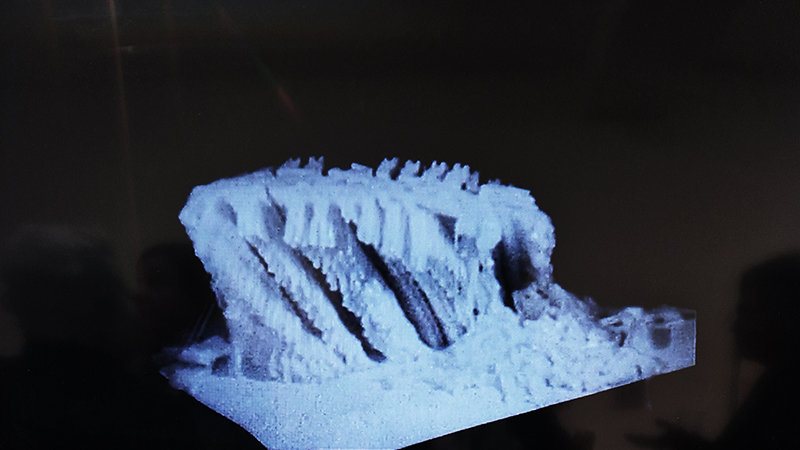
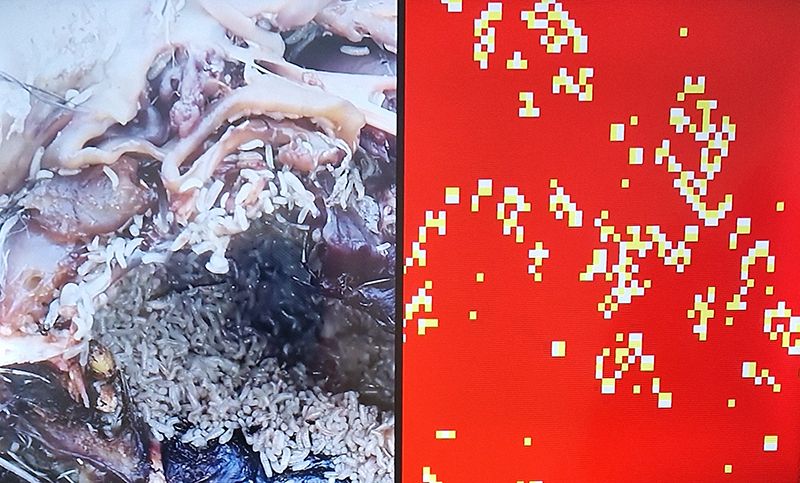
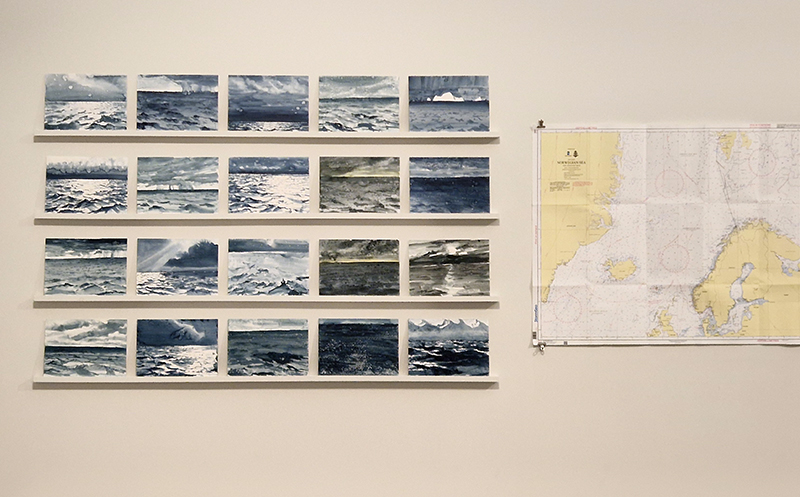
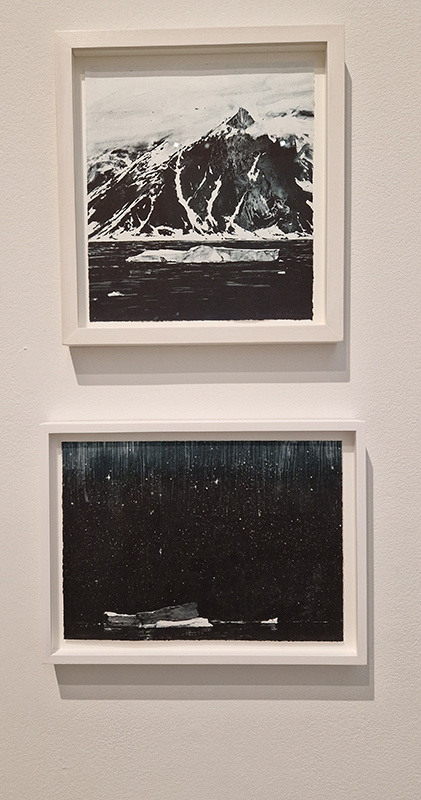
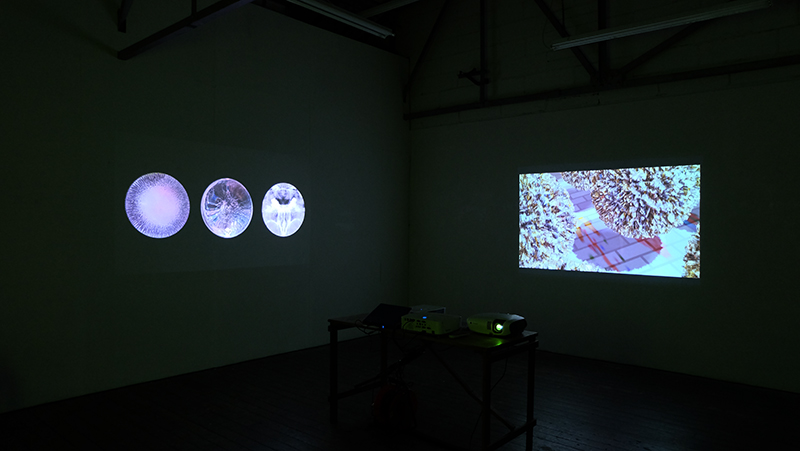
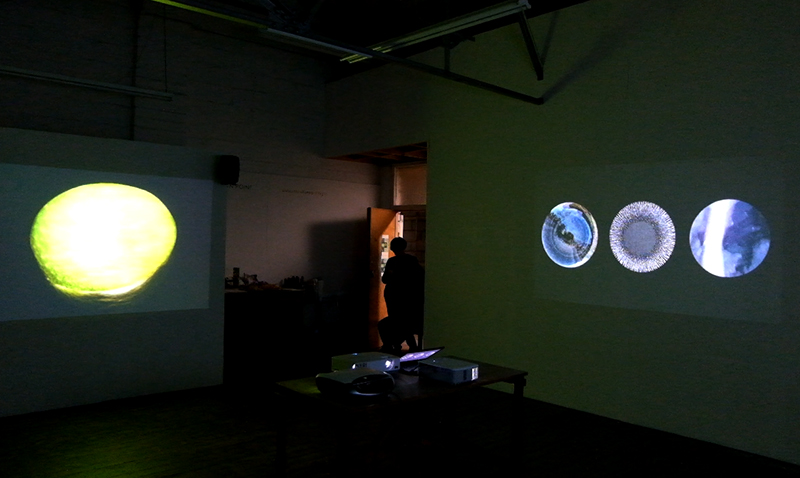
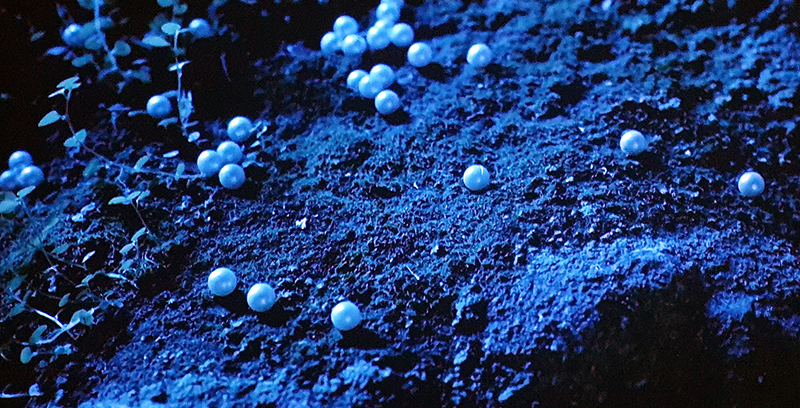
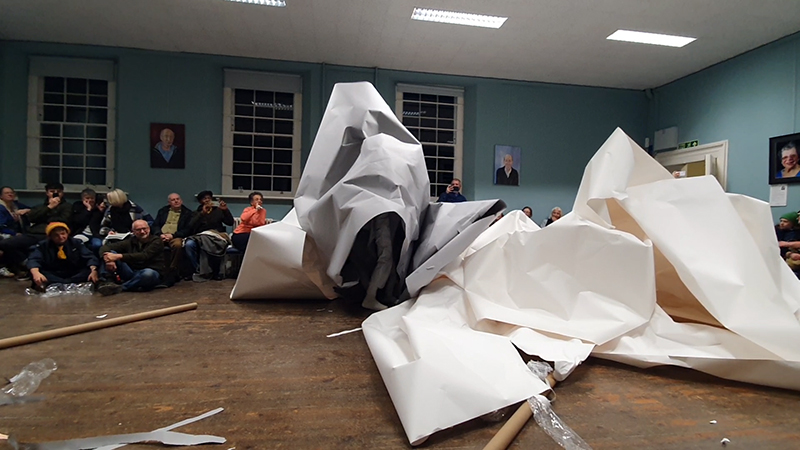
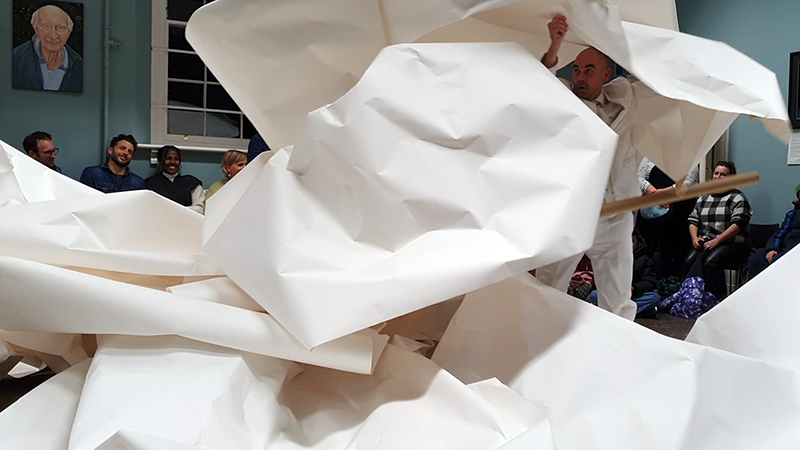
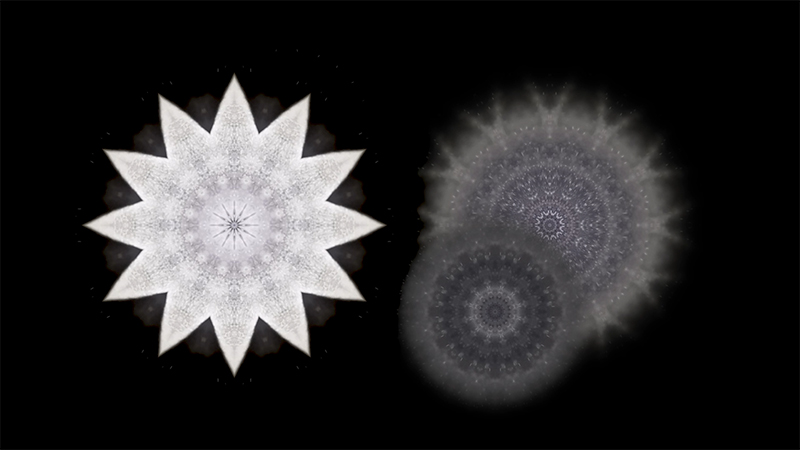
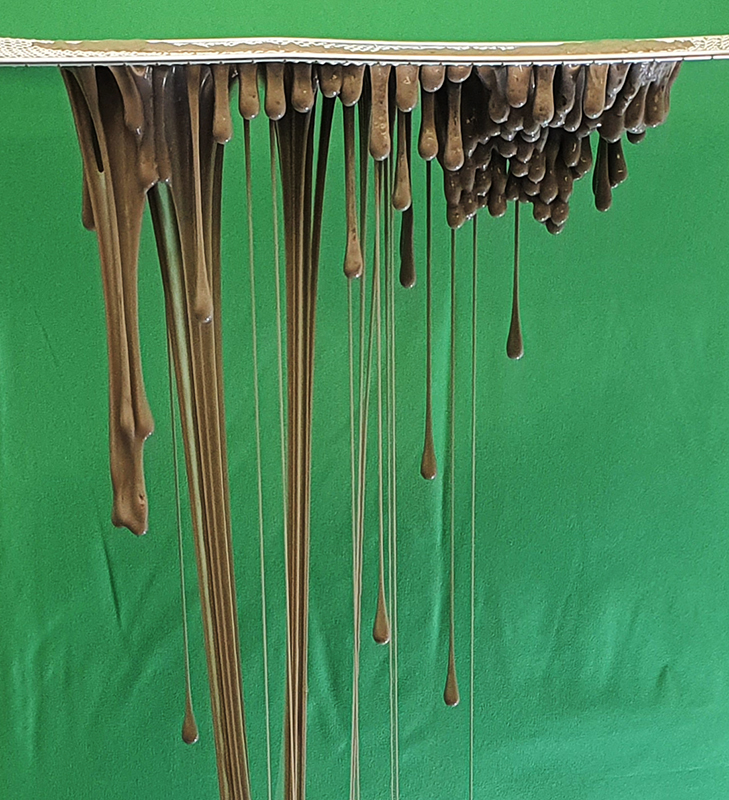
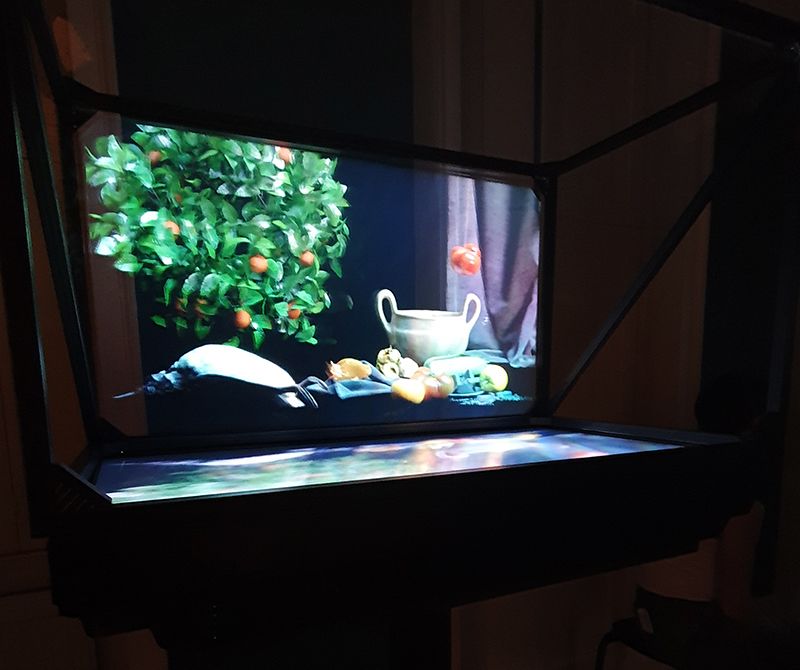
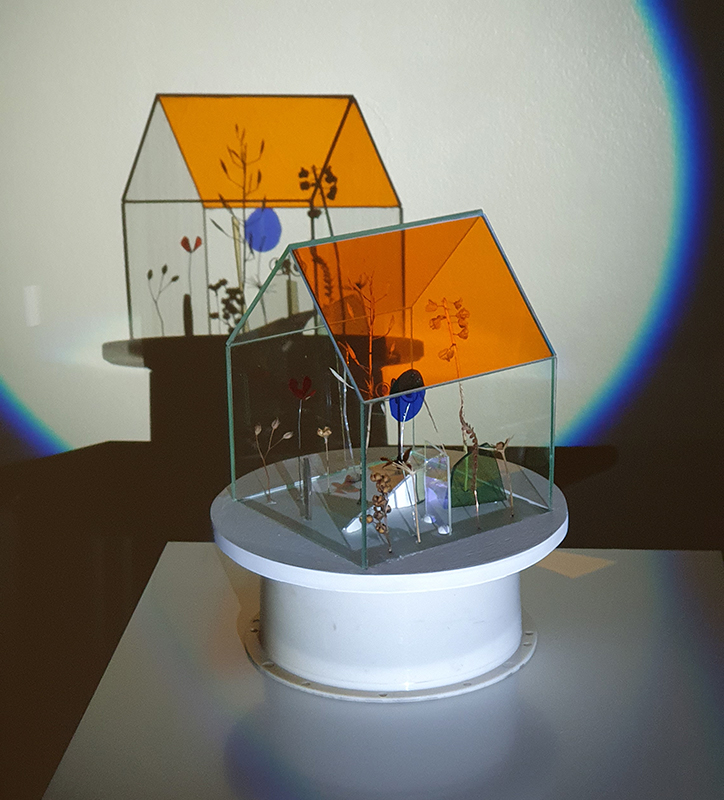
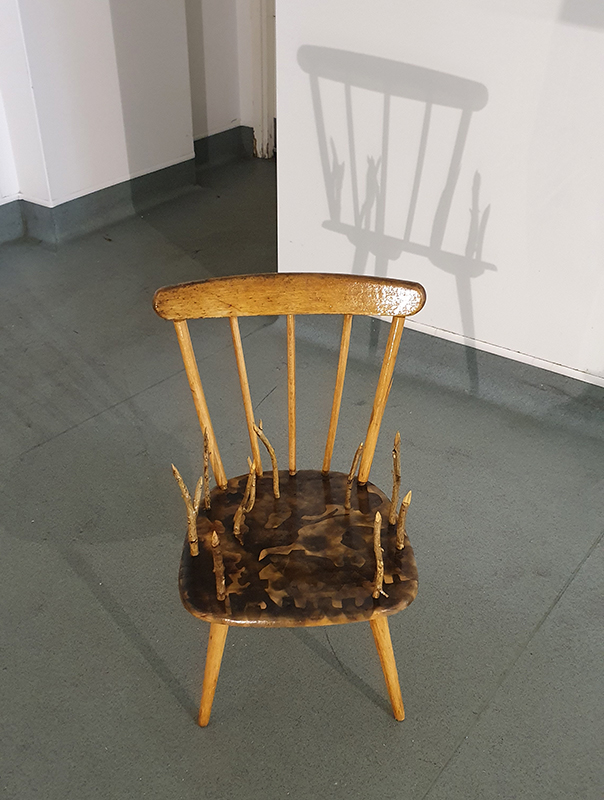
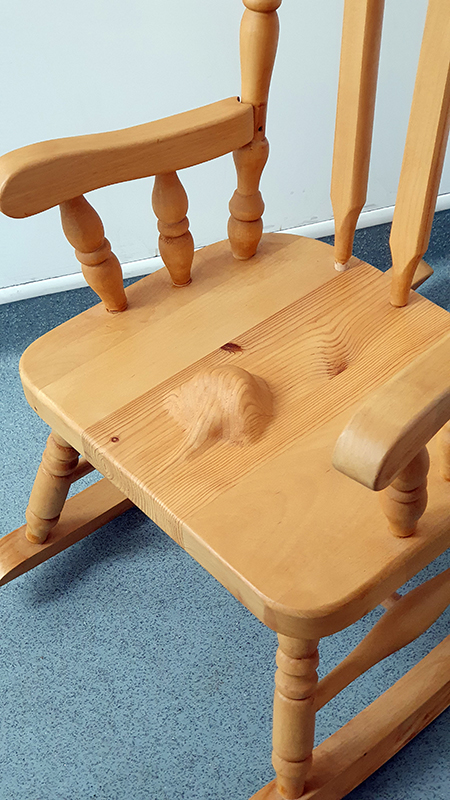
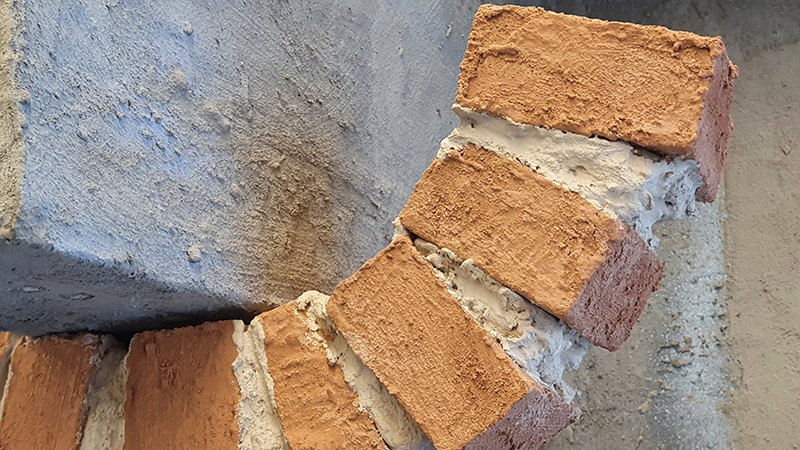
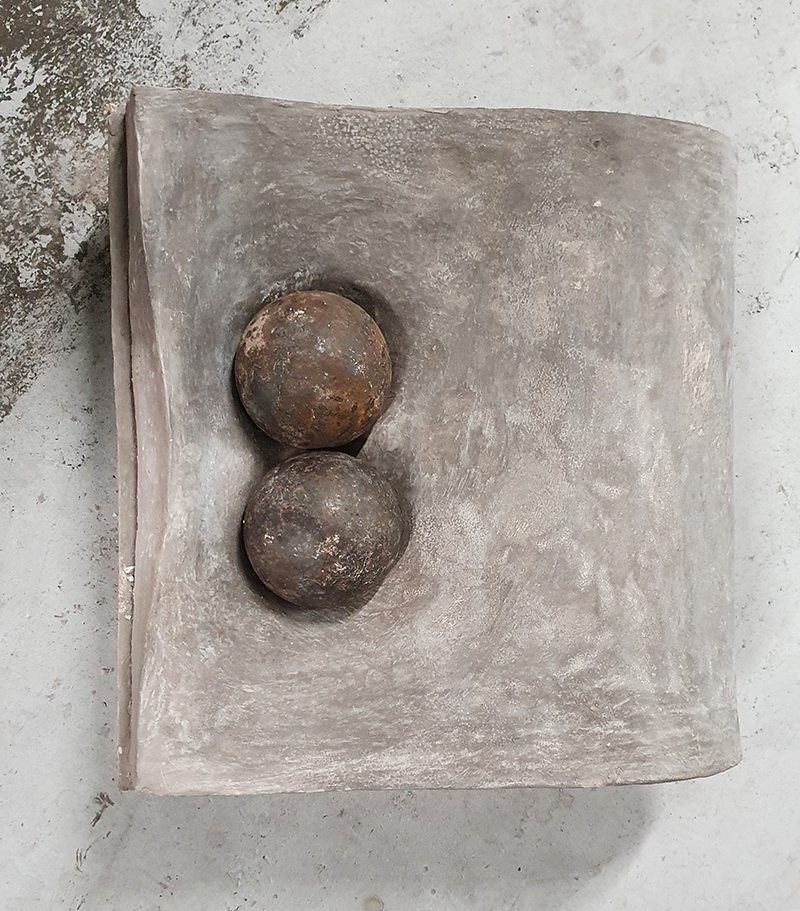
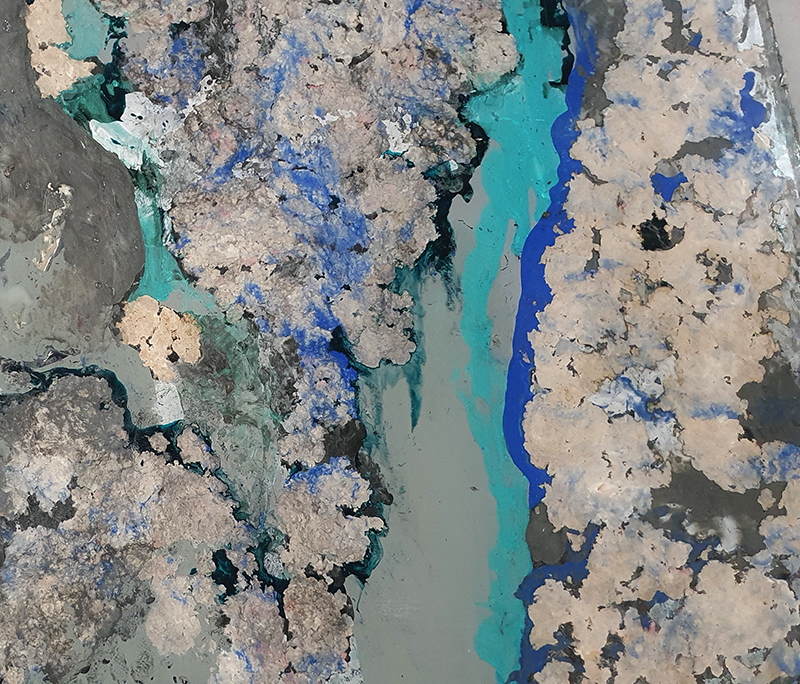
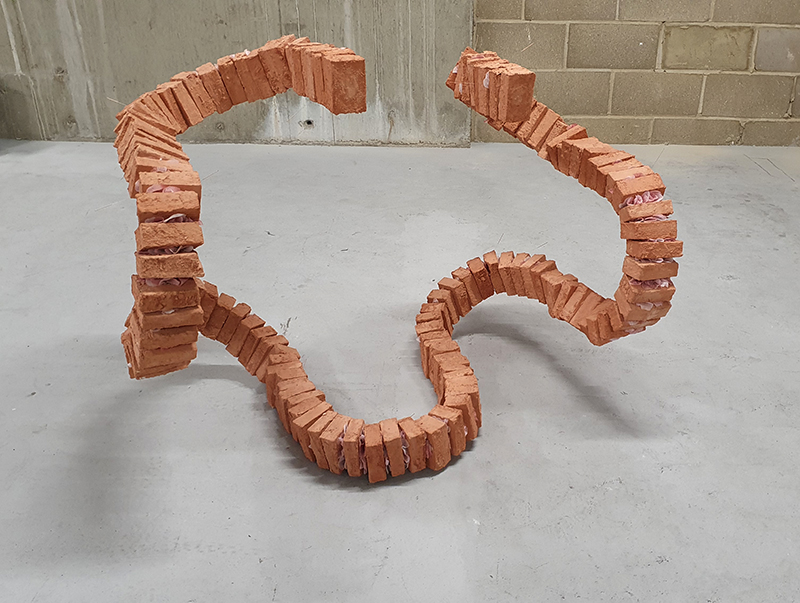
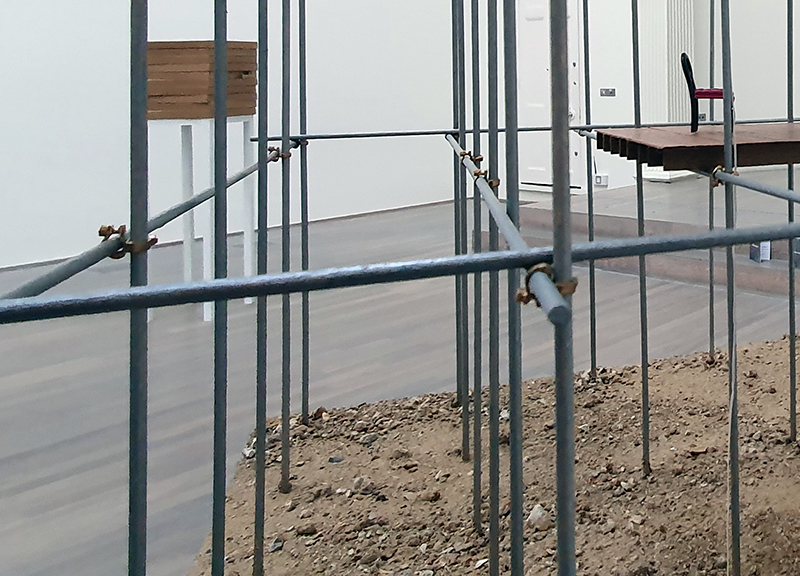
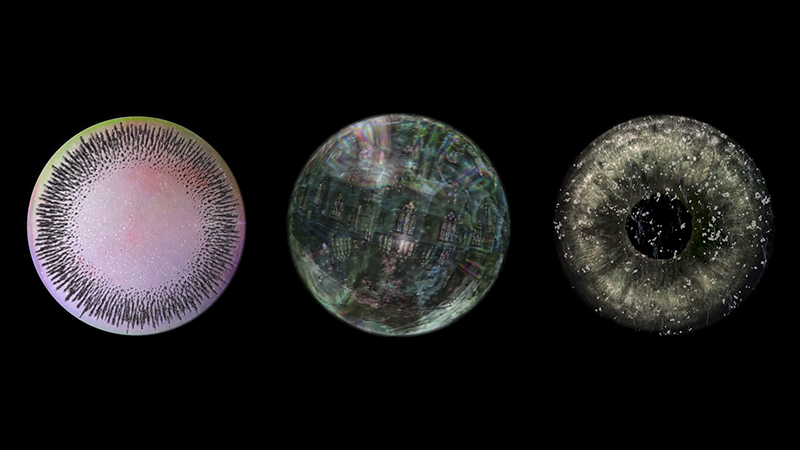
I am enjoying discovering the gutter creatures who share my home. Gathering video footage of an alternative cosmos to go towards making work which will be shown in Occupied: Strange Company at the Safehouse next year, a group exhibition curated by Julie Hoyle.
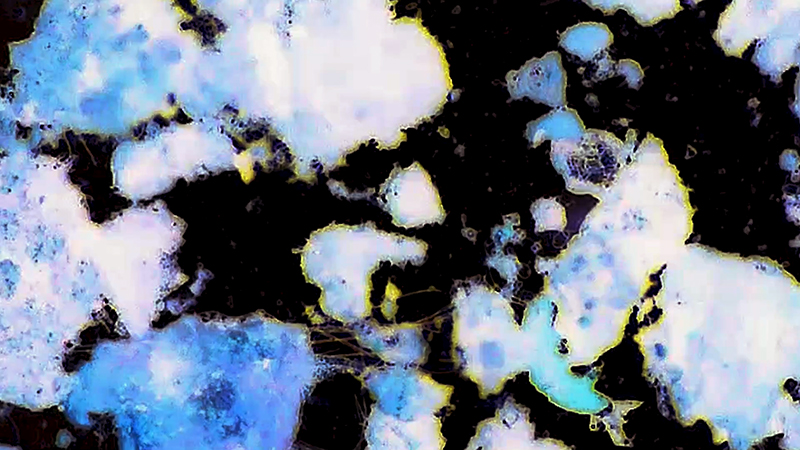

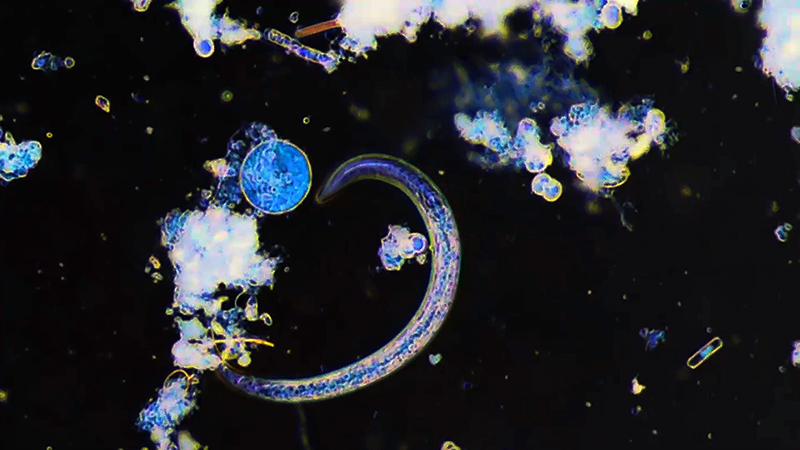
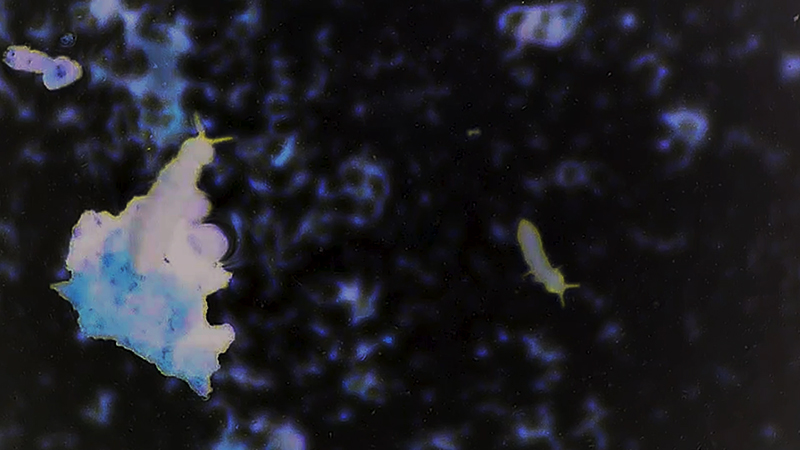
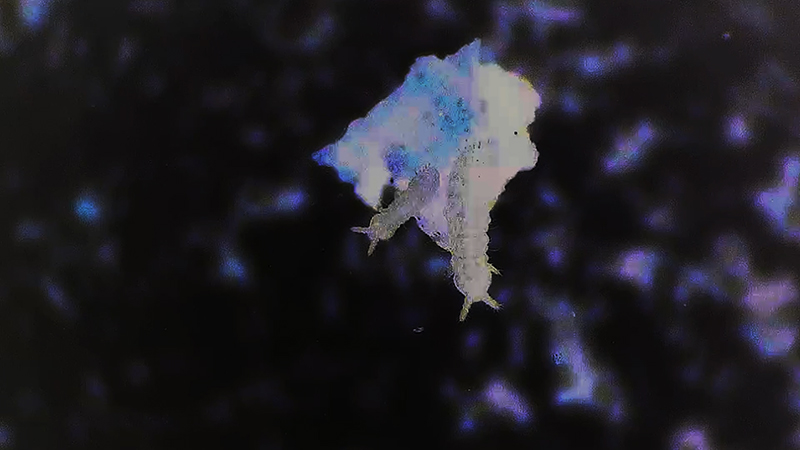
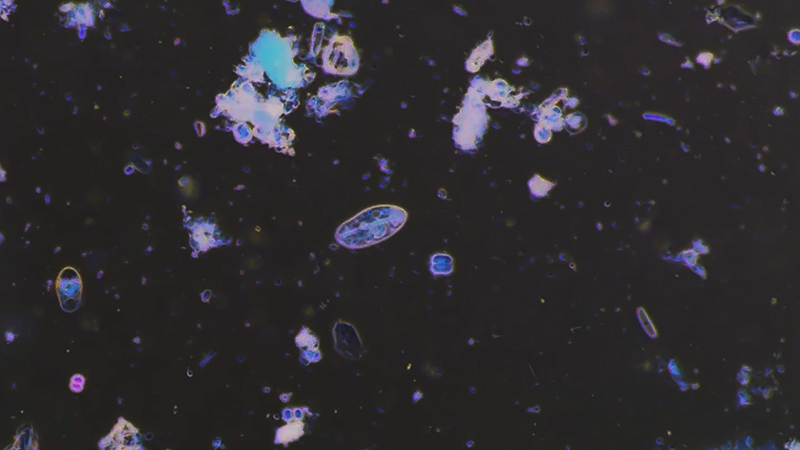
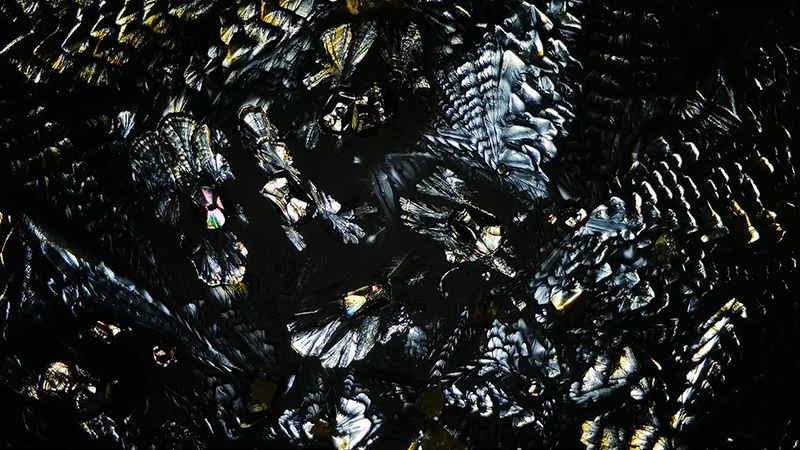
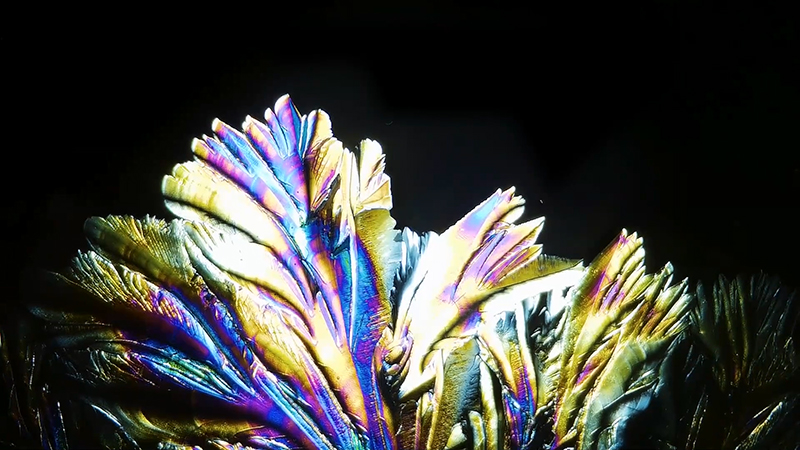
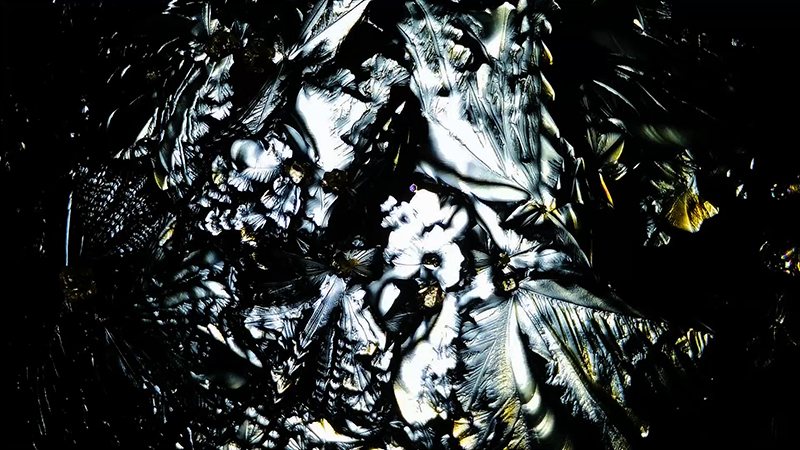
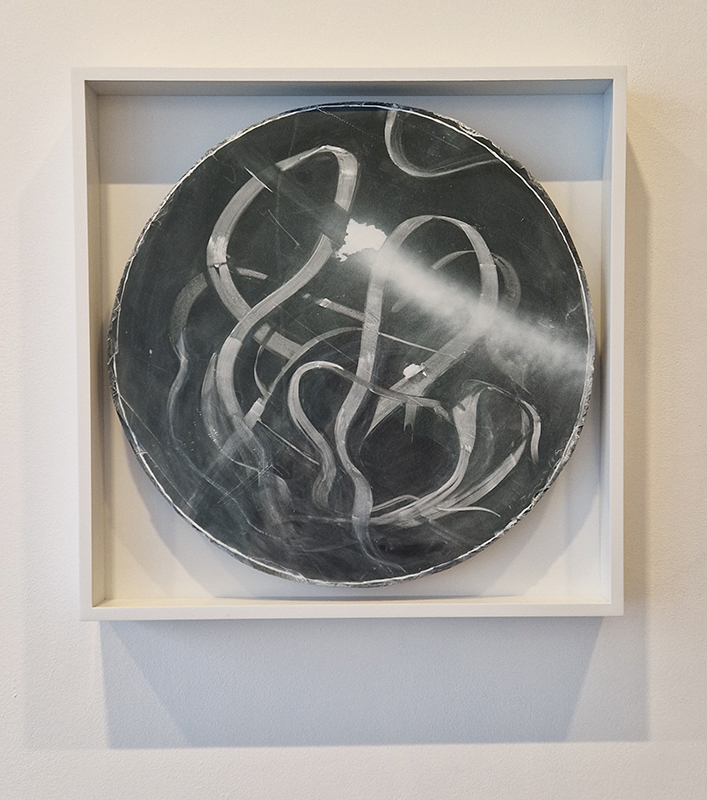
My experiments growing citric acid crystals have been going well. I am filming these transformations under polarised light which reveals the many vibrant colours but I also like the images without the filter. The structures remind me of feathers so I am thinking about creatures that flutter as well as those that swim.




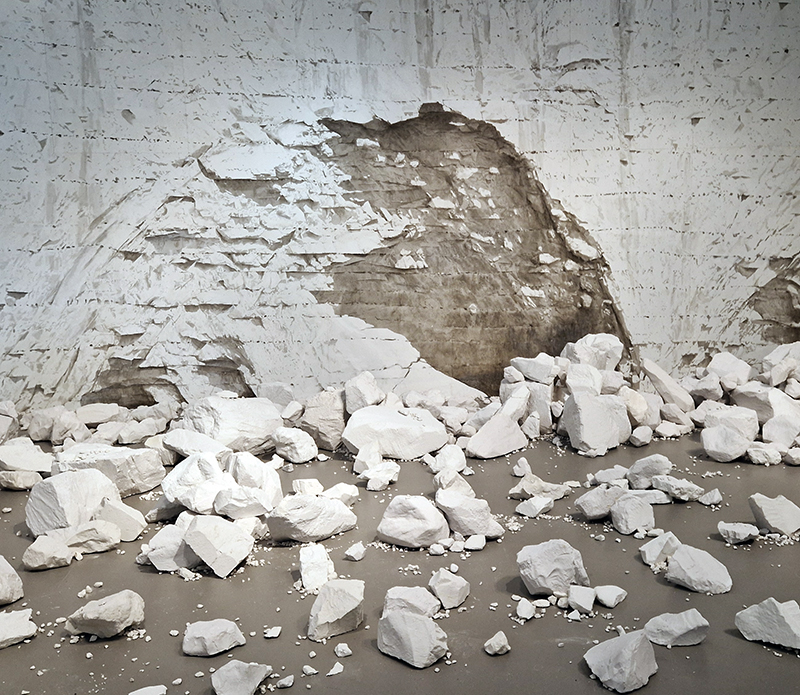
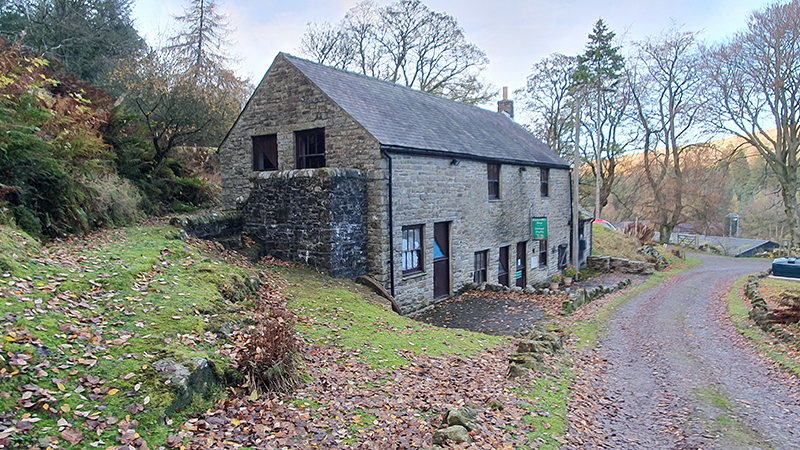
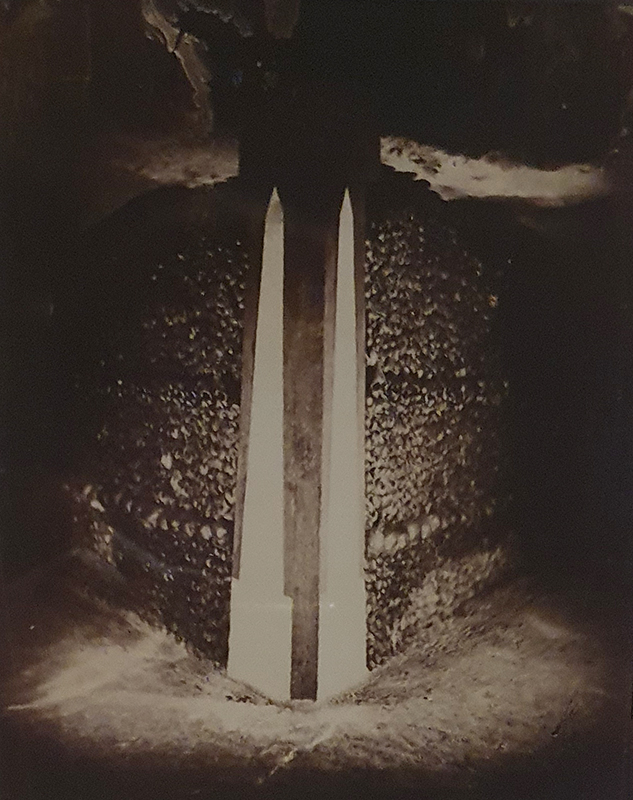
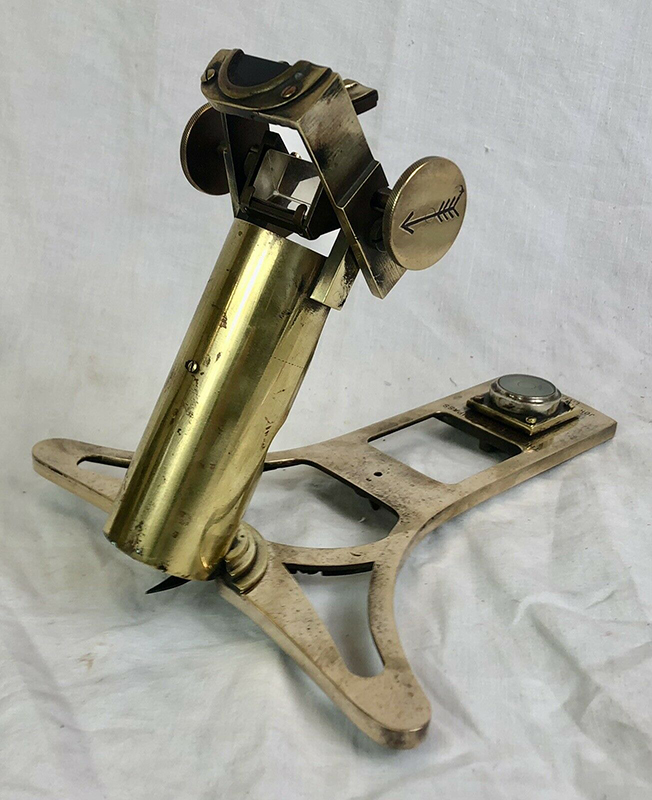
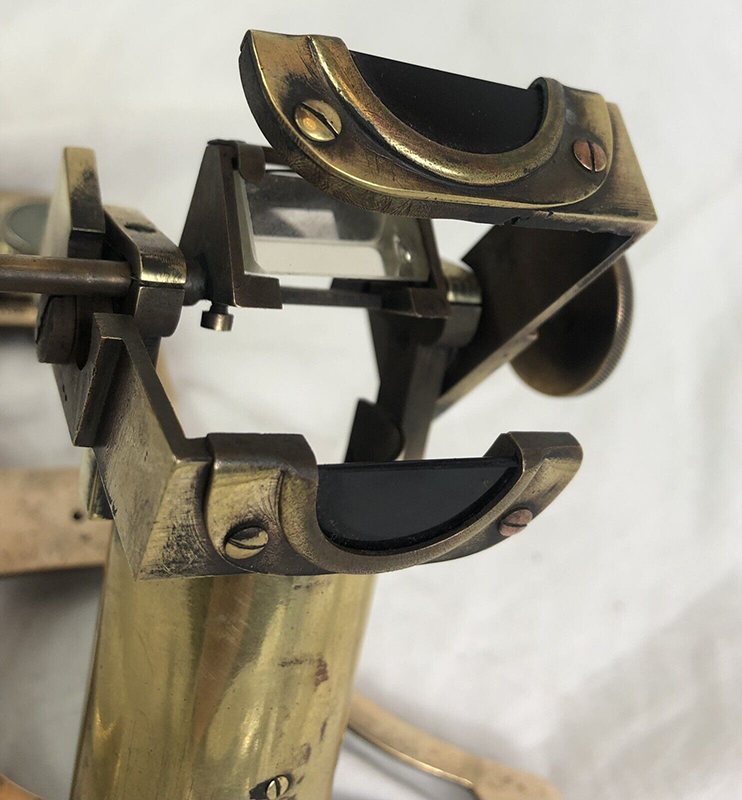
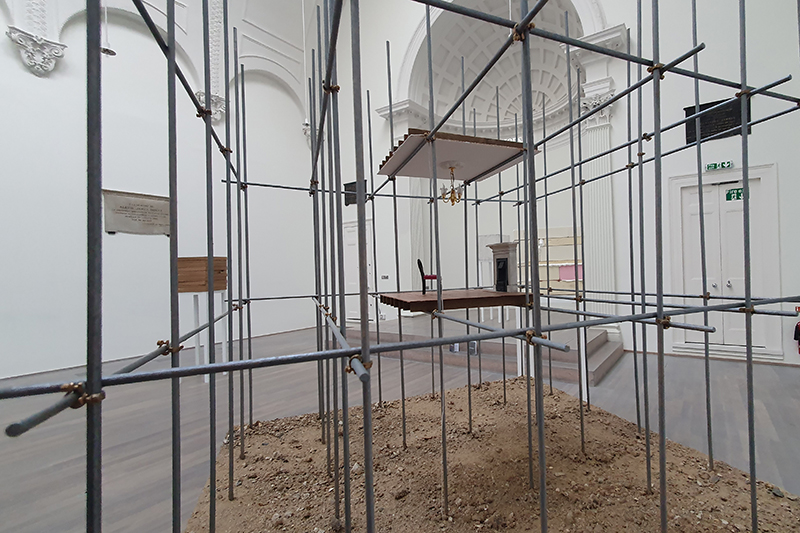
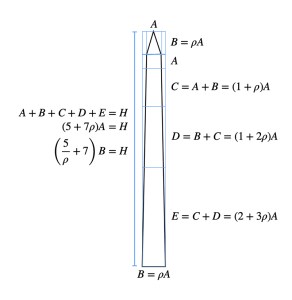
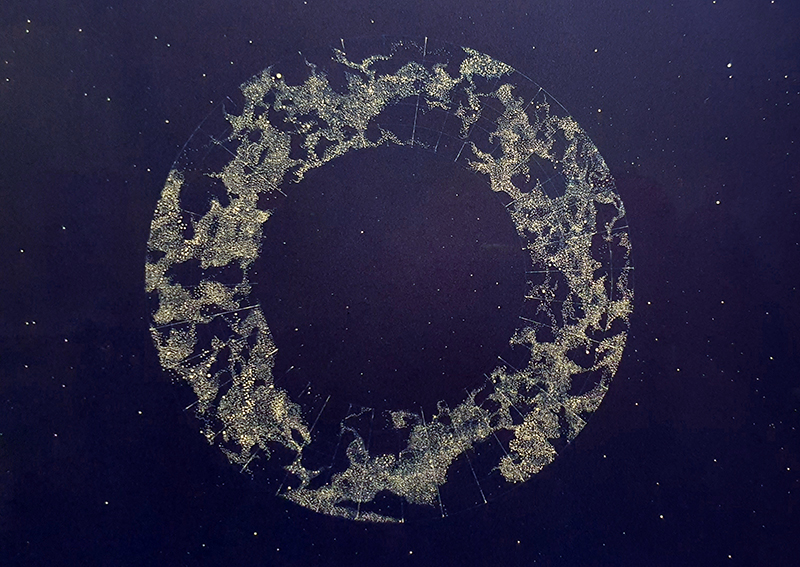
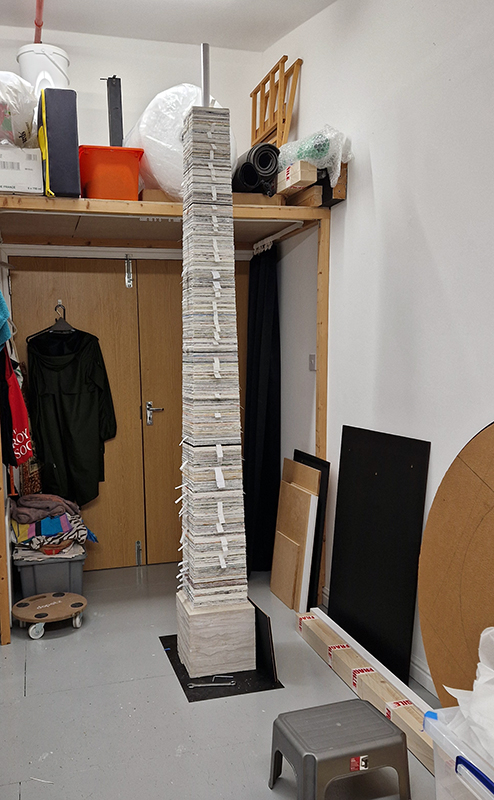
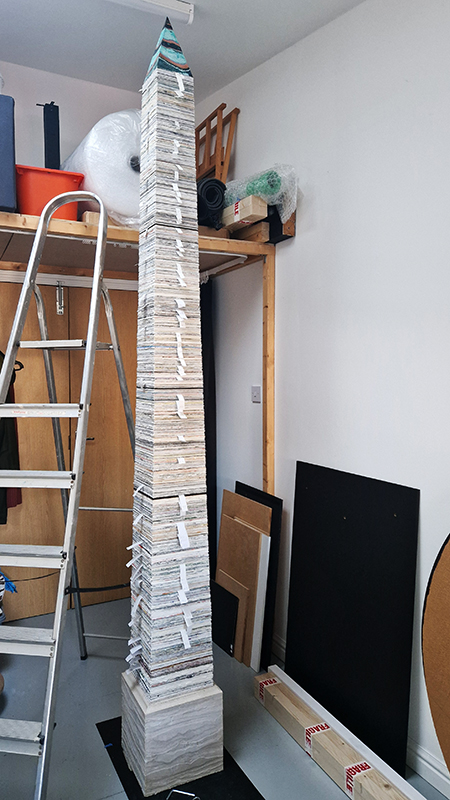
Time in the studio has been spent checking over and preparing works that will be showing in Cosmos: The Art of Observing Space curated by Ione Parkin which opens in the new year. I am thrilled to be part of this exhibition bringing together contemporary and historic artists and featuring an extraordinary range of work inspired by the cosmos. I have completed a test build of The Azimuth Obelisk (of sedimentary knowledge) using a new internal structure for before packing it all away again ready for transport to The Royal West of England Academy in Bristol. This work is a reimagining of an permanent azimuth mark erected at Hartland Magnetic Observatory in North Devon from which the drift of the magnetic north pole is monitored. Made of many layers hand torn from recycled works on paper it echoes the geological and magnetic history of the Earth which is secreted in the strata of sedimentary rock. The protruding tabs of paper seen in these studio images are markers for each section of paper squares of a tapering size and will get tucked away at installation in the gallery. With the added thickness of my new studio roof insulation the obelisk only just fits in now.




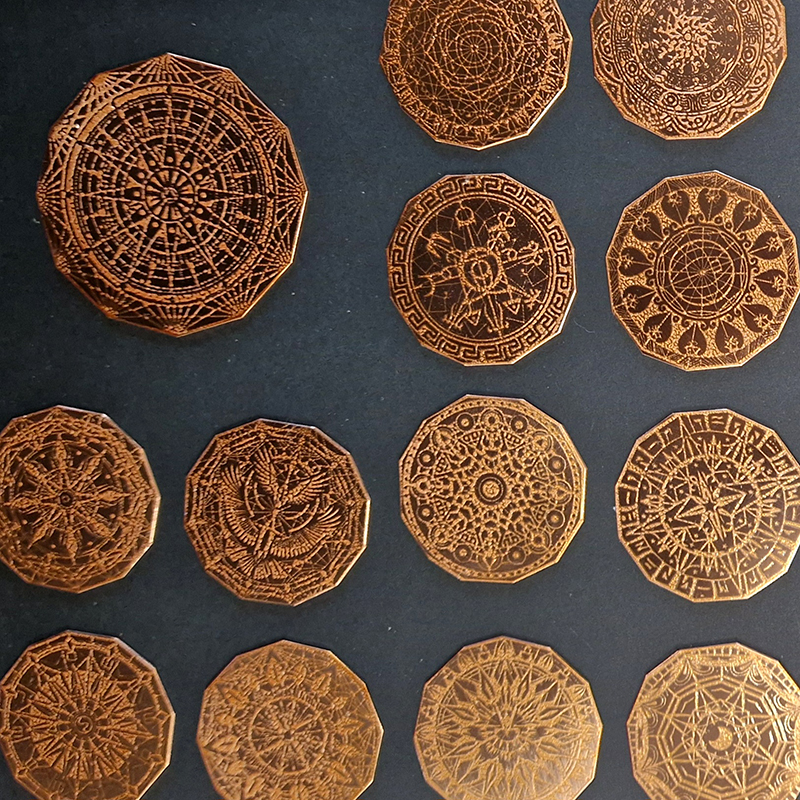
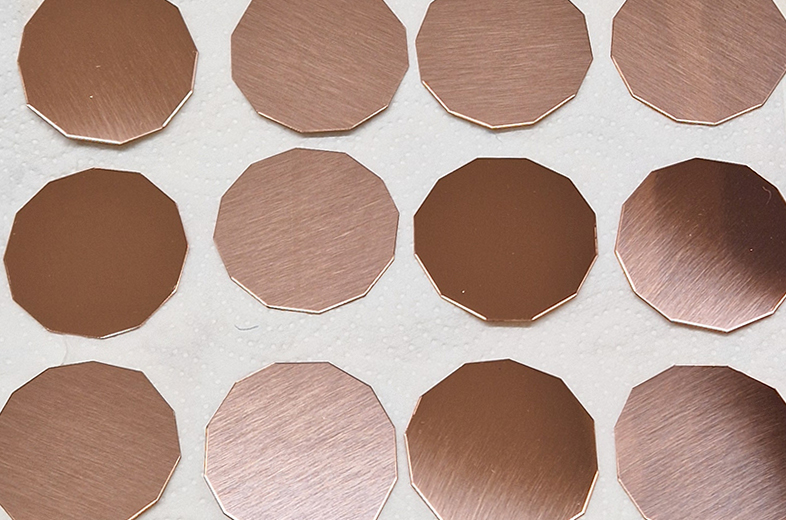
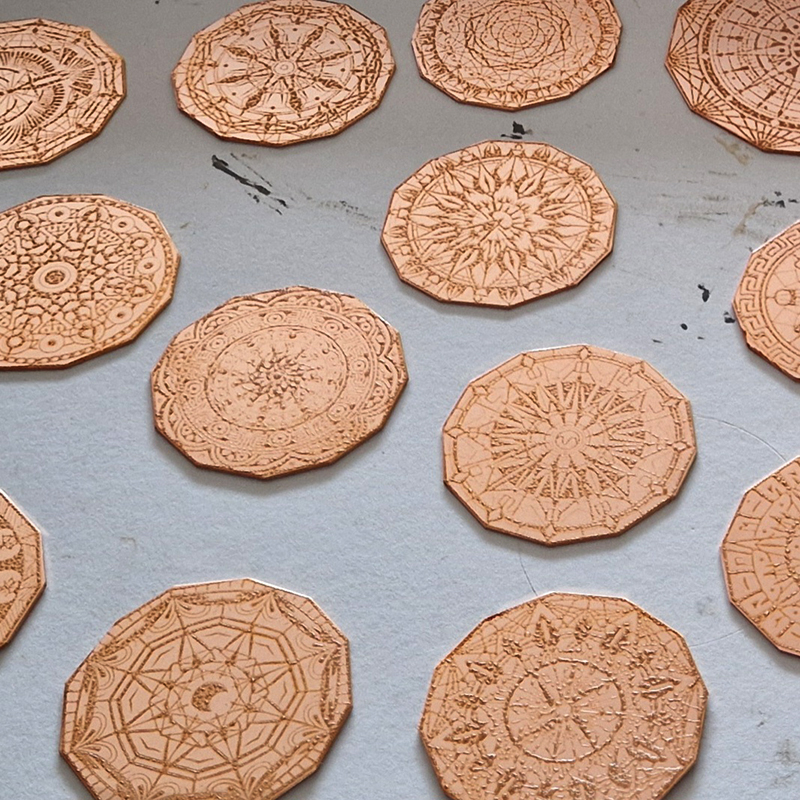
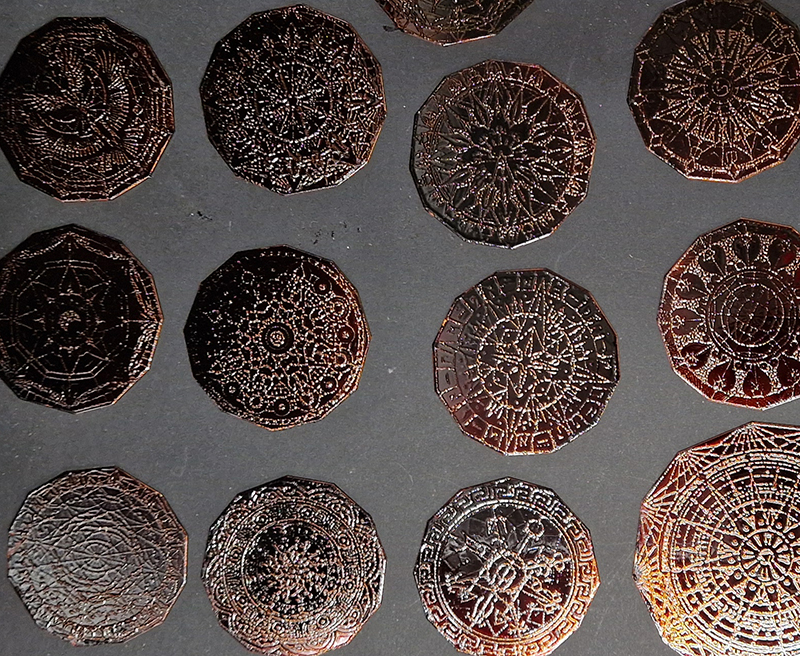
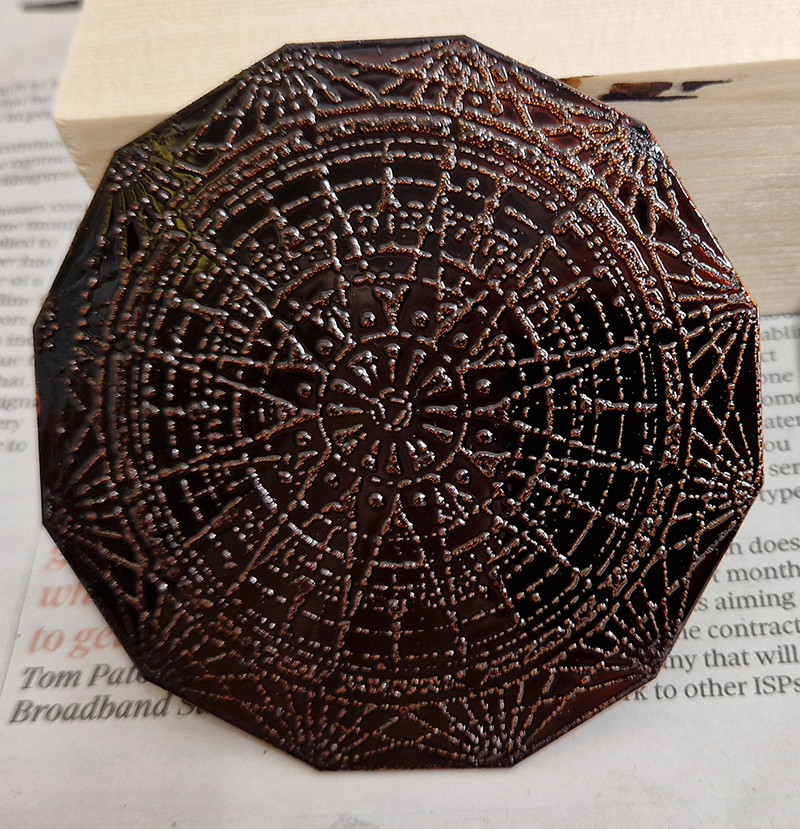
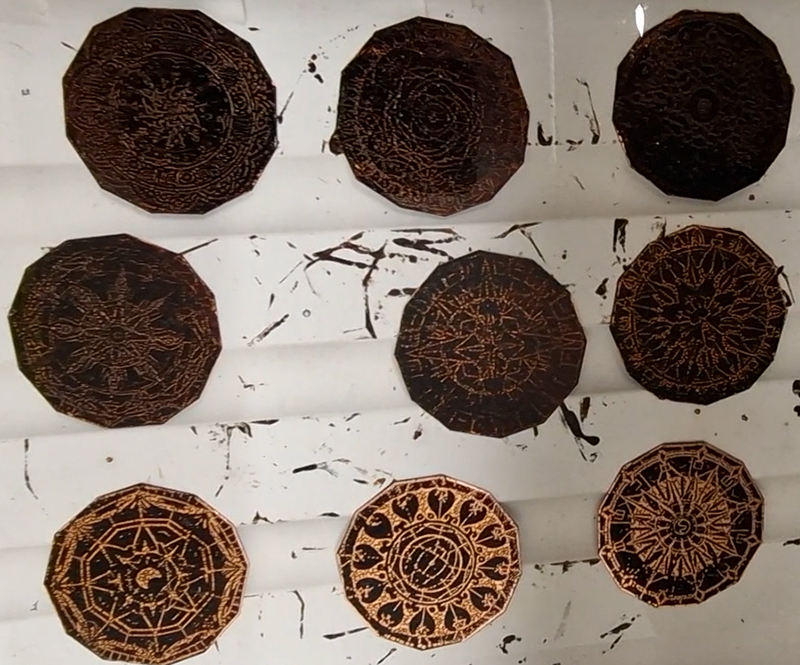
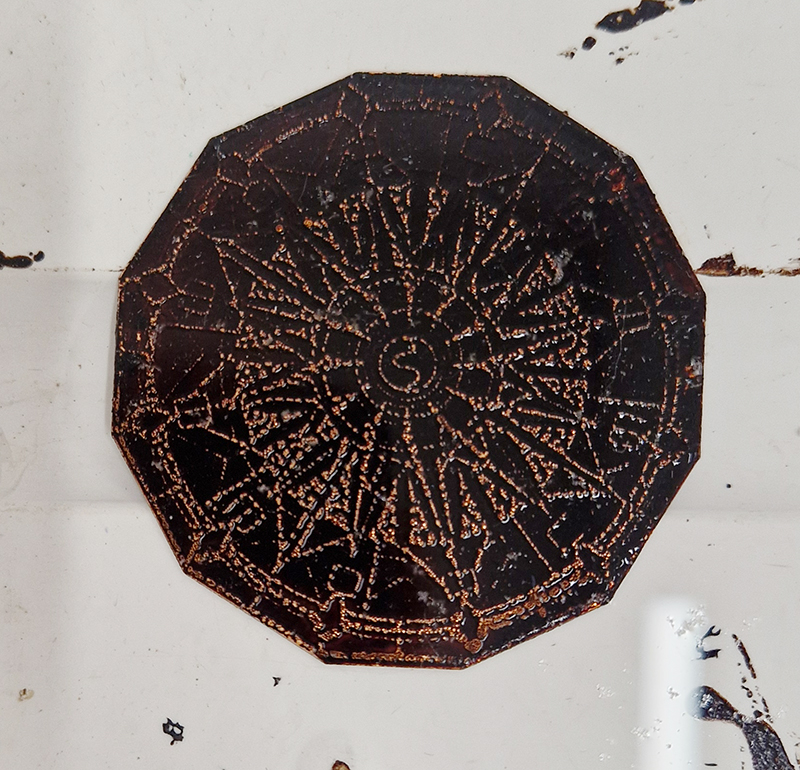
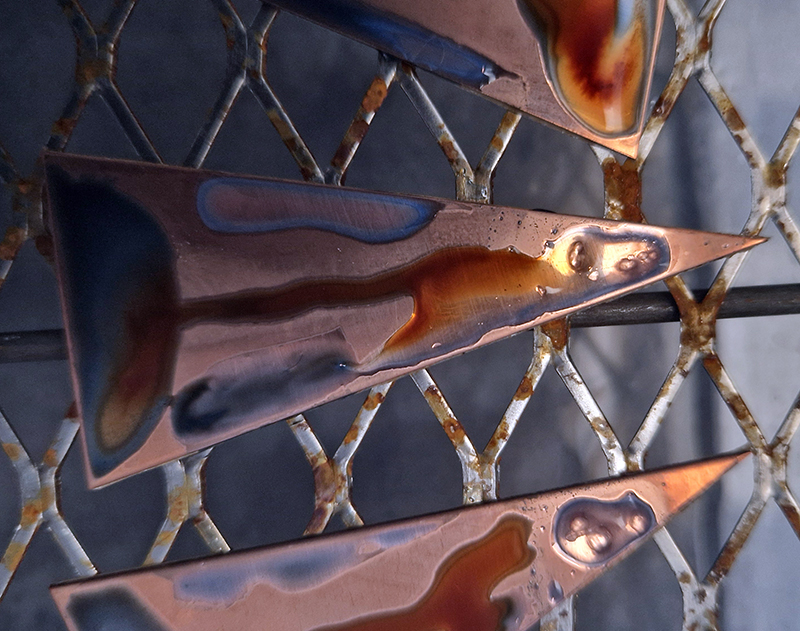
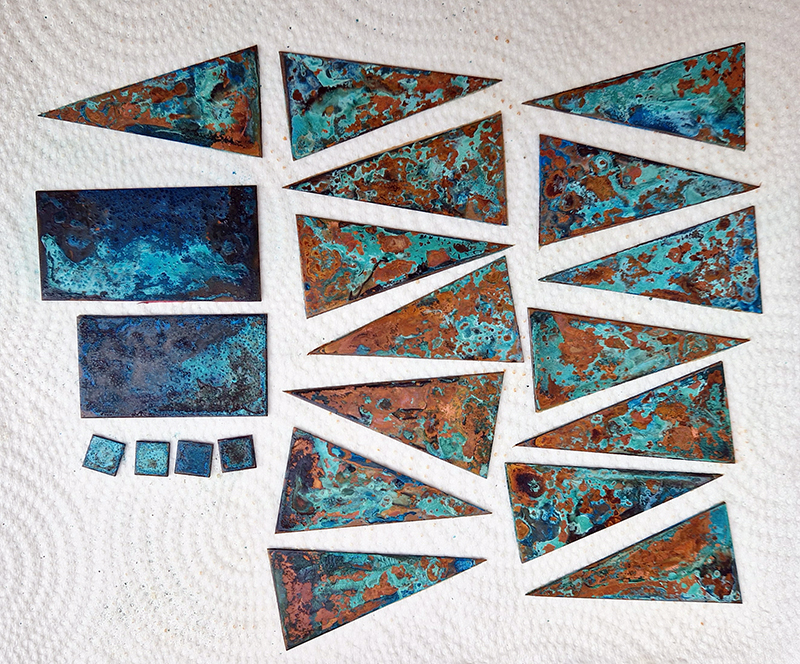
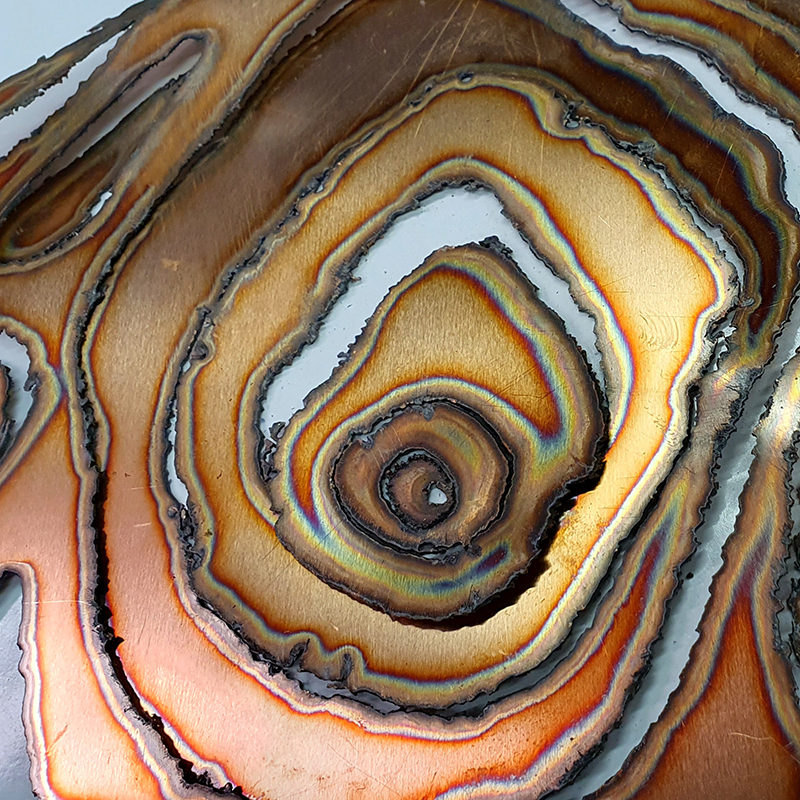
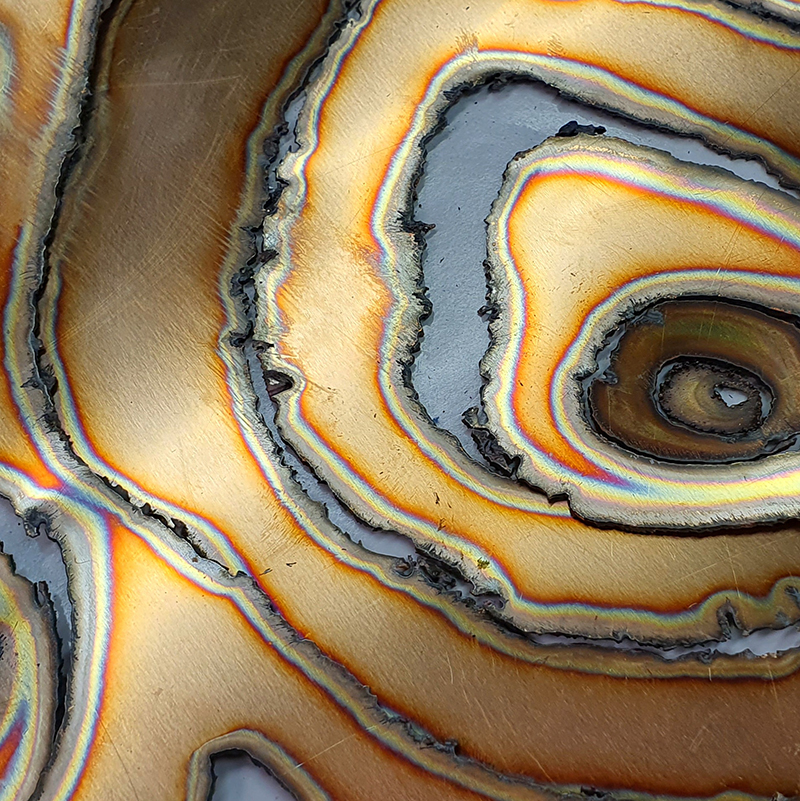
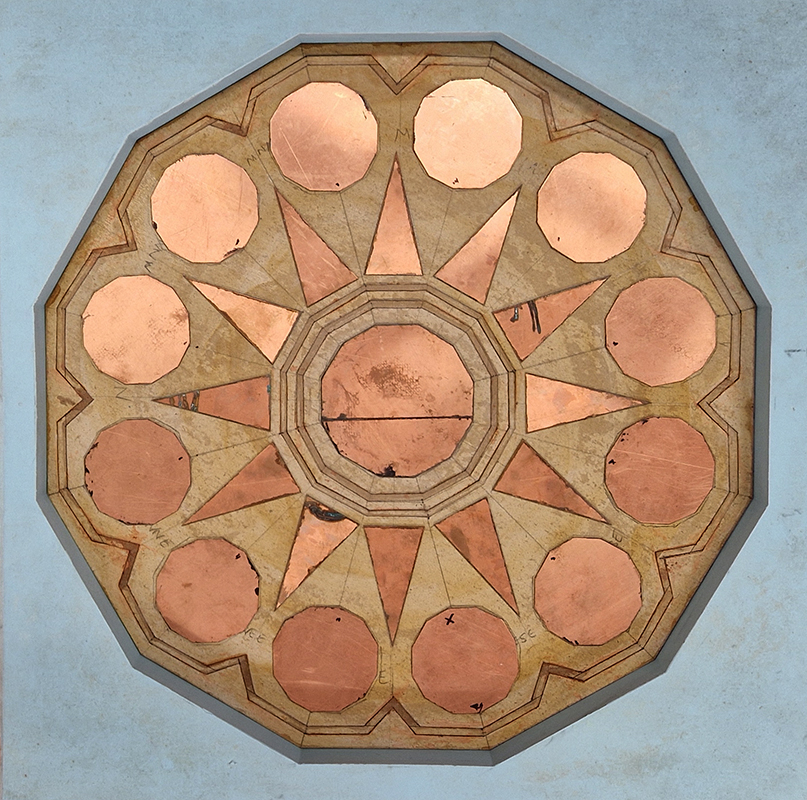
I have started work on inserting copper segments into the new sculpture for the Instruments of the Anemoi series. The other larger pieces of etched and patinated copper were added at the time of casting, held in place with tape and hope when the concrete was poured into the mould. This series of sculptures are suggestive of the pedestals that support various instruments used in monitoring the Earths’ magnetic field but are envisaged here as speculative objects used by the wind gods as the first emissaries of navigation.


I am still battling with writing text for The Book of Reversals, an artist book that responds to the record of Earth’s magnetic field reversals being written in bands of minerals on the ocean floor.

The crisp crust fractures / Fragments slide across a viscous veneer
Submarine mountains tower / Ocean trenches gape
Tectonic plates subduct / melting into the mantle
Deep time traces are consumed / surfaces ceaselessly reformed
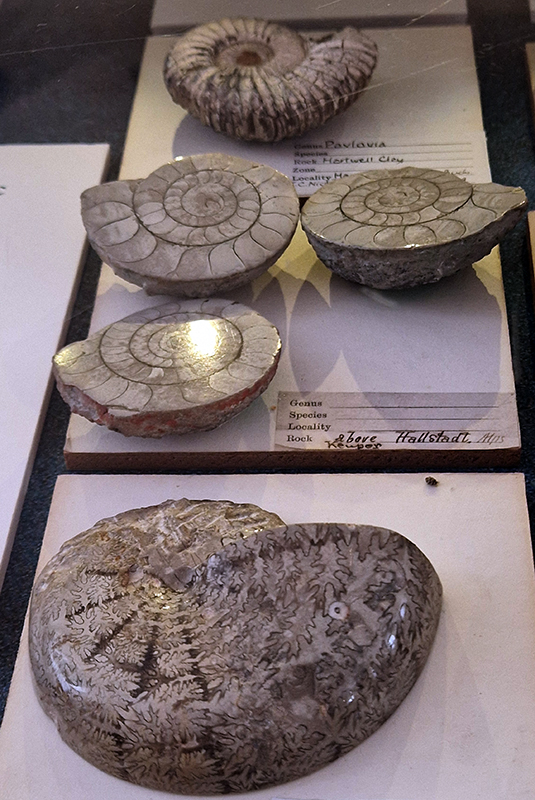
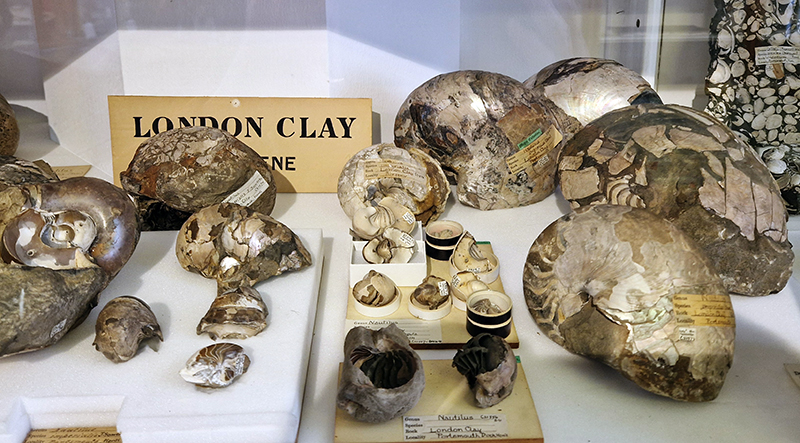
The Earth’s magnetic field has been a fascinating mystery for many hundreds of years and Gillian Turner’s book North Pole, South Pole recounts the stories of those who sought to solve its origin and mechanism. Something I hope to look at in more depth is how pottery and bricks preserve the direction of the magnetic field in their minerals during the process of firing which heats and then cools the clay – the same process that occurs in a lava flow. Iron-bearing minerals (like magnetite) in clay become “magnetic” when heated in a kiln. As the pottery cools, these minerals lock into the Earth’s magnetic field direction and strength at that time. The study of the magnetic properties of ancient pottery, known as archaeomagnetism, has been used to make records of the inclination of the magnetic field from past millennia. Inspired by these studies of manmade artefacts to determine the historical position of the north magnetic pole, physicists Bernard Brunhes and Pierre David took samples from exposed lava flows and their underlying clay in central France. In 1906 they came to the astonishing conclusion that about six million years ago the magnetic field seemed to point in the opposite direction, the first indication of magnetic field reversals.
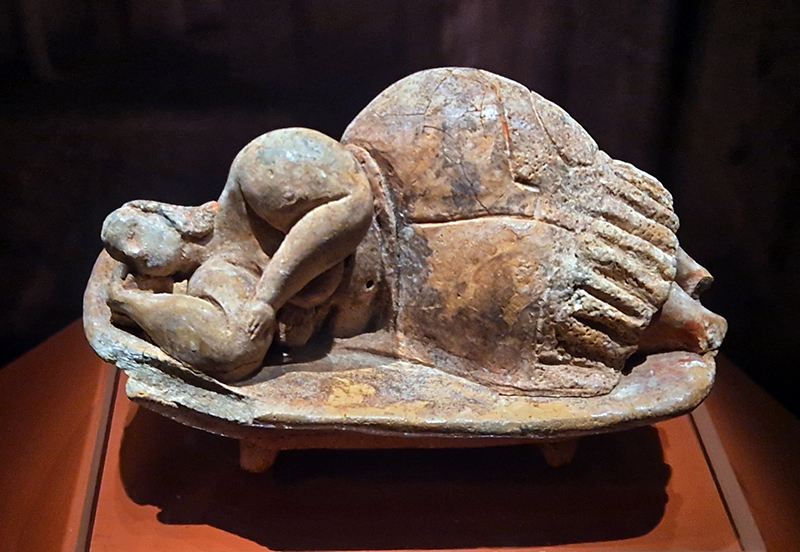

Also with thanks to Gillian Turner’s book North Pole, South Pole I have learnt that there were early hydrogen balloon ascents to determine if the Earth’s magnetic field intensity varied with altitude, helping to decide if the magnetic field came from within the Earth or was extra terrestrial. In 1804 Jean-Baptiste Biot and Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac made a pioneering ascent to 4,000 feet (1.2km). In Turner’s book she writes that the dip needle necessary to take the measurements iced up and so the results were unreliable. I feel for them, but it seems they conducted many other experiments on temperature and gases in the atmosphere while aloft and in any case we now know they would have needed to ascend many kilometres higher than they achieved to notice any weakening in the magnetic field.
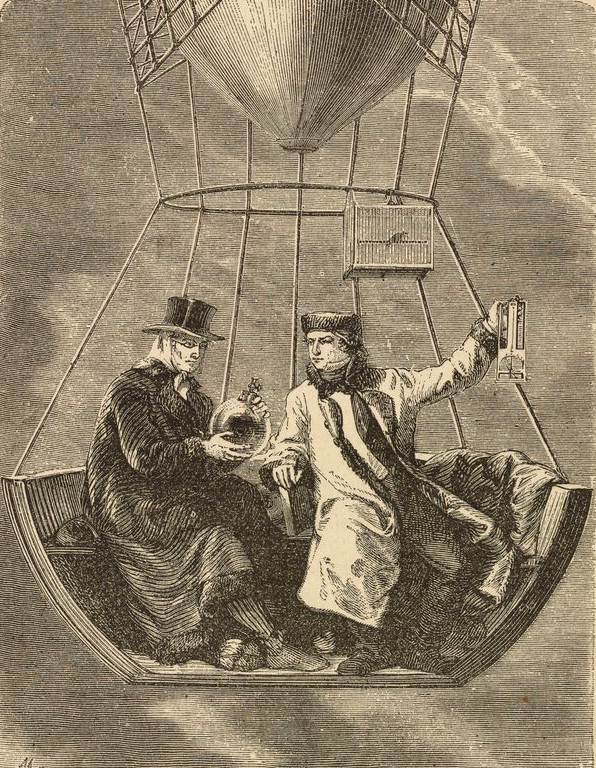

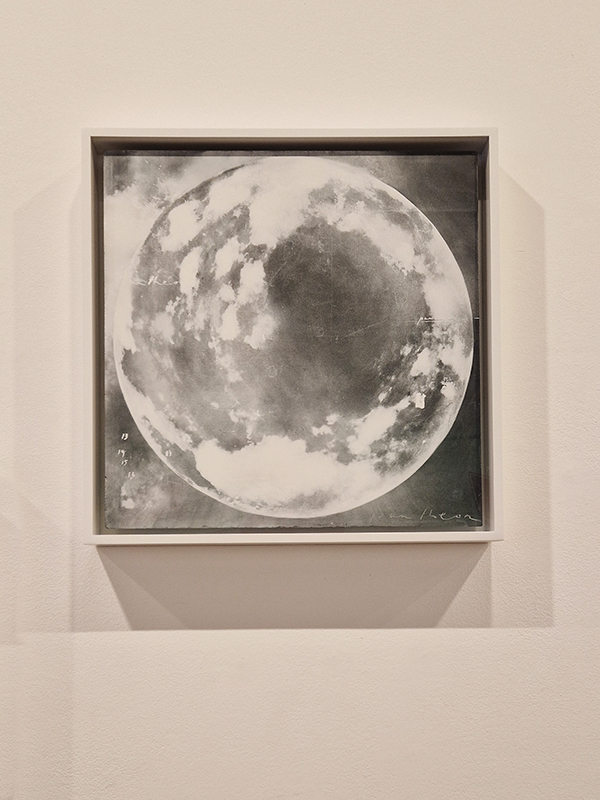
This plate is from John Howard Appleton’s (1844-1930) Chemistry, Developed by Facts and Principles Drawn Chiefly from the Non-Metals, published in 1884.
I am trying to remember when I first had the idea to launch a cloud chamber in the payload of a high altitude balloon. I knew about the hot-air balloon experiments carried by Victor Hess to determine the origin of cosmic radiation, and his discovery in 1912, when he made an ascent to over 5km during a near-total eclipse of the Sun, that radiation had to be coming from further out in space.
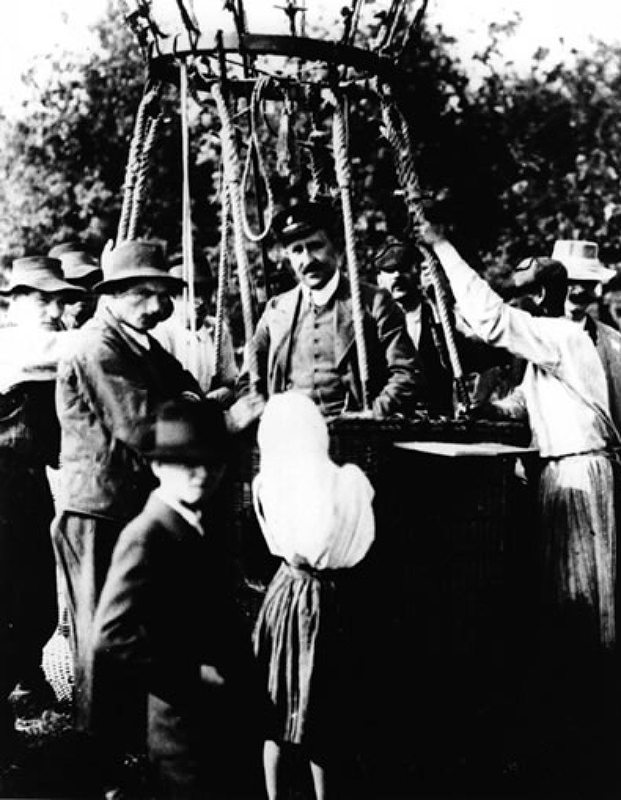

Hess on his return from the 1912 balloon ascent – Alan Watson pointed out that this was obviously staged at another time as he would not have been standing looking so well after his ordeal.
I remember looking into the dark skies during a residency at Allenheads Contemporary Arts and wondering about all the activity that I couldn’t see. I decided then I would like to film at 15km where most subatomic cosmic ray activity takes place, even if nothing would show on the film.
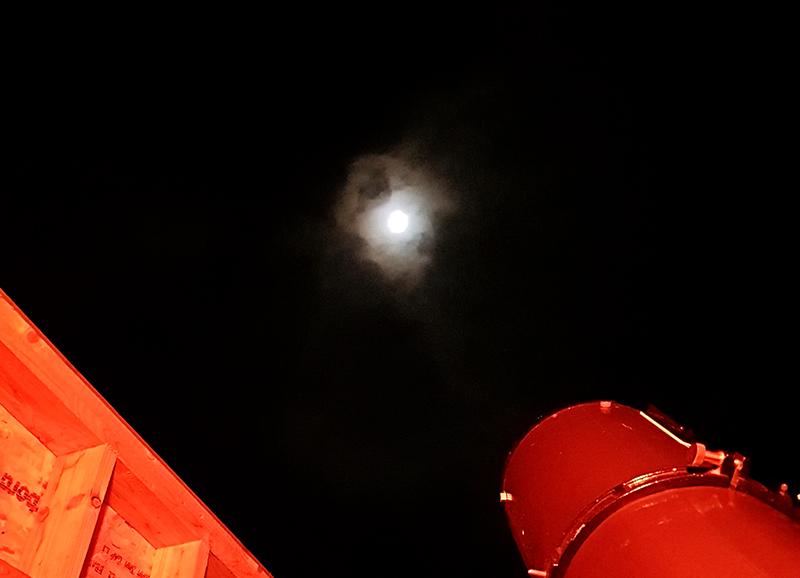

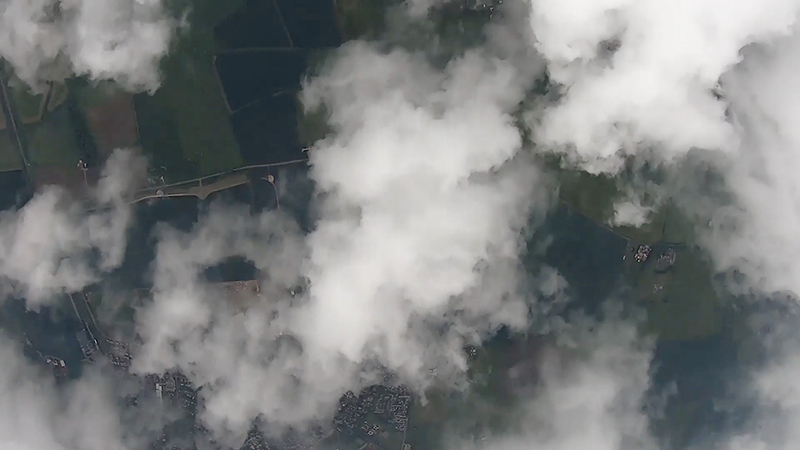
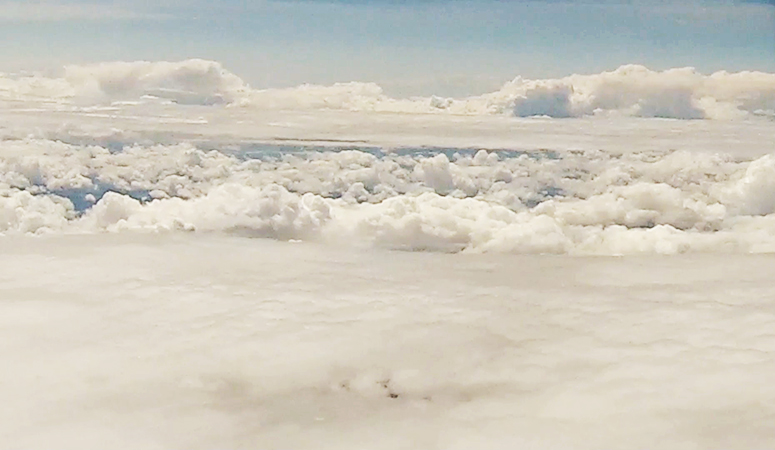
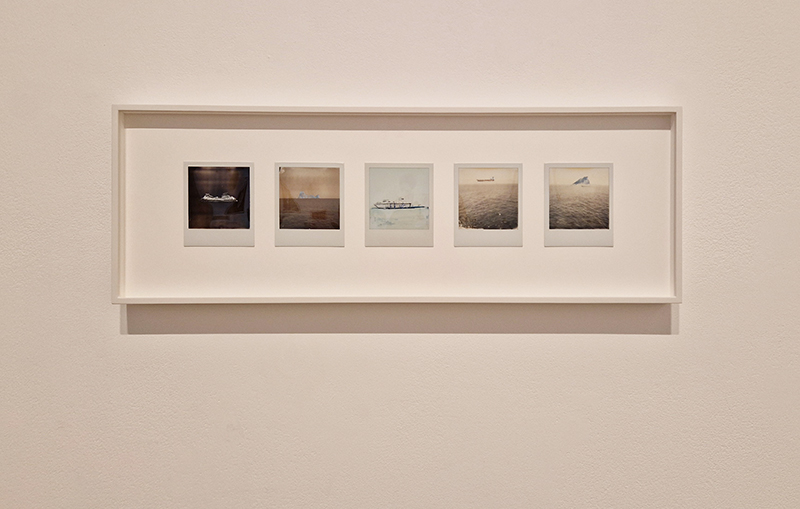
A high altitude balloon flight seemed the perfect solution and I was very grateful for the help I subsequently received from Imperial College Space Society and The UK High Altitude Society. The decision to include a cloud chamber in the payload was always a risk and as it turned out nothing of the cosmic ray activity was captured on film. However, the balloon did reach an altitude of over 37km and the payload was successfully recovered with some amazing video footage of its journey.
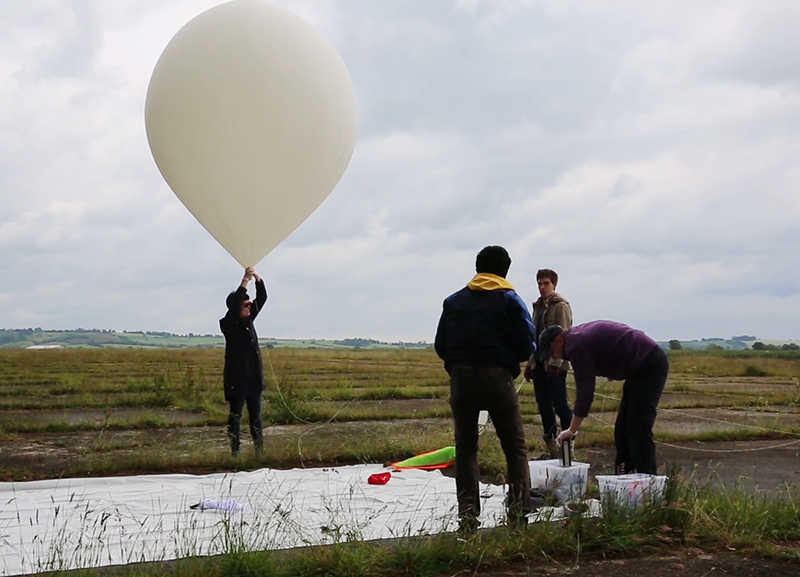
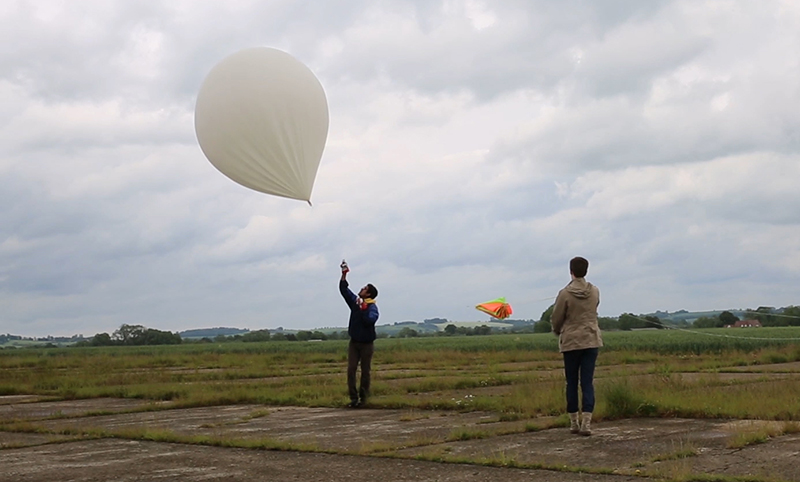


The record height for a hot air balloon ascent is 21km so in theory it could be possible to send a cloud chamber up in a hot-air balloon and film at altitude with potential for more success if some brave person were on board to operate the camera. Unlikely to be me.


Some intriguing news of ORC’s on the RAS website – The most distant and most powerful ‘odd radio circle’ (ORC) known so far has been discovered by astronomers. These curious rings are a relatively new astronomical phenomenon, having been detected for the first time just six years ago. Only a handful of confirmed examples are known – most of which are 10-20 times the size of our Milky Way galaxy. ORCs are enormous, faint, ring-shaped structures of radio emission surrounding galaxies which are visible only in the radio band of the electromagnetic spectrum and consist of relativistic, magnetised plasma. the three new cosmic rings – discovered not by automated software but by sharp-eyed citizen scientists – represent an important step toward unlocking the secrets of these vast, puzzling structures.
Out and About
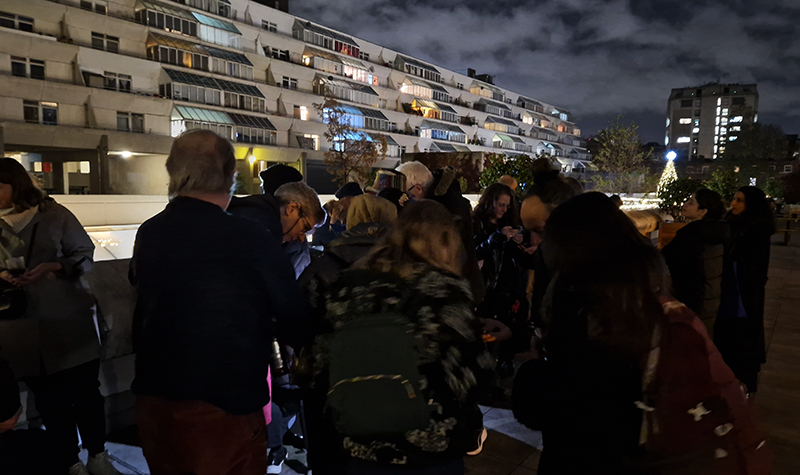
A wonderful evening with artist in residence Melanie King at Passengers connecting the celestial with the architecture of the grade II listed Brunswick Centre in Bloomsbury, London. Melanie used the residency opportunity to explore the duotone cyanotype process using multiple layers of cyanotype to mimic astronomical imaging construction and even used cyanotypes to create an of the Moon. The beautiful results were presented at an evening event with the additional treat of live telescope viewing of the Moon and Saturn from the second floor terrace of the Brunswick centre under the engaging guidance of astronomer and science communicator Paul Hill.




Liz Elton’s sensitive work Black and Blue (compostable bio materials, cabbage and fruit dye saddened with iron, silk, poppy and sage seeds) showing in A Changed Environment at Messums London. This group show examines changing ideas of beauty, ecology, and sustainability, as well as themes of place, memory, and identity, revealing how connections to the natural world can inspire both understanding and hope. I love the delicacy of this new work and the term ‘saddened by iron’ which is used in the dying process to dull a colour, and which, as Liz says, also emotes the hardships of industrial life.


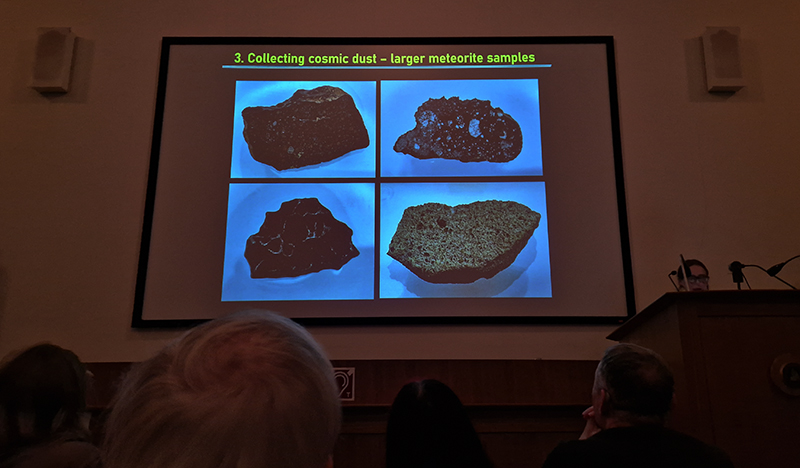
Cosmic Dust talk by expert on extraterrestrial space dust, and how it can impact astronomy and wider human endeavours in space, Penny Wozniakiewicz at The Royal Astronomical Society. ‘Natural’ cosmic dust is being polluted by man made dust from space debris. This is a real problem created by dead satellites, old upper stages of rockets, fragments form exploded rocket or stages, flecks of paint, aluminium oxide spheres from solid rocket burns, dropped space equipment. When any of this debris collides a cloud of smaller debris is ejected, this process is self propagating and even the tiniest piece of debris can cause serious damage to spacecraft and satellites. This is called the Kessler syndrome, a cascading effect that could render orbital space unusable for generations, threatening satellites, the International Space Station, and future space travel.



Good to visit the The London Group show 2025 at Copeland Gallery where lots of friends are showing excellent work and also to discover new work and artists.
I found Majid Majid’s video Faith Amongst The Ruins a difficult but compelling work. So scary and horrific because we know this is real footage, some of which I had seen before at the time of the attacks on hotels housing asylum seekers and refugees, but it is still so disturbing to watch these people, with so many children present, cheer on the violence. They have no empathy with the terrified people trapped inside the hotel or for the person in the car who is ambushed and stabbed. The glee of those filming the assault is chilling.
He writes: “As a refugee, I know places shaped by fear and rejection. This work revisits UK sites of last summer’s Islamophobic and racist violence, a mosque, a street, and a hotel housing asylum seekers transforming them through prayer. Placing a mat where hostility flared, I reclaim space as sacred ground. Video and traces of violence form a counter-narrative of dignity, belonging, and resilience.”
Images: Majid Majid, Sayako Sugawara, R James Healy, Victoria Rance, Jonathan Armour, Sandra Crisp, Jenny Wiggins, Victoria Arney, Carol Wyss, Sandra Crisp, Genetic Moo, Jacqueline Yuen-Ling Chiu.
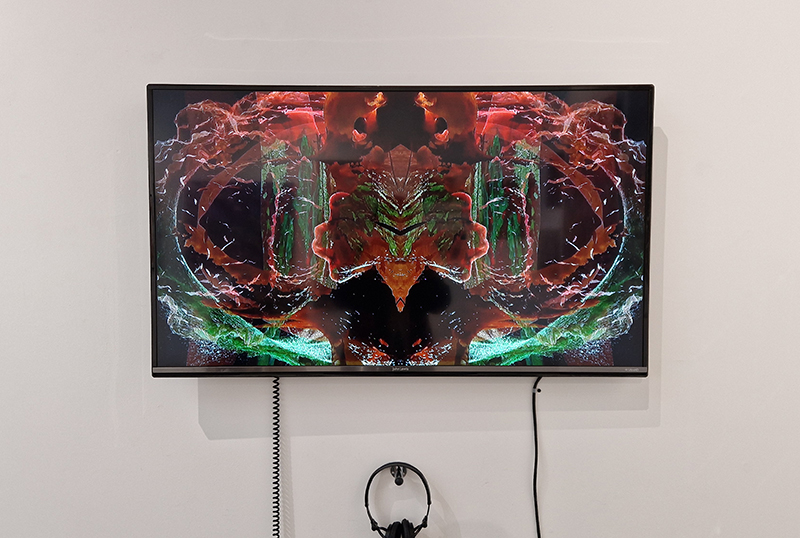
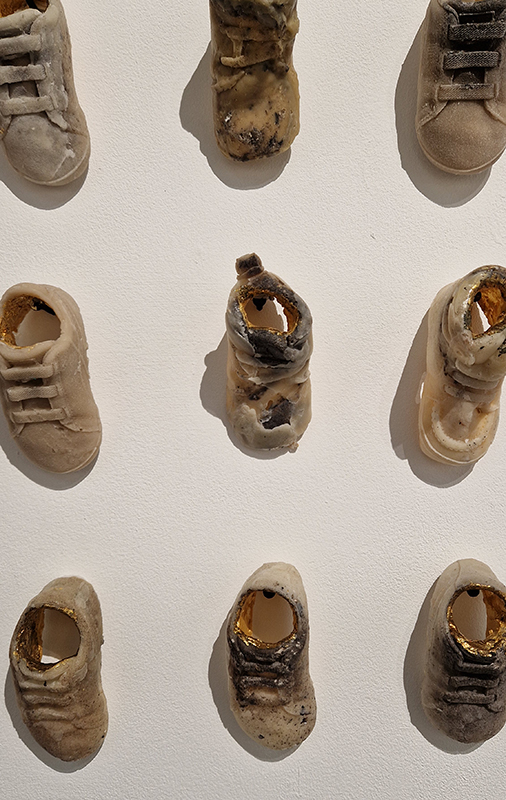
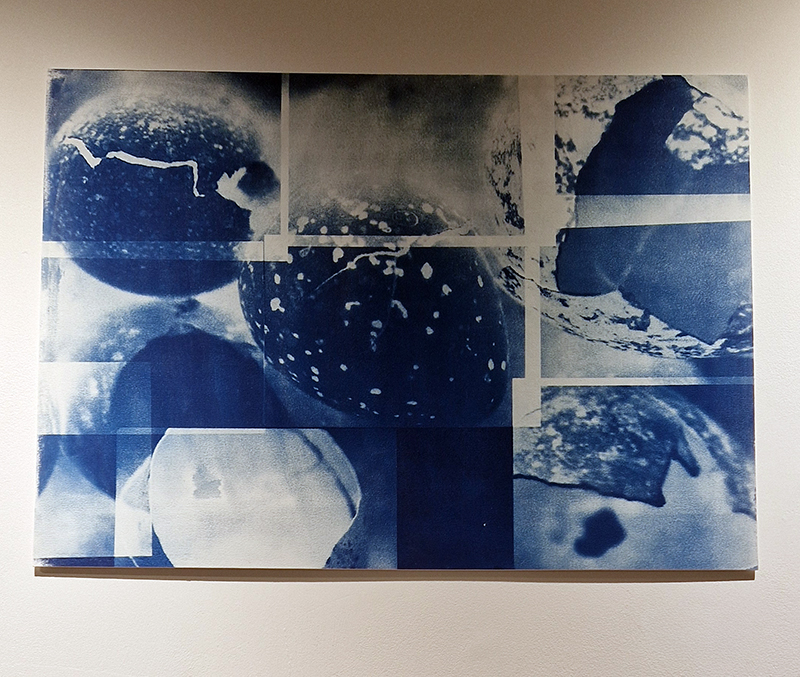
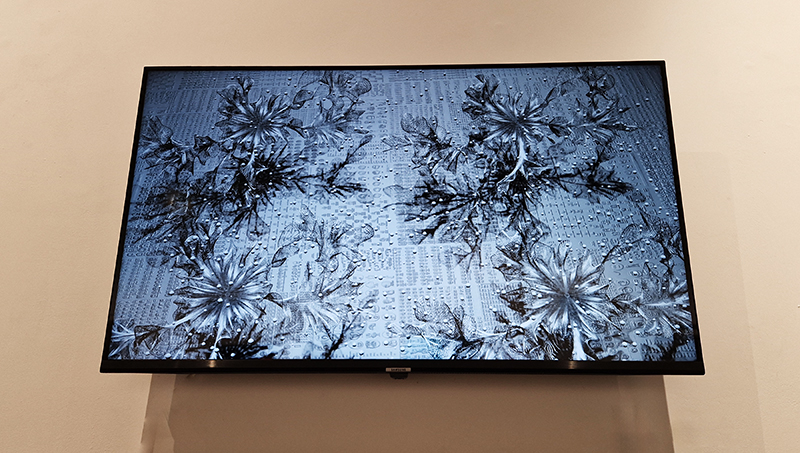












Three beautifully directed films screened at FormaHQ as part of The Open Road series of artists moving image works, co-commissioned by a partnership of visual arts organisations. The works are loosely inspired by The Canterbury Tales, drawing from a disparate cast of characters to recount competing stories in a patchwork of styles. David Blandy (Commons), Amaal Said (Open Country) and Sam Williams (The Eel’s Tale) each draw on storytelling traditions to give fresh perspectives on their journeys, on foot, by sea and through time. Heartbreaking to hear how terrified Amaal Said was to leave London for the open country of the south coast, especially with the current rise in overt racism, when out looking for locations and that they did suffer racist abuse while filming. Hers is a gentle and warm study of a mother and daughter and an absent grandmother, a longing for home and to feel ‘at home’. Sam William’s film sets the plight of the highly endangered glass eels who journey 4,000 miles from the Sargasso Sea to the Medway wetlands in Kent, swept along by currents, undergoing bodily transformation, following an instinctive desire on this epic migration alongside two other watery tales of transformative journeys across boundaries of identity and freedom. Coincidently, a recent episode of the Infinite Monkey Cage is all about these mysterious eels. David Blandy turned his attention to the vast and disparate collection of artefacts held in the Tunbridge Wells museum and gave some of these specimens a voice to tell of how they had lived before they became a part of this collective of human taxonomy.


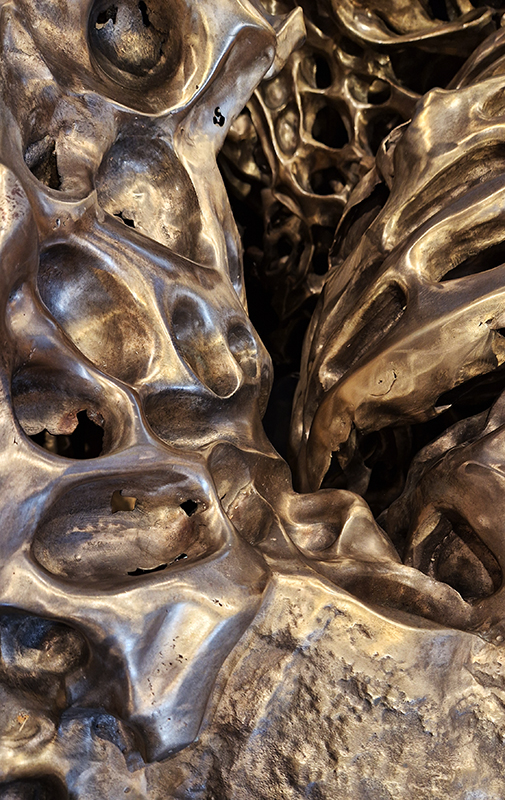
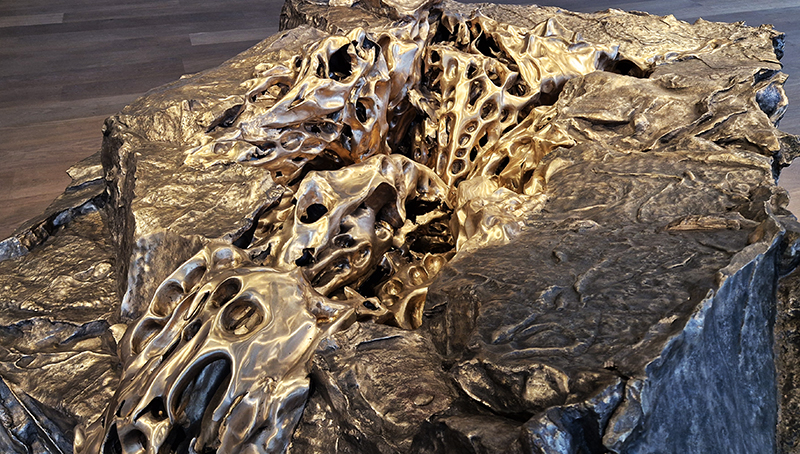
Cristina Iglesias The Shore at Hauser & Wirth features large-scale bronze works from the artist’s Littoral (Lunar Meteorite) series, part of her ongoing exploration of geological themes. The word ‘littoral’ refers to something relating to or situated along a coast or shore, or the region where the land meets the water. The weightiness of the objects is impressive ( I can’t imagine how they were brought into the gallery even with the technology available today – after coming here from the talk on stone henge and the incredible feat of bringing the standing stones across rough terrain for many kilometres and up a slope 5000 years ago seems even more impossible – yet there they are). The sound of water bubbling within each piece draws you to peer within and stay with the piece perhaps longer. The audience is invited to touch the sculptures. The bronze is polished and does need to be used and worn away in a more effective organic and dirty process. They are very clean.


The Royal Astronomical Society lecture Sighting the Sun and Moon? at Stonehenge – by Archaeoastronomist Prof. Clive Ruggles. Debunking many myths and overspeculation, concerning the use of the monument for observations of the sky the professor was clear about what can sensibly be said about the relationship of Stonehenge to the Sun, considering the conventional archaeological evidence that has been uncovered in recent years. He also recommended visiting the day before or after the actual solstice if possible for an experience without the many crowds as the alignment is almost identical. Also visiting at sunset can be just as magical and quieter. He turned his attention to the Moon, questioning if our prehistoric forebears also celebrated the occurrence of a major lunar standstill, an event occurring every 18.6 years around which time the Moon can be seen at fortnightly intervals exceptionally far to the north and south.

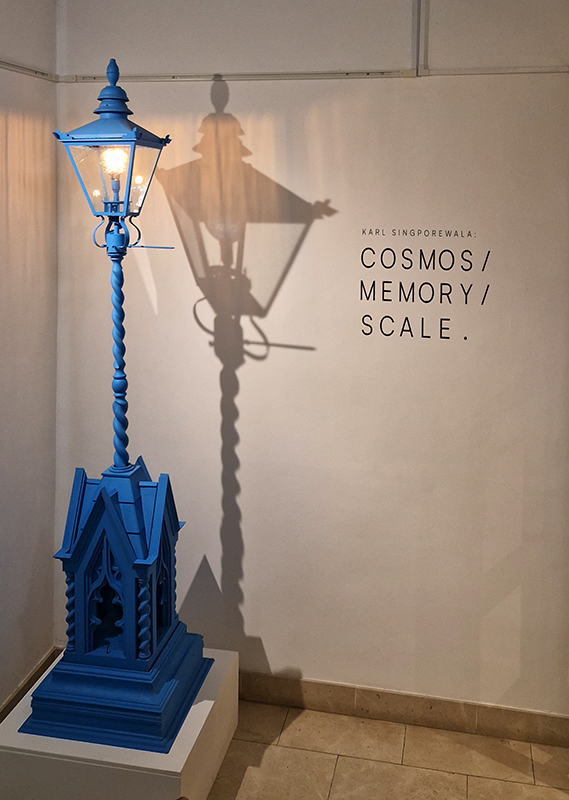
Karl Singporewala’s sculptural interpretations of Zoroastrian symbolism in Cosmos, Memory, Scale at SOAS Gallery convey a meditation on how material and memory intersect to shape the human experience. Cosmos speaks to both his fascination with astrophysics together with a metaphysical belief in the alignments of life. Stars and geometric forms recur as motifs, refracting both spiritual navigation and mathematical structure. Memory is treated as a living, shifting phenomenon. Inspired by oral tradition, family stories and inherited rituals. Scale, is used both literally and metaphorically in shifting perspectives and unexpected relationships. Good Thoughts, Good Words, Good Deeds.
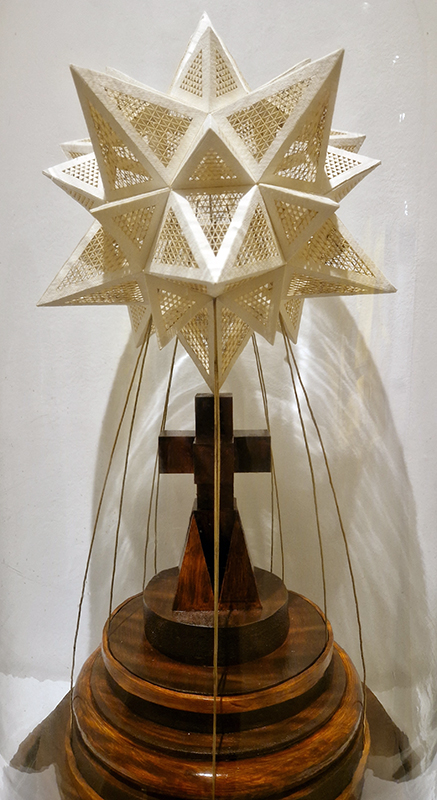
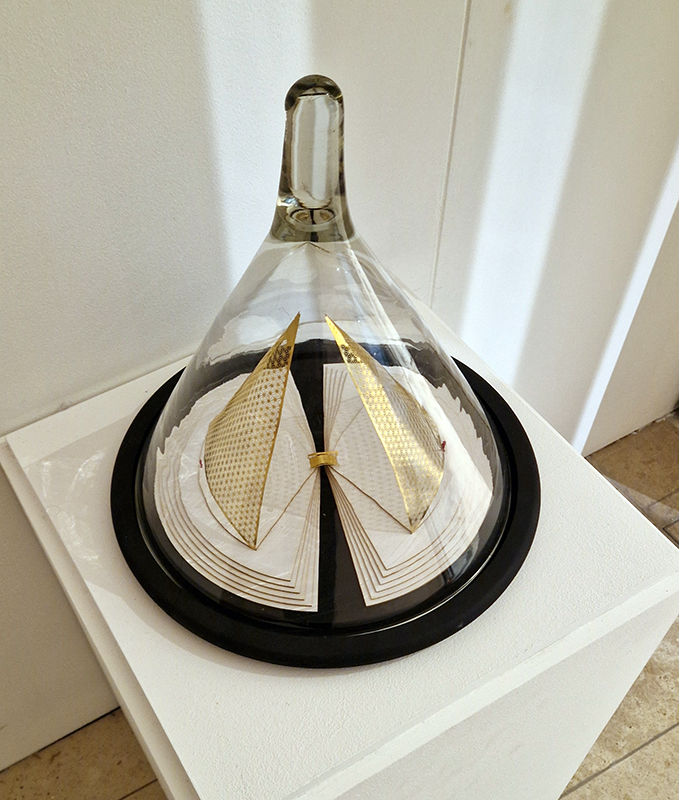








Dusty, chalky mythical drawings and solar eclipse traces from Tacita Dean in Black, Grey, Green and White at Frith Street Gallery Golden Square.





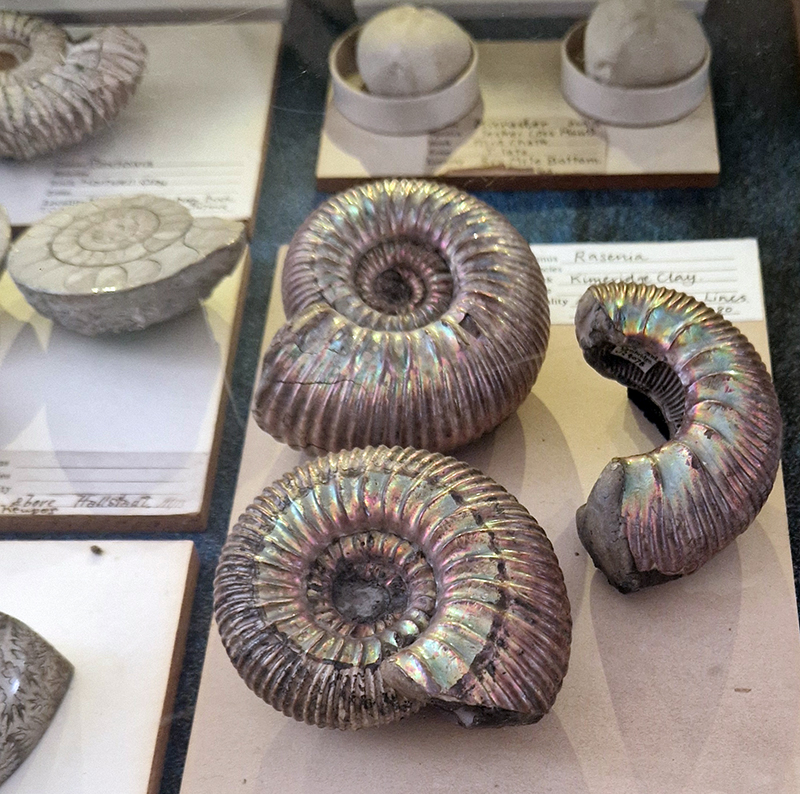
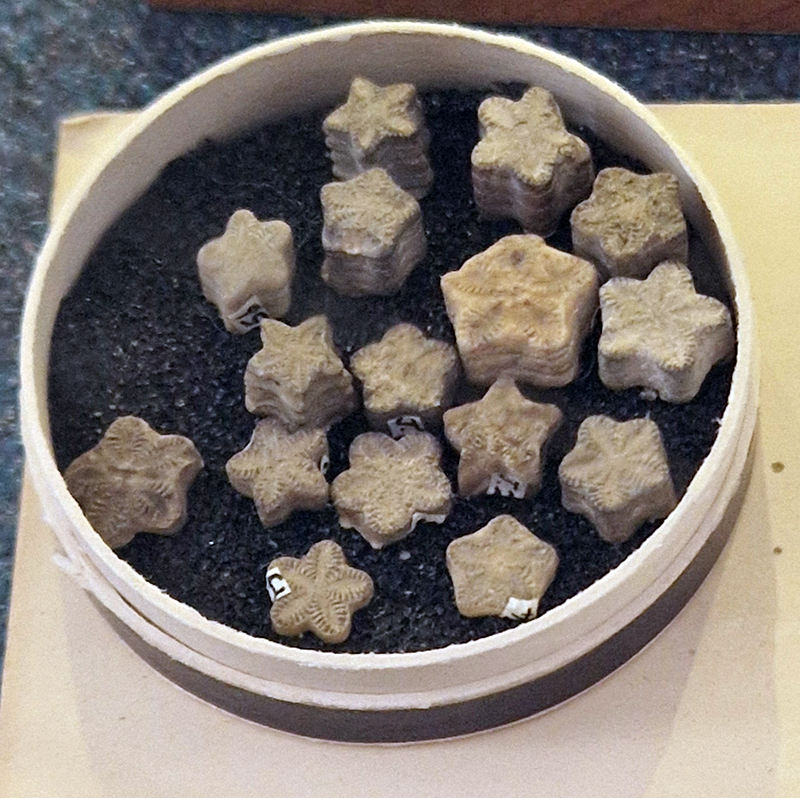
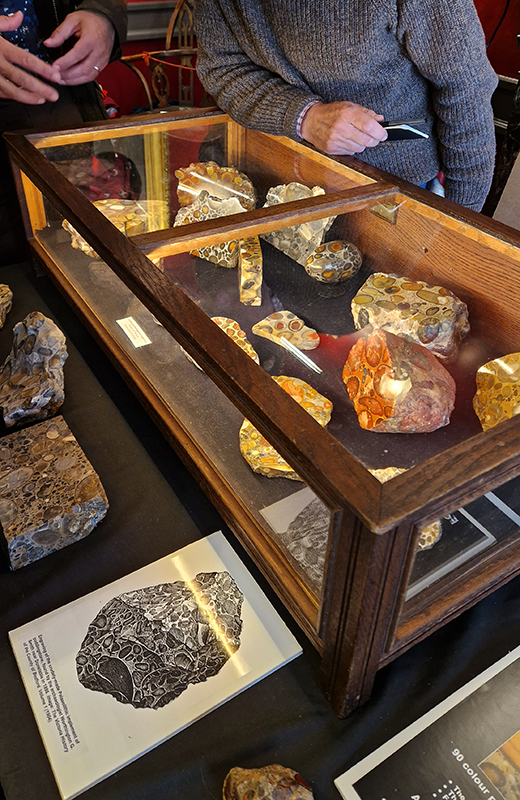
I spent a happy morning at the Geologists Association Festival of Geology 2025. This included a fascinating lecture The Early Evolution of Animal Life by palaeobiologist Frankie Dunn focused on the origin and early evolution of animals and particularly on the fossil record of the late Ediacaran Period (approximately 570 – 540 million years ago) – just before the Cambrian explosion of life. The aim of her research is to understand how animal body plans evolved in deep time. There also was some amazing and unique pudding stone on display.




I also picked up a great little book full of wonderful geologically enriching words by Marcia Bjornerud.