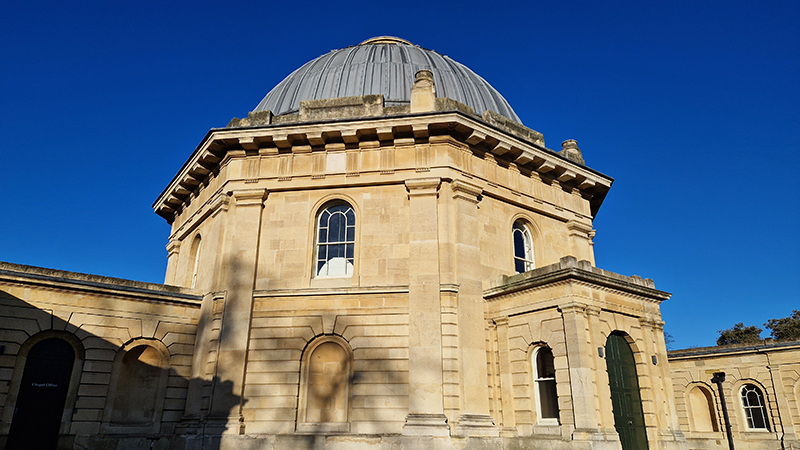
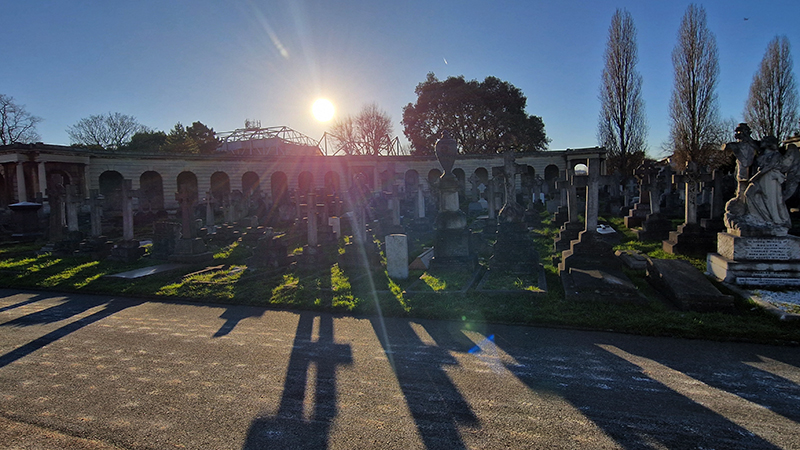
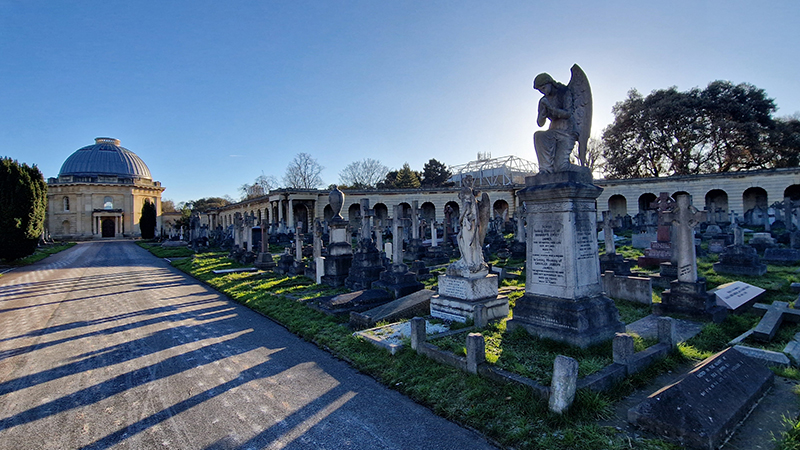
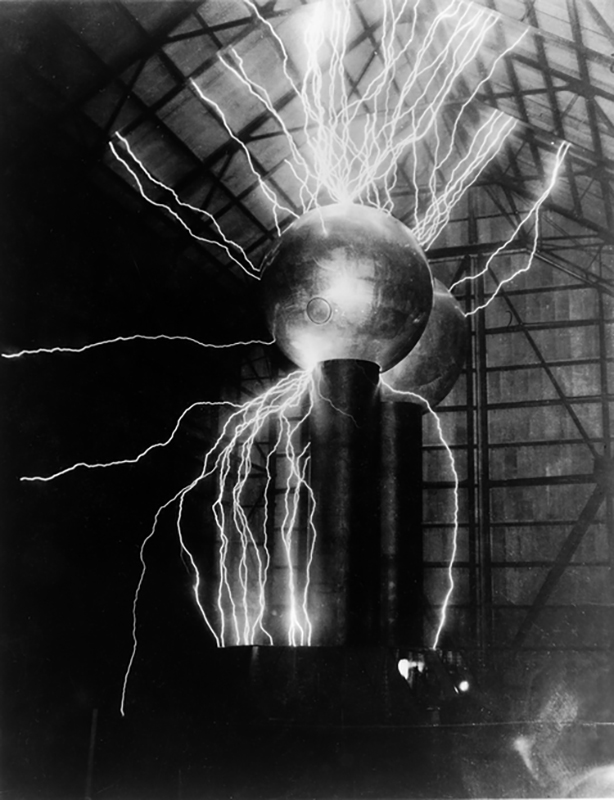
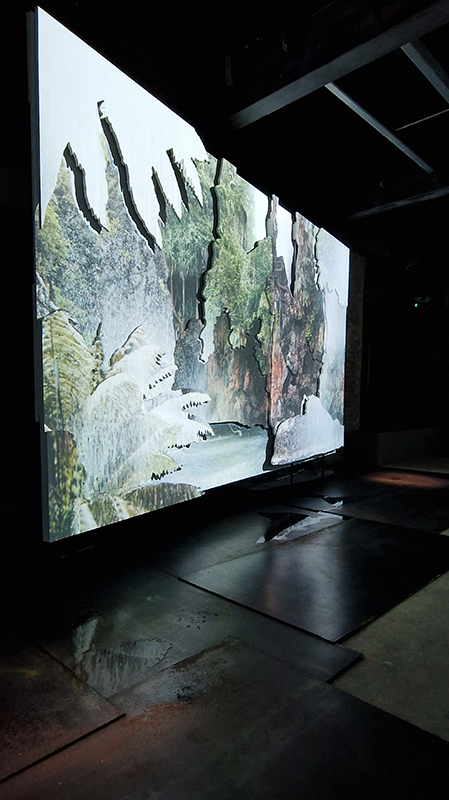
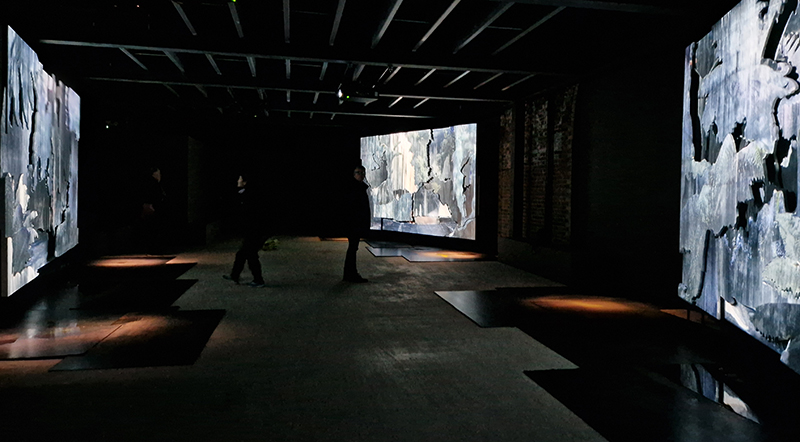
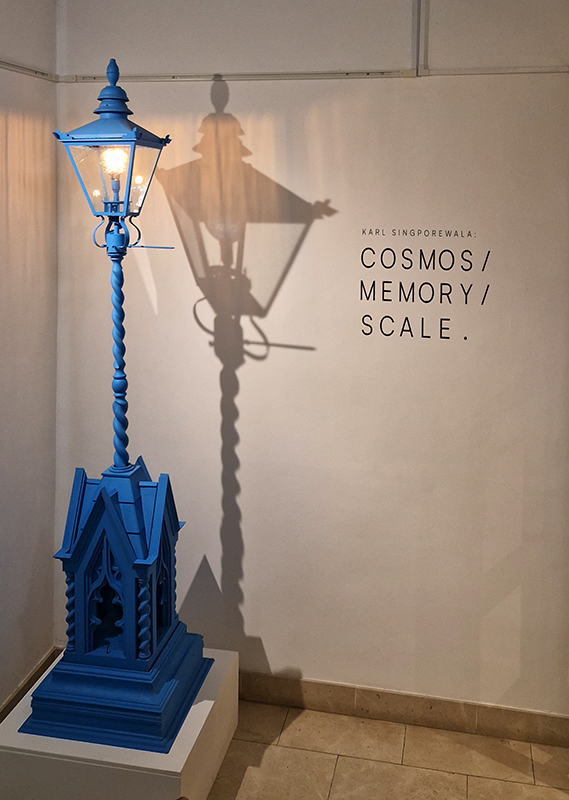
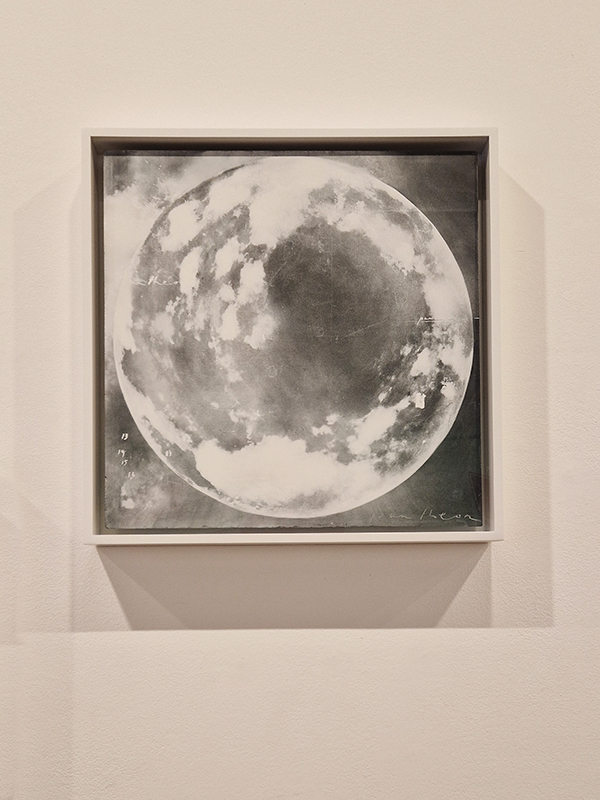
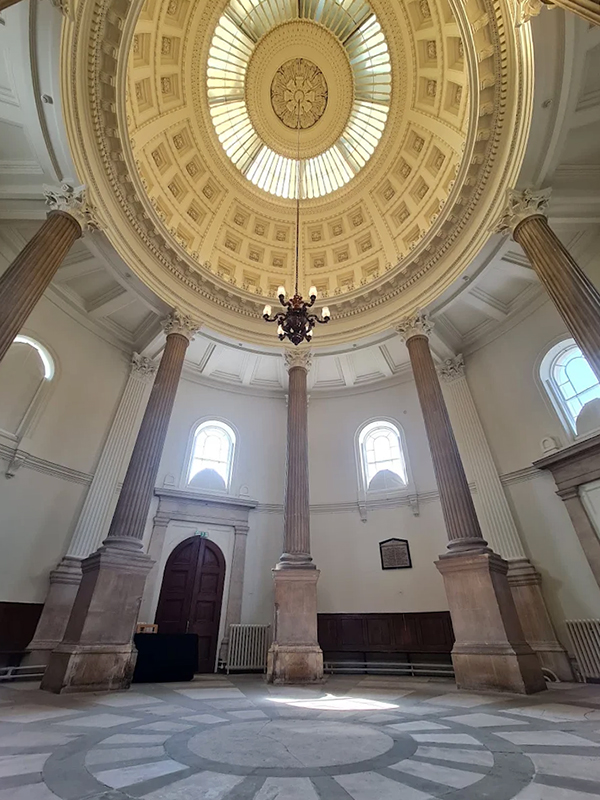
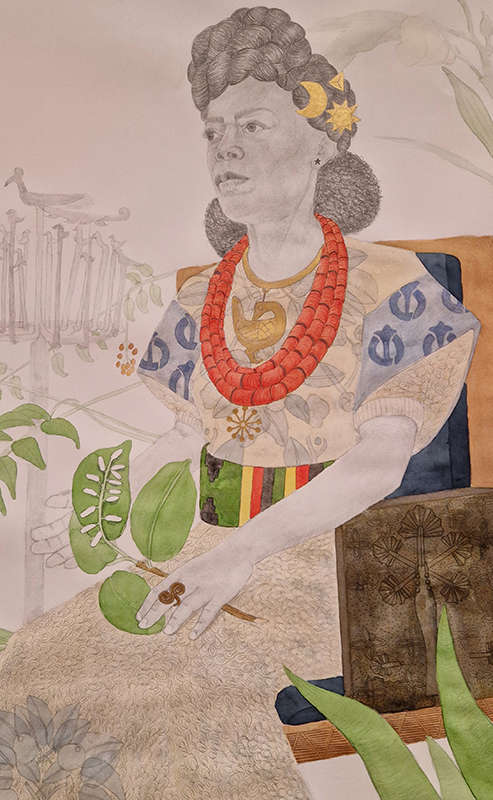
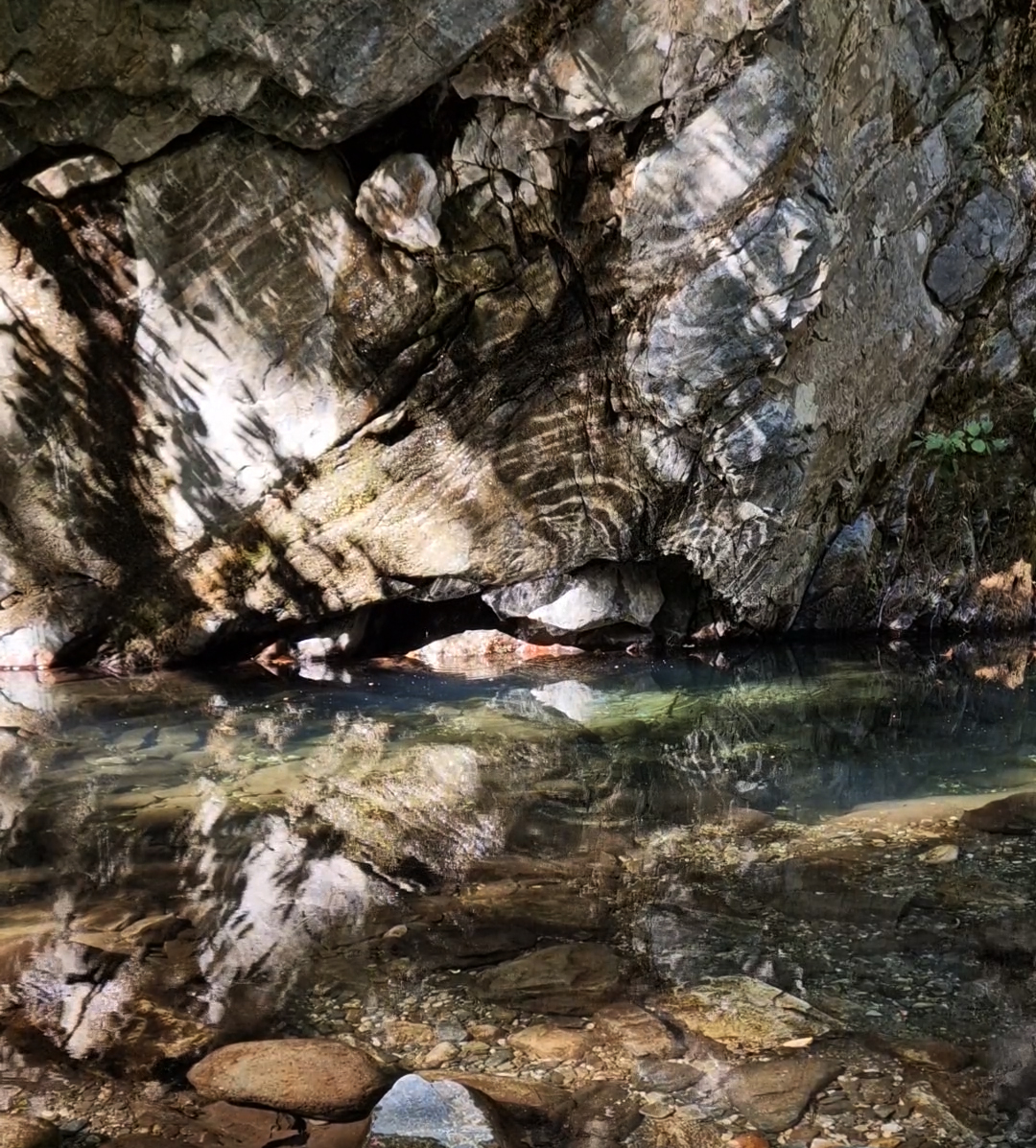
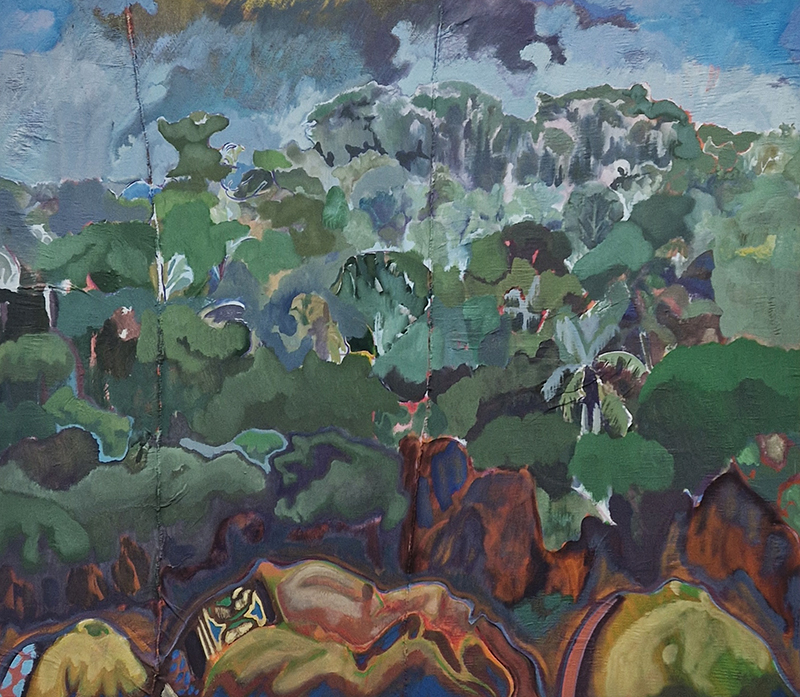
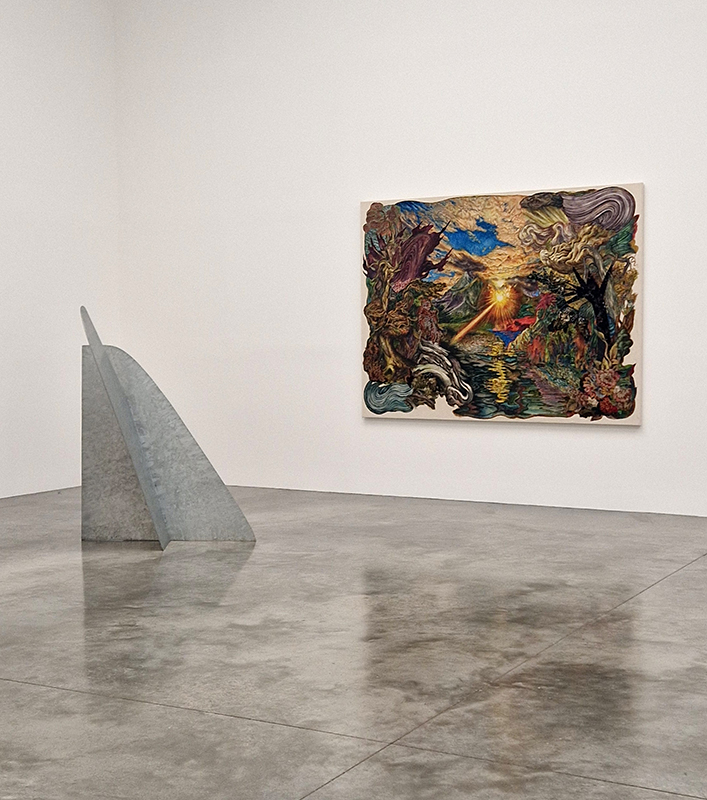
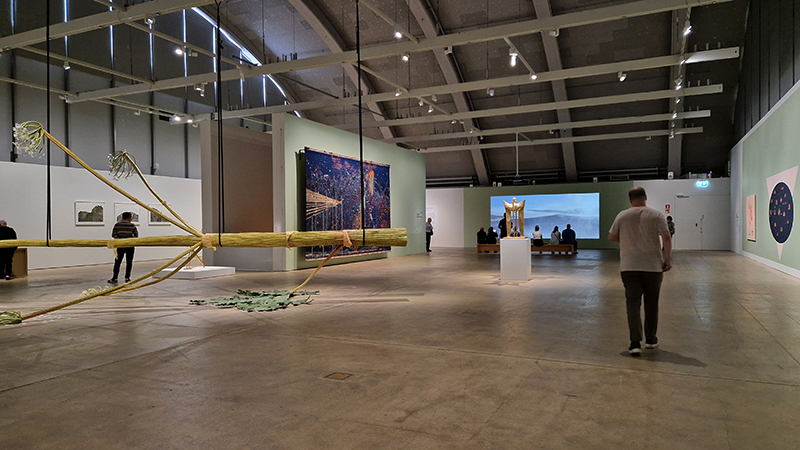
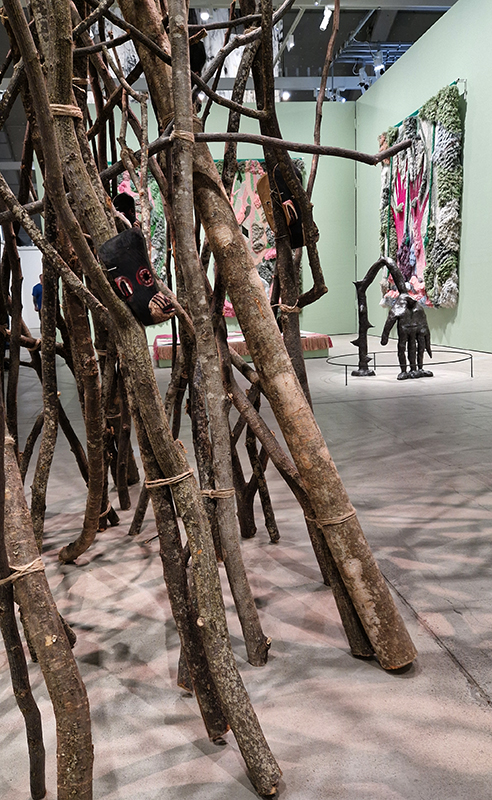
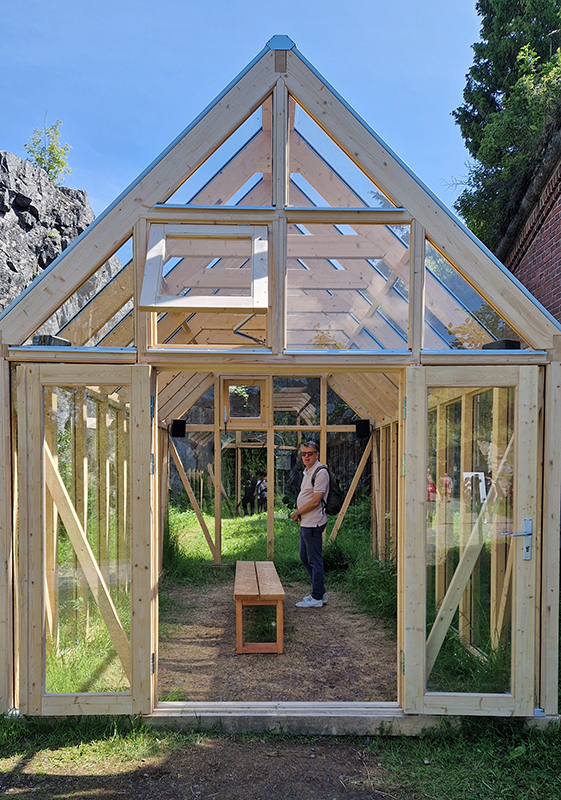
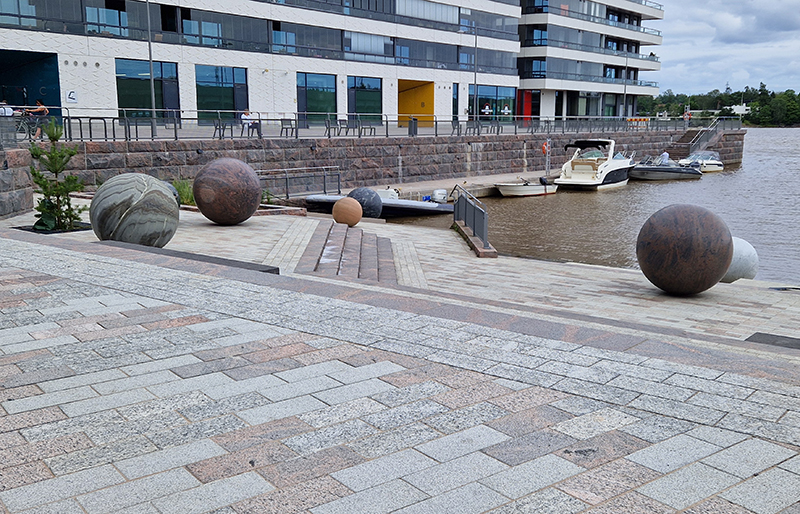
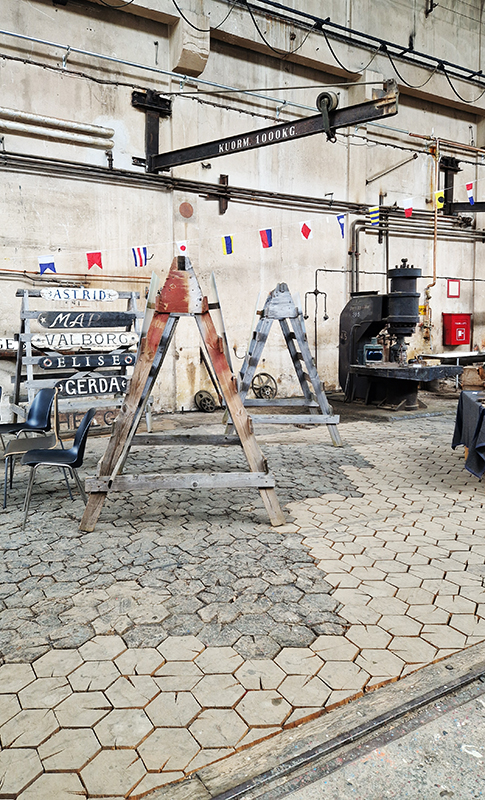
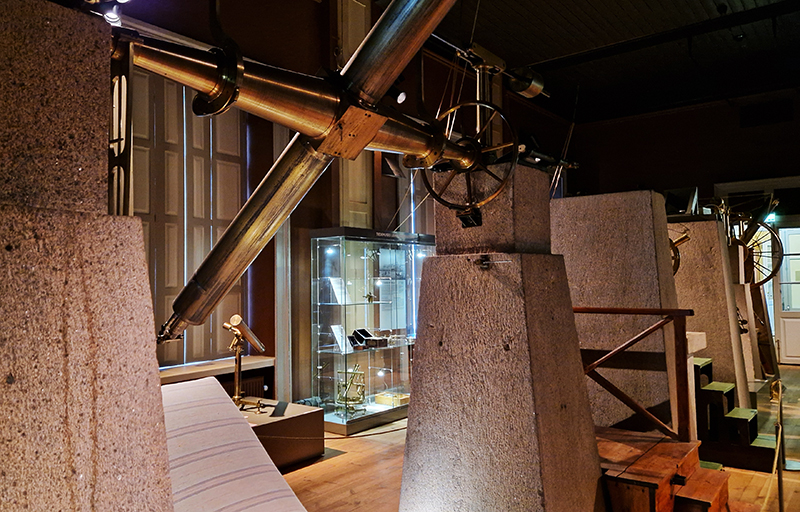
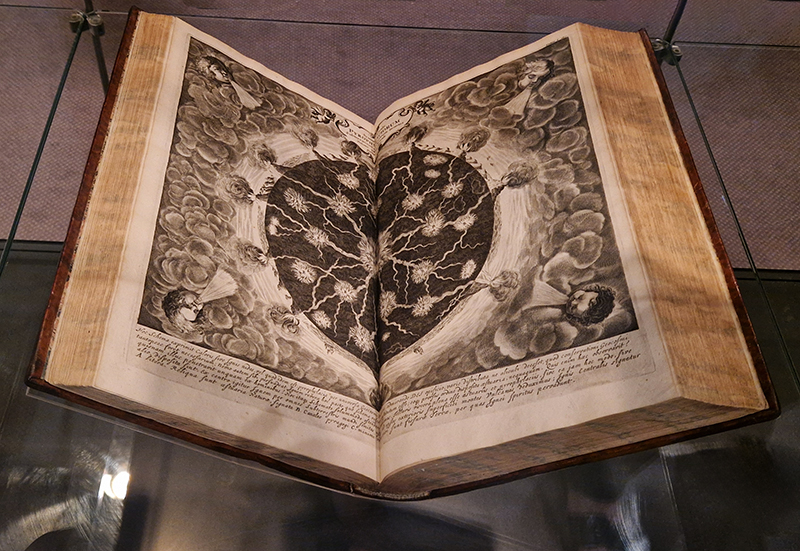
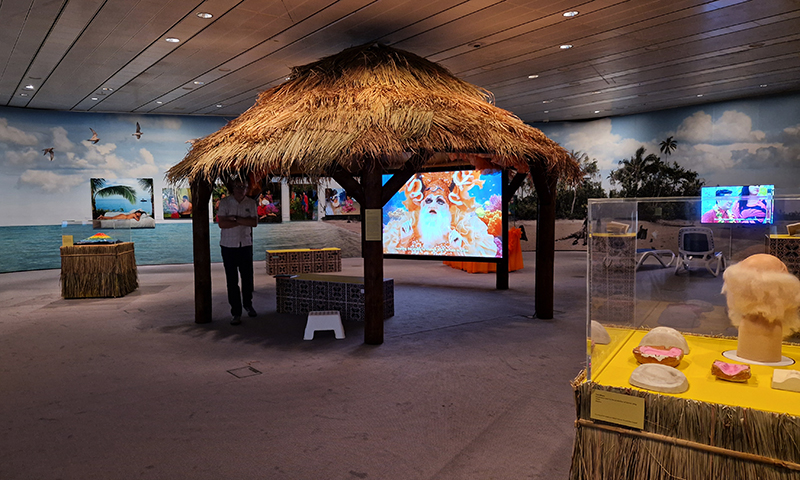
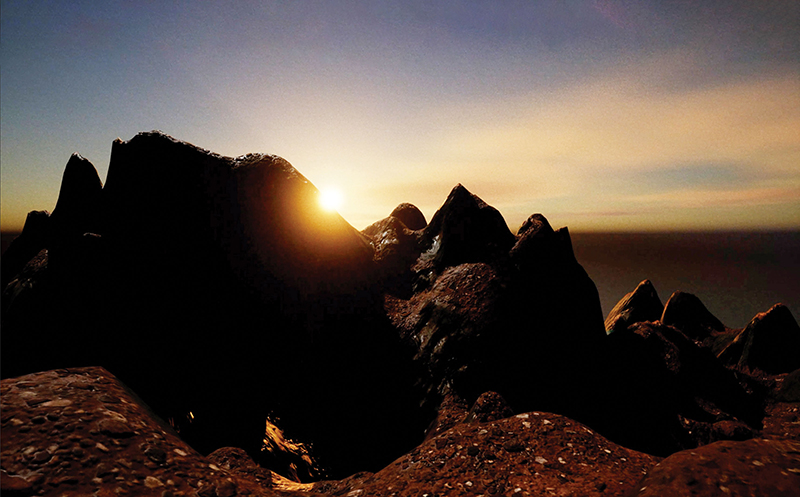
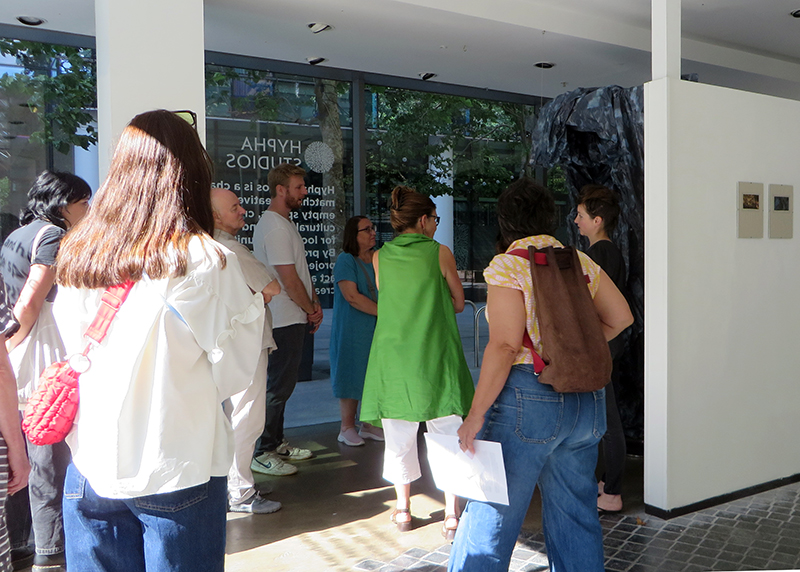
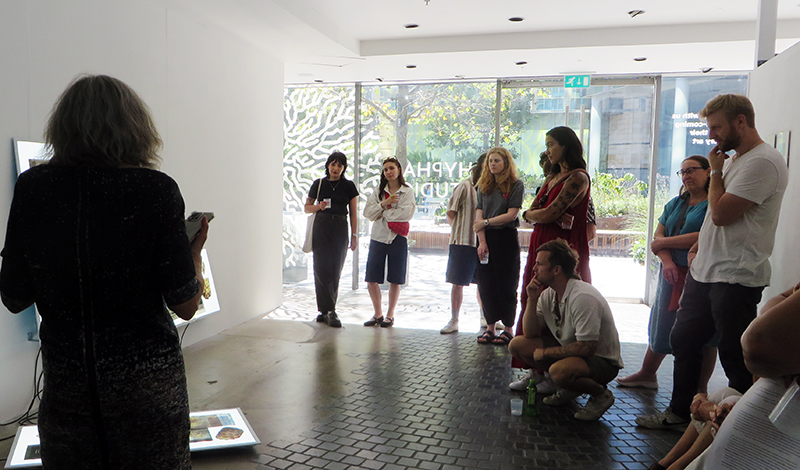
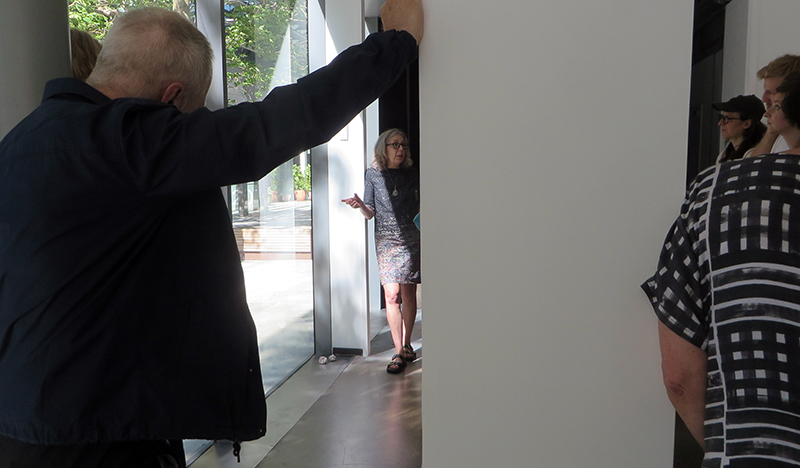
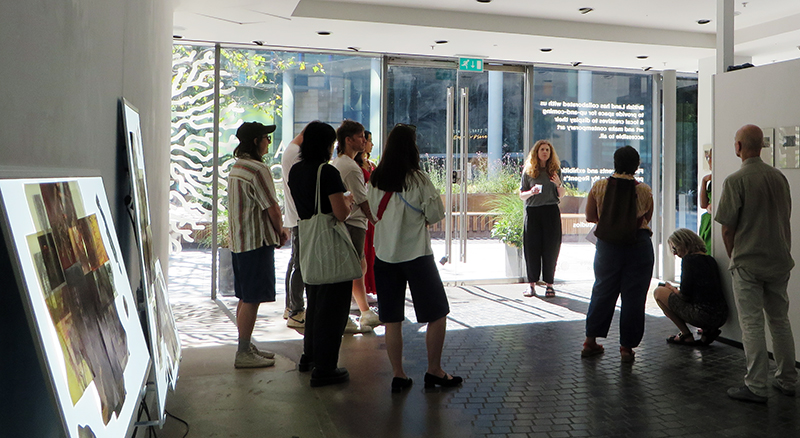
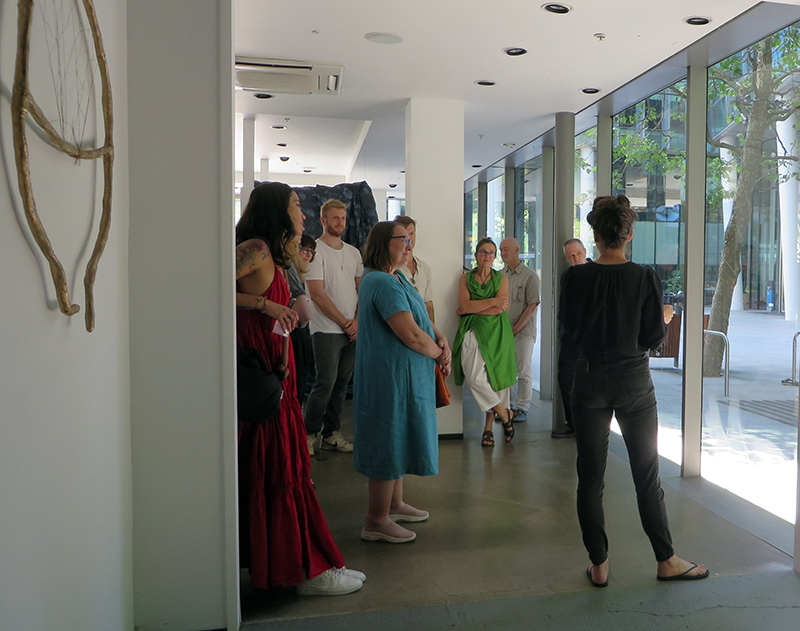
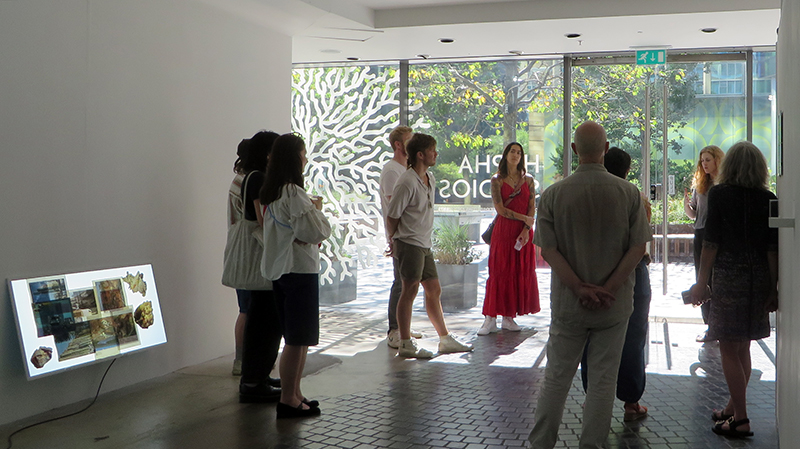
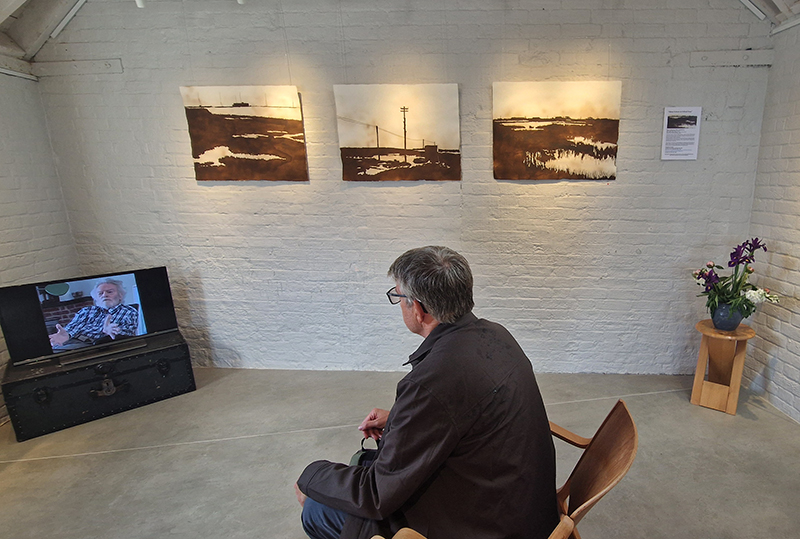
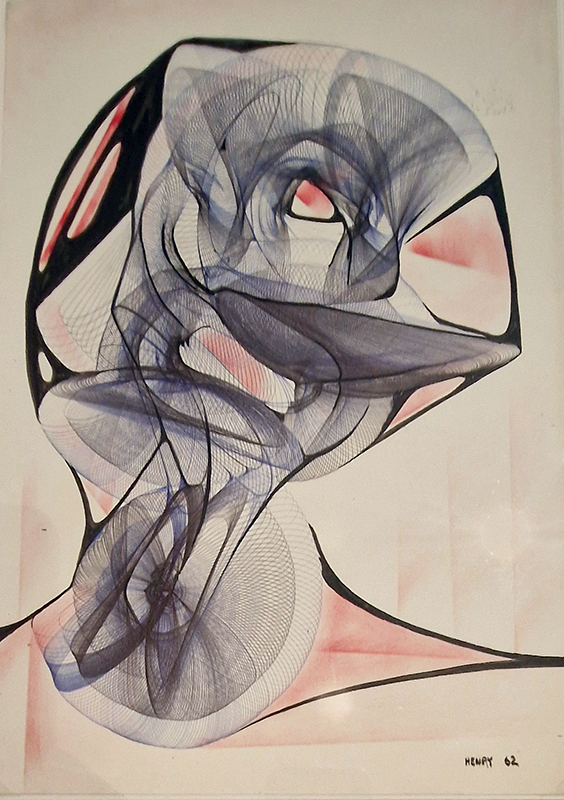
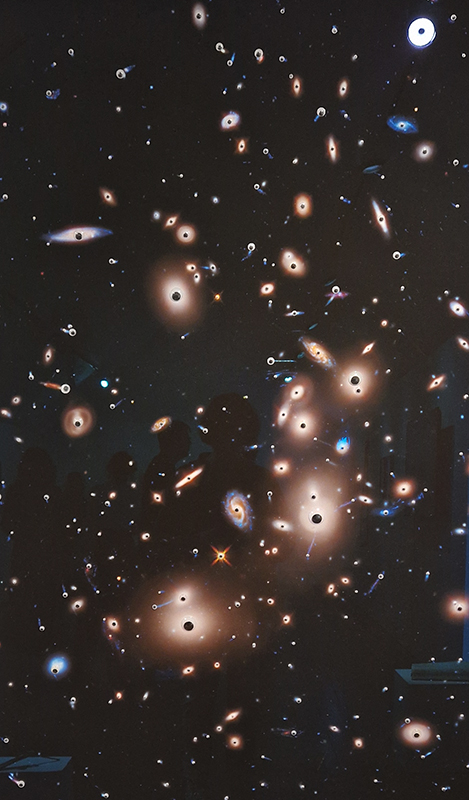
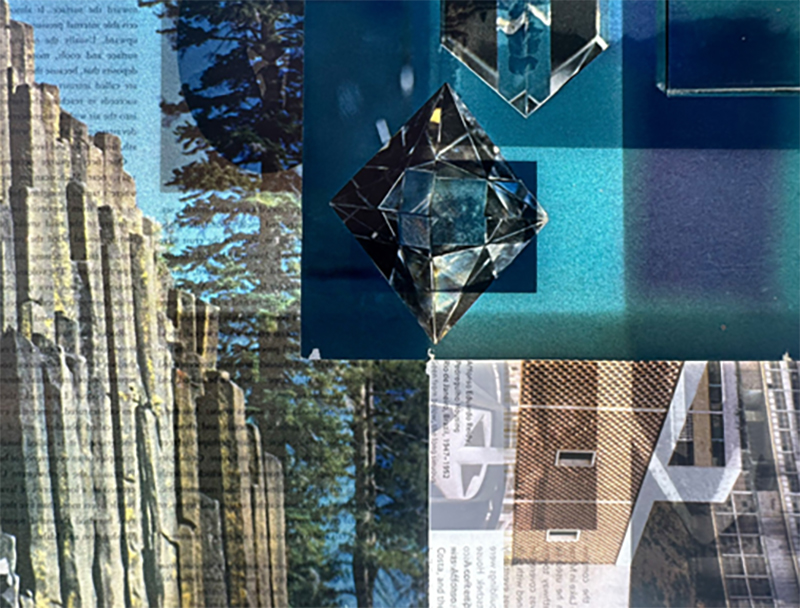
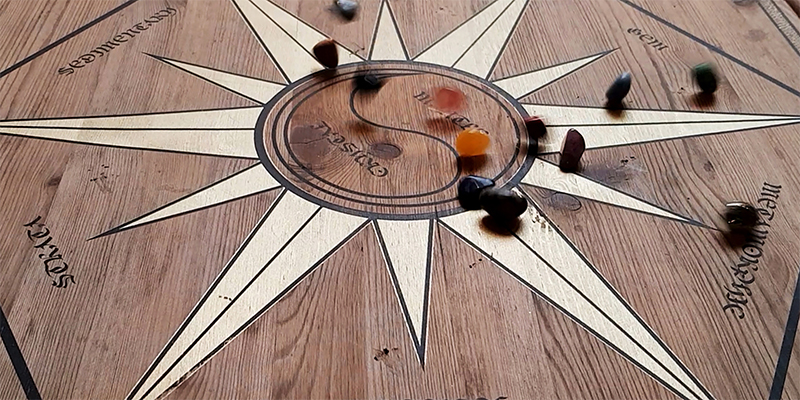
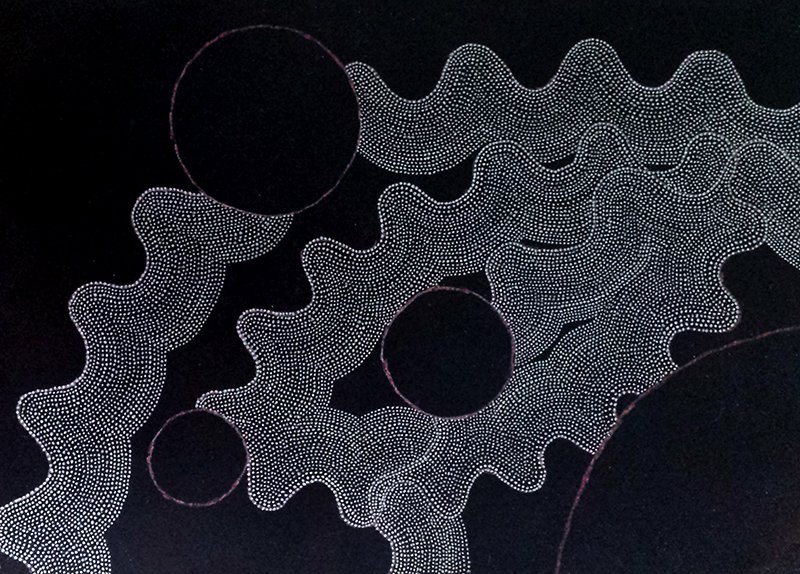
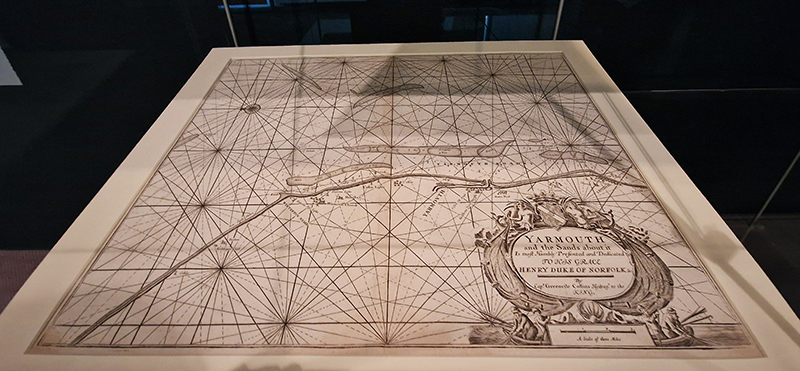
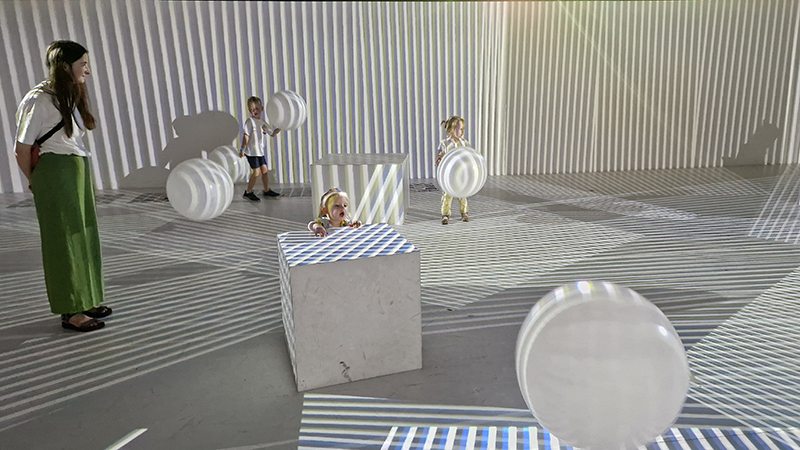
A packed and buzzing opening at The Royal West of England Academy for Cosmos: the art of observing space, curated by Ione Parkin. There was so much to take in, I will need to go back another time to be sure of seeing everything. I feel so lucky to be a part of this exhibition that includes so many wonderful artists as well as precious artifacts from the Royal Astronomical Society.
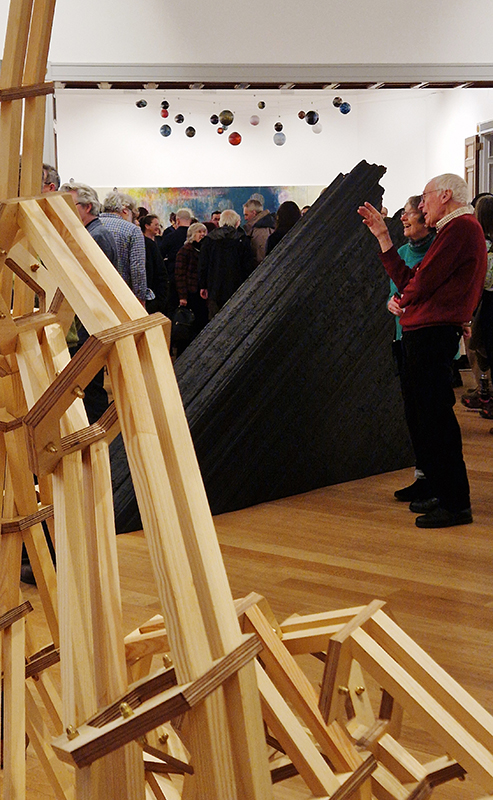
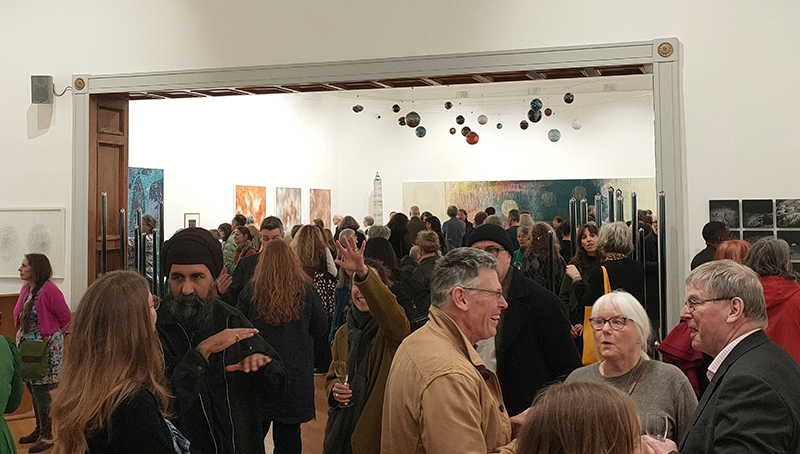
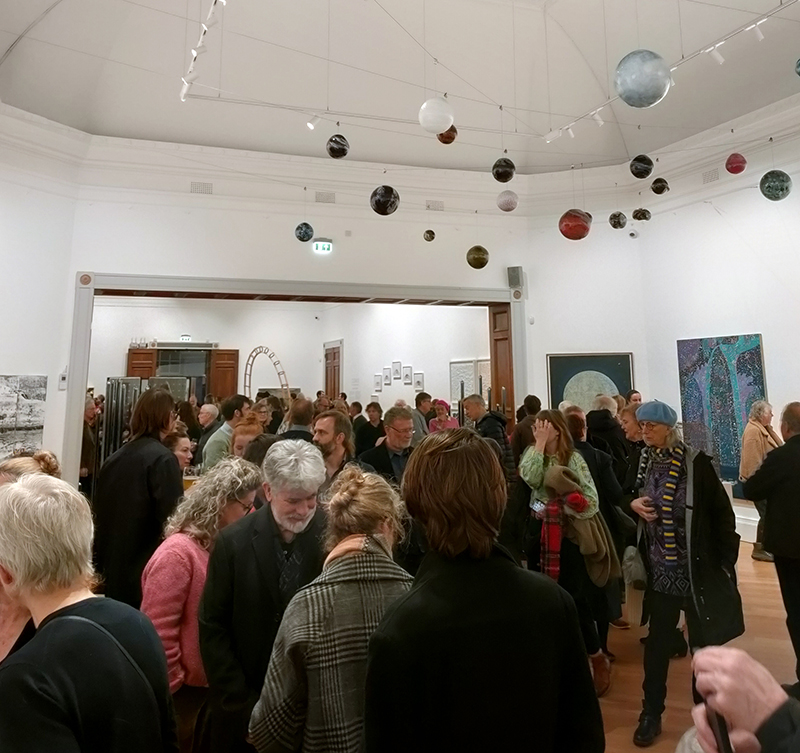
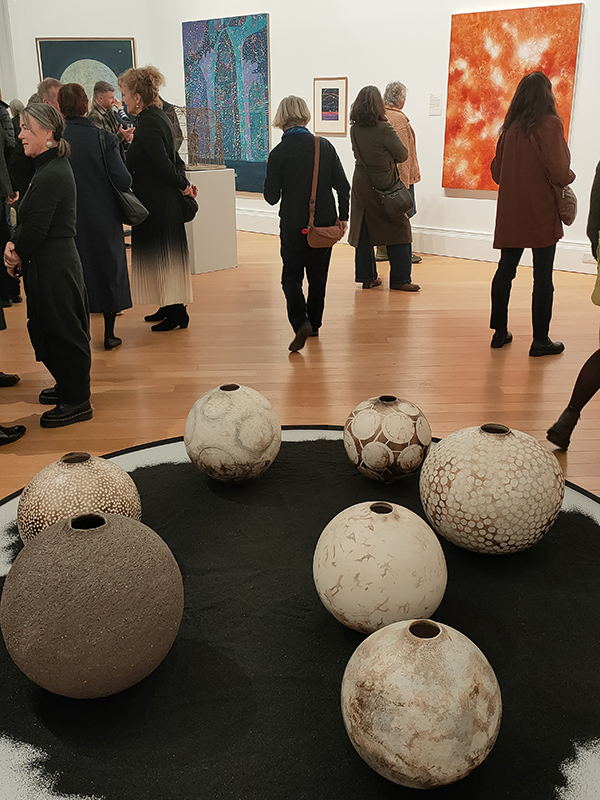
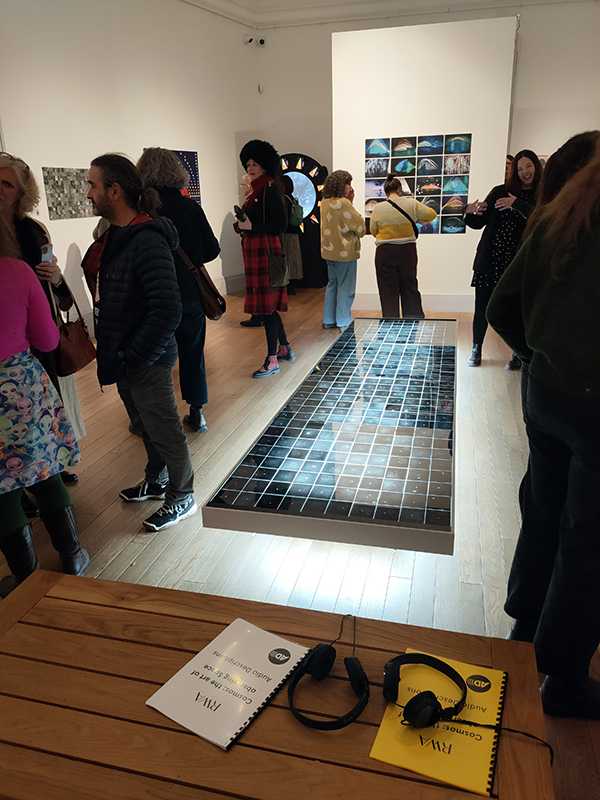
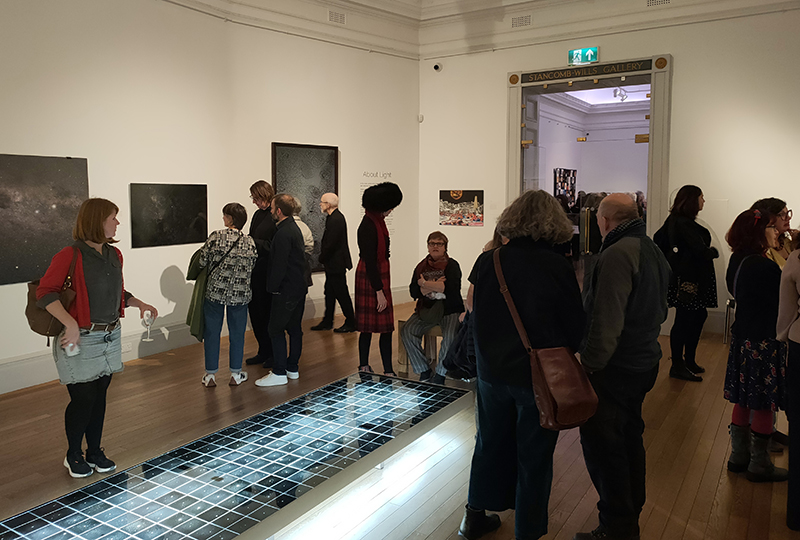
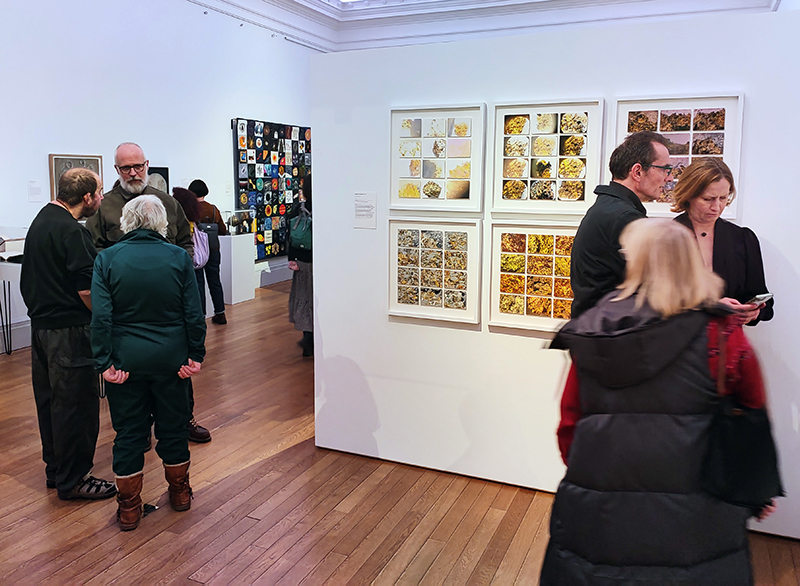
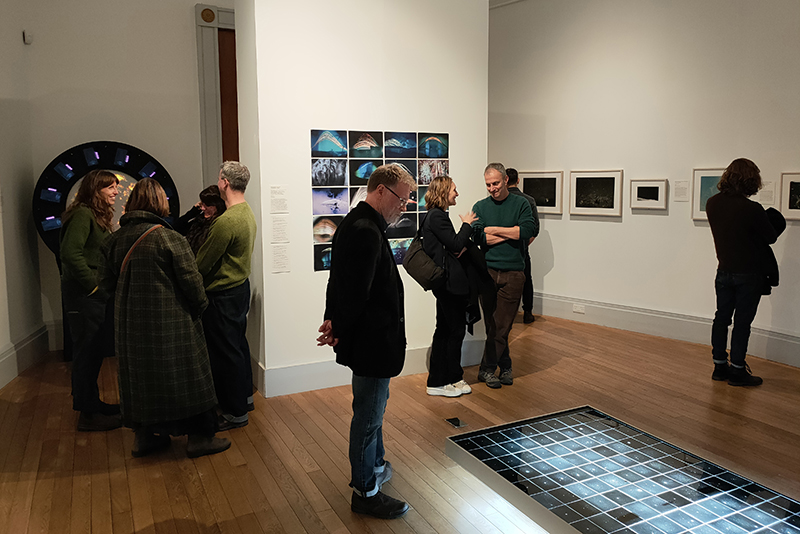
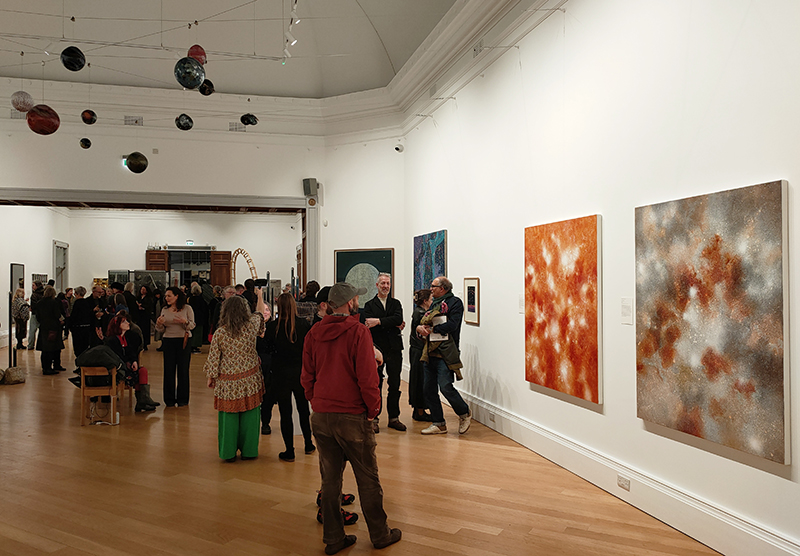





















The following Private View images are courtesy of Alastair Brookes, KoLab Studios




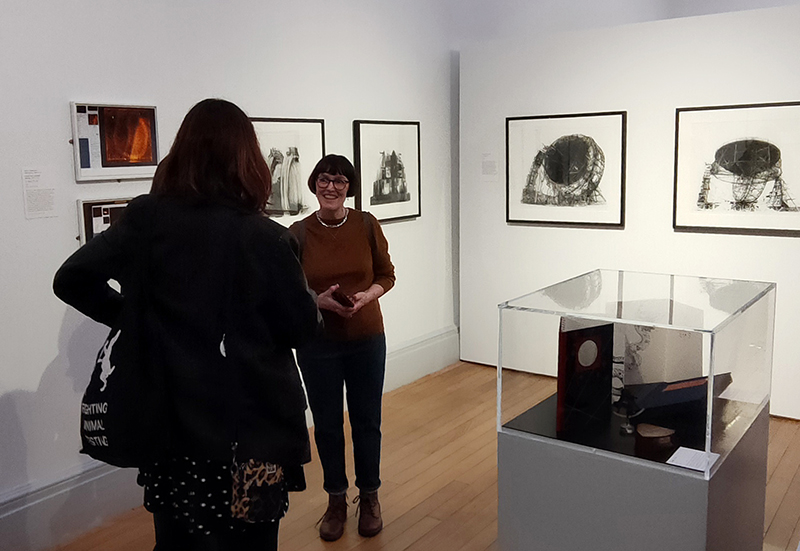
There is a fabulous exhibition catalogue to accompany the exhibition with foreword by astrophysicist, author and broadcaster, Chris Lintott and contributions from Ione Parkin RWA, visiting Honorary Fellow of the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Leicester; Sian Prosser, library and archives manager at the Royal Astronomical Society; and Amaury Triaud, Professor of Exoplanetology at the University of Birmingham. Image Alastair Brookes, KoLab Studios.

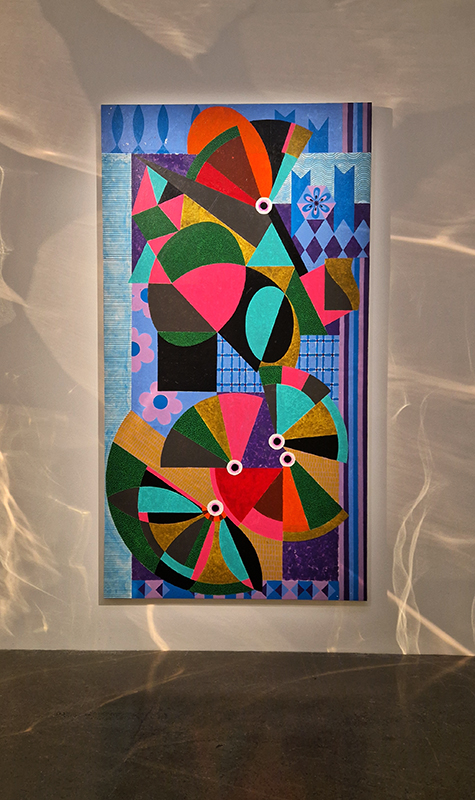
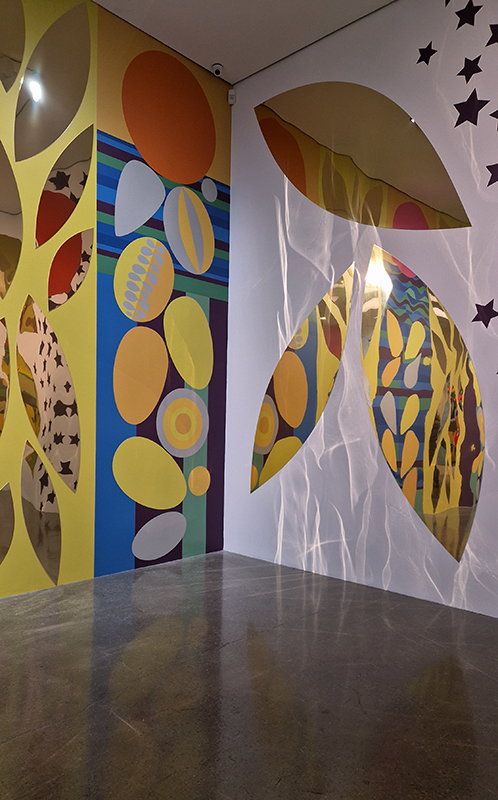
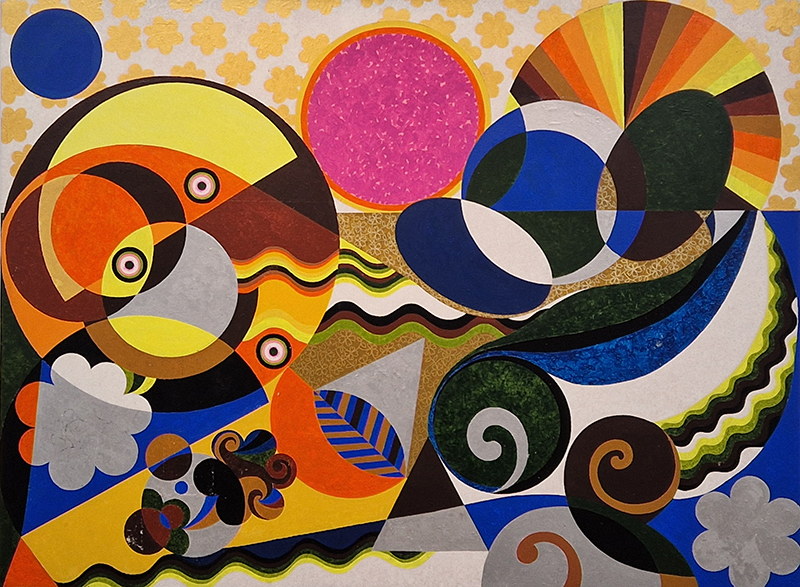
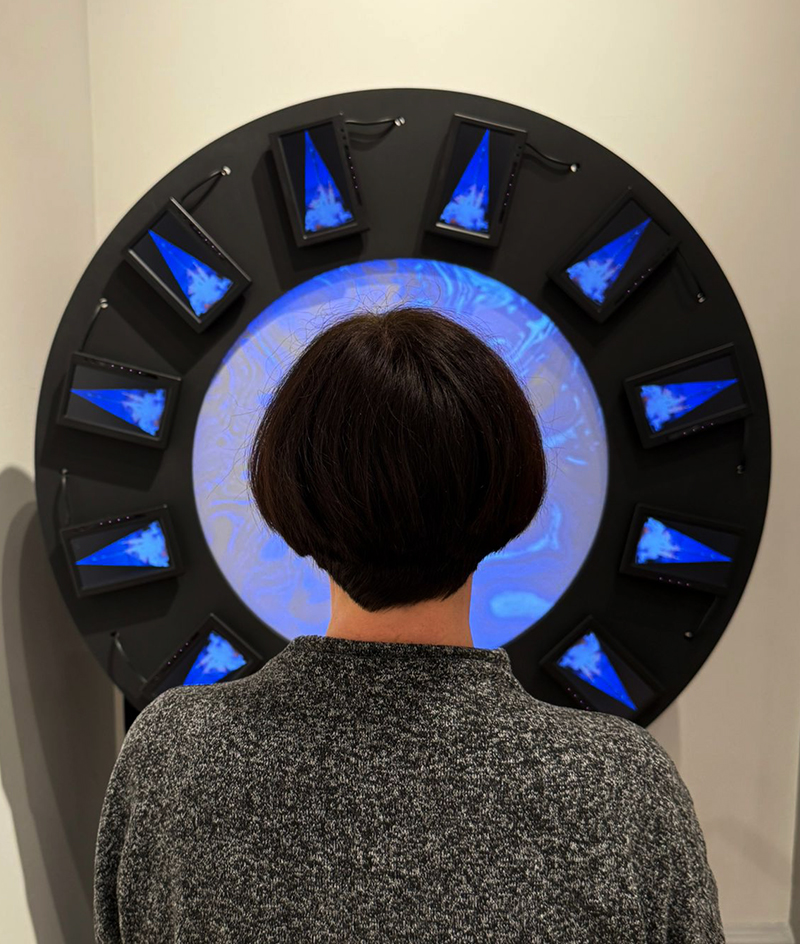
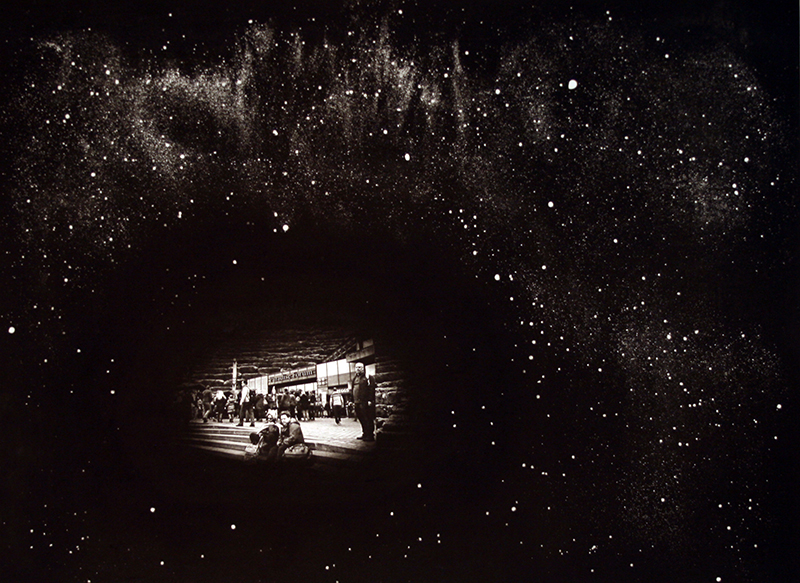
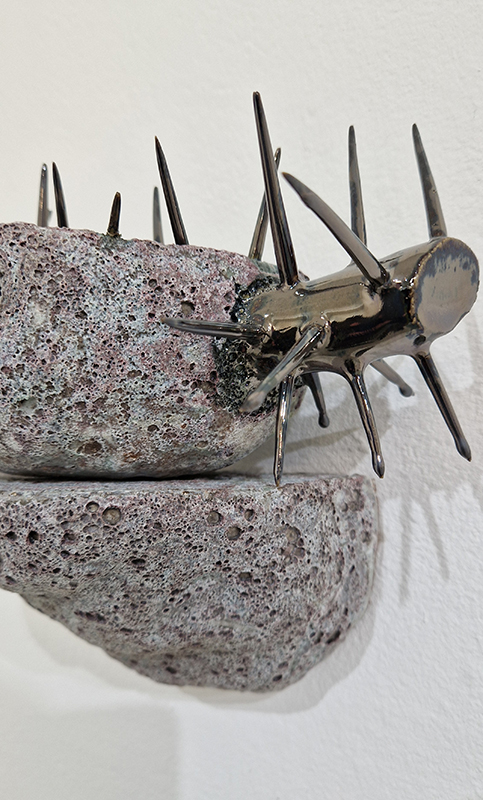
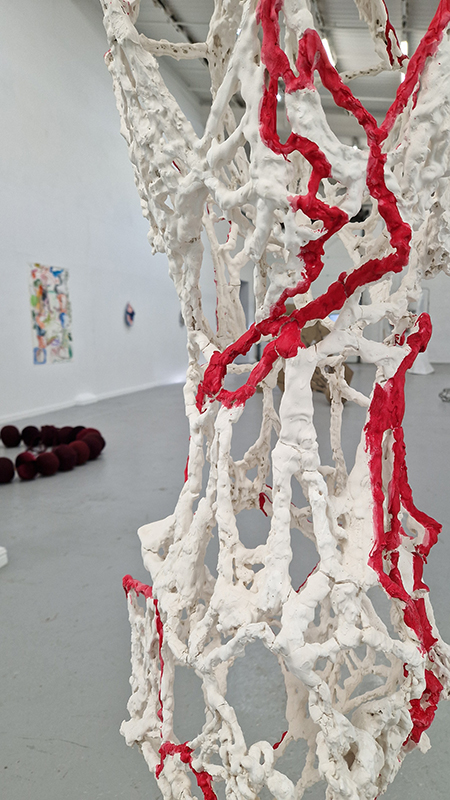
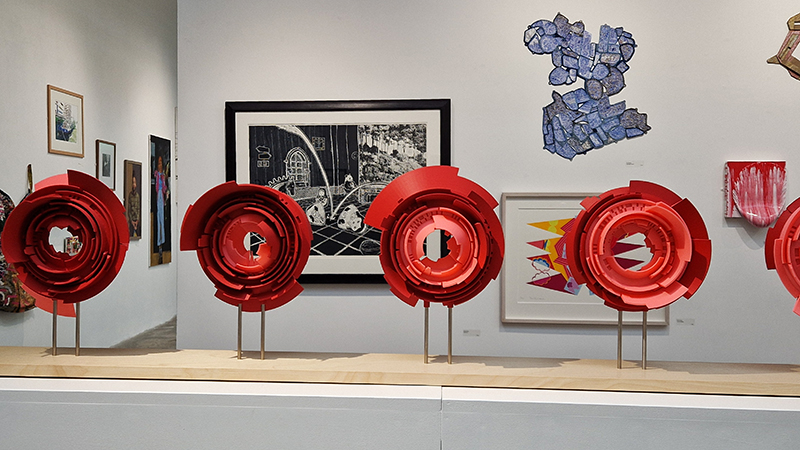
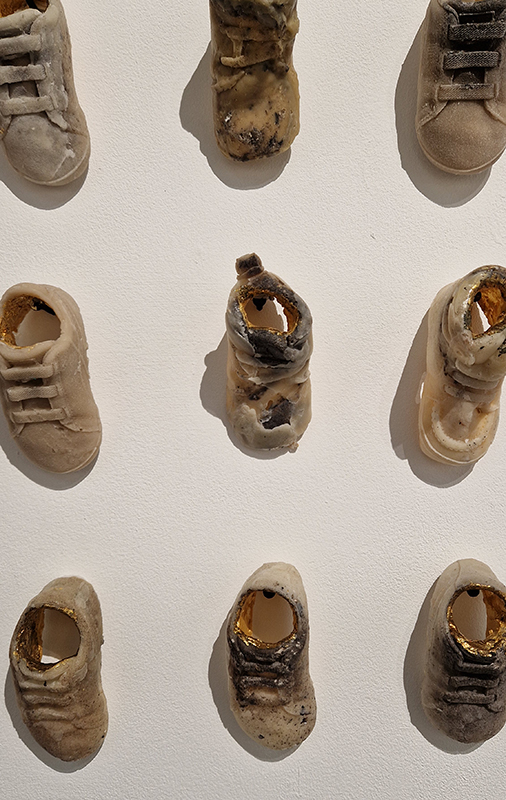
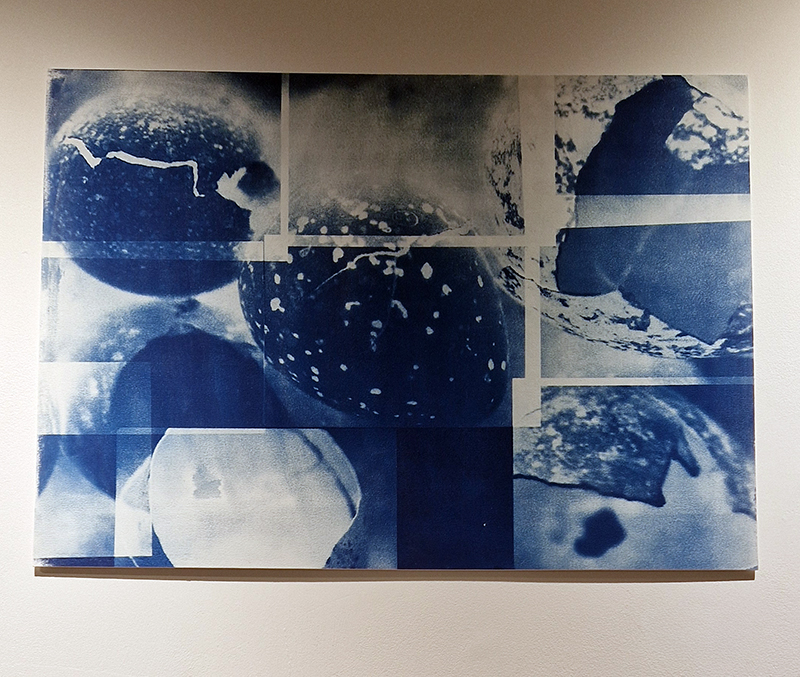
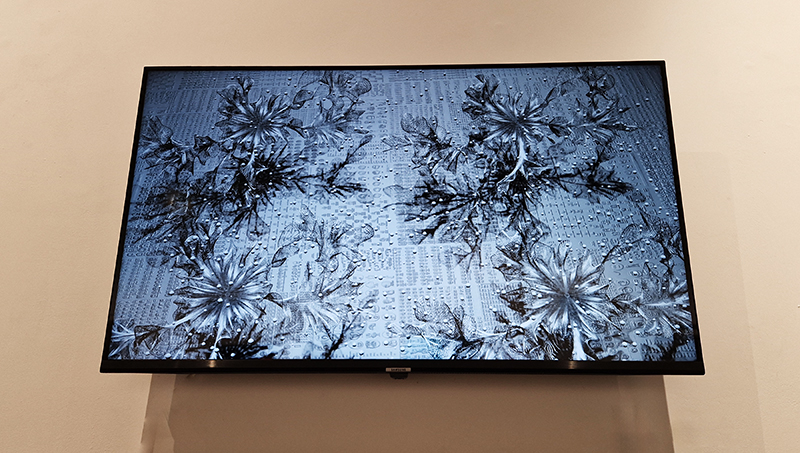
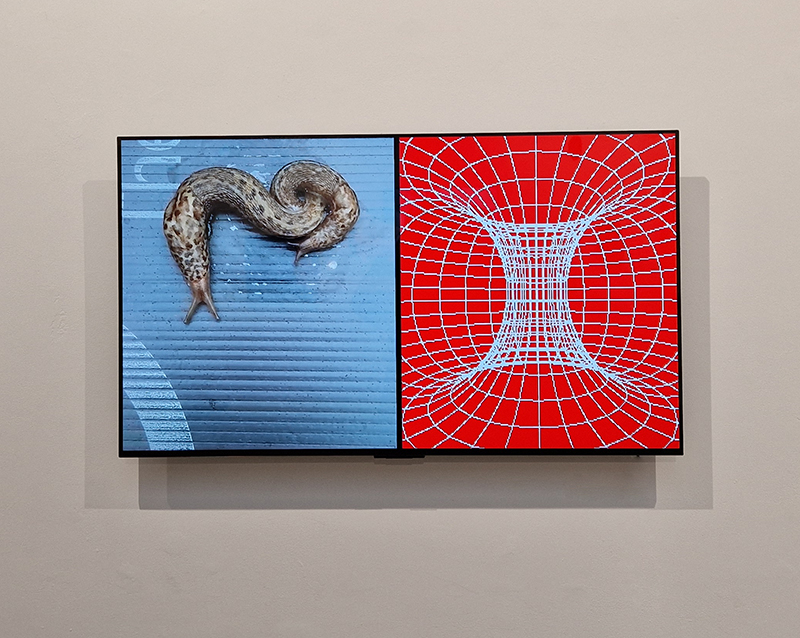
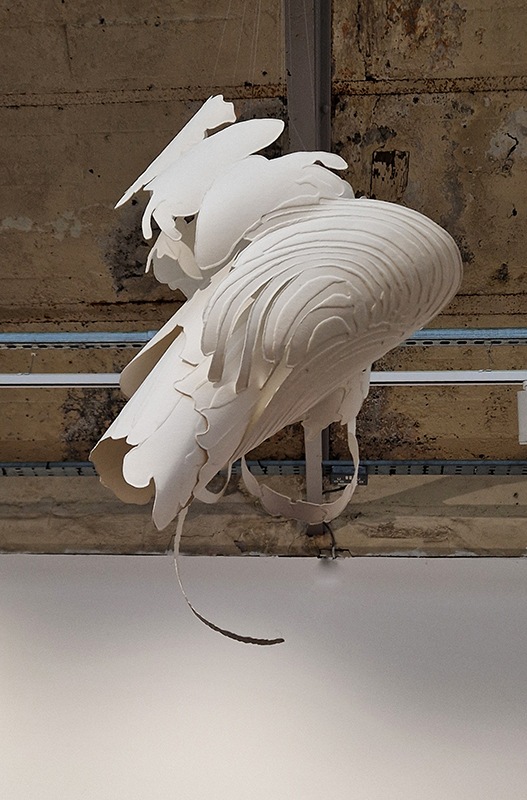
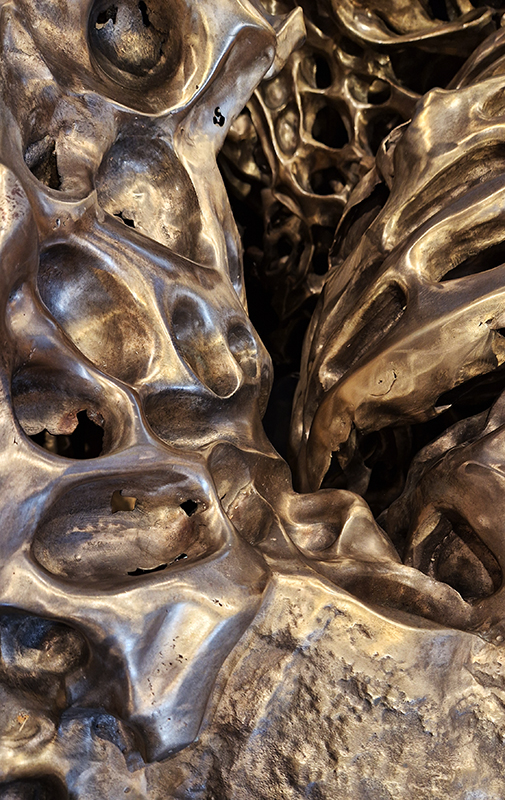
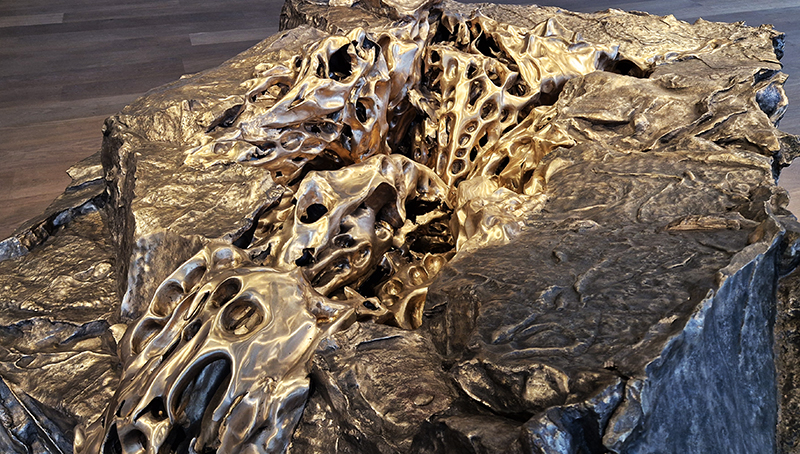
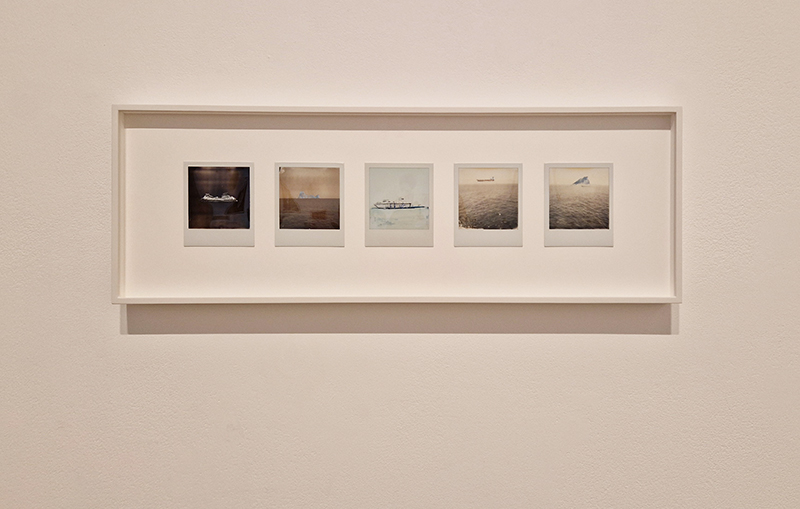
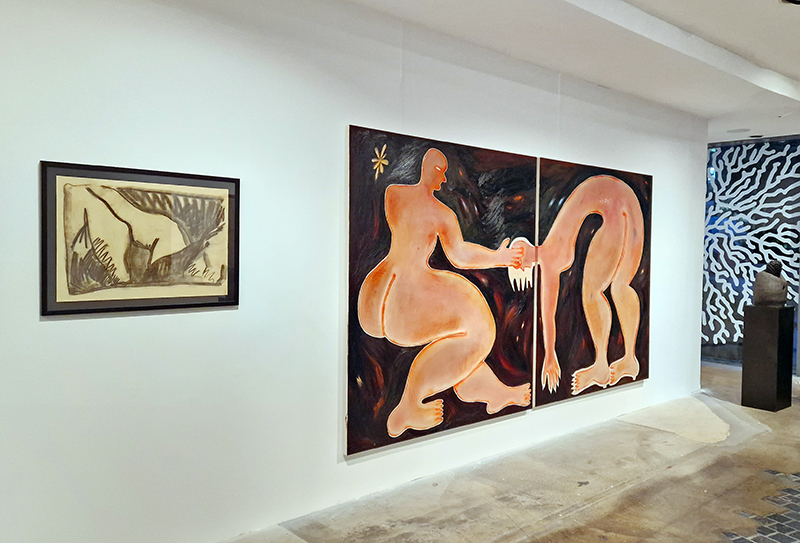
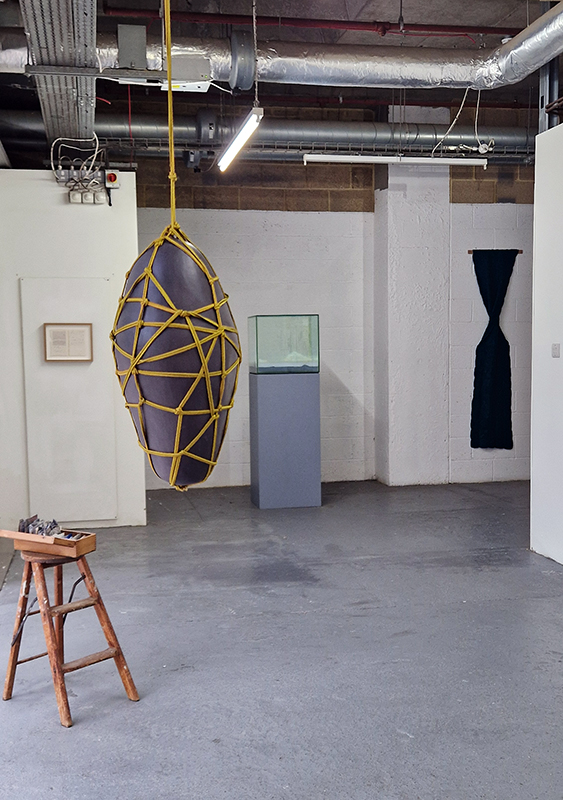
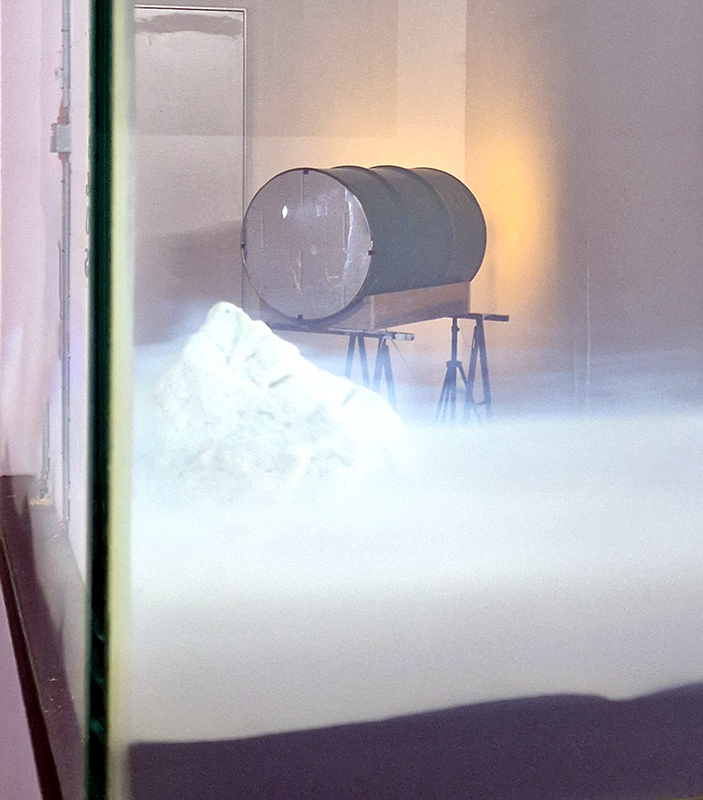
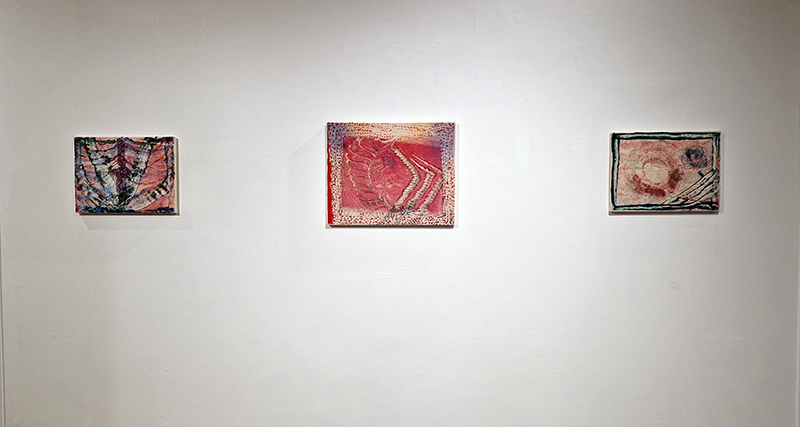
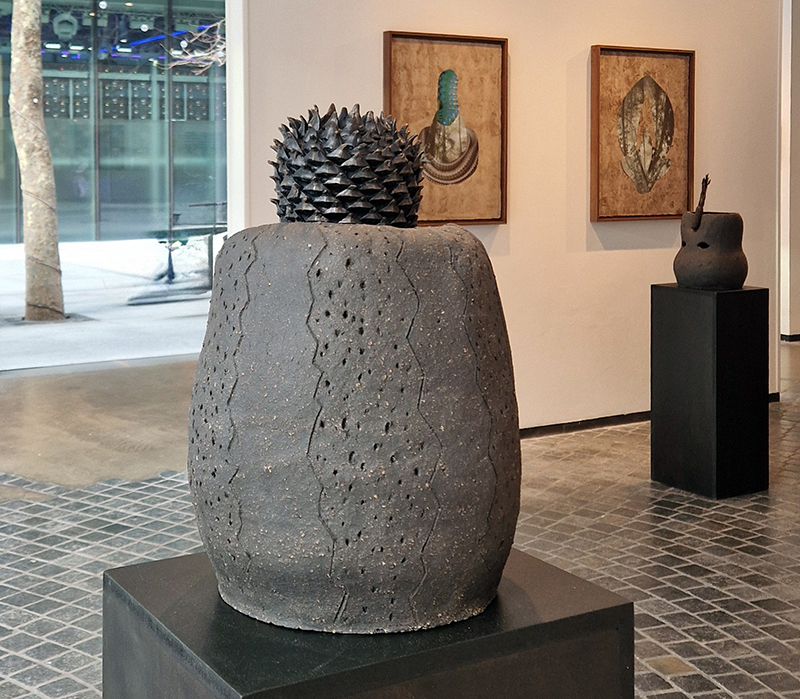
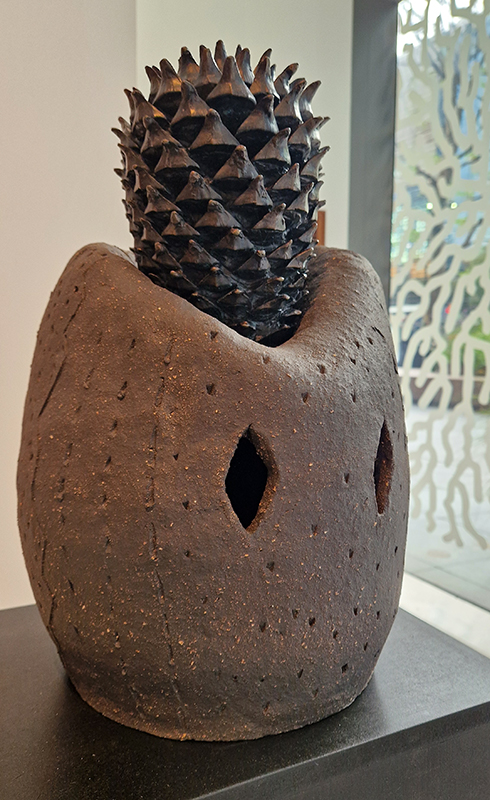
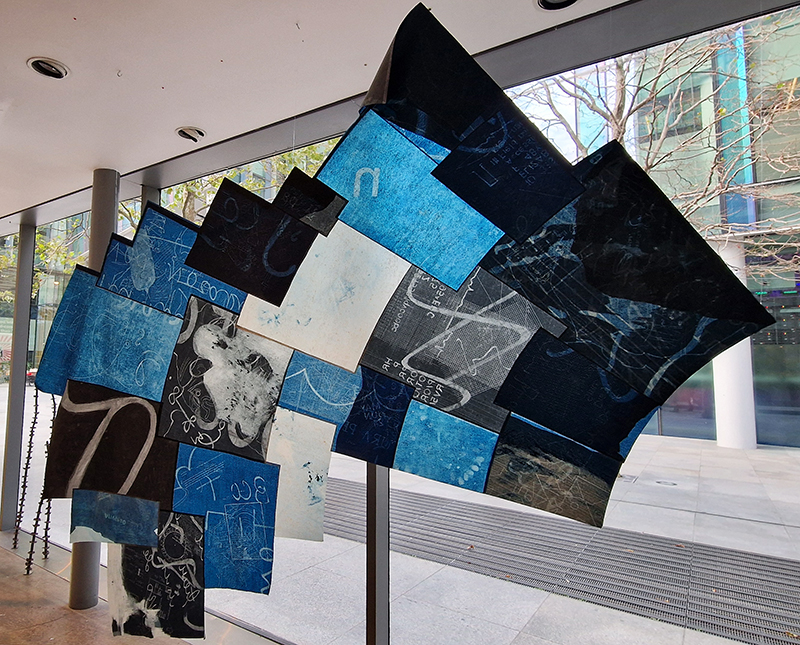
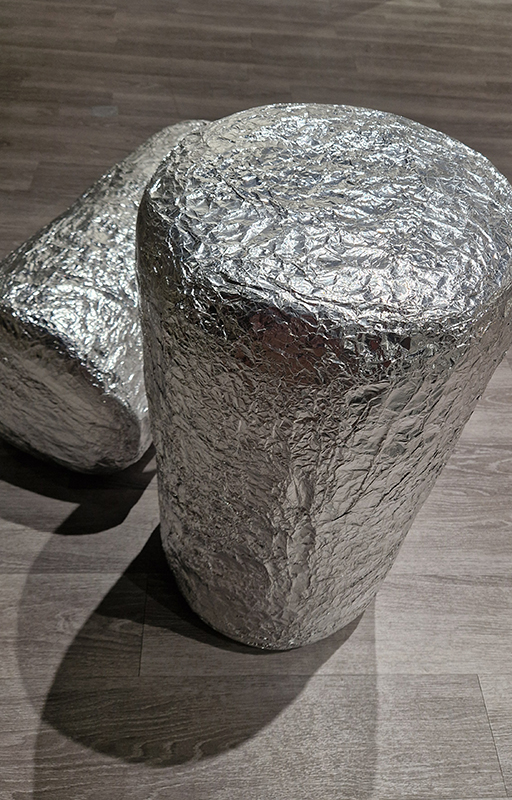
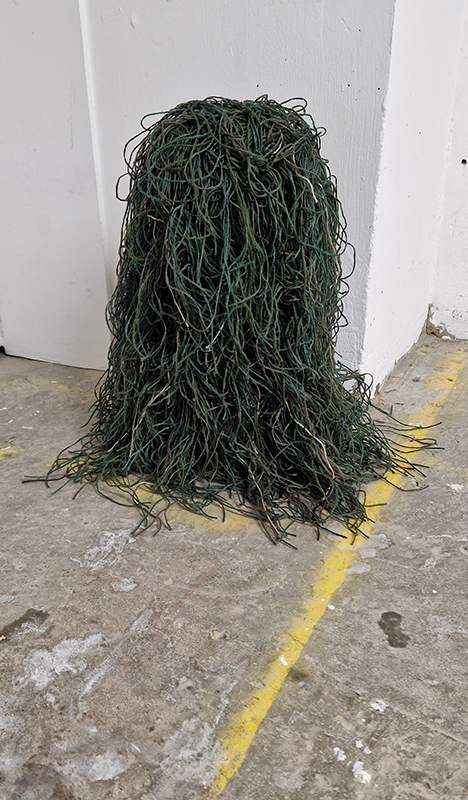
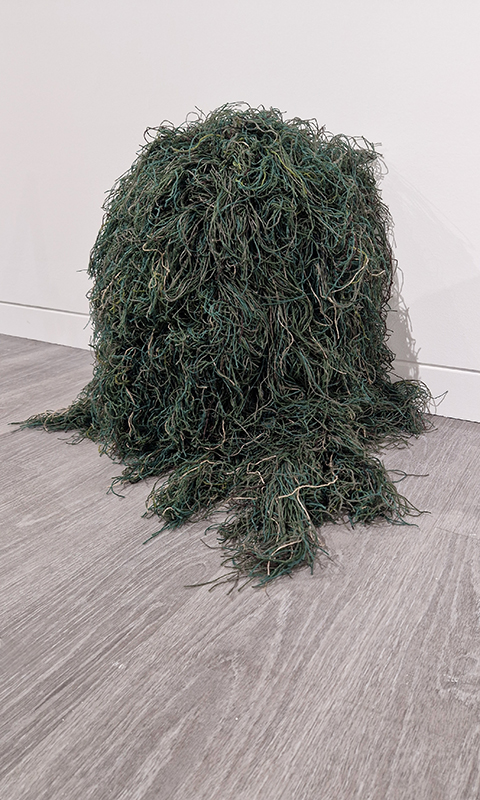
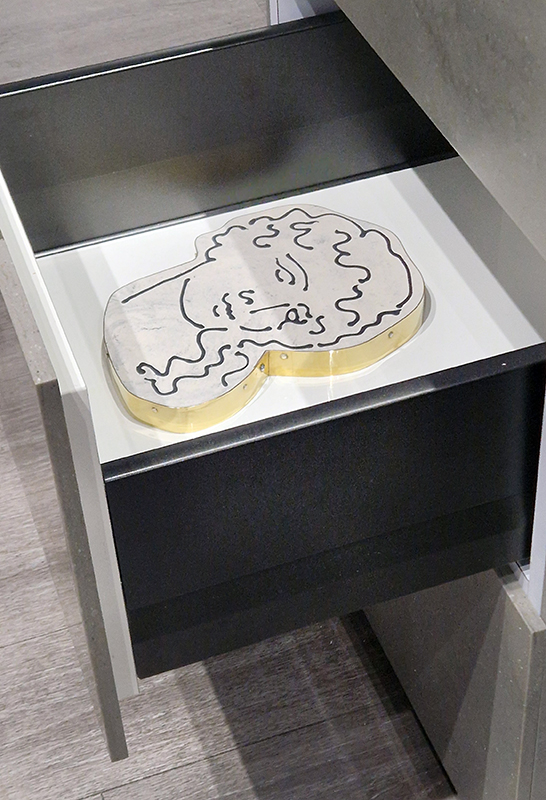
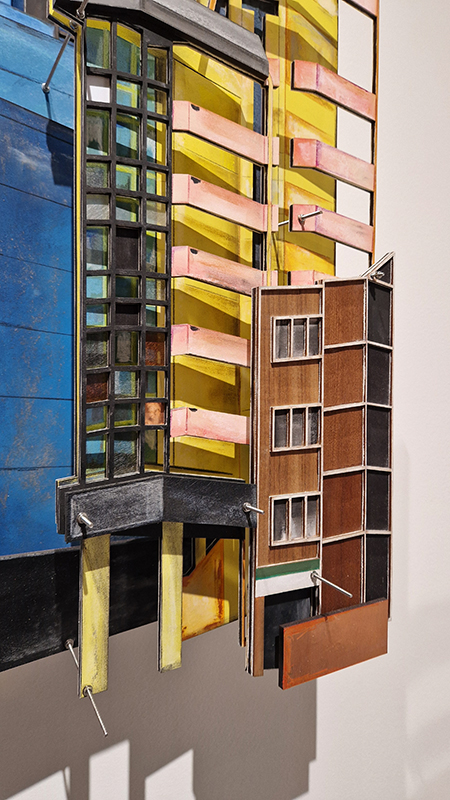
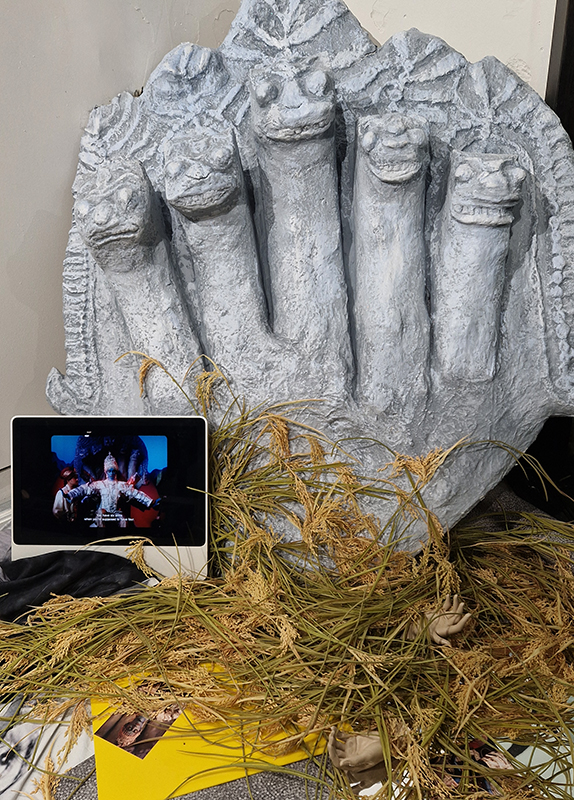
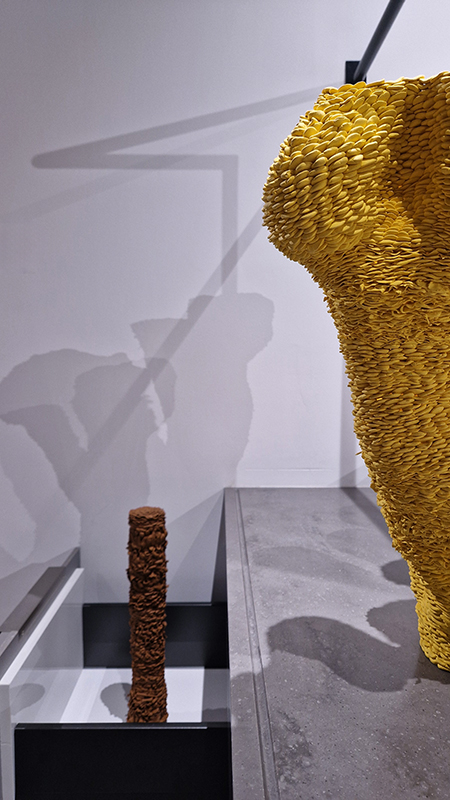
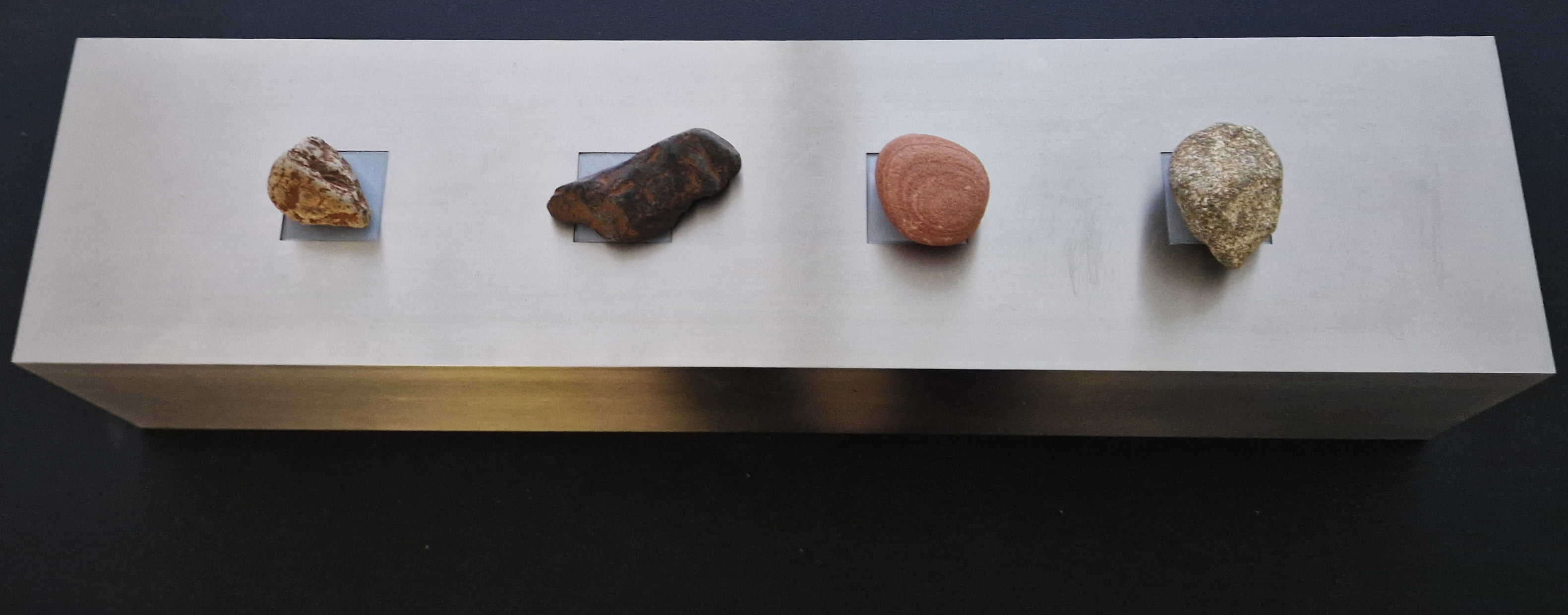
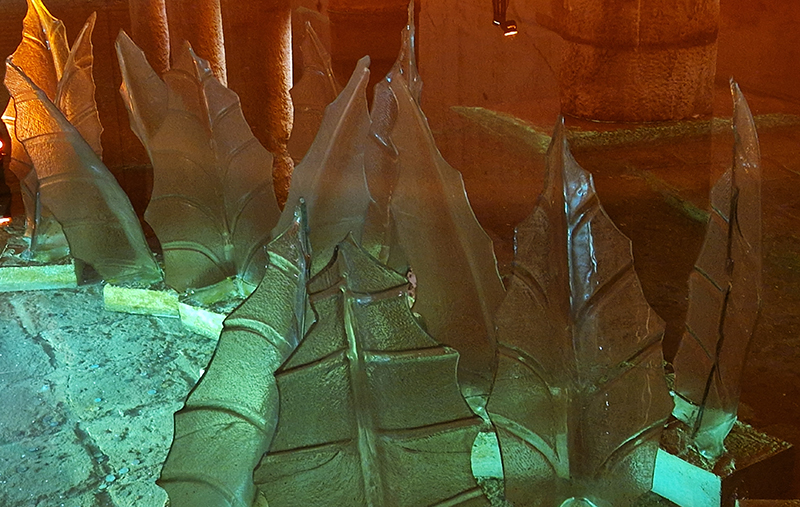
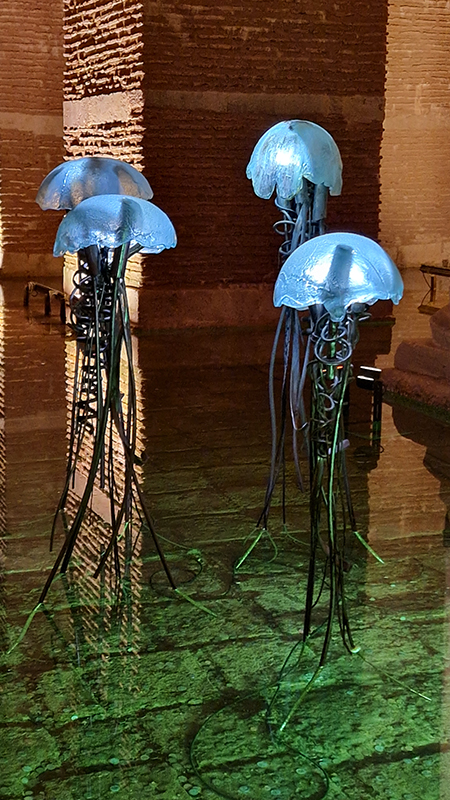
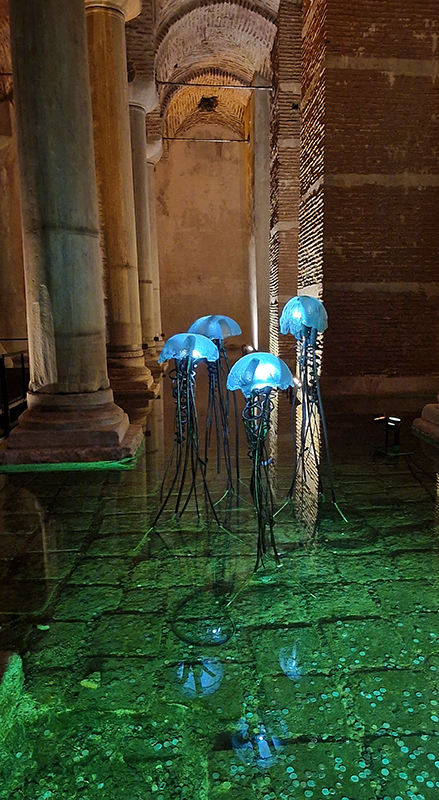
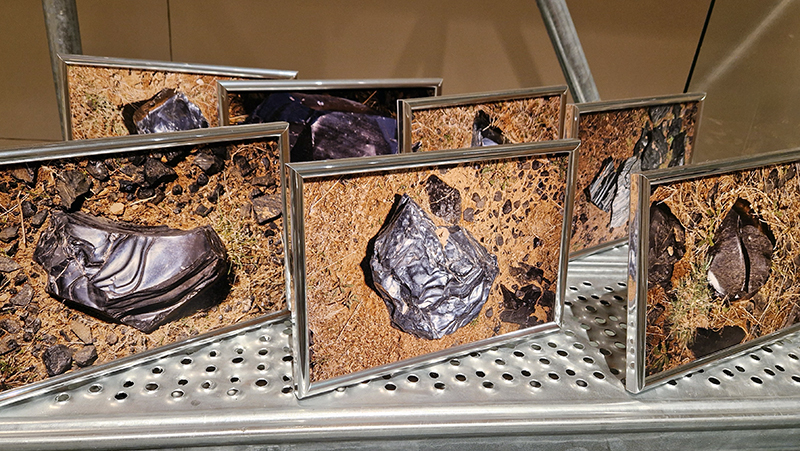
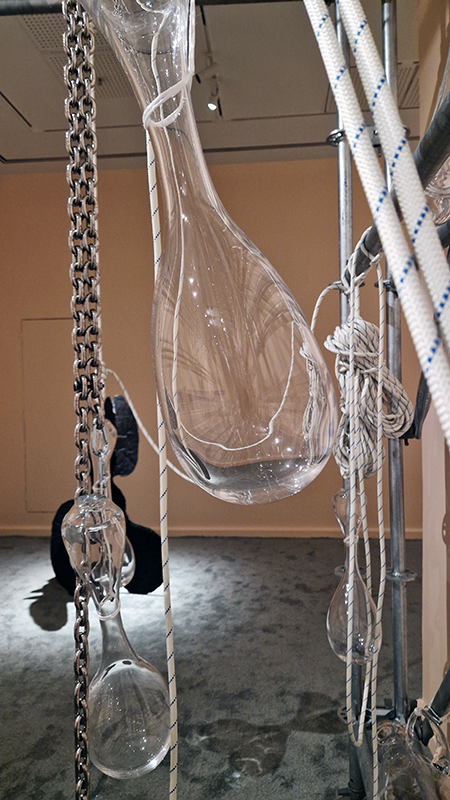
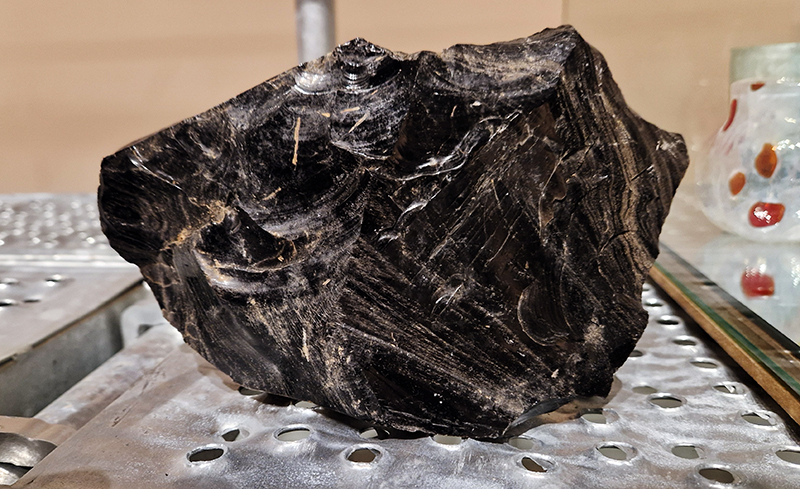
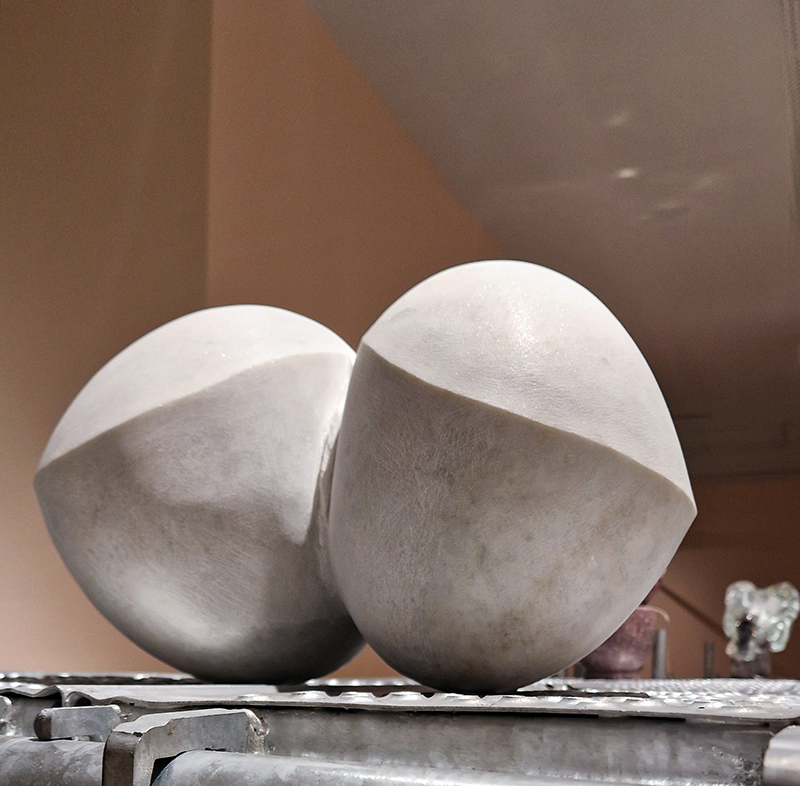
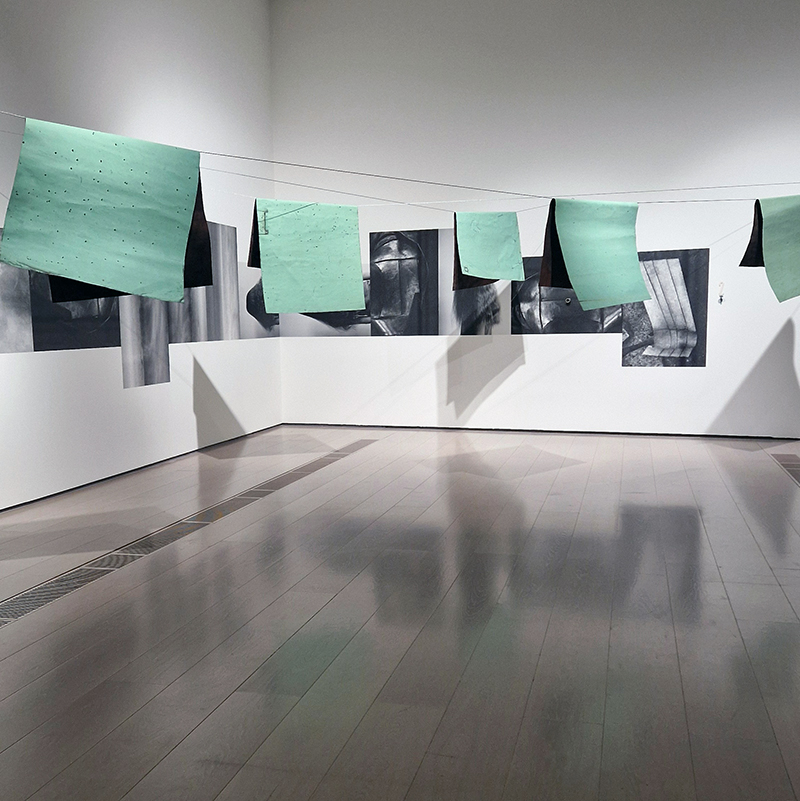
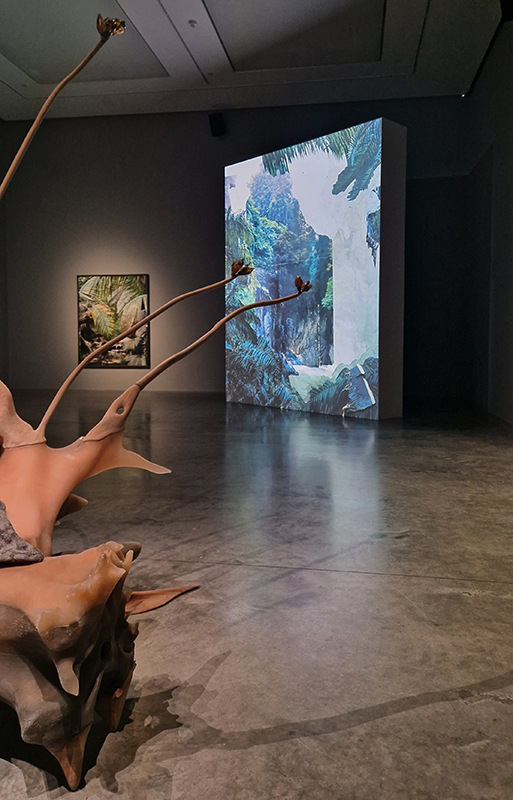
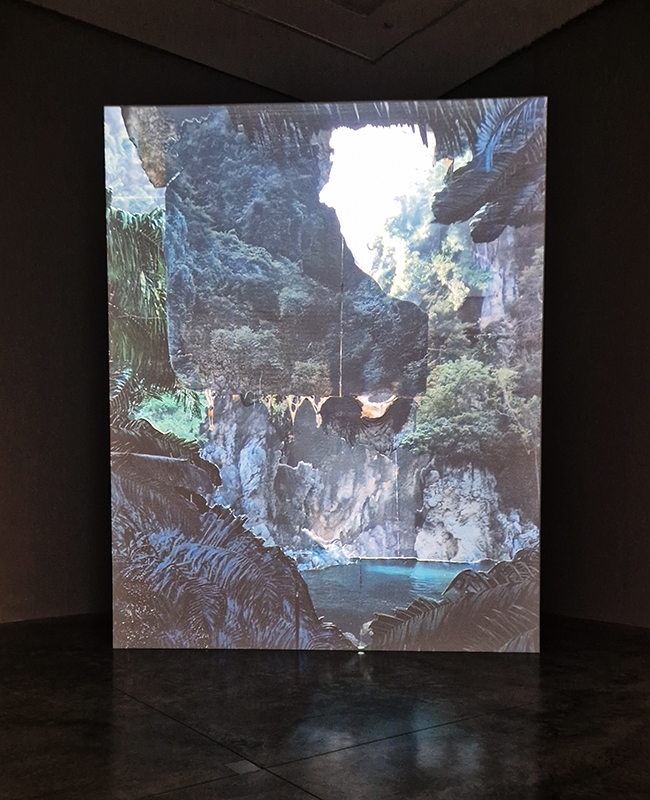
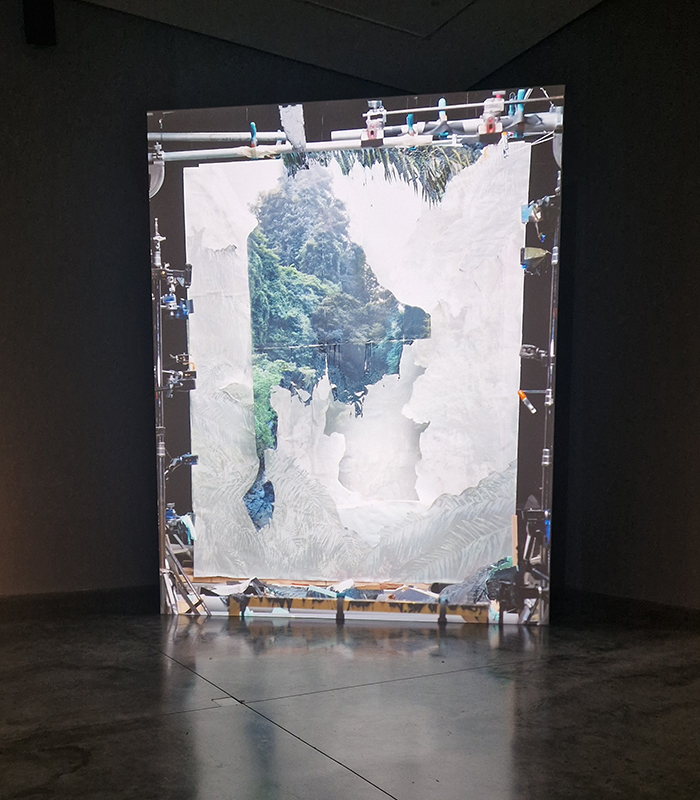
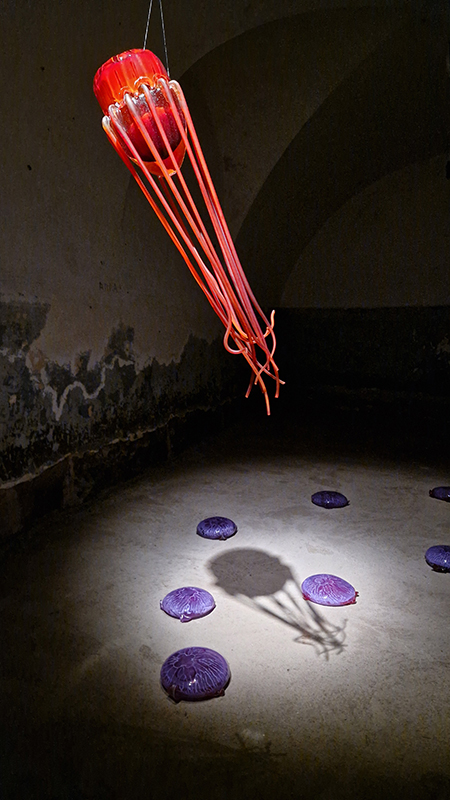
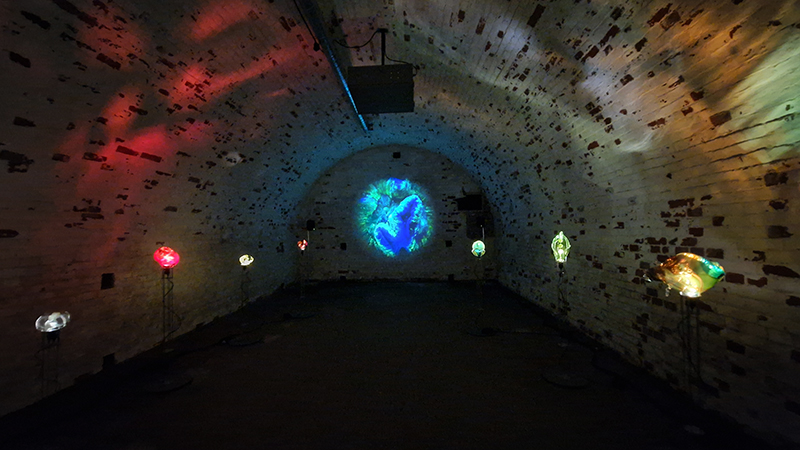
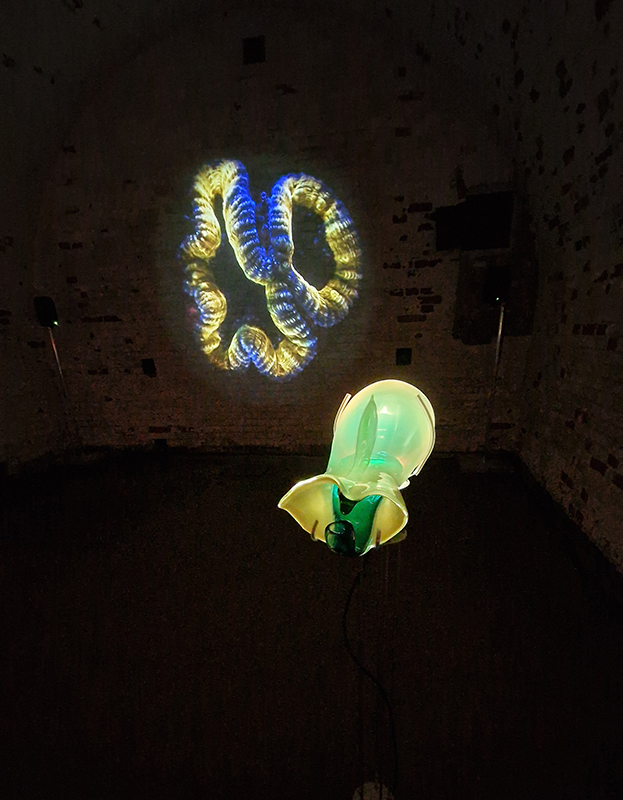
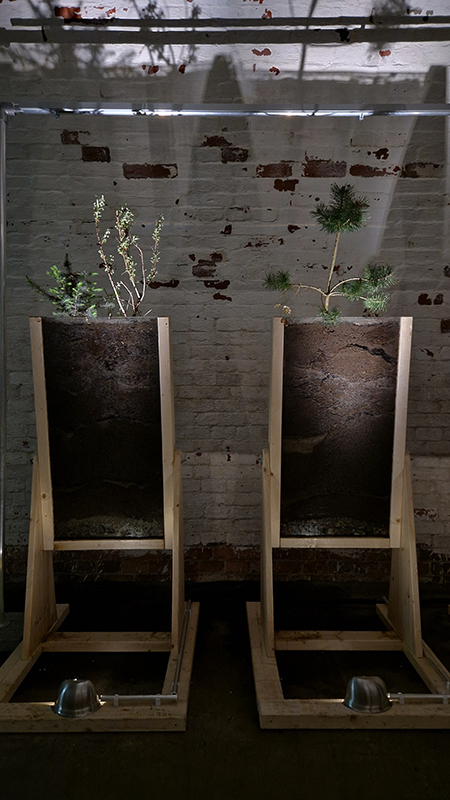
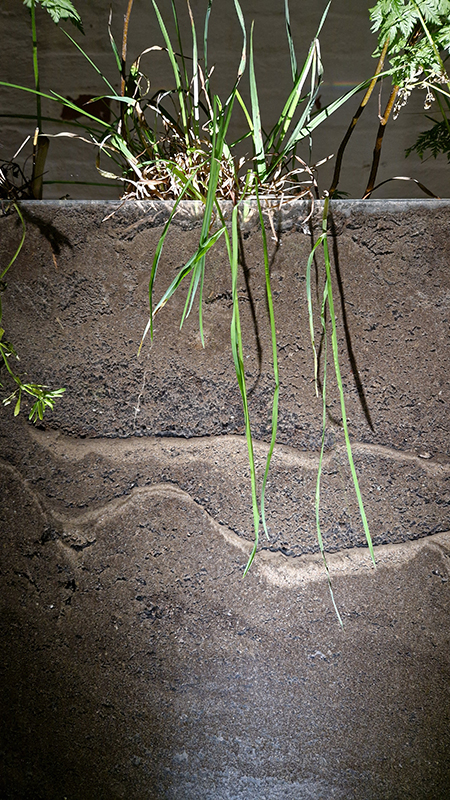
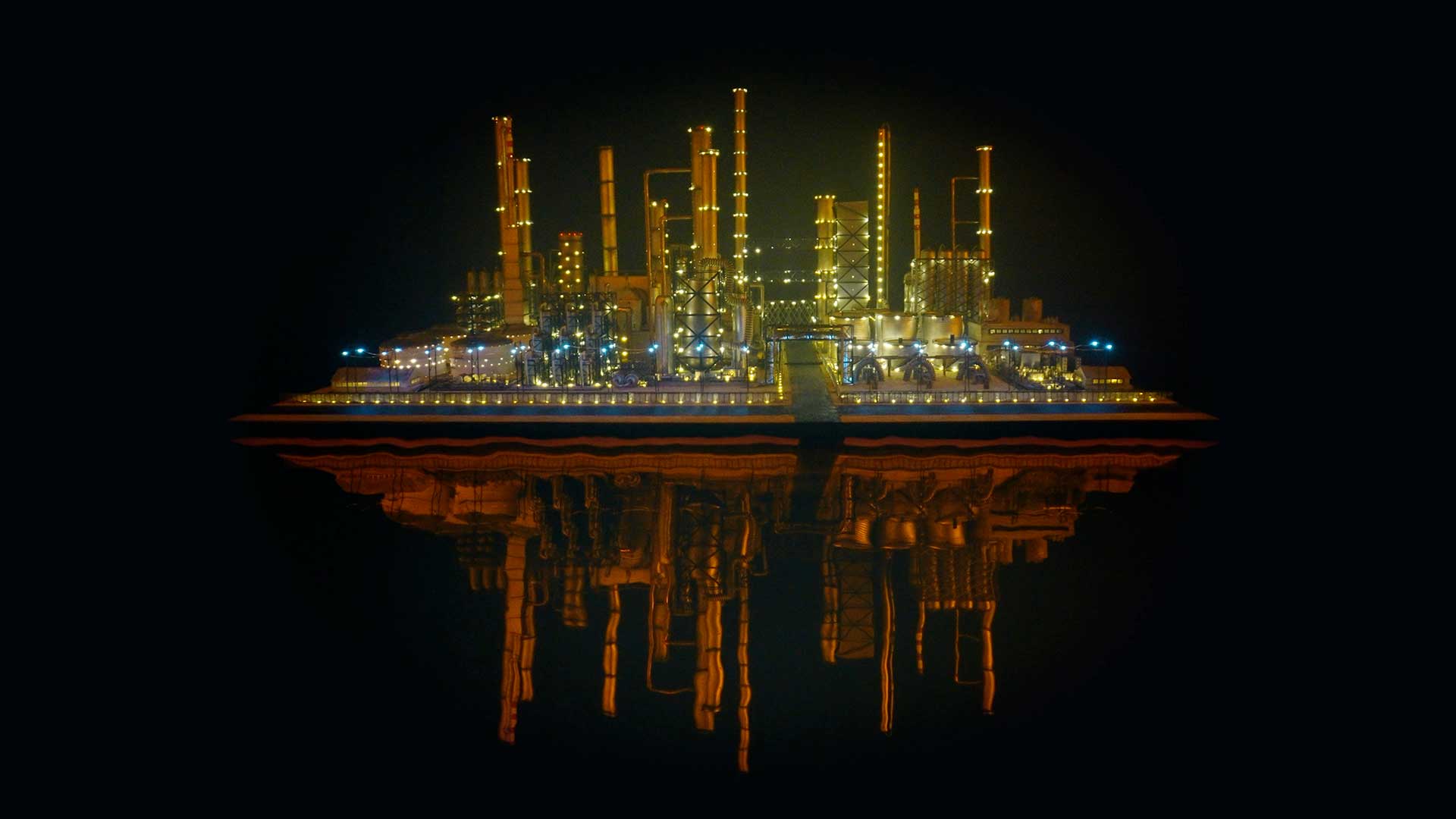
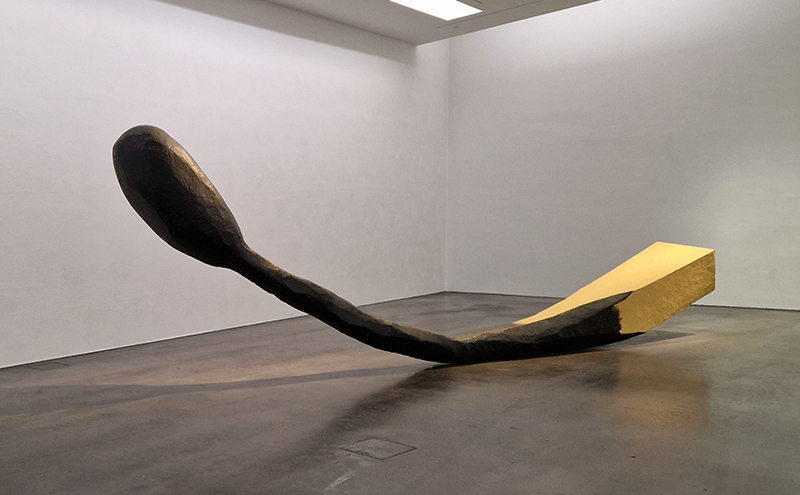
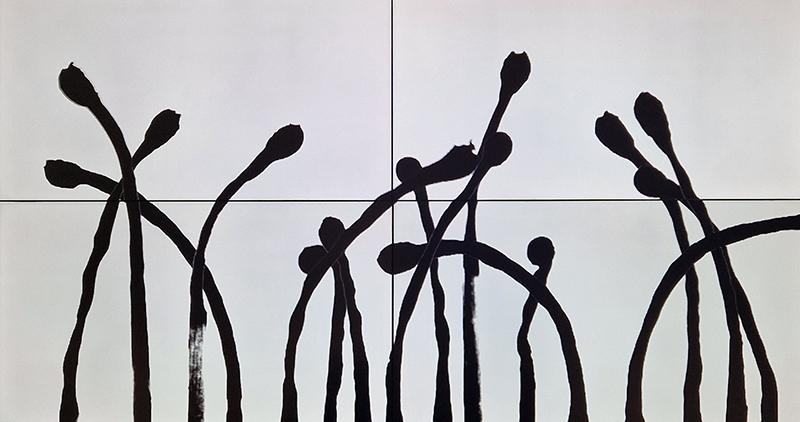
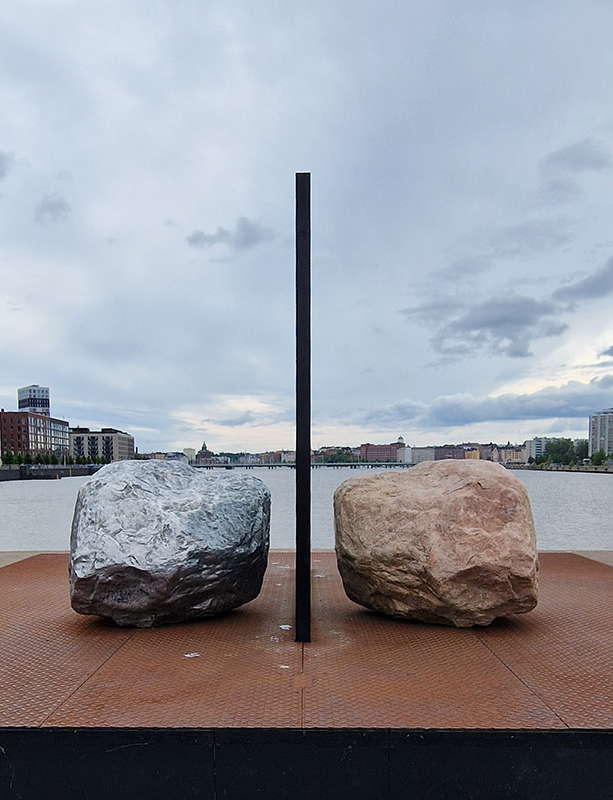
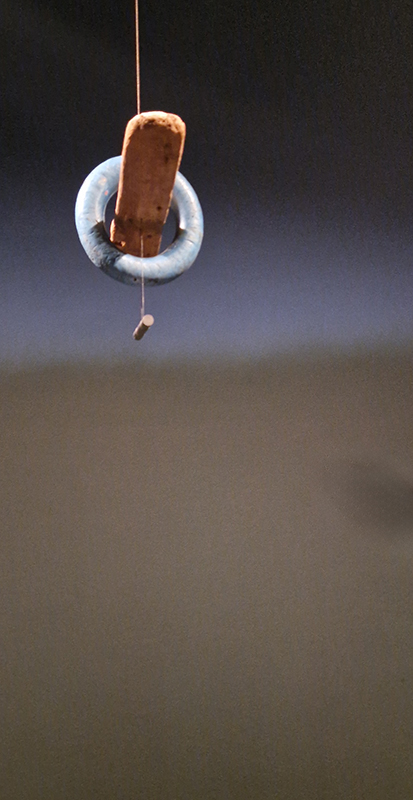
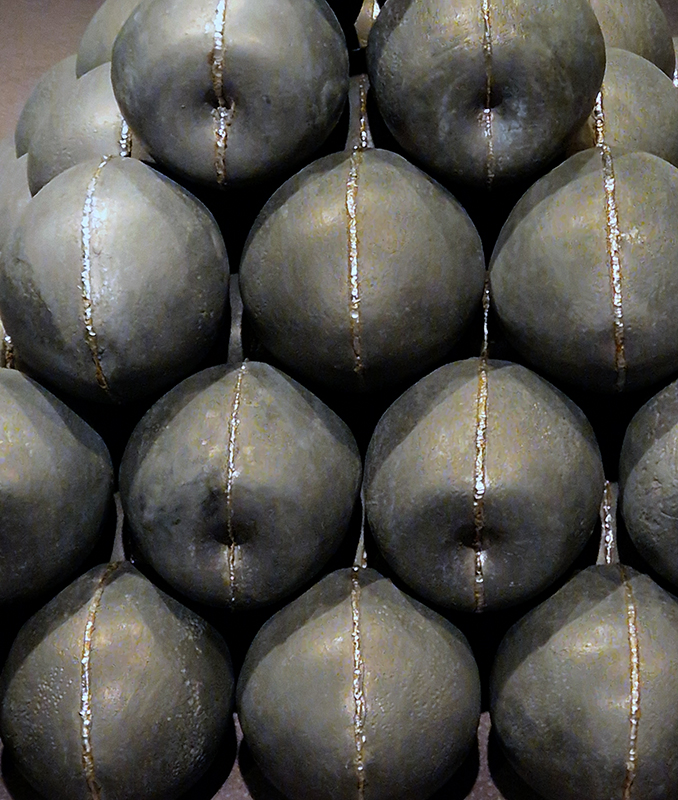
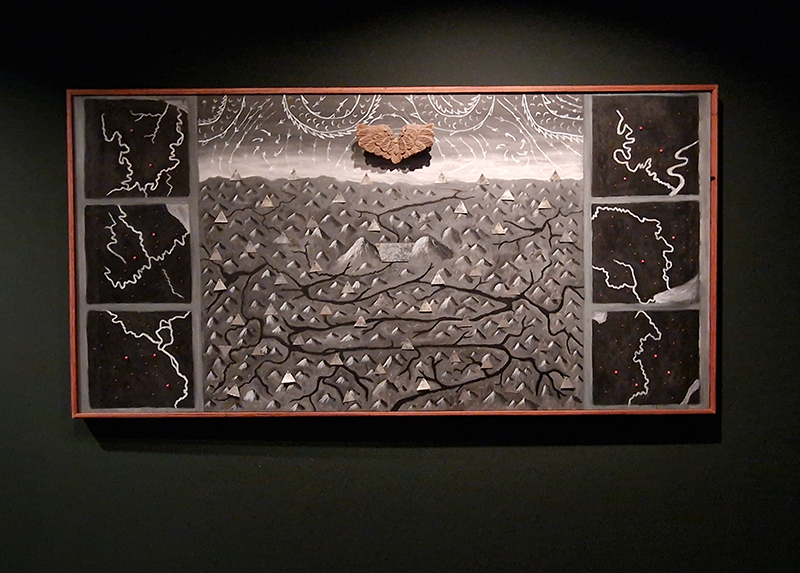
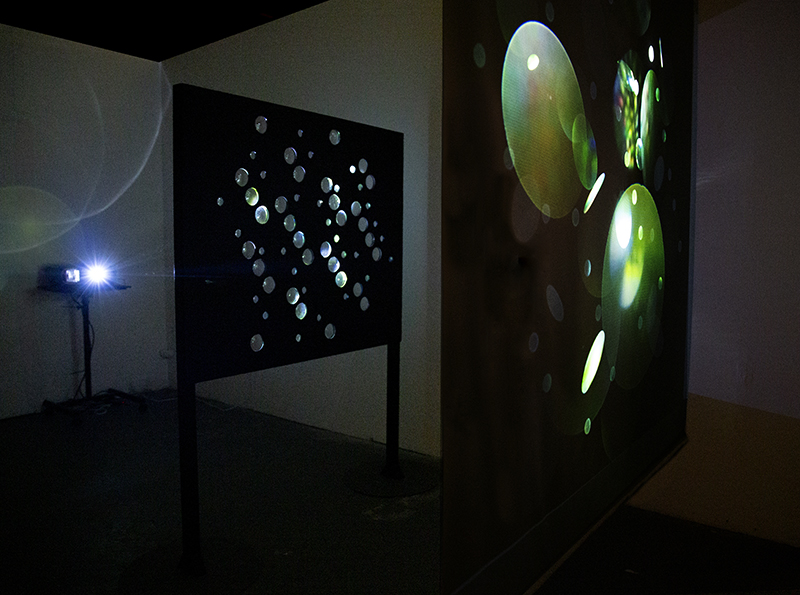
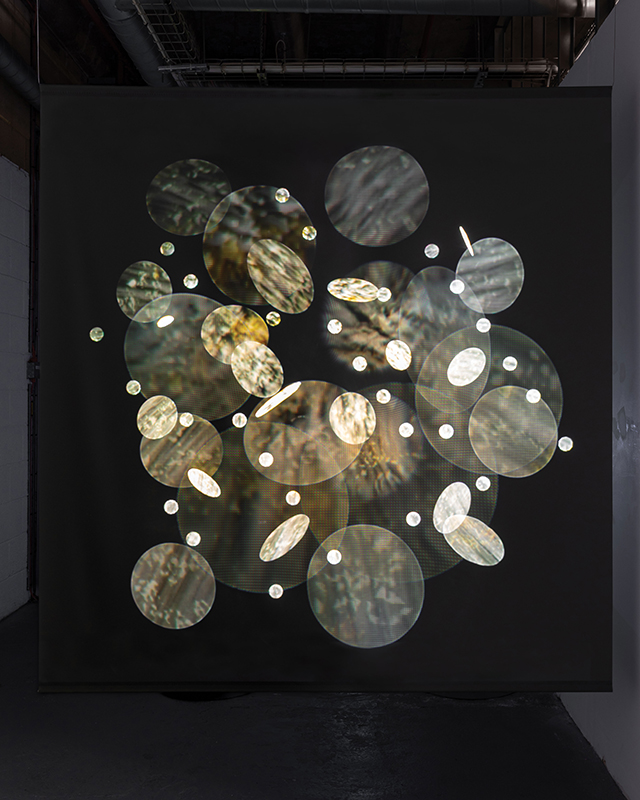
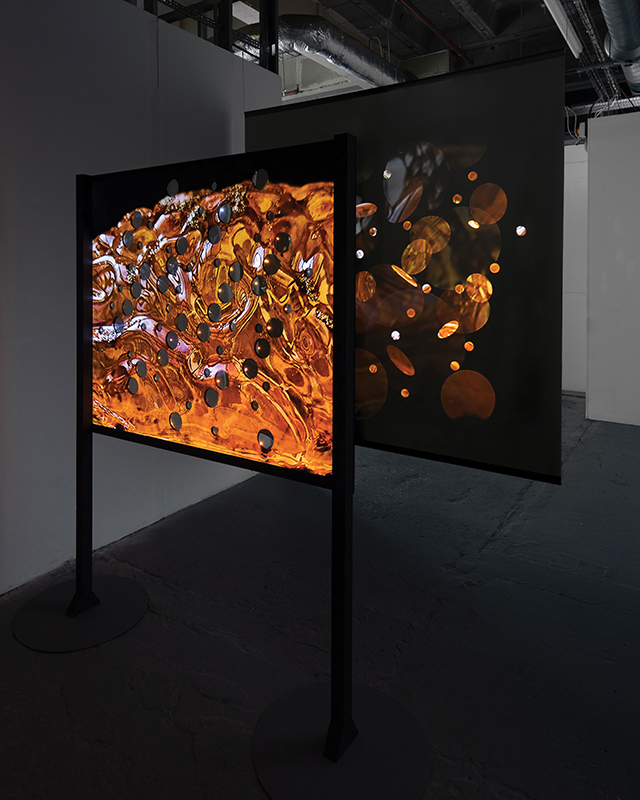
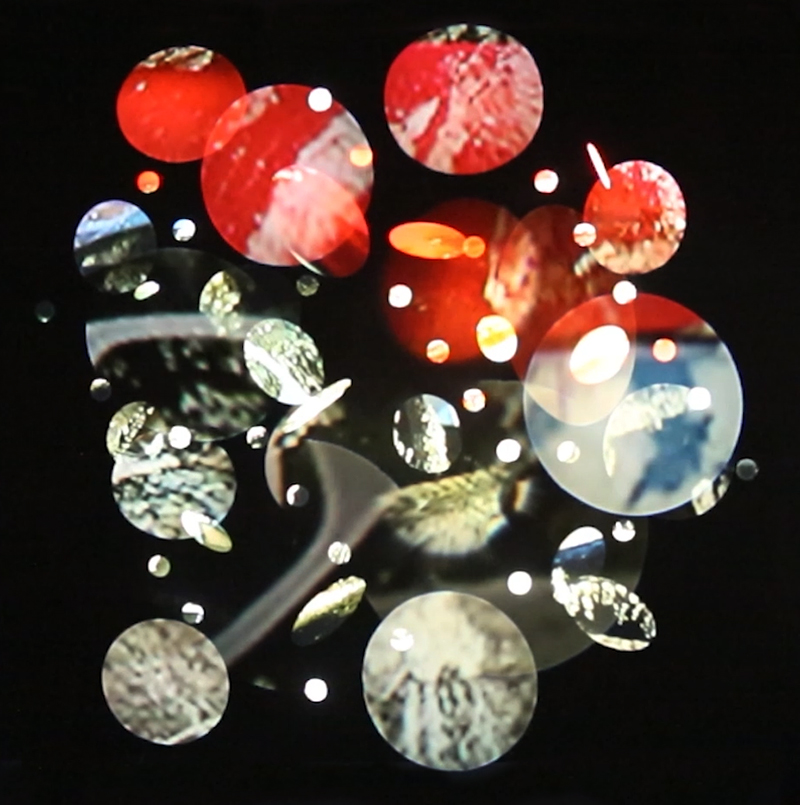
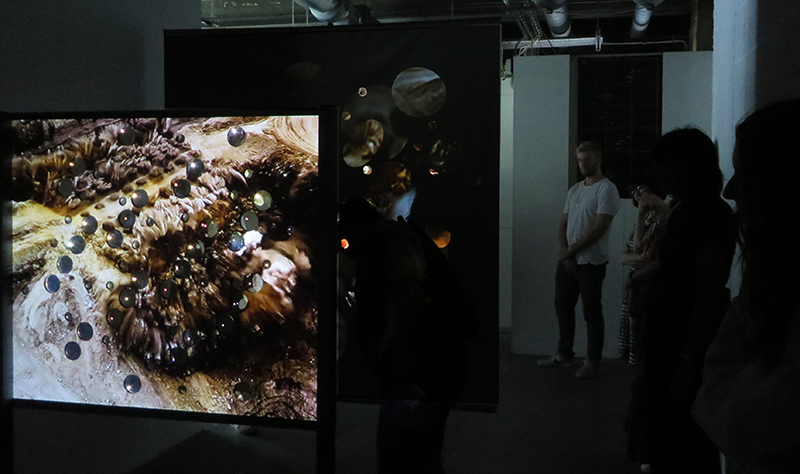
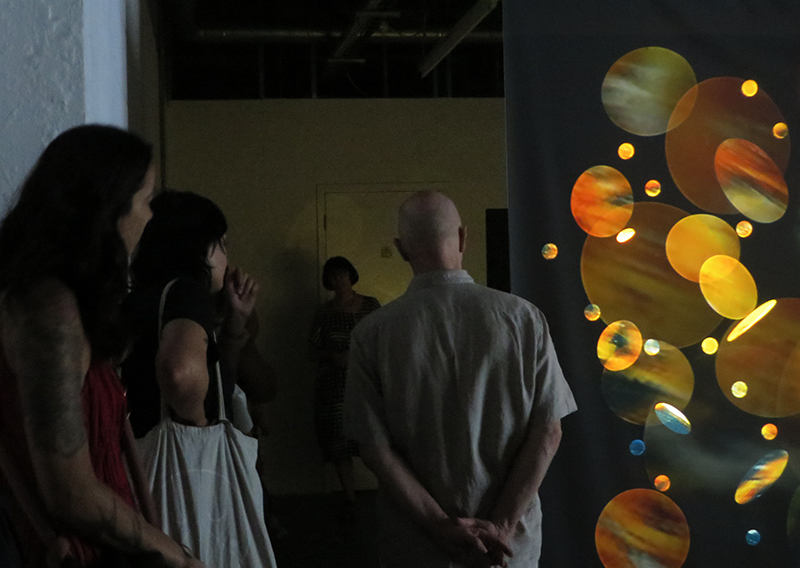
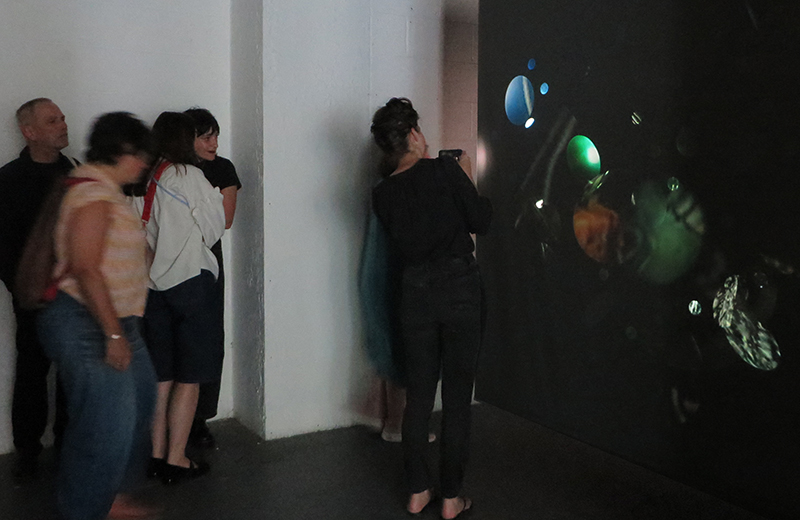
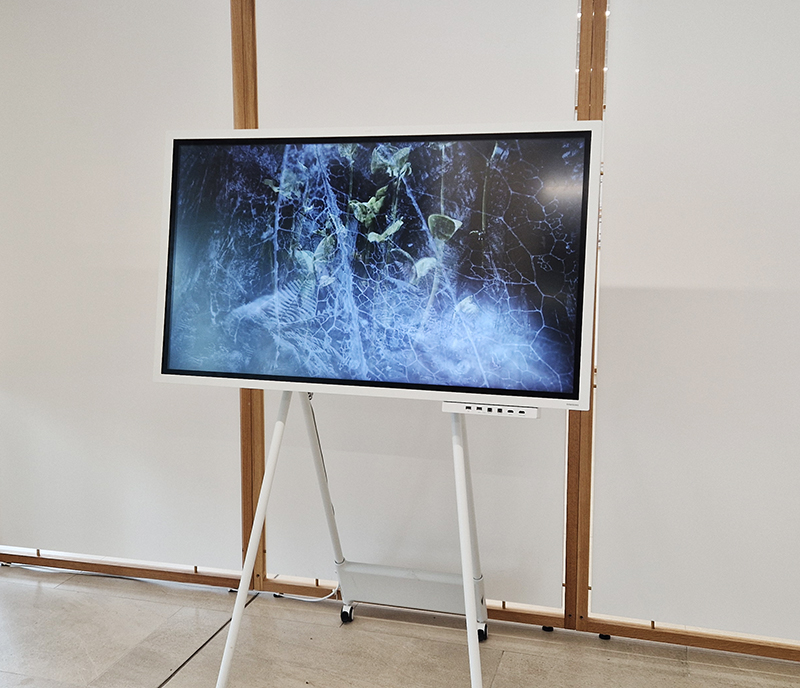
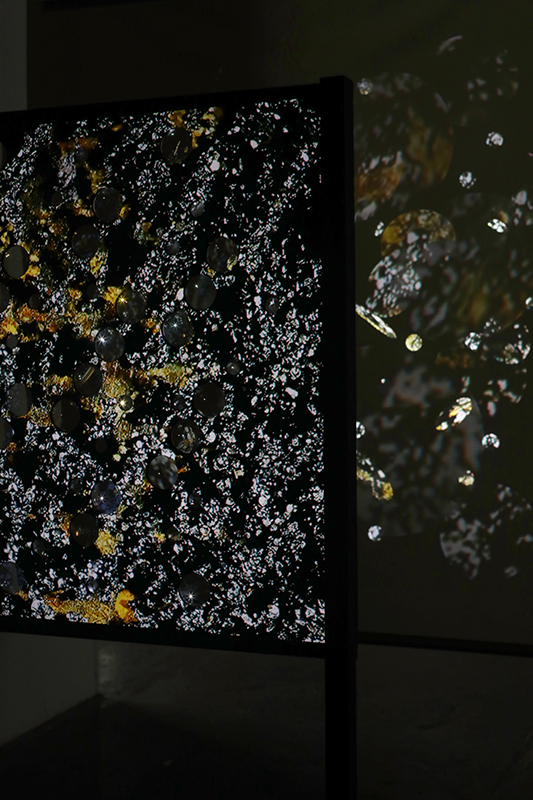
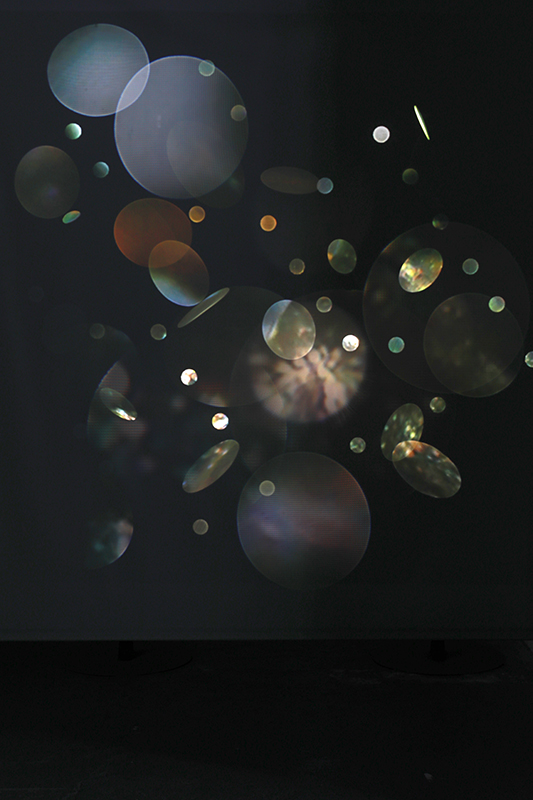
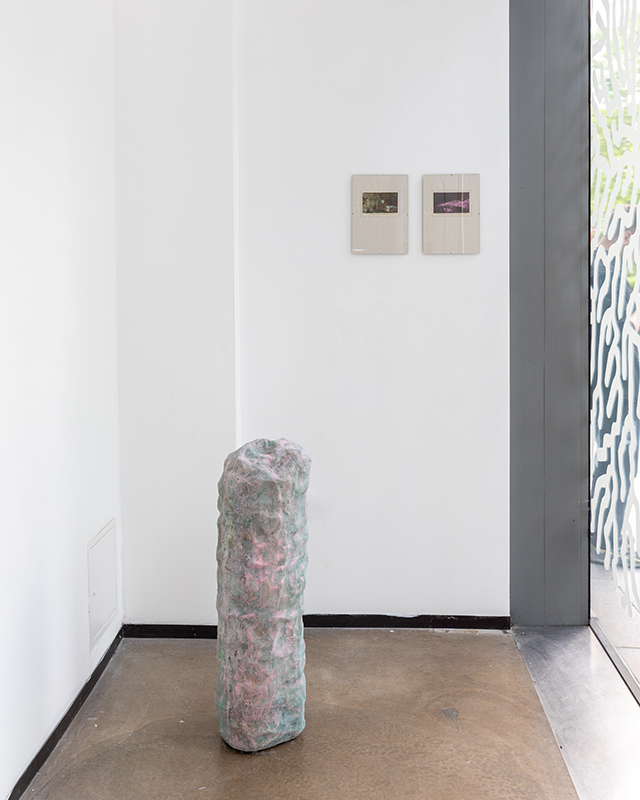
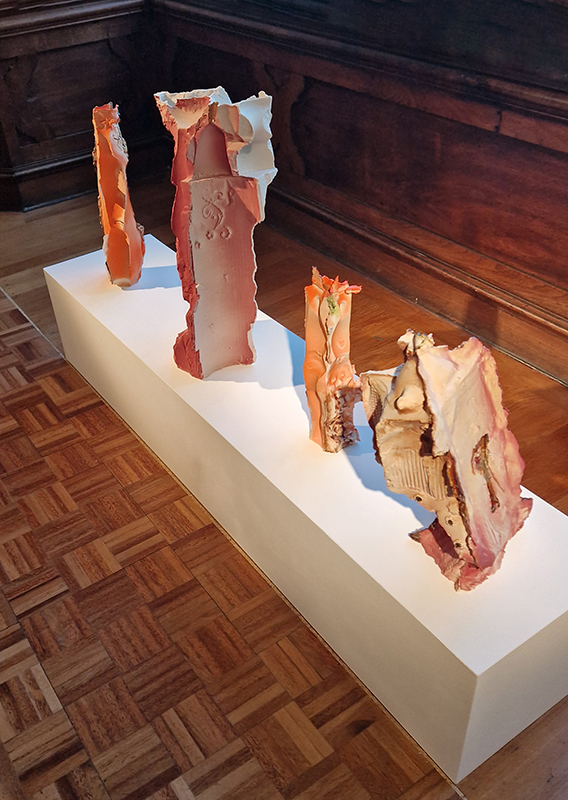
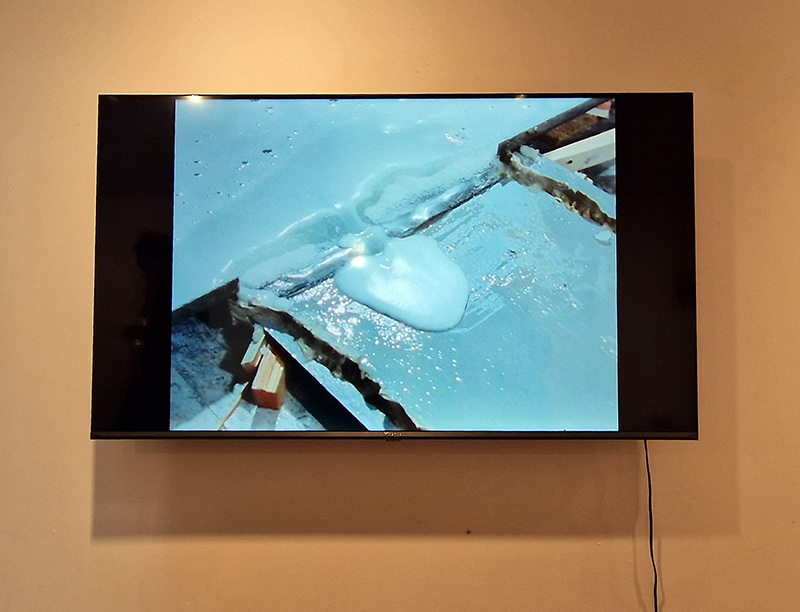
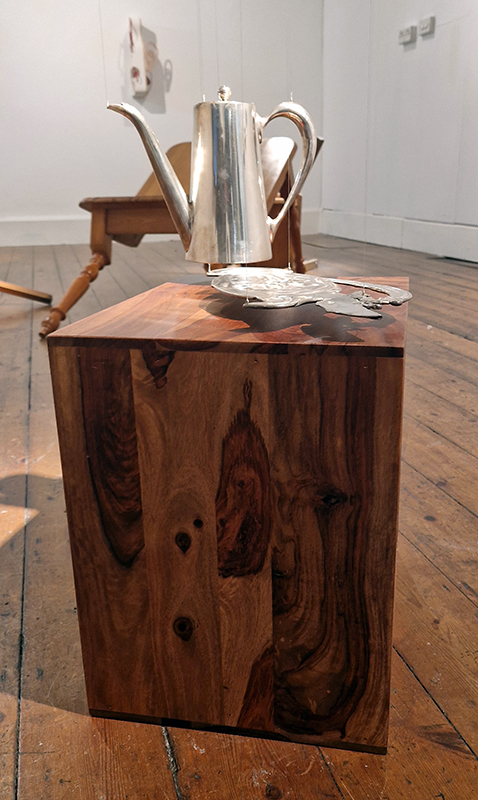
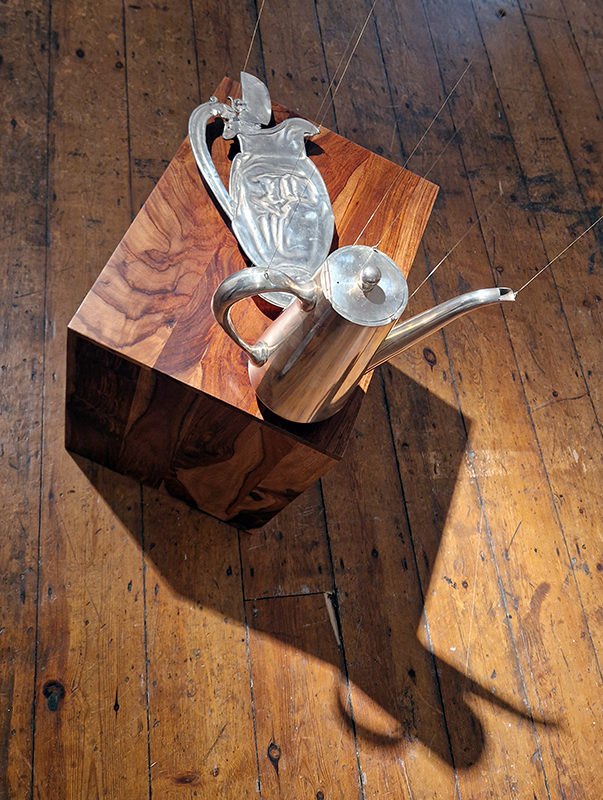
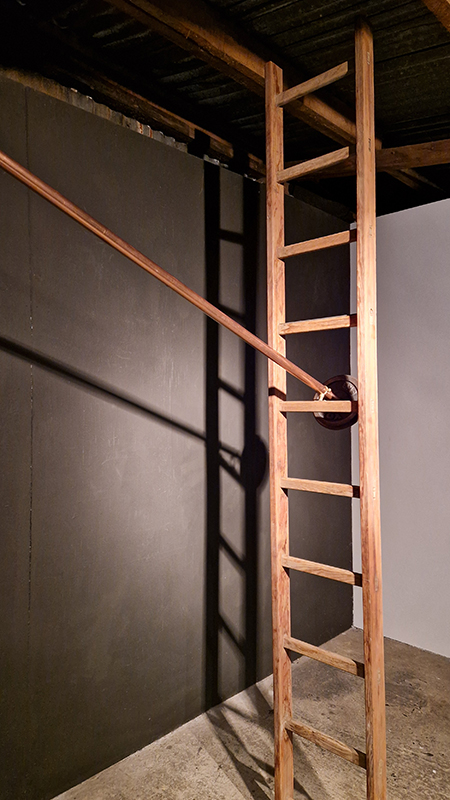
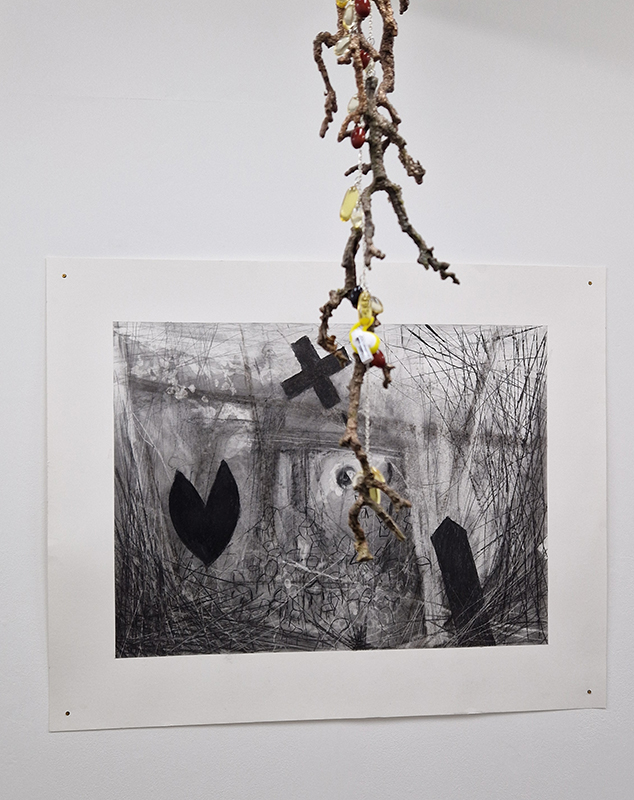
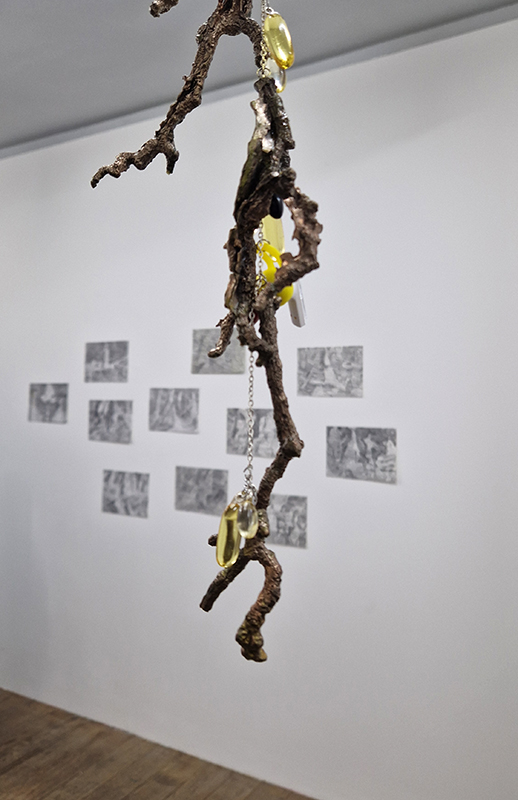
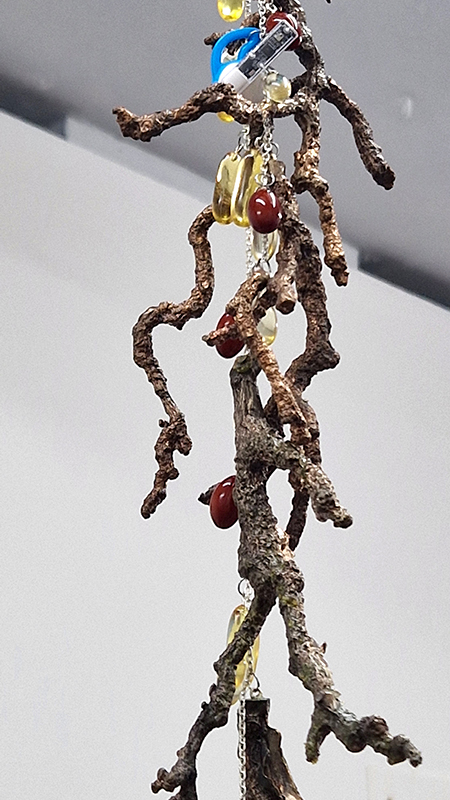
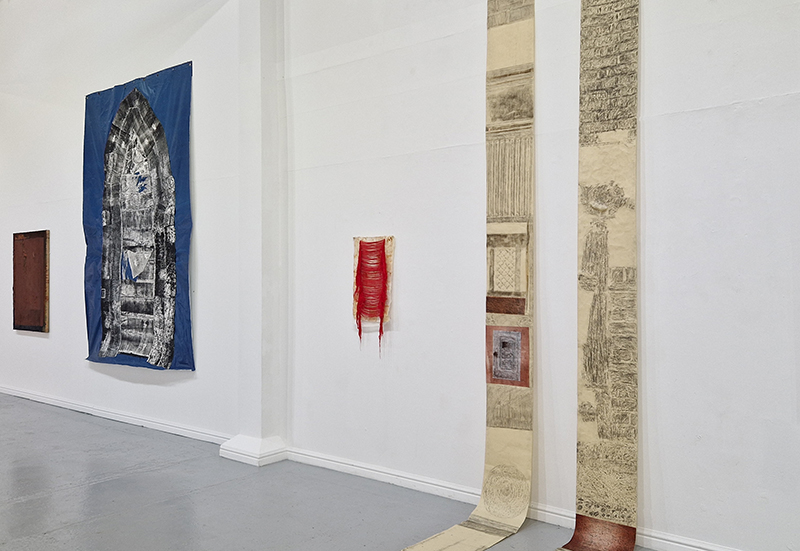
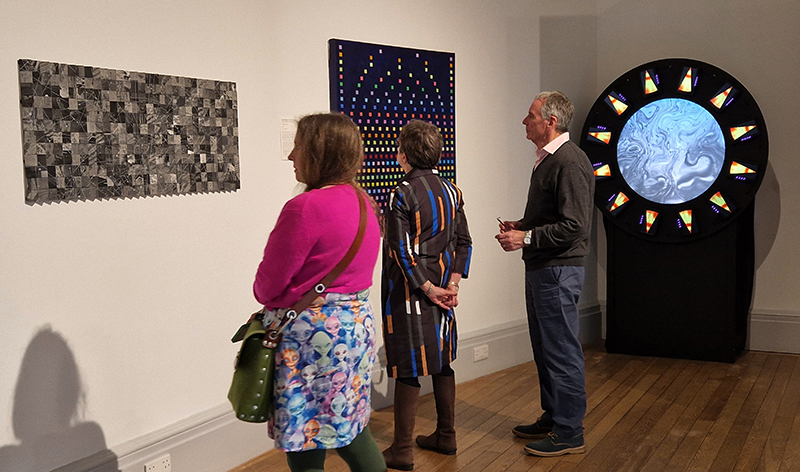
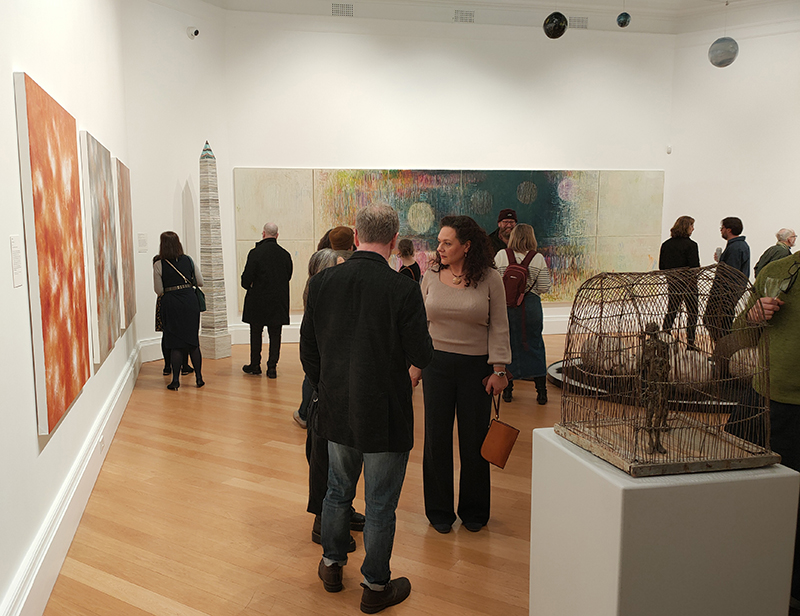
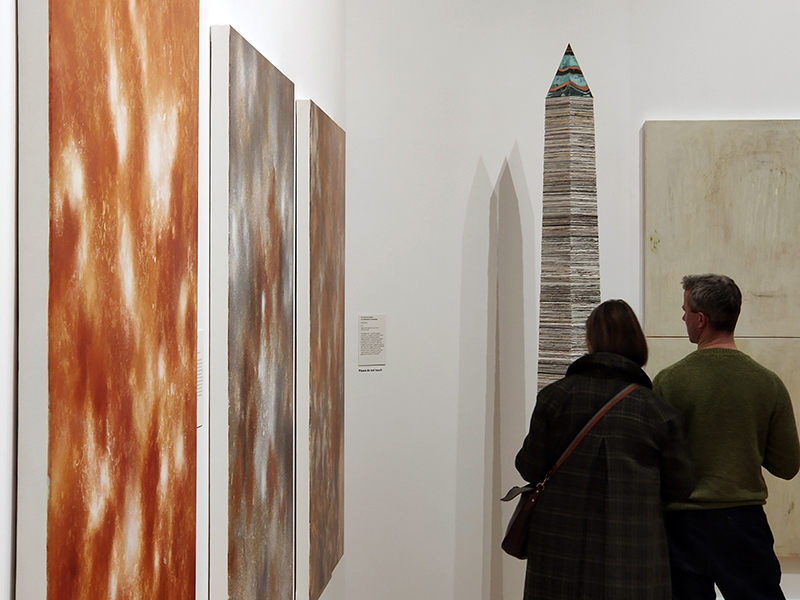
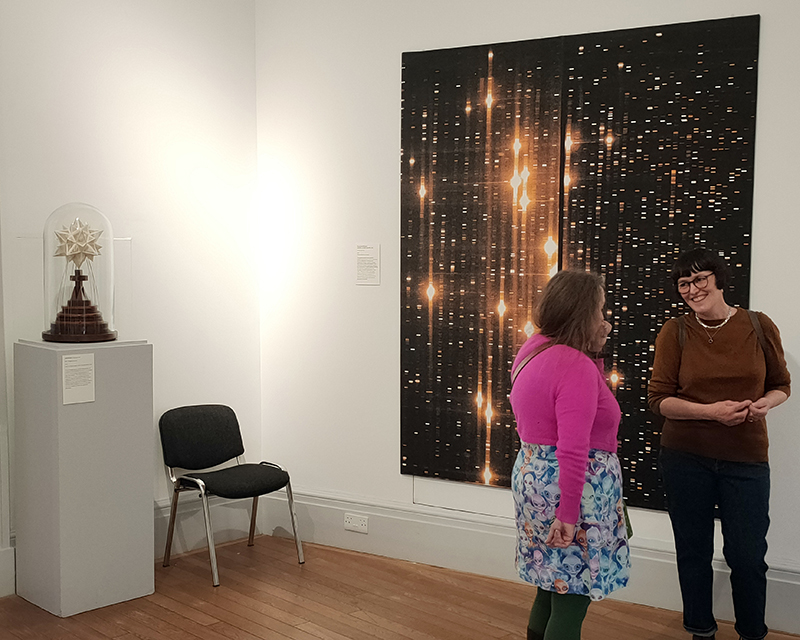
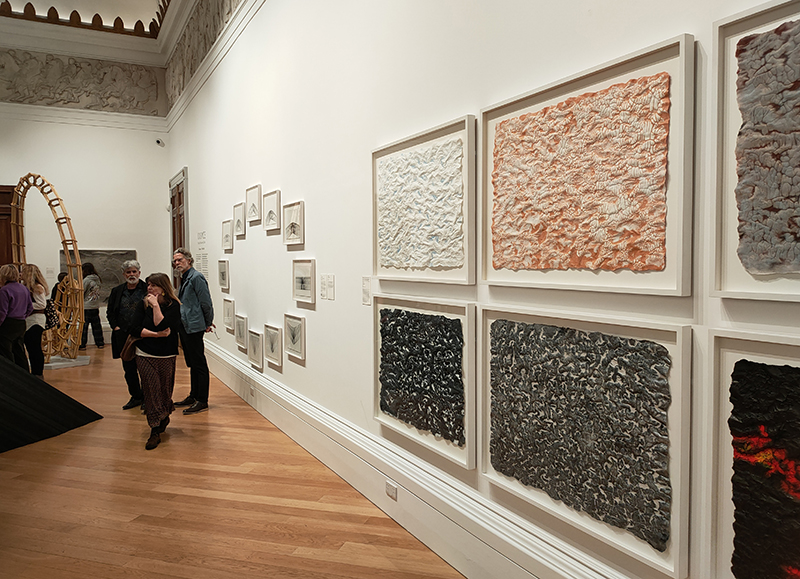
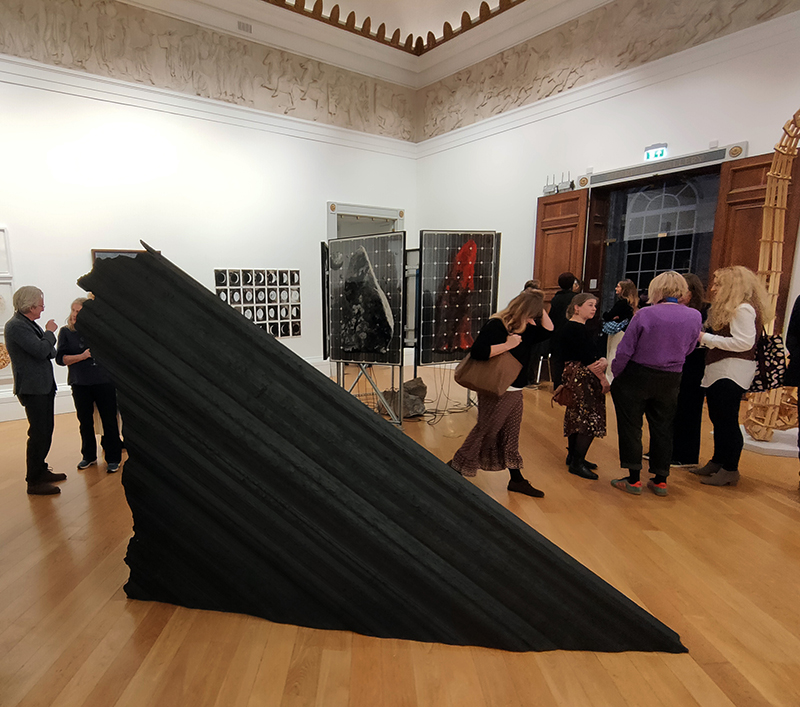
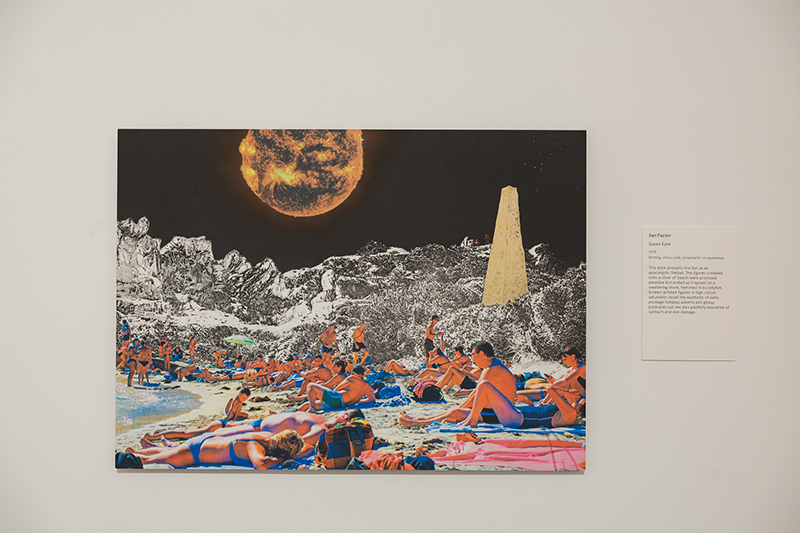
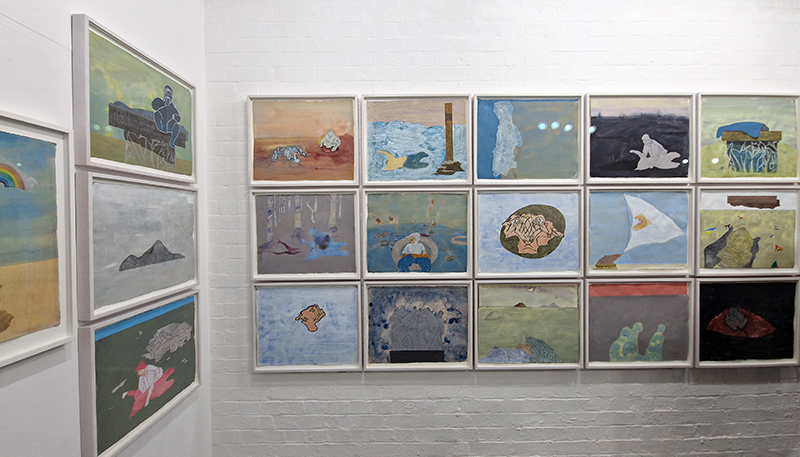
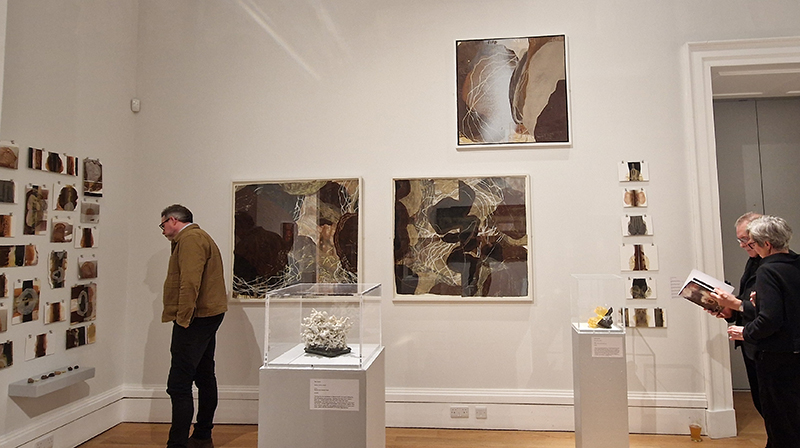
The following installation images of my four works in Cosmos are courtesy of Alastair Brookes, KoLab Studios
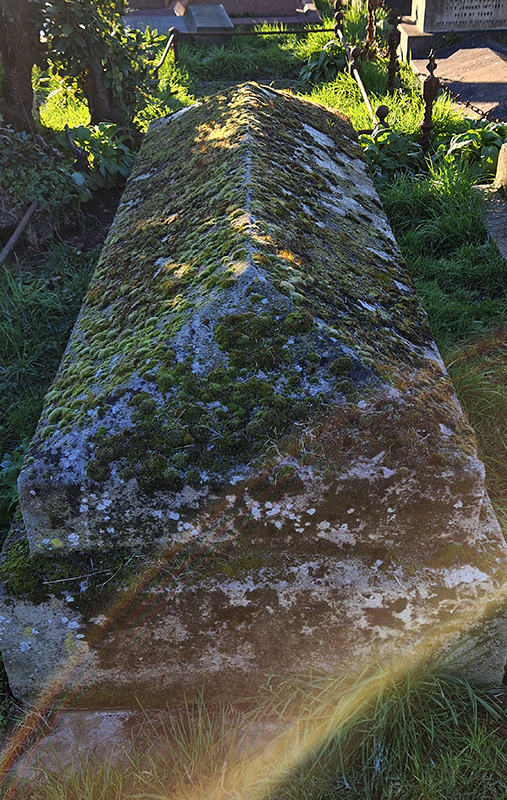
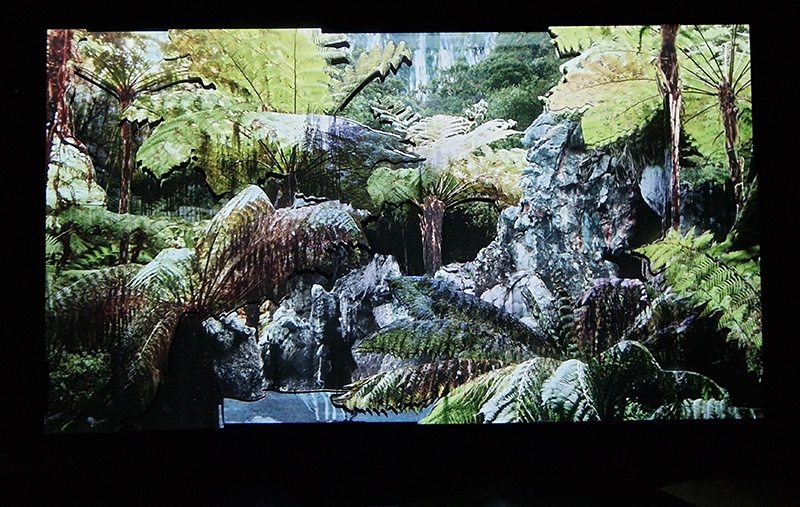
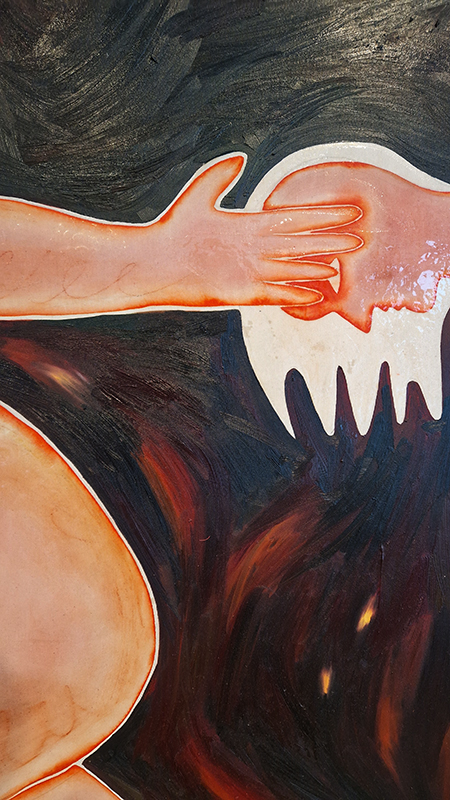
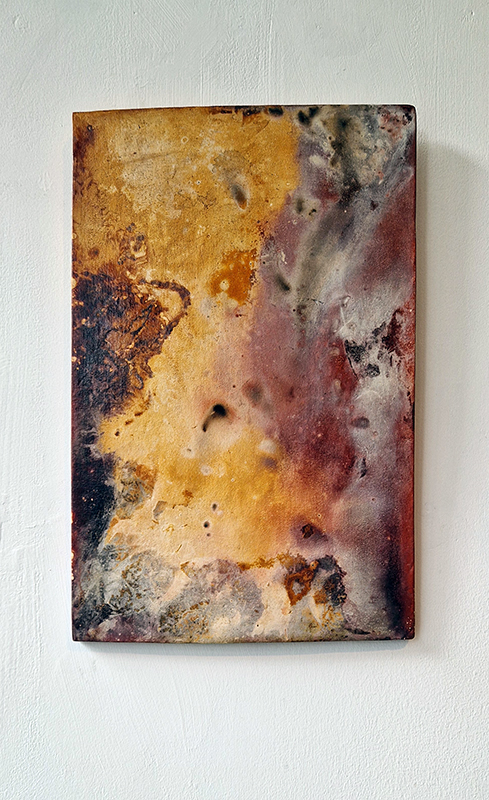
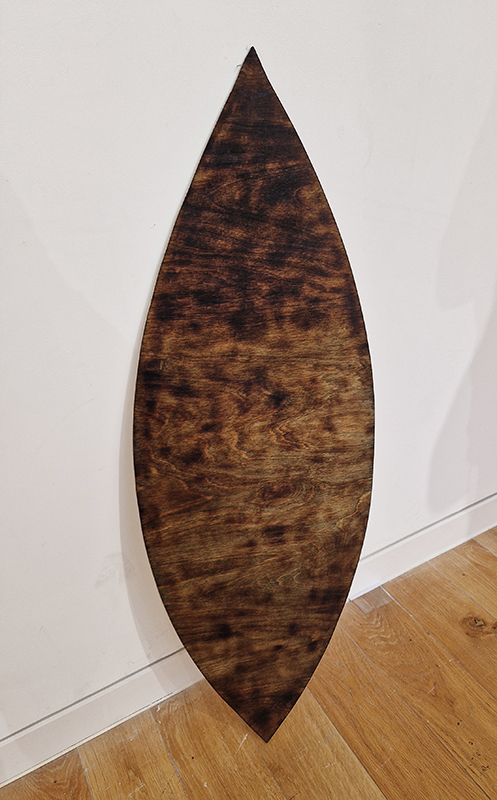
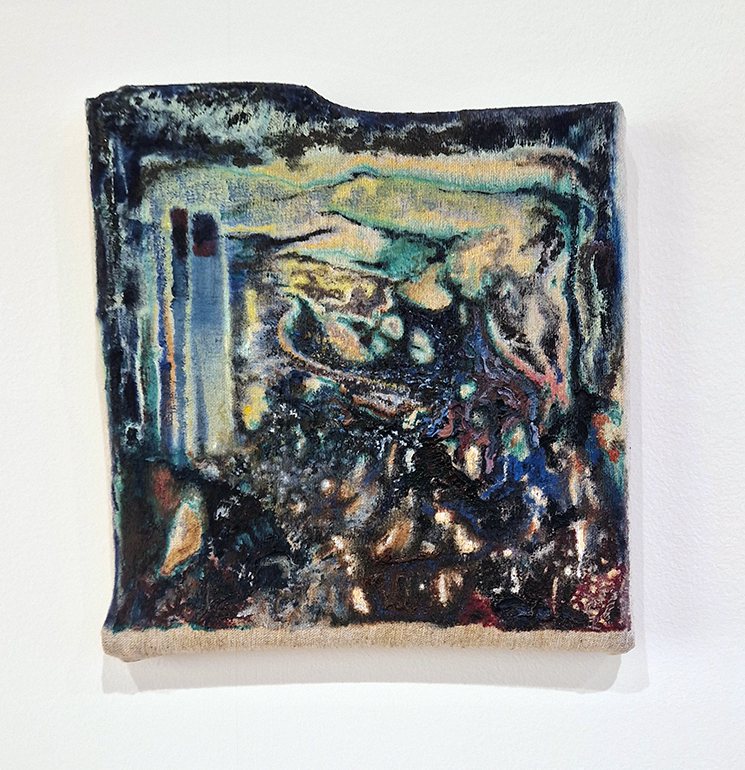
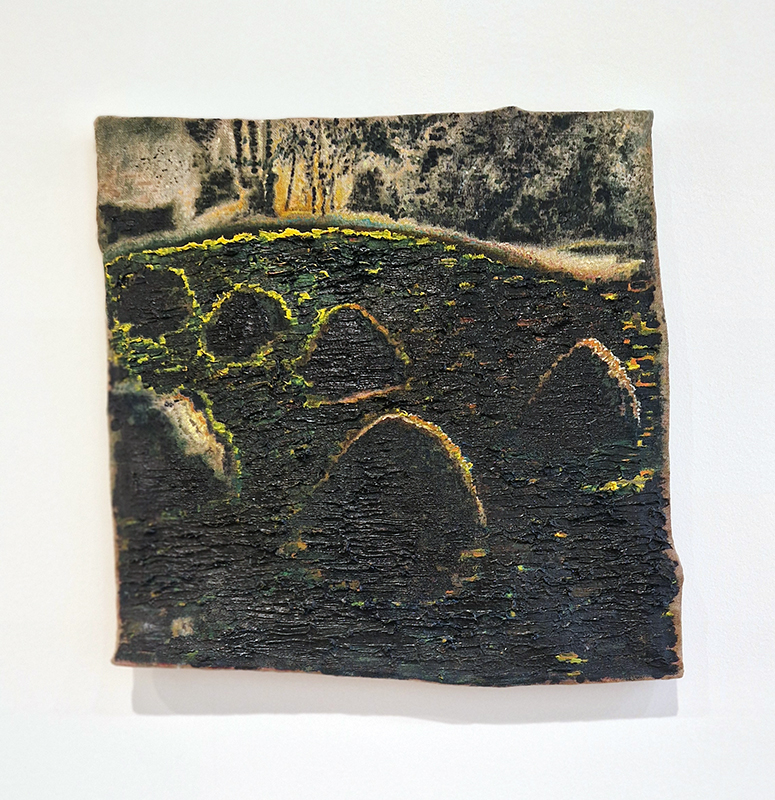
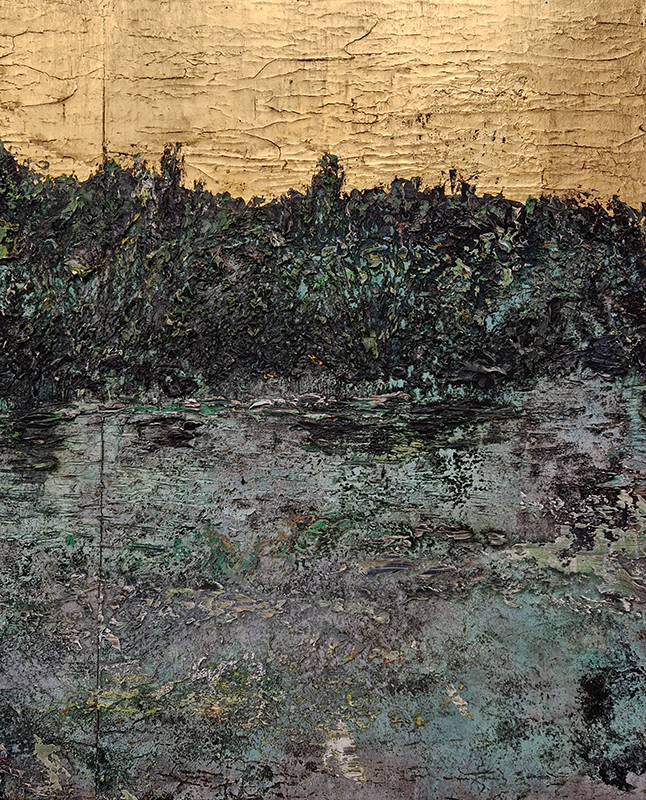
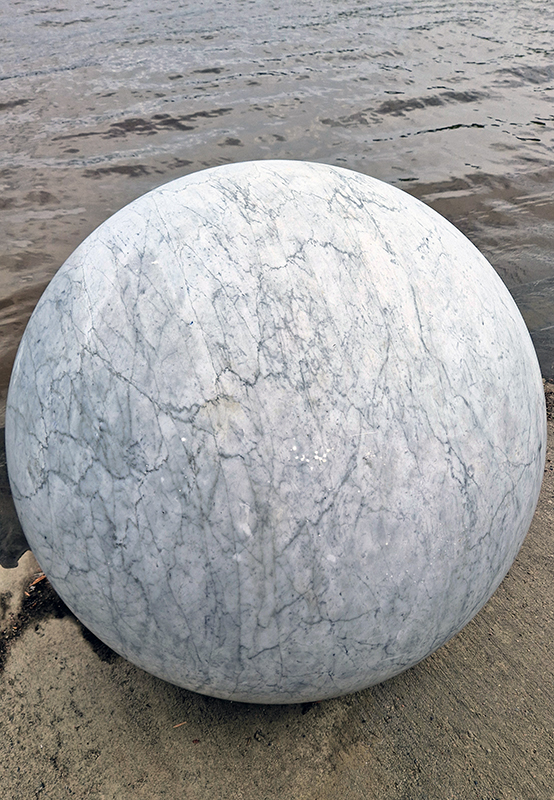
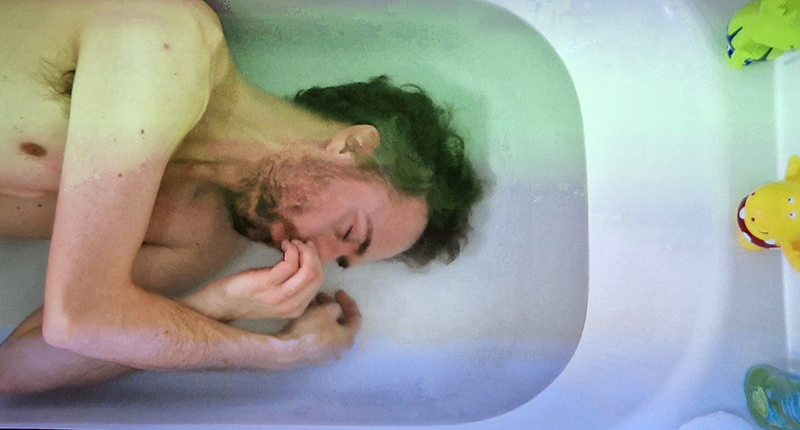
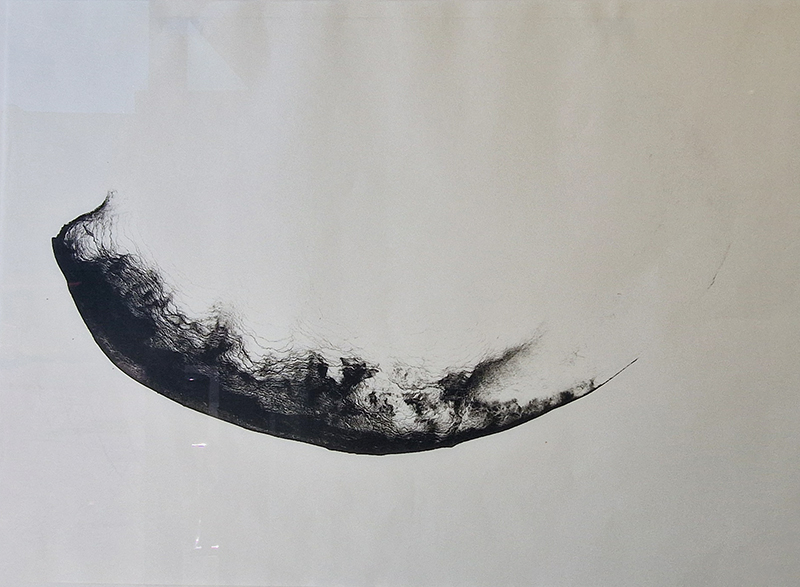
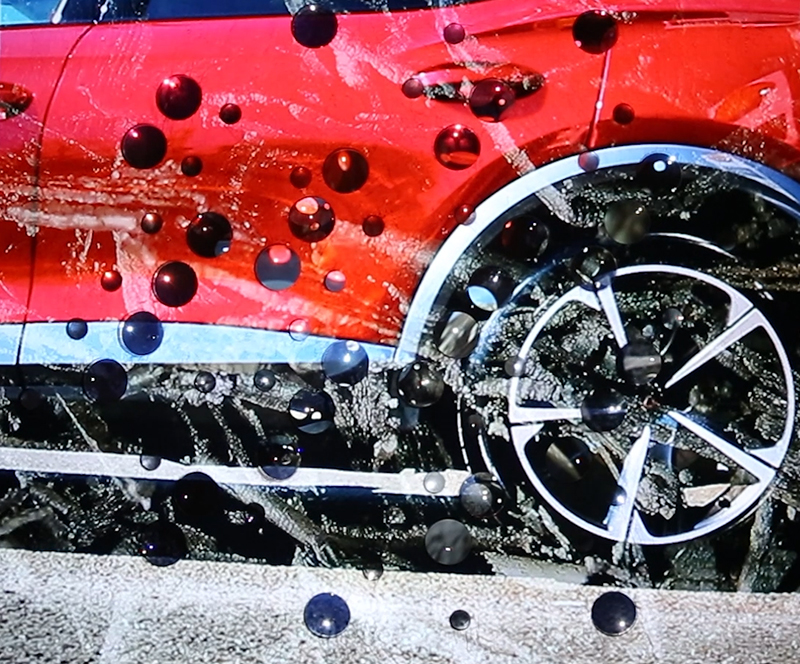
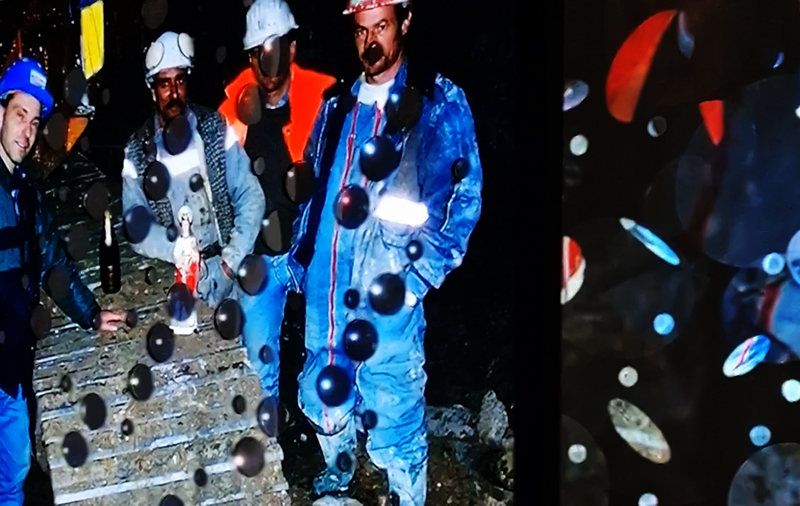
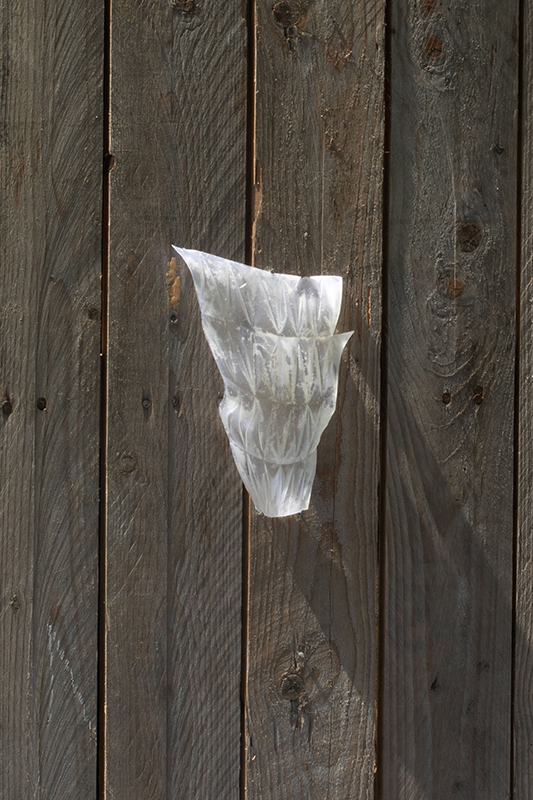
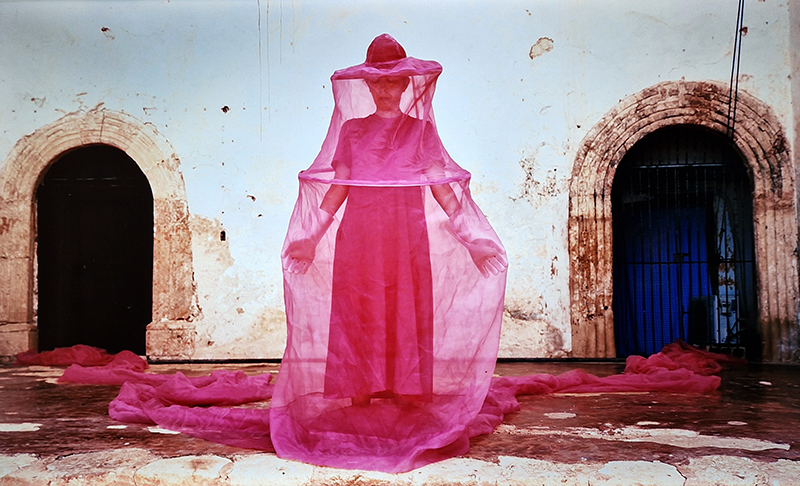
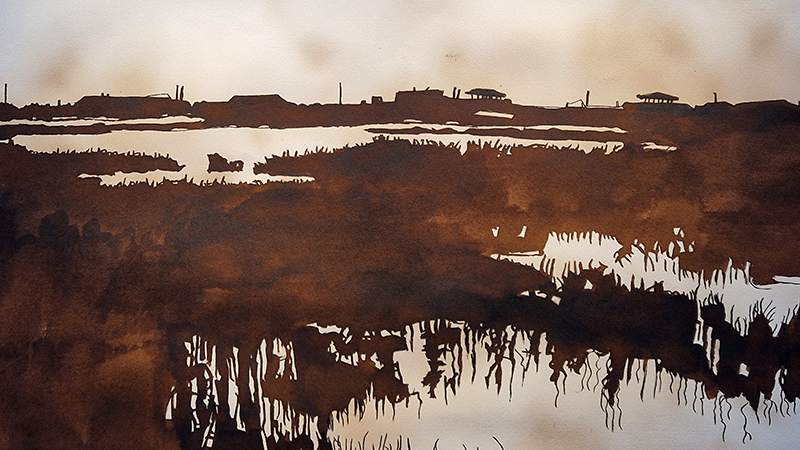
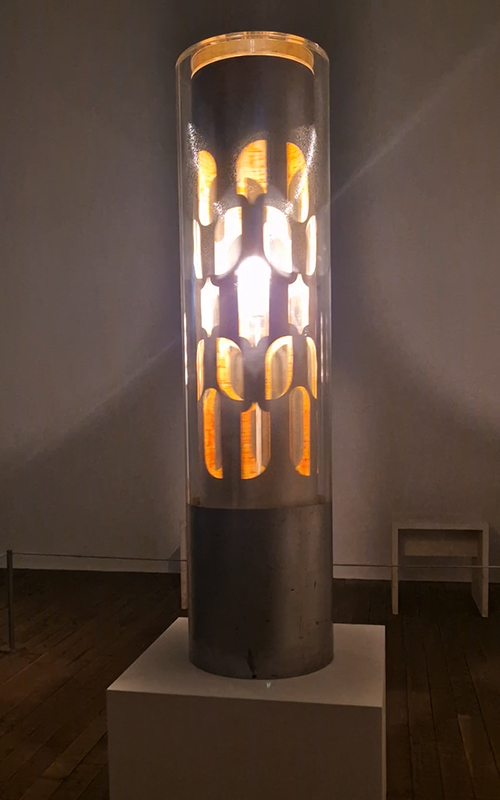
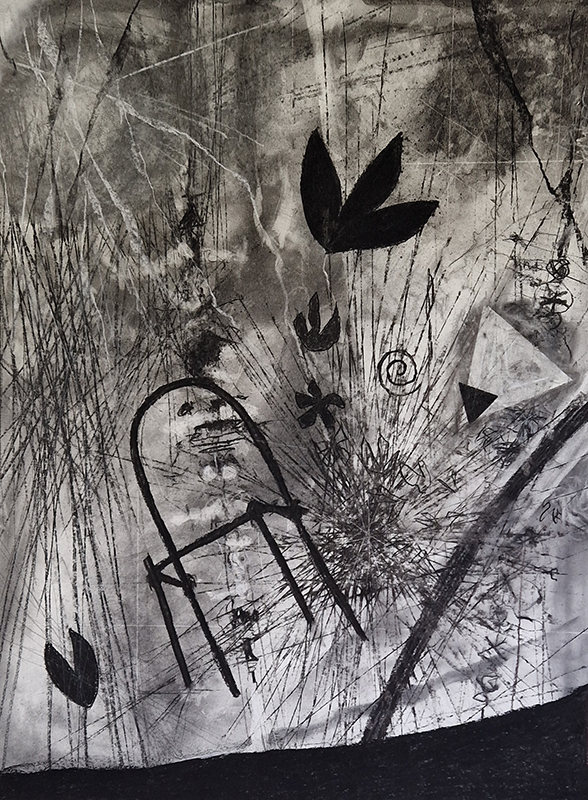
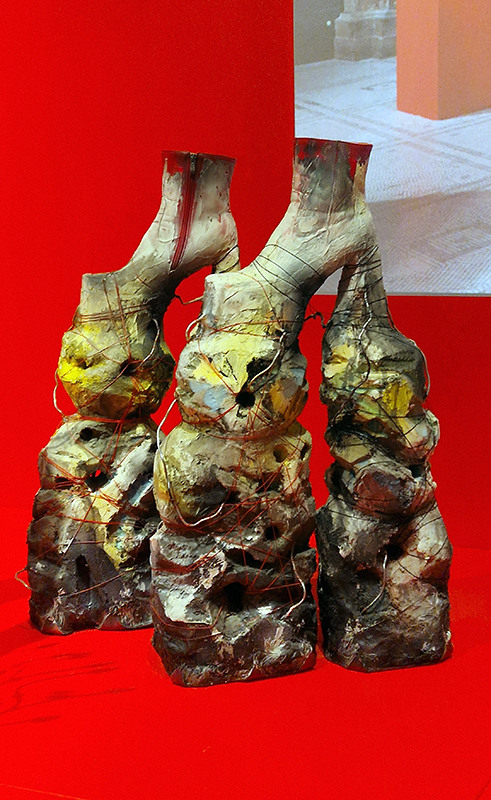
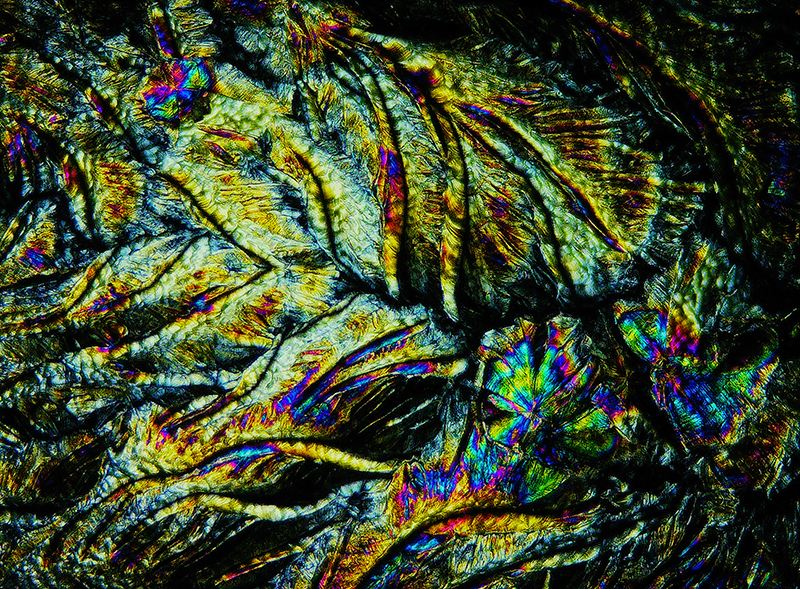
Sun Factor, 2015, comes from a period in my practice when I was looking at the human disconnect with the natural world and impending climate change. I was focusing on concepts of paradise as a state of being at one with a natural order. During this period we took a family holiday to Sardinia and one day we were offered a boat trip to an island that was described by the sales tout as ‘paradise’ – so we had to go. It turned out to be the opposite of what one might expect of paradise and this work is a direct translation of our experience. Bizarrely there was a concrete obelisk at the beach, – a signifier of an ancient totem to the power of the sun. The figures are printed in high saturation colours, a reminder of the early days of package holidays and glossy postcards. It also speaks of skin damage and the ritual behaviour of tourists flocking to the sun – perhaps without acknowledging its true power and the vulnerability of human biology.

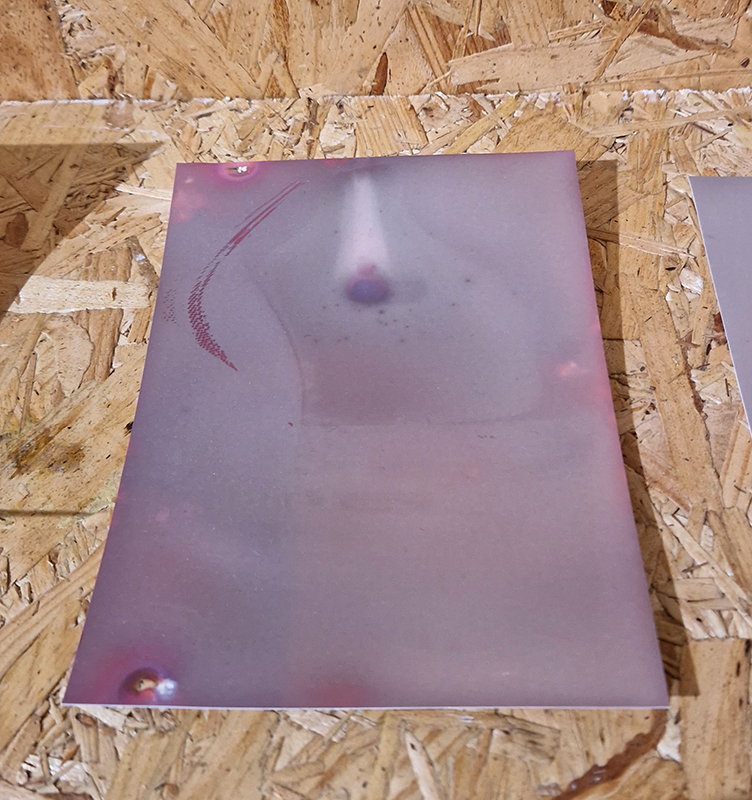
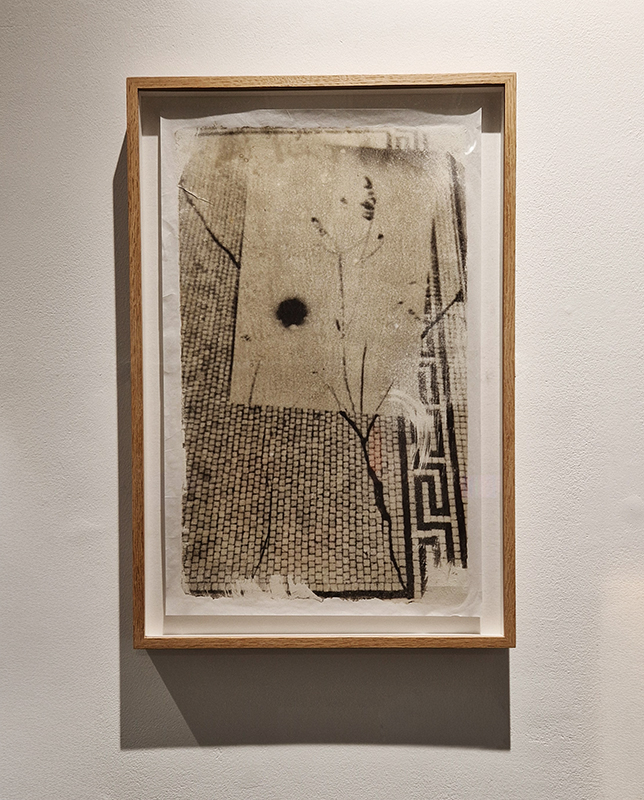
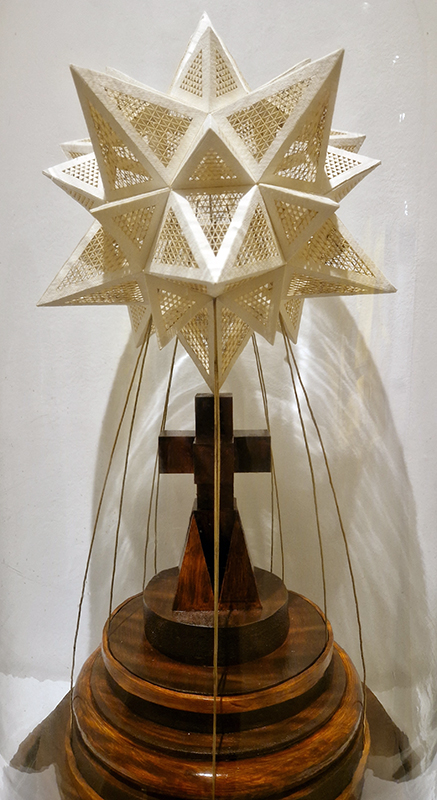
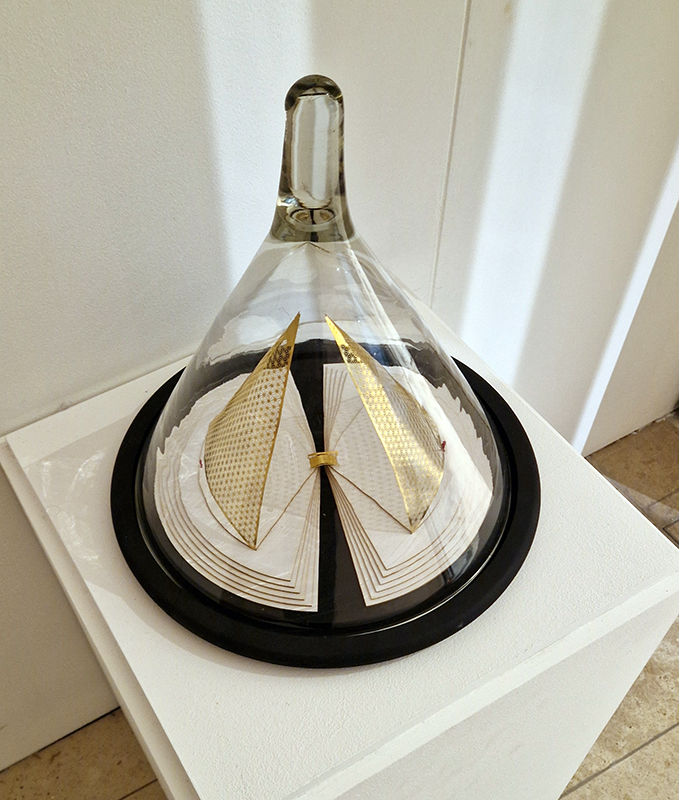
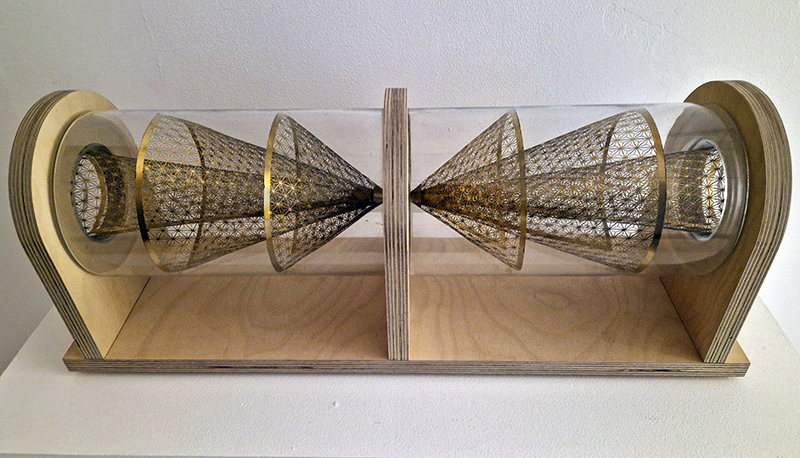
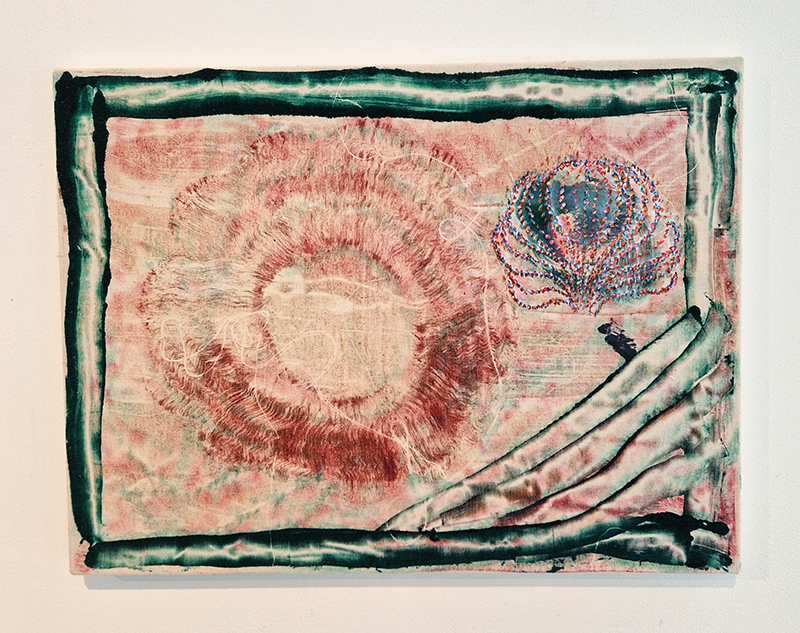
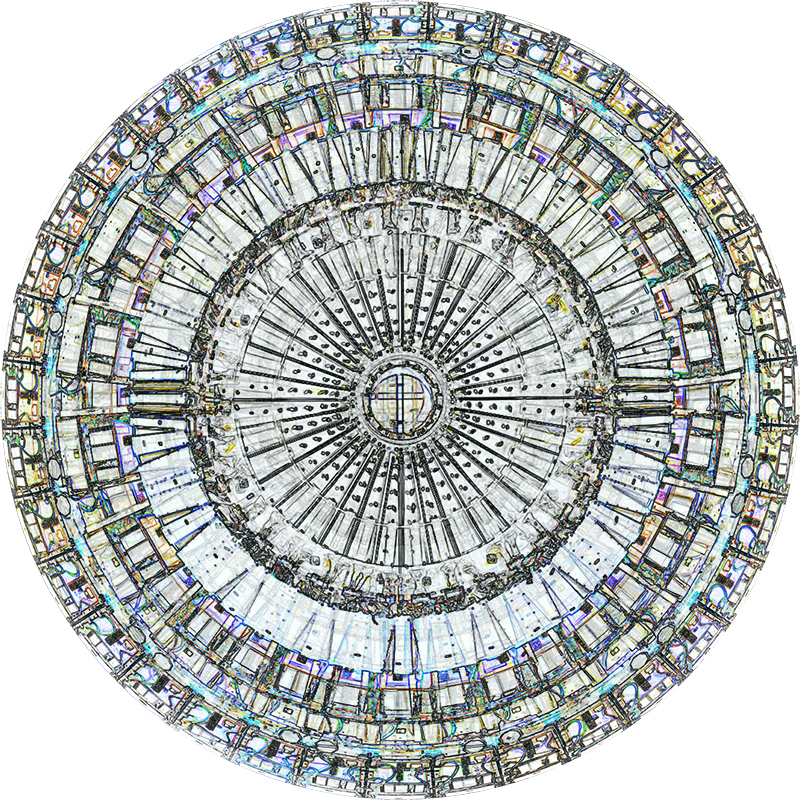
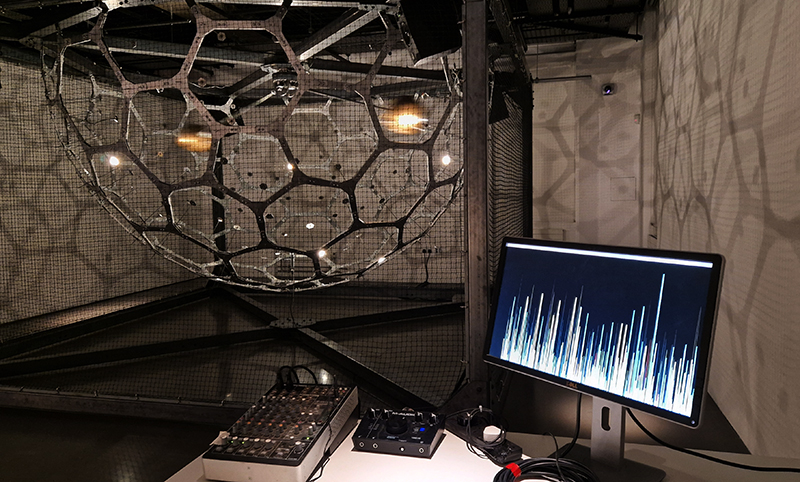
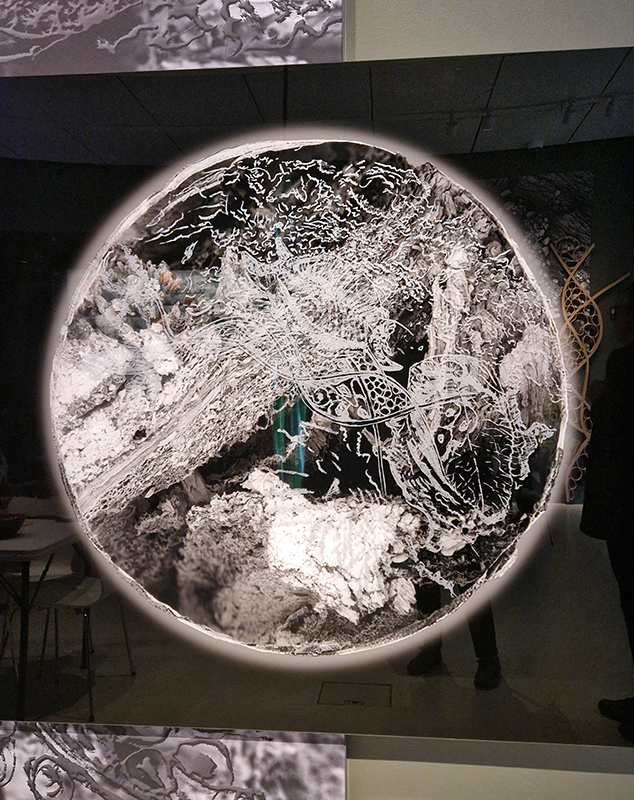
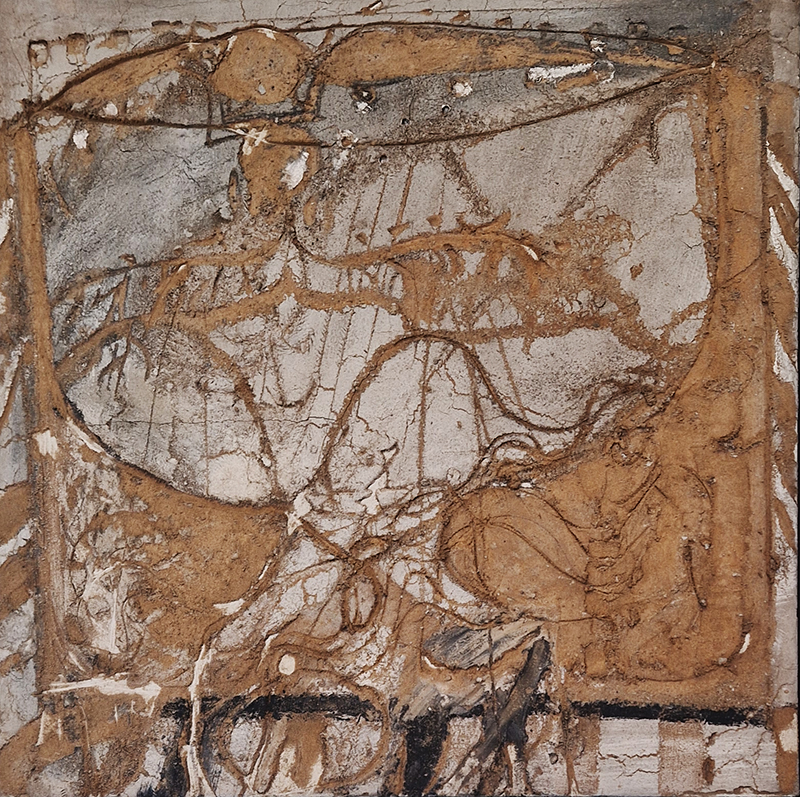
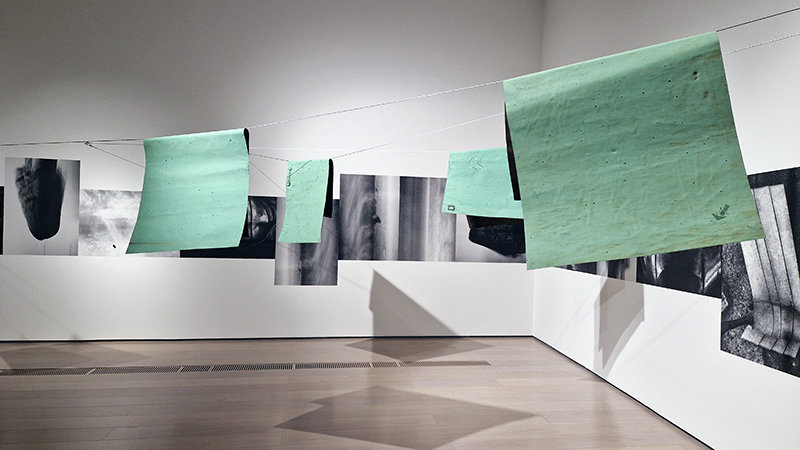
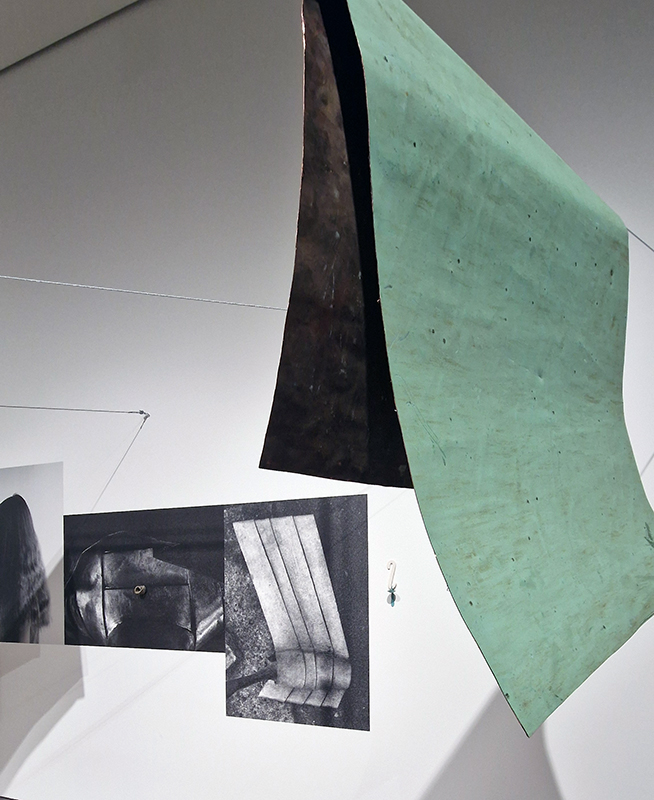
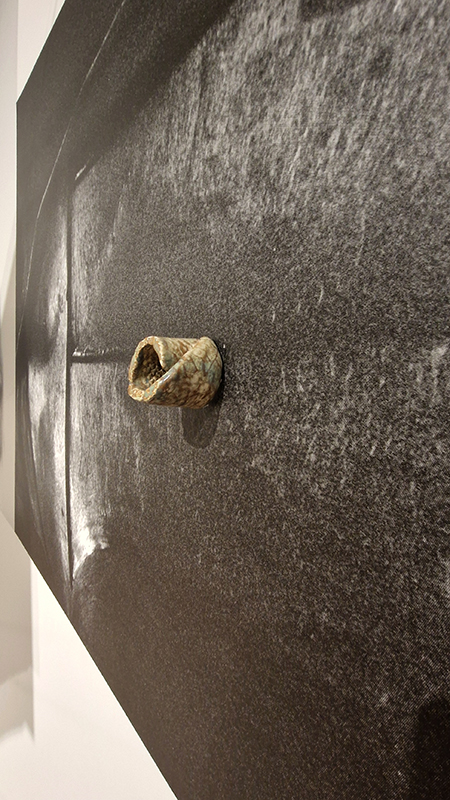
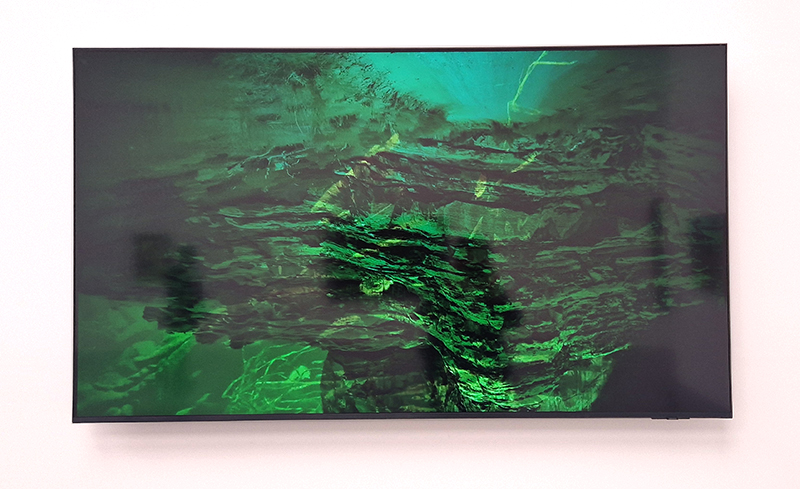
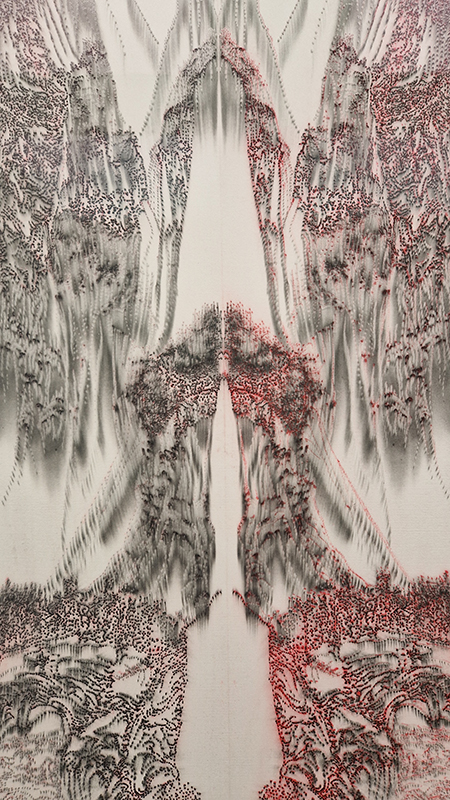
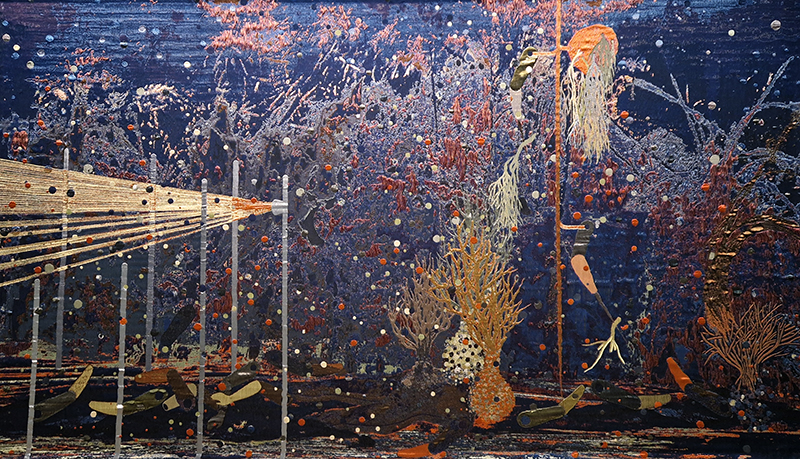
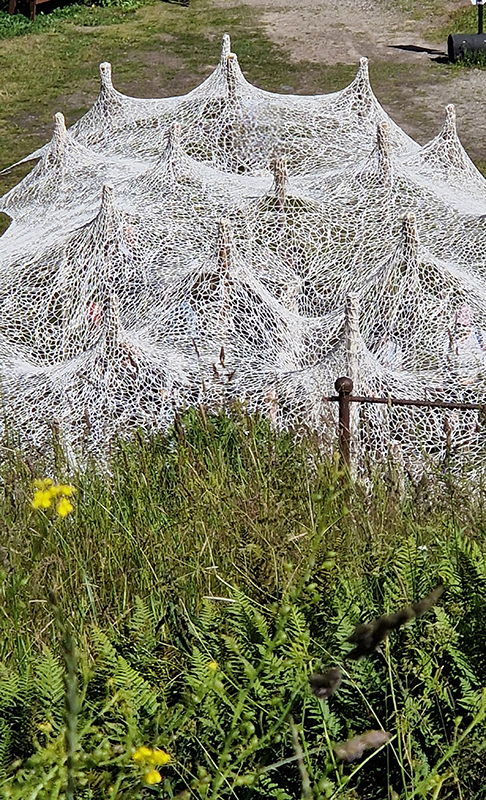
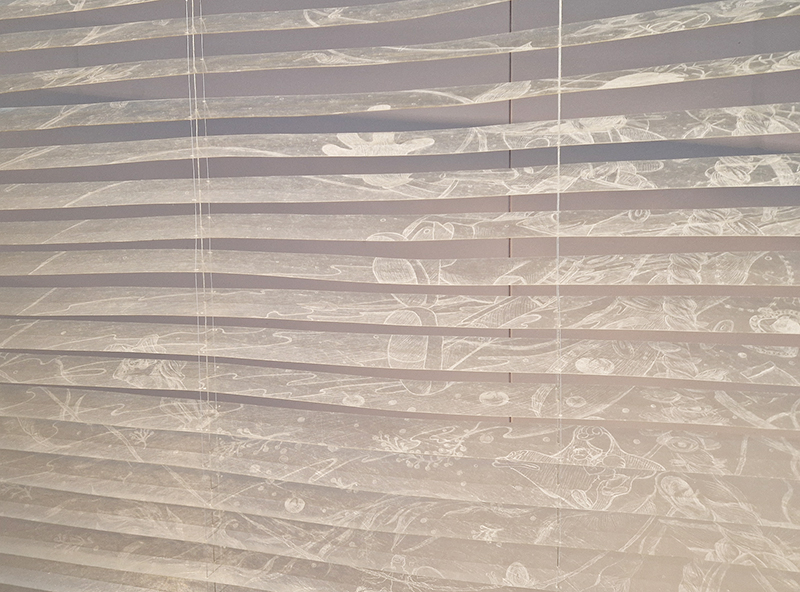
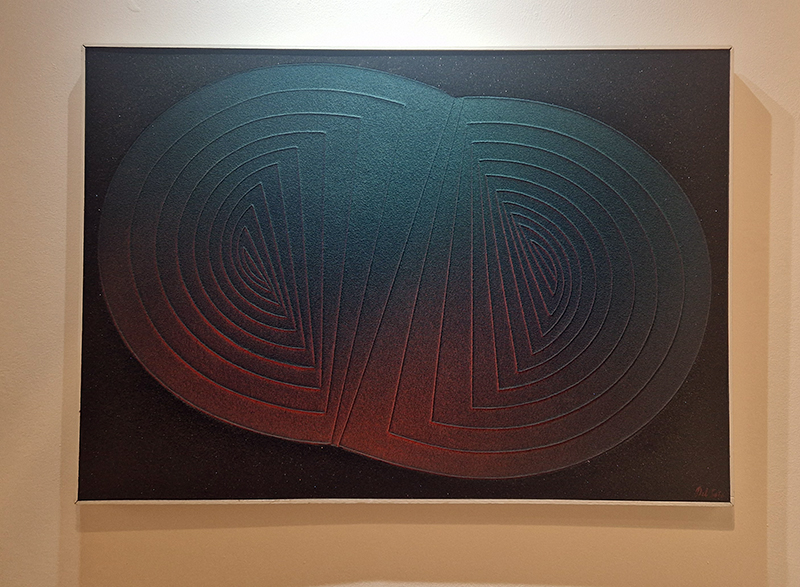
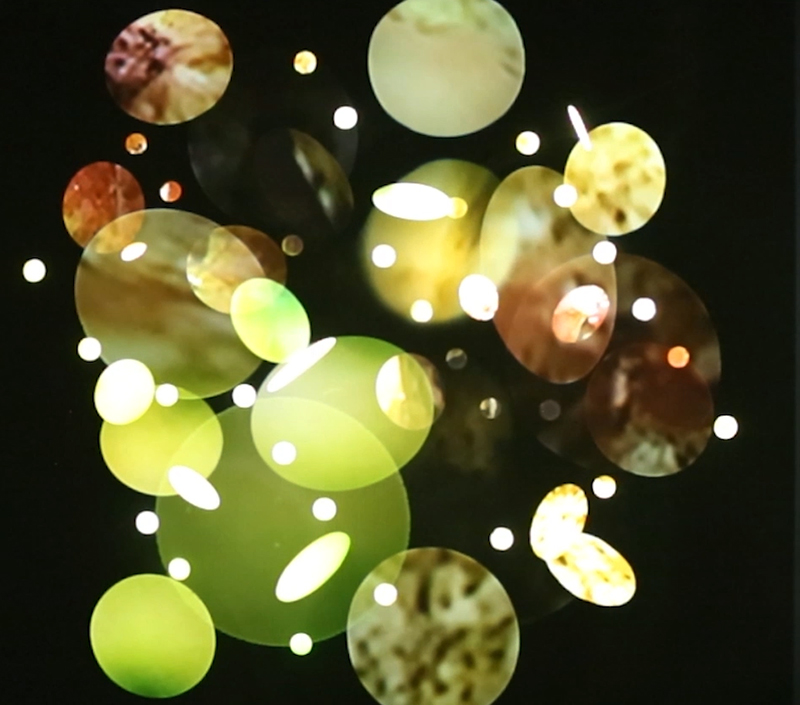
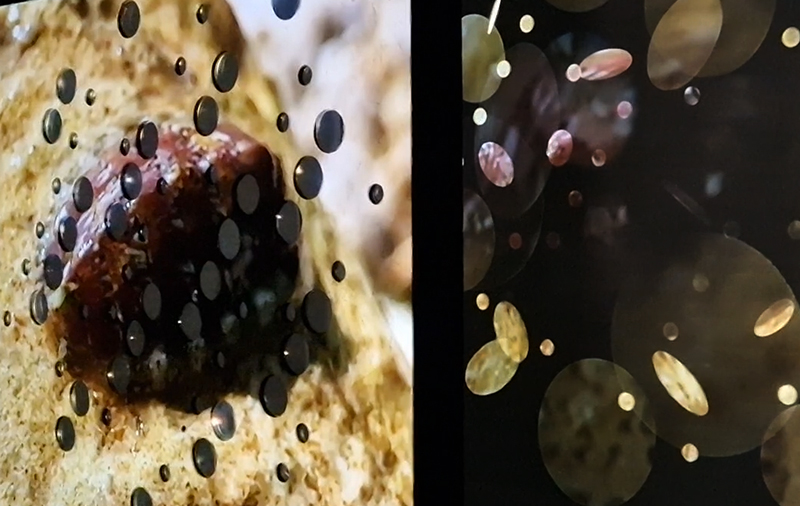
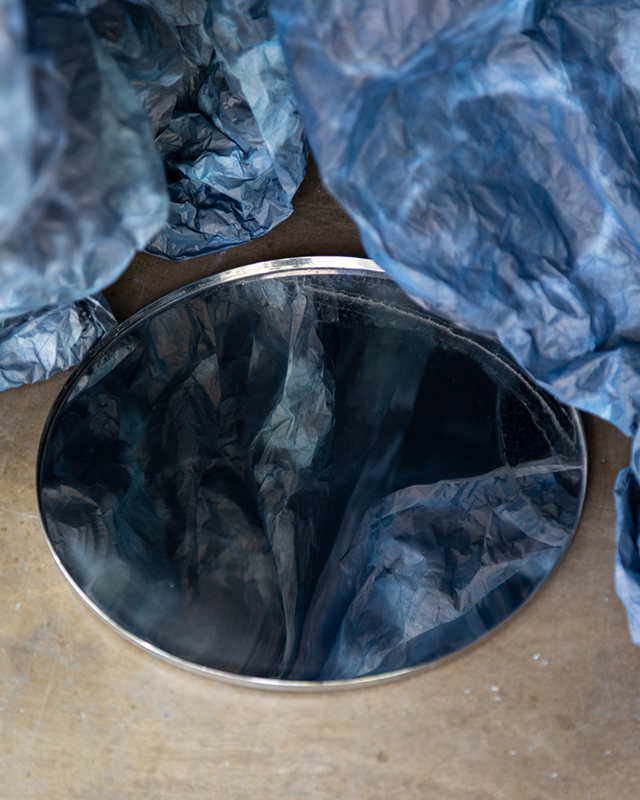
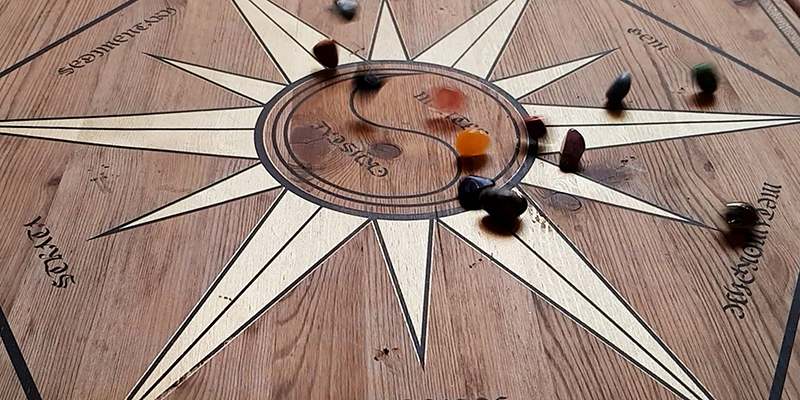
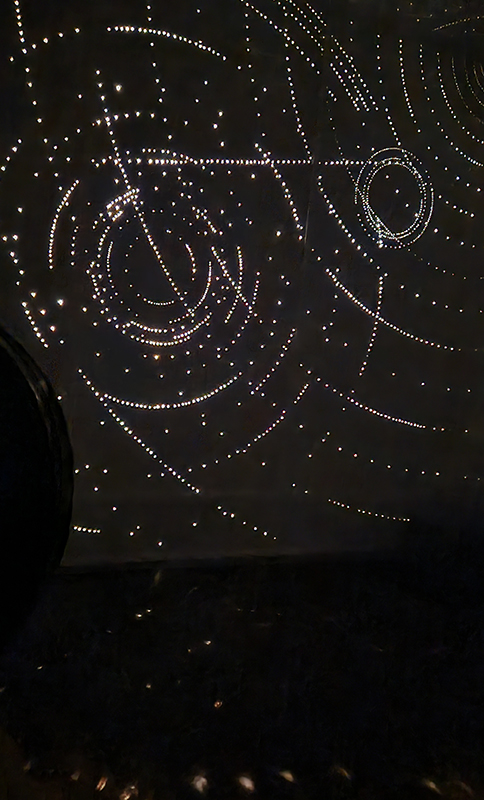
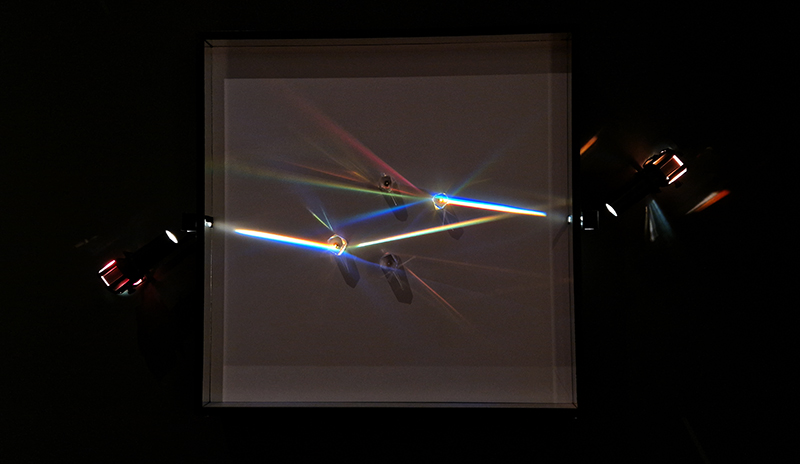
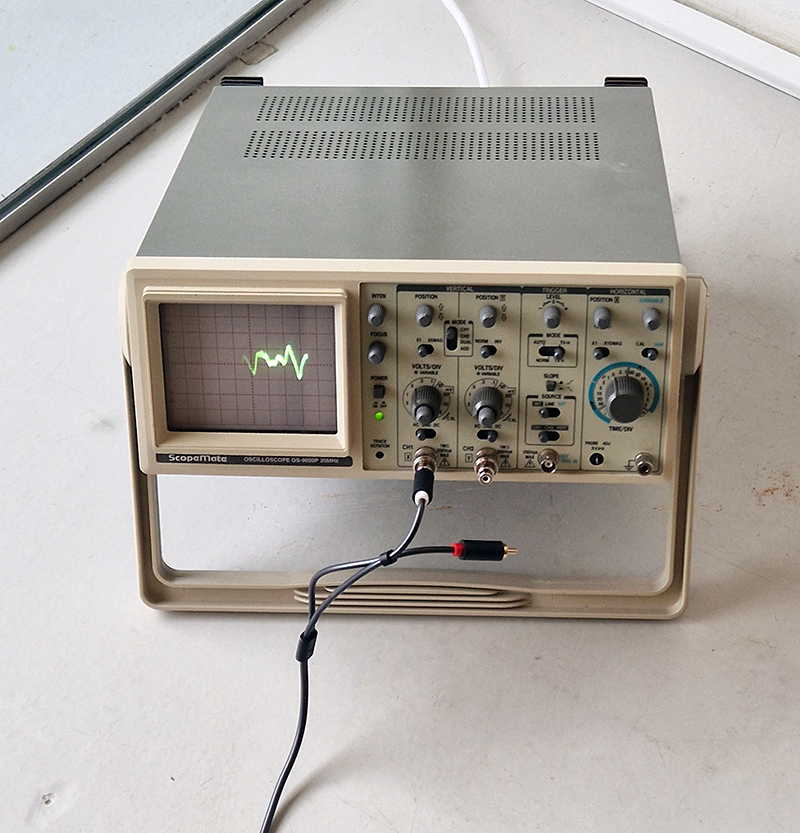
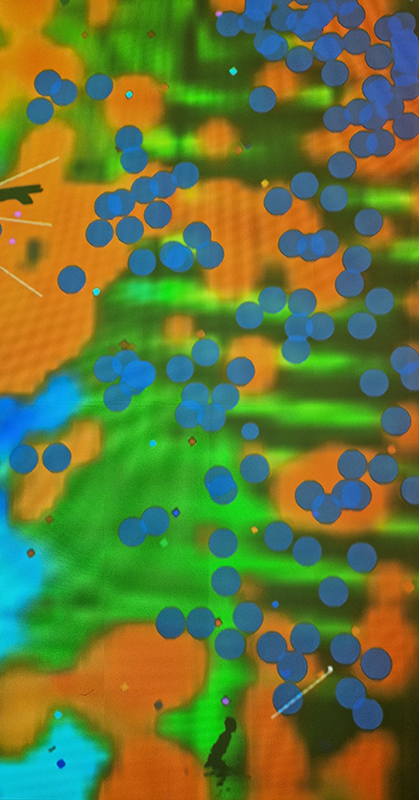
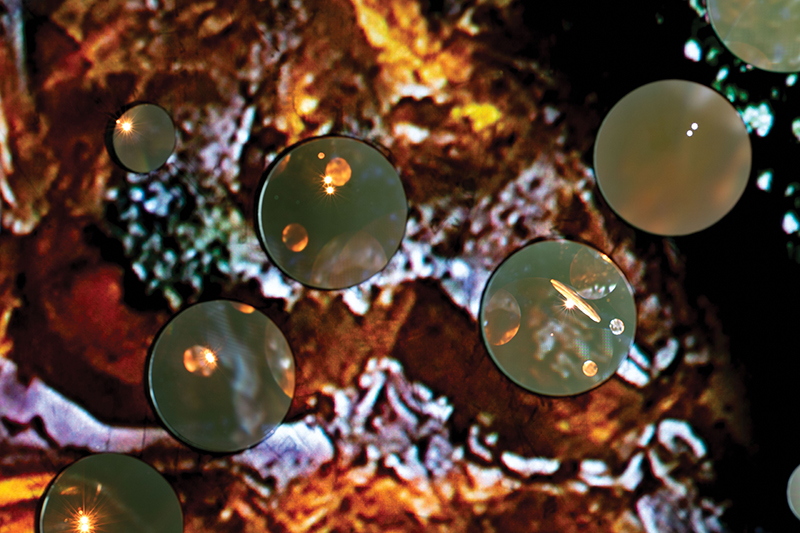
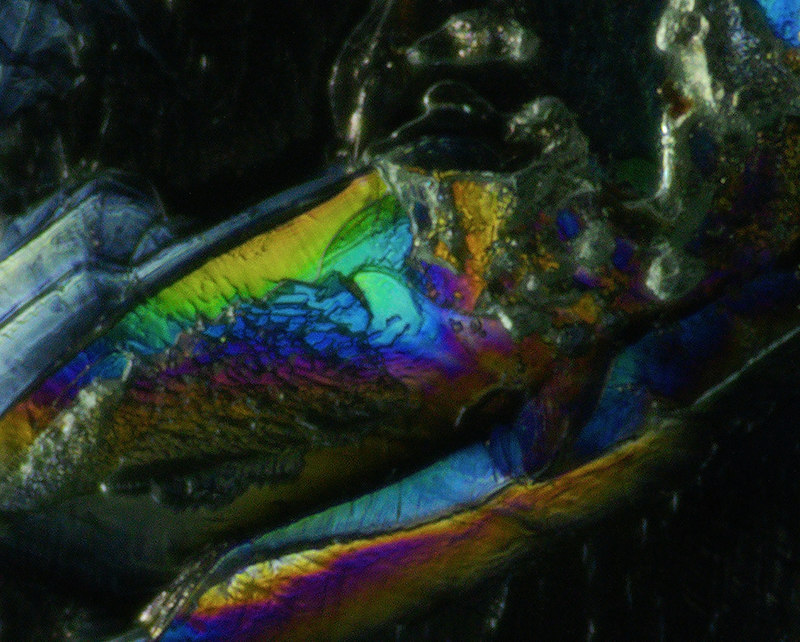
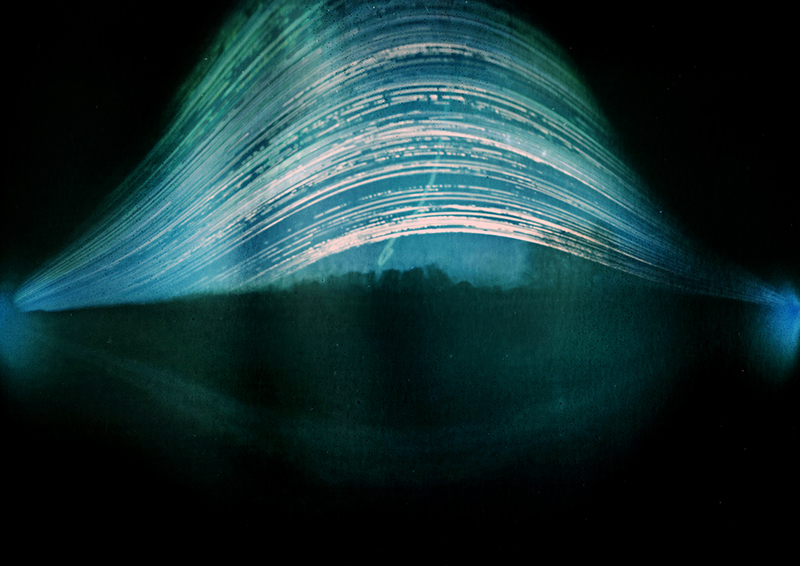
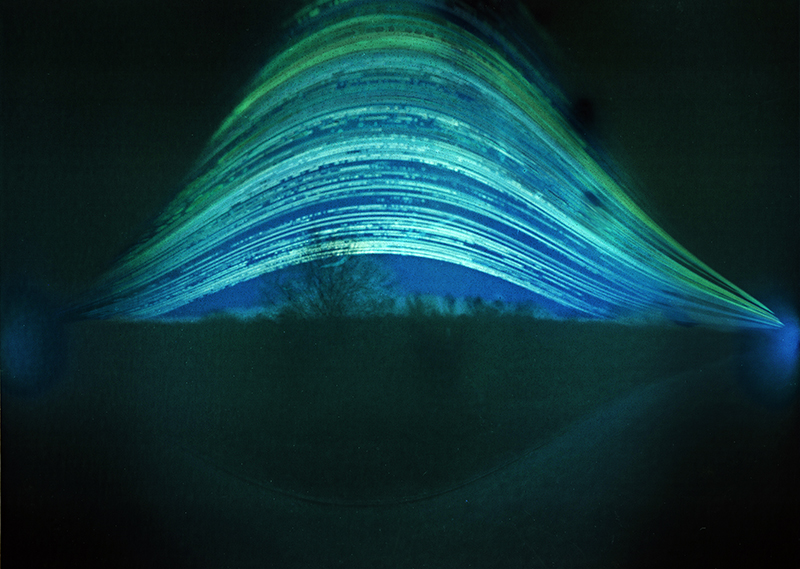
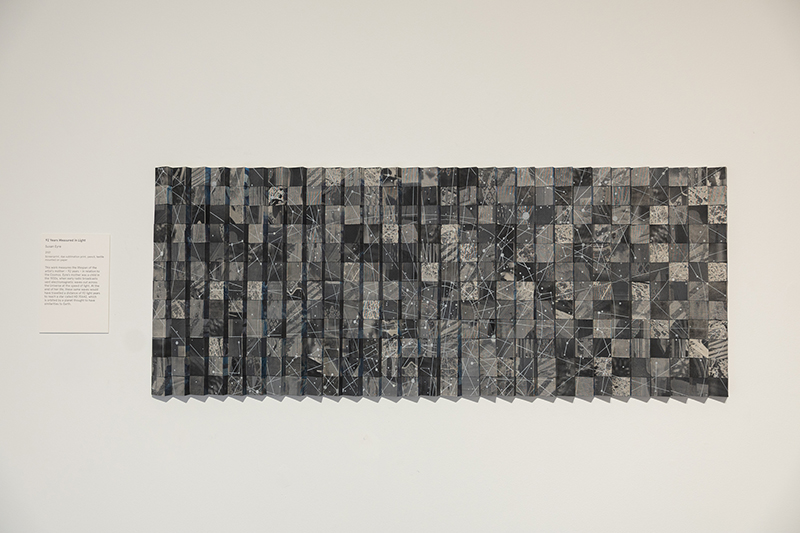
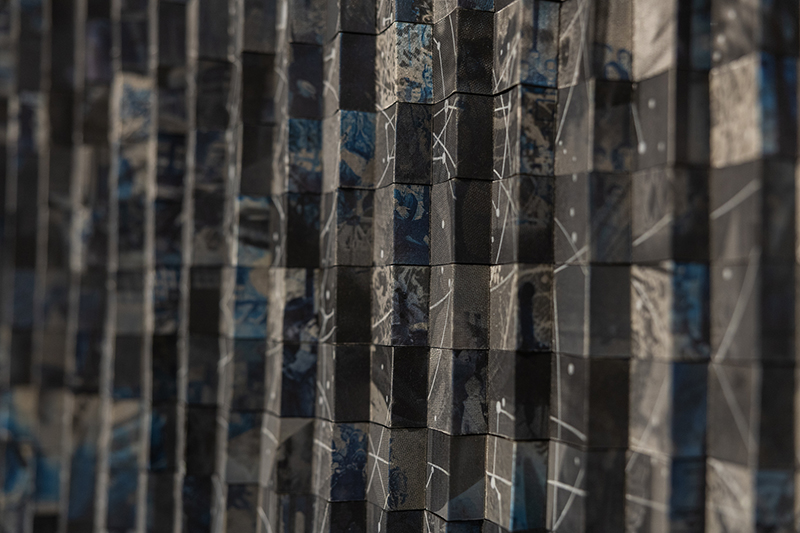
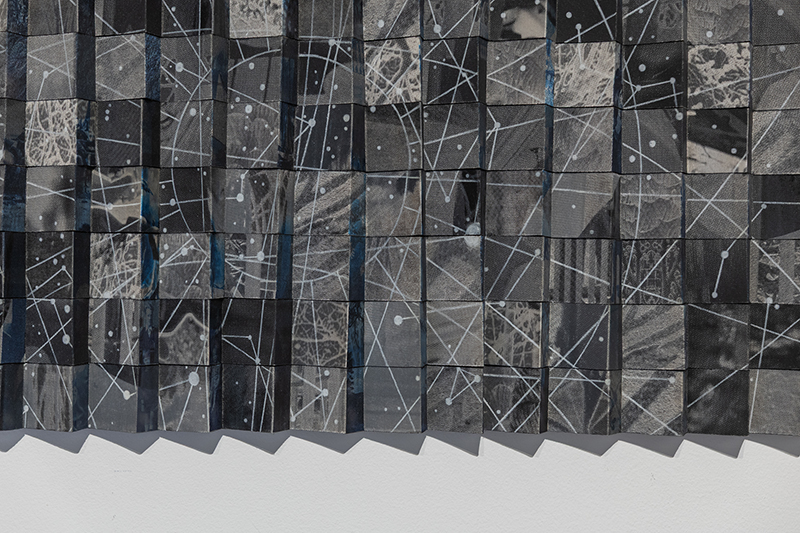
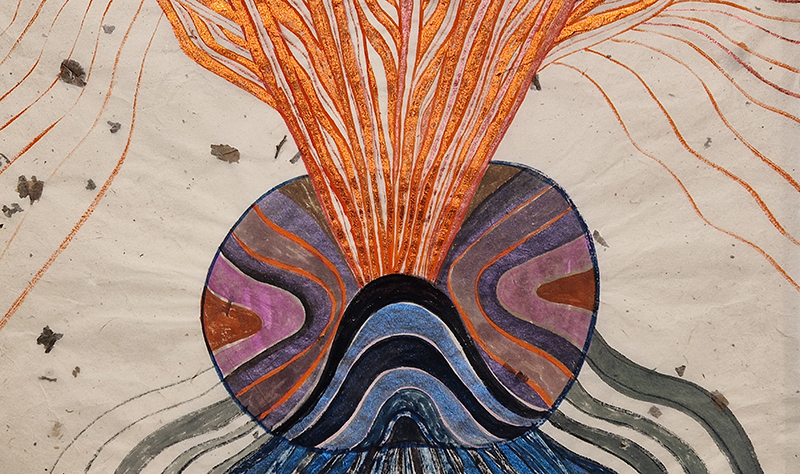
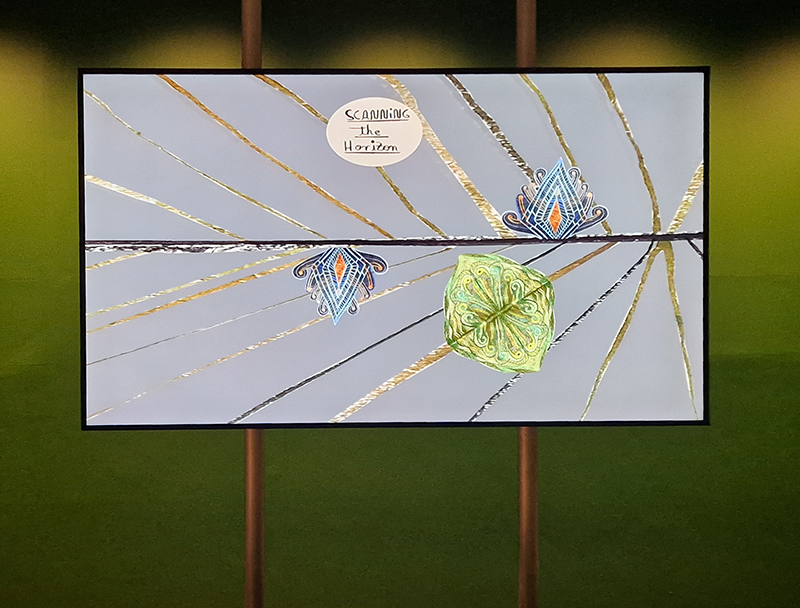
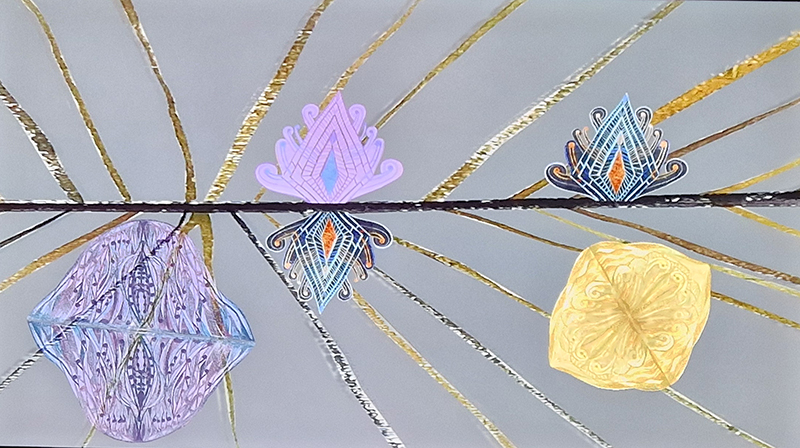
92 Years Measured in Light, 2021, is a very personal work made just after the pandemic, reflecting on the human experience of time in relation to the vastness of the Cosmos. There is a star, similar to our sun, with planets orbiting in a motion comparable to how the planets orbit here in our solar system. This star, in the constellation of Puppis, is about 92 light years away. The time it has taken the first radio and television signals travelling at the speed of light to reach this prospective home-from-home is roughly the same time as the lifespan of my mother who was born around the time of these early broadcasts. The folded sections in this work emulate the raster pattern of early TV signals which were sent in segments and must be reassembled on arrival to make sense of the message. The artwork includes fragmented images from this historical period viewed from one direction, and a chart depicting the star from the other. It is an interesting thought to consider what alien life forms might make of these messages travelling across the universe, should they be able to interact with them.



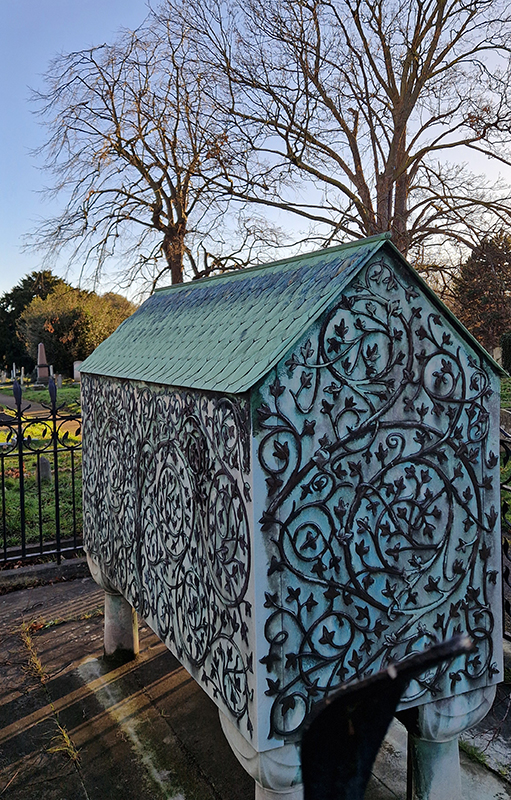
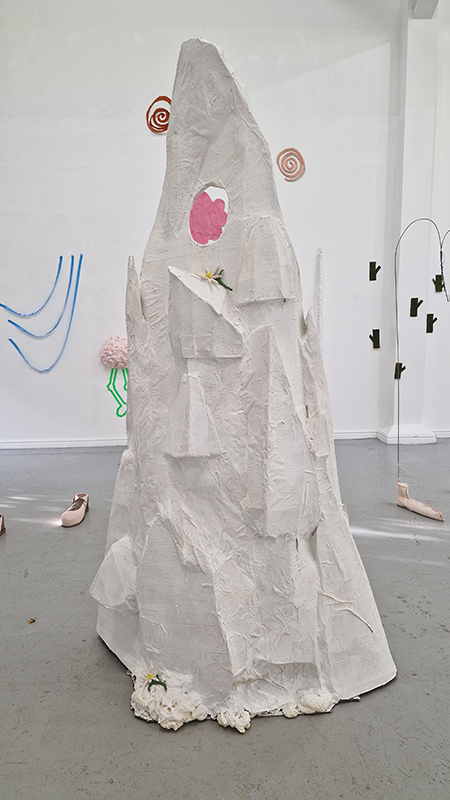
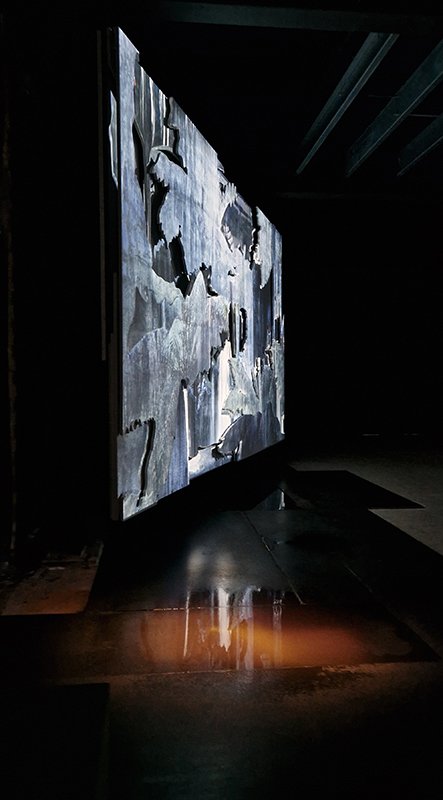
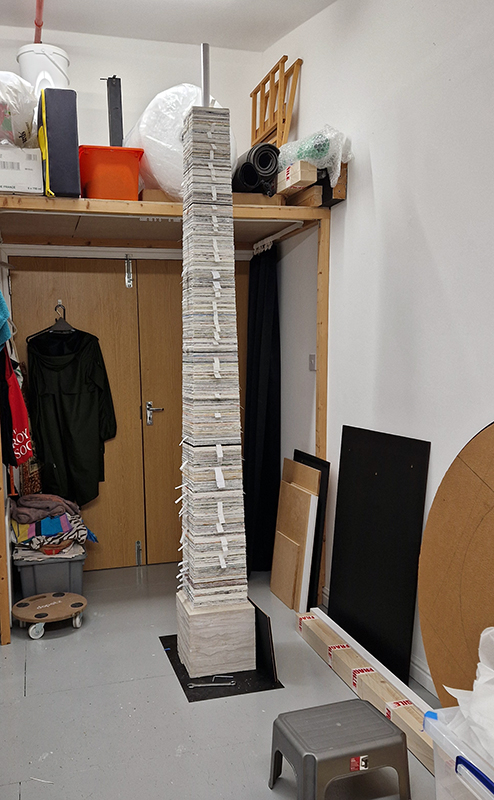
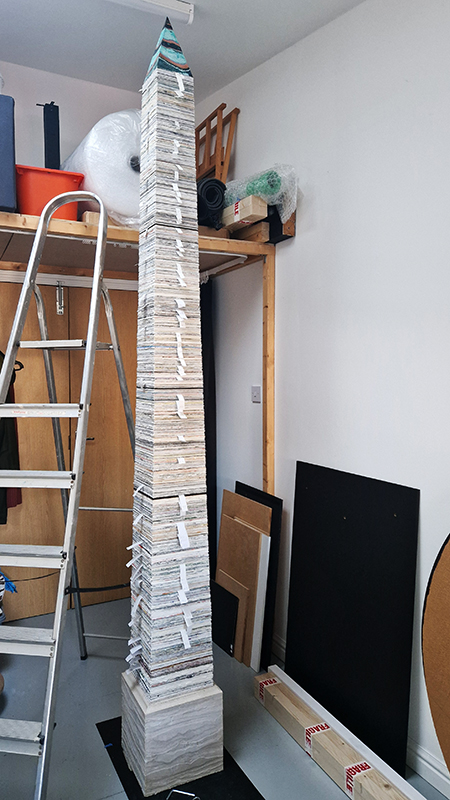
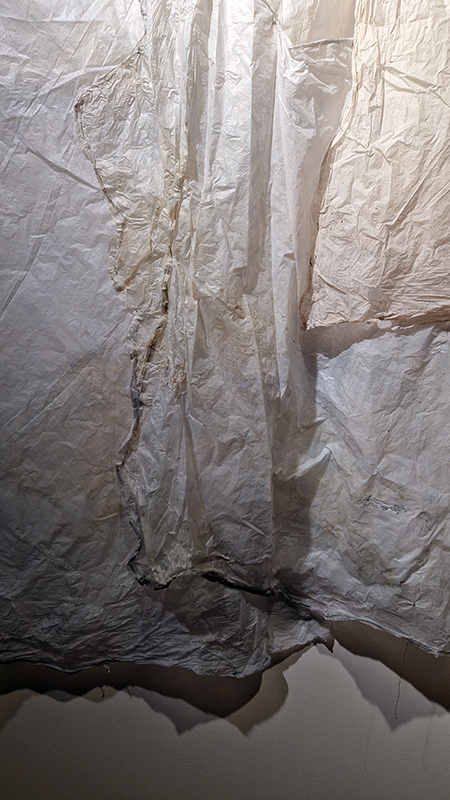
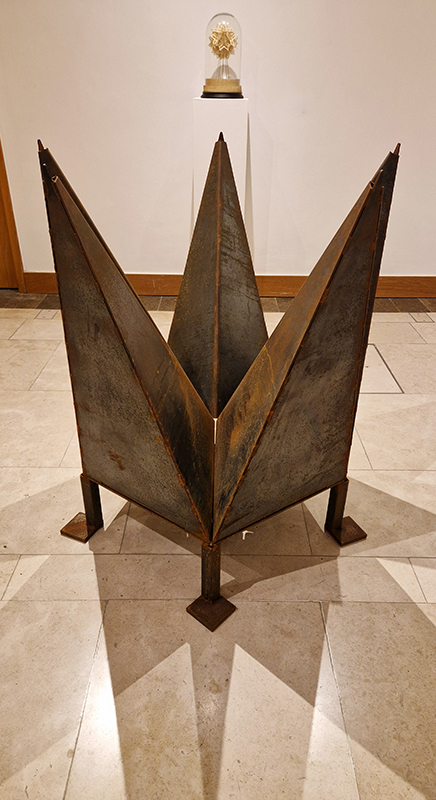
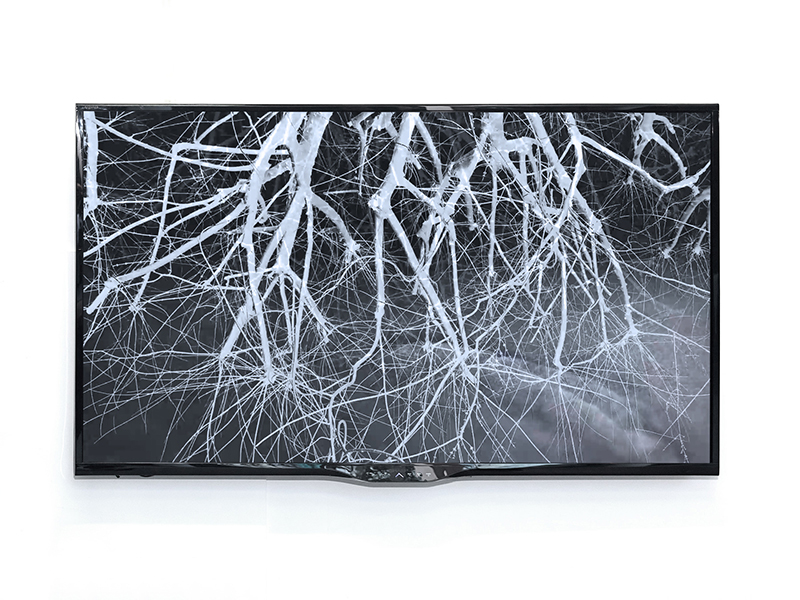
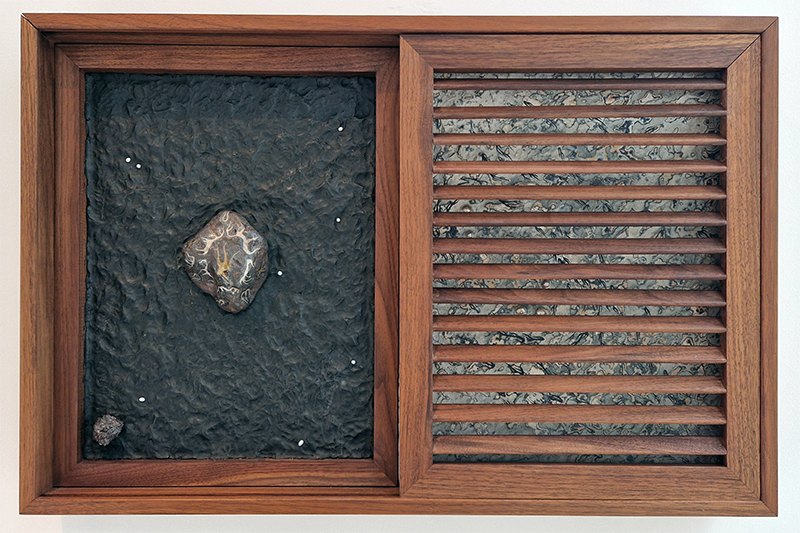
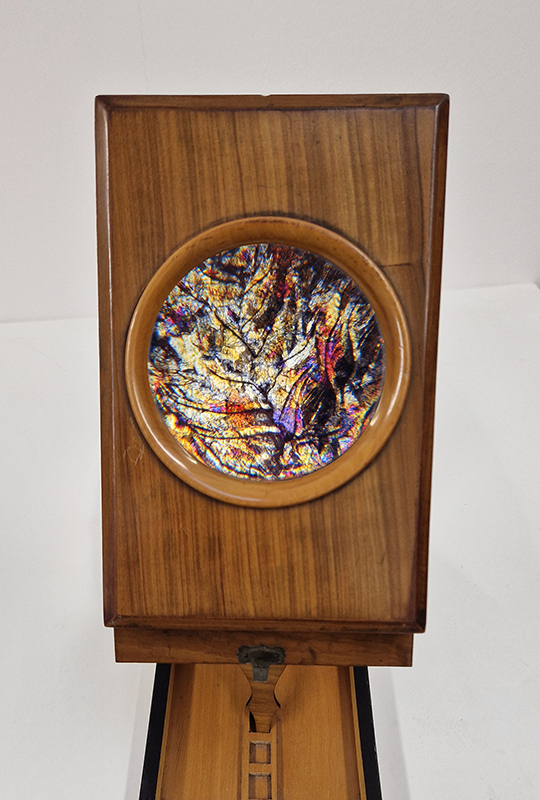
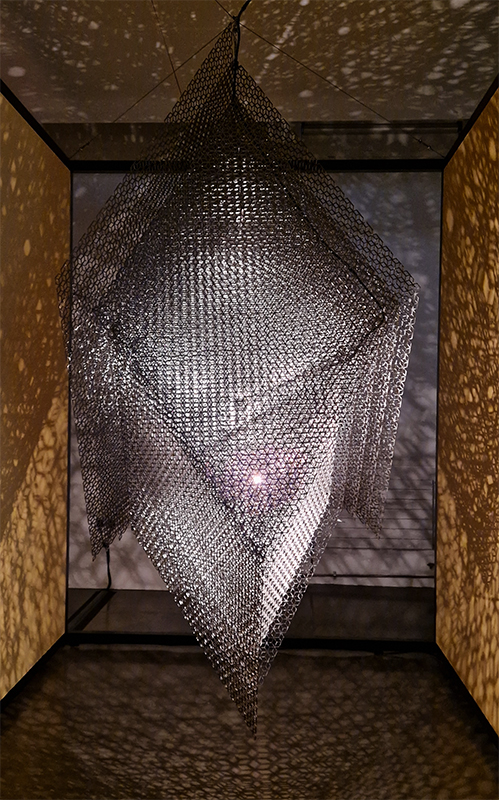
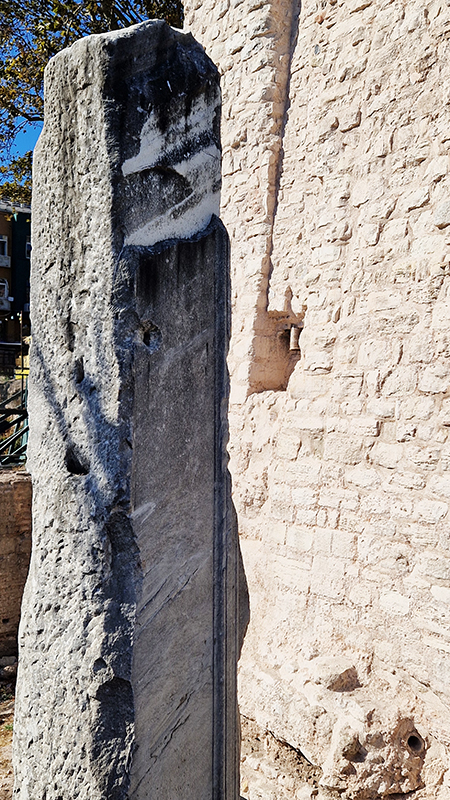
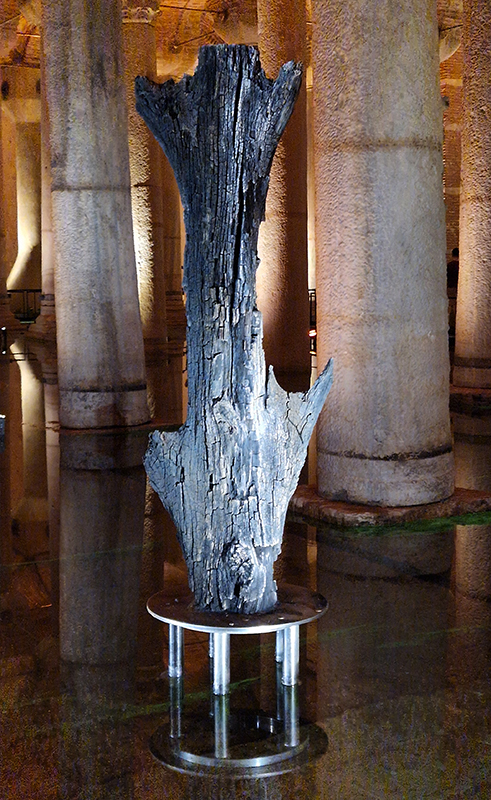
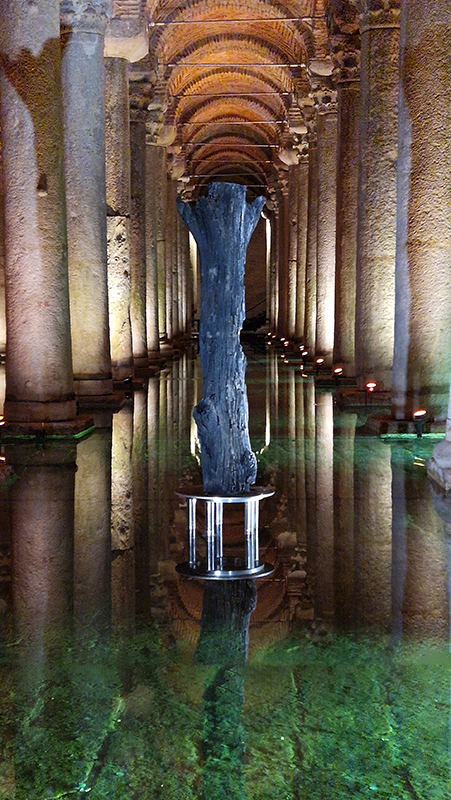
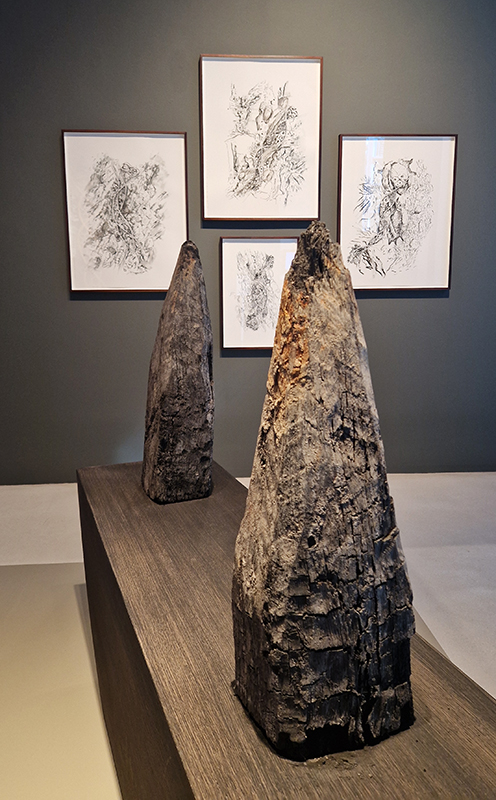
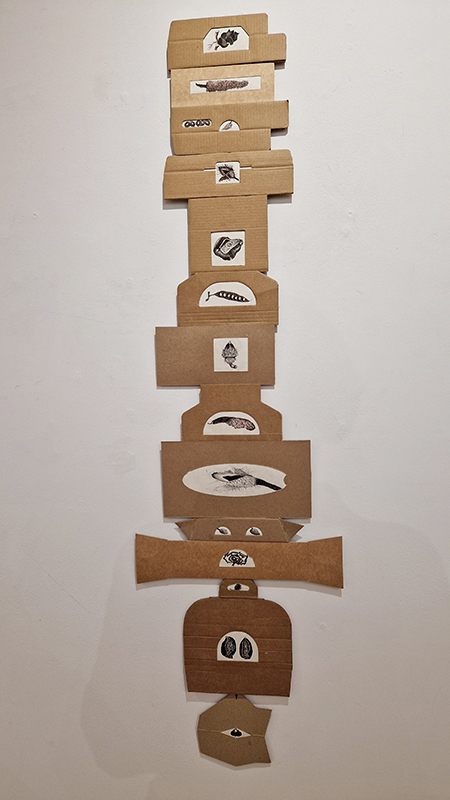
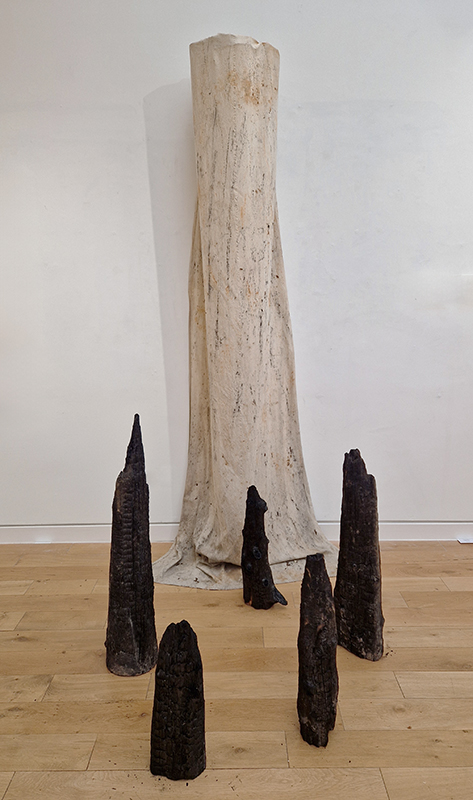
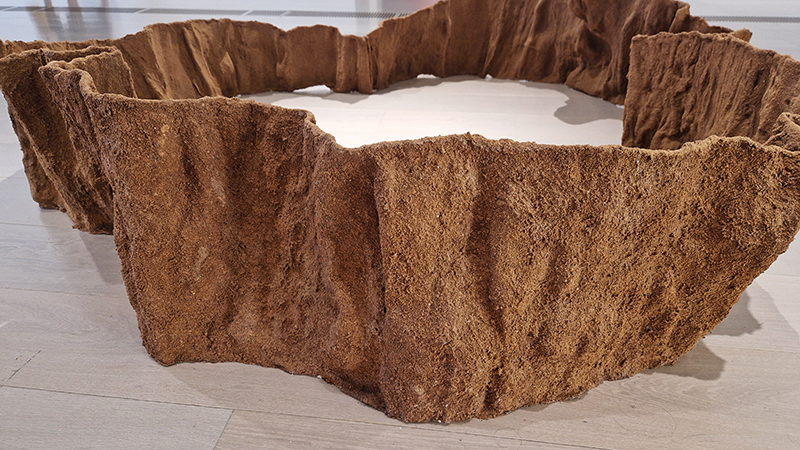
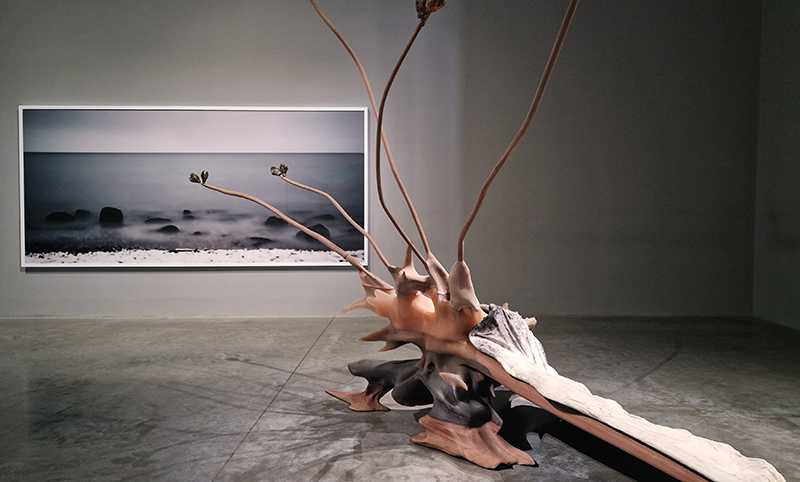
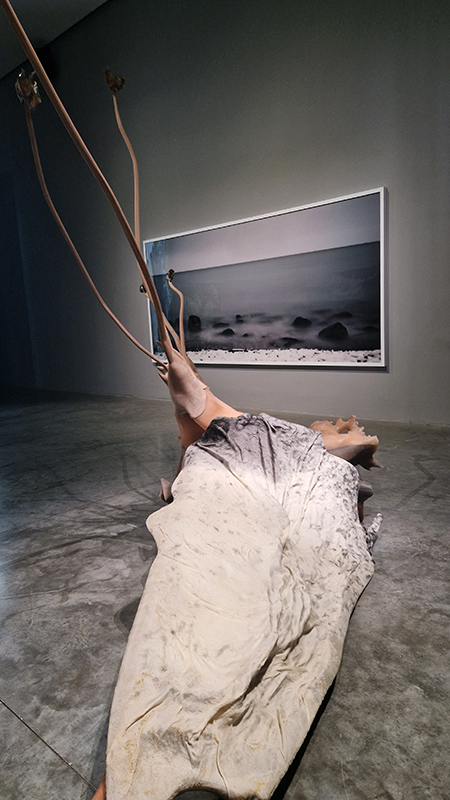
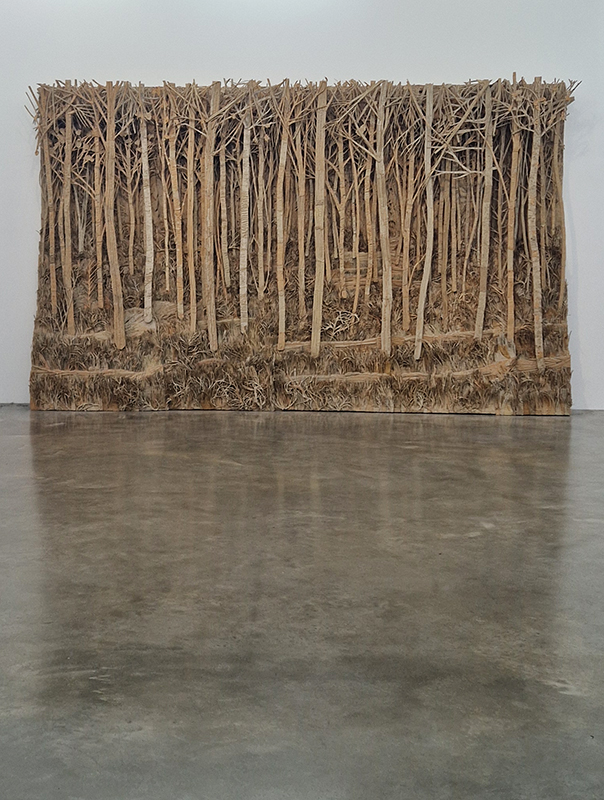
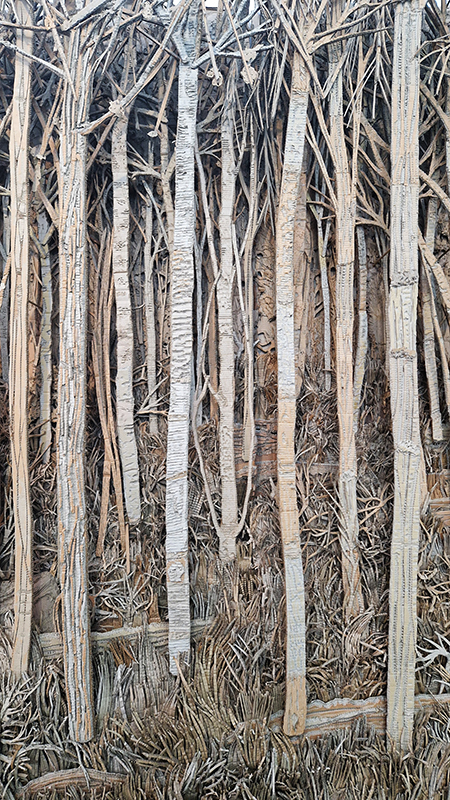
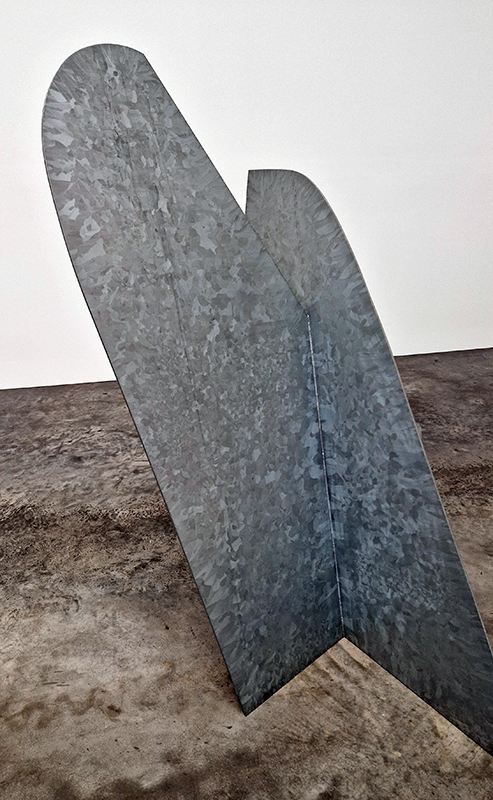
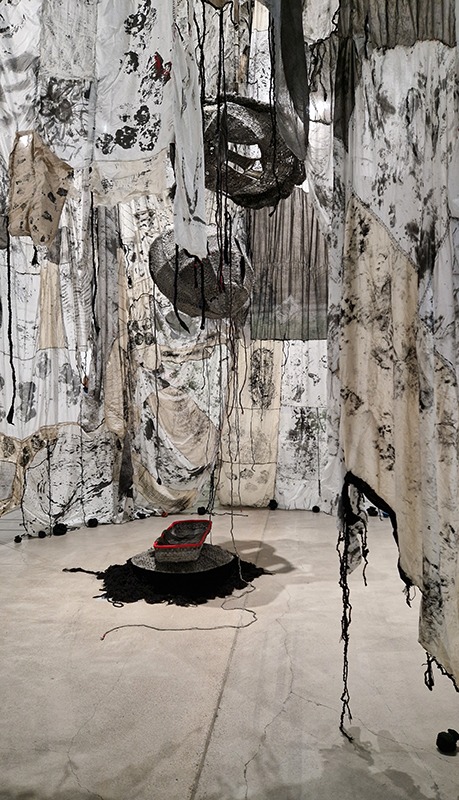
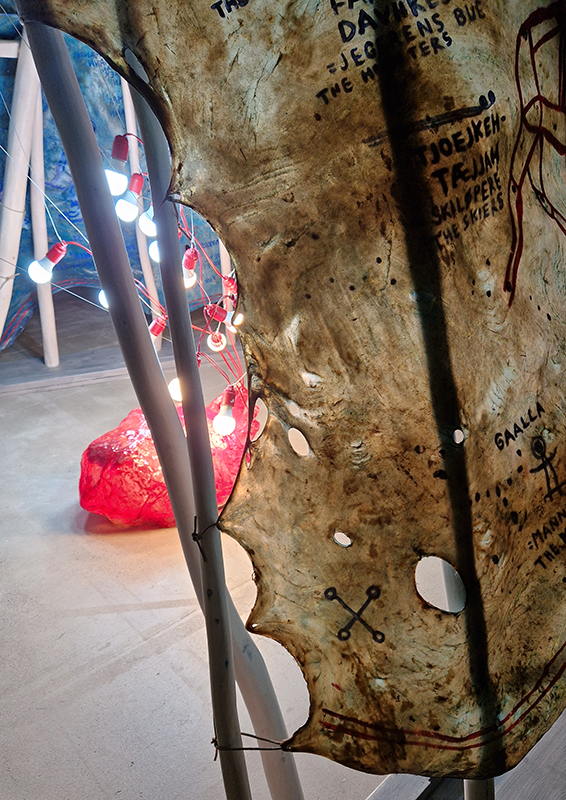
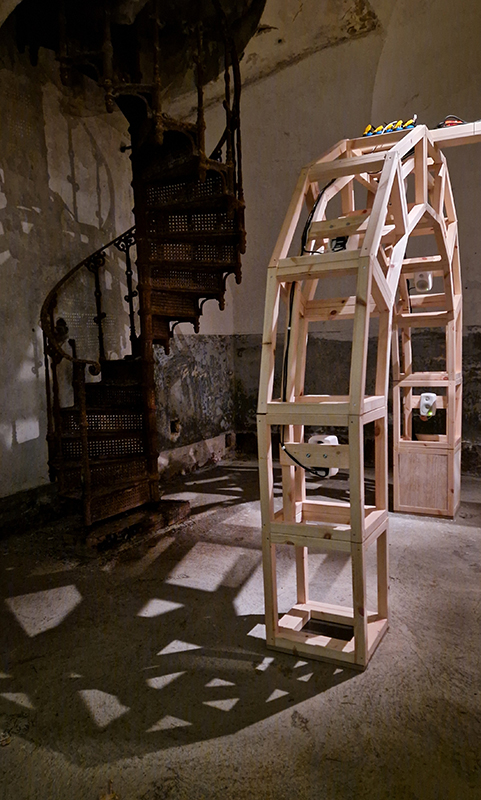
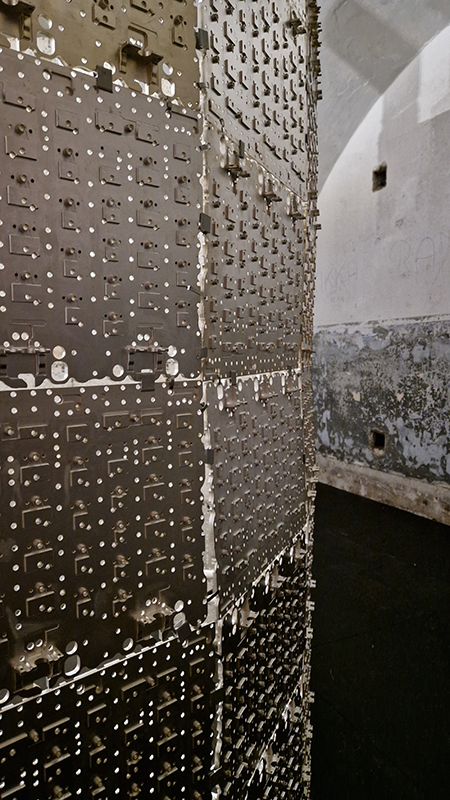
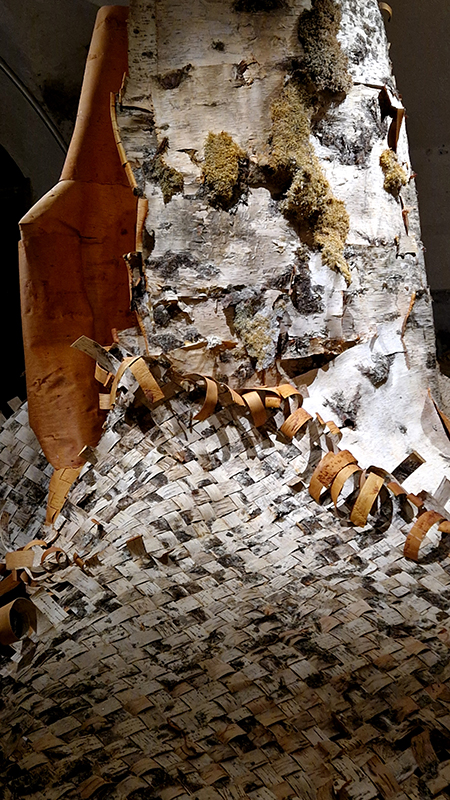
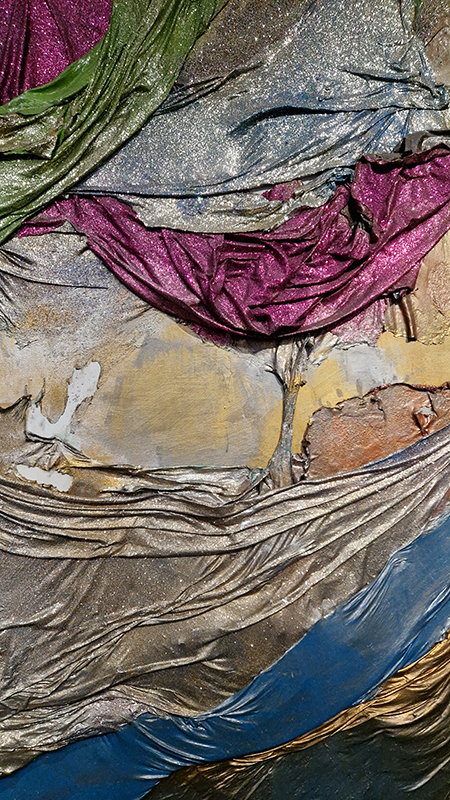
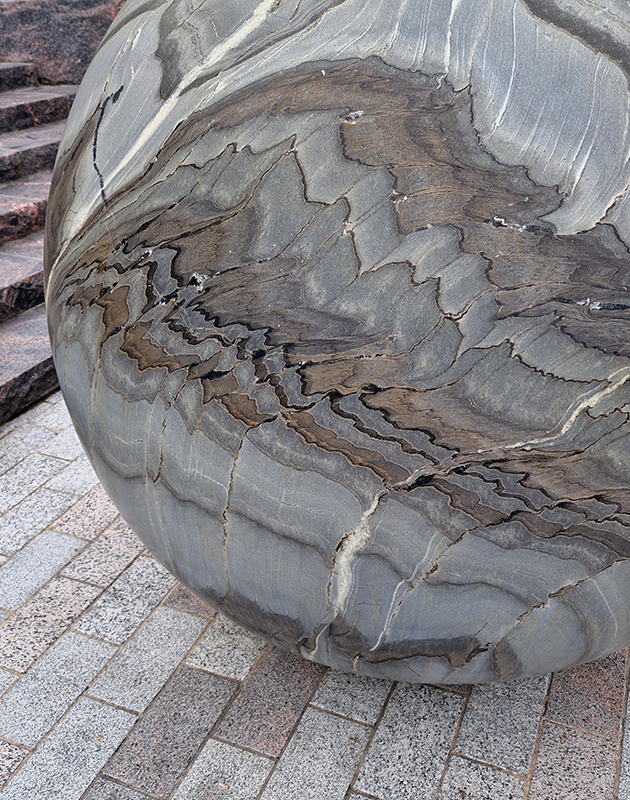
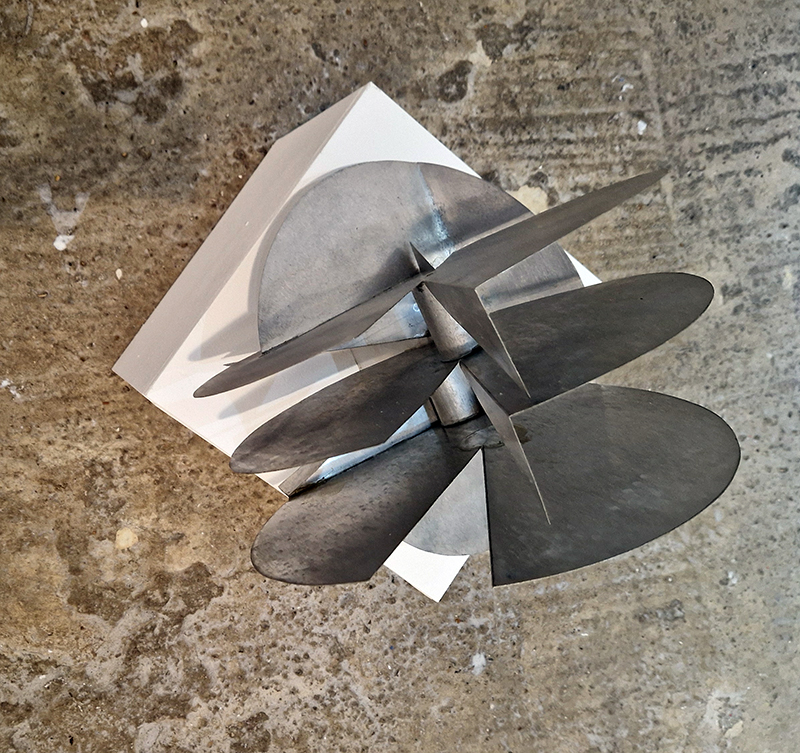
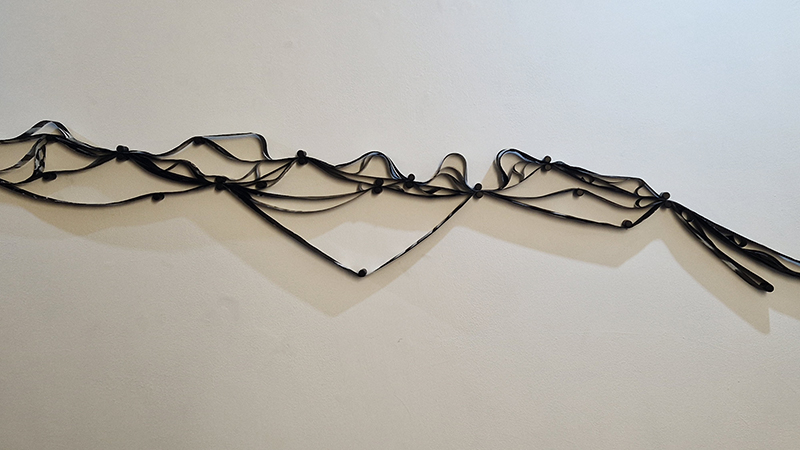
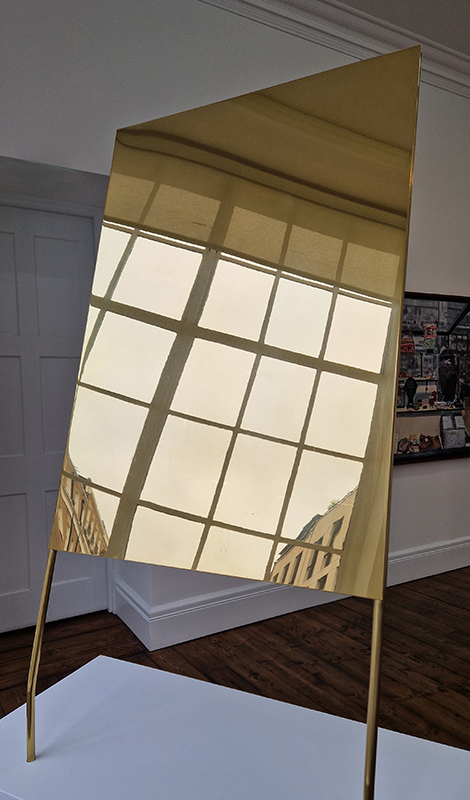
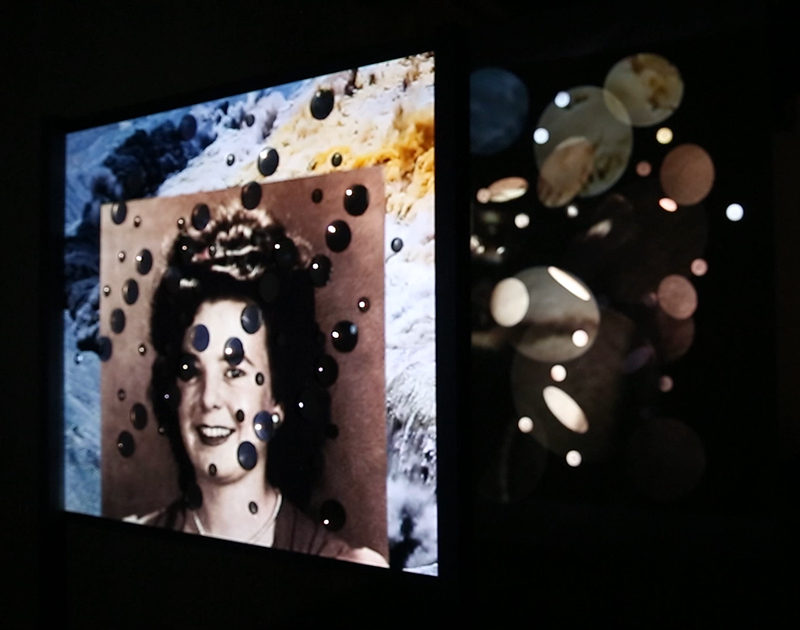
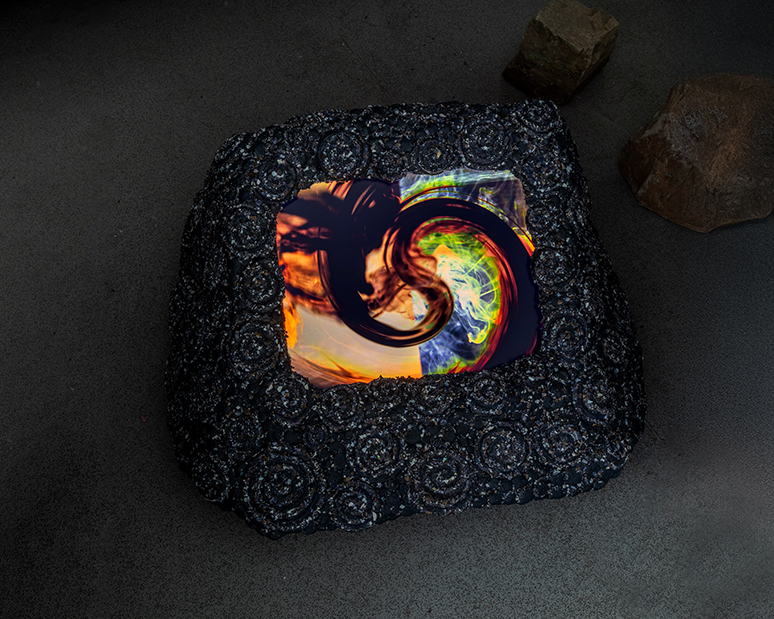
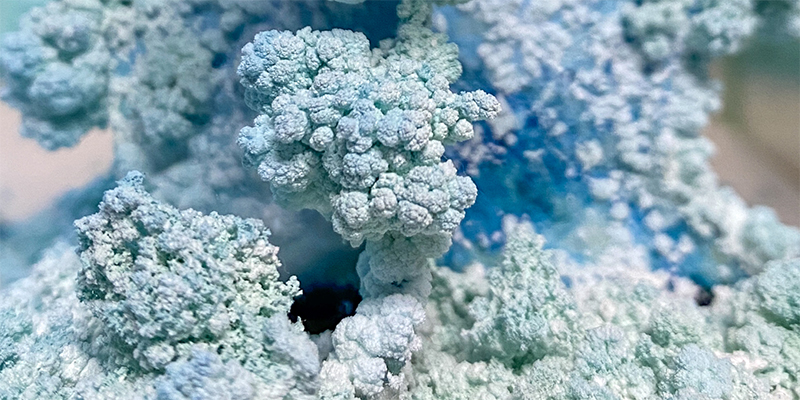
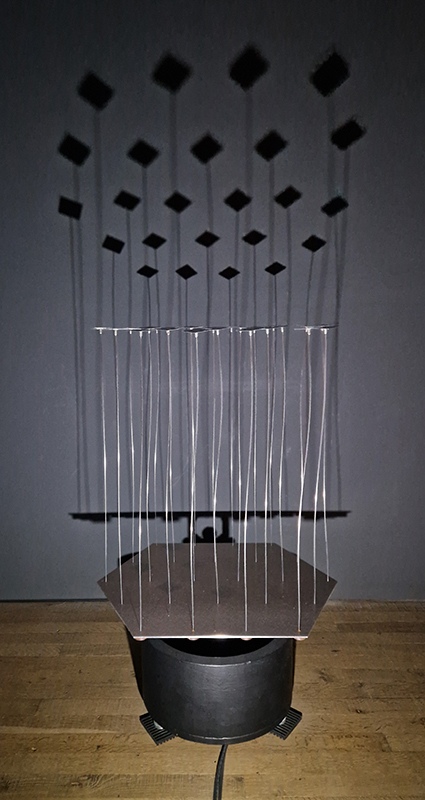
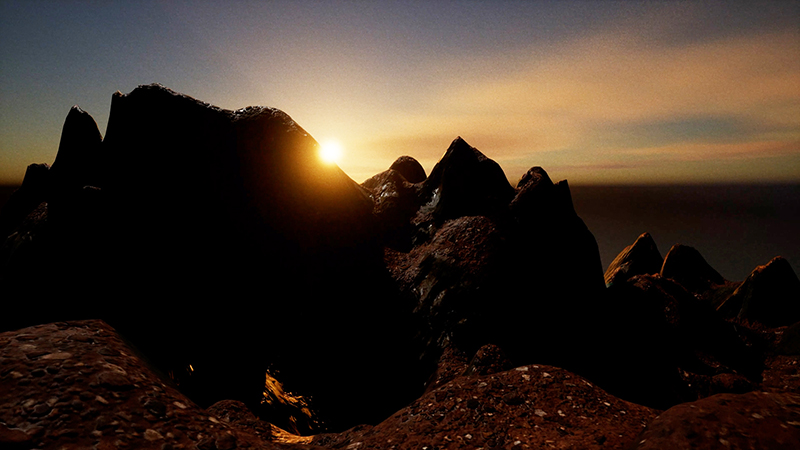
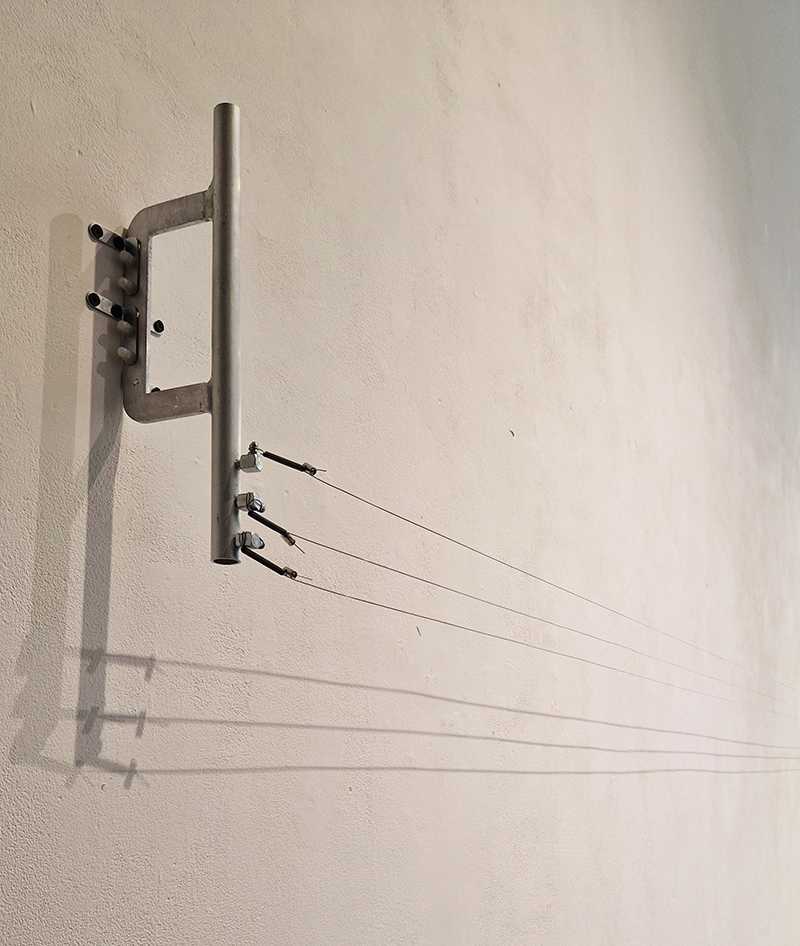
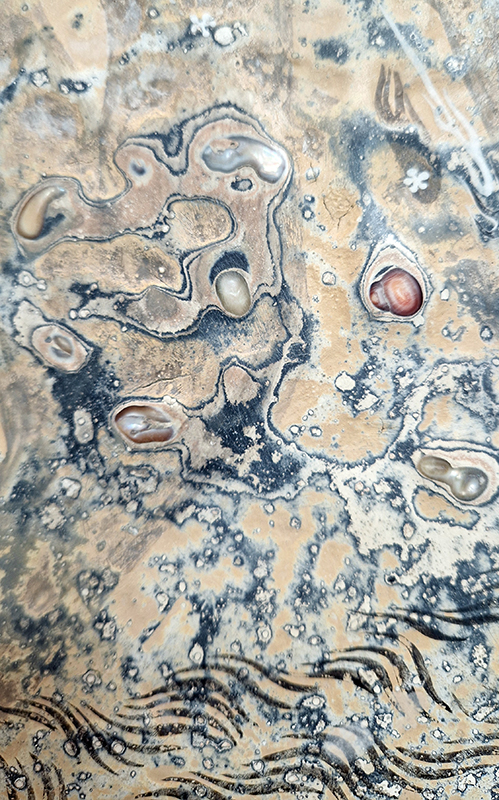
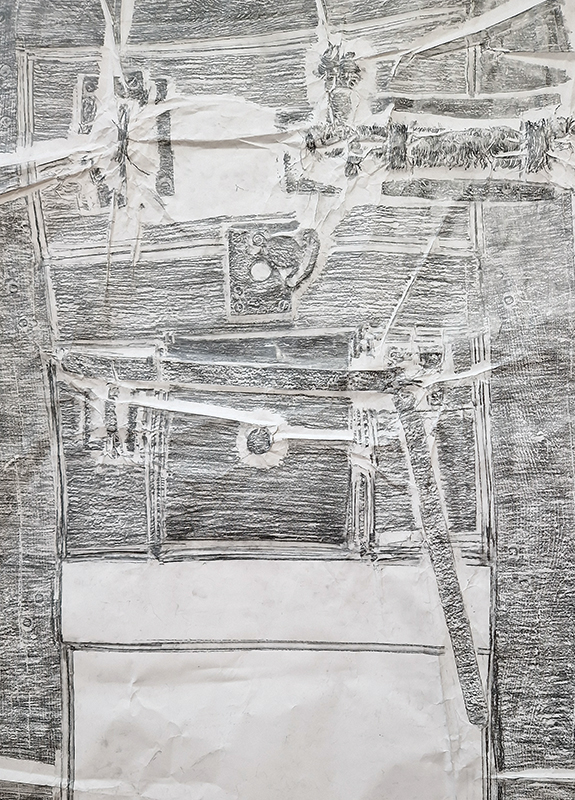
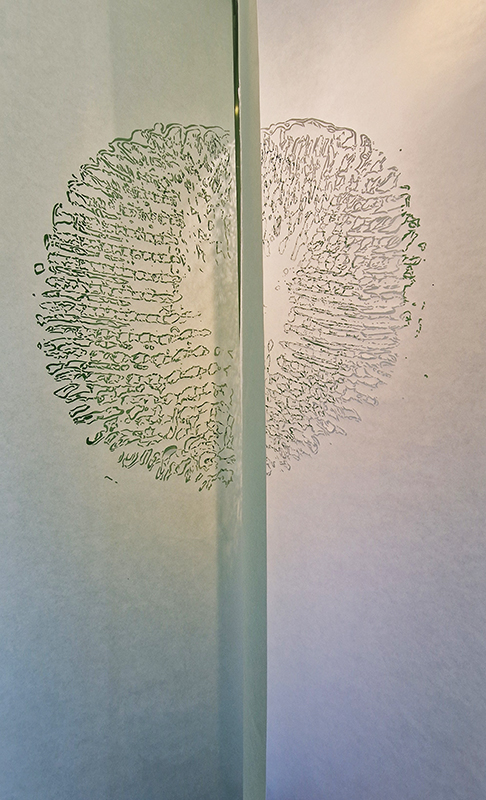
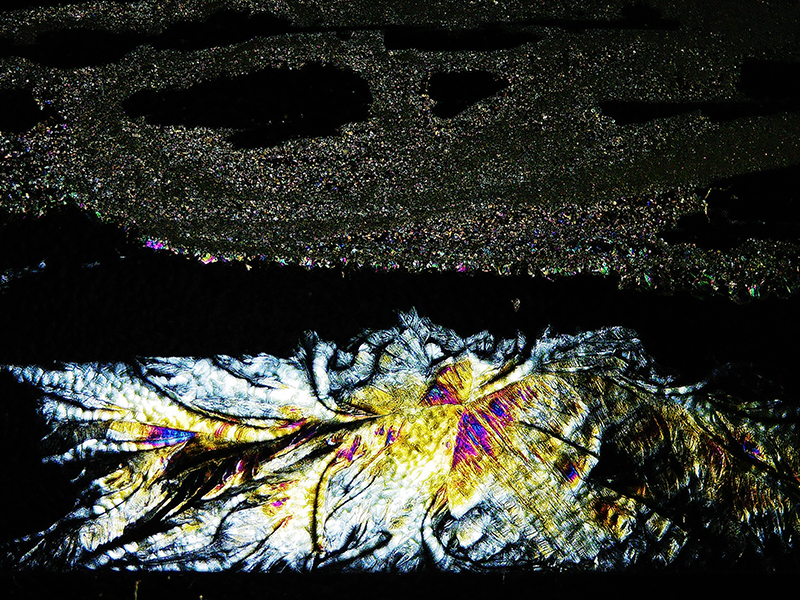
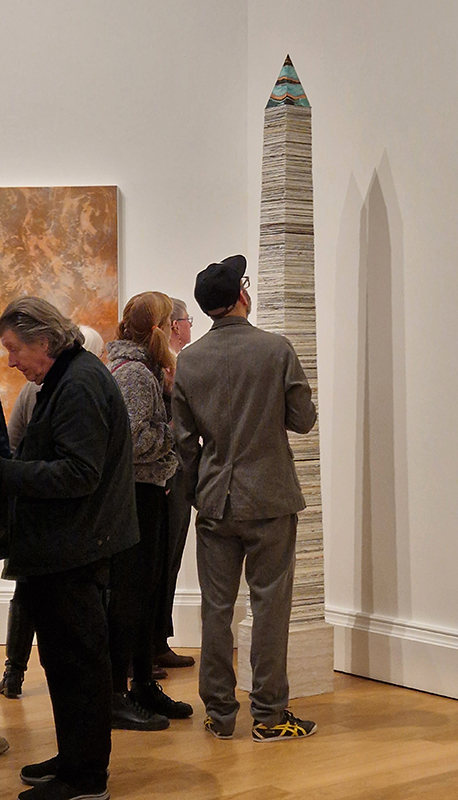
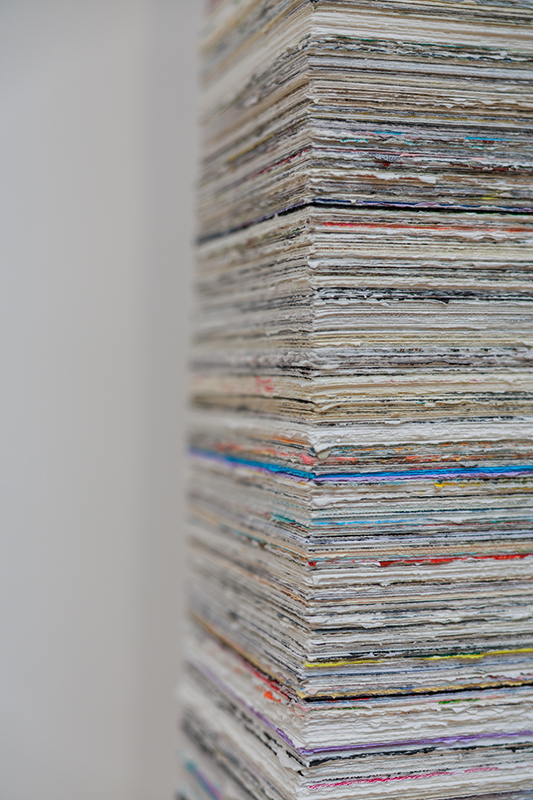
The Azimuth Obelisk (of sedimentary knowledge) 2023 is a reimagining of a concrete obelisk, erected in 1955 at Hartland Magnetic Observatory, as a permanent azimuth mark from which to monitor the drift of the magnetic north pole. Measurements are taken via a theodolite through a north facing window in what is known as the Absolute Hut. My sculpture echoes the hidden history of Earth’s wandering magnetic field, which has been secreted by magnetic minerals in the strata of sedimentary rock over millennia. To make the piece, hundreds of works on paper were painstakingly hand-torn, layered and stacked, expressing the passage of time at both geological and human scales.


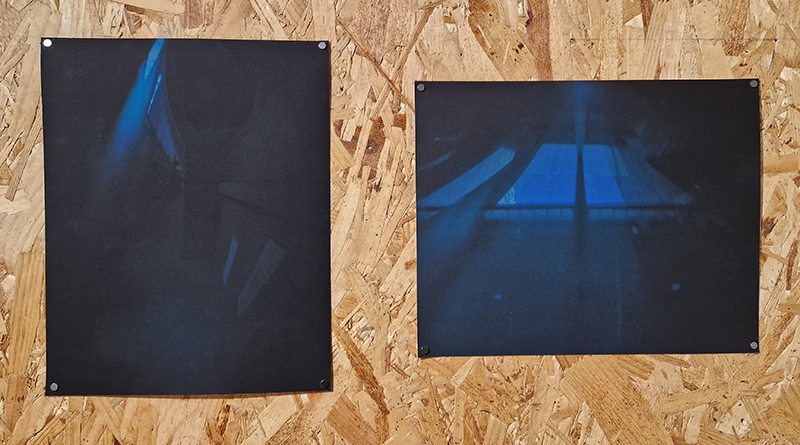
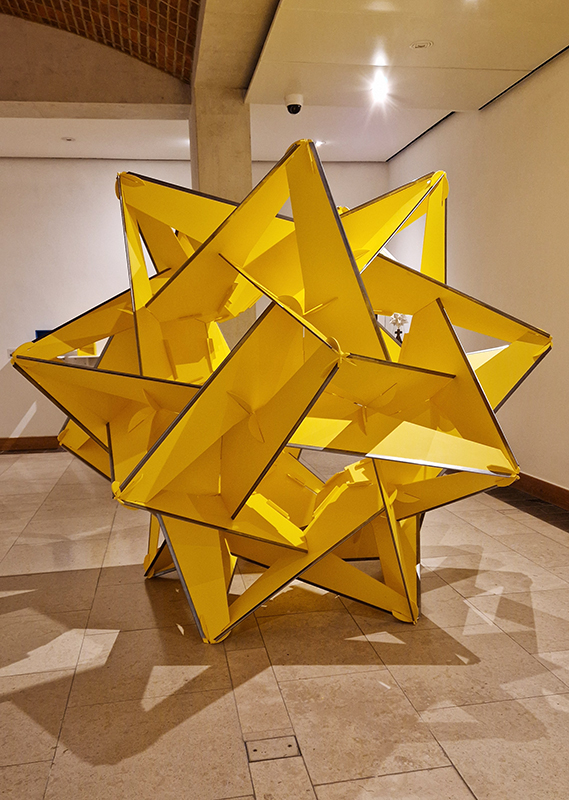
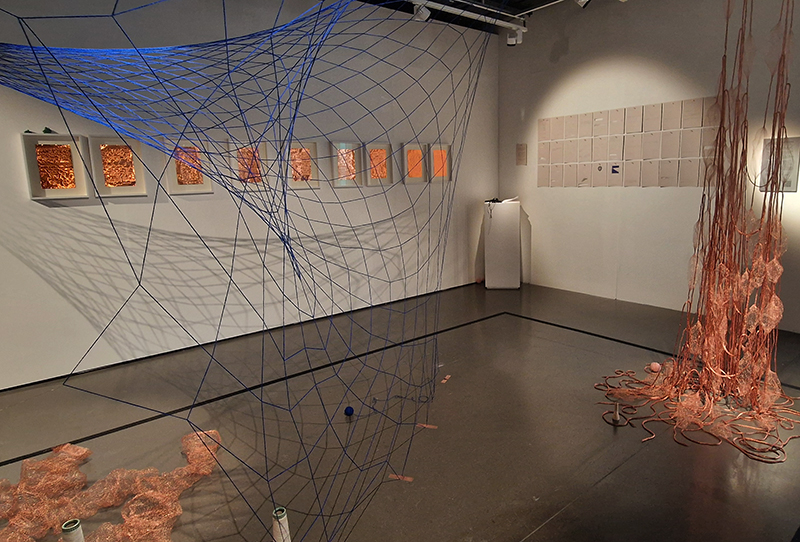
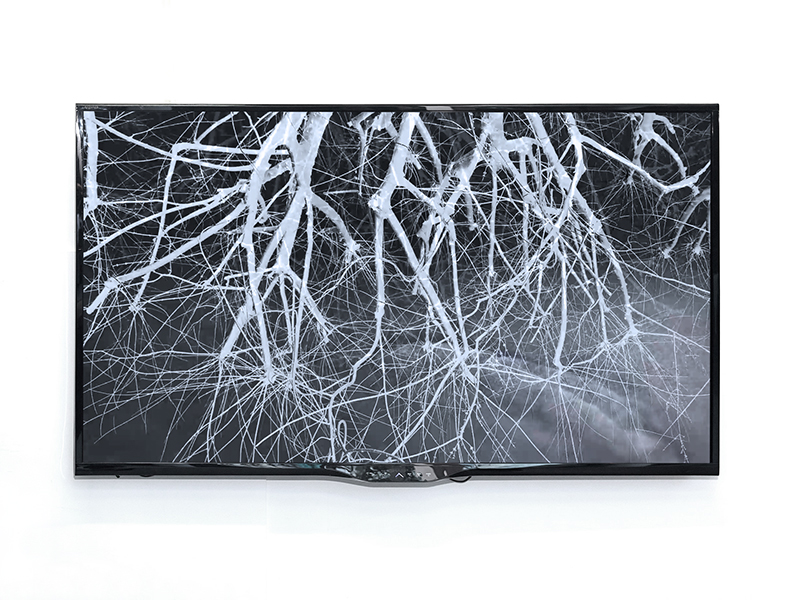
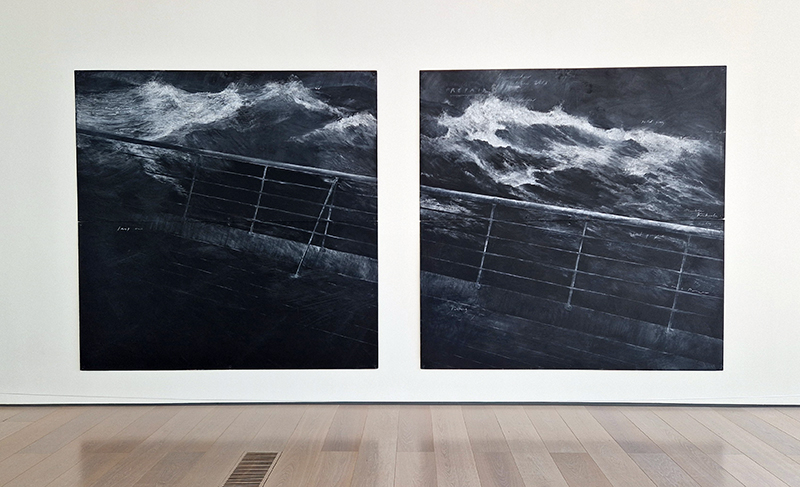
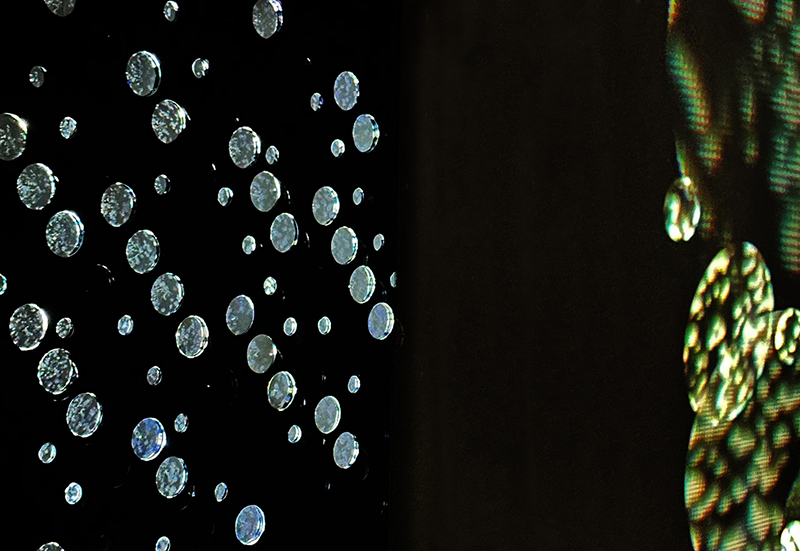
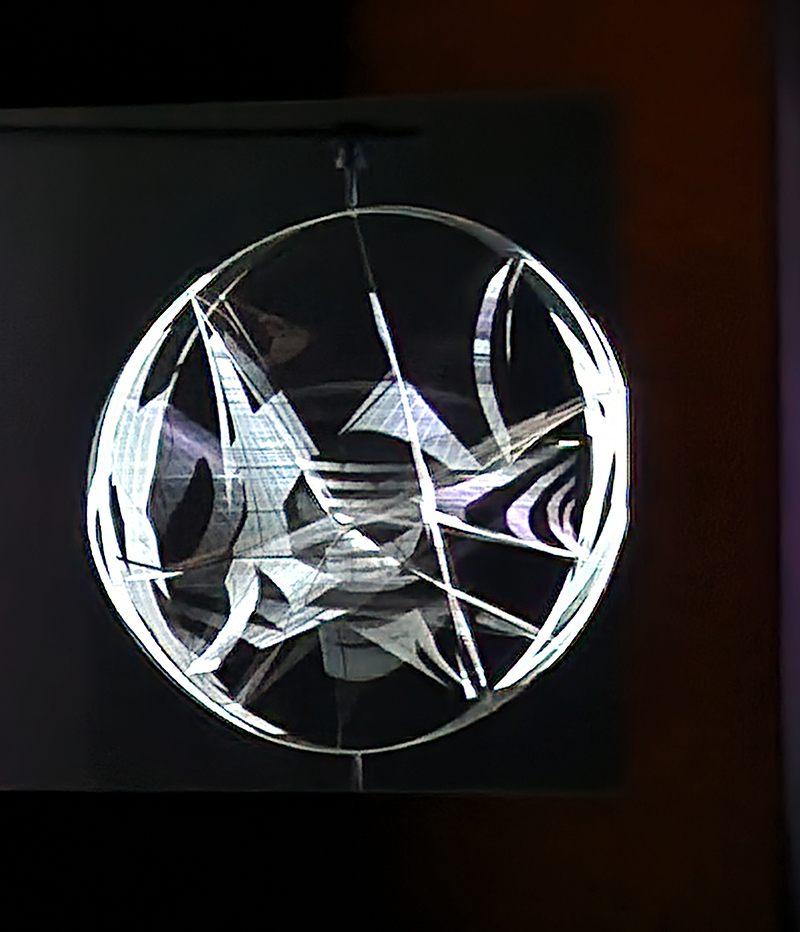
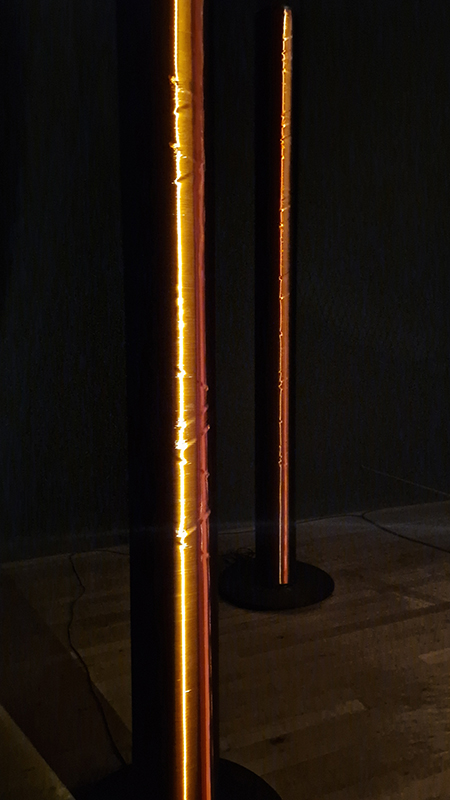
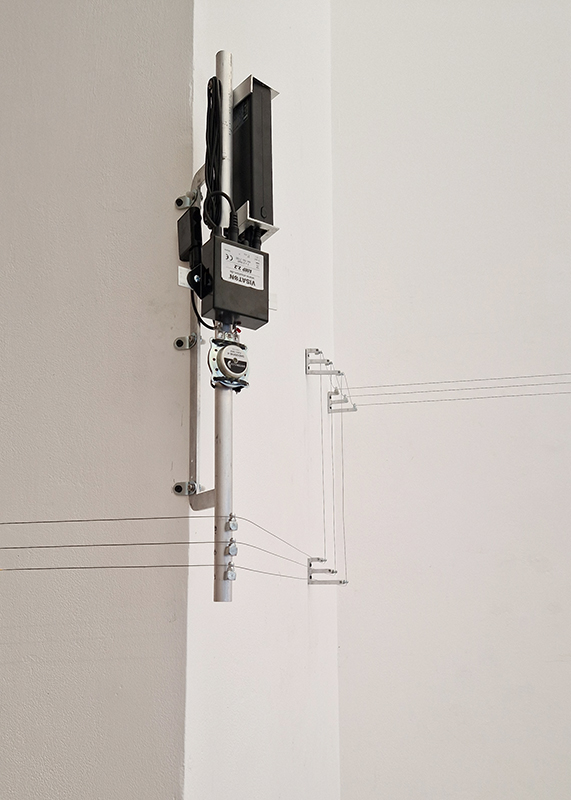
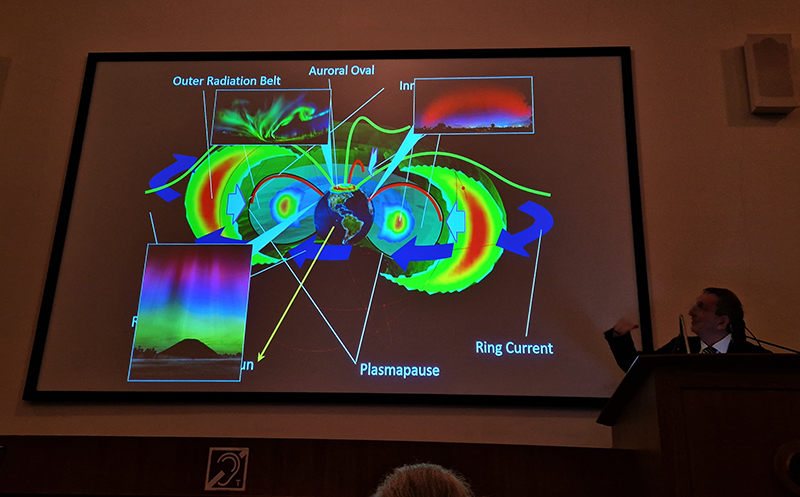
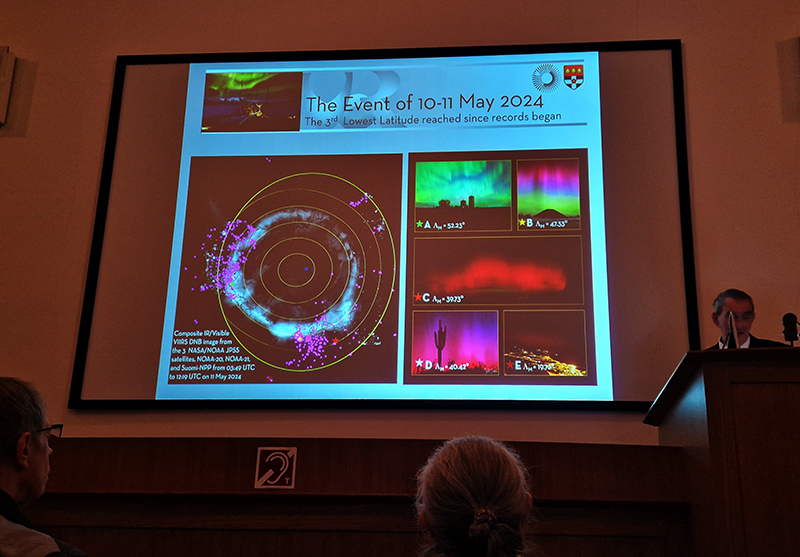
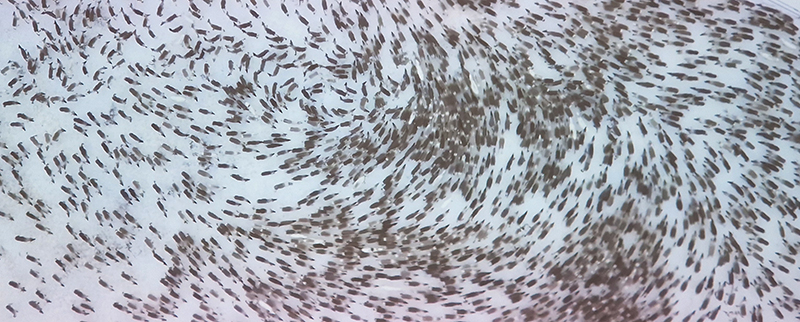
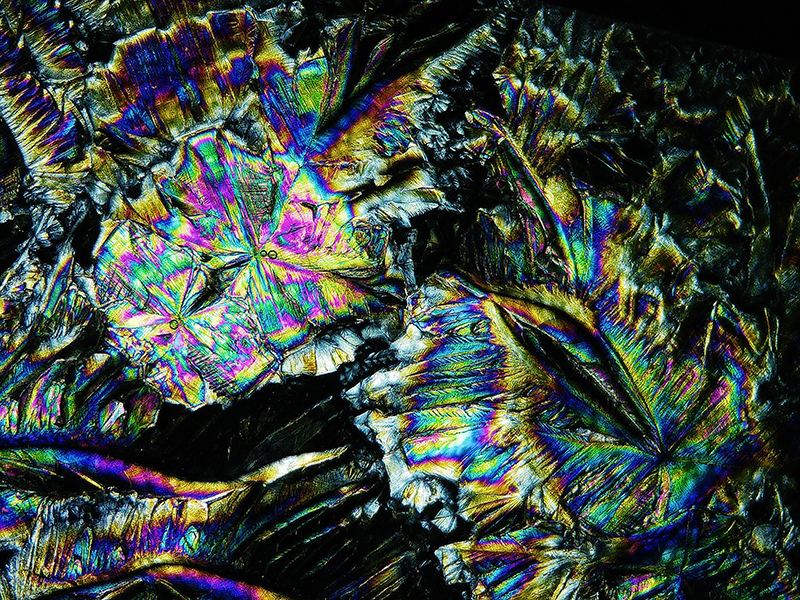
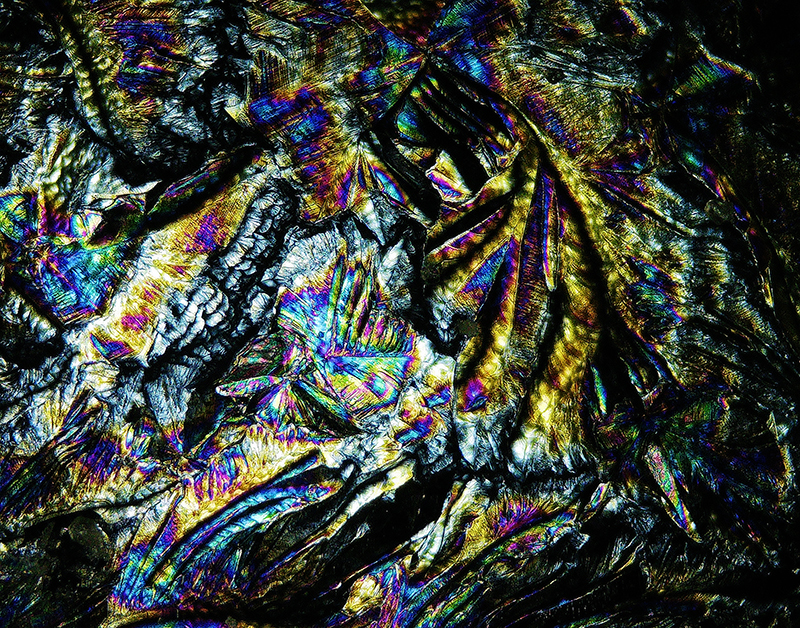
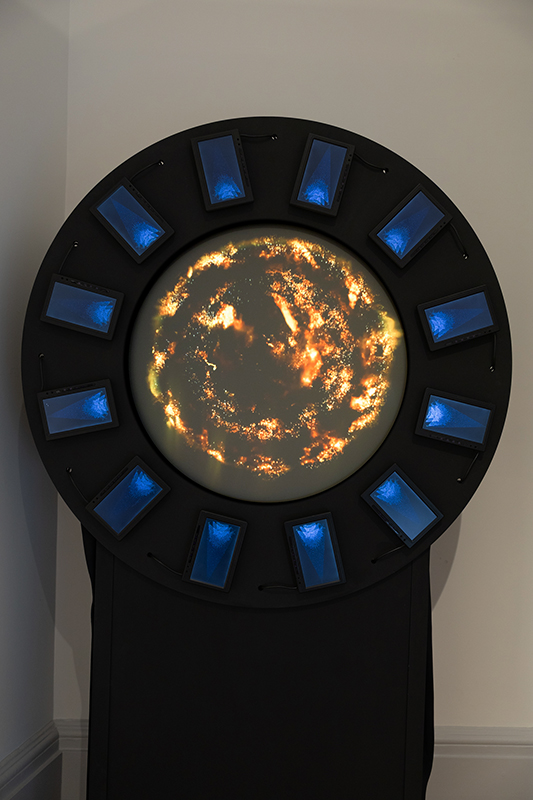
Orbital, 2024, reflects on the interaction between space weather and Earth’s magnetic field and its impact on human infrastructure. The Earth’s magnetic field is quite a weak force requiring sensitive equipment to detect it, yet it provides valuable protection to life on Earth. It’s interaction with the solar wind has been very visible recently as the sun reaches peak activity in its 11 year cycle, lighting up skies with the aurora borealis much further south than is usual. Auroras may be beautiful to witness but belie the potential damage to satellites and electric grids from a violent solar storm. Our daily lives have become increasingly reliant on satellite technology for communication and data gathering and disruption to these systems would have wide reaching global effects. There is also research that suggests the number of satellites orbiting Earth and the growing space junk graveyard forming a metal cage could weaken Earth’s protective magnetic field, making us even more vulnerable to space weather and cosmic radiation. Space pollution and over use of low orbit space is not only gambling with disaster but it’s also disrupting the view of the night sky and will make it increasingly difficult for us to exit the Earth for space exploration.

Out, About and Online
Michael Taylor Dog eats Lion at Standpoint Gallery. I was lucky to be in the audience for his ‘in conversation’ with Johanna Love and his following introduction to the workings of Paupers Press, with lots of juicy insider knowledge about the artists, such as Grayson Parry, Damian Hurst and Paula Rego, who go to Michael for editioning their works. There was lots of show and tell and also his own solo show to see. Three hours well spent. Down to earth and entertaining, it was refreshing to hear such honesty about the creative process. The not knowing. His press release is basically a list of disturbing incidents that have stayed in his mind. Maybe sometime, the dog will have his day.
In his own words: Michael Taylor is the founder of the Paupers Press and co-founder of Standpoint Studios and Mark Tanner Sculpture Award. He has had a few shows but won no prizes. His work is held in a collection. He has taught at several art schools, a few of which are still open, some have closed. He has travelled extensively within the EU and considers himself a man for warm seasons.





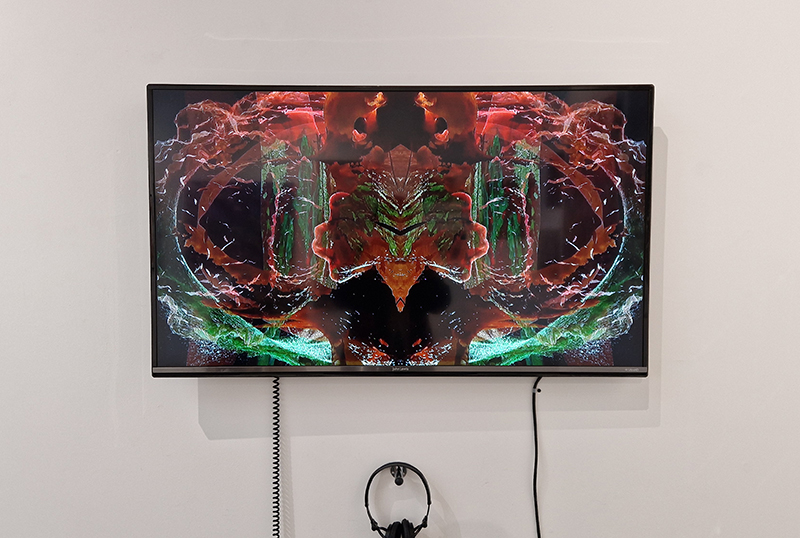
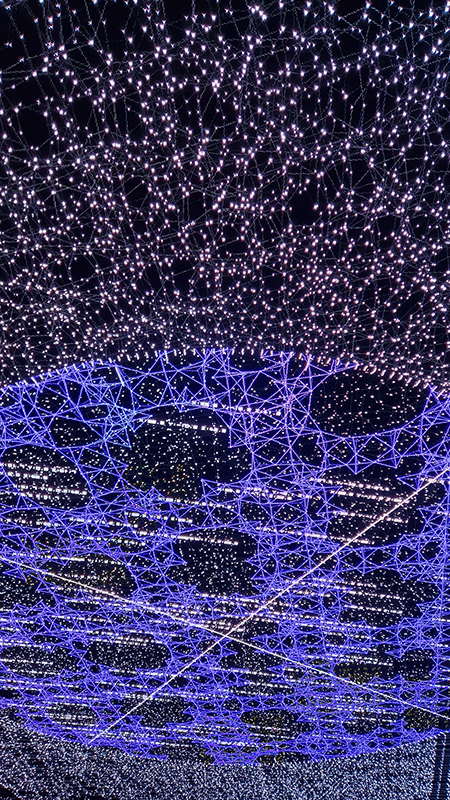
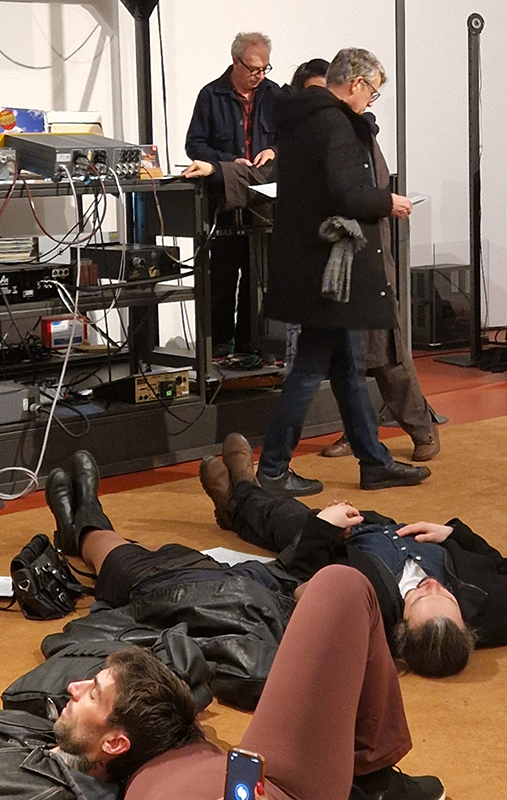
A little disappointed with Ryoji Ikeda’s new site-specific audio-visual installation data-cosm [n°1] at 180 Strand. Visitors are invited to lie down on the floor and look up at the large LED screen set on the ceiling above them, their bodies surrounded by Ikeda’s soundscapes – a total sensory experience. The set up is impressive and the experience is immersive, at times blinding and at times has the thrill of a fairground ride but overall I felt the imagery could have been more engaging.


Paradigm Shift at 180 Strand spans moving image works from the 1970s to today, drawing on avant-garde cinema, television, music video, performance, fashion, gaming, and internet culture. Featuring works by artists: Sophia Al-Maria, Meriem Bennani, Dara Birnbaum, Foday Dumbuya, Cao Fei, Tremaine Emory, Nan Goldin, Arthur Jafa, Derek Jarman, JulianKnxx, Mark Leckey, Josèfa Ntjam, Pipilotti Rist, Martine Syms, TELFAR, Ryan Trecartin, Gillian Wearing and Andy Warhol. Many, many videos. Exit feeling like it’s been a long night in the underworld.










I joined a webinar in connection with Earth, a Cosmic Spectacle exhibition at Everybody Arts Together. Presented by exhibiting artist Louise Beer, with speakers Dr Anik Halder, postdoctoral research associate at the Institute of Astronomy, Cambridge and Jesus College Cambridge. and Miranda Lowe CBE, principal curator, natural historian and marine invertebrate specialist at the Natural History Museum, London. The importance of establishing connections to the cosmos through stargazing and learning more about astronomy and other life that shares our planet was emphasised as vital to building hope for the future.

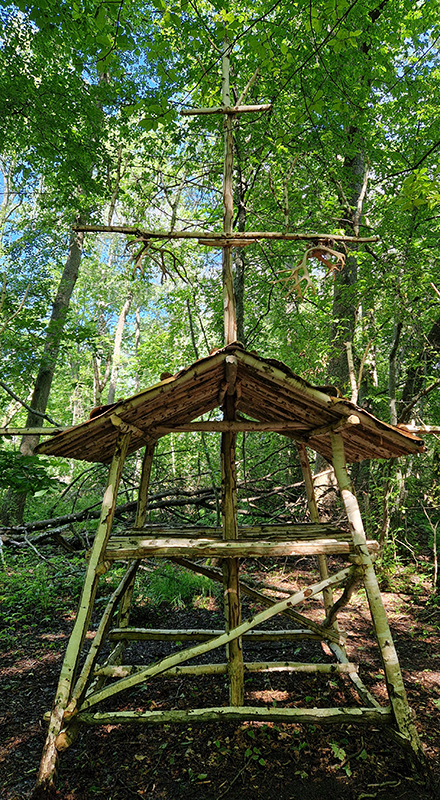
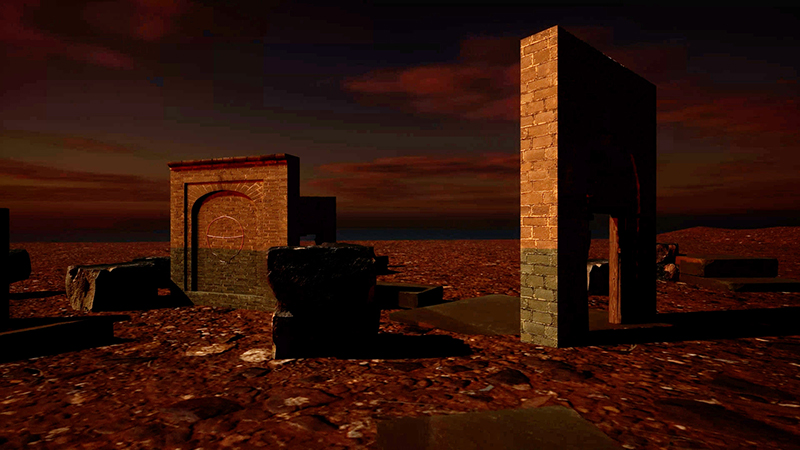
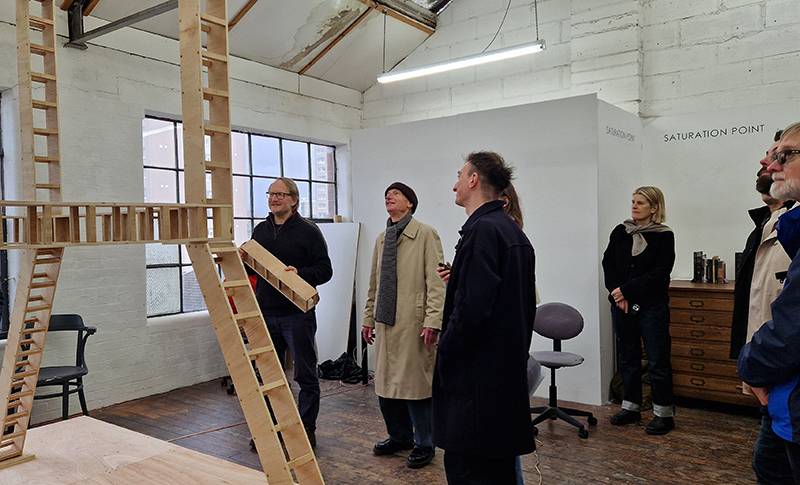
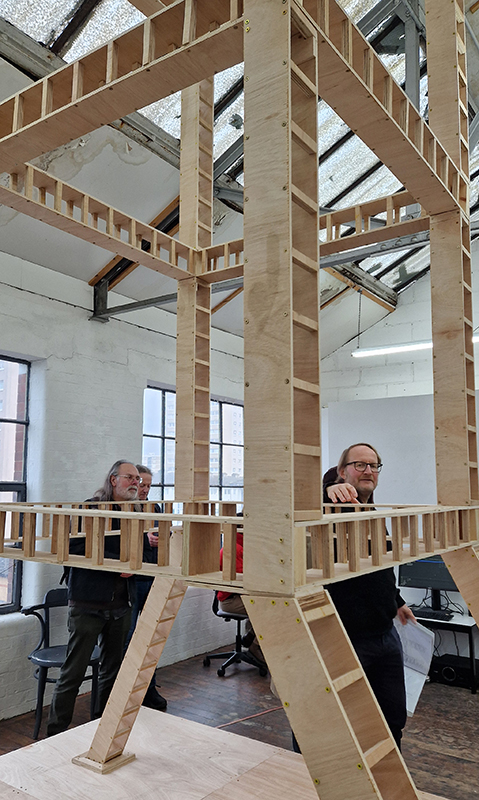
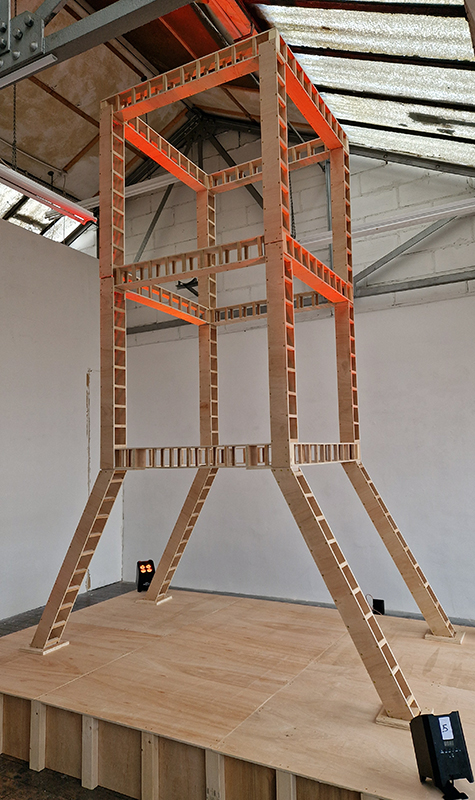
Robert Good Tower No 1a (Looks Like A Good Trajectory So Far) at Saturation Point. The tower is inspired by the iconic launch gantry at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A from which Apollo 11 blasted off to the moon. The title quote is taken from the CBS News commentary at about 1:05 minutes into the flight, and reflects the optimism and excitement of the launch, whilst also perhaps inviting the viewer to consider whether we are still on such a good trajectory today.
I enjoyed the poignancy of the structure as something that no longer has purpose, but also in the context of it being built inside a room, reaching to the ceiling in quite an optimistic defiance.



Also opening at the RWA was Elemental Curated by Malcolm Ashman RWA and Stephen Jacobson RWA. This exhibition brings together works by four RWA Academicians that trace deep and individual responses to the natural world. Each work holds fragments of place that move beyond representation to connect with elements that are both intimate and universal. Great to catch up with Sara Dudman who I met during the Lizard Point Residency in 2019. Her dynamic paintings are vibrant evocations of “what it is to be a volcano. Feeling the sulphurous breath of the earth, watching her move; these paintings adopt the animist view of the volcano as a living being. Trekking the winding paths to the craters, we can never surmount a volcano but feel the awe of her role in reshaping the land”. Sara Dudman RWA
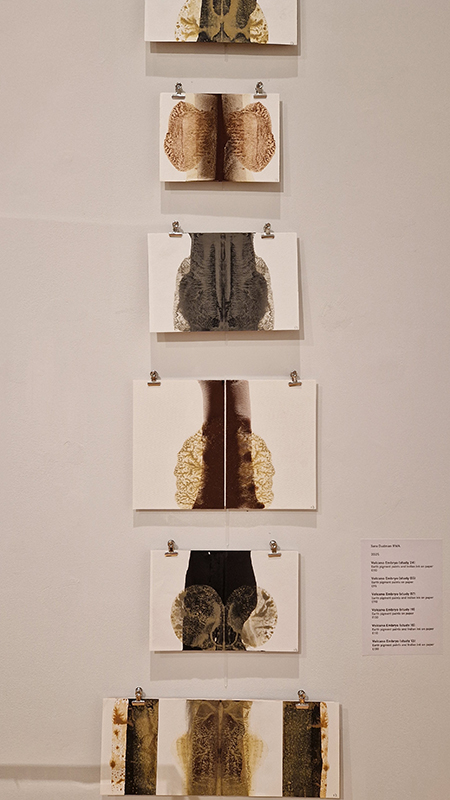
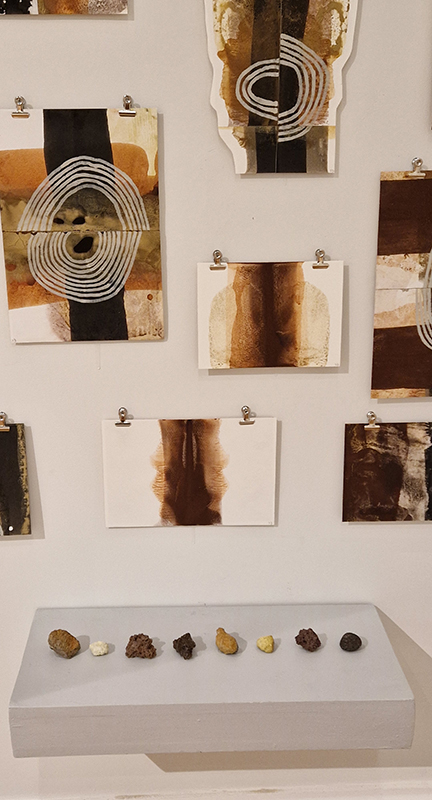



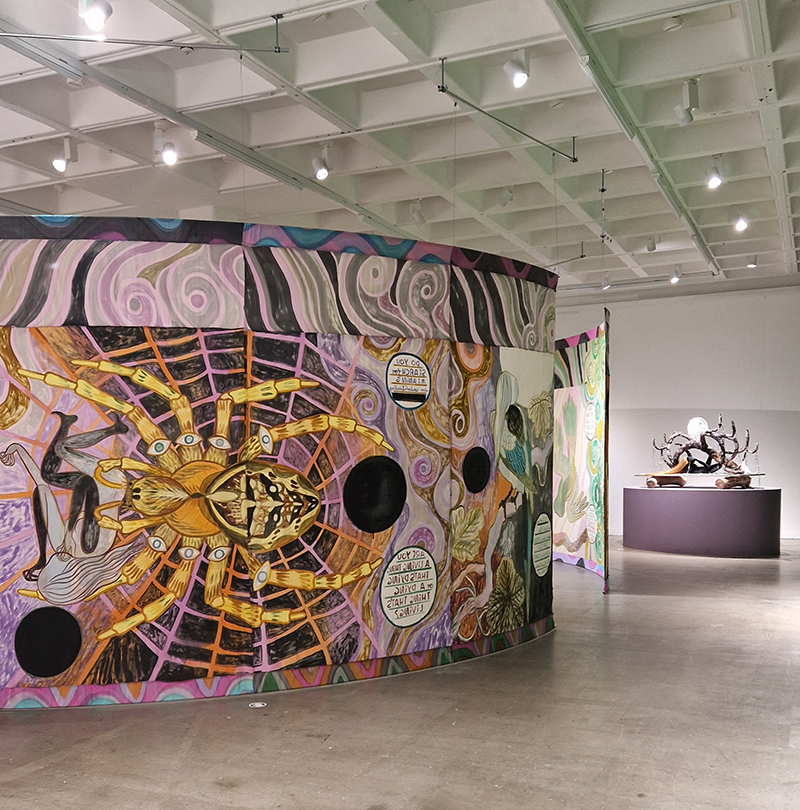
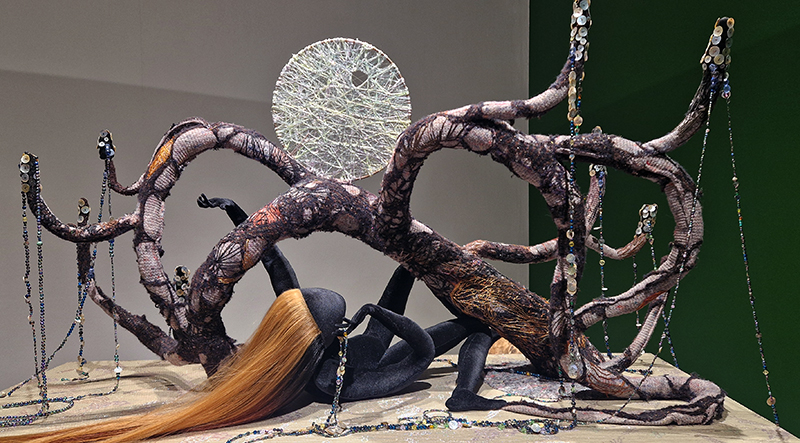
Emma Talbot Everything is Energy at The Arnolfini, Bristol in which the artist leads us through a rich eco-system of works – including silk painting installations, intimate drawings, sculptural forms (Talbot calls them ‘intangible things’) and animation – each exploring the complexity of our relationship with nature, technology and the world around us.
‘What is life. A container for magic. A conductor for nameless frissons & frictions. Electricities & energies that sustain endless expansion.’ (Emma Talbot)
I thought the aminations were beautifully made. I found the text a bit intrusive and prescriptive but it does get her points across I suppose and it is very much a part of how she works.








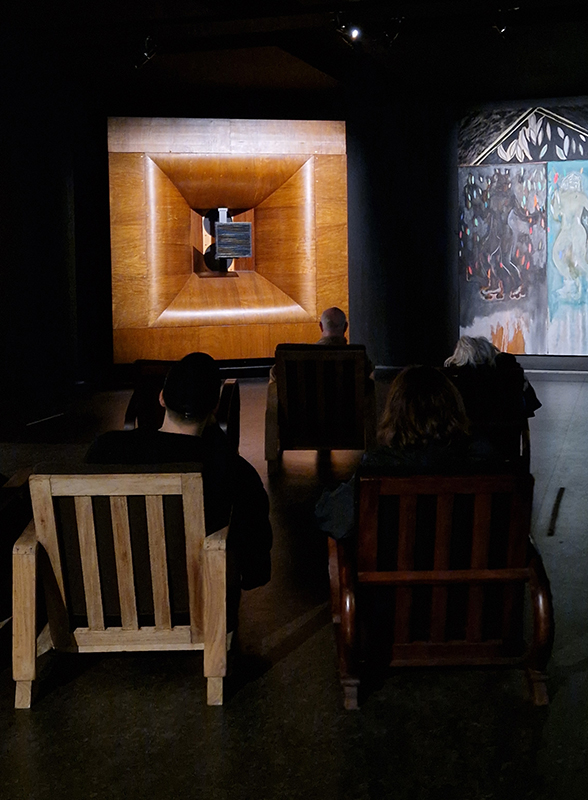
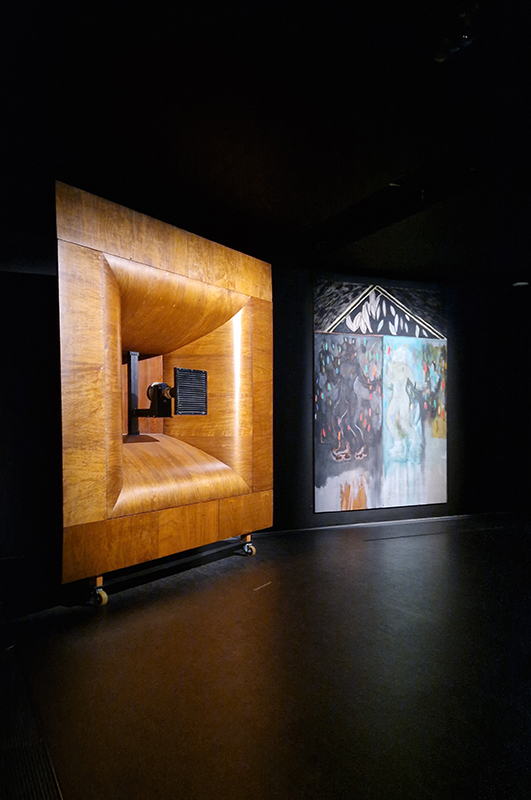
Peter Doig: House of Music at the Serpentine. The exhibition features two sets of rare, restored analogue speakers, originally designed for cinemas and large auditoriums. Music selected by the artist – from his substantial archive of vinyl records and cassette tapes accumulated over decades – plays through a set of ‘high fidelity’ 1950s wooden Klangfilm Euronor speakers. At the centre of the exhibition is an original Western Electric / Bell Labs sound system, produced in the late 1920s and early 1930s. Developed to respond to the demands of modern movie sound, this extremely rare ‘loud speaking telephone’ consists of valve amplifiers and mains-energised field-coil loudspeakers, which were designed specifically to herald in the new era of ‘talking movies’. These speakers were salvaged from derelict cinemas across the UK by Laurence Passera, with whom Doig has collaborated closely on this project. Laurence Passera is a London-based expert and devoted enthusiast of cinematic sound systems. The speakers offer a unique listening experience due to the technical mastery achieved in their construction that places them as the great grandfathers of modern ‘hi-end’ audio.
Settling down to listen to the music meant lingering longer than would be usual when just looking at paintings.
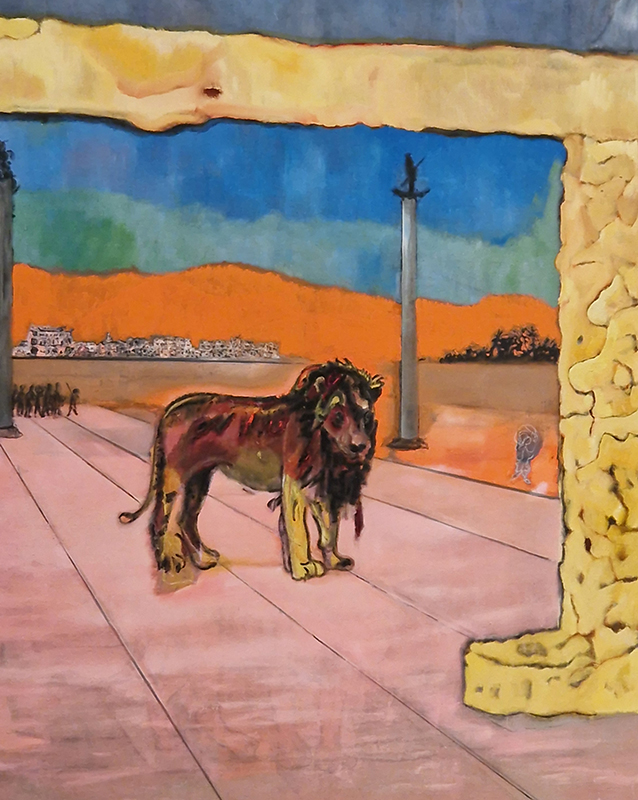
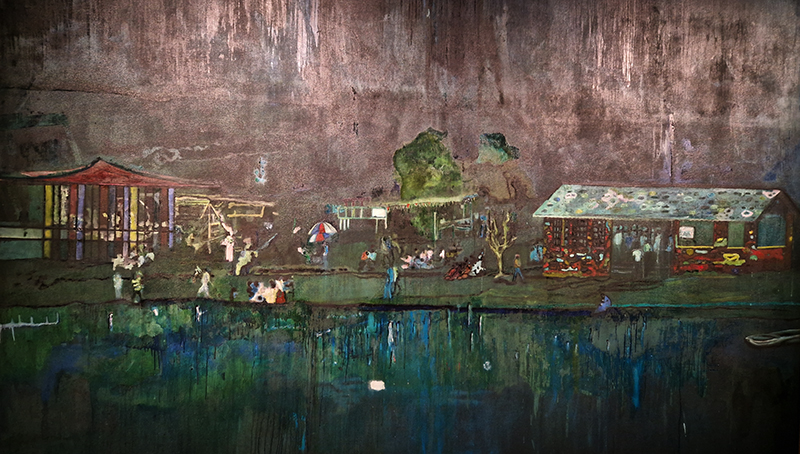





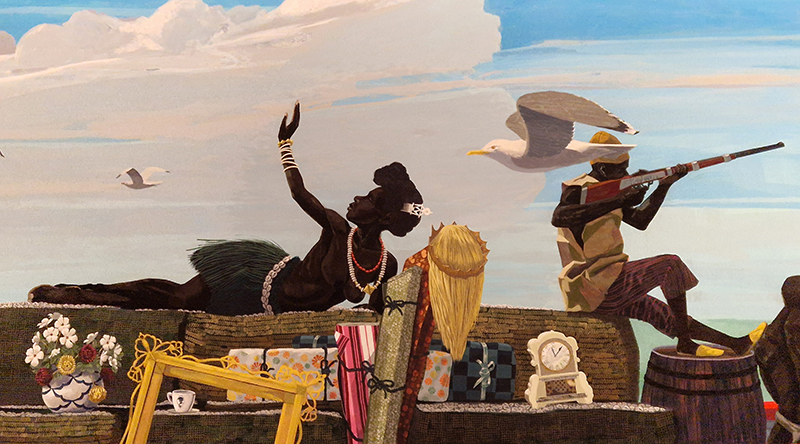
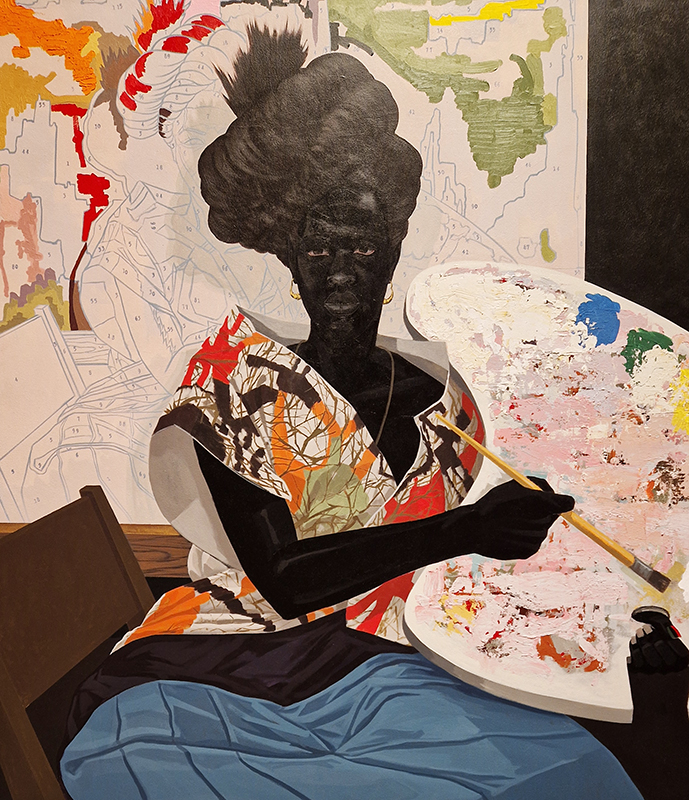
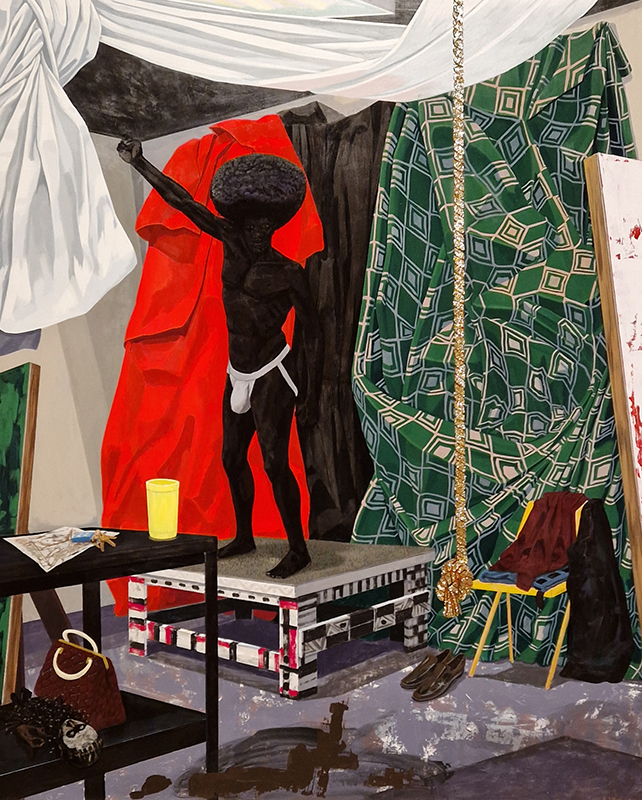
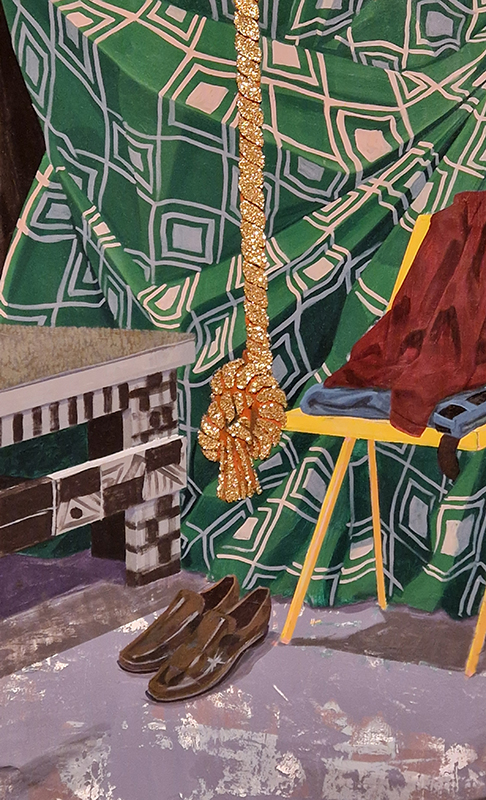
The terrific Kelly James Marshall: The Histories at the Royal Academy. These powerful paintings are full of references which span art history, civil rights, comics, science fiction, his own memories and more. He uses these to comment on the past, celebrate everyday life and imagine more optimistic futures. Full of vibrant energy, fabulous use of glitter and text, truly stunning.





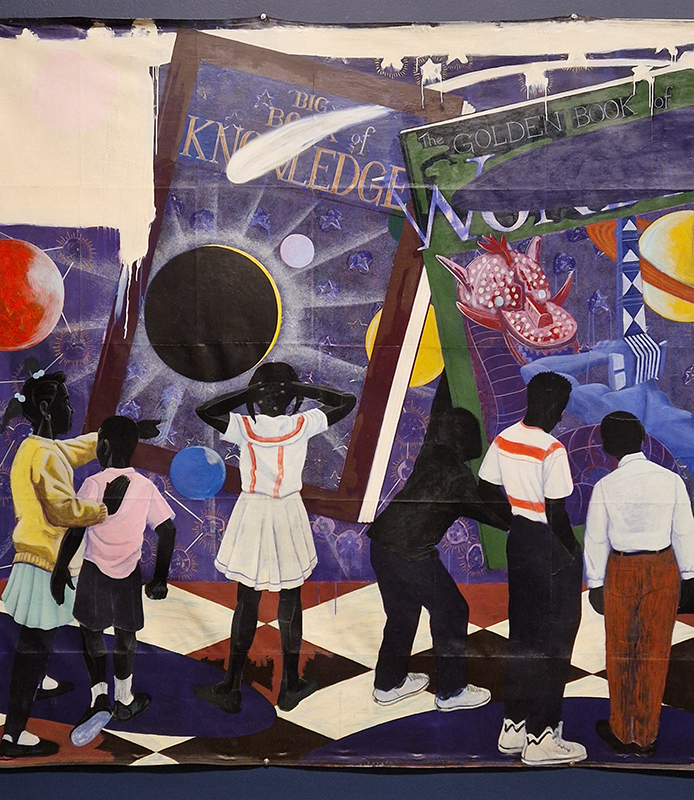
Beatriz Milhazes ‘Além do Horizonte’ (‘Beyond the Horizon’) at White Cube Mason’s Yard. A dose of grey day medicine.