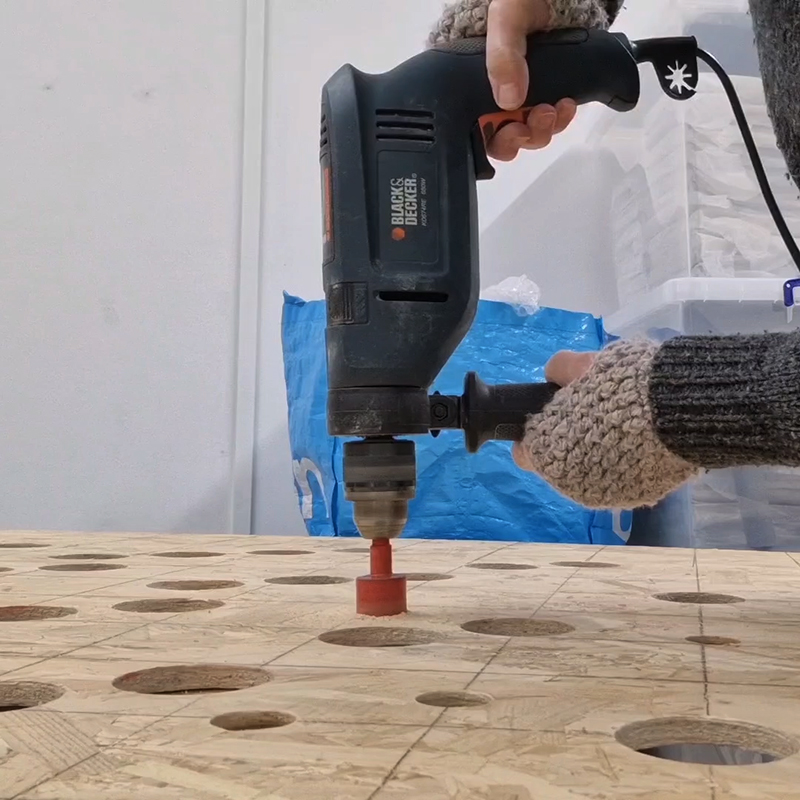
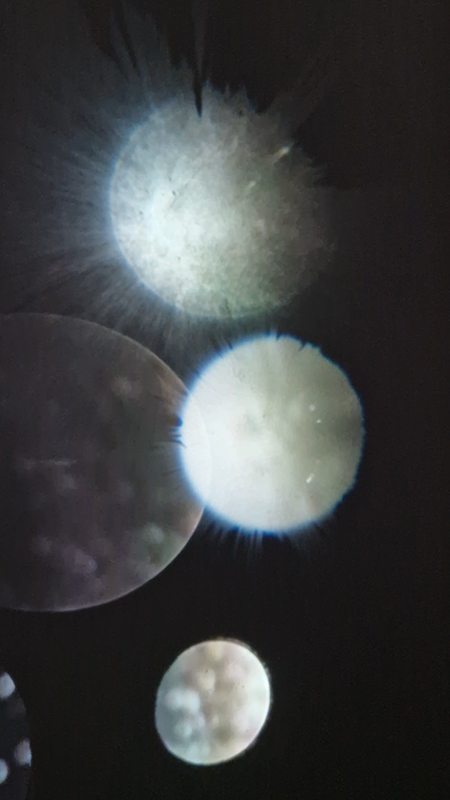
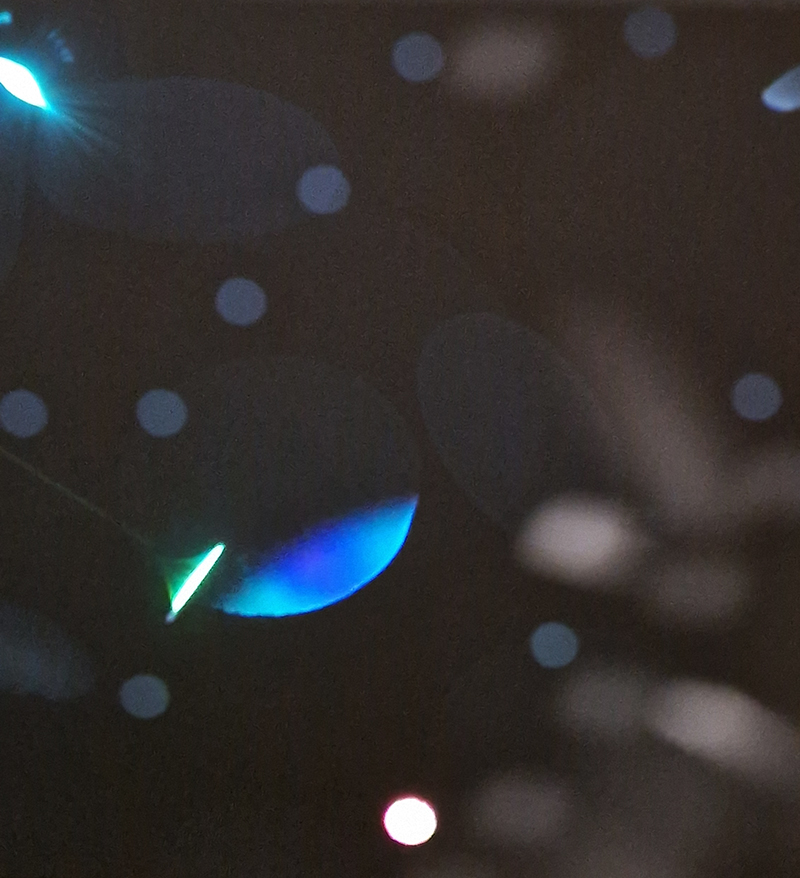
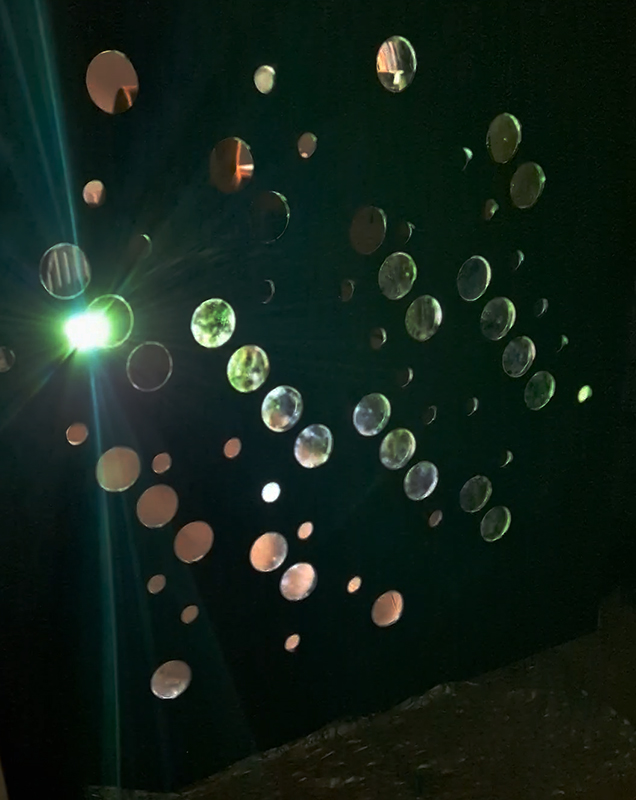
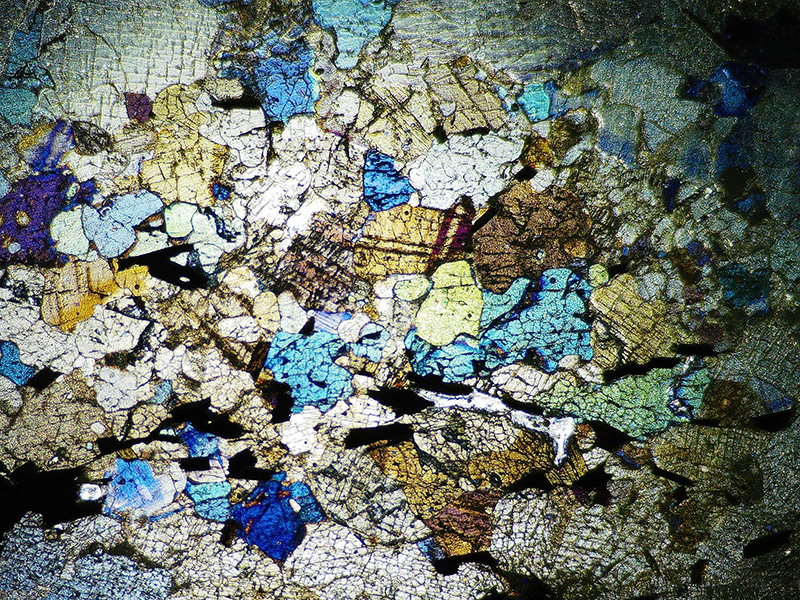
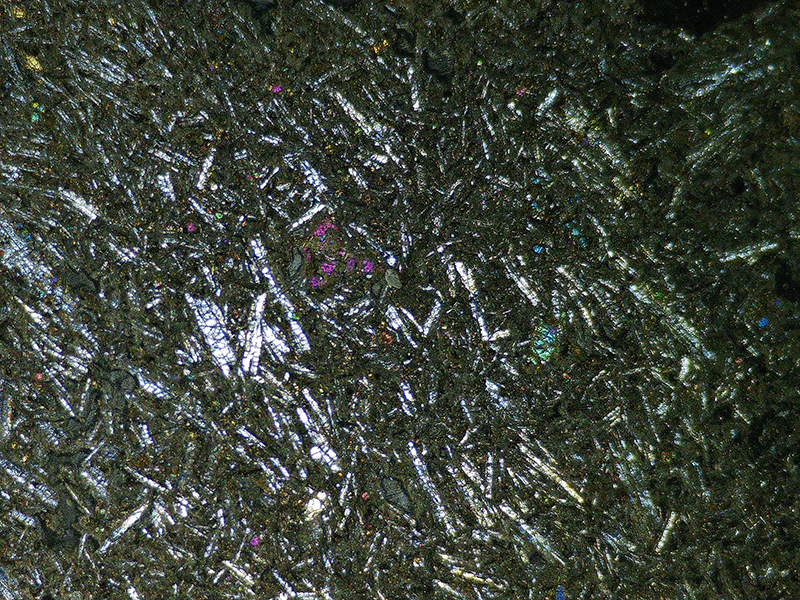
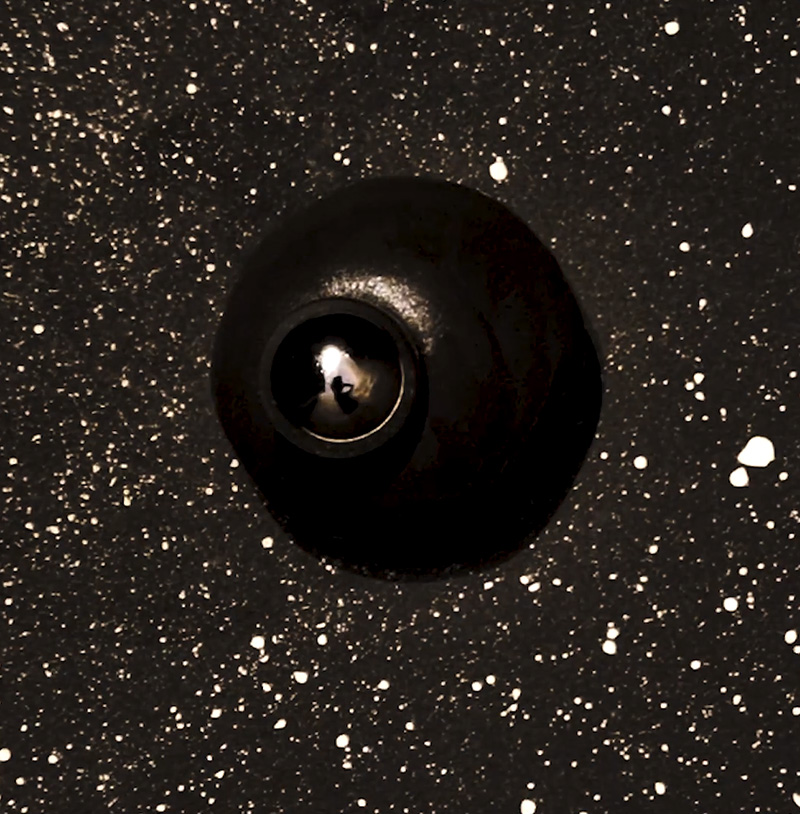
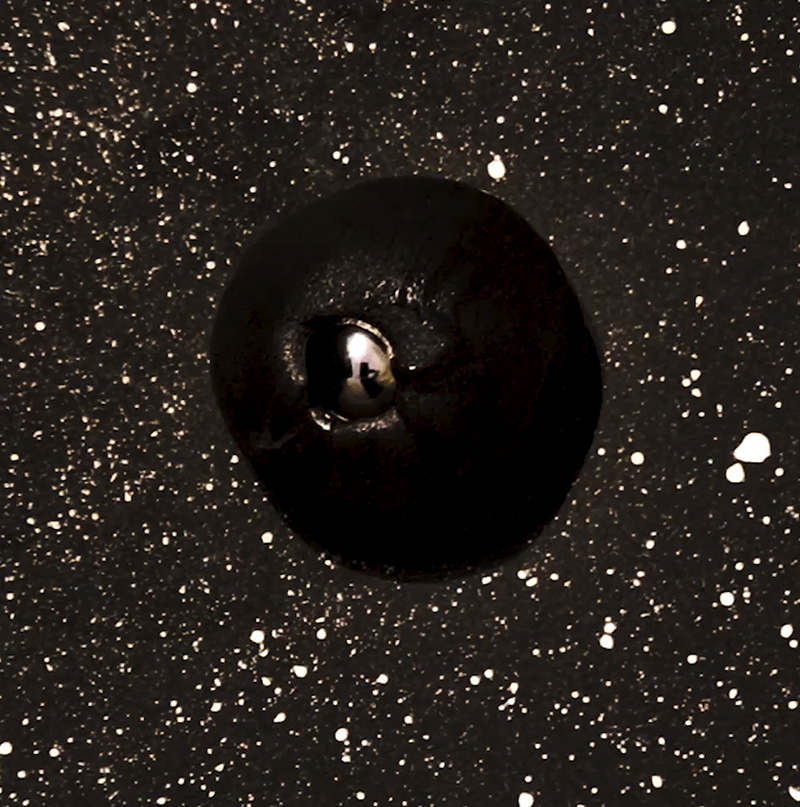
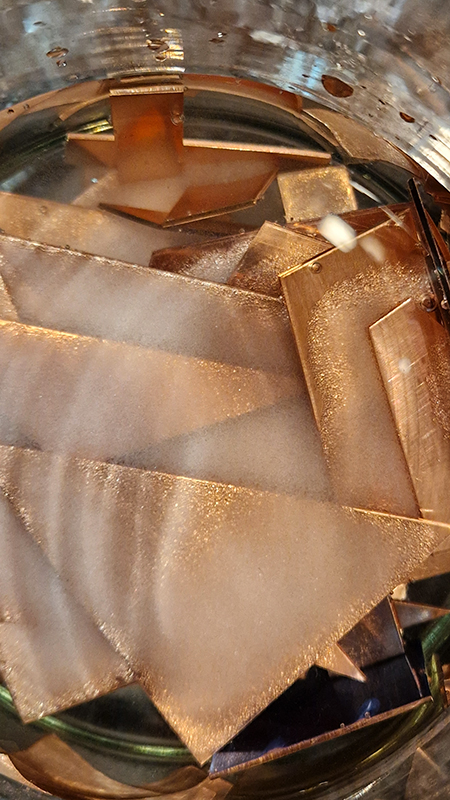
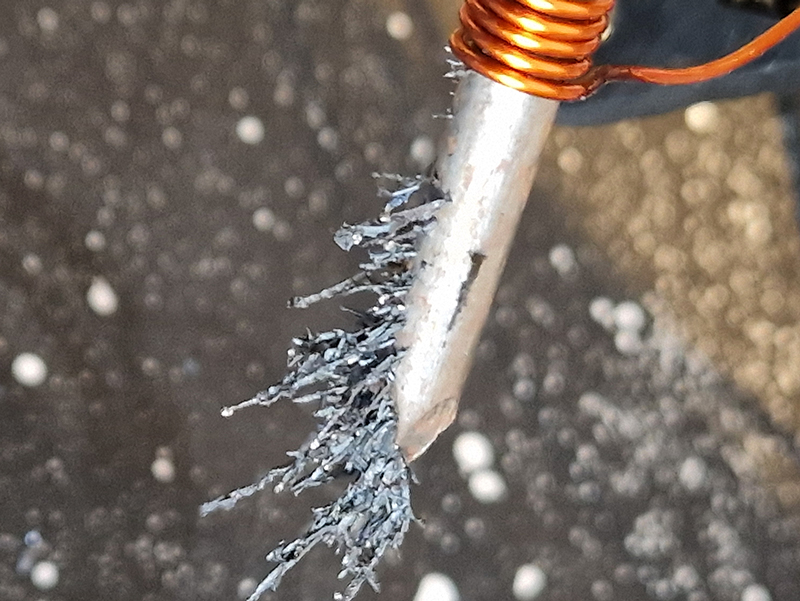
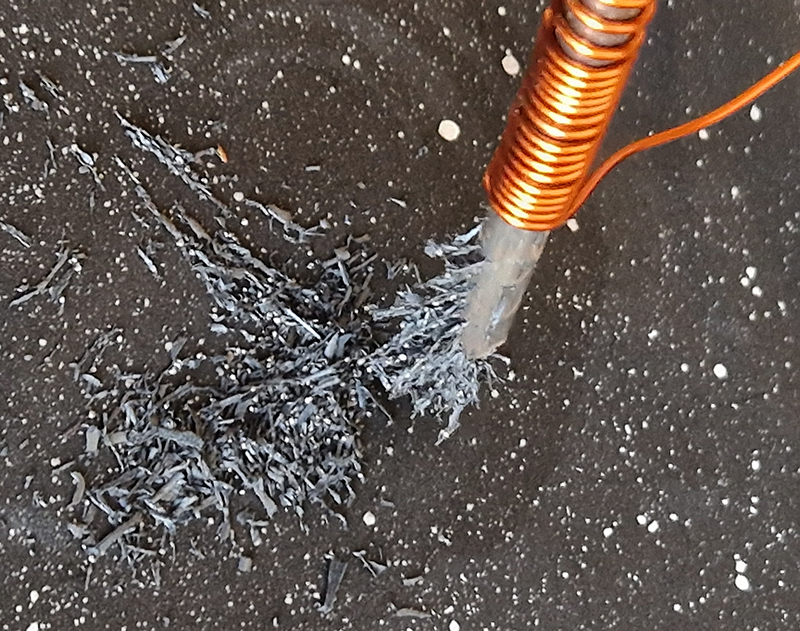
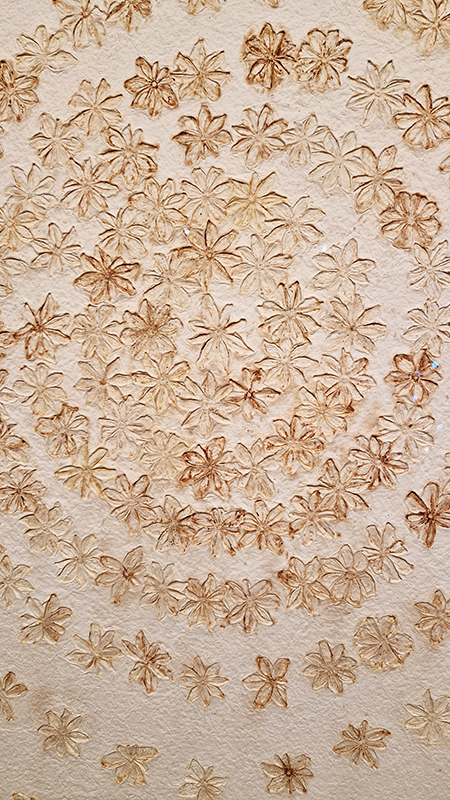
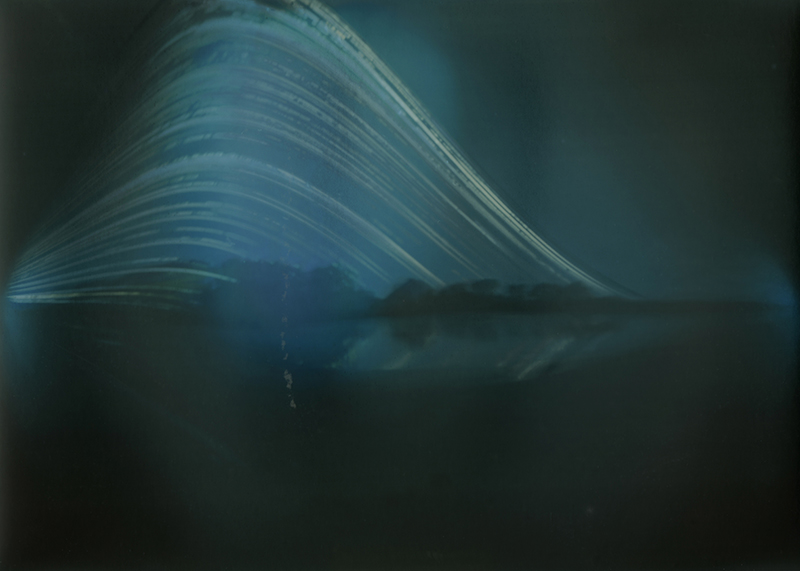
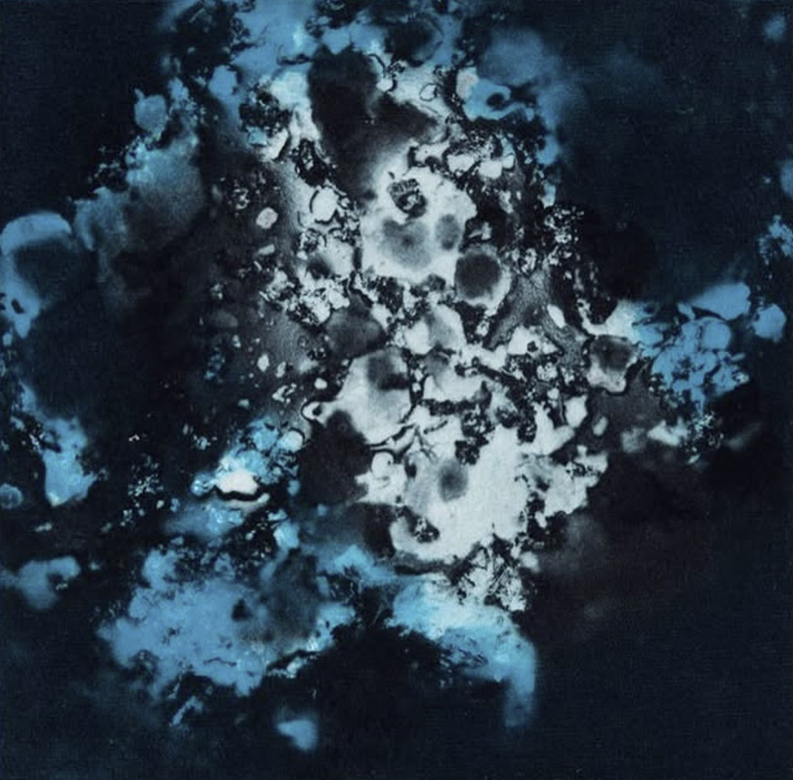
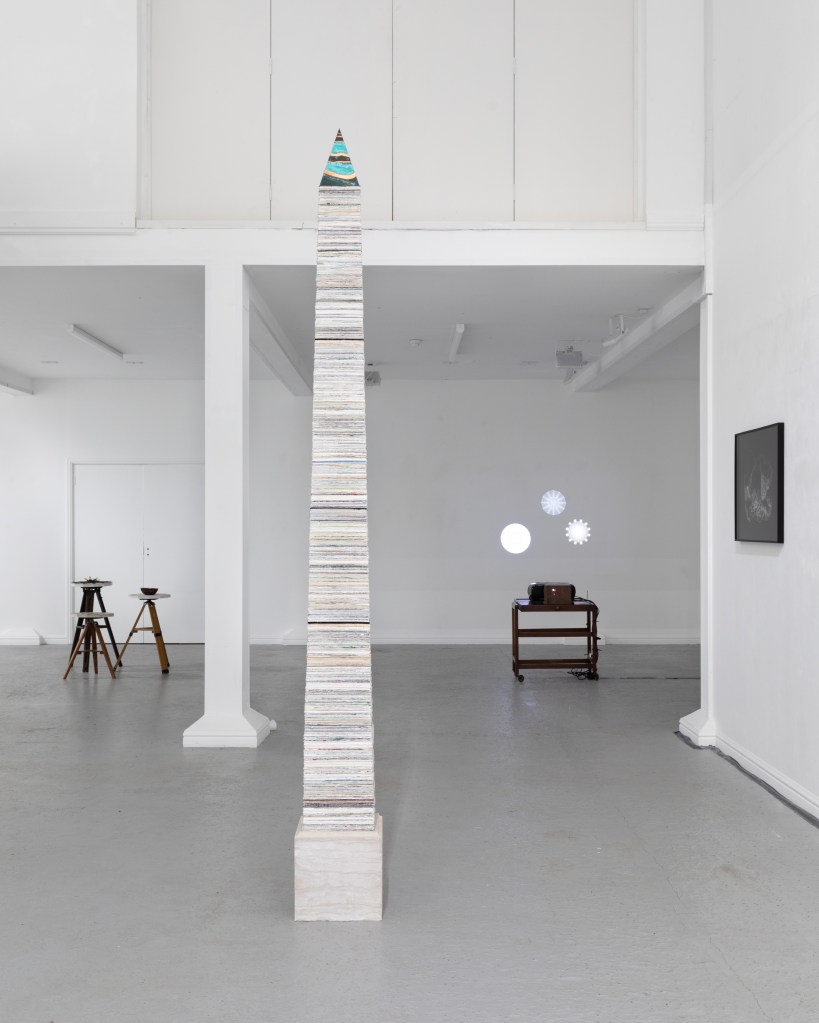
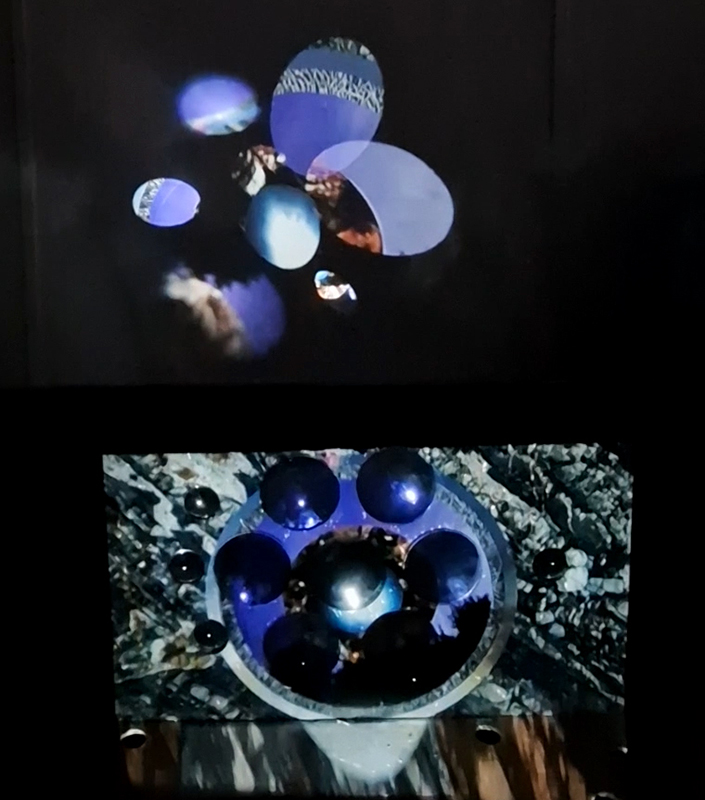
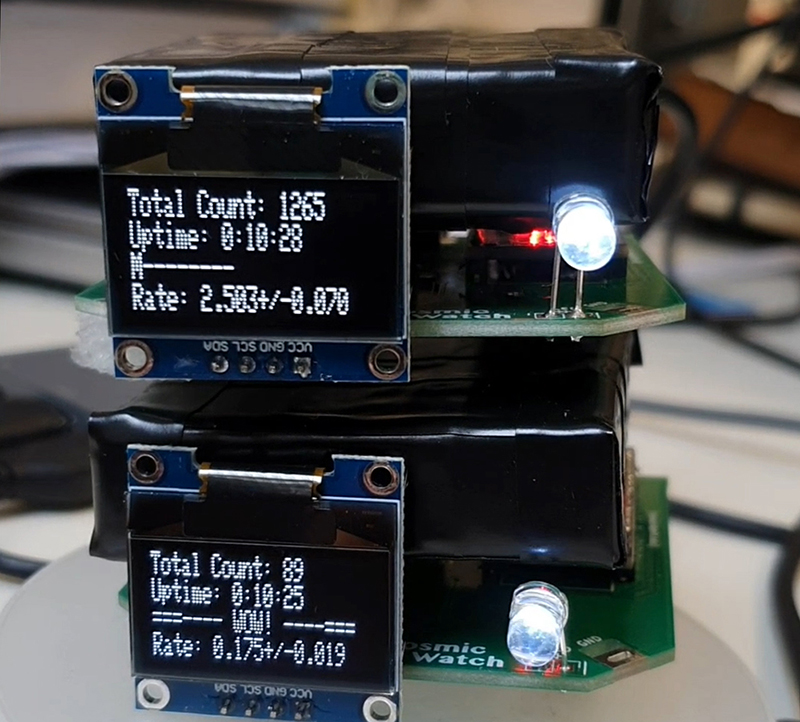
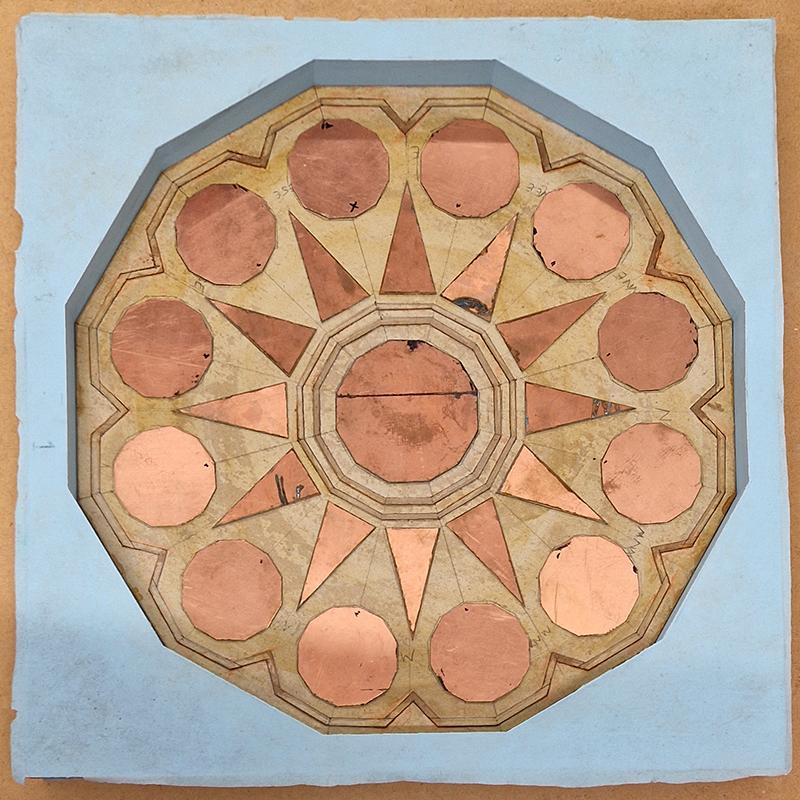
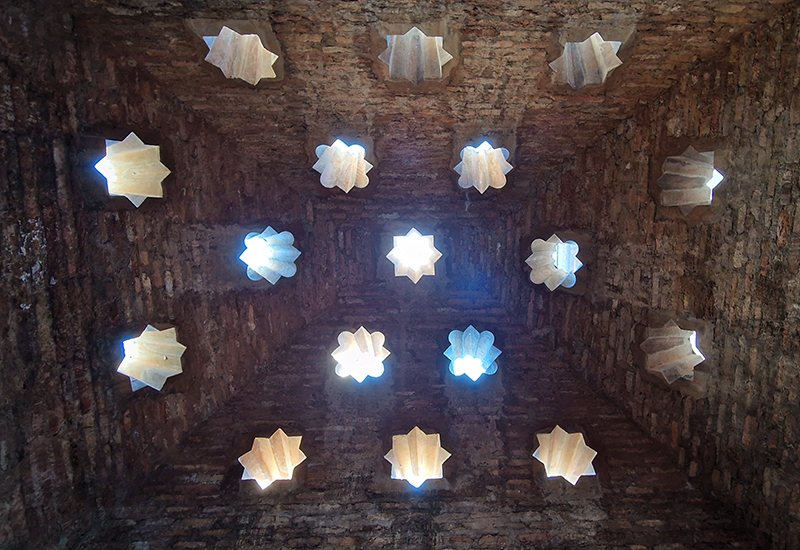
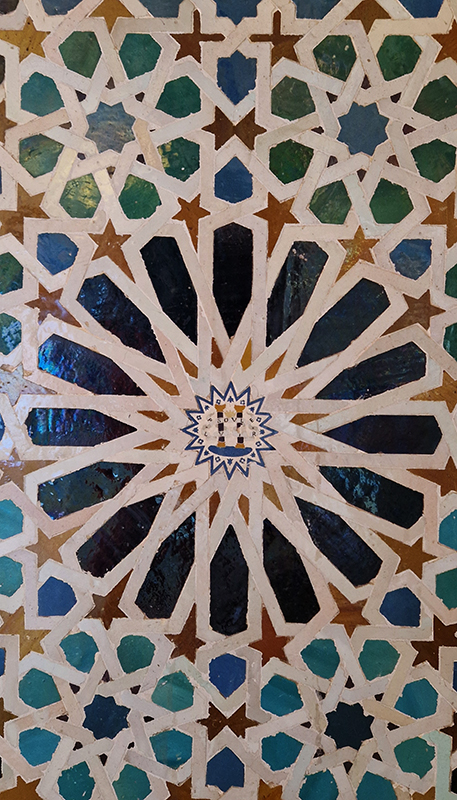
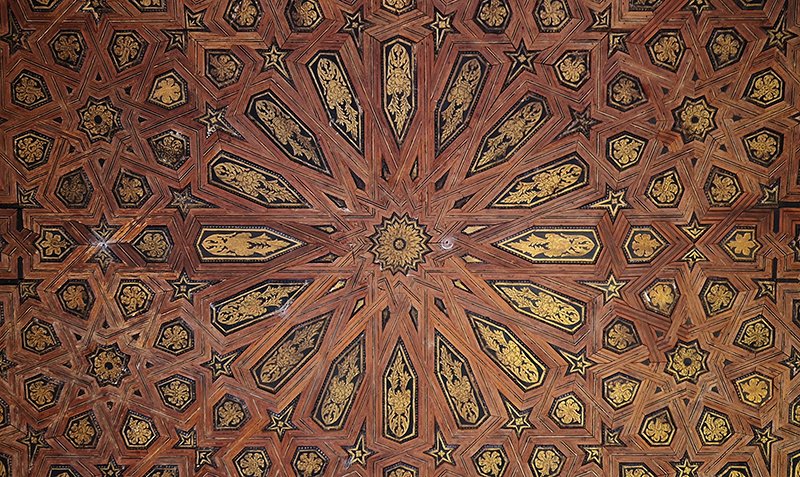
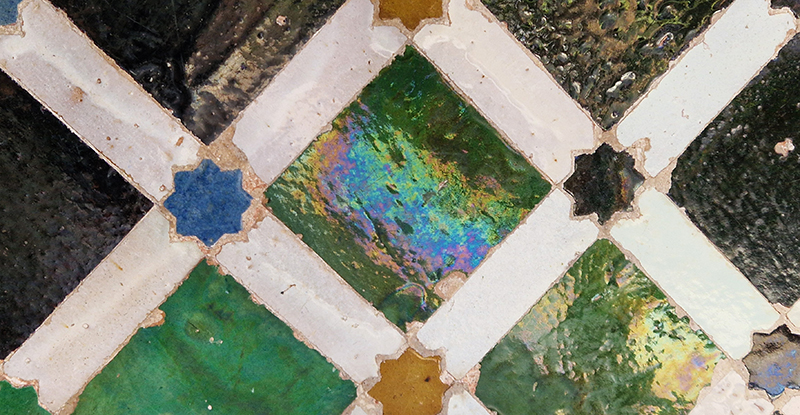
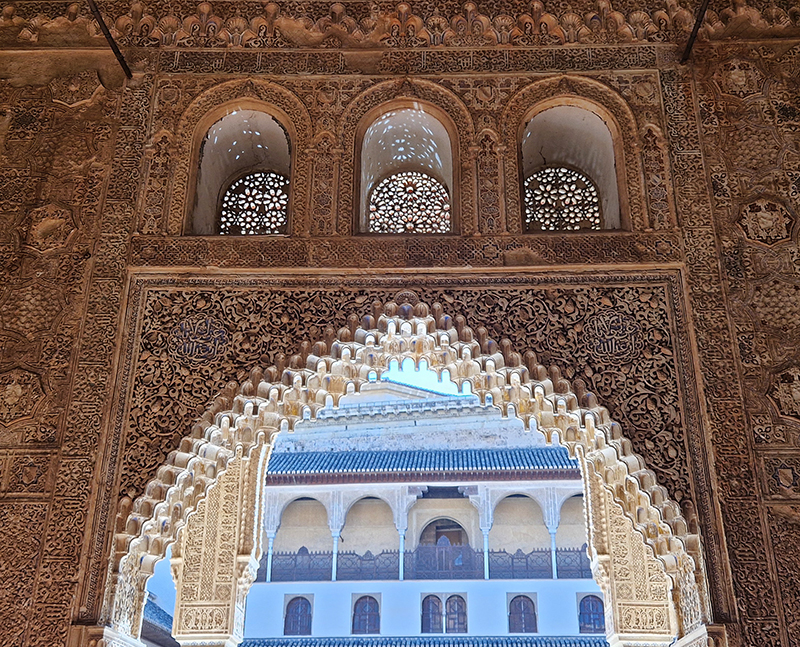
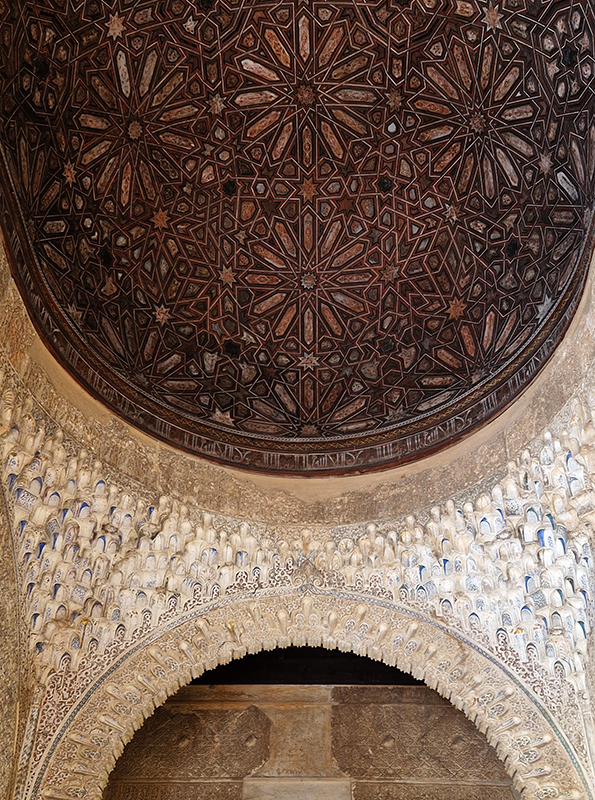
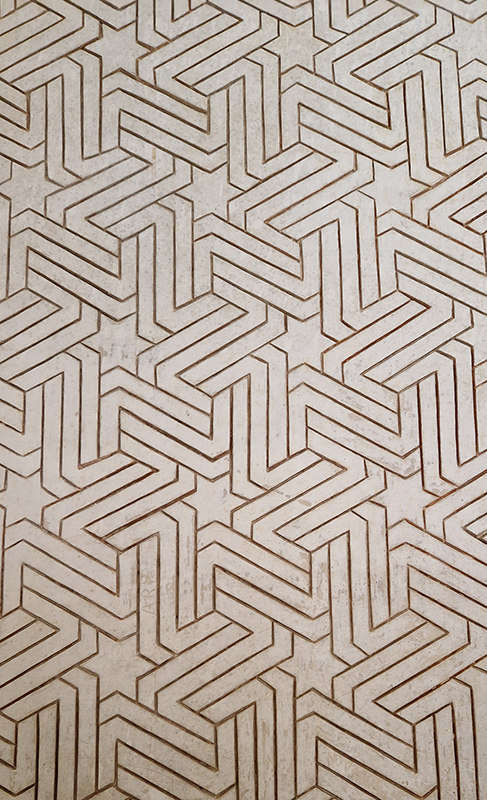
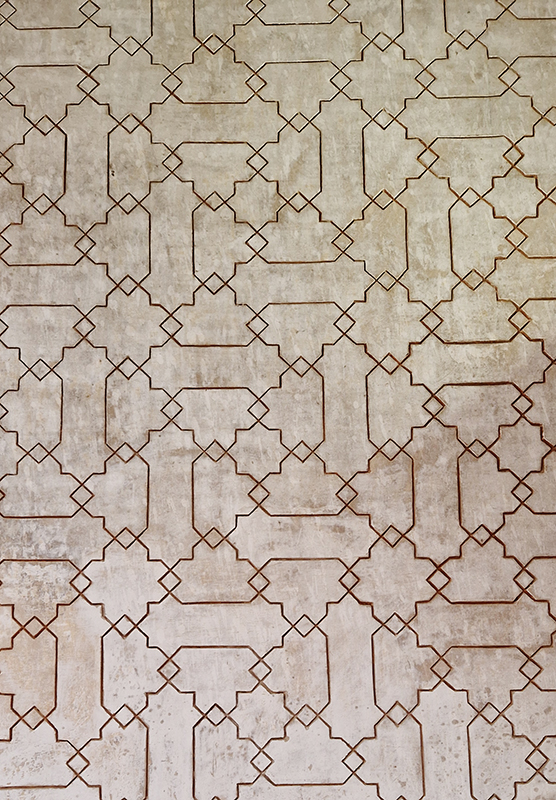
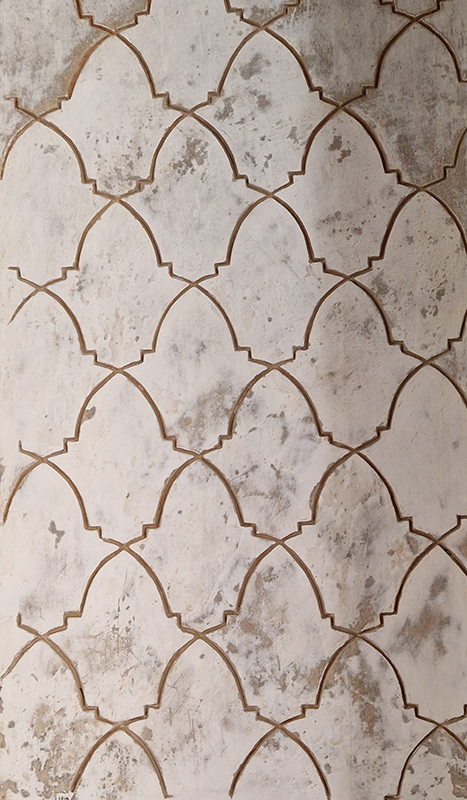
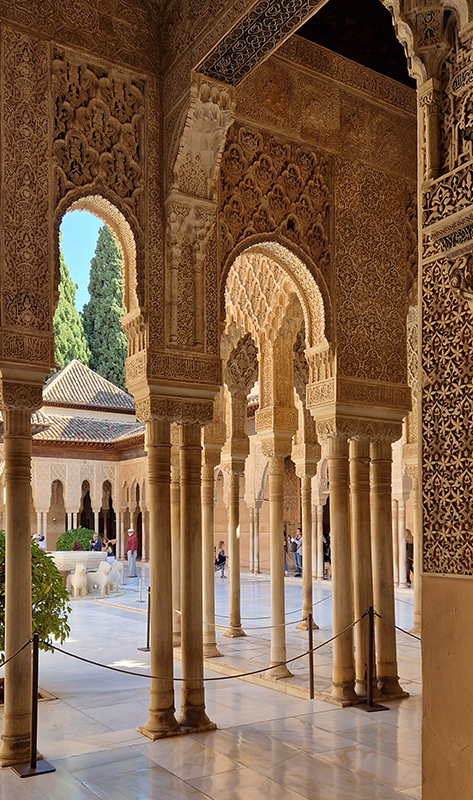
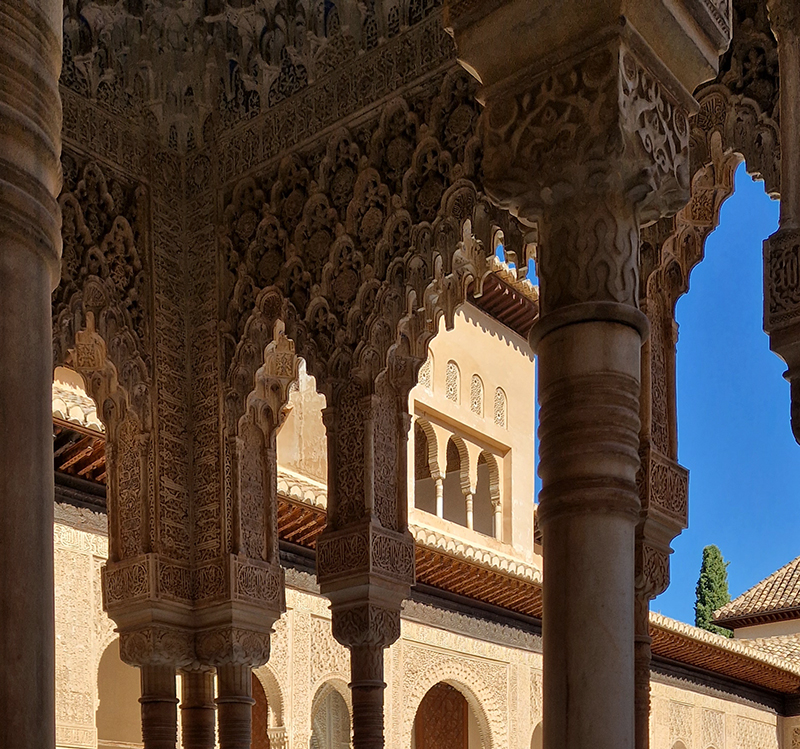
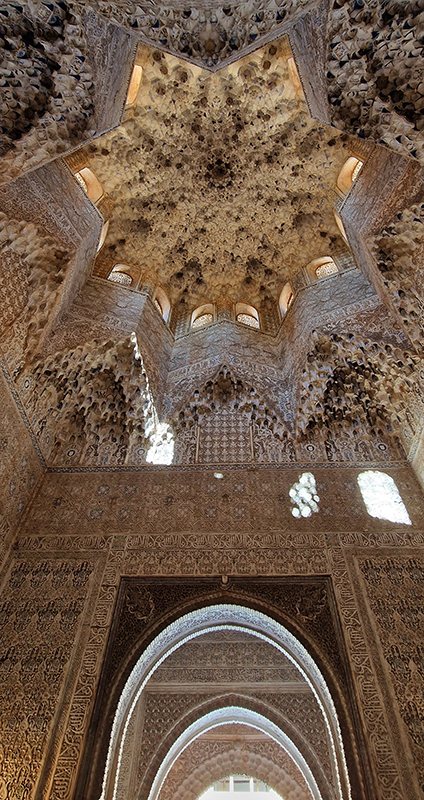
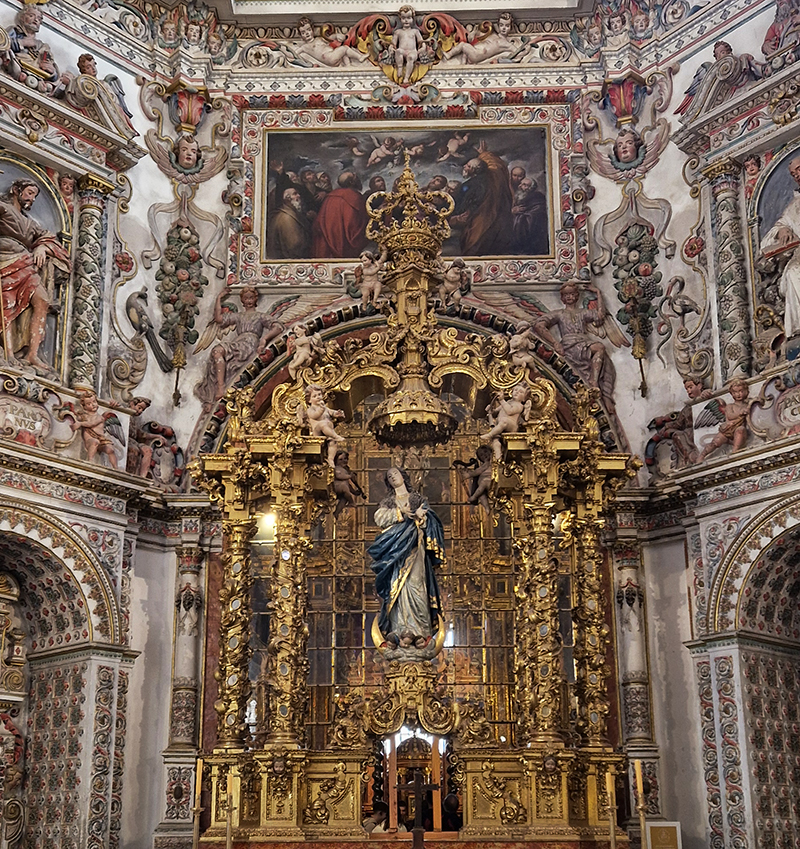
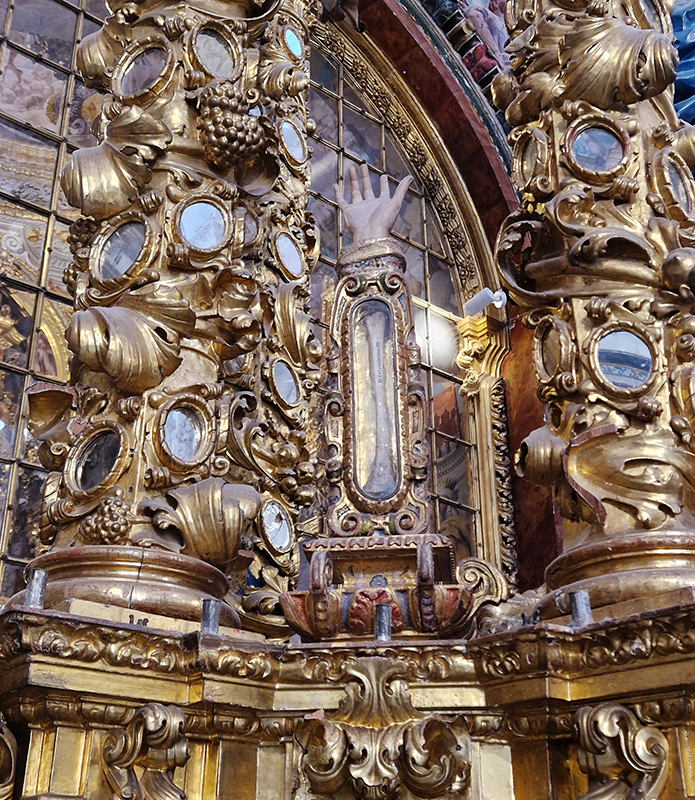
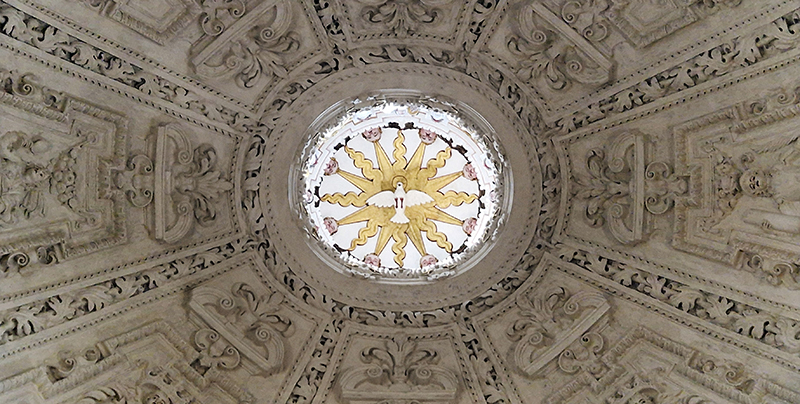
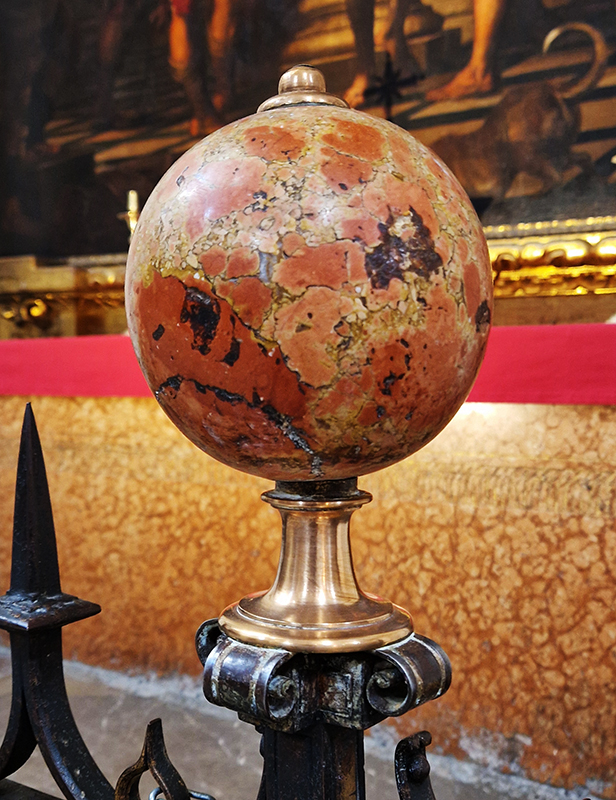
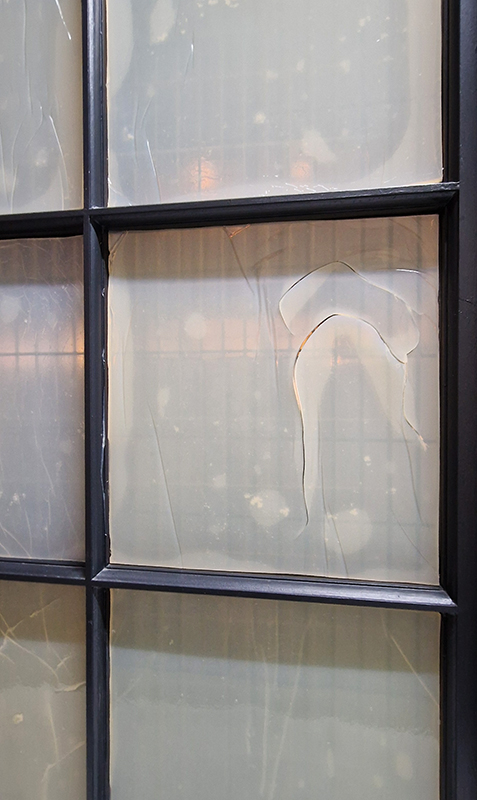
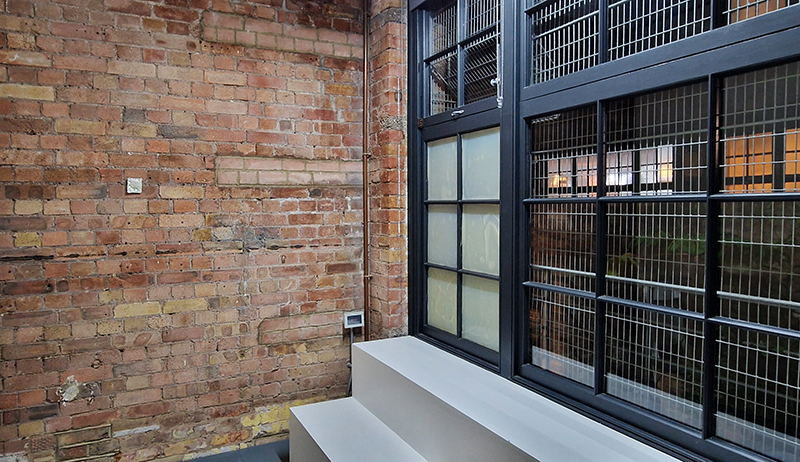
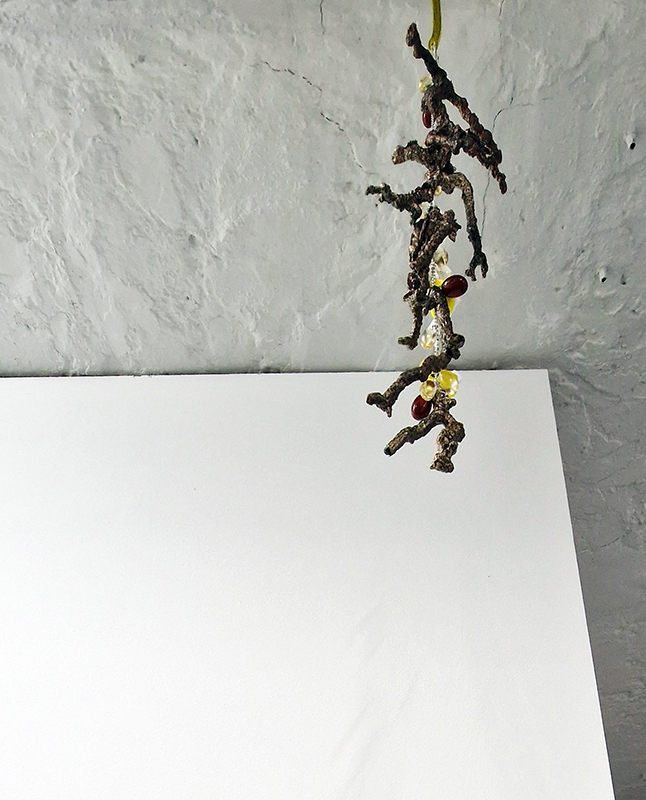
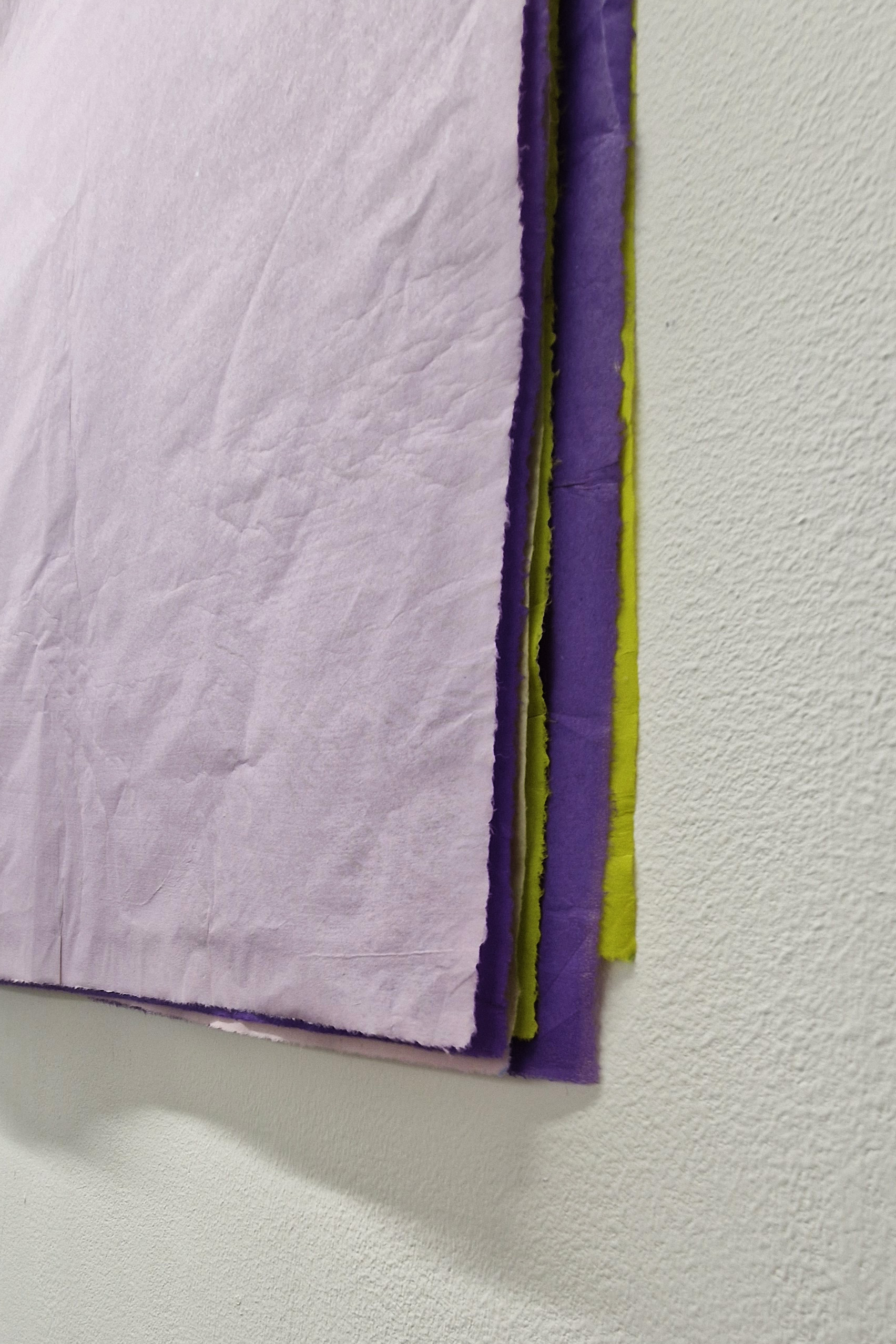
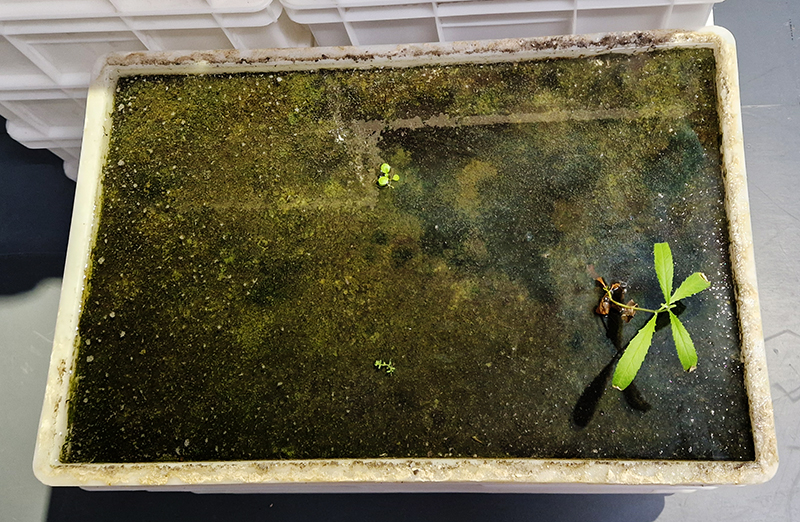
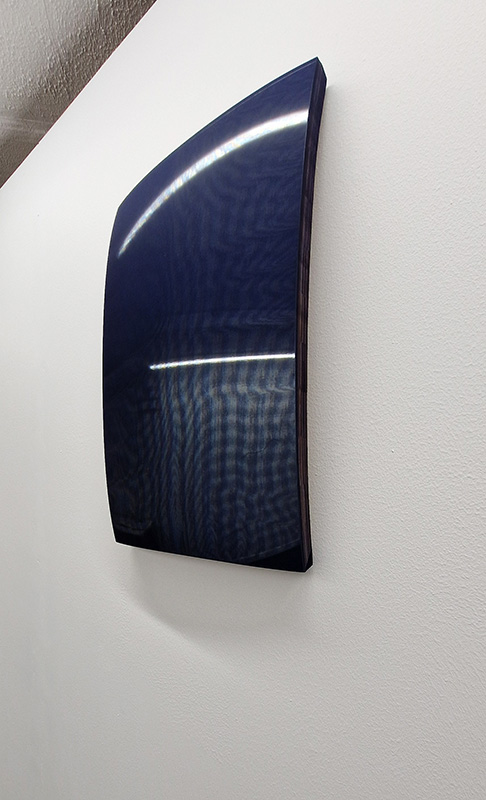
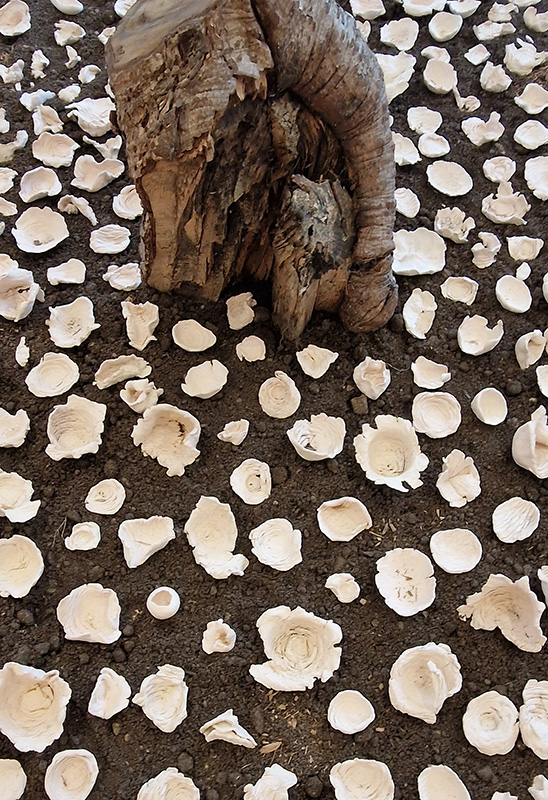
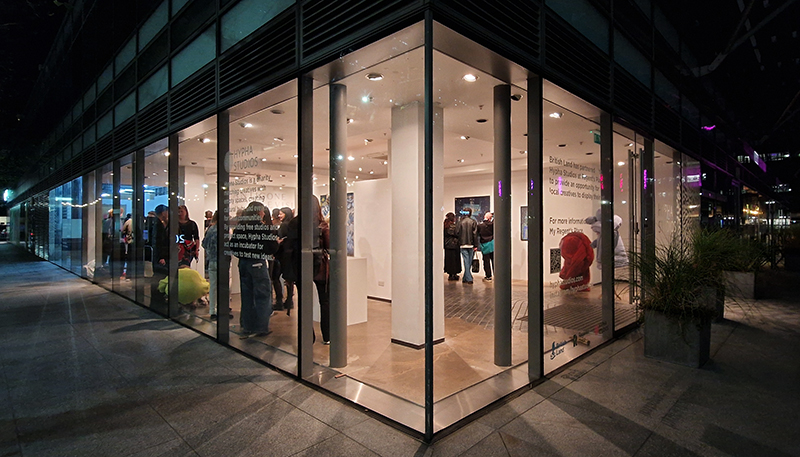
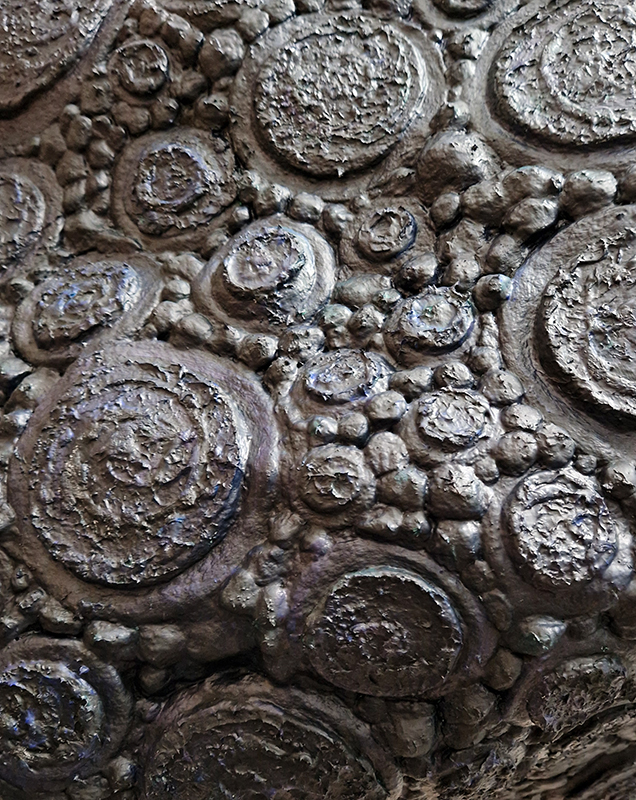
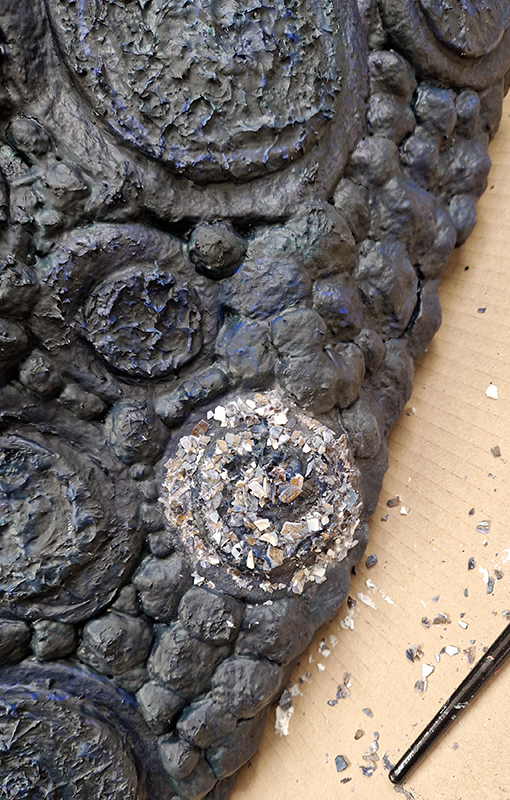
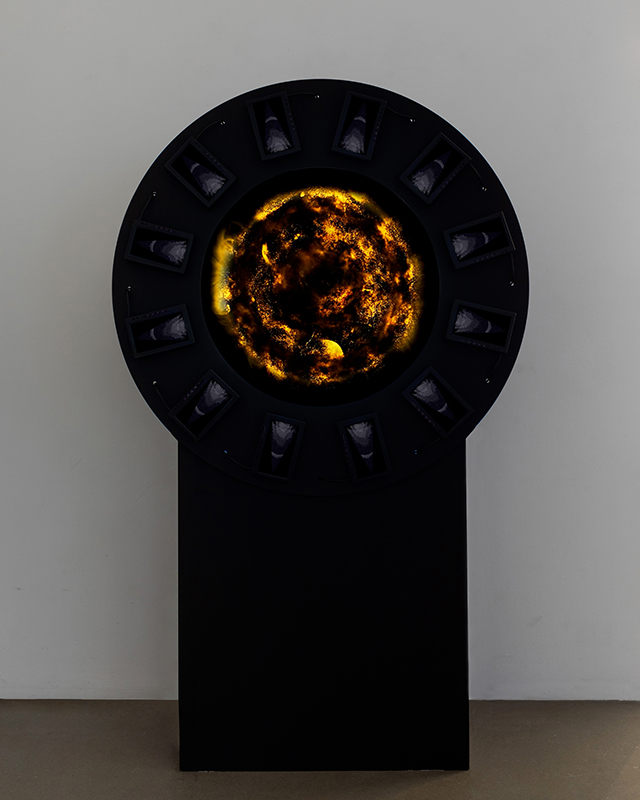
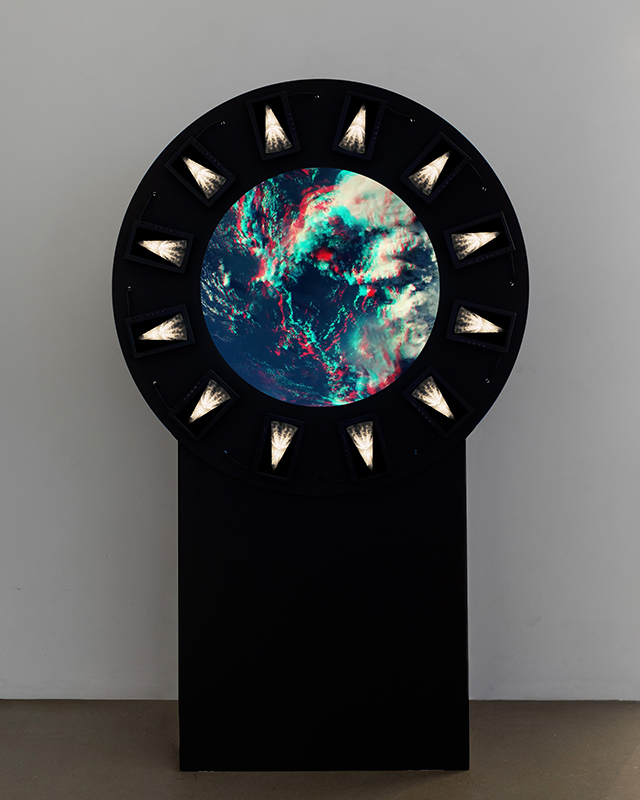
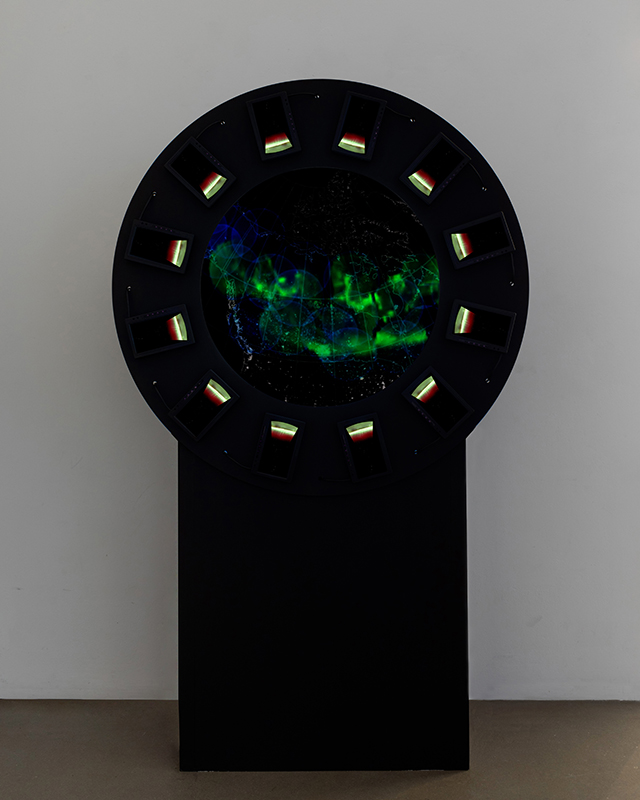
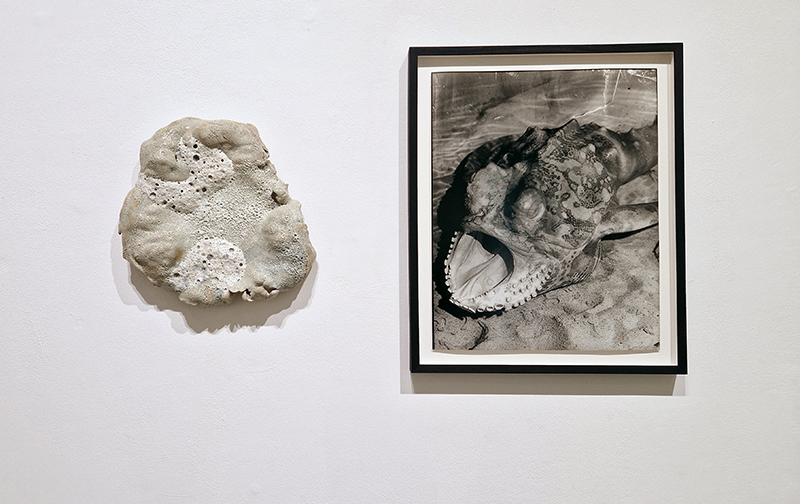
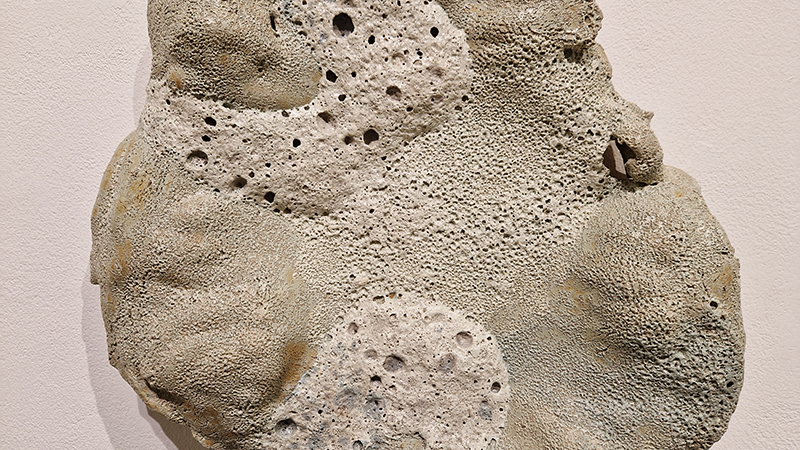
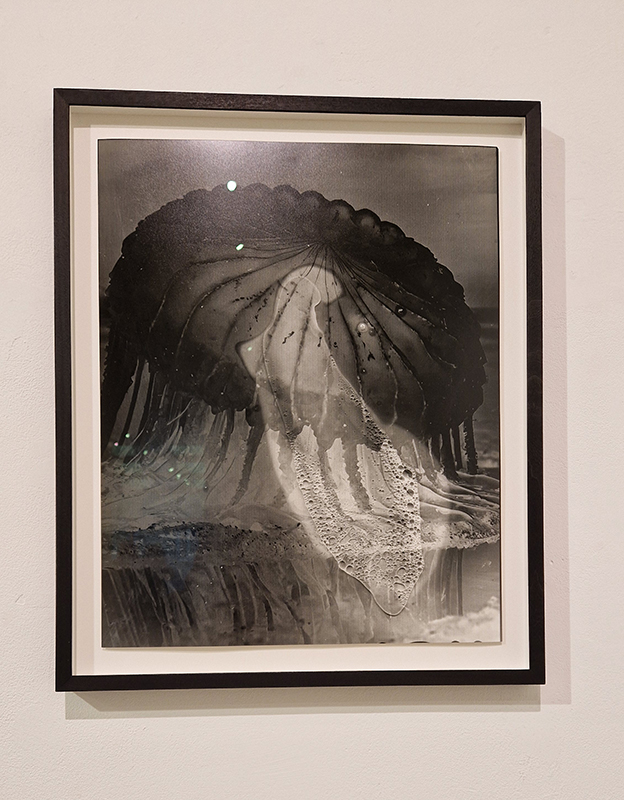
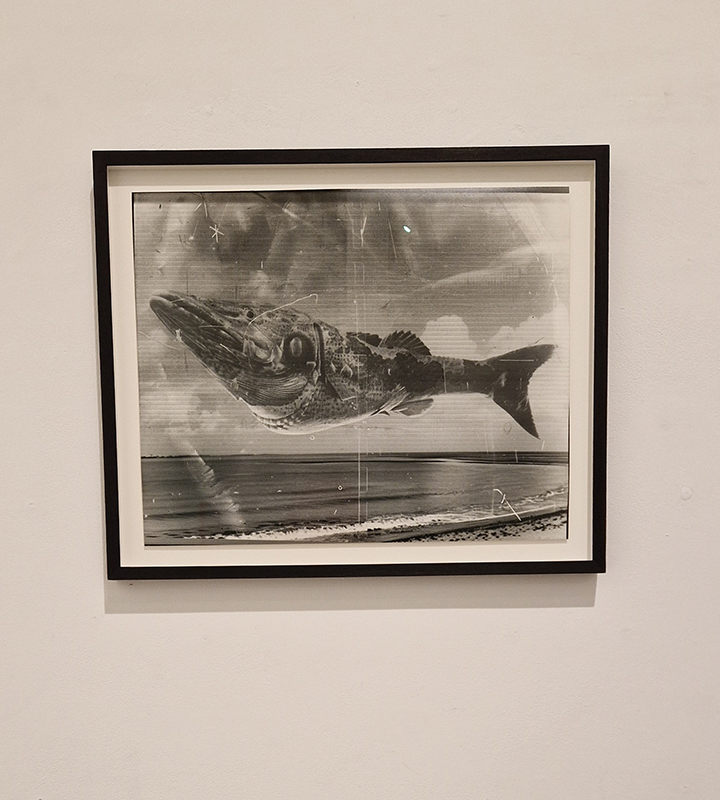
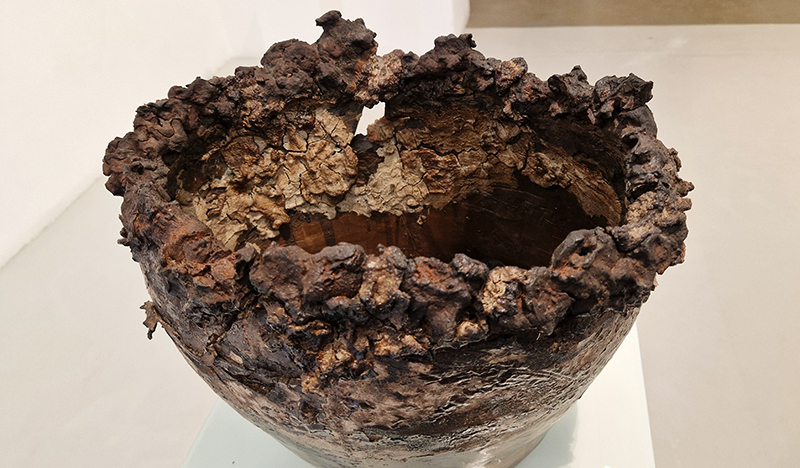
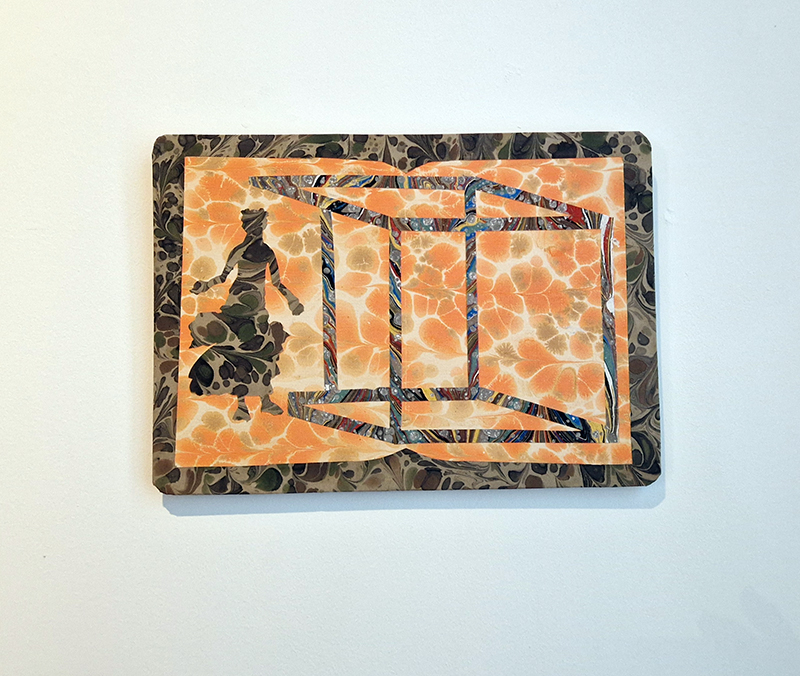
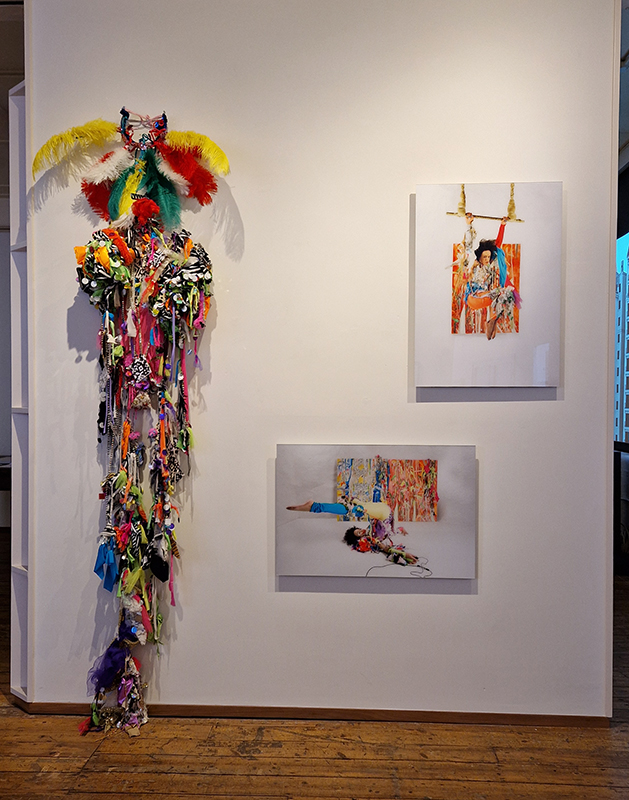
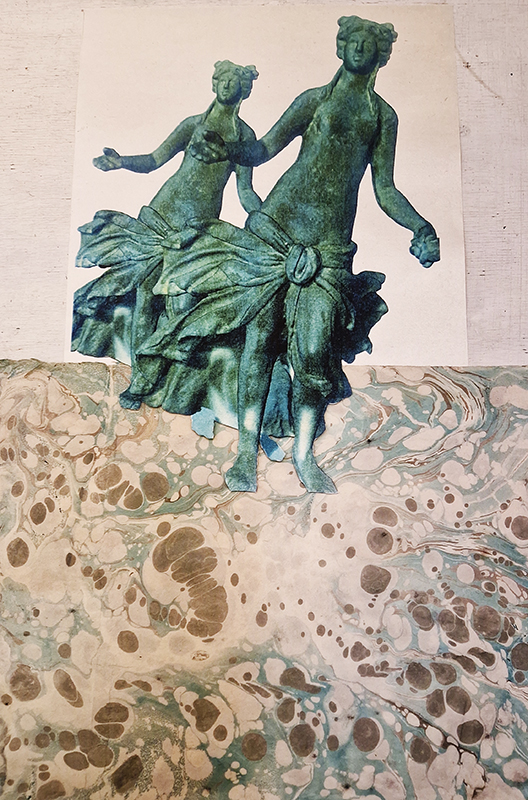
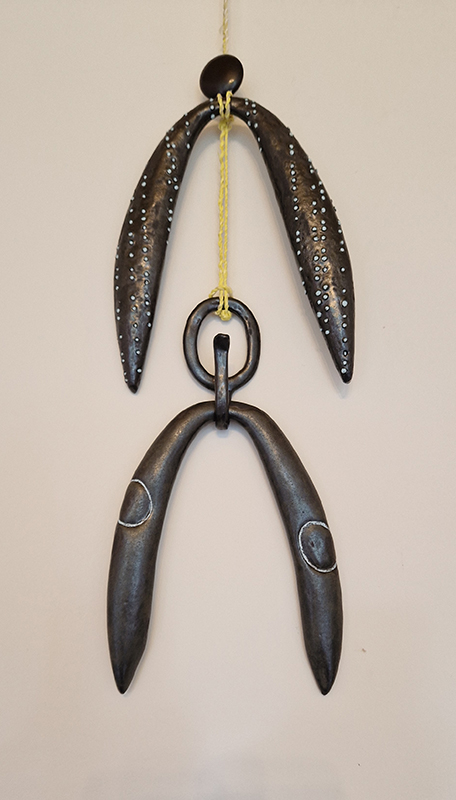
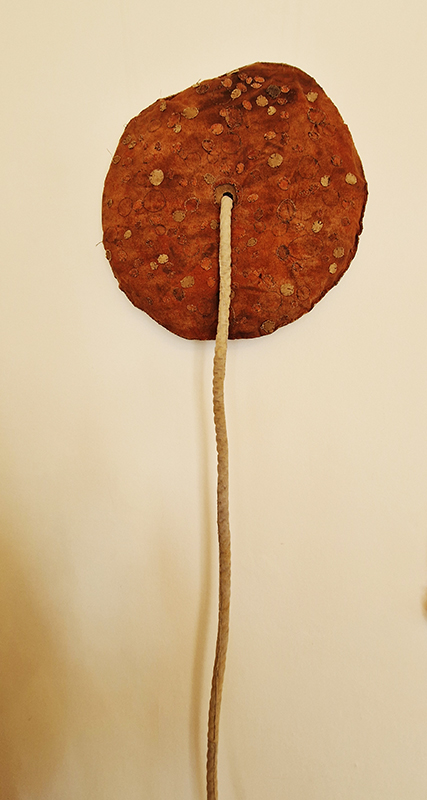
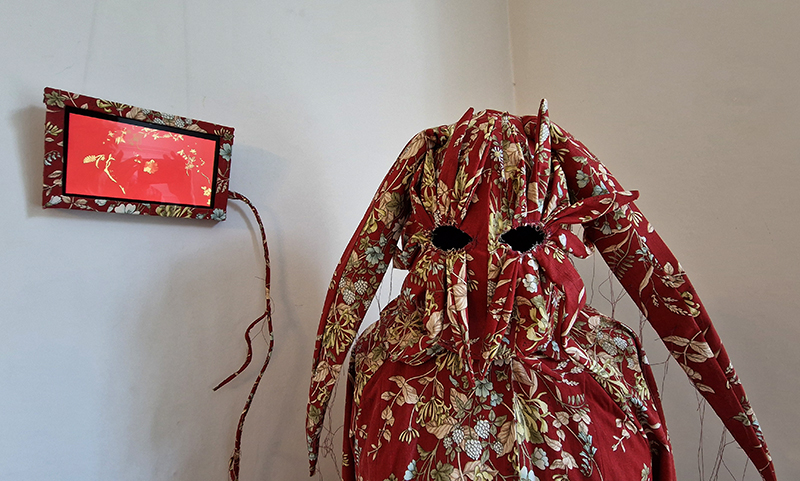
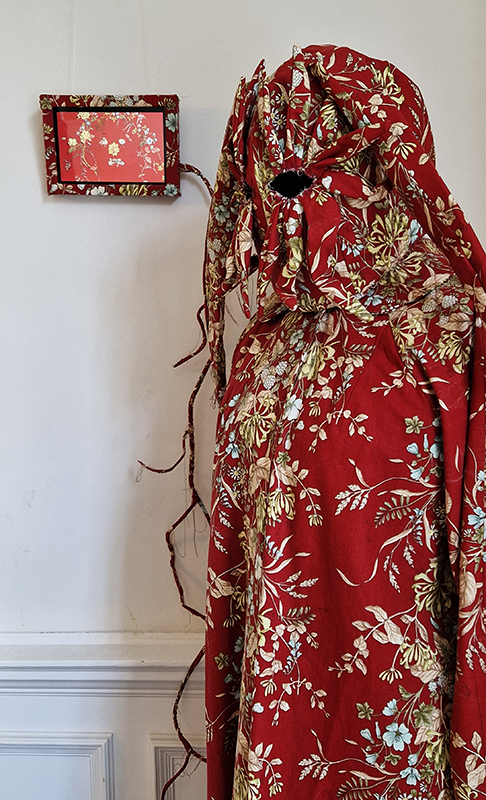
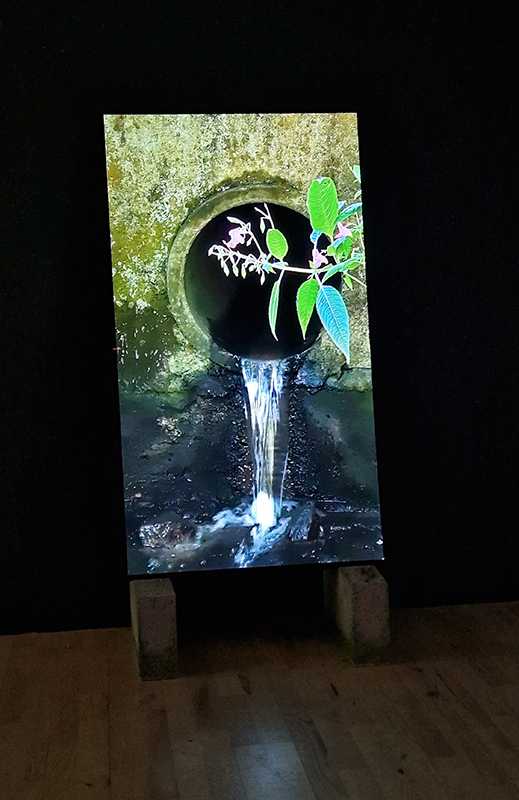
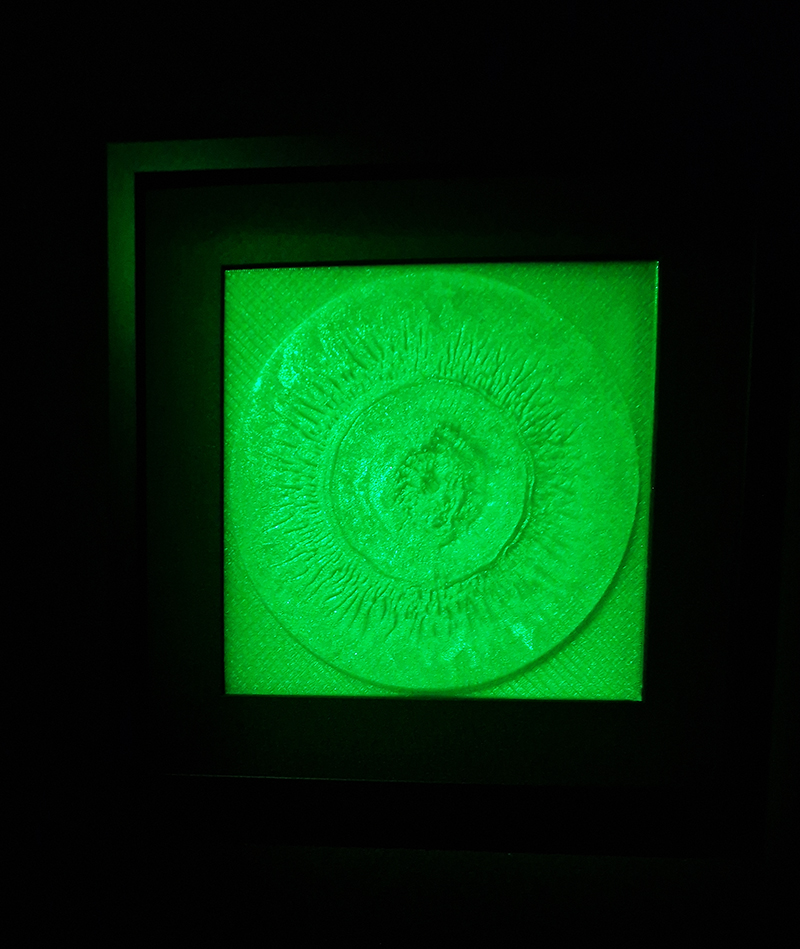
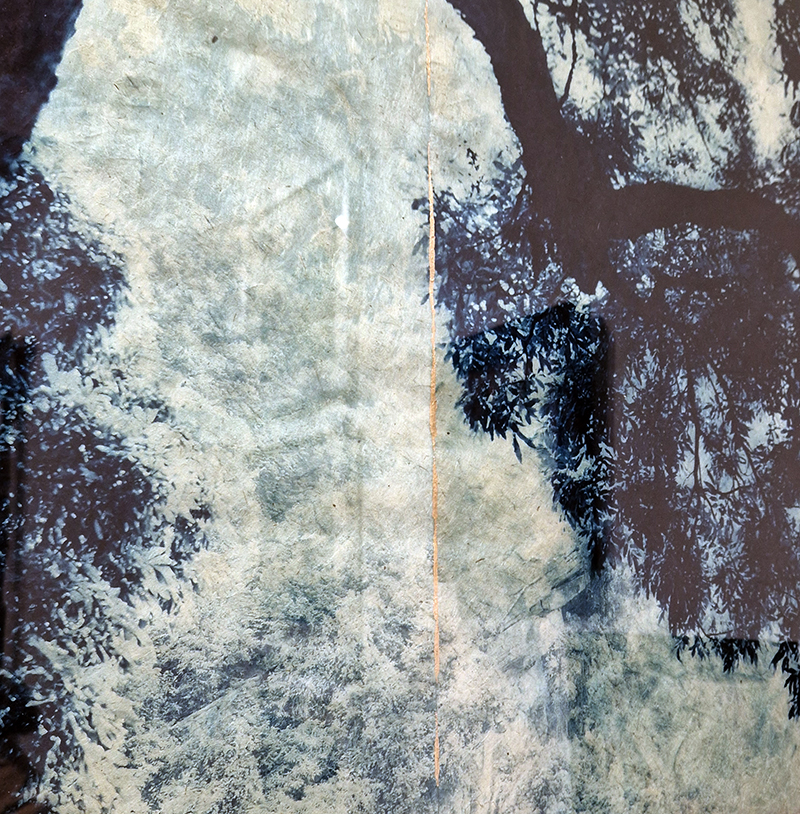
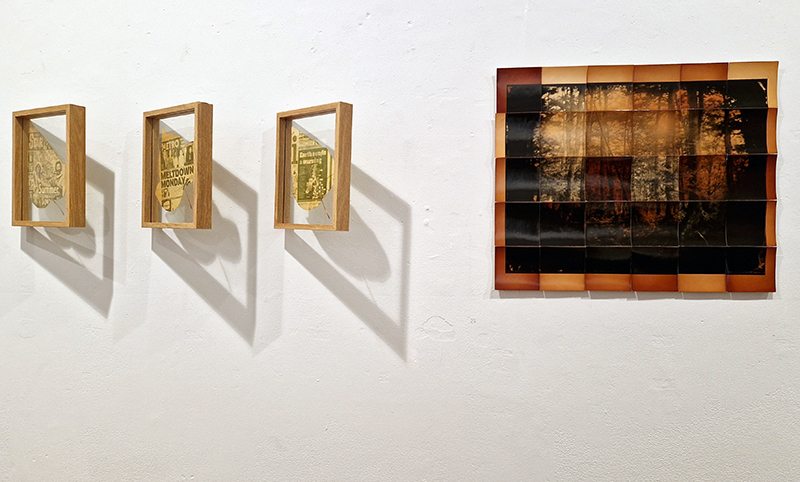
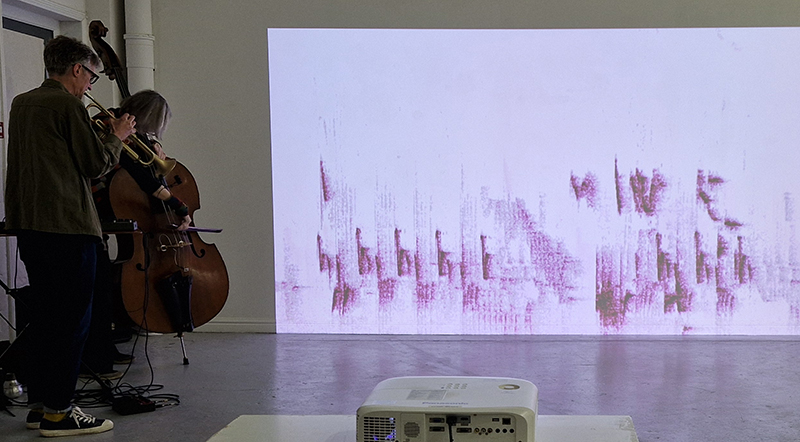
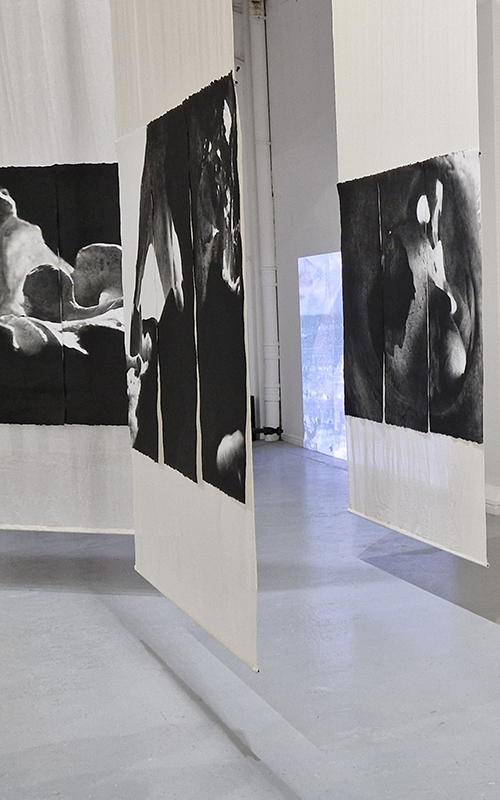
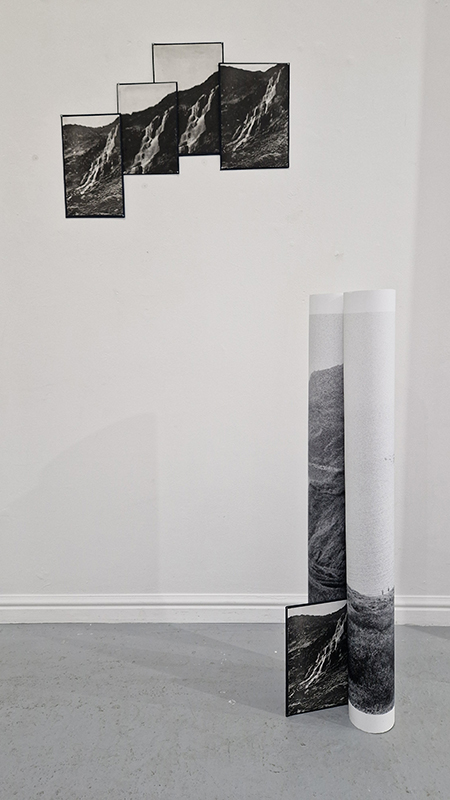
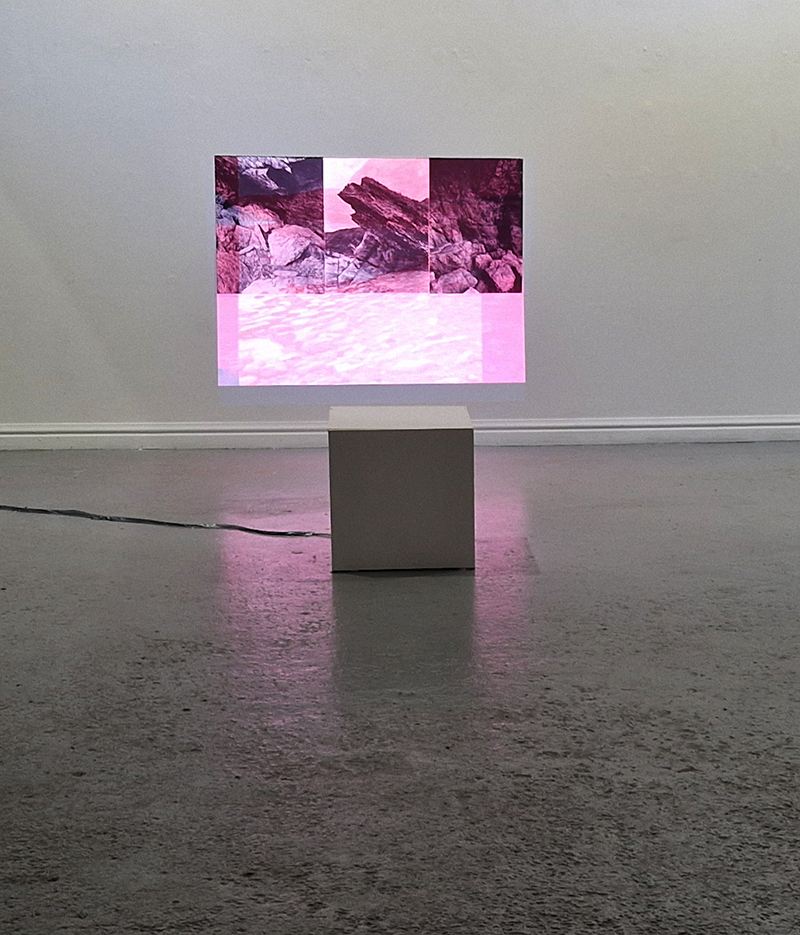
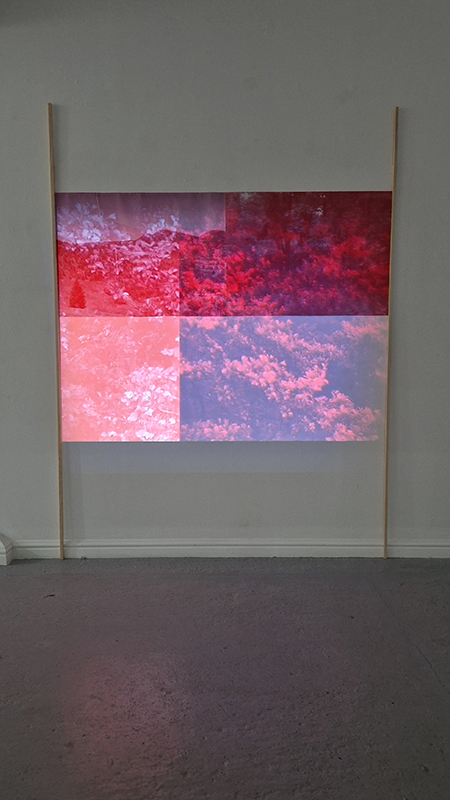
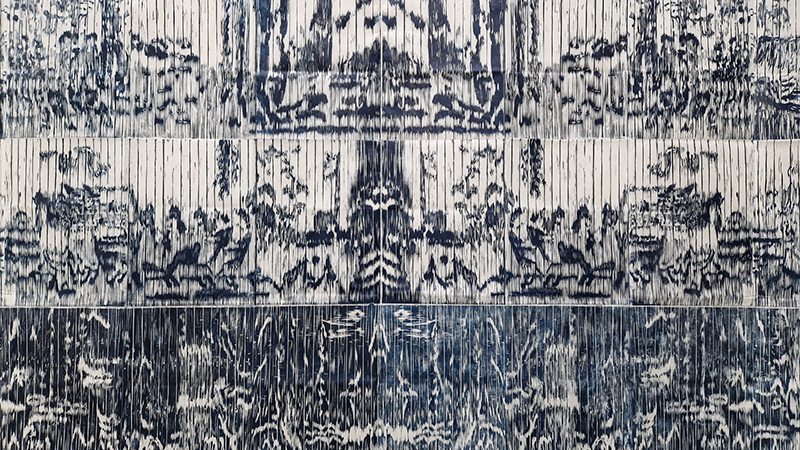
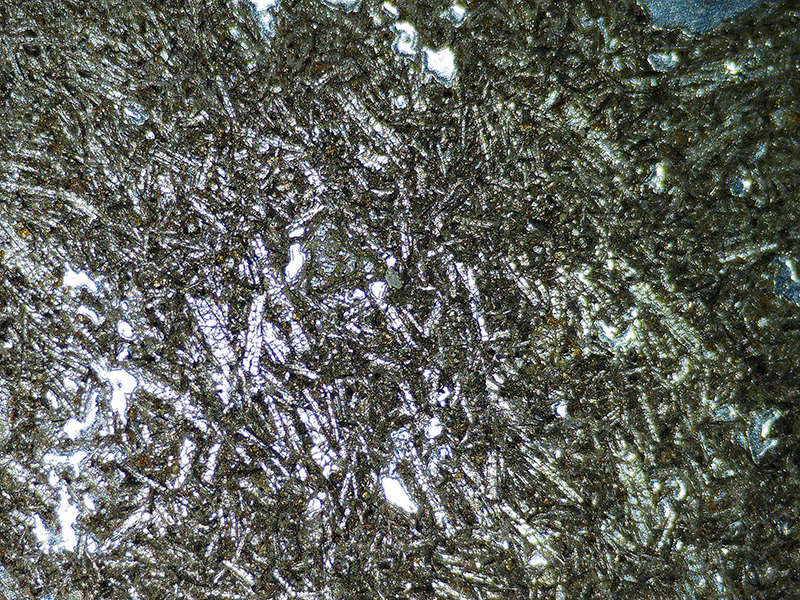
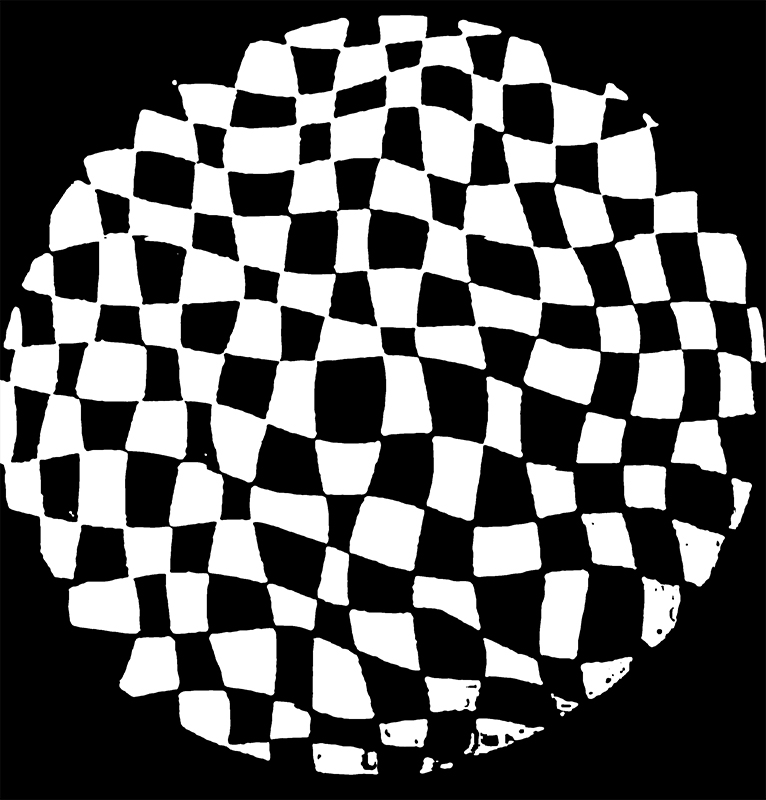
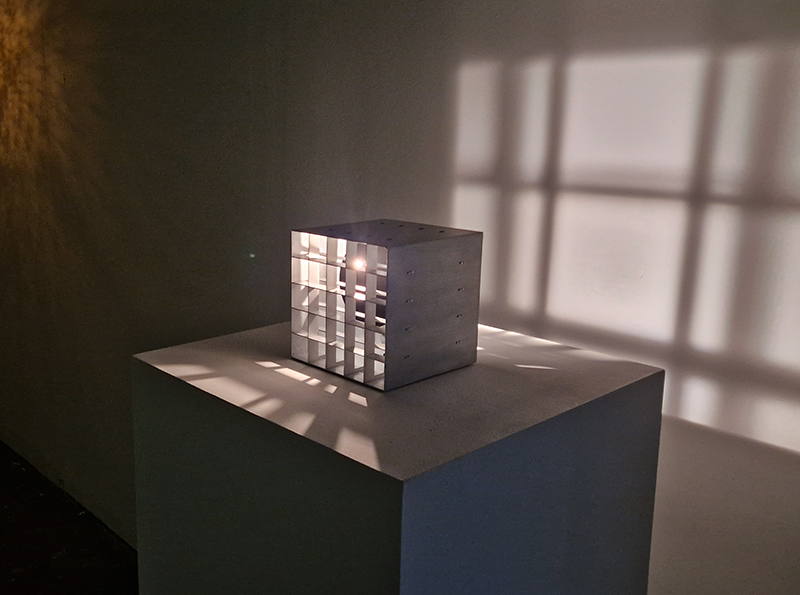
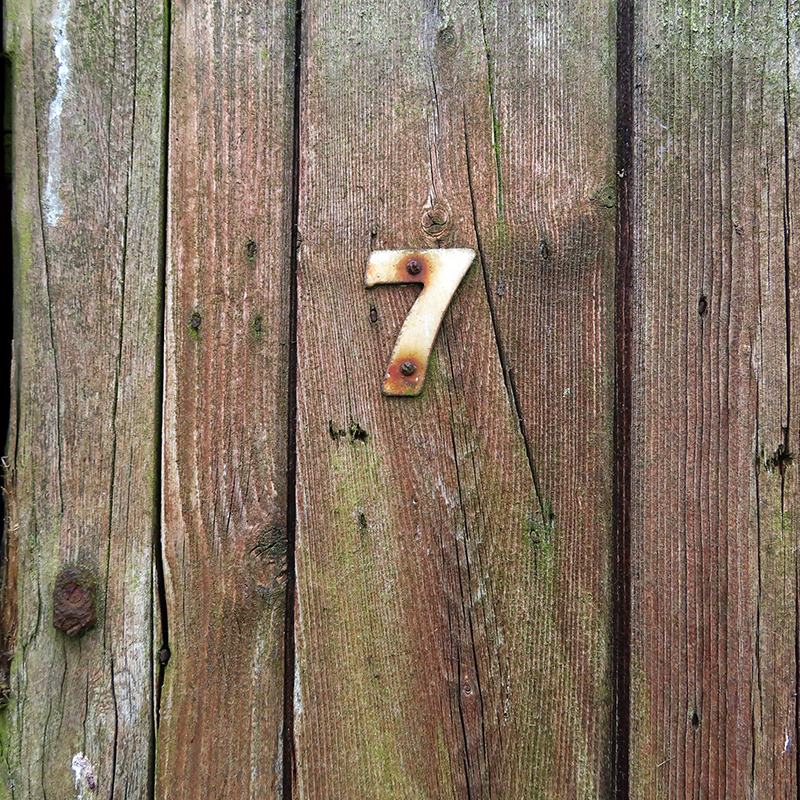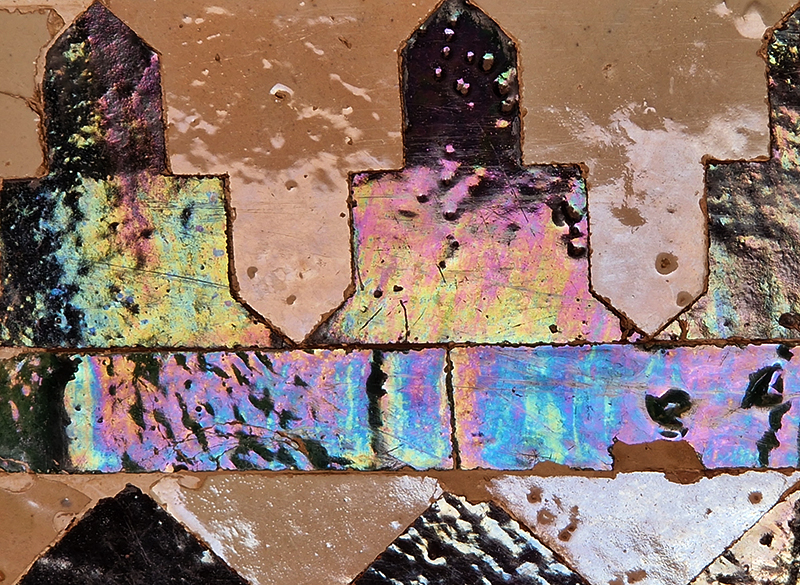Work continues on ‘mineral visions’ testing projecting through a variety of optical lenses set in a pattern reflecting the crystal structure of magnetite. Magnetite is a mineral we are very intimate with. It is in our cells, in our brain but this delicate balance is being disrupted as magnetite crystals from air pollution now outnumber natural magnetite in the brain by 100:1. The full consequences of this imbalance are not known yet but it could be implicated in neurodegenerative disease like Alzheimer’s.
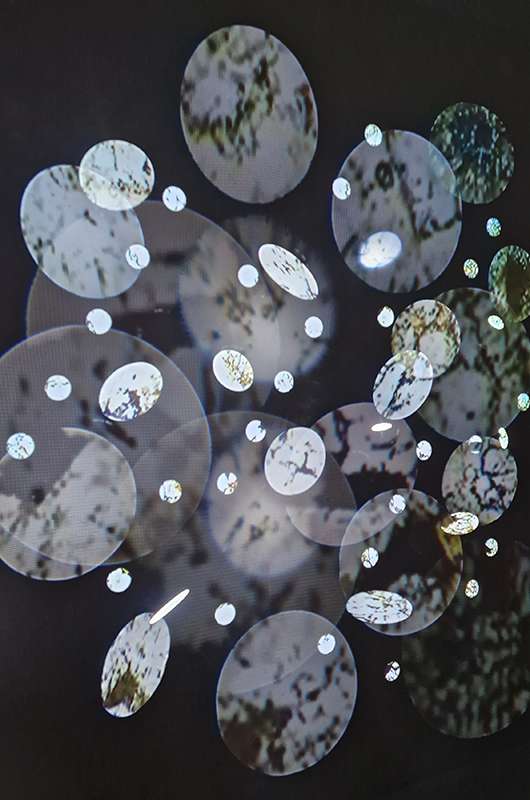
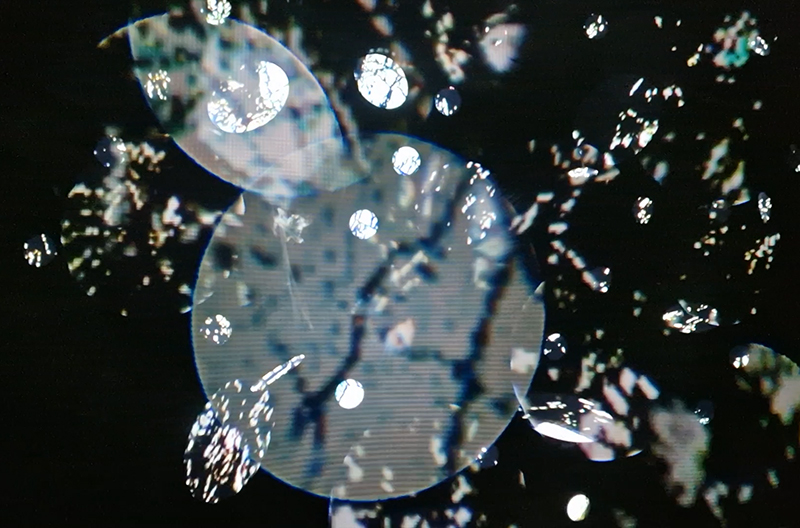
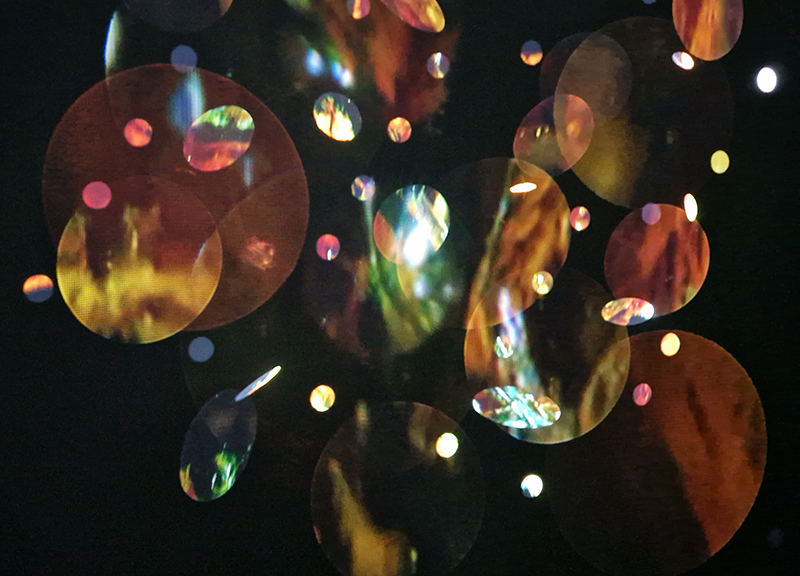
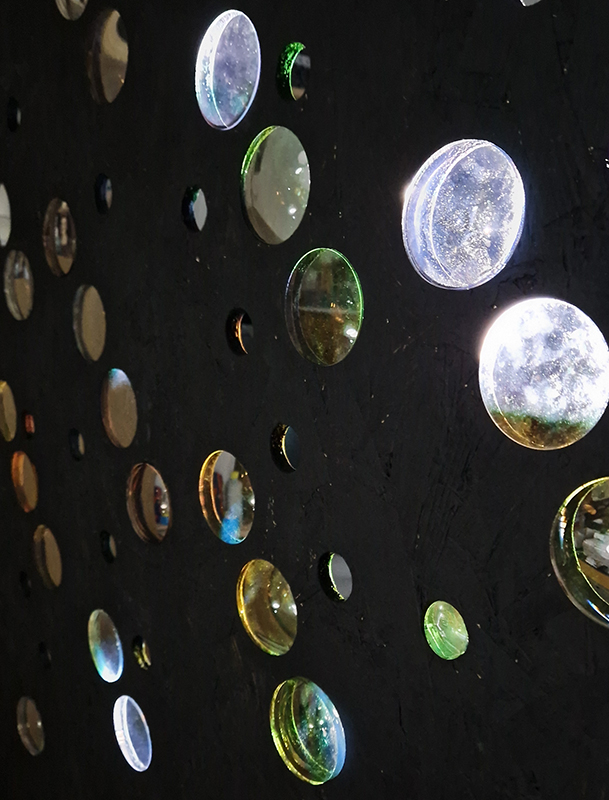





I spent an enjoyable day at London Centre for Book Arts learning how to create a classic full cloth-covered case bound book with a rounded spine. I hope to have picked up some skills here which I will use to make a sculptural book embodying the history of magnetic field reversals stored in the minerals of lava beds on the ocean floor.
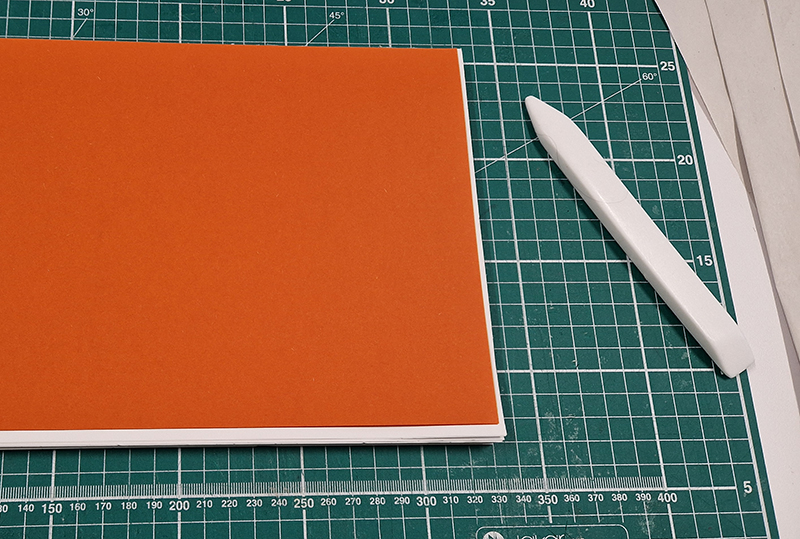
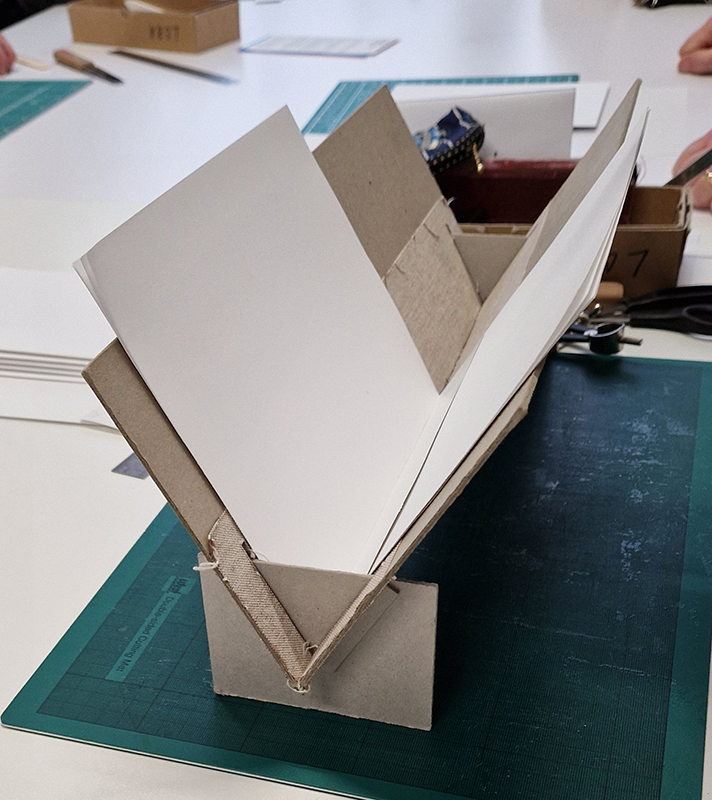
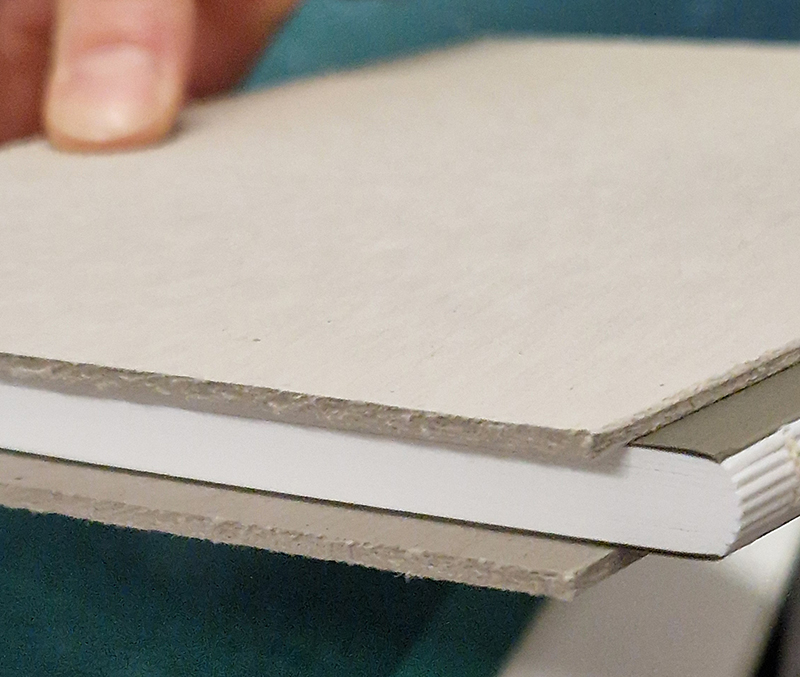
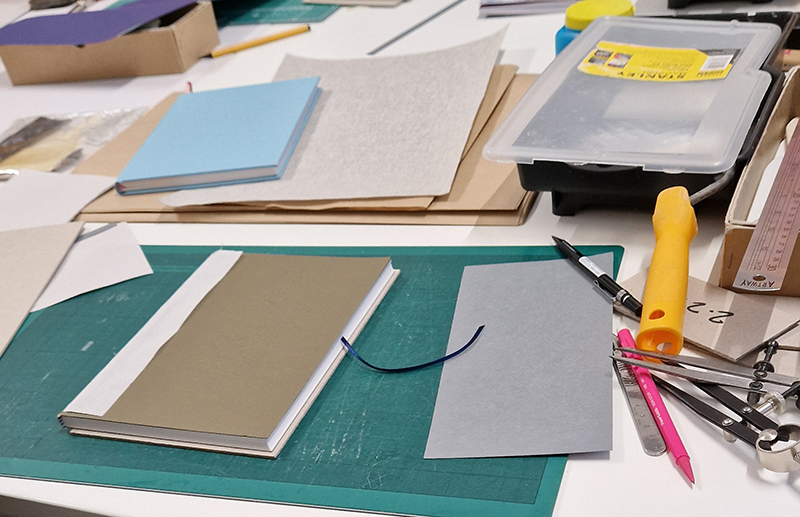







Studio visits
Julie F Hill and I had been in contact with writer/producer/curator Ariane Koek since our duo exhibition The Stone Sky at Thames-side Studios Gallery which she had been unable to attend, but with her interest in physics, geology and cosmology had suggested we keep in touch. We finally had the pleasure of meeting Ariane at Julie’s Bomb Factory Studio and were able to share some of our plans for our upcoming show The Geological Unconscious which we are co-curating at Hypha HQ this spring.
It was so good to meet curators Maria Hinel and Indira Dyussebayeva-Ziyabek at my studio to discuss their upcoming project inspired by the essay on carbon in Primo Levi’s The Periodic Table. Levi weaves a story following a single atom of carbon as it is transformed through the many relationships and bonds made with other atoms, moving from rock to atmosphere to living organism and back to mineral.

Gallery visits
Exhibition research trip to Exeter with Julie to see Dartmoor: A Radical Landscape at the Royal Albert Memorial Museum & Art Gallery. Artists include: Fern Leigh Albert, Jo Bradford, Chris Chapman, John Curno, Robert Darch, Siân Davey, Susan Derges, Robin Friend, Ashish Ghadiali, Alex Hartley, Nancy Holt, Laura Hopes and Katharine Earnshaw, Richard Long, Garry Fabian Miller, James Ravilious, Tanoa Sasraku, David Spero, Nicholas J R White, Marie Yates.
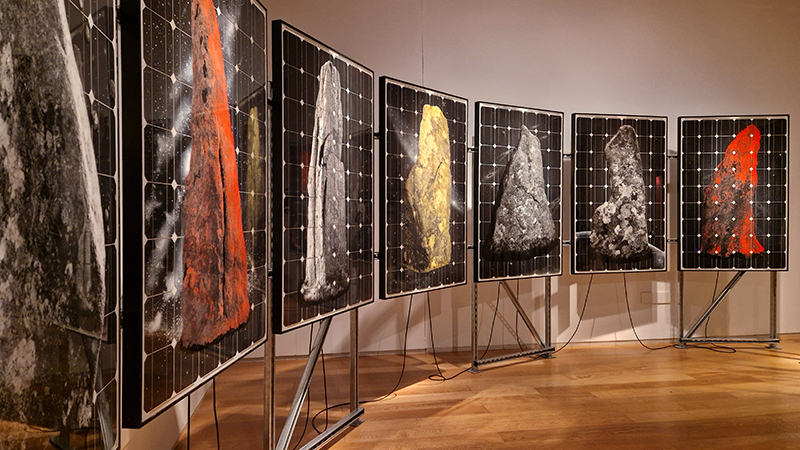
I was particularly interested in seeing Alex Hartley’s, The Summoning Stones, which is a series of hand coloured prints of standing stones embedded into recycled solar panels. Aiming to bring together ancient and contemporary ways of engaging with the sun they are positioned to put the viewer in the centre of a magical arc of energy; the contemporary may have the bias here and the ancient magic dispersed in the gallery setting but I still enjoyed the aesthetic. The works felt rather cramped in the space. There was a lot of photographic work documenting artist’s interest in the moor from the 60’s/70’s onwards and several prints using the process of dye destruction (luminograms) which I was unfamiliar with, such as those by Gary Fabian Miller – this is a photographic printing process in which colour dyes embedded in the paper are selectively bleached away (destroyed) to form a full-colour image. The papers used in this process are no longer manufactured and Miller spent a year creating one direct long exposure to paper luminogram every day as a reflection on time passing. Extraordinary fluid images from Susan Derges were a highlight.







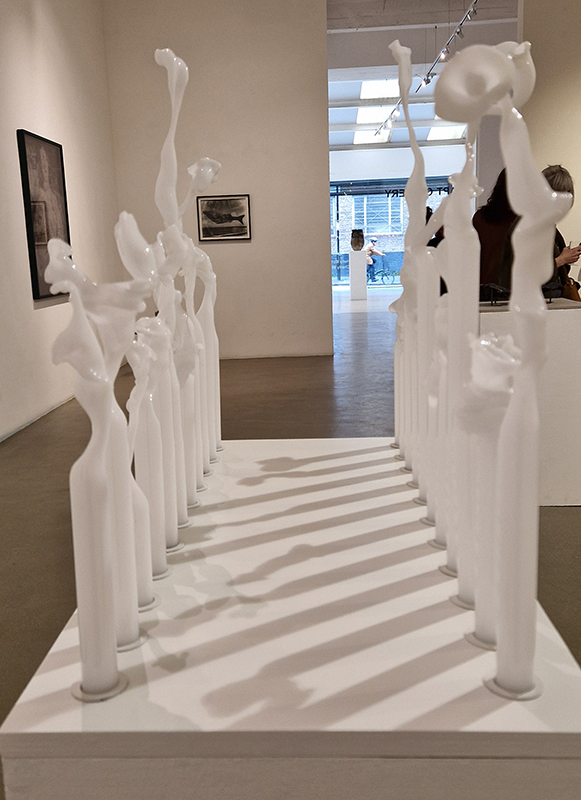
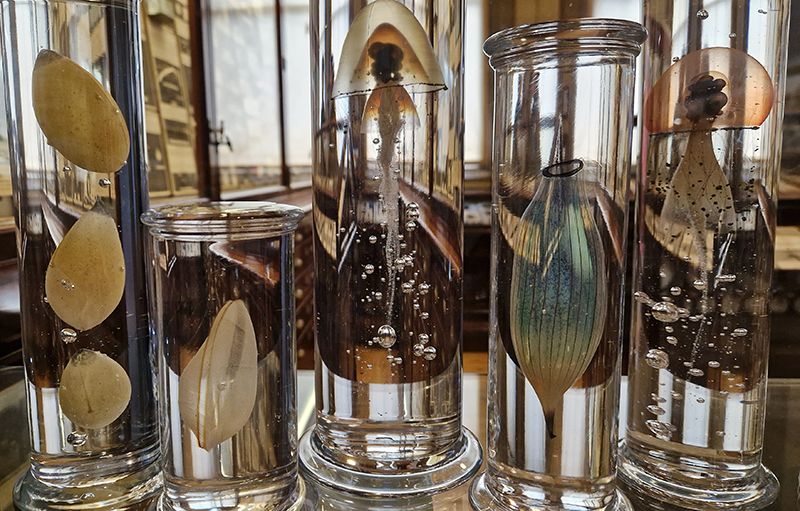
A luminous intervention of glass Specimens from an Imaginary Voyage by Steffen Dam in the main collection at RAMM.

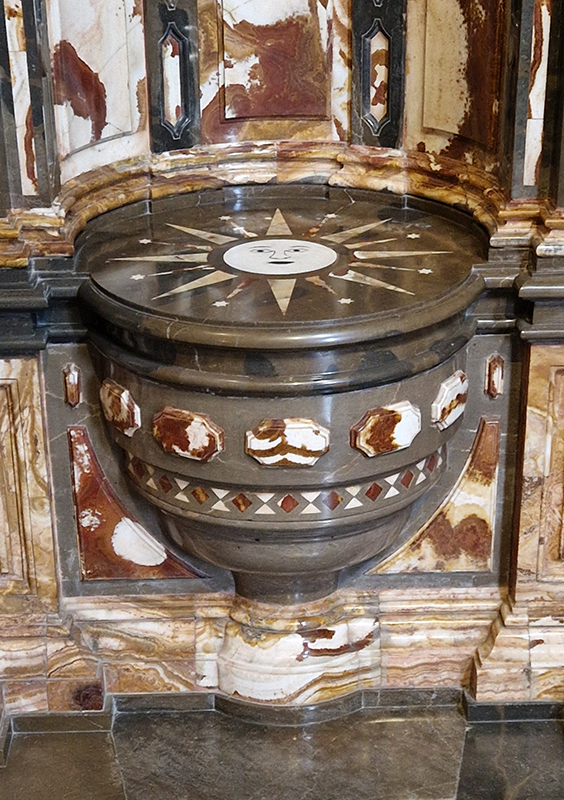
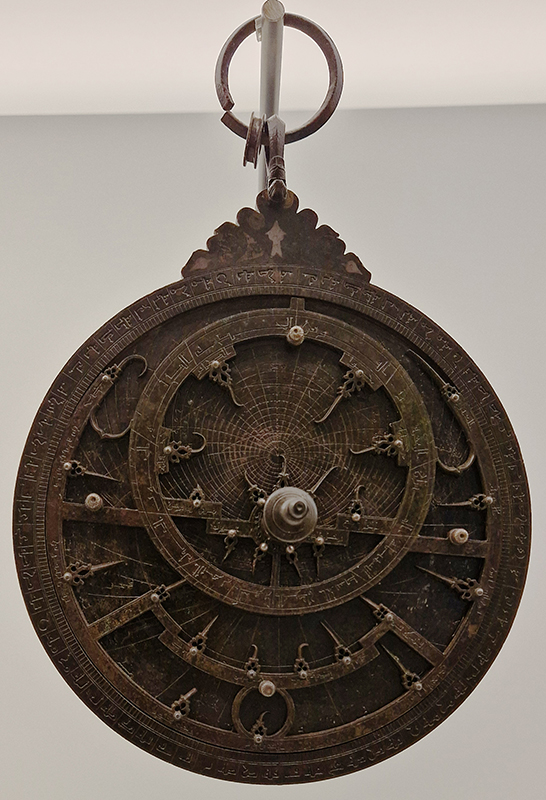
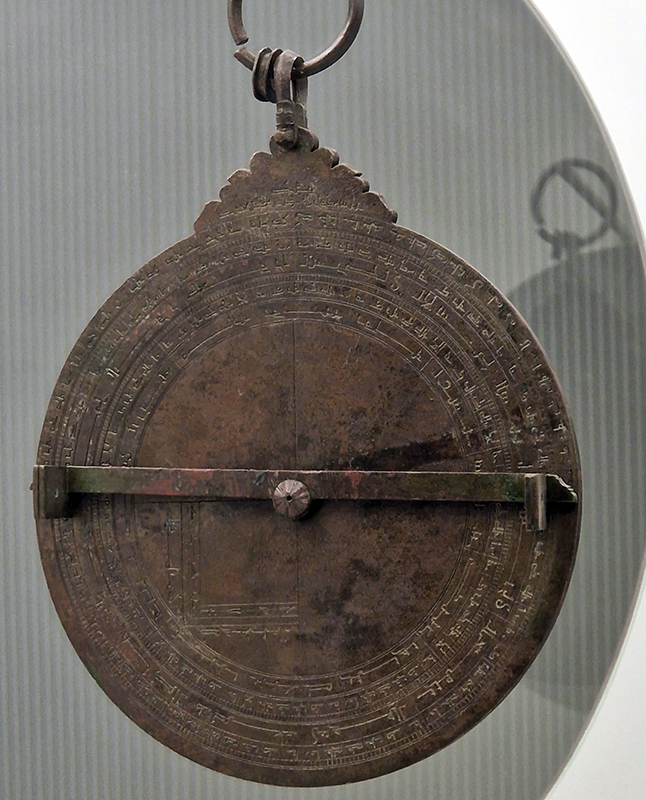
This splendid Chinese Compass, Lo P’an, also spotted at Royal Albert Memorial Museum, Exeter – used more for alignment of positive energy than navigation.

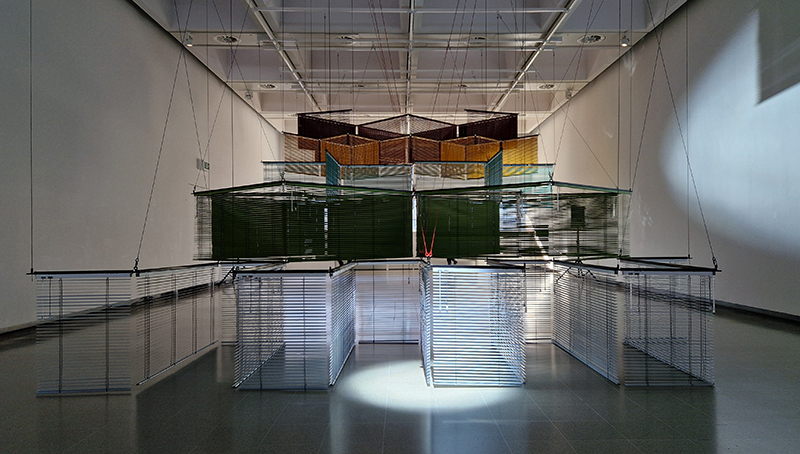
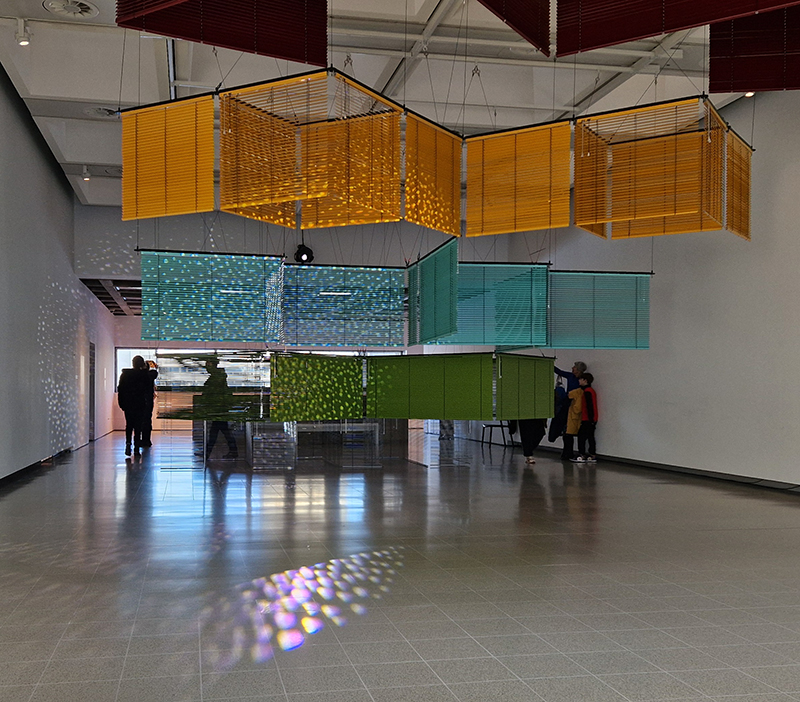
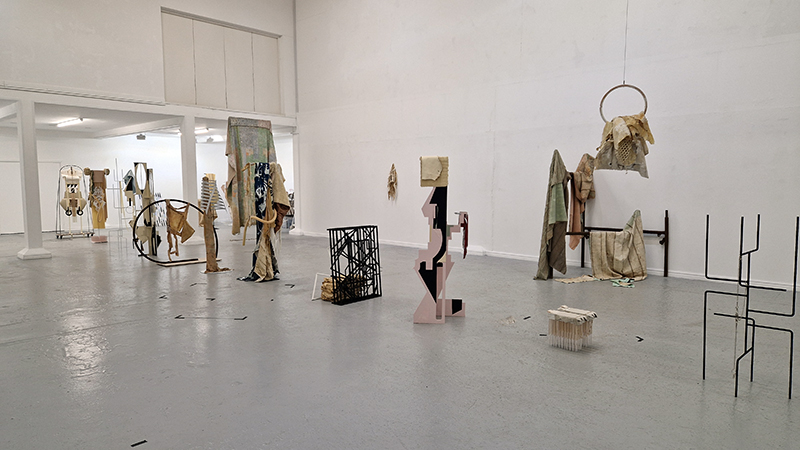
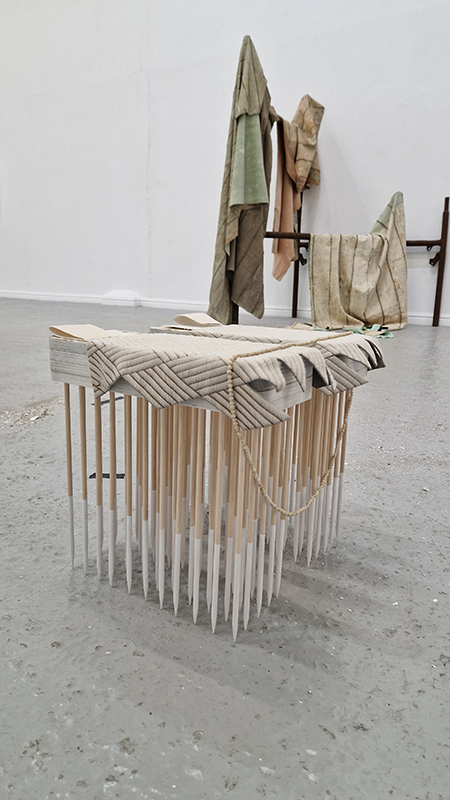
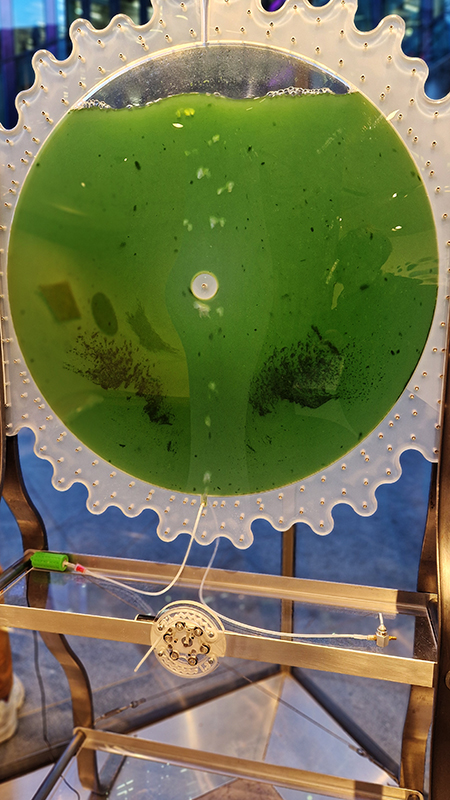
In Scope at Hypha HQ, Euston curated by James Grossman. An exhibition examining nested systems in nature, there were some fascinating symbioses of technology and natural materials such as live algae prints and sculpture capturing the tidal forces of the Thames estuary. Images 1-3 Alexander Clarke, 4 Will Laslett, 5-7 Kerrie O’Leary, 8 Star Holden, 9-10 James Grossman, 11 Peter James Nasielski, 12-13 James Grossman + Peter James Nasielski, 14 Hanne Peeraer
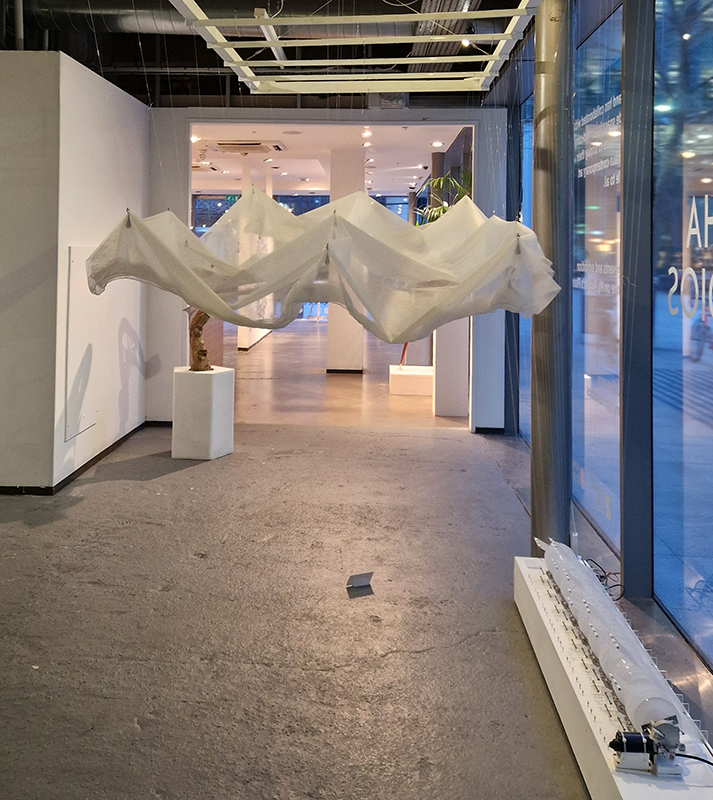
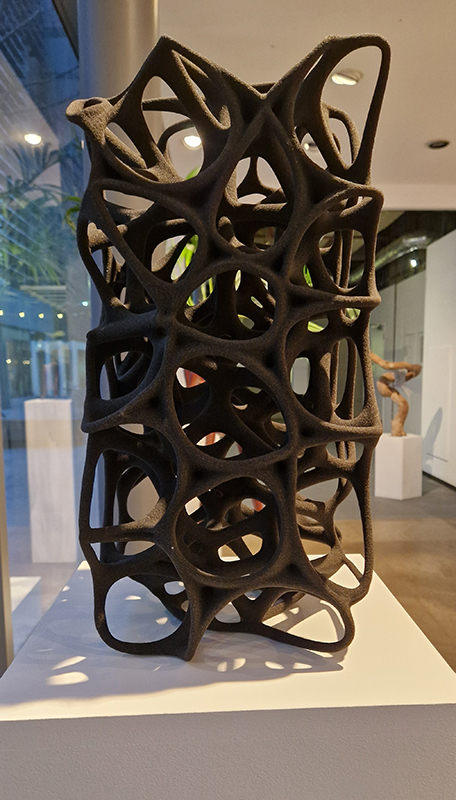
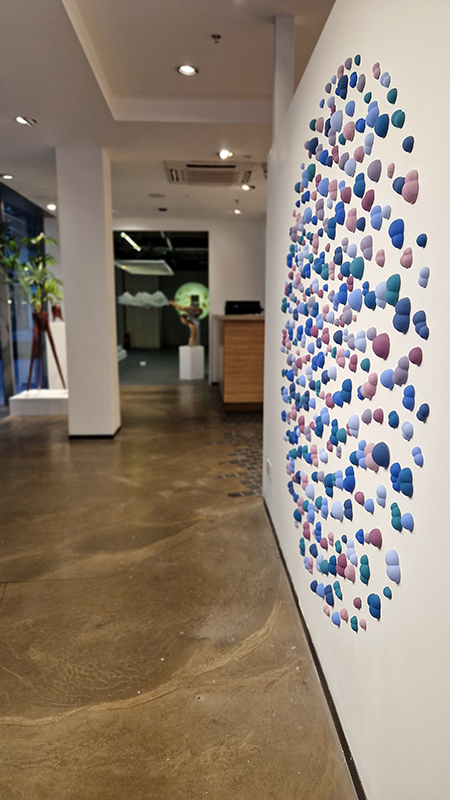
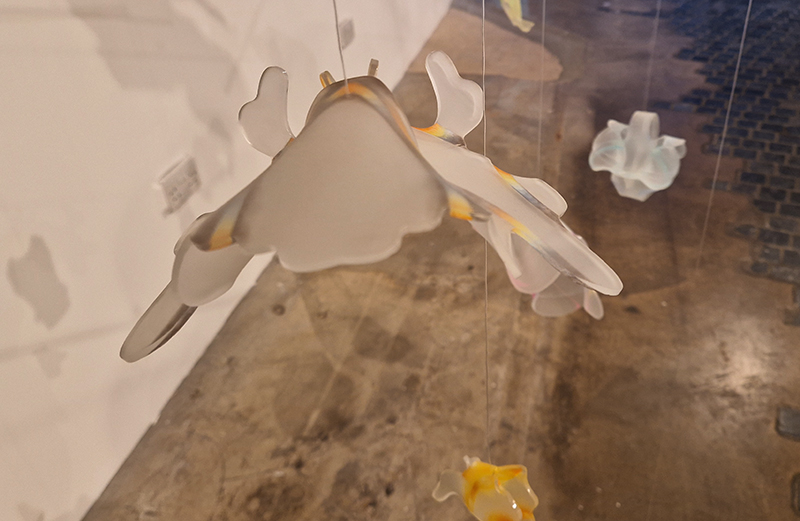













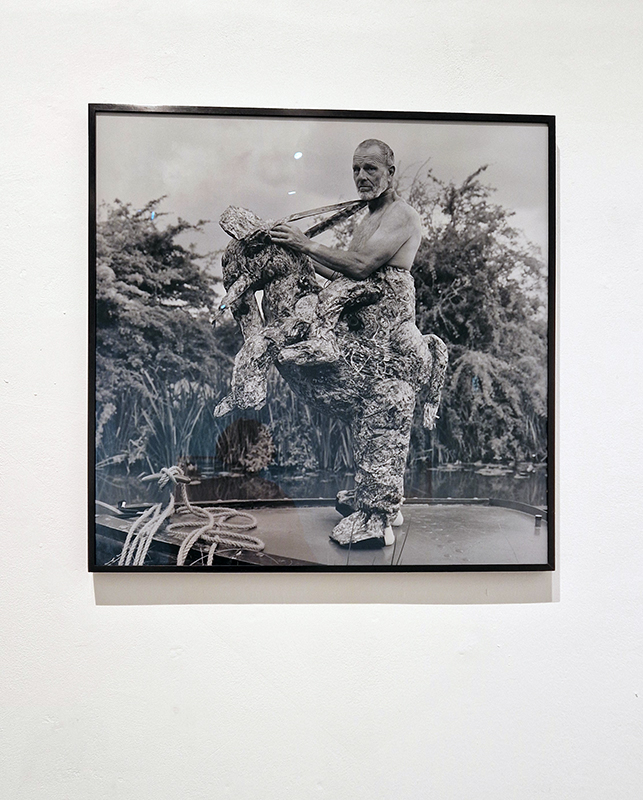
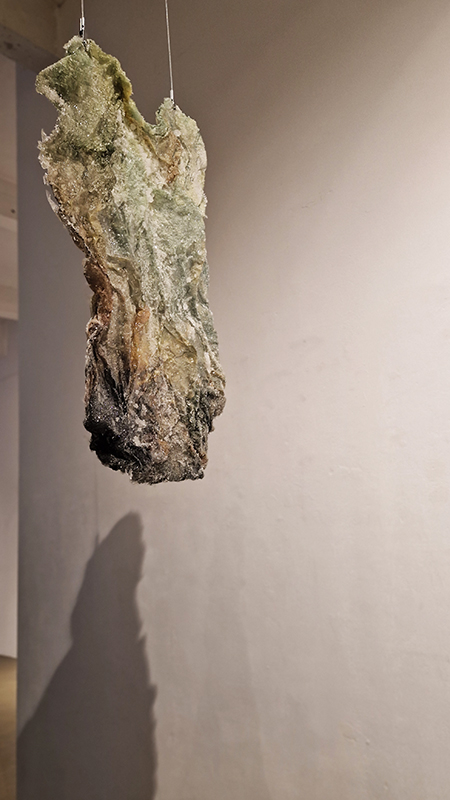
Great to see Sophie Mei Birkin’s Vestige in Joining Doggerland at APT Gallery. A semi-translucent, glittering, crystal encrusted form suspended like messenger from both the past and the future – a reminder of what once was and what might be.


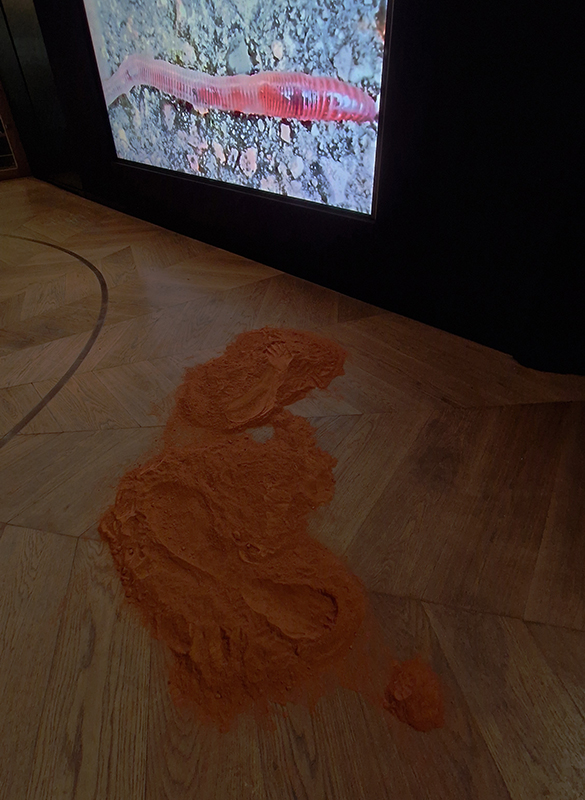
Citra Sasmita Into Eternal Land at Barbican The Curve. Having turned my hands and kitchen yellow recently grating fresh turmeric I understand why this circle of turmeric powder in the meditation zone was so closely invigilated. A calm scented area after walking the curve of colonial atrocities.

Mike Kelley Ghost and Spirit at Tate Modern. Sublevel (1998) is a model of the basement of CalArts, where he had studied in the 1970s. The spaces that Kelley couldn’t recall from memory are lined with pink crystal resin. The work stages a site of hidden memories and repressed desires, underscored by the symbolism of the pink coloured crystals, as Kelley explained: Because, as everyone knows, regardless of meaningless, exterior coloration, it’s all pink inside. Janelle Monae would agree and regardless of honourable/ironic sentiments employed the aesthetics left me feeling a bit like I’d time travelled to a seedy fairground scenario.


Glad I made it to see UBIK Hypha Studios at Sugar House Island from the Changeable Beast sculpture group. Inspired by the eponymous Philp K Dick novel, the artists invite viewers into speculative narratives of alternative futures. Images left to right: Weeping Willow Ellie Reid, Untitled (from the series ‘You Follow Me Around’) Ellie Reid, Things Said Susan Young, Return of the Dinosaurs Ornela Novello, Sunspots Tessa Garland, Timebeing Diana Wolzak, Inertials Clare Jarrett, Broken Nights Kay Senior
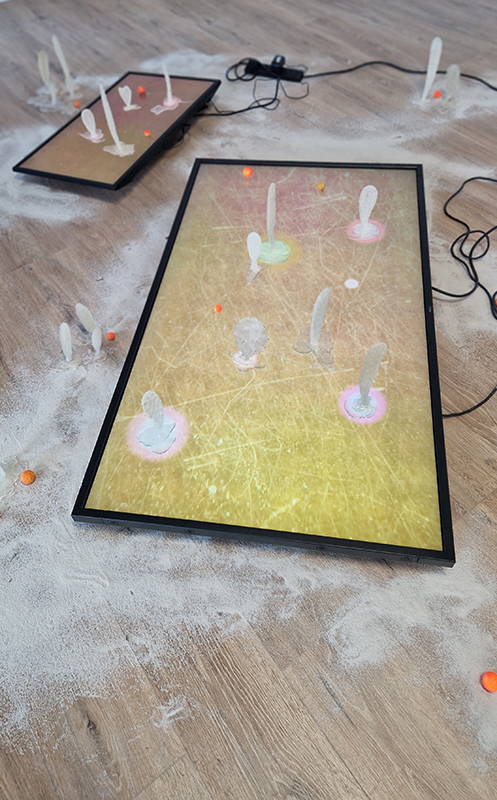
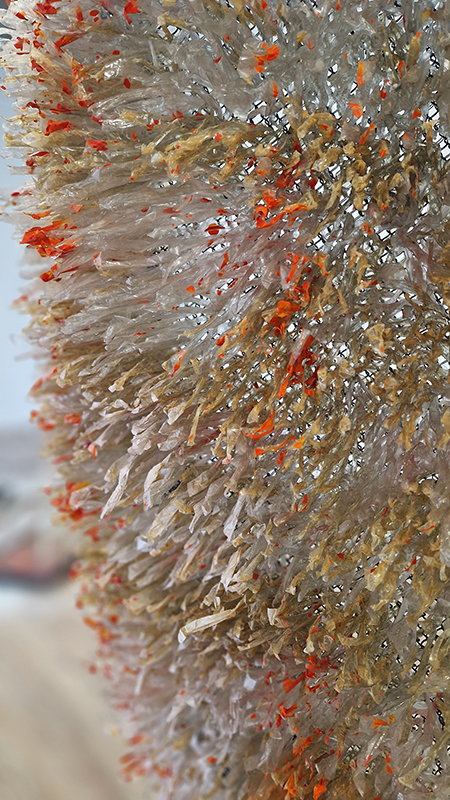
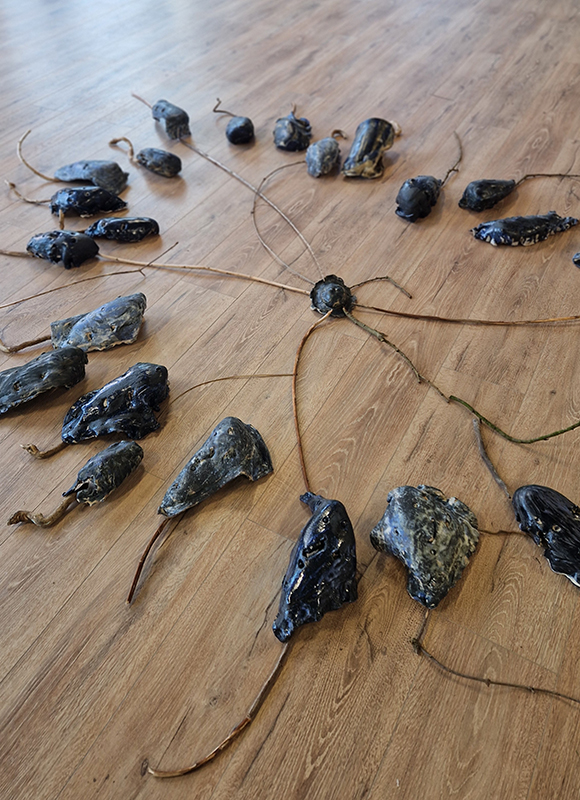
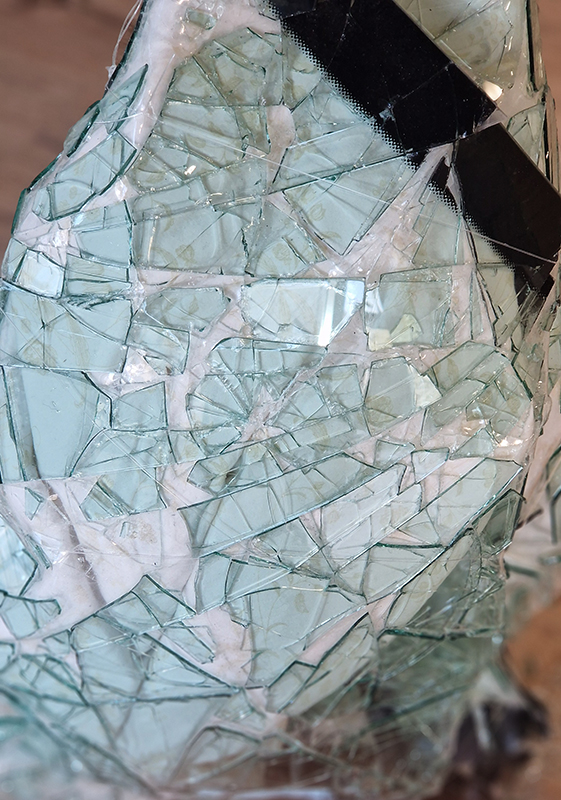








Soil: The World at Our Feet at Somerset House. As it says on the tin – the exhibition sets out to inspire and educate visitors about the power and the fragility of soil, its fundamental role in human civilisation and its remarkable potential to heal our planet. There is so much educational text that the bias of the experience veers towards the didactic. A lot of worms and impressive time lapse video – both of which I like very much and there are some interesting works here but after been slammed with so much ‘fact’ and repetitive tropes it becomes a bit wearying, which is a shame. Sam Williams Wormshine seven channel video collage had a fitting sensitivity to worms as unsung heroes of soft power. Maeve Brennan roman soil with microplastic contamination gave stark evidence of a toxic legacy leaching through the water table to infect roman artefacts. Diana Scherer has woven an intriguing substrate using natural growth processes to generate structures from root tissues. I was interested to see how microscopic soil bacteria can have the appearance of agate and a cross section drawing of a root reminded me of my Mum’s crocheted doilies.
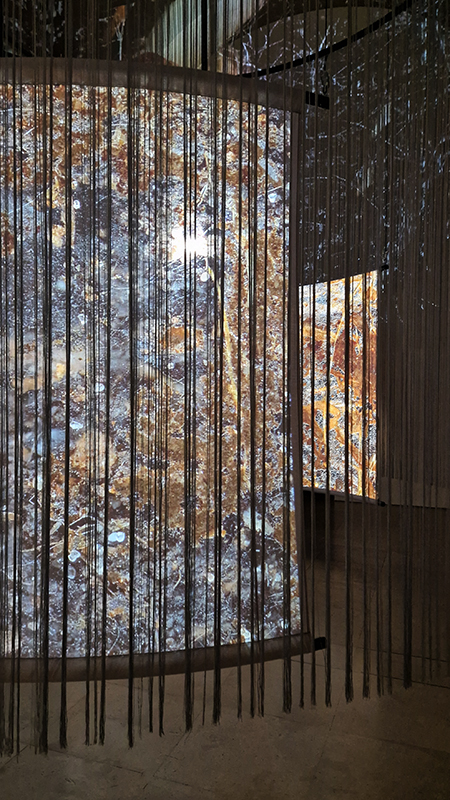
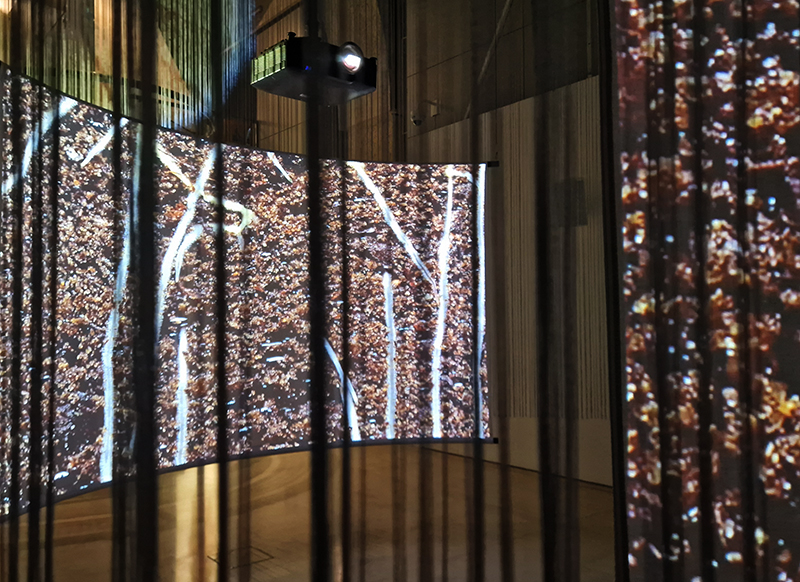
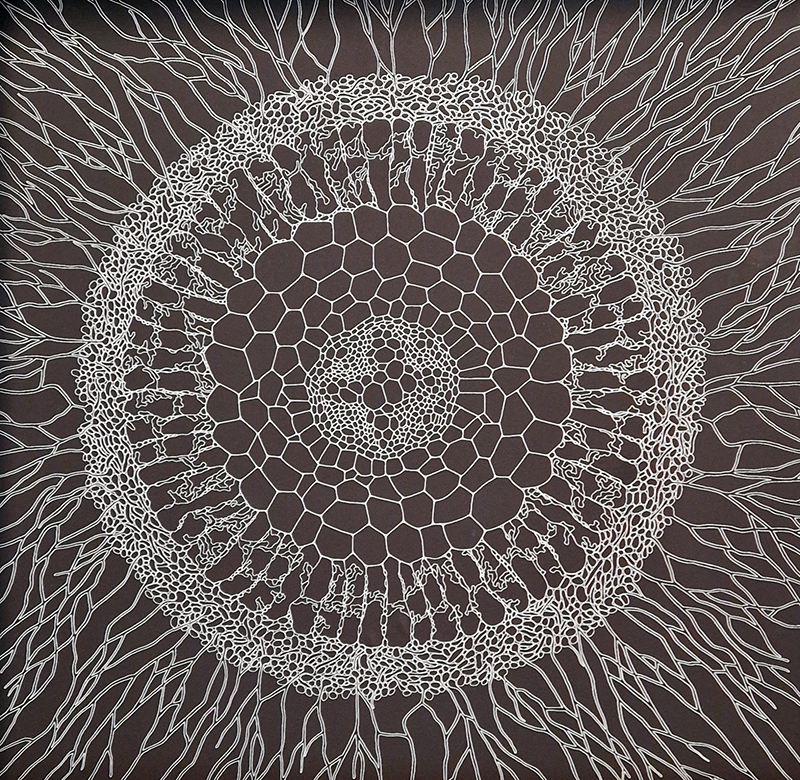
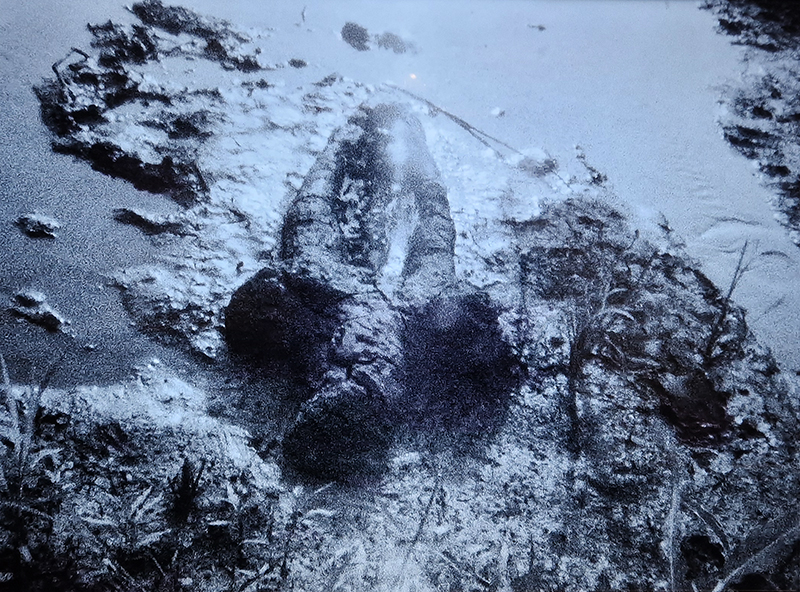
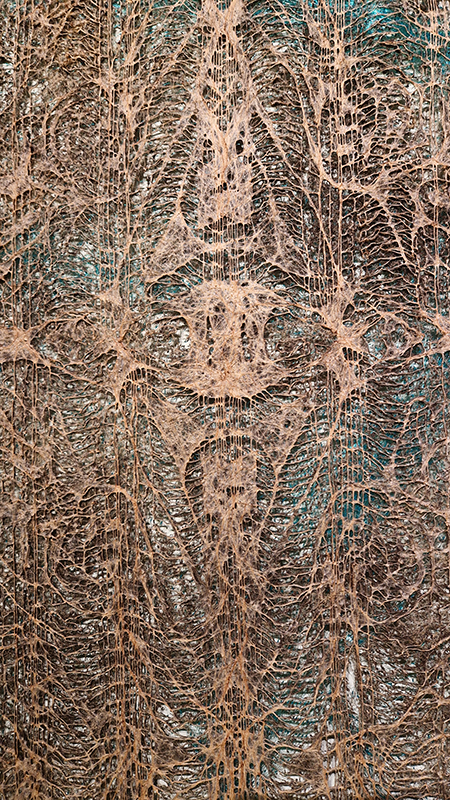
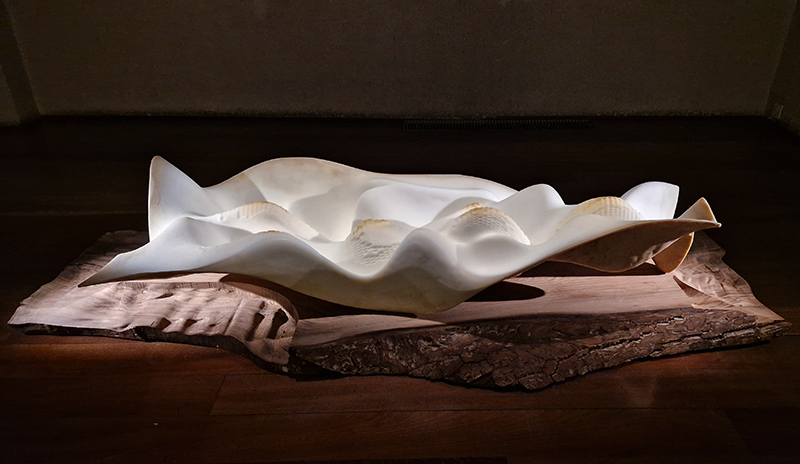
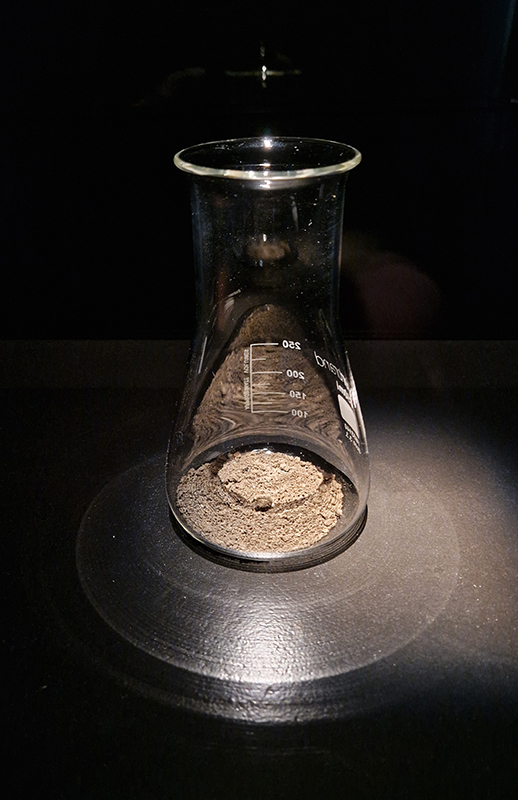












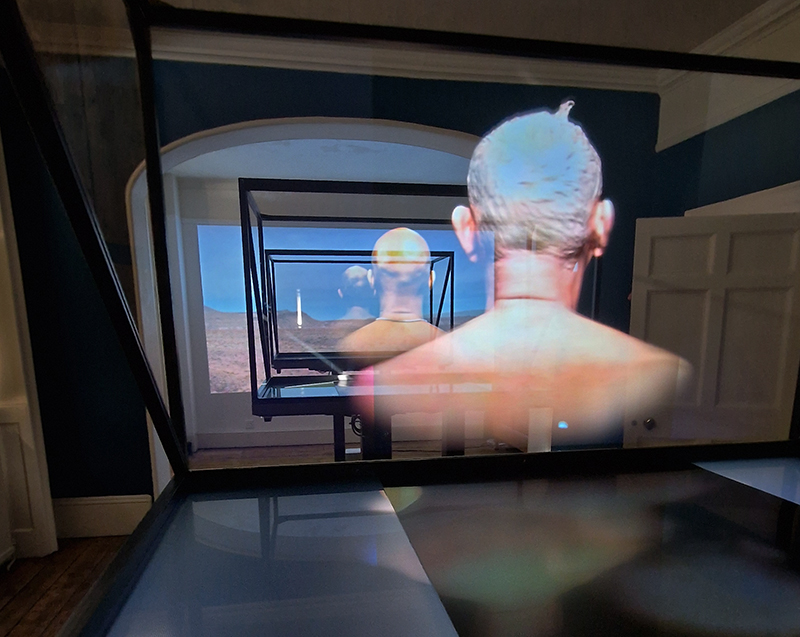
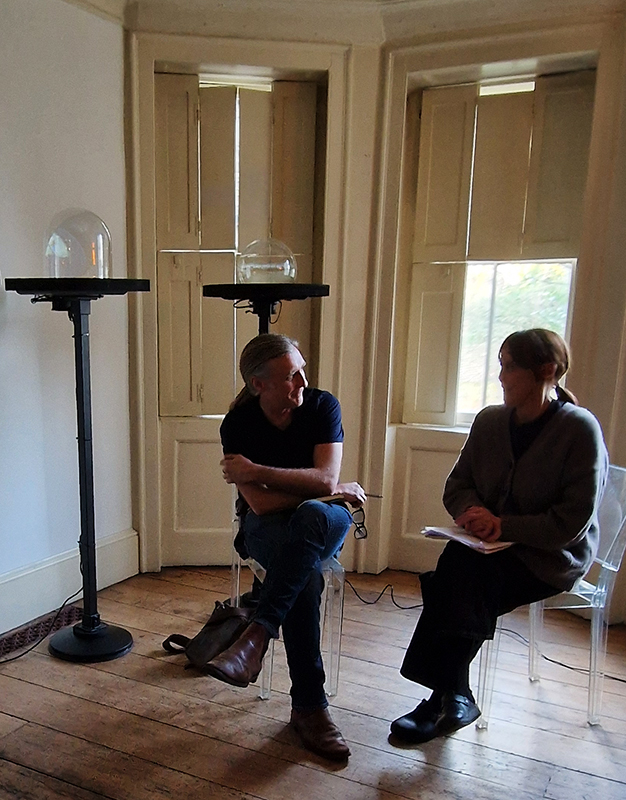
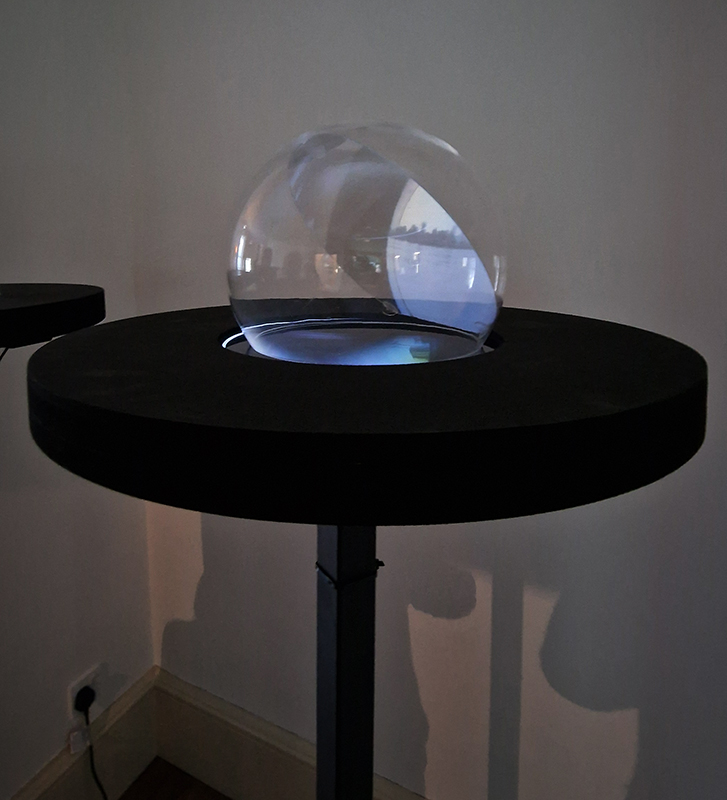
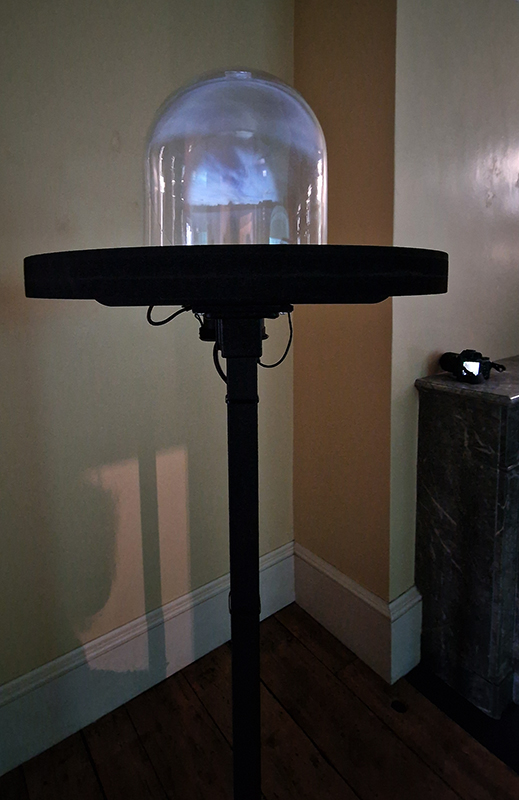
David Cotterell in conversation with Amanda Crawley Jackson, (LCC Professor of Place and Culture / Dean of Research and Knowledge Exchange), at Danielle Arnaud discussing the exhibition and underlying themes of the sublime, suburbia, estuaries, deserts, and human inconsequentiality. Albert Camus’ absurdism philosophy was referenced in respect of the inability to know the world and the world’s indifference to human attempts to even try. David has visited and documented some amazing wide open landscapes of Afghanistan and Mexico where the sublime is inherent in the experience of isolation, vulnerability and awe. We see these in the projected works here. The choppy expanse of the Thames estuary is encapsulated into spherical and domed microcosms, like seeing visions in a series of crystal balls set at eye/brain level – so also a bit like peering directly into the mind’s eye. He expressed the desire to share the experience of being in these landscapes – I think he did share the wonder. He also talked about his visit to Donald Judd’s sculptures in Marfa, Texas where even megalithic sculptures are overwhelmed by the scale of the environment and the milky way is not beyond, but within touching distance.
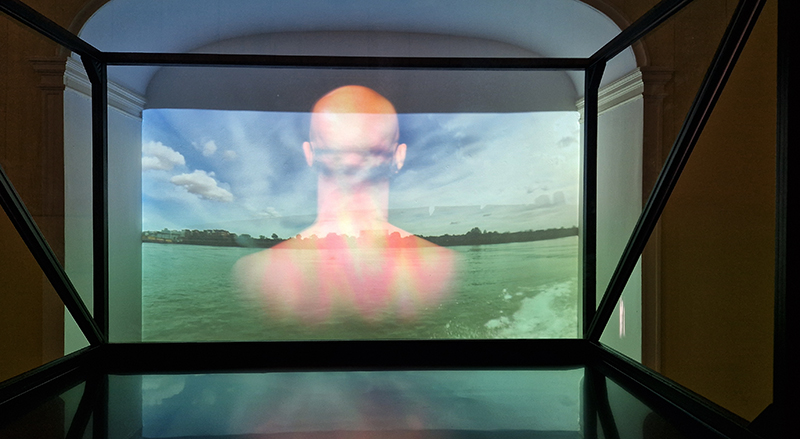






Events
Royal Astronomical Society Friends Lecture from Dr Steven Banham, Imperial College London. This was an in depth reveal on the geology of Mars. The Mars Science Laboratory mission’s Curiosity rover landed in Mars’ Gale Crater in August 2012. About the size of a MINI Cooper, Curiosity is equipped with 17 cameras and a robotic arm containing specialized instruments. It has explored the northern margin of Mount Sharp for 4451 Martian sols providing compelling evidence that shortly after crater formation, a habitable environment existed here. The rocks that form lower Mount Sharp preserve a record of persistent lakes fed by fluvial systems originating from the crater rim. As the rivers entered the lake, they released plumes of sediment and assorted nutrients into the water column to be distributed across the lakebed — recorded as the Murray formation. Geochemical and mineralogical assessments indicate that environmental conditions preserved in these layered rocks would have sustained life, if it were present. On Sol 3047, Curiosity made a sharp right turn after crossing the phyllosilicate unit, to drive up into the orbitally-defined sulphate-bearing unit. From this point, Curiosity witnessed distinct changes in the stratigraphy, recording a progressive drying of the ancient environment. The rover identified a gradual change from humid conditions containing a record of perennial lakes, to isolated ephemeral lakes, and onto desolate deserts. During this ascent, interstratification of aeolian strata became increasingly common, including sand sheets, dune strata and deflation scours. However, despite this general aridification, the succession was occasionally punctuated by episodes of abundant water: the Amapari ripple bed for example, records a brief shallow lake: a veritable oasis, free of ice.

I travelled to Manchester to see Figures in Extinction, a dance trilogy exploring the age of disconnection. A beautiful, haunting and sobering collaboration between choreographer Crystal Pite, NDT 1 dancers and Complicité director Simon McBurney. The first section confronts the extinction crisis and climate change deniers, listing the last of each species vanishing from our world; the second section addresses human isolation in a world dominated by technology and data, the divided brain where the intuitive side of our brain has not been nurtured leaving the rational unempathetic side to be dominant, and the final section draws our focus to death, physical decay of the body and grief, urging an honouring of our ancestors – the dead, having lived are not inert. The lighting throughout was amazing but particularly extraordinary in the closing scenes as ethereal spectres swarm the stage. The dancers, so precise in their movements delivered a hugely emotional homage to life on Earth.

East is South by Beau Willimon at Hampstead Theatre. There was a lengthy monologue on equivalence in this fast paced play projecting a future where AI or AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) learns to take on the experience of faith over logic. Two coders stand accused of releasing a dangerous AI to infect processors globally. Their motivation interrogated as potential spy or subject to religious cult beliefs. “God didn’t create the universe,” it may be “the universe’s project to create God.” After all, if Agi escapes to colonise the internet, knowing everything about everything, and having power over everything, wouldn’t “she” become our “God?” With personal memories questioned as truth as much as being duped by others for their own ends, there is no clear path in a complete breakdown of trust and authority. I see this play has had a lot of bad reviews – it is dense with ideas and maybe the interrogation format is not new but it has a lot to say that is relevant.