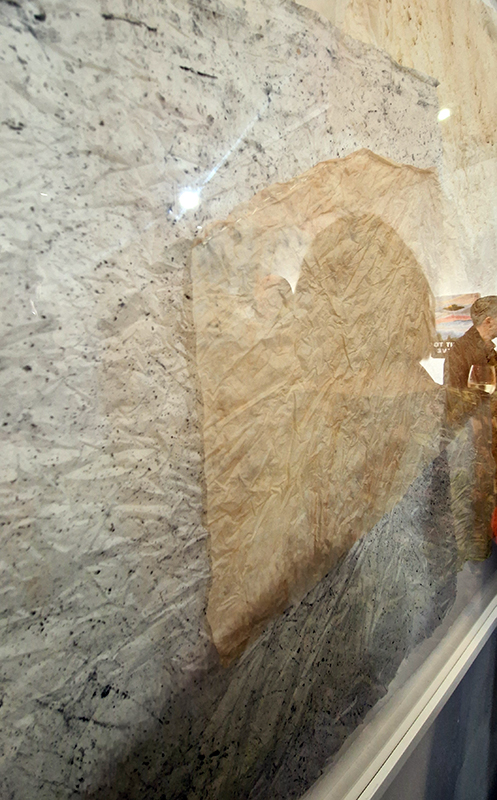
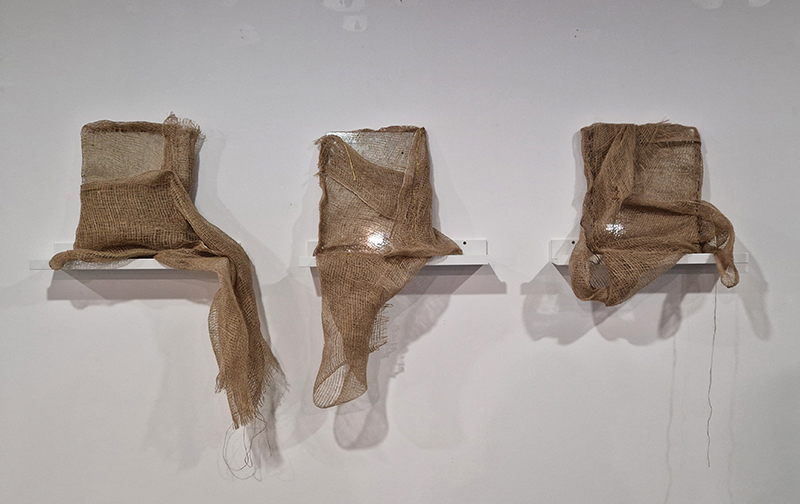
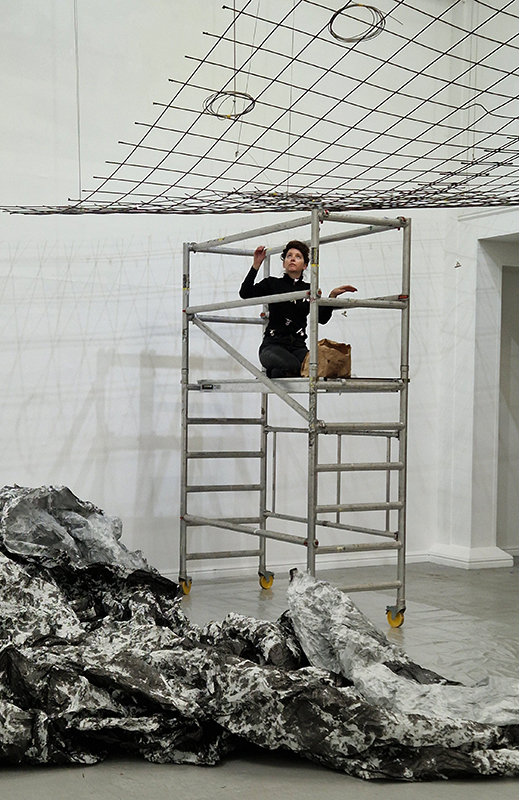
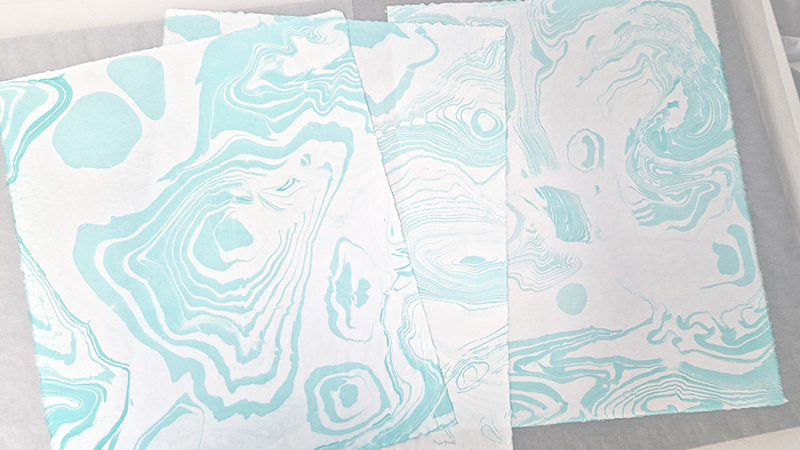
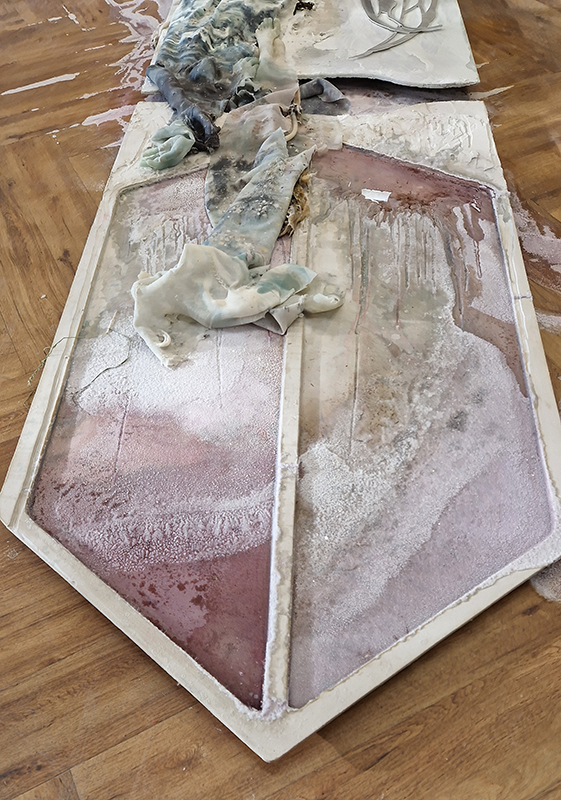
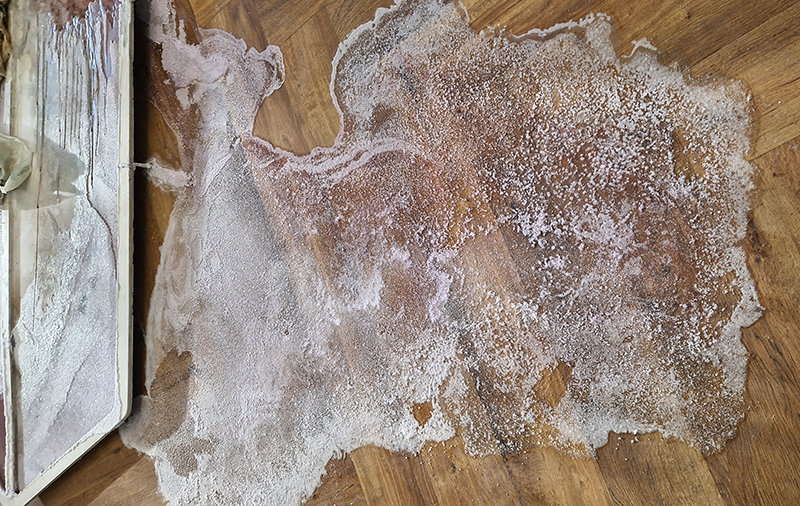
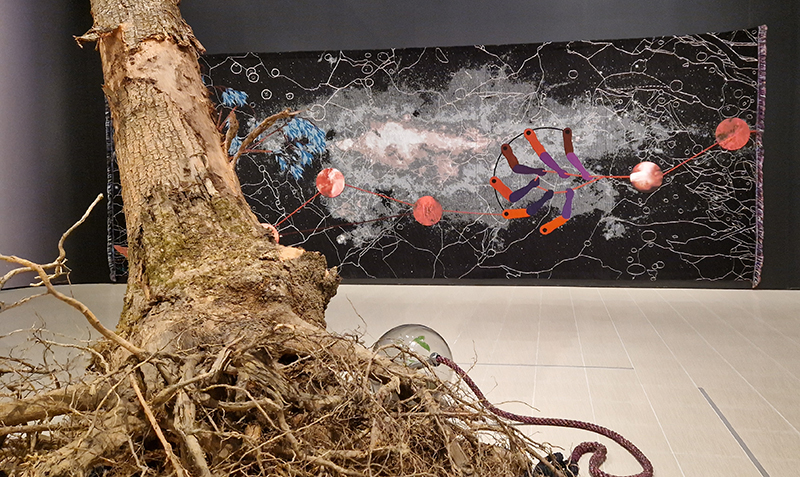
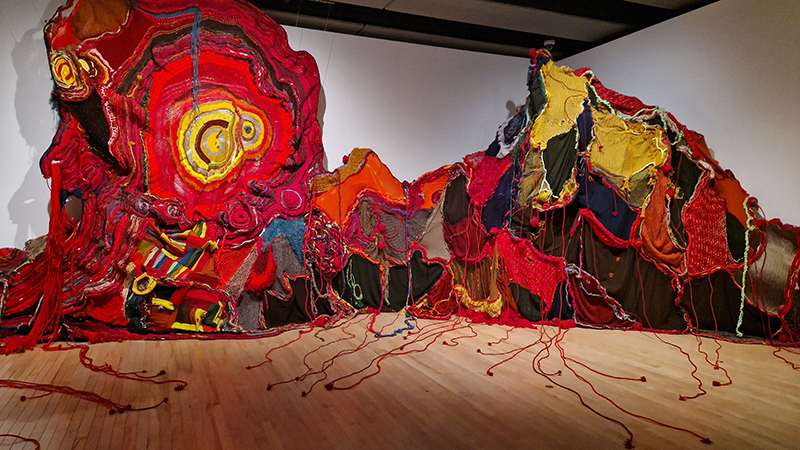
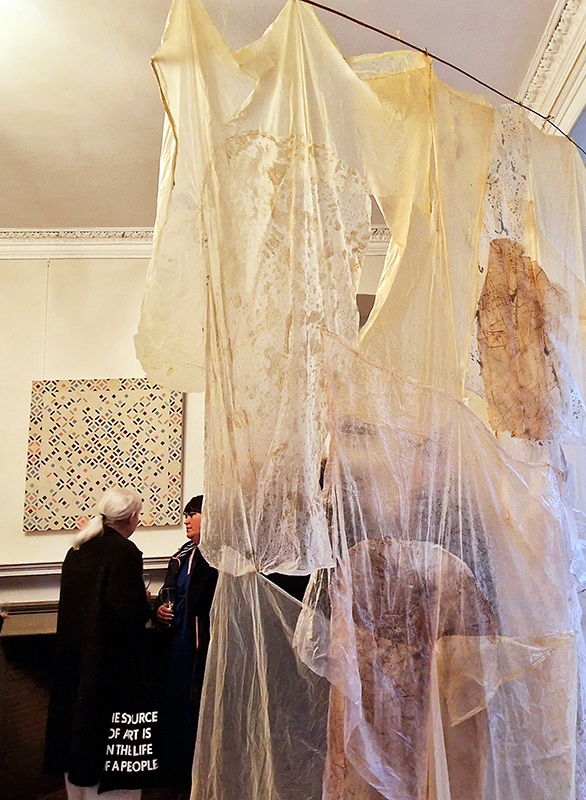
submīrārī (earthbound), 2018, steel, earth, water, sublimation printed textile, 12 pieces dimensions variable approx. 200 x 200 cm. Reflections of a no longer certain world hover in pools fluctuating on the cusp of disappearance. The ethereal images float or submerge revealing the hidden activity of water which also refracts light across the surface prompting the viewer to repeatedly shift perspective. Donna Haraway, drawing from Latour, proposes the ‘Earthbound’ as those humans who are ready to rethink and create new narratives with Gaia at the centre, who recognise the entanglement of society and nature and aim to pursue a ‘nonarrogant collaboration with all those in the muddle’. The shift in perspective embraced by the ‘Earthbound’ embodies a grief shared with other species at loss of habitat and disappearing landscapes. It is not a nostalgia for paradise lost but a reappraisal of what paradise could be.

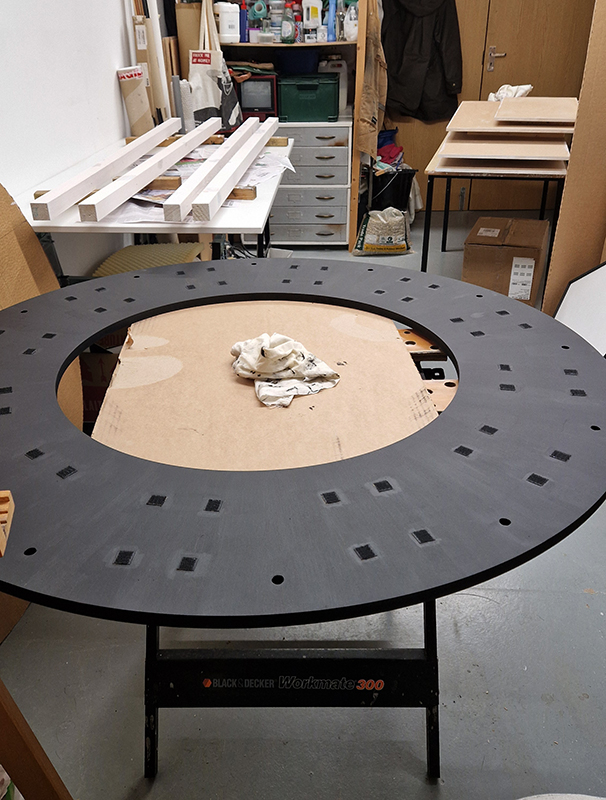
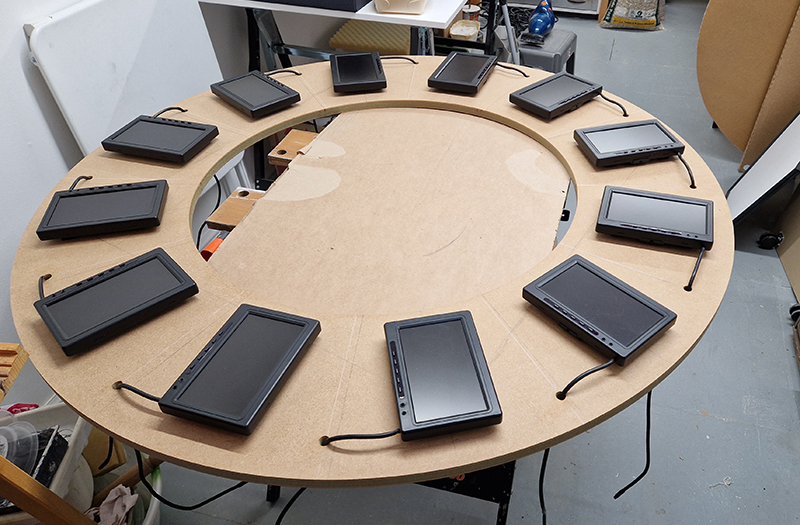
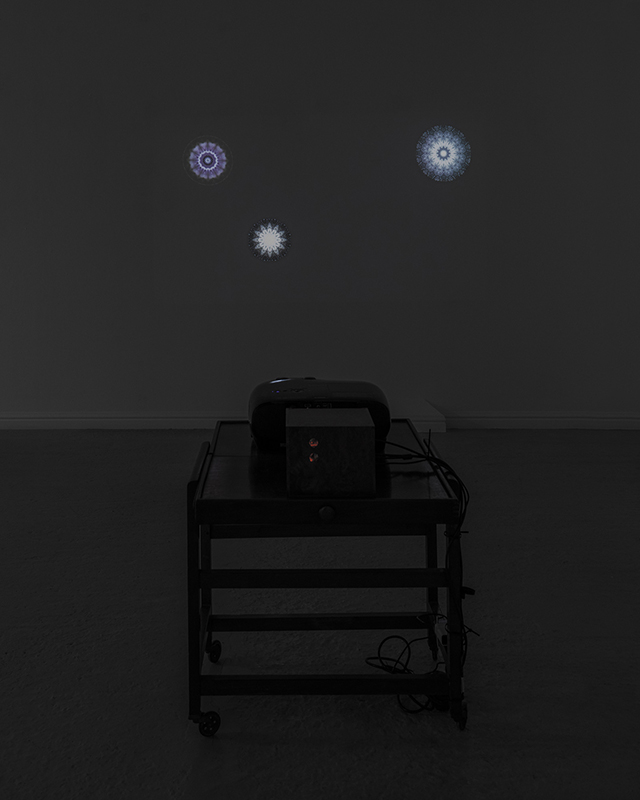
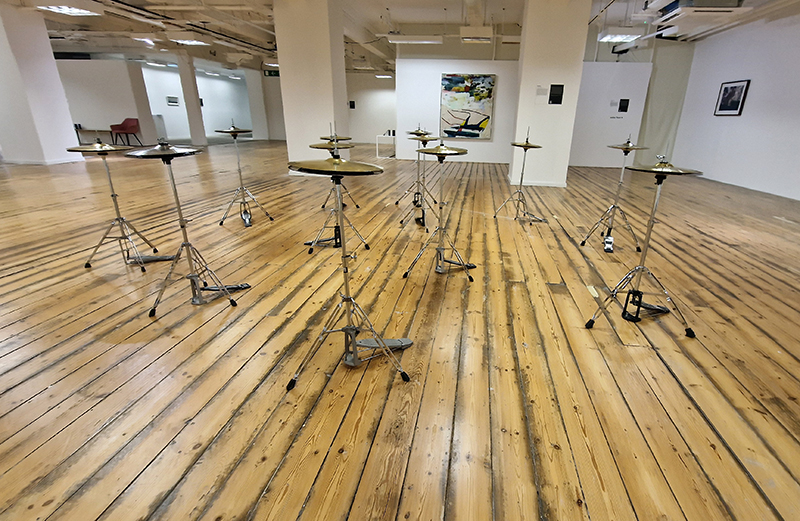
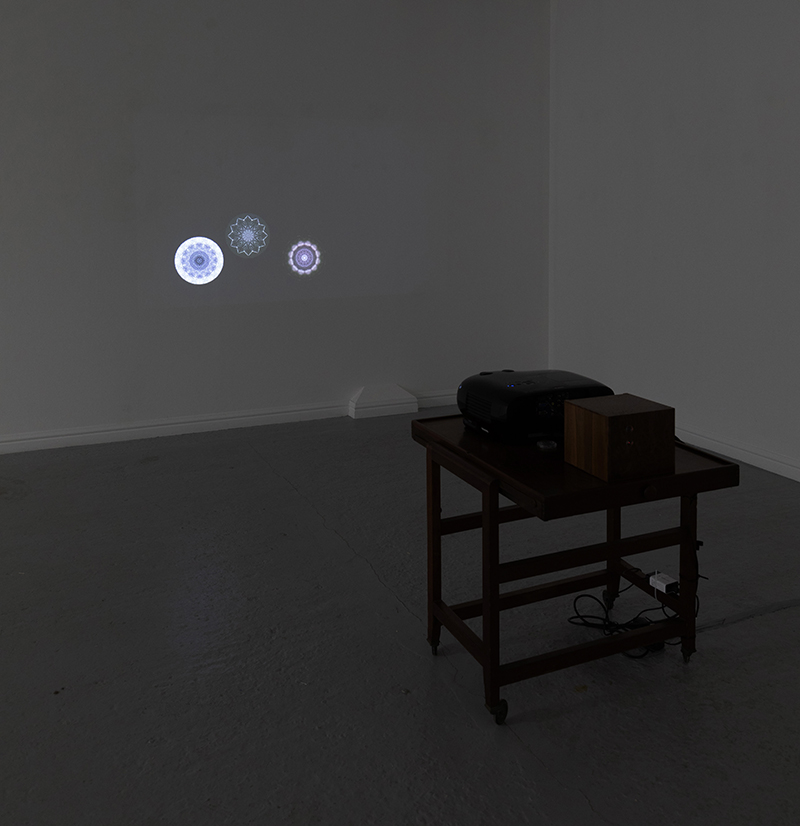
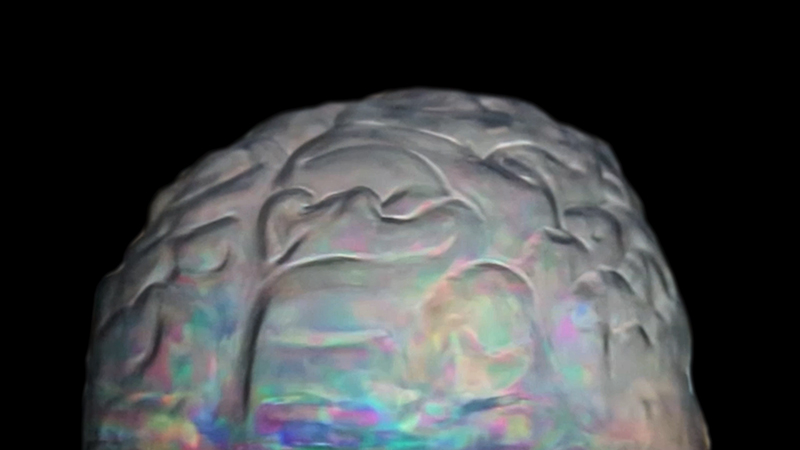
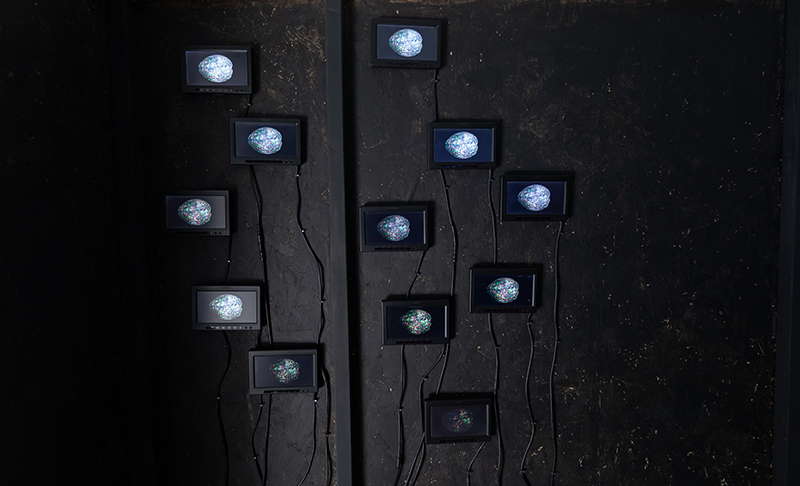
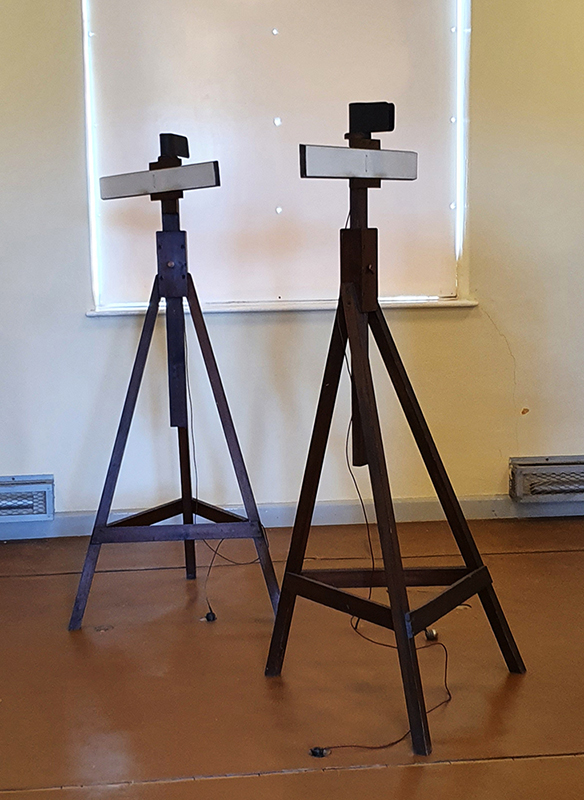
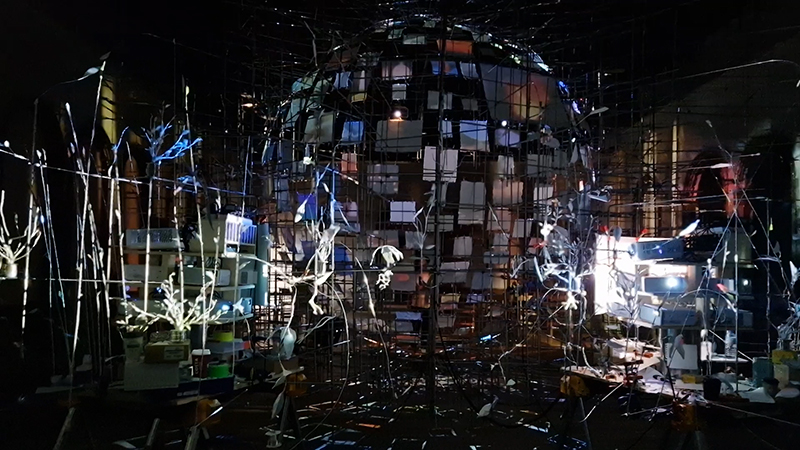
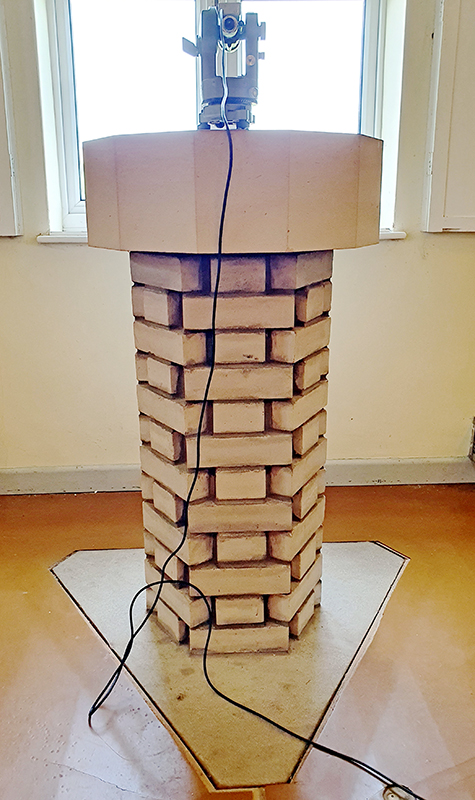
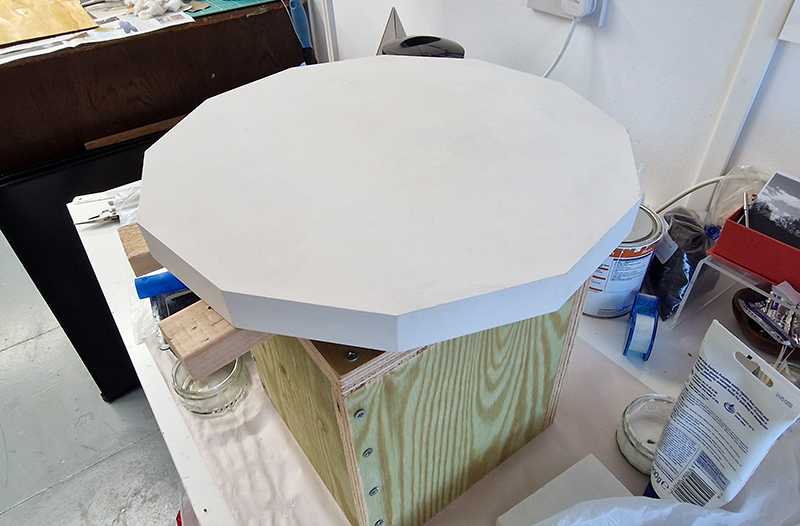
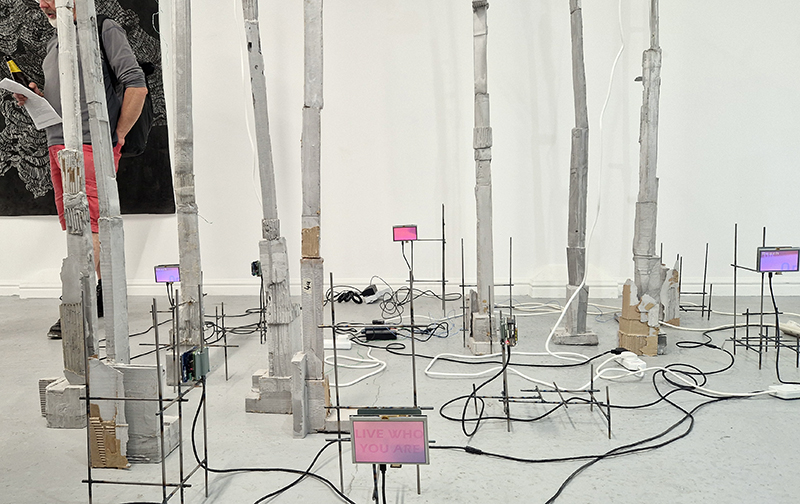
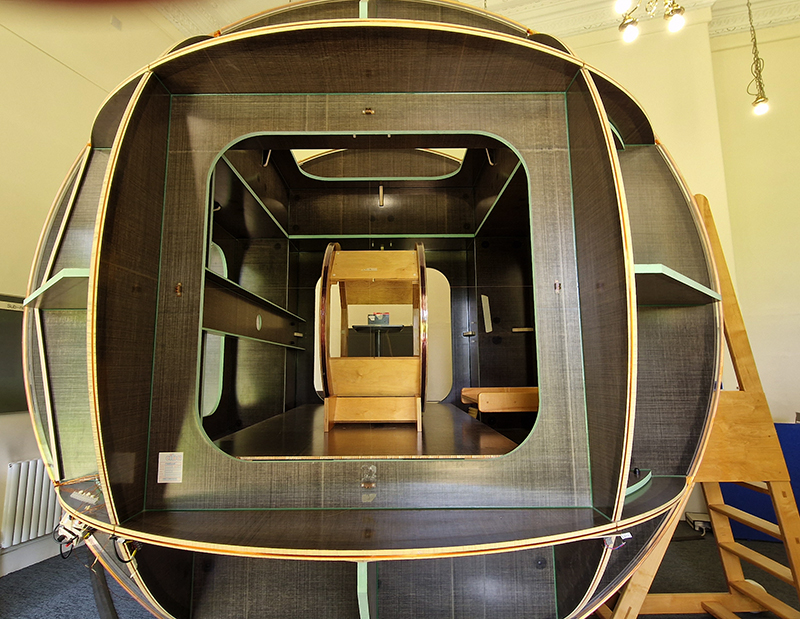
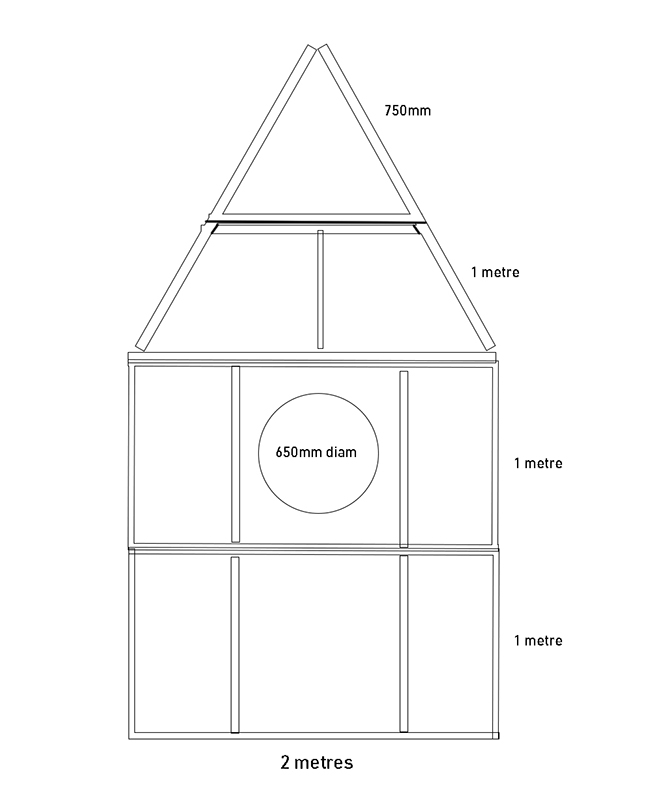
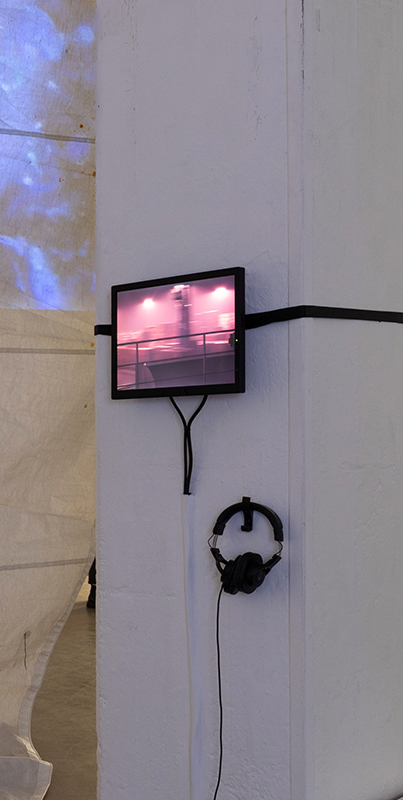
Orbital, 2024, Back projection video, mini screen array, board, installation 122 x 200 x 50 cm, video 05:44 min. An exploration of the potential risks of space weather on human technology and infrastructure and non-human navigation.
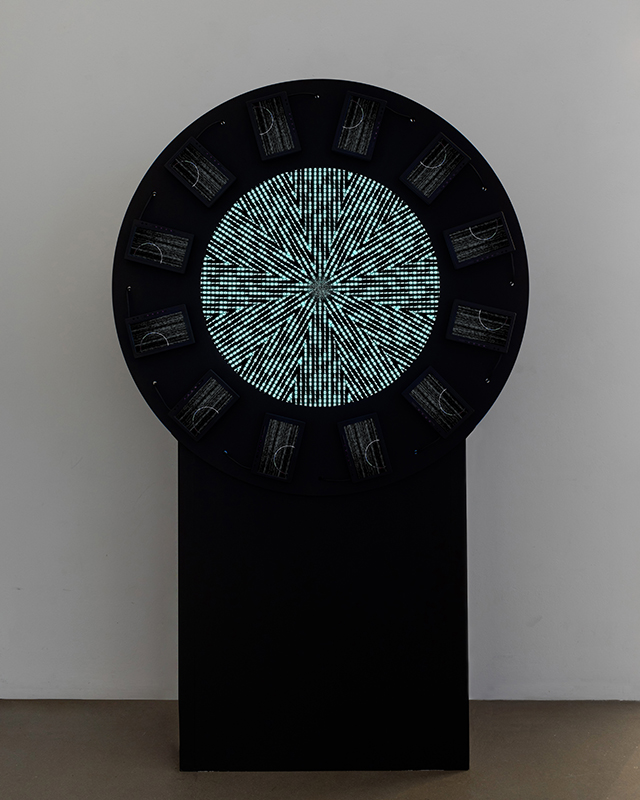

The Sun is about 150 million kilometres (93 million miles) from Earth, but space weather can affect Earth and the rest of the solar system. It can cause damage to satellites and electrical blackouts on Earth. Small satellites have come to dominate low Earth orbit, and we have become reliant on this technology for communication, military strategy, and data gathering.
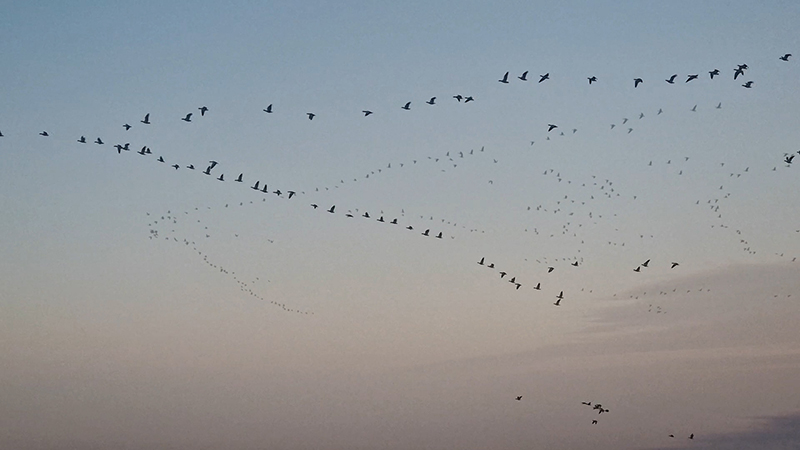
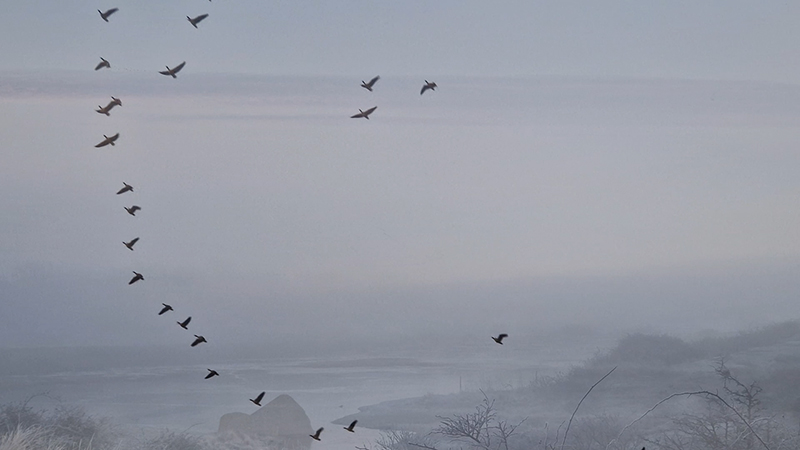
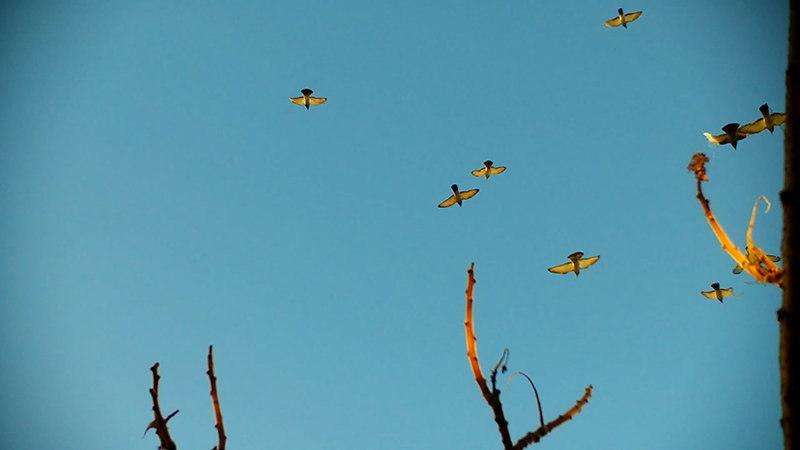
A blast of high energy particles hitting Earth during a solar storm can interfere with Earth’s magnetic field, confusing birds that use this for navigation. In America, pigeon racers postpone the big race if bad space weather is predicted. There is also new research that might suggest the number of satellites orbiting Earth and the growing satellite space junk graveyard could weaken Earth’s protective magnetic field, making us even more vulnerable to space weather and cosmic radiation.

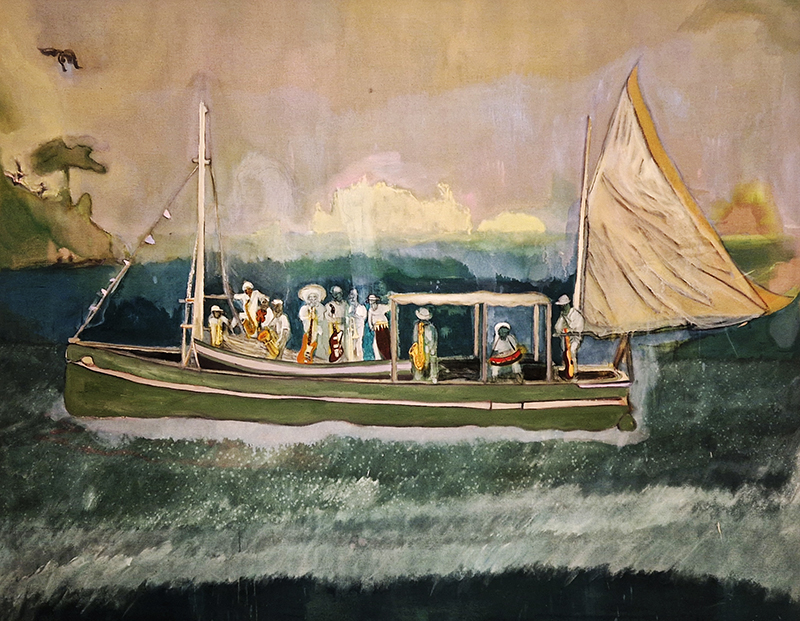
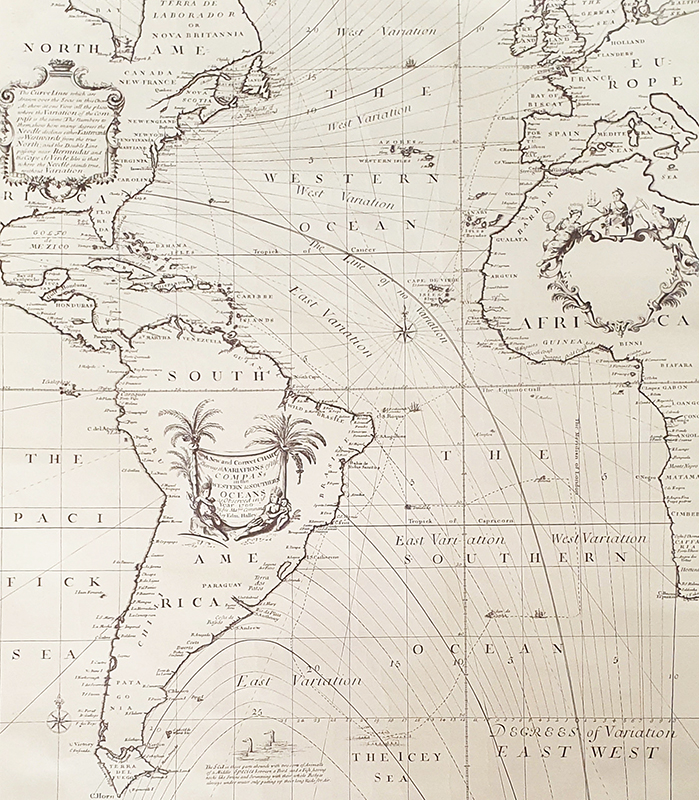
The gallery location in Deptford, once a major departure point for maritime trade and scientific expeditions from Deptford Dockyard, resonates with the exhibition’s concept of being ‘at sea’, in the sense of negotiating the unknown. It was Deptford Dockyard that Edmund Halley set sail from to make the first circumnavigation of the Earth to map the declination of the magnetic field. The ship that he captained, the Paramour, was the first vessel built specifically as a research vessel and launched in April 1694.

Other video and mixed media works in Life Boat draw on material gathered from the Arctic Ocean in the Svalbard Archipelago, The Sea of Hebrides and Long Beach Peninsula in the Pacific Northwest, to reflect on disappearing, threatened and polluted landscapes. Other fieldwork undertaken feeds into work that considers the human experience of dislocation from nature and the need for faith, hope and resilience.
Rachael Allain’s current doctoral project ‘Above and Below the Horizon: A practice-led investigation into liminal thresholds of bodies of water’ has been undertaken in response to various aquatic locations. The work shown in this exhibition documents mapping aspects of an unexpected journey of discovery made in the upper reaches of the Arctic Ocean during an international art and science expeditionary residency in the Svalbard Archipelago during midsummer 2022. ‘Circumnavigation of a ‘Bergy Bit’’ is a film with sound of a close and intimate encounter with a section of an iceberg, calved from its mass and found beached and melting close to shore in Eolusneset, Sorgfjorden in the Bay of Grief.

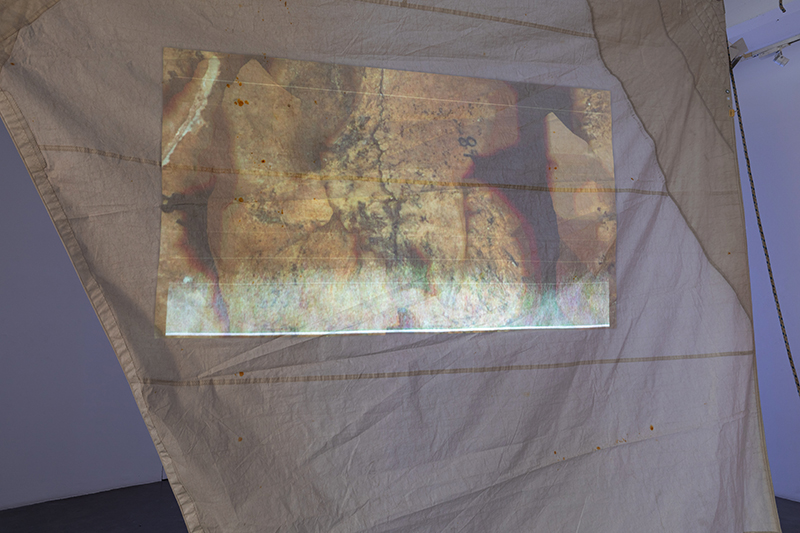
In 2019 Caroline AreskogJones spent time on the Sea of Hebrides making a series of responses whilst researching more viscerally the ocean as a site of ‘field research’ and gathering recordings. ‘Sounding Line’ (2024, sail, audio/video single channel as projection 07:32 min. Sail courtesy of Sail Britain) was created in deliberate wave format being inspired by Jean Painleve, whose hybrid films overlaid with jazz soundtracks occupy the uncertain space between art and science. Oskar Jones was invited to create the sonic composition in response – the saxophone being a wind instrument of extraordinary virtuosity. Since 2023 Caroline has been visiting the Natural History Museum Cetacean Archive – at the invitation of Principal Curator, Richard Sabin. Through conversations including those with environmental historian Sophia Nicolov, her research has broadened and this updated presentation includes recordings of the two remaining Orcas who inhabit the Sea of Hebrides courtesy of the Hebridean Whale and Dolphin Trust.


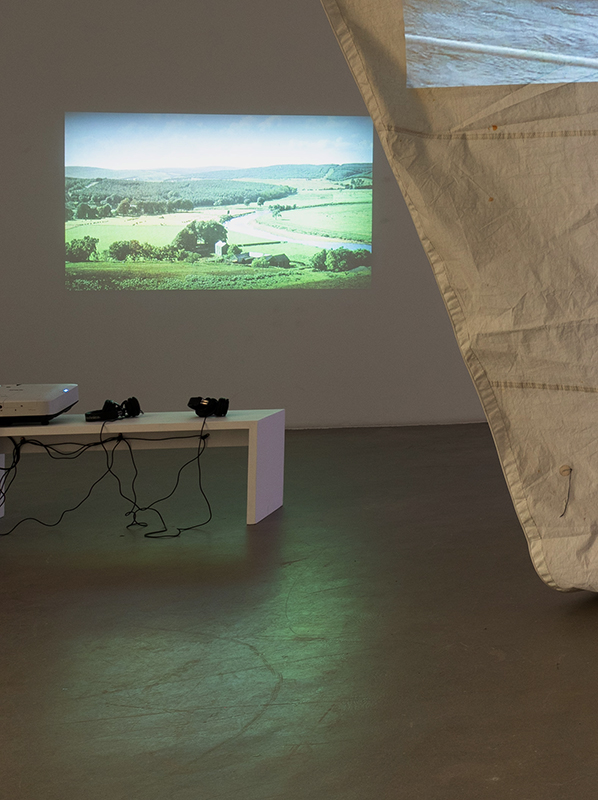
Anne Krinsky Boiling Seas Acid Seas (Work-in-progress), 2024, Video, 12:26 min, filmed on location at Long Beach Peninsula in the Pacific Northwest.

A History Of The Receding Horizon (2015, HD Video, 16:9, sound, projection, 28 min) is a digital film installation by Kathleen Herbert, exploring different concepts of time within the landscape. Based upon Kielder in Northumberland, the narrator whose script was developed from the artists research interviews with environmental historians, astronomers at Kielder Observatory and local people from the area, leads the viewer through the film weaving together past, present and future timelines. The Chaplin (2006, standard HD video, 4:3, sound, monitor, 07: 20 min) is a film installation recalling a conversation held between the artist, Kathleen Herbert, and the Port Chaplin based at the Mission to Seafarers centre in Avonmouth docks. The Port Chaplin boards every ship as it enters the docks, his role is to provide emotional and practical support to seafarers while they are in port. The piece was produced while Kathleen was based at the centre researching for a new commission by Picture This Moving Image and Situations Bristol. Her research at the centre culminated in a 3 day voyage aboard a cargo ship in which she took her camera and the extracts of film from this journey provide the visual background of the film.


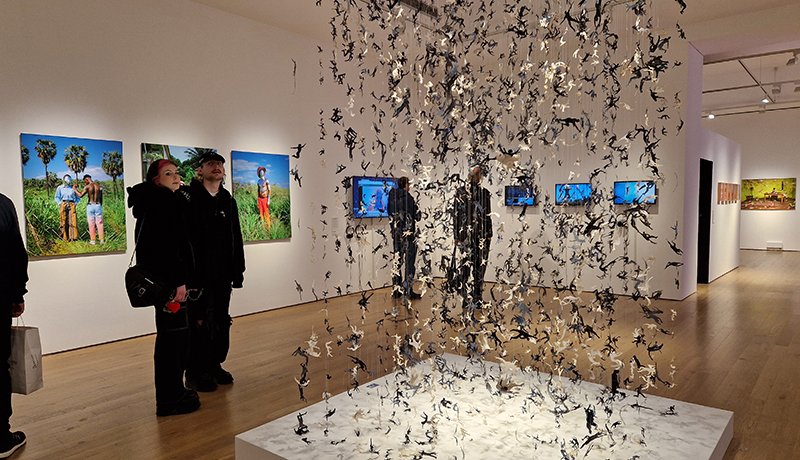
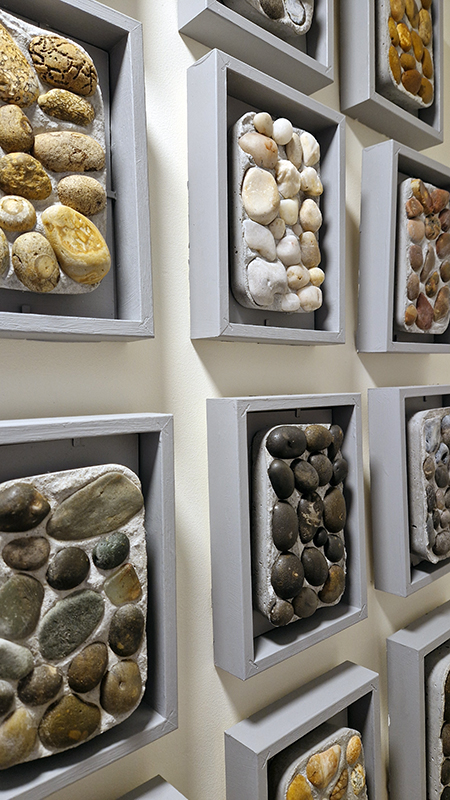
Fragility and vulnerability are embodied in layered works on paper, a large suspended sculpture made from delicate compostable material and living installations incorporating transient elements that transform over the exhibition period.
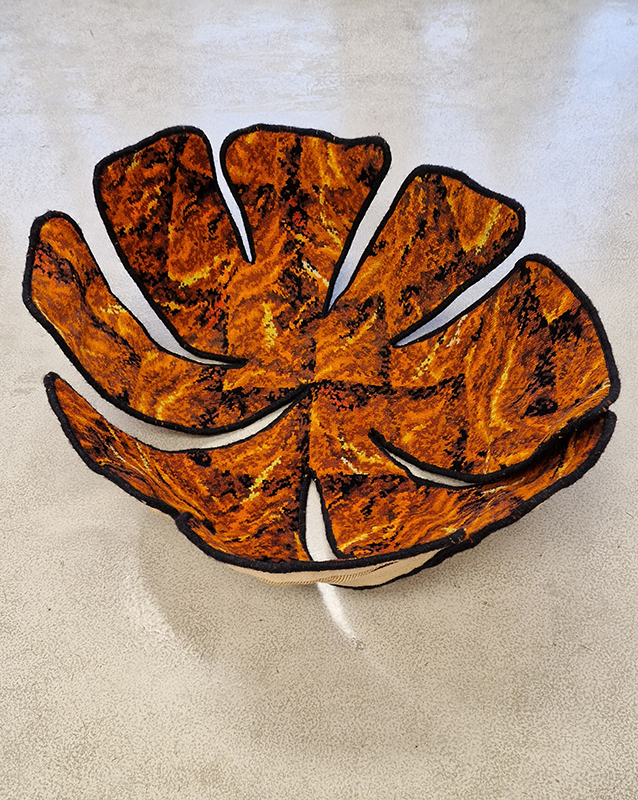
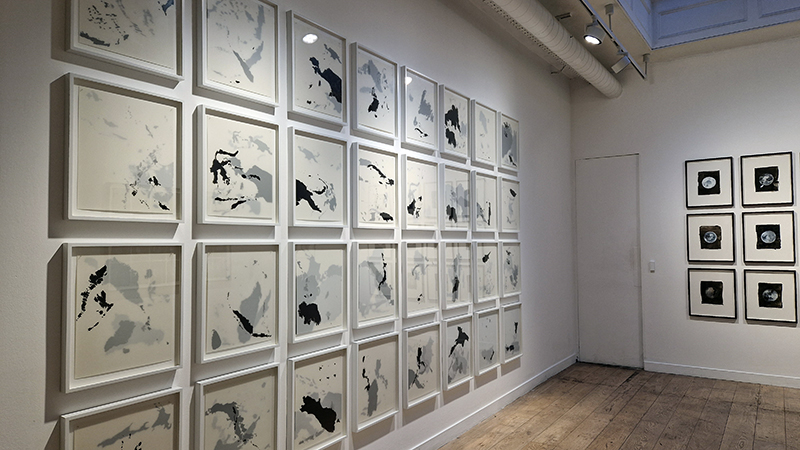
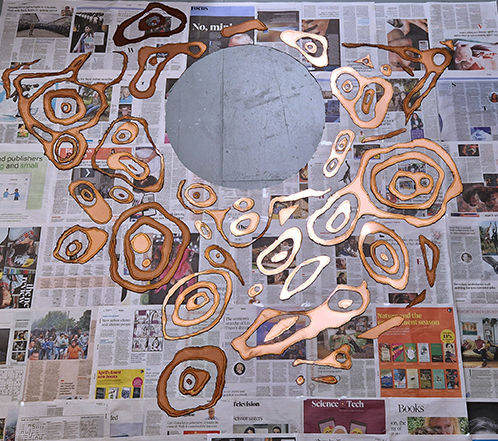
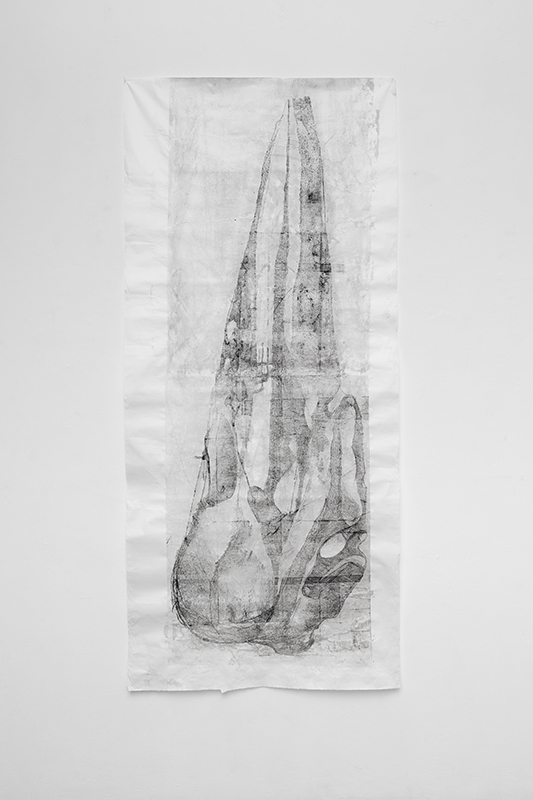
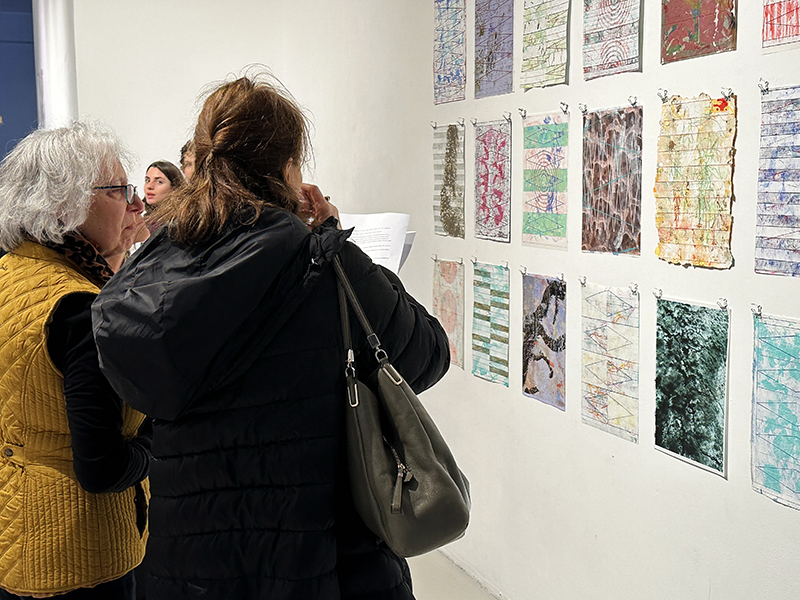
Anne Krinsky has been working on a research-based project about vulnerable wetlands and climate change since 2018. Coastal wetlands worldwide are at risk from rising sea levels caused by climate change, while inland watersheds are threatened by heat, drought and agricultural runoff. These ecosystems are critical to the plants and animals that inhabit them and to human survival. She is drawn to biodiverse habitat edges – where water meets land or where fresh water meets the sea and is interested in recording both the beauty of – and human impacts on – fragile habitats. She uses documentation as an archive of raw materials to generate work in other media, including site-responsive print and video installation and tactile work on paper. In responding creatively to wetlands and watersheds, she wants to raise public awareness of climate threats to these life-sustaining habitats. Before They Vanish, 2024, 24 small works: paper, mylar, acrylic, digital print, mixed media, 150 x 300 cm.

Caroline AreskogJones Float 2023, Paper lithography on shoji, 60 x 120 cm forms part of a series of works inspired by the Natural History Museum Cetacean Archive, rendered onto Shoji paper, used in museum conservation.
Liz Elton begins in landscape and still-life painting to explore the potential of waste and the recycling of matter. Her ephemeral work is often made on compostable ground, coloured with kitchen waste and embedded with seeds. Showing Habitat, 2024, Compostable cornstarch food waste recycling bags, household textiles from a house clearance, vegetable dyes from kitchen waste, water colour, silk, soil from various locations and gleaned from vegetables bought in the market, vegetable seeds saved from food preparation, seeds of varieties of self-seeding edible plants typically found on the wasteland around Deptford creek, found wood, Approx. 360 x 250 x 150 cm (variable).


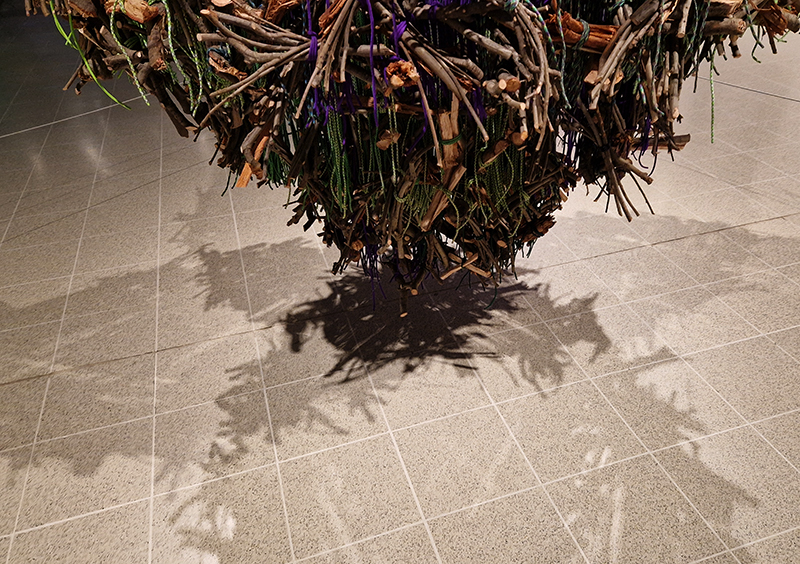
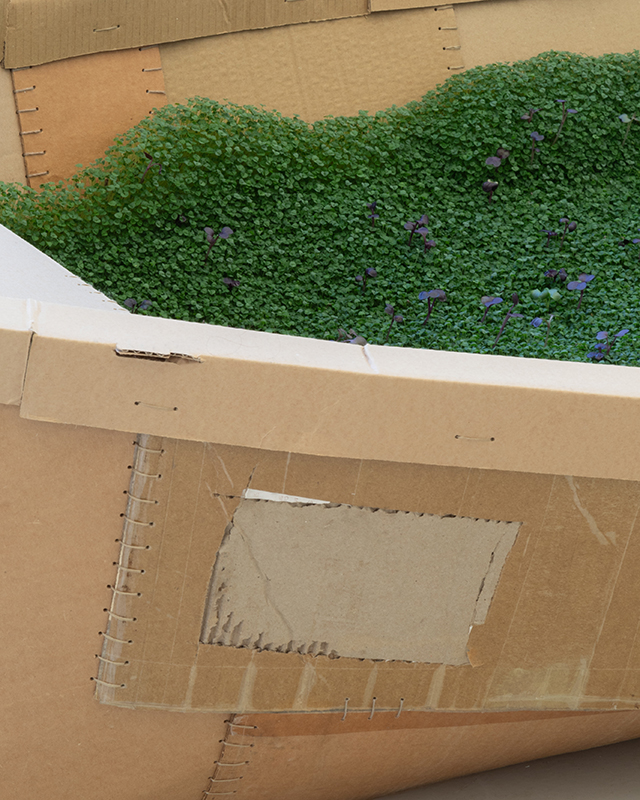
Working with living sculpture and installation, Beverley Duckworth creates spaces and moments which connect the smallest, poetic actions of plants with precarious issues facing humanity. Her practice centres on the afterlife of the discarded and is rooted in small acts of reparation – sewing scraps together, watering fragile seedlings and nurturing the regenerative power of composting from waste materials. Works include Husk, 2024, Discarded cardboard, thread, flax, seeds, water, 90 x 70 x 280 cm; Raze, 2023, Discarded clothes, binder, 48 x 51 x 10 cm.



Etchings and spatial interventions explore the use of the natural world as human resource and land as a site of geopolitical conflict.
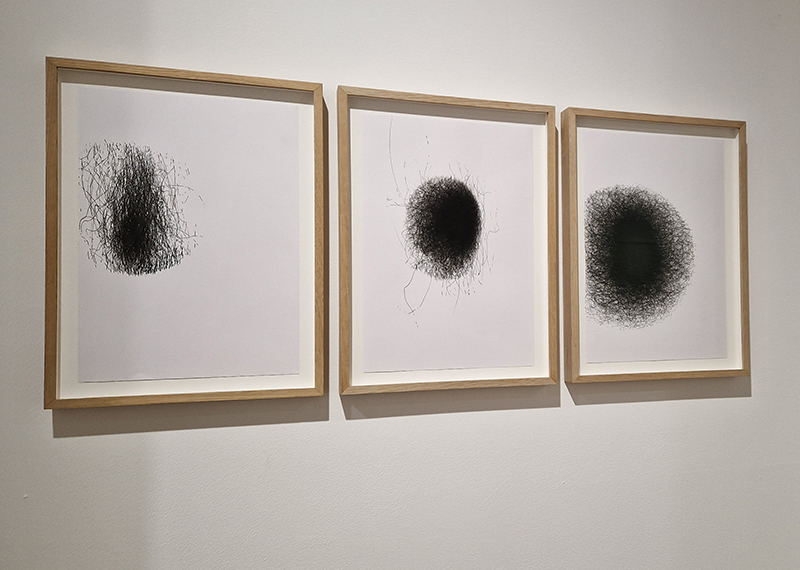
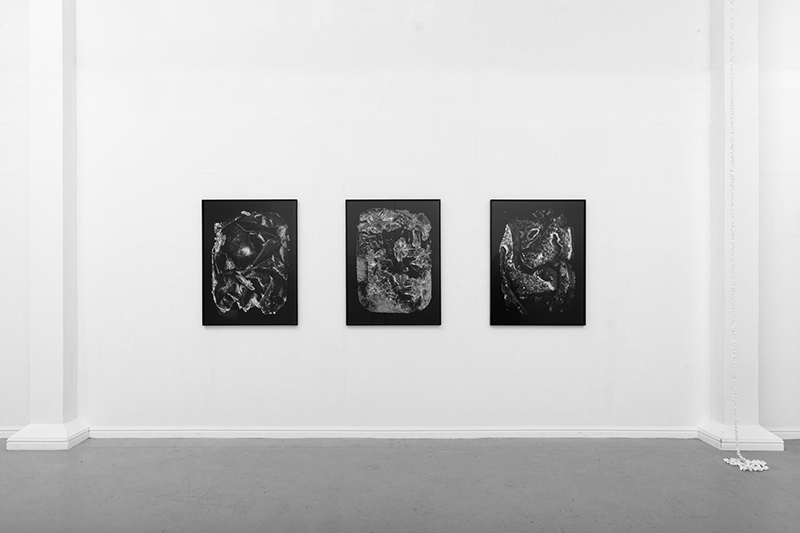
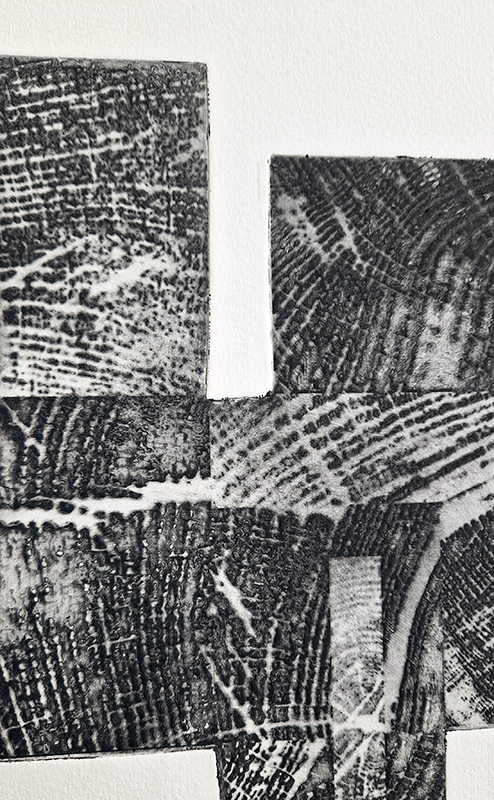
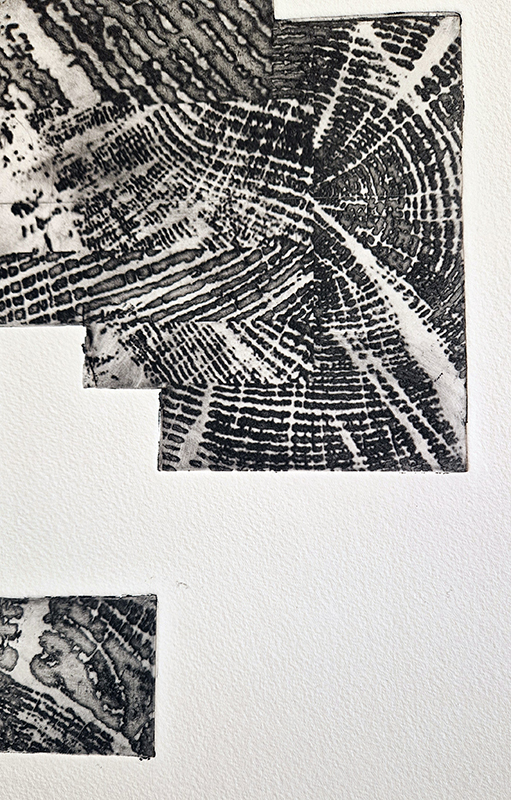
Kathleen Herbert Lost Dimensions I, II, III, 2022-23, Photopolymer Etching on Somerset Satin Paper, 75 x 57 cm.



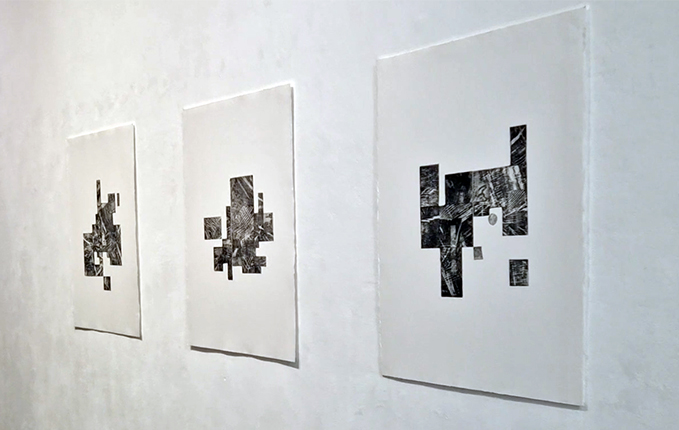
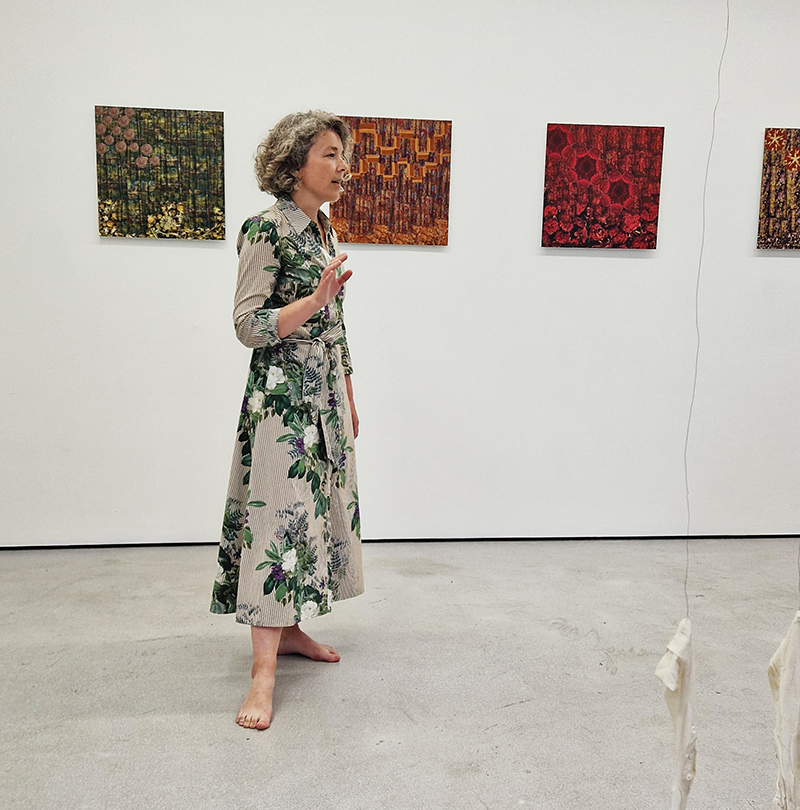
Kaori Homma’s multi-site Homma Meridian project asks us to reconsider and to challenge the cartographic demarcations that govern so much of our world and that we so frequently take for granted. With the deceptively simple move of ‘repositioning’ the Greenwich Prime Meridian, the artist radically shifts our perspective, as well as our sure footing, both figuratively and even literally. At each of its iterations (which have included Budapest, Margate, Wales, Paris, London and Pennsylvania) the artist and participating audiences draw an impermanent line running north-south, always using ephemeral materials, as a substitute for the ‘Prime’ meridian. The project’s act of displacement and its ephemerality work to highlight the imaginary nature of boundaries and to shake up our perception of our position on the earth as it spins on its titled axis. Works include Homma Meridian, Deptford, 2024, Vinyl Letters, tape, dimensions variable; Floating 0 degree Longitude, 2024, Abrudashi Fire Etching, Water, Bucket, 60 x 38 x 25 cm; Four corners of the earth, 2024, Aburidashi Fire Etching on Paper, 50 x 80 x 3 cm



Alongside the exhibition we held a series of events including a Low Tide Walk in Deptford Creek – led by Anne Krinsky in partnership with Creekside Discovery Centre followed by refreshments and a tour of the Life Boat exhibition at APT Gallery just two minutes from this amazing natural habitat in Deptford.







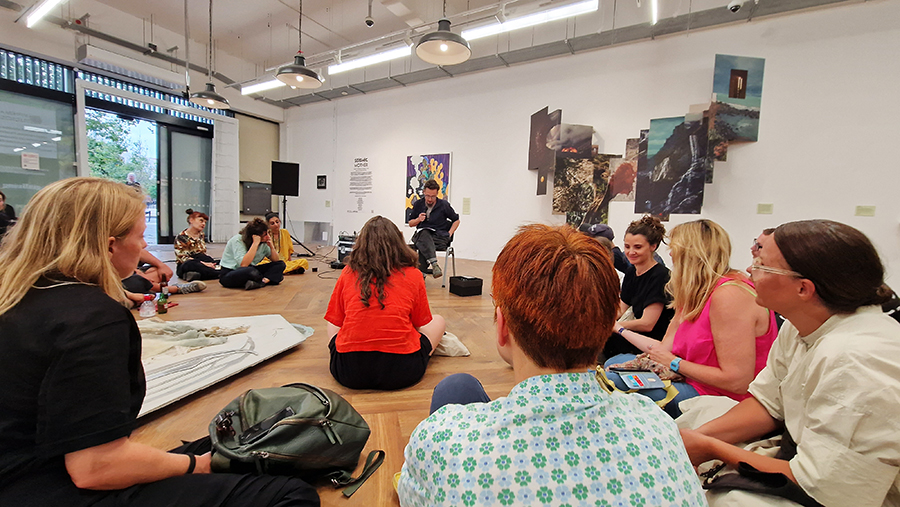
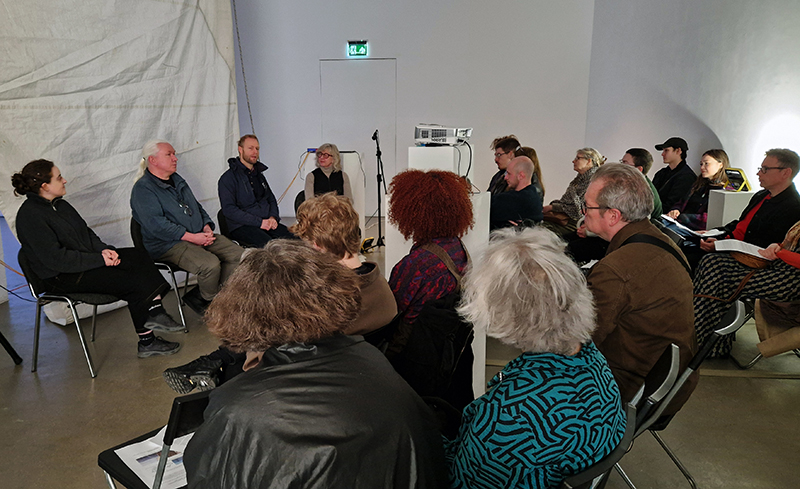
FIELDWORK AS PRACTICE – A live sonic performance by Oskar Jones and a conversation led by Caroline AreskogJones bringing together Oliver Beardon (Founder and Skipper of ‘Sail Britain’) Richard Sabin (Principal Curator of Mammals at the Natural History Museum, London) and Sophie Nicolov (AHRC Early Career Research Fellow, Natural History Museum, London) for a discussion around the potential overlaps between ‘field’ and research, artistic practice and ecological activism.


Homma Meridian and the Secret of Invisible Ink/Fire Etching Workshop where Kaori Homma shared her technique using Invisible Ink as part of the Aburidashi/Fire Etching process, historically used for espionage, she also gave a fascinating presentation on the history of this process and how it relates to her own art practice and her Homma Meridian Project.



In tackling concepts of the perilous, the vulnerable and the lost, Life Boat raises the alarm on the passive position of waiting for rescue and encourages urgent action in troubled waters.
Gallery Visits
Women In Revolt at Tate Britain. A lot of documentation here of social history. Many texts, posters, zines, not so much art but a great piece from the inimitable Susan Hiller, with personal incites accompanying images of her ever increasing pregnant belly such as: – She writes, one is born into time. And in time introduced to language….Or rather — one is born. And through language, introduced to time…Perhaps even — one is born, in time, through language.



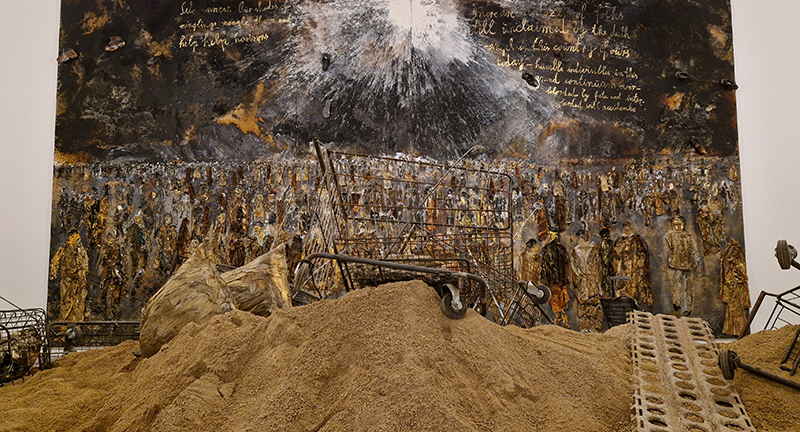
Mary Yacoob, captivates with astonishing precision of detail as always in Brutal Space at Bobinska Brownlee exploring the subject of future adaptations to life in space.




Listening
A webinar from British Geological Survey on how we measure the magnetic field, everyday applications and mitigating the threats of space weather. From the Earth’s core to outer space: understanding the magnetic field